Abstract
Accurate characterization of aquifer hydrogeological parameters is critical for sustainable groundwater resource management. Traditional methods such as pumping tests often assume aquifer homogeneity and require substantial resources, limiting their applicability for large-scale heterogeneous systems. This study proposes a novel approach to estimate the spatial distribution of hydraulic conductivity (T) and specific storage (Ss) in the Qingtongxia Irrigation Area, utilizing canal stage fluctuations as natural stimuli. By analyzing high-frequency groundwater level responses from monitoring wells during irrigation channel operations, we employed a Sequential Linear Estimator (SLE) method combined with canal stage tomography to invert aquifer parameters. The results demonstrate that the inverted hydraulic conductivity distribution aligns well with lithological variations and historical data, showing higher values in the southern alluvial fan and lower values in the northern plains. The SLE method effectively captured aquifer heterogeneity, with RMSE and correlation coefficients between pumping test and inversion results improving to 1.81 and 0.76 after excluding outliers. This work highlights the potential of natural stimuli (e.g., irrigation-induced canal fluctuations) for basin-scale hydrogeological parameter estimation, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. The findings provide valuable insights for groundwater modeling and resource management in arid regions with intensive irrigation systems.
1. Introduction
Accurate understanding of the hydrological characteristics and parameters of aquifers is required for effective assessment and management of regional groundwater resources. Aquifer parameters are an important basis for the evaluation, numerical simulation and forecasting, development, utilization and protection, and scientific management of groundwater resources. Hydraulic conductivity is an important aquifer parameter, and its detailed spatial distribution is a key prerequisite for predicting solute transport [1,2,3]. However, hydraulic conductivity is inherently of significant spatial heterogeneity [4,5]. Conventionally, the hydrological parameters are generally obtained through drilling and field pumping tests, but the pumping tests are conducted under the assumption that the aquifer is homogeneous. While the obtained parameter can be treated as the average value of the entire aquifer, the spatial distribution of the parameters cannot be provided [6,7]. Moreover, it does require a lot of materials, manpower, and financial resources to obtain hydrogeological data of aquifer through field pumping tests.
More recently, Yeh and Liu [8], Zhu and Yeh [9], Xiang et al. [10], and others have developed a new generation of inverse modeling approaches (hydraulic tomography, HT) for characterizing subsurface heterogeneity. HT is a new technology for pumping tests to effectively obtain the information on the spatial distribution of aquifer parameters. The groundwater flow equation is inverted by use of the data obtained through a series of cross-well pumping or injection tests to obtain the spatial distribution of hydraulic parameters of the aquifer. Over past decades, it has been tested, validated, and demonstrated in synthetic experiments, e.g., [11,12,13], laboratory sandboxes, e.g., [14,15], and field-scale aquifers, e.g., [16,17,18]. Ultimately, HT has evolved as a mature technology for high-resolution aquifer characterization.
However, it is impractical to apply HT to basin-scale aquifers since the basin-scale groundwater flow field cannot be effectively changed by artificial pumping tests [13], Thus, Yeh et al. [19,20] proposed the characterization of the heterogeneity of groundwater aquifers by natural stimulus. They believe that natural stimulus sources such as storms, tides, floods, landslides, lightning, earthquakes, changes in river stage, changes in atmospheric pressure, etc., often occur in different locations in the groundwater basin, and provide larger and widespread energy to disturb the groundwater flow. Therefore, the spatial hydrogeological feature can be reflected by the groundwater disturbances. If the stimulus source data and the distribution and responding changes of relevant water level in the aquifer can be collected, it is equivalent to obtaining a series of hydraulic test data. In recent years, there have been many cases of calculating aquifer system parameters by natural stimulus methods. For example, Wang et al. [13] studied the two-dimensional spatial distribution of the hydraulic diffusion coefficient of the alluvial fan of Zhuoshui River in Taiwan based on water level changes of observation wells around Zhuoshui River caused by rainfall data in the alluvial fan of Zhuoshui River. Jia and Li [21] estimated the aquifer parameters in Beihai Peninsula by the tidal effect. Fang H.N [22] carried out the research on inversion of aquifer parameters by the groundwater pressure perturbations before and after Wenchuan Earthquake. Park and Lee [23] used a non-Bayesian nonparametric model to characterize the hydraulic properties of a basin-scale aquifer based on the natural stimulus of recharge from precipitation via a geostatistical principal component adaptation evolution strategy.
Numerous studies have been studied to estimate the hydrogeologic parameters of aquifers by interpreting the aquifer response due to river stage variations. Ferris [24,25] presented analytical methods to calculate aquifer diffusivity based on well hydrographs in response to river stage variations. Duffy et al. [26] and Gelhar et al. [27] utilized a spectral approach to estimate transmissivity and storage coefficient of homogeneous aquifers by using the relationship between the well hydrograph and the stream variation. Sophocleous et al. [28] pointed out that the change of groundwater level is not only influenced by surface water seepage but also has a correlation with river flow. Especially in aquifers with large hydraulic conductivity by using a long-time monitoring data, they revealed the feasibility of using river stage fluctuations as a source of stimulation. Under suitable field conditions, it is possible to calculate the hydraulic diffusivity of alluvial aquifers by analyzing their response to river stage fluctuations, which is known as the flood wave response technique [29,30,31], and is relatively simple to implement because it only requires time series data of river stage fluctuations and the corresponding hydraulic head variations of a riparian zone observation well [32,33,34].
In summary, only a few HT studies have been performed for large-scale field problems due to the difficulty in conducting dedicated HT surveys at large-scale sites, as well as the uncertainty regarding estimated initial and boundary conditions for inverse modeling. The actual groundwater flow is much more complicated than the idealized simulation process of the numerical experiment. Much higher accuracy in heterogeneity characterizing is required for solute transport problems. Therefore, it is uncertain whether the simulation prediction of the groundwater flow, especially the solute transport, is effective.
Using river stage fluctuations to estimate aquifer parameters is still mostly limited to the site scale or point scale, and there are no practical cases of obtaining hydrological parameters on a large scale. Estimation of the distribution of basin-scale aquifer parameters by river stage tomography using natural stimulus methods is limited to theoretical research. Moreover, in fact, groundwater level information may be affected by many other factors (such as precipitation, pumping, irrigation, etc.). It is still a challenge to extract useful information from these datasets to characterize the basin-scale heterogeneity and to invert regional aquifer parameters. In addition, there is currently no simple and effective theoretical method to invert the transient relationship between rivers and groundwater based on the response of aquifers to natural stimuli such as floods and rainstorms.
This study aims to estimate the spatial distribution of hydraulic conductivity and specific storage using canal stage fluctuations as an excitation source for basin-scale aquifer characterization, providing a scalable alternative to traditional field tests. Accordingly, we set up 11 groundwater level observation holes along the Hanyan and Huinong Canal irrigation areas in the Qingtongxia Irrigation Area of Ningxia since October 2017, and we obtained high-precision observation data of the canal stage and groundwater level. With the sharp rise in the water level of the agricultural irrigation canal in Qingtongxia Irrigation Area in October annually as the stimulus source, and the water level changes in the 11 groundwater observation wells as the response signal, the correlation between the river stage and the groundwater level changes was obtained and analyzed, and then the successive linear estimator method was used to invert the spatial distribution of the regional hydraulic conductivity coefficients. It was intended to explore the possibility of inverting hydrological parameters of aquifers by natural stimulus methods in practice.
2. The Study Area
2.1. Topography
Located in the southern part of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, the study area is the middle and front part of the alluvial fan formed by the Yellow River at the narrows of the Qingtongxia Gorge, where the Yellow River flows in a southwest–northeast direction on the east side, so that the terrain is slightly higher in the southwest than the northeast parts, and slightly tilted toward the Yellow River (Figure 1). The area is about 20 km long, 15 km wide, and covers an area of about 300 km2. With flat and open terrain and fertile land, it is one of the oldest irrigation areas along Yellow River in China [35]. Water from the Yellow River is diverted to irrigate farmland in the study area. The two irrigation canals, Huinong Canal and Hanyan Canal, pass through the middle of the study area. The Yellow River is at the furthest east side of the study area. The aquifer in this area is mainly recharged from percolation of agricultural irrigation [36].
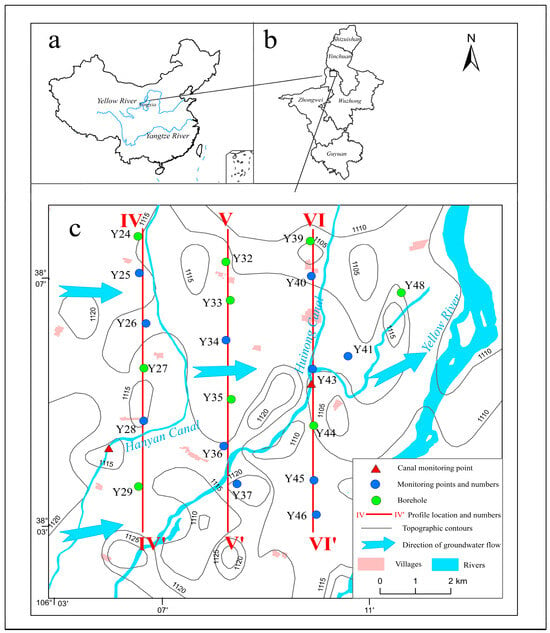
Figure 1.
Location map of the study area and layout of monitoring points (a–c).
2.2. Meteorology
The study area belongs to a temperate continental semi-arid climate region, with four distinct seasons, abundant sunshine, intense evaporation, few rain and snow, and large temperature difference between day and night. The annual average temperature is 10.1 °C, the extreme low temperature is −18.1 °C, and the extreme high temperature is 34.7 °C. The average annual precipitation is 186.2 mm, the maximum annual precipitation is 322.1 mm, the minimum annual precipitation is 59.8 mm, and the average annual evaporation is 1847.5 mm, which is about 10 times of the precipitation. The distribution of precipitation throughout the year is extremely uneven, mainly concentrated in June, July, August and September, accounting for about 73.4% of the annual precipitation [37,38].
2.3. Geology
The study area is located in the transition zone between the Yellow River alluvial fan at Qingtongxia and the Yinchuan alluvial lacustrine plain, where loose sediments of alluvial facies and alluvial lacustrine facies mainly composed of pebbles, gravel-cobble, coarse sand, medium sand, and fine sand. It belongs to an unconfined aquifer area according to the hydraulic properties and hydrogeological structure of the aquifer, and the water depth is 0.58–4.69 m [37,38]. The main hydrogeological characteristics in the study area are loose stratum, developed pores, large thickness, stable aquifer, shallow groundwater level and strong water enrichment (Figure 2).
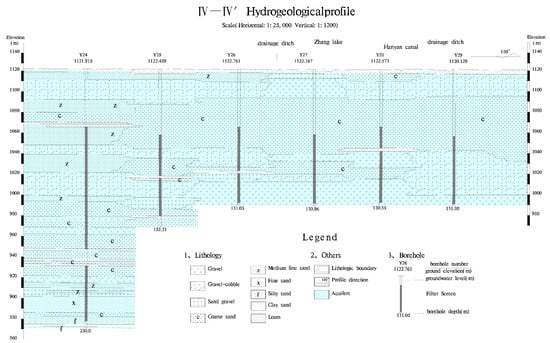
Figure 2.
Hydrostratigraphic cross-section along profile IV–IV’. The location of this profile is indicated in Figure 1.
With a long history of irrigation from the Yellow River in the study area, the irrigation area is densely covered with farmland and crisscrossed ditches, where a relatively complete irrigation and drainage system has been established [35,39]. The average annual diversion is 4628.4 million m3 and discharge is 2527.2 million m3 from 2002–2014 in Qingtongxia Irrigation District Average [40]. The main irrigation canals in the study area are Hanyan Canal and Huinong Canal. Diversion irrigation from the canal system is carried out twice every year from late April to mid-August and from mid-October to mid-November respectively, which is named as summer irrigation and winter irrigation, and the annual water flowing time is 170 days. The aquifer in this area is mainly recharged from canal system leakage and percolation of irrigated water, and precipitation infiltration and lateral runoff will also provide certain recharge to aquifer in this area. As a result, the dynamic changes of groundwater level in the region are characterized by a continuous decline from the end of last year to the beginning of the second year, as shown in Figure 3. From April, the water level rises under the influence of summer irrigation, and the water level reaches its maximum in August, forming the first annual water level peak, and then the water level starts to fall in September when the channels stop running and field irrigation. Since winter irrigation, the water level began to rise again, and a second high water level peak appeared until early December, the rise was smaller than the first annual water level peak, and the groundwater level began to fall again in the second year. The highest water level occurs in August and November, and the lowest water level occurs in March and April, with an annual variation of 1 m to 2.1 m, and the type of groundwater dynamics is of irrigation infiltration type. The groundwater in this area mainly drained by evaporation, drainage ditch, and lateral runoff. The depth of groundwater is relatively shallow, with an average water level of 2–3 m, and the flow direction is from west to east [37].
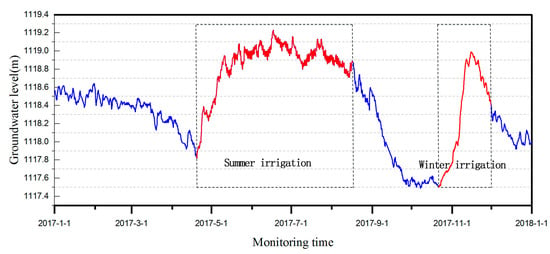
Figure 3.
Groundwater level variation in monitoring point Y36 in 2017. The location of Y36 is shown in Figure 1.
The Hui Canal is the longest main canal in the Hexi Irrigation Area of Yinchuan Plain. The Han Canal, which diverts water from the Yellow River, meets the Hui Canal to the north. During the agricultural irrigation of the two irrigation canals, the water level of the canal system is higher than the groundwater, and the canal system supplies the groundwater. When the irrigation canals are empty, the groundwater elevation at the bottom of the irrigation canal is higher than the surrounding groundwater, and groundwater will not discharge to the irrigation canal.
The annual precipitation in Qingtongxia Irrigation Area is scarce, and the source of groundwater recharge in this area is mainly the seepage from the canal system and field irrigation. The stratum of the irrigation area is dominated by the loose sediments of the Yellow River alluvial fan, and the aquifers are highly permeable and relatively uniform in spatial distribution, which reduces the interference of the geologic complexity on the parameters identification. The irrigation area has two main canals, Hanyan Canal and Huinong Canal, and the irrigation system is as dense as a network, and summer and winter irrigation are carried out every year, which provides a natural and repeatable “stimulation source” for the study of the dynamic response of groundwater due to the artificially controlled regular changes of the canal level.
3. Methodology
3.1. Layout of Monitoring Network
A large number of field geological drilling, geophysical prospecting, and engineering geological drilling were carried out during the survey in the study area in 2017, and seven exploration lines were laid in the roughly perpendicular to groundwater flow direction with a separate distance of 2.5 km. The distance of between two adjacent boreholes is 1.5 km, and 20 exploration boreholes were completed. Three hydrogeological sections are completed by interpolation of lithology based on borehole data, each of which was similar in lithology, such as profile IV–IV’ shown in Figure 2. The depth of the wells was from 100 to 180 m, and the length of the screen pipe was between 54 and 70 m. In order to implement the river stage tomography test, we selected 20 exploration wells for groundwater level monitoring. Among them, monitoring wells numbered Y36, Y37, Y39, Y40, Y41, Y43, Y44, Y48, and they were deployed along the Huinong Canal. The monitoring wells numbered Y24, Y25, Y26, Y27, Y28, Y29 were deployed along the Hanyan Canal for automatic monitoring (Blue borehole in Figure 1), while the other nine exploration wells (Green borehole in Figure 1) were deployed for regular manual groundwater level monitoring on the 1st, 5th, 15th, and 25th days per month. The automatic monitoring wells are equipped with the Solinst 3001 Levelogger 5 (made in Solinst Canada Ltd., Georgetown, ON, Canada) groundwater level automatic recorder, which records groundwater level and groundwater temperature every 10 min. Most of the automatic groundwater monitoring work started in the middle of September 2017, with some individual monitoring holes starting in December 2016, such as Y36, Y37. At the same time in Huinong Canal and Hanyan Canal, automatic water level monitoring instrumentations monitor the variation in the canal stage. The water elevation in the two irrigation canals ranged from 1118 to 1121 m, and the monitoring frequency was set for every 10 min to collect a set of monitoring data.
3.2. Hydrological Parameter Acquisition
Single-hole constant-rate pumping tests were conducted at Y28, Y34, Y36, Y37, Y40, Y41, Y43, Y45, Y46, Y48, Y25, Y26 boreholes deployed in the study area. The purpose of the pumping tests is to obtain the hydrological parameters of the aquifer and to provide initial values for the numerical modeling. Three sets of pumping tests with different drawdown were conducted in each exploring well, and the stabilizing times were 16 h, 8 h, 8 h (total 32 h), respectively. One set of pumping test with a certain descending depth was conducted in each monitoring well, with a stabilizing time of 8 h. The results of these pumping tests are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Hydraulic conductivity (K) and radius of influence derived from constant-rate pumping tests.
3.3. Spatial Cross-Correlation Analysis
In this study, since the groundwater level has a consequent response to the sharp increase in the canal stage, the correlation between the groundwater level in the monitoring wells and the canal stage was analyzed first to determine the correlation between the canal stage and the groundwater level in the monitoring wells, as well as the lagging response of groundwater level at different locations to changes of canal stage. The lagging response can be studied through cross-correlation analysis. The cross-correlation function represents the degree of correlation between the two time series under specific conditions, that is, the degree of correlation between the two time series when taking the values of them at any time lag, which is an indicator for judging whether there is lagging correlation between two signals. For the analysis of time series in a mathematical method, the cross-correlation between two time series is the normalized cross-covariance function.
If Xt and Yt represent two time series, the cross-covariance function and cross-correlation function are respectively expressed as
In the formula, and represent the mean and standard deviation, is the lag time, and E[] represents the mathematical expectation. After calculating the correlation coefficient of two time series in multiple time lags , the corresponding to the largest or smallest correlation coefficient is the best matching lag time. Here, the water level of the canal is used as the target signal, and the groundwater level of the observation wells in various places is used as the observation signal to study the lag response relationship between the canal stage and the groundwater level.
3.4. Successive Linear Estimator
A stochastic inverse algorithm, Sequential Linear Estimator (SLE), is employed to estimate the spatial distribution of hydraulic conductivity and specific storage with observed groundwater level variations.
SLE is an extension of the kriging or co-kriging-based method for stochastic linear estimation of spatial variables. Compared with traditional methods such as Monte Carlo and geostatistical methods, the advantage of this method is that it does not require a large amount of supporting data and can use limited geological data to make a reasonable estimate of the aquifer hydrogeology at an unknown location. SLE is based on the Bayesian principle, which updates the posterior mean and covariance of the parameters based on the correlation between the observed states and unknown parameter.
Using the Gauss–Newton algorithm in a stochastic framework, the estimated conditional parameter fields is iteratively determined using the linear estimator (3):
in which is an m × 1 vector, representing perturbations of the estimated lnT or lnS (i.e., the estimates minus the unconditional mean lnT or lnS. ln denotes natural logarithm.), and the superscript r is the iteration index. (n × 1) is the simulated heads at the observation wells, based on the lnT or lnS estimated from the rth iteration. If parameter measurements are not available, is zero and (m × m) is the unconditional covariance from geologic information. The unconditional covariance of parameters is assumed to take the form (4):
in which represents the unconditional ensemble variance of the parameter T. (m × 1) and (m × 1) are the distance [m] between two parameters in x and y directions. and are the correlation lengths [m] in x and y directions.
After the linear estimation, the conditional residual covariance of is updated by (5):
These iterative processes adjust the given prior geostatistical parameters using the observed head. The diagonal term of the residual covariance matrix (i.e., residual variance) represents the remaining uncertainty of the estimated lnT or lnSs after the head information is included. A small residual variance indicates that the estimated lnT or lnSs is close to the true fields, while a large value indicates that the estimate is close to the prior mean value (i.e., heterogeneity is not resolved).
The estimated field is considered as the final one when either the mean squared error of the simulated and observed heads is smaller than a given tolerance or the increase in the spatial variance of the estimated parameter becomes insignificant between successive iterations.
The coefficient of determination (R2) and the mean squared error (i.e., L2 norm) are utilized for the evaluation of estimates for each realization. L2 norm is defined as (6):
They evaluate the similarity between the reference and estimated lnT or lnSs fields. and denote the reference and estimated lnT or lnSs fields, respectively. Detailed discussions could be found in [8,9,10,18].
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Groundwater Level and Irrigation Channel Stage Variation
According to the characteristics of groundwater level dynamics introduced in Section 2.3, the groundwater level in this region is influenced by spring and winter irrigation. In contrast, the groundwater level is less affected by other factors (such as precipitation and pumping) during winter irrigation, so river channel stage variations during winter irrigation and the variations in the surrounding monitoring wells are used to study the hydrological parameters of the area. The Hanyan Canal was diverted water from the Yellow River on 30 October 2017, and the Huinong Canal was diverted on 22 October 2017. Thus, 16 October was used as the reference date to calculate the relationship between river channel stage changes and groundwater level changes during this period.
Figure 4a presents the groundwater level variations near Huinong Canal (Y36, Y37, Y40, Y41, Y43, Y48). As shown in the Figure 4a, the groundwater level near the Huinong Canal is affected significantly by the canal stage in the Huinong Canal (from 5 cm to 30 cm within 7 days). On the other hand, the water level of Hanyan Canal has a minor effect on the nearby groundwater level variations (Figure 4b, wells Y25, Y26, Y28, and Y34). This is also closely related to the groundwater flow direction, where the overall groundwater flows from southwest to northeast. Prior to the release of water from the two irrigation canals on 22 October, the groundwater level in all monitoring holes maintained a decreasing trend (approximately 1 to 2 cm per day) due to the influence of coitional factors such as evaporation or other pumping actions. From day 19 (5 November 2017) onwards, the groundwater levels in all monitoring wells increased significantly, which is caused by large-scale agricultural irrigation in the area.
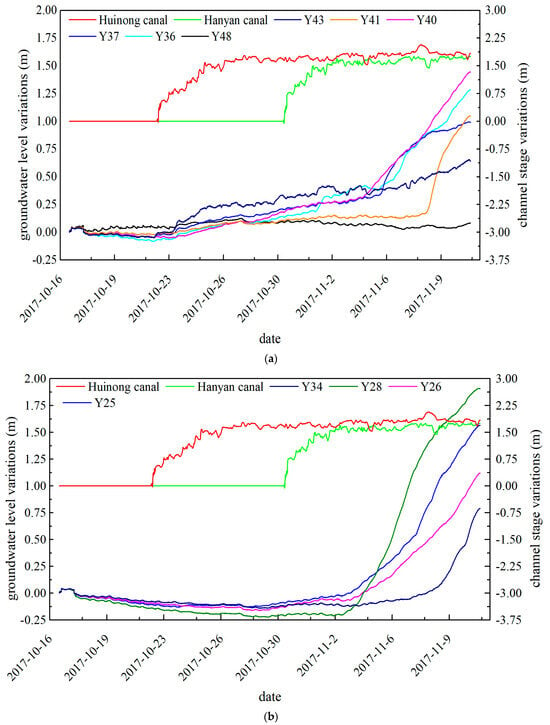
Figure 4.
Groundwater levels and channel stage variations near the Huinong Canal (a), and the Hanyan Canal (b).
4.2. Regional Groundwater Flow Field Analysis
Based on the automatic and regular manual groundwater level monitoring, the regional groundwater level flow field was plotted in Figure 5, including the four flow fields before diversion water on 15 October, after diversion water on 1 and 5 November, and at the time of irrigation on 1 and 5 November. From the groundwater level and flow fields of the two irrigation canals before diversion and irrigation (15 October in Figure 5), it can be seen that the groundwater generally flows from west–south to east–north. When the two canals started to divert water from the Yellow River, but before irrigation started (as shown in the Figure 5 on 1 November and 5 November), it can be seen from the water level and flow field that the Huinong Canal recharges groundwater obviously, whereas the Hanyan Canal recharges groundwater slightly, which is also consistent with the Figure 5. The groundwater level of the monitoring wells around the Huinong Canal rise quickly when the Huinong Canal is diverted, while the groundwater level of the monitoring wells around the Hanyan Canal is not very obvious when the water is diverted. In fact, from the overall water level and flow field, the later groundwater level change of the monitoring wells around the Huinong Canal should be due to the effect of the superimposed water diversion from the two irrigation canals. Meantime, significant change in the flow field occurs since Nov. 15, due to agricultural irrigation. Accordingly, in the actual simulation, only the groundwater level change from 22 October to 3 November when the irrigation water was diverted was used for parameter identification.
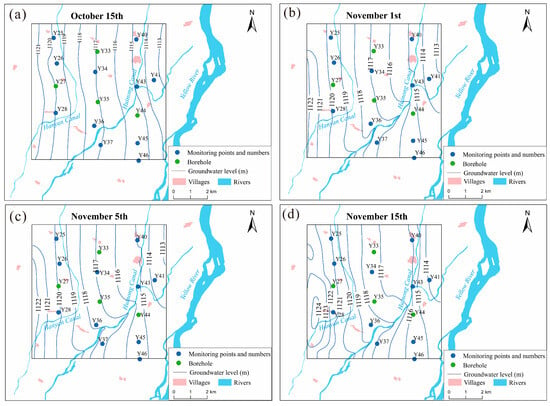
Figure 5.
The regional groundwater level flow field variation map at different times (a) 15th October (b) 1st November (c) 5th November (d) 15th November.
4.3. Correlation Analysis of Groundwater Level and Irrigation Channel Stage Variation
In order to study the interaction between groundwater level variations and irrigation channel stage variation, the correlation between the groundwater level changes in the monitoring wells at different locations and irrigation channel stage was investigated by mutual correlation analysis. The spatial lag characteristics of the groundwater level on the irrigation channel diversion were obtained through the correlation analysis evaluation using irrigation channel stage and groundwater level data of Hanyan Canal as signal sources, and the contour plots of the correlation coefficients and lag times were drawn in Figure 6a,b. The maximum correlation coefficient between the groundwater level of each monitoring well and irrigation channel stage variation is above 0.9, indicating that there is an obvious correlation between the irrigation channel stage and the fluctuation of the surrounding groundwater level, and the change of the irrigation channel stage can obviously cause the fluctuation of the surrounding groundwater level. However, the maximum correlation coefficient decreases as the distance of the observation borehole from the irrigation channel increases; the lag time increases, i.e., the lag time increases from approximately 0.5 days for every 0.3 km to approximately 0.5 days for every 1 km. Through the trend of spatial changes in lag time and correlation coefficient, it can be judged that the groundwater flow shows a uniform flow direction from northwest to southeast. The signal of the fluctuation of irrigation channel stage can be propagated to the aquifer far away from the irrigation channel.
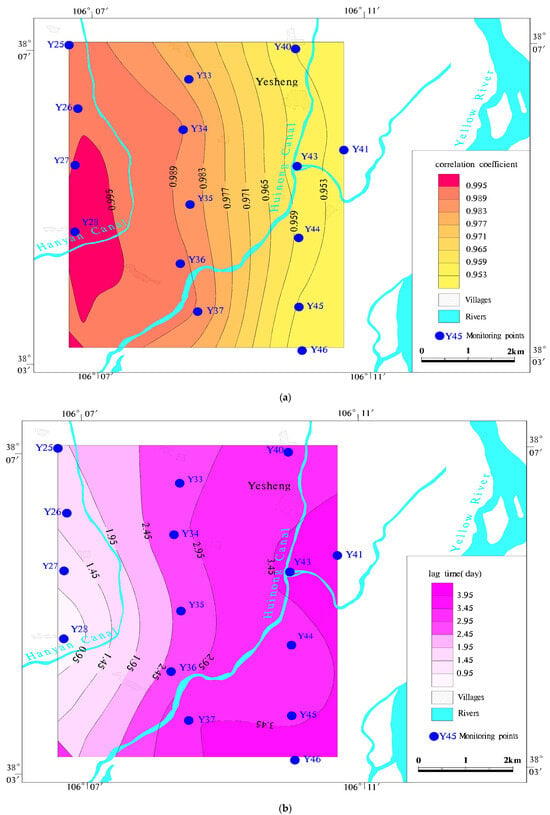
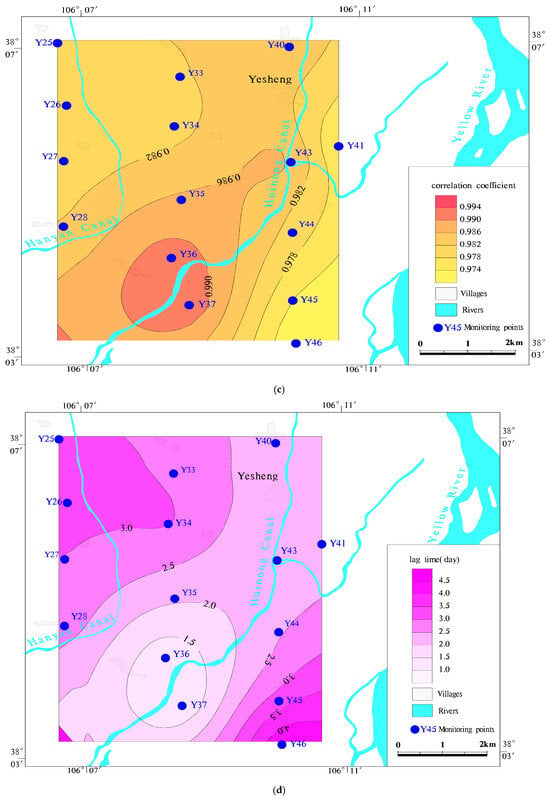
Figure 6.
The spatial distribution map of the correlation coefficient and the lag time between the irrigation canal and the groundwater under the diversion irrigation (a) correlation coefficient through Hanyan Canal. (b) the lag time through Hanyan Canal. (c) correlation coefficient through Huinong Canal. (d) the lag time through Huinong Canal.
The relationship between river stage change and groundwater level response during water diversion in Huinong Canal is similar to that in Hanyan Canal (Figure 6c,d), and their correlation coefficients are above 0.9 with relatively small lag time. It can be seen from Figure 6 that the lag time change gradient in the southeast direction of Huinong Canal is relatively uniform, about 0.2 days/100 m, and the lag time within 400 m downstream of the canal is relatively stable about 2.3 days. It indicates that the groundwater level around the upstream of the canal responds faster during the gradual rise to stable state of the water level in the Huinong Canal, and the water level around the downstream of the canal system responds more smoothly to the water level, and there is time–space variability in the process and intensity of groundwater recharging from the canal in the whole study area. In particular, although Y43 is the closest to the Huinong Canal, the bottom and sides of the Huinong Canal close to Y43 are lined, so the response of Y43 to the water level in the irrigation channel is not as pronounced as in Y36 and Y37.
Based on the above correlation analysis, it can be found that the hydraulic connection between the groundwater and the irrigation channel in the study area is strong, the stratigraphic inhomogeneity is not obvious, the lithology in the study area is basically the same within 5 km except near the riverbed, and the correlation coefficient between the groundwater level and the irrigation channel stage within 4 km from the diversion channel is higher than 0.9 with a lag time of less than 3 days. The irrigation channel stage first rises upstream and then increase smoothly downstream to stable state. The spatial and temporal variability of the correlation between groundwater level and irrigation channel stage is due to these process rises first in the upstream area and increases smoothly in the downstream area to stabilization. At the same time, this response process also responds to the fact that irrigation channel stage variation can cause groundwater level changes in the surrounding monitoring wells within several kilometers, and it also verifies the previous theory that the aquifer pressure response to river stage changes can propagate for tens of kilometers in aquifers [28,41,42,43].
4.4. Parameter Identification with SLE Inverse
The numerical model of this study is based on the VSAFT2 (2018.08.30) (Variably Saturated Flow and Transport utilizing the Modified Method of Characteristics, in 2D) program developed by Yeh et al. [44] and the software integrates Sequential Linear Estimator (SLE) inversion method.
Because SLE is based on the variation in the canal stage and groundwater observation wells, the more important is the change instead of its absolute value of water level. In order to simplify the calculation, all the monitoring wells and canal stage value were unified minus the first observation value. In the inversion calculation, in order to ensure the positive water head, all head values were leveraged by 30 m, so the system is also set to the initial value of 30 m.
According to the layout of the monitoring holes (the distance between two monitoring holes is about 2 km), a two-dimensional horizontal aquifer of 28 × 30 square elements is created for the simulation (Figure 7). Each element is 500 [m] × 500 [m]. The aquifer is bounded by constant head boundaries (30 m) on the west and east and by no flux boundaries on the north and south. The initial head is uniform (30 m) everywhere. The surface water flow through the two canals (Hanyan Canal and Huinong Canal) and a river (Tuishui) are mimicked by the time varying prescribed head boundaries. Because the stages of the canals are measured on a single point near the downstream side, we assume the stages along the canal are uniform. The observed groundwater level variations from 22 October to 3 November are selected to estimate the aquifer hydraulic properties. The time step is 0.17 [day]. The mean T of the aquifer is 180 [m2/day], mean S is 0.06 [-], the variance of lnT and lnS are one [-], and the correlation lengths and of T and S are 6000 [m].
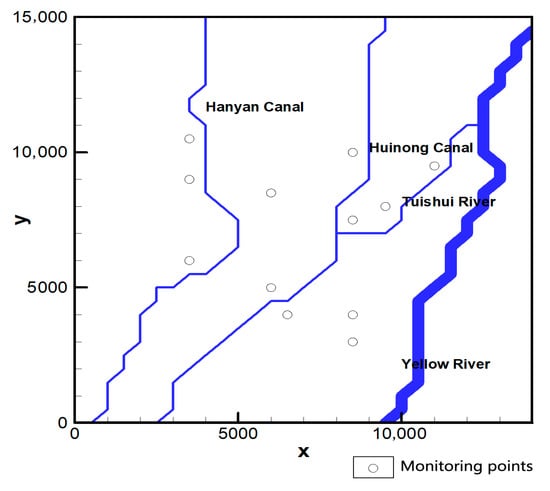
Figure 7.
The simulation domain.
Figure 8a,b illustrate the estimated T and Ss fields. The scatterplot of calibrated verses observed groundwater level variations is presented in Figure 8c. The unbiased groundwater levels scattering along the 45 degrees line suggest the estimated parameter fields are reasonable. As shown by the Figure 8a,b, the T values are slightly larger on the south, intermediate on the northwest, and smaller on the northeast. On the contrary, the Ss values are smaller on the south, intermediate on the northwest, and larger on the northeast. Although the estimated T and Ss fields show some spatial variabilities, they are not significant. The maximum and minimum values are within the same order of magnitude. Thus, the hydraulic properties of this region can be treated as homogeneous. This is consistent with the previous research results in the local area [37,45]. The permeability coefficients identified by previous authors in the southern part of the region are around 6.8, and around 5.1 in the northern part, indicating that the hydraulic parameters inversed using the SLE inversion method with the river stage tomography method are consistent with the actual system. Studies in the Indo-Gangetic Basin report T values of 3–15 m/d for alluvial systems under comparable climatic conditions [31]. This consistency underscores the reliability of natural stimuli methods in capturing aquifer heterogeneity.
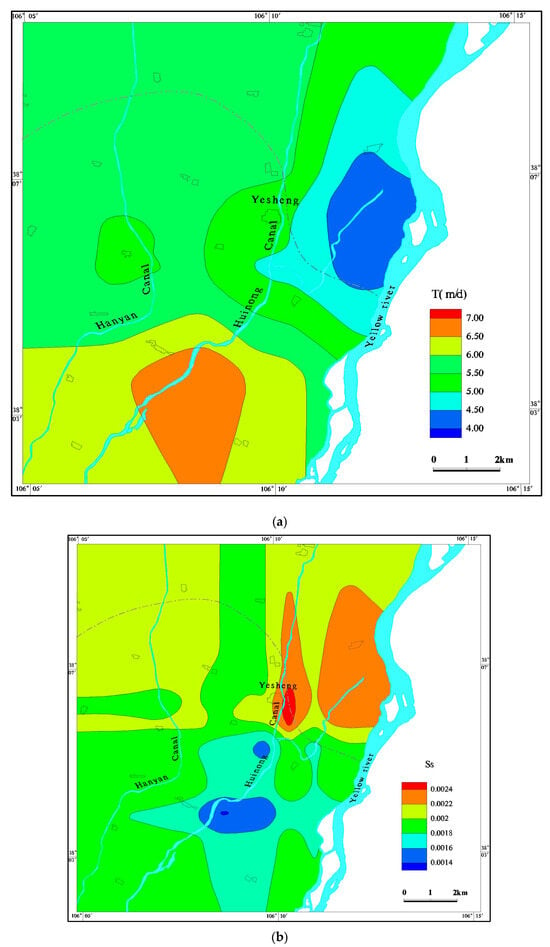
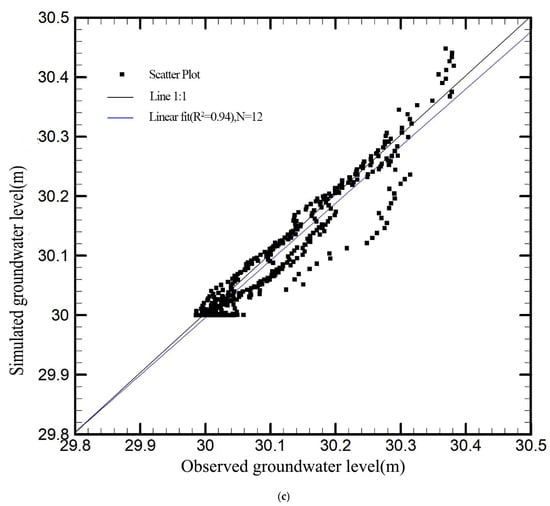
Figure 8.
(a) The parameters of the inversion T. (b) The parameters of the inversion Ss. (c) The scatterplot of simulated verse observed groundwater levels.
Regarding the regional hydrogeological conditions, the southern area belongs to the middle and front part of the Qingtongxia Yellow River alluvial fan, and the permeability coefficient is slightly larger. The lithology of this area is mainly gravel and sandy gravel. Moving northward to the Yellow River alluvial plain, the lithology gradually transitions to medium-fine sand and powder-fine sand with clayey soil, so the distribution of the permeability coefficient is also larger in the south than in the north. From the site distribution of permeability coefficient (Figure 8a), the overall permeability coefficient shows spatial variation with some heterogeneity, but the overall variation is not large. Moreover, the results of this simulation are more reflective of the non-homogeneity of the aquifer when compared with the previous simulations [37,45].
The results of the pumping test and the parameters of the model inversion are compared in Table 2. The discrepancy between the results of the pumping test and the model calculation are rather limited, mostly within 20%. The root-mean-square error (RMSE) and correlation coefficients (CC) were also used to measure the accuracy of the model [46,47]. We used RMSE and CC to evaluate the model on Table 1 and the model calculations were calculated yielding a relatively high RMSE = 1.8127. The result of the CC analysis shows that the correlation coefficient of K of the pumping test and Inversed K is 0.468, which indicates that there is a moderately weak positive correlation between K (pumping test) and Inversed K. If well Y28, Y34, and Y26, which have a large bias, are removed, the result of the correlation coefficient turned out to be 0.763, indicating that the two sets of data have a strong positive correlation. Because the purpose of the exploration wells in the study area is for the later water production, the K values of Y28, Y34 and Y26 in the exploration wells are the large deviations in the study area, and the actual parameter inversion is the average permeability coefficient of the study area obtained. The model calculation is the average value on the whole aquifer thickness, while the pumping test is the average of the permeability coefficient values of the aquifer in the pumping section. The aquifer parameters over the area obtained by the model inversion better reflect the non-homogeneity of the area.

Table 2.
Comparison of inversion values and pumping test values.
Despite discrepancies in outliers (e.g., Y28, Y34 and Y26), the correlation coefficient between the pumping test and the inversion results improved from 0.47 to 0.76 after excluding biased wells, demonstrating the SLE method’s effectiveness in resolving regional aquifer heterogeneity. This performance is comparable to hydraulic tomography applications in the Zhuoshui River alluvial fan [13] and the Kansas River Basin [28] where similar correlation improvements (0.5–0.8) were achieved.
4.5. Implications and Challenges
This study has demonstrated that the canal(river) stage hydraulic tomography provides useful information for delineating basin-scale aquifer heterogeneity. The proposed approach eliminates the need for resource-intensive pumping tests, offering a cost-effective alternative for parameter estimation in data-scarce regions. Its application is particularly valuable in arid areas where irrigation-induced canal fluctuations provide consistent natural stimuli, as demonstrated in analogous studies in Tunisia’s Merguellil Basin [34] and California’s Central Valley [27].
Despite this study’s advances in basin-scale parameter estimation, challenges remain in isolating groundwater responses solely caused by canal stage variations, as other factors (e.g., precipitation, pumping) may introduce noise. Future work should integrate multi-source data (e.g., satellite-based evaporation rates, pumping logs) and leverage global datasets (e.g., the World Karst Aquifer Map) to refine comparisons with regional and global benchmarks. Extending this framework to 3D models and other aquifer types (e.g., fractured systems in the Loess Plateau) could further validate its universality.
The findings contribute to a growing body of work emphasizing natural stimuli methods in hydrogeology, aligning with global efforts to optimize groundwater management in water-stressed regions [2]. By contextualizing Qingtongxia’s results within both regional (Yellow River Basin) and global (arid alluvial aquifers) frameworks, this study highlights scalable solutions for sustainable water resource strategies in irrigation-dominated basins.
The spatial heterogeneity of aquifer parameters derived from this study provides actionable insights for optimizing irrigation practices and groundwater resource management in the Qingtongxia Irrigation Area. The inverted hydraulic conductivity (T) maps indicate higher permeability in the southern alluvial fan compared to the northern plains. To minimize seepage losses in high-K zones, priority should be given to lining canal segments in these areas with low-permeability materials (e.g., concrete or geomembranes). Conversely, in regions requiring enhanced groundwater recharge (e.g., overexploited northern plains), controlled unlined sections could be strategically retained. About Flow Regulation Based on Lag Time: The observed lag time of groundwater response to canal stage changes suggests that canal operations should account for delayed aquifer recharge. For instance, irrigation schedules could be staggered to align with the propagation of water table responses, ensuring uniform soil moisture distribution across fields. The correlation between canal proximity and groundwater response magnitude (Figure 6) implies that farms closer to canals require less irrigation water due to lateral seepage. Tailoring water allotments based on distance-to-canal gradients could reduce over-irrigation and energy costs.
5. Conclusions
Based on the latest developments in the theory of Hydraulic tomography, the inversion of large-scale regional hydrological parameters was carried out by using the changes of surrounding monitoring wells caused by the changes of river (canal) water stage. This method makes full use of the natural process of irrigation channel diversions in arid areas and is able to carry out the identification of large-scale hydrological parameters. If it can be combined with other methods, it is a good method for improving the reliability of the estimated hydrological parameters of aquifers. This method first used correlation analysis for the analysis of irrigation channel stage variation and groundwater level variation in monitoring wells, and then it used the SLE method to inverse the spatial distribution of regional-scale aquifer hydraulic conductivity coefficients T and Ss by back propagation iterative methods. This method is particularly suitable for regions where rivers recharge groundwater and where there is a strong correlation between river stage and water level changes in monitoring wells. This method makes full use of the natural stimulation method to calculate hydrological parameters at the regional scale, and it has a certain promotion value in arid regions. The results of this study can provide a direct reference for water resources management in similar regions (e.g., Hetao Irrigation District and Hexi Corridor in China), and not only promote the development of groundwater parameter estimation methods in arid zones but also provide a replicable technological framework for water resources management in similar irrigation districts around the world.
With the construction and improvement of the national groundwater dynamic monitoring network, a large amount of high-frequency monitoring data of groundwater response to natural stimuli will be obtained. The hydrological parameters of aquifers will be calculated by using the natural stimuli method, and a set of model algorithms for inversion of hydrological parameters using river stage changes will be developed, which is of great significance for obtaining regional hydrological parameters of the study area and guiding water resources development and utilization. However, in the actual field situation, the water level variation of groundwater monitoring wells is influenced by many natural factors, such as nearby river stage variation, tides, barometric pressure, precipitation, evapotranspiration, recharge, groundwater extraction and so on. It is difficult to strip out the groundwater changes in monitoring wells caused by river level changes from the many signals. Detailed analysis of various factors of specific water level changes is required in field practice to obtain more accurate hydrological parameters.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, C.L.; Investigation, P.W.; Data curation, W.X., L.F. and Y.L.; Writing–original draft, Z.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41672241).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Delleur, J.W. Elementary Groundwater Flow and Transport Processes. In The Handbook of Groundwater Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 2.1–2.40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Illman, W.A. On the Importance of Considering Specific Storage Heterogeneity in Hydraulic Tomography: Laboratory Sandbox and Synthetic Studies. J. Hydrol. 2021, 593, 125874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirlas, M.C. Assessment of Porous Aquifer Hydrogeological Parameters Using Automated Groundwater Level Measurements in Greece. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzedine, S.; Rubin, Y.; Chen, J. Hydrological-Geophysical Bayesian Method for Subsurface Site Characterization: Theory and Application to LLNL Superfund Site. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2671–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltermann, C.E.; Gorelick, S.M. Heterogeneity in Sedimentary Deposits: A Review of Structure-Imitating, Process-Imitating, and Descriptive Approaches. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2617–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckie, R.; Harvey, C.F. What Does a Slug Test Measure: An Investigation of Instrument Response and the Effects of Heterogeneity. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 26-1–26-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.M.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Zhu, J.; Lee, T.H.; Hsu, N.S.; Chen, C.H.; Sancho, A.F. Traditional Analysis of Aquifer Tests: Comparing Apples to Oranges? Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W09402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Liu, S. Hydraulic Tomography: Development of a New Aquifer Test Method. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yeh, T.C.J. Characterization of Aquifer Heterogeneity Using Transient Hydraulic Tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W07028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Wen, J.C. A Simultaneous Successive Linear Estimator and a Guide for Hydraulic Tomography Analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W02432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, M.; Barrash, W.; Kitanidis, P.K.; Malama, B.; Revil, A.; Straface, S.; Rizzo, E. A Potential-Based Inversion of Unconfined Steady-State Hydraulic Tomography. Groundwater 2009, 47, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, Z.; Illman, W.A. Detection of Karst Conduit Patterns via Hydraulic Tomography: A Synthetic Inverse Modeling Study. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Wen, J.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Zha, Y.; Tsai, J.P. Characterizing Subsurface Hydraulic Heterogeneity of Alluvial Fan Using Riverstage Fluctuations. J. Hydrol. 2019, 547, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illman, W.A.; Liu, X.; Craig, A. Steady-State Hydraulic Tomography in a Laboratory Aquifer with Deterministic Heterogeneity: Multi-Method and Multiscale Validation of Hydraulic Conductivity Tomograms. J. Hydrol. 2007, 341, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.; Zhao, Z.; Illman, W.A.; Berg, S.J. Comparative Study of Transient Hydraulic Tomography with Varying Parameterizations and Zonations: Laboratory Sandbox Investigation. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 758–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, M.; Zhou, Y.; Barrash, W.; Kitanidis, P.K. Aquifer Imaging with Oscillatory Hydraulic Tomography: Application at the Field Scale. Groundwater 2020, 58, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straface, S.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Zhu, J.; Troisi, S.; Lee, C.H. Sequential Aquifer Tests at a Well Field, Montalto Uffugo Scalo, Italy. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W07432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Yeh, T.C.J.; Illman, W.A.; Tanaka, T.; Bruines, P.; Onoe, H. An Application of Hydraulic Tomography to a Large-Scale Fractured Granite Site, Mizunami, Japan. Groundwater 2016, 54, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, K.C.; Illman, W.A.; Barrash, W.; Cai, X.; Daniels, J.; Sudicky, E.; Wan, L.; Li, G.; et al. A View Toward the Future of Subsurface Characterization: CAT Scanning Groundwater Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W03301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Xiang, J.; Suribhatla, R.M.; Hsu, K.C.; Lee, C.H.; Wen, J.C. Riverstage Tomography: A New Approach for Characterizing Groundwater Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W05409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, H. The Estimation of Aquifer Parameters Using Tidal Effect in a Coastal Aquifer: A Case Study in Beihai Peninsula, Guangxi China. Earth Sci. Front. 2009, 16, 276–281. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.N. Estimating Aquifer Parameters from Barometric-Pressure Effect of Groundwater Before and After Wenchuan Earthquake. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.; Lee, J. A Non-Bayesian Nonparametric Model for Characterization of Basin-Scale Aquifers Using Groundwater Level Fluctuations. J. Hydrol. 2021, 602, 126710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.G.; Knowles, D.B.; Brown, R.H.; Stallman, R.W. Theory of Aquifer Tests. In U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 1536 E; United States Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1963; 174p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferris, J.G. Cyclic Fluctuations of Water Level as a Basis for Determining Aquifer Transmissibility. In U.S. Geological Survey, Ground Water Hydraulics Section, Contribution No. 1; United States Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1952; 17p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.J.; Gelhar, L.W.; Gross, G.W. Recharge and Groundwater Conditions in the Western Region of the Roswell Basin. Report; New Mexico State University MSC: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Gelhar; Duffy, C.J.; Gross, G.W. Stochastic Methods of Analysing Groundwater Recharge: Symposium on Hydrology of Areas of Low Precipitation. 1979. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261722292_Stochastic_Methods_of_Analysing_Groundwater_Recharge (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Sophocleous, M. Stream-Floodwave Propagation Through the Great Bend Alluvial Aquifer, Kansas: Field Measurements and Numerical Simulations. J. Hydrol. 1991, 124, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinder, G.F.; Bredehoeft, J.D.; Cooper, H.H. Numerical Determination of Aquifer Diffusivity from Aquifer Response to Fluctuations in River Stage. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.R.; Moench, A.F. Application of the Convolution Equation to Stream-Aquifer Relationships. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Jayalekshmi, K.; Machiwal, D.; Kamii, Y.; Chikamori, K. Determination of Hydraulic Parameters of an Unconfined Alluvial Aquifer by the Floodwave-Response Technique. Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, G.; Richon, J.; Perrochet, P.; Vogel, A.; Brunner, P. Rapid Identification of Transience in Streambed Conductance by Inversion of Floodwave Responses. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.K.; Singh, A. Application of Genetic Algorithm Technique to Inverse Modeling of Tide-Aquifer Interaction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3655–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, H. Consideration of the Use of Direct Recharge in Analytical Models of Floodwave Response: A Case Study of the Merguellil Alluvial Aquifer, Central Tunisia. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 2395–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Luo, W.; Fang, S.; Wang, L.; Tian, S. Quantifying Drainage Components and Salt and Water Balance in YinNan Irrigation District, China, Based on a Controlled Drainage Experiment. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hollanders, P.H.J.; Wang, S.; Fang, S. Effect of Field Groundwater Table Control on Water and Salinity Balance and Crop Yield in the Qingtongxia Irrigation District, China. Irrig. Drain. 2004, 53, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z. Water Resources Evaluation of Urban Water Sources in Wuzhong City of Ningxia. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y. Interaction Between Surface Water and Groundwater in Yinchuan Plain. Water 2020, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P. Stable Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotopes as Indicators of Lake Water Recharge and Evaporation in the Lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Dynamic Change of Shallow Aquifer in Qingtongxia Irrigation District and Water Ecology Protection. China Water Resour. 2016. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SLZG201613027.htm (accessed on 12 March 2025). (In Chinese).
- Promma, K.; Zheng, C.; Asnachinda, P. Groundwater and Surface-Water Interactions in a Confined Alluvial Aquifer Between Two Rivers: Effects of Groundwater Flow Dynamics on High Iron Anomaly. Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardani, A.; Dupont, J.P.; Revil, A.; Massei, N.; Fournier, M.; Laignel, B. Geostatistical Inverse Modeling of the Transmissivity Field of a Heterogeneous Alluvial Aquifer Under Tidal Influence. J. Hydrol. 2012, 472–473, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.T.; Chang, L.C.; Tsai, J.P.; Chen, Y.C. Features of Spatiotemporal Groundwater Head Variation Using Independent Component Analysis. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.C.J.; Srivastava, R.; Guzman, A.; Harter, T. A Numerical Model for Water Flow and Chemical Transport in Variably Saturated Porous Media. Groundwater 1993, 31, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Sun, Y. The Report on the Hydrogeological Environmental Geological Survey of the Yellow River Economic Zone in Ningxia. 2016. Available online: https://www.cgl.org.cn/new/szzy0516.html (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- El-Azhari, A.; Karaoui, I.; Brahim, Y.A.; Azhar, M.; Chehbouni, A.; Bouchaou, L. Analyses of Groundwater Level in a Data-Scarce Region Based on Assessed Precipitation Products and Machine Learning. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, S.; Golian, M.R.; Kavianpour, Y.; Hong, Y. Comparison of PERSIANN and V7 TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Products with Rain Gauge Data over Iran. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2024, 34, 8156–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).