Abstract
The Arabian Desert is characterised by very low rainfall and high evaporation, yet over 210 springs are on its northeastern edge in central Iraq along the Abu Jir lineament, which represents the western depositional margin of a foreland basin infilled by the floodplain sediments of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers; there is little evidence of faulting. The springs discharge from gently east-dipping Paleocene–Eocene limestones, either where groundwater flowpaths intersect the ground surface or where groundwater flow is forced to the surface by confining aquitards. Calculated annual recharge to the aquifer system across the Arabian Desert plateau (130–500 million m3) is significant, largely due to rapid infiltration through karst dolines, such that karst porosity is the primary enabler of groundwater recharge. The recharge is enough to maintain flow at the Abu Jir springs, but active management of groundwater extraction for agriculture is required for their long-term sustainability. The hydrochemistry of the springs is determined by evaporation, rainfall composition (high SO4 concentrations are due to the dissolution of wind-blown gypsum in rainfall), and plant uptake of Ca and K (despite the sparse vegetation). Limestone dissolution has relatively little impact; many of the springs are undersaturated with respect to calcite and lack tufa/travertine deposits. The springs at Hit-Kubaysa contain tar and high levels of H2S that probably seeped upwards along subvertical faults from underlying oil reservoirs; this is the only location along the Abu Jir lineament where deep-seated faults penetrate to the surface. The presence of hydrocarbons reduces the Hit-Kubaysa spring water and converts the dissolved SO4 to H2S.
1. Introduction
The Arabian Desert extends across much of Saudi Arabia and Iraq and is characterised by very low rainfall, high evaporation, and sparse vegetation. Nevertheless, along its northeastern edge in central Iraq, there is an extensive line of over 210 springs along the northwest–southeast geographical divide between the desert and the fertile Mesopotamia plains of the Euphrates and Tigris Rivers (Figure 1). These springs also lie along a cultural divide between the desert, the realm of nomadic people, and the floodplain, where a reliable supply of water has allowed for the development of the flourishing permanent human settlements [1].
For this study, we carried out the first comprehensive mapping of the Abu-Jir Springs and integrated this with a reassessment of the significant amount of available data on the springs in order to determine the reasons for their existence in such an arid region.
The linear feature associated with the springs is generally identified as a major fault (the Abu Jir Fault) [2]. However, geological mapping has failed to identify a near-surface rupture that coincides with the springs, e.g., [3], so the interpretation of this fault seems to be largely conjectural. To understand the nature of the geomorphological/geological structure associated with the springs, we reassessed the regional geological mapping and seismic data for the area.
The springs are supplied by groundwater from the Umm er Radhuma-Dammam aquifer underlying the Arabian Desert to their west [4]. This aquifer has been exploited by recent extraction for irrigated agriculture in some areas [5,6], although much of the groundwater from the aquifer is saline [7]. The exploitation has impacted many of the springs and has been regarded as unsustainable. However, the potential recharge area of the aquifer feeding the springs is enormous, even though it coincides with a landscape of very low rainfall. Here, we assess the sustainability of the springs under current rainfall using two different methods to calculate the recharge potential.
The chemical composition of the springs is characterised by high levels of SO4 and often high salinity; the Hit-Kubaysa springs also contain tar and H2S. The interpretation of these characteristics has invoked many different processes: evaporation [7,8],the dissolution of gypsum [7,9], evaporites [7], and carbonates [5,7,8], the input of connate sea water [10,11], and, for the Hit-Kubaysa springs, the input of petroleum and brines from reservoirs deep beneath the springs [12]. Here, we reassess the hydrochemical evidence using new methods of interpretation, including a comparison with rainfall composition, as this is essential for determining which species in solution were derived from rainfall and which from rock–water interactions in the aquifers.
2. Materials and Methods
For the mapping of the springs, we used the CORONA satellite photography derived from the United States intelligence program of satellite reconnaissance from 1959 to 1972 [13,14], which was verified by fieldwork for many springs during this study. The CORONA images dating from August 1968 are essential for locating the springs on the Abu Jir lineament because they predate the groundwater extraction for agricultural development that has deactivated many springs. The mapping was also informed by the detailed map and journal compiled by Alois Musil, a Czech theologian and explorer who made multiple journeys through the Middle East. He travelled southeast along the Abu Jir lineament in 1912, providing locations and names for the springs [15].
Data on the hydrogeology of the region and the spring hydrochemistry were obtained from existing published sources and then integrated and reassessed. For the hydrochemical study, the spring compositions were plotted on a Piper plot. In addition, the median composition of spring water from four different sets of springs along the Abu Jir lineament (Hit-Kubaysa, Haqlaniyah, Shinafiyah, and Najaf) was compared with rainfall (obtained at Riyadh) using a standardised Schoeller plot. A Schoeller plot is a semi-logarithmic diagram of species concentrations from multiple samples, with the advantage that, unlike trilinear plots, the actual concentrations are displayed [16]. The data in the present study were standardised to the Cl− value of rainfall. This removes any influence of evaporation [17], i.e., if the spring waters represented just evaporated rainwater, with no other influence on their chemistry, all lines on the Schoeller plot for spring water would plot over the top of the rainfall line. This procedure assumes that all Cl− arrives in rainfall and that processes in the soil or aquifer (apart from evapotranspiration) do not affect the Cl− concentration.
The saturation indices (SIs) with respect to calcite were calculated for the spring water compositions [18]:
where
The recharge for the springs was calculated using two methods. The first, the chloride (Cl−) mass balance (CMB) method [19,20], is based on the relationship between Cl− concentrations in groundwater and in precipitation (rainfall) (Equation (3)). As for the Schoeller plot, this calculation assumes that all Cl− in the groundwater is derived from rainfall and remains in solution within the groundwater system and that there is no significant loss of chloride in runoff:
The second method for calculating recharge used the empirical relationship between rainfall and recharge from MacDonald et al. [21]:
3. Abu Jir Springs
The Abu Jir springs total 214 in number and lie along the Abu Jir lineament, which extends in a slightly arced line for ~520 km (Figure 1). The maximum distance between the springs along the lineament is 42 km northwest of Razazza Lake, and the maximum width across the complex of springs is 26 km in the Hit-Kubaysa area. The springs are closely aligned along the western edge of the Mesopotamian floodplain (Figure 2), which is here called the Abu Jir lineament (discussed further below).
In general, the springs have low flows, with an average discharge of <1 L/s, and provide little inflow to the Euphrates River, which is mostly located to the east of the spring line (Figure 1). At Haqlaniyah and Hit, the springs provide a minor inflow to the main channel of the river, and to the northwest of Qaryat al Gharab (Figure 1), the springs occur on either side of the Al-Atshan River, a channel of the main Euphrates stream crossing an area of marshland. The springs do not discharge into most of the large ephemeral salt lakes to the east of the lineament, although a spring that provides a groundwater source for Sawa Lake (Figure 1) is occasionally exposed when the lake levels recede (Figure 3). Some springs have associated travertine deposits, especially near Hit and Abu Jir (Figure 1).
3.1. Geological and Geomorphological Setting
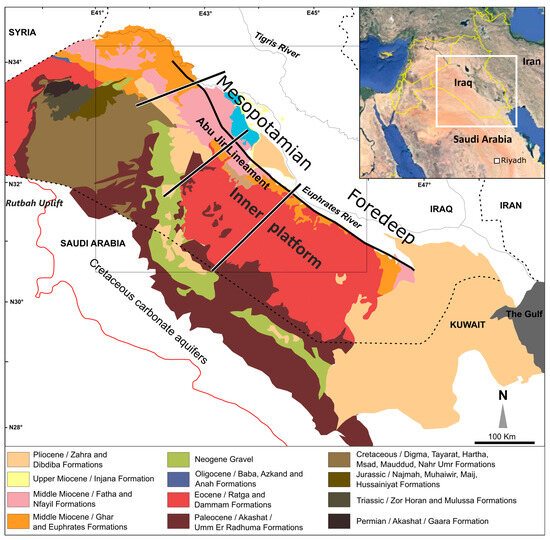
The geology and geomorphology of Iraq are the result of its tectonic history, in particular, the collision between the Arabian and Eurasian plates during the Alpine Orogeny, which began in the Early Paleogene, with a significant phase in the Pliocene–Early Pleistocene [22,23]. Tectonism continues today; the Arabian Plate is still moving northeastwards at ~1.5 cm/year. The thrusting of the Eurasian Plate over the Arabian Plate formed, in increasing distance from the collision zone (i.e., northeast to southwest), the Zagros fold and thrust belt, the Mesopotamian foredeep, and the inner Arabian platform [23,24] (Figure 4). These three tectonic units correspond to the three major geomorphic subdivisions of Iraq (Figure 2). In the northeast are the rugged peaks and linear ridges of the Zagros Mountains, uplifted by the collision and rising to over 3000 m. To the southwest is the flat Mesopotamian Plain, almost entirely < 100 m in elevation, which slopes very gently towards the Persian Gulf; it is crossed by the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers [22]. Beneath the plain are gently folded Cretaceous limestones and sandstones, which are important oil reservoirs in central and southern Iraq [25]. The Mesopotamian Plain represents a foreland basin that subsided in front of the rising Zagros Mountains and was infilled by the floodplain sediments of the rivers. To the southwest is the Arabian desert plateau, rising slowly westwards to over 800 m at the border with Saudi Arabia, and composed largely of Paleogene and Neogene carbonate sediments that dip very gently eastwards.
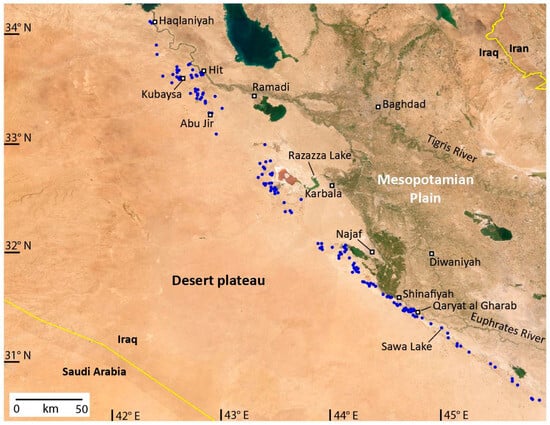
Figure 1.
Location of springs (blue dots) along the Abu Jir lineament, and modern cities (squares). For location, see Figure 4.
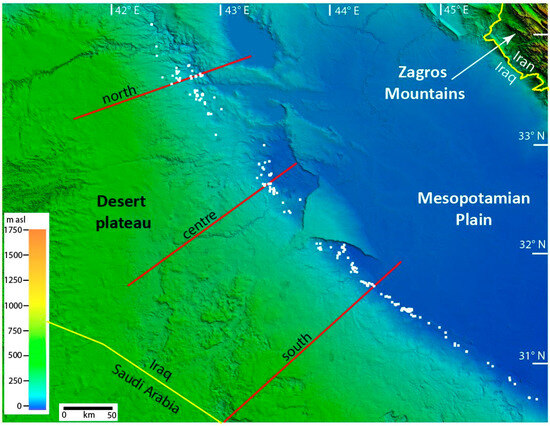

Figure 3.
Spring exposed in the bed of Sawa Lake when the lake receded (see Figure 1 for location).
The well-defined topographic boundary between the Mesopotamian Plain and the desert plateau, which trends northwest–southeast for ~520 km (Figure 2), is referred to here as the Abu Jir lineament, because it is a well-marked linear feature. It has also been called the Abu Jir Fault, e.g., [24], but there is little evidence of surface displacement along most of the lineament [28], and cross-sections on the 1:250,000 geological maps covering the lineament show uninterrupted east-dipping strata, e.g., [3]. Even in the Hit-Kubaysa area, where there is evidence of hydrocarbon leakage up steeply dipping faults along or close to the lineament, no displacement has been documented at the surface [8,29]. Seismic sections show that right-lateral strike-slip faults (flower structures) exist at depths beneath the Abu Jir lineament [28], but these have minimal vertical displacement and also occur beneath the Mesopotamian Plain [30].
To confirm this interpretation, new cross-sections were constructed along the lineament using all available geological and geomorphological information (Figure 5); these show clearly that the Abu Jir lineament does not coincide with a fault. It is instead a topographic feature that forms the western edge of the floodplains of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. It, therefore, represents the western depositional margin of the foreland basin (Mesopotamian Plain) that subsided in front of the rising Zagros Mountains as the Eurasian Plate was thrust over the Arabian Plate and was infilled by the floodplain sediments of the rivers.
To the west of the Abu Jir lineament is the Arabian Desert plateau (Figure 2). This has very low relief, increasing gradually westwards in elevation from ~100 m at the lineament to over 800 m at the border with Saudi Arabia. The exposed strata in the eastern part of the plateau are predominantly carbonates of Paleocene to Miocene age (Figure 4); older sediments of Permian to Cretaceous age (mostly carbonates) outcrop to the west. The northeastern part of the plateau is dissected by shallow valleys running northeastwards; elsewhere it is characterised by a rocky surface with numerous solution features, such as karst depressions (dolines) (Figure 2), some of which lead to caves. On the desert plateau in eastern Saudi Arabia, horizontally developed shallow caves and vertical shafts have been reported; these are believed to have formed predominantly during wetter climate phases in the Pleistocene [31,32].
3.2. Hydrogeological Setting
The hydrogeology of the springs along the Abu Jir lineament is determined by the geology of the Arabian Desert plateau, which represents the recharge area for the springs. Carbonate aquifers of Cretaceous–Miocene age are exposed across most of the plateau (Figure 4) and extend continuously eastwards beneath the clay-rich aquitard of the Quaternary sediments of the Mesopotamian Plain (Figure 5). Miocene–Pliocene aquitards overlie the carbonate aquifers in places along the easternmost margin of the desert plateau, close to the Abu Jir lineament (Figure 5) [4].
The oldest carbonate units that form significant aquifers are Cretaceous in age; these outcrop in the central and western parts of the desert plateau. In stratigraphic order, these are the Mauddud Formation (horizons up to 50 m thick of limestone and marl), the Rutbah Formation (sandstone and some limestone, 20–30 m thick), and the Ms’ad Formation (about 65 m of limestone with thin sandstone tongues) [2]. These are overlain by the Late Cretaceous Hartha, Tayarat, and Digma Formations, with a total thickness of >100 m; all of these latter units contain marl horizons, particularly the Digma Formation, which may act as aquicludes separating the Cretaceous aquifers from younger Paleogene aquifers.
The two main aquifers of the desert plateau are the Paleocene Umm Er Radhuma Formation and the Eocene Dammam Formation [4] (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Over most of the plateau, the Dammam Formation directly overlies the Umm Er Radhuma Formation [2], and the two form a single unconfined aquifer system. The Umm Er Radhuma Formation consists of microcrystalline, porous, anhydritic, and dolomitic limestones, mostly dull white or buff, with a thickness of 120–180 m. The Dammam Formation comprises whitish grey, porous, dolomitised limestone, sometimes chalky, and is up to 225 m thick. Two members of the Dammam Formation are exposed in the eastern and southern parts of the desert plateau, a Lower Member of whitish grey fossiliferous (nummulites) limestone, and a Middle Member of white, massive shelly limestone; shells are mainly oysters with few small nummulites [2].
Overlying the Dammam Formation is the Early Miocene Euphrates Formation, which consists of white and grey fossiliferous limestone and dolomite. Although it can be over 100 m thick, it is generally much thinner. This formation is also an aquifer, so it represents an additional part of the Umm Er Radhuma Formation/Dammam Formation aquifer system.
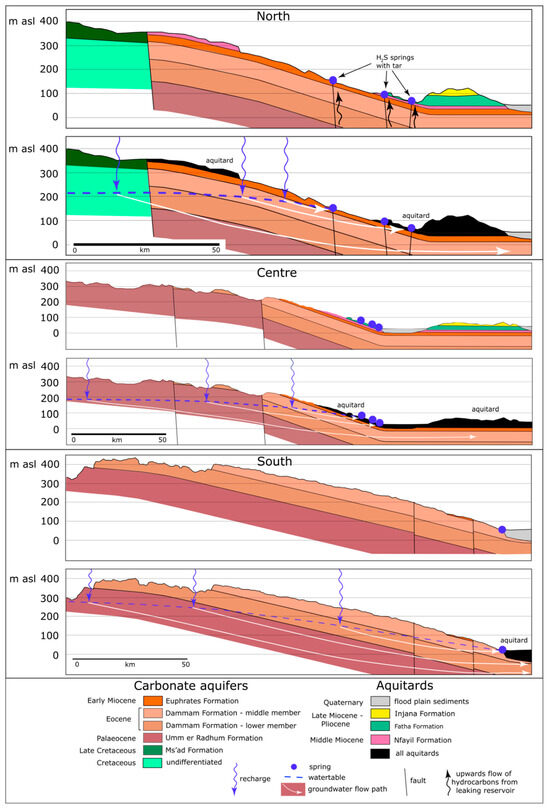
Figure 5.
Geological cross-sections along the Abu Jir lineament (for locations, see Figure 2 and Figure 4), showing the hydrogeology of the springs. Note the vertical exaggeration (x82); the actual westwards dip of the strata is <1°. Stratigraphy derived from the outcrop distribution and bore logs on the following 1:250,000 geological maps: Karbala [33]; Al Najaf [34]; Baghdad [35]; Al Birreet [36]; Al Ramadi [37]; Shithatha [38].
The porosity and permeability of the carbonate aquifers are due to both dissolution cavities and tectonic fractures [39]; as a result, the hydraulic conductivity of the Umm Er Radhuma and Dammam Formations can reach 20 and 100 m/day, respectively [4]. The Middle Member of the Dammam Formation in the vicinity of the Abu Jir lineament has an average porosity of 22% and hydraulic conductivity of 6 m/day [3]; to the south, in Kuwait, the porosity and permeability of the Dammam Formation can be as much as 53% and 5 m/day, respectively [40].
Groundwater flow within the carbonate aquifers beneath the desert plateau follows the topographic gradient, flowing from southwest to northeast in the northern part of the plateau and west to east in the south [4]. The watertable within the unconfined carbonate aquifers lies up to 300 m below the ground surface along the Saudi Arabian border, and approaches the surface towards the east, as it slopes gently towards the Abu Jir lineament (Figure 5); the slope of the watertable is gentler than that of the topography. East of the lineament, the Umm Er Radhuma and the Dammam Formations extend continuously beneath the sediments of the Mesopotamian Plain as a confined aquifer [4] (Figure 5), and bores within these units close to the lineament are often artesian [3,41].
Along the eastern edge of the desert plateau, the Umm Er Radhuma/Dammam/Euphrates Formation aquifer system is overlain by several thin, Middle and Late Miocene clay-rich units that, together, form an aquitard (Figure 5): the Nfayil Formation (green marl, grey limestone, and red-brown mudstone), the Fat’ha Formation (green marl and bedded limestone), and the Injana Formation (red brown mudstone and sandstone). Each of these units is typically only a few meters thick.
East of the Abu Jir lineament, beneath the Mesopotamian Plain, the Paleogene–Neogene carbonate aquifers are unconformably overlain by Quaternary floodplain muds and sands (Figure 5), up to 100 m thick, forming an extensive aquitard.
3.3. Hydrogeology of Abu Jir Springs
Along the southern part of the Abu Jir lineament, the springs are mostly sited at the break in slope between the desert plateau and the Mesopotamian Plain. Here, the carbonate aquifers outcrop right up to the lineament (Figure 5), so the boundary between the aquifers and the aquitard of the flood plain sediments lies directly along the lineament. The effect of the clay-rich aquitard sediments of the floodplain is to impede the eastward groundwater flow and force the groundwater to the surface as springs, which are, therefore, located where the watertable intersects the ground surface (Figure 5). Many of the springs are probably fed by conduits dissolved in the limestone, accounting for their occurrence as discrete vents rather than strike-parallel linear seeps.
In contrast, further north along the Abu Jir lineament, the springs are located both at the break in slope and 10 km or more to the west (upslope) due to a different geological setting. In the north, the carbonate aquifers are overlain by Miocene aquitards along the base of the slope immediately west of the Abu Jir lineament (Figure 5); these aquitard outcrops raise the watertable and force the springs higher up the slope. As a result, the springs occur at the upslope extent of the aquitard outcrops but also lower down the slope, where they have broken through the thin aquitard beds. As in the southern area, the springs are most likely conduit-fed.
Among the northern springs are the Hit-Kubaysa springs, which are notable for their tar and H2S content [12]. These springs may lie along faults that allow for an upwards leakage of hydrocarbons from reservoirs beneath (Figure 5) (discussed further below). However, there is no evident surface displacement of the carbonate aquifers in this area [8,29], so the role of the faults in determining the spring locations is uncertain.
3.4. Recharge to the Abu Jir Springs
Although the Umm er Radhuma-Dammam aquifer system has recently been categorised as non-renewable [42], recharge is demonstrably occurring at present, as shown by the presence of measurable tritium in the groundwater, indicating recharge in the last 50 years [43,44]. To estimate this recharge, the chloride (Cl−) mass balance method (Equation (3)) was applied, using the precipitation-weighted mean Cl concentration of rainfall in Iraq and Saudi Arabia, (10–20 mg/L) [45,46,47], the average chloride concentration of the springs at Najaf (Table 1) and the groundwater in the Dammam Formation, (588 and 980 mg/L, respectively) [10], and the average annual rainfall of the desert plateau (100 mm; ranging from 64 mm at Ar’ar in Saudi Arabia to 142 mm on the eastern edge of the desert; much of the rain falls during erratic events of >50 mm). This gave an annual recharge of 1–3.4 mm.
Employing the MacDonald et al. [21] empirical relationship between rainfall and recharge (Equation (4)) using the average annual rainfall of the desert plateau gave an annual recharge of 4 mm. The results of both calculations are close to the measured average recharge of 2.2 mm/yr on the Arabian Peninsula to the southeast [44].
The overall annual recharge to the Neogene carbonate aquifer can be calculated from these recharge estimates and the catchment (outcrop) area in Iraq and immediately across the border to the southwest in Saudi Arabia, which is ~123,000 km2, giving an overall annual recharge of 126–420 million m3 (344–1150 ML/day). If the outcrop of the Cretaceous carbonates to the west in Saudi Arabia is included, the catchment area increases to 208,000 km2, and the annual recharge rises to 210–700 million m3 (580–1900 ML/day).
Recharge over the desert plateau occurs despite the low rainfall (50–150 mm) and the very high evaporation (>2000 mm). This is probably because much infiltration occurs rapidly through the outcrop, assisted by the numerous karst dolines scattered over the plateau, which funnel rainfall underground, so that the amount of recharge after rainfall events can be substantial [43]. Some of these dolines are large enough to be visible on the low-resolution DEM of the region (south-central part of Figure 2). Thus, the karst porosity is the primary enabler of groundwater recharge due to its recognisable effect on the nature of runoff dynamics. In the southwestern part of the plateau, within Saudi Arabia, recharge also occurs directly through overlying sand dunes [43].
If all the recharge to the Neogene carbonates discharged at the 214 springs along the Abu Jir lineament, it would give an average spring flow of 20–60 L/sec (1.6–5.5 ML/day). This is much greater than the average spring discharge of <1 L/sec (0.04–20 ML/day, average < 0.1 ML/day) [12,48,49]. The total volume of discharge through the springs has been estimated as only 137 ML/day [42]. Spring discharge may have been substantially greater prior to extraction for agriculture in some areas, but the excess of recharge over spring discharge indicates that the bulk of groundwater flow through the Umm er Radhuma-Dammam aquifer system bypasses the springs and probably flows through the carbonates beneath them (Figure 5).
The aquifer system is exploited for irrigated agriculture in some areas, and this has been regarded as unsustainable, but the calculated annual recharge for the Neogene carbonates (>344 ML/day) should be sufficient to maintain spring flow along the Abu Jir lineament (~137 ML/day). However, excessive extraction in localised areas will cause the watertable to fall, and many of the springs have already been impacted. Therefore, the long-term sustainability of the springs relies on the active management of groundwater extraction rates.
On the Arabian Peninsula, the groundwater residence times within the Umm er Radhuma and Dammam aquifers are up to 20,000–30,000 years, indicating that recharge may have been greater in the past, such as during the relatively wet ‘Pluvial Period’ from 9500 to 5000 years ago [44,50].
3.5. Hydrochemistry of the Abu Jir Springs
There is high variability in the salinity of the springs along the Abu Jir lineament and even between nearby locations, e.g., Hit-Kubaysa (Table 1), from high (>10,000 µS/cm at Hit), unsuitable for both drinking and irrigation, to moderate (>1800 µS/cm at Najaf). Even the latter levels are marginal for sustained irrigated agriculture, exceeding the recommended levels for drinking water in Europe and noticeably mineralised for unaccustomed users. The levels of fluoride and arsenic are low and safe for human consumption [8,29]. As would be expected, the springs’ salinity reflects that of the groundwater in the carbonate aquifers, which increases progressively from, on average, ~1000 mg/L in the west to over 5000 mg/L in the east towards the Euphrates River [4,43].
The spring water composition is variable (Figure 6, Table 1). Anions are dominated by high levels of either Cl or SO4, with much lower amounts of HCO3; for the cations, there are significant concentrations of Ca, Na, and Mg, and relatively minor K. The average composition of the springs broadly reflects that of the average Damman Formation groundwater (Figure 6), as might be expected. However, the Hit-Kubaysa springs show a separate linear trend of increasing Na and Cl; this probably reflects increasing contributions of deep-seated oilfield brine (discussed further below).
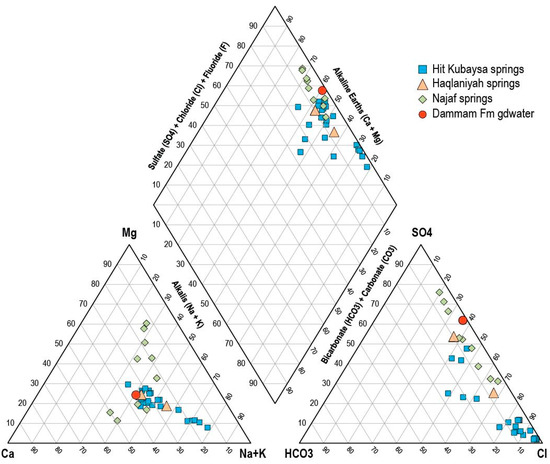
Figure 6.
Piper plot of compositions of Abu Jir springs (data from) [8,10,11]; note that many available spring compositions, including the Shinafiyah springs, were incomplete as published and could not be plotted.

Table 1.
Water chemistry data for the Abu Jir springs (medians: bold, ranges; number of samples: italics) and rainfall at Riyadh (precipitation-weighted mean). All values are mg/L unless indicated otherwise. See Figure 1 for spring locations. The saturation indices with respect to calcite were calculated using Equations (1) and (2).
Table 1.
Water chemistry data for the Abu Jir springs (medians: bold, ranges; number of samples: italics) and rainfall at Riyadh (precipitation-weighted mean). All values are mg/L unless indicated otherwise. See Figure 1 for spring locations. The saturation indices with respect to calcite were calculated using Equations (1) and (2).
| Location | T°C | pH | EC µS/cm | Ca | Mg | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | HCO3 | NO3 | SIcalcite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haqlaniyah [8,49] | 29 29–29 3 | 7.2 7.1–7.3 3 | 5068 5038–5523 3 | 312 288–320 3 | 144 134–146 3 | 251 230–709 7 | 22 21–94 3 | 1620 643–1925 7 | 674 403–1260 7 | 265 223–270 3 | 3 2–3 3 | 0.46 0.29–0.5 3 |
| Hit-Kubaysa [8,10,12,29,49] | 27 16–34 49 | 7.2 6.0–7.8 48 | 7100 1800–35418 23 | 400 225–1783 21 | 210 94–607 21 | 619 200–6876 27 | 85 5–540 21 | 1488 320–16100 45 | 480 91–3120 45 | 197 85–1380 21 | 7 2–10 8 | 0.31 −1.54–2.1 21 |
| Najaf [9,11,49] | 25 23–27 20 | 7.2 6.9–7.8 20 | 2360 1820–3200 20 | 188 112–326 10 | 185 46–342 10 | 271 203–457 13 | 54 41–74 9 | 588 350–2591 13 | 785 538–1765 13 | 116 45–140 9 | −0.19 −1.11–0.69 9 | |
| Shinafiyah [51] | 7.7 7.0–8.0 12 | 4815 4010–6080 12 | 391 346–496 12 | 242 160–294 12 | 817 690–1094 12 | 2610 1330–2861 12 | 178 121–211 12 | 0.77 −0.18–1.15 12 | ||||
| Riyadh rainfall [47] | 32 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 17 |
To better understand the factors responsible for the chemical composition of the spring water, a standardised Schoeller plot was constructed (Figure 7), comparing the median major ion chemistry of the springs with that of the nearest available rainfall data on the desert plateau at Riyadh [34] (Table 1); all data were standardised to the Cl− value of the rainfall to remove any influence of evaporation. Using median compositions illustrates overall trends, on which processes specific to particular spring groups are superimposed, causing the variability in the composition evident for the Hit-Kubaysa and Najaf springs (Figure 6), as discussed further below.
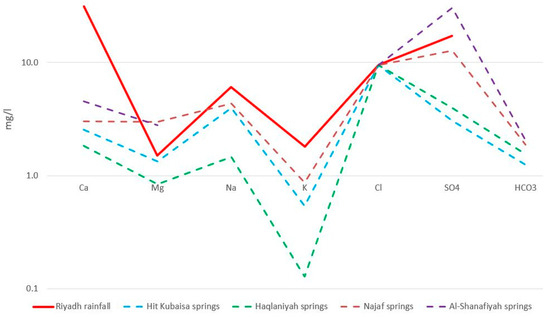
Figure 7.
Schoeller plot (standardised to Cl) comparing the median compositions of Abu Jir springs with desert plateau rainfall (see Table 1 for data).
The SO4 and Cl contents of the rainfall over the desert plateau (20–50 mg/L and 10–20 mg/L, respectively) reflect the dissolution of wind-blown gypsum and salt (halite), respectively, deflated from the extensive sabhkas in the region [47]. This contrasts with the typical rainfall compositions around the world, which are dominated by Na and Cl among the major ions in places where rainfall derives much of its dissolved content from seaspray, particularly along the coast, e.g., [52], but also inland, often called cyclic salt, e.g., [53]. The higher Ca and SO4 levels in the rainfall relative to Na and Cl (Figure 7) indicate that gypsum dissolution exceeds that of halite.
The standardised Schoeller plot (Figure 7) shows that, apart from Ca and, for the Hit-Kubaysa springs, SO4, the composition of the spring water broadly matches that of the rainfall, so the major source of dissolved Ca, SO4, Na, and Cl in the groundwater within the carbonate aquifers (and therefore, the springs issuing from these aquifers) is likely to be the dissolution of wind-blown evaporites in the rainfall. Therefore, it is not necessary to invoke congruent dissolution of gypsum along the groundwater flow path [7,9] to explain the high SO4 content of the springs. Incongruent dissolution of gypsum is also unlikely; in this process, gypsum dissolves, releasing calcium and sulphate, and some of the calcium precipitates as calcite, resulting in water compositions with relatively lower calcium than sulphate concentrations. Although the spring compositions have, on average, lower Ca than SO4 (Figure 7), many are undersaturated with respect to calcite (negative calcite saturation indices; Table 1) and so cannot precipitate calcite, and the depletion in Ca is more likely due to plant uptake (discussed below). In any case, the carbonate aquifers do not contain gypsum [2,4].
The species concentrations in the springs and groundwater are much greater than those in the rainfall (Table 1), because they were increased by evaporation during recharge [7,8]. The progressive increase in groundwater salinity from west to east within the carbonate aquifers is probably due to the progressive downflow addition of saline soil–water (concentration by evaporation during slow infiltration) to fresher groundwaters that were recharged rapidly through karst dolines; similar increases in salinity down-gradient have been documented elsewhere [52]. Additional evaporation during discharge may have further raised the salinity of the springs.
Interestingly, the standardised Schoeller plot (Figure 7) shows that the spring waters are depleted in Ca compared to the rainfall (but have approximately the same Mg content). There is, therefore, relatively little input to the groundwater of Ca and Mg due to limestone/dolomite dissolution within the carbonate aquifers, contrary to the hypotheses of previous studies [5,7,8]. The relative lack of carbonate dissolution is also evident by the fact that many springs, particularly those at Najaf, are undersaturated with respect to calcite (negative calcite saturation indices) (Table 1). If extensive carbonate dissolution had occurred along the groundwater flow paths, the spring waters would be saturated. In addition, the springs have relatively low HCO3 concentrations (Figure 6) and lack tufa/travertine precipitation around the spring vents. Furthermore, the morphology of limestone caves on the Arabian Peninsula, which formed during wetter climates in the Pleistocene, has been modified only slightly by dissolution under the present-day arid climate [54].
Nevertheless, some carbonate dissolution has contributed to the spring water composition; the variability in the relative Ca and Mg contents of the Najaf springs (Figure 6) is probably due to differences in the amount of limestone and dolomite dissolution along the flow path.
The spring waters show a notable depletion in K as well as Ca compared to rainfall (Figure 7). This is most likely due to the preferential uptake of Ca and K by plants as rainfall infiltrates through the soil. These ions are plant macronutrients; plants take up relatively large quantities of these species directly from the soil solution and/or from the cation exchange sites of clay minerals [55,56]. In contrast, plant uptake of Na and Mg is much lower, so the spring waters are not significantly depleted in these species relative to the rainfall (Figure 7). The mechanism of plant uptake has been identified as significant in determining groundwater composition elsewhere in the world, e.g., [17,57,58,59]. In Saudi Arabia and Iraq, the depletion in Ca and K due to plant uptake is surprising given the very arid climate and sparse vegetation cover.
There is no evidence that the depletion in Ca and K relative to rainfall is due to cation exchange because this would cause the spring waters to be enriched in Na and/or Mg, and this is not the case (Figure 7). Furthermore, the carbonate aquifers have a low clay content [2,4].
The springs in the Hit-Kubaysa area (Figure 1) are the best studied springs along the Abu Jir lineament because they are characterised by high H2S contents (up to 305 ppm) [24] and floating spongy tar (Figure 8), as well as elevated nitrate concentrations [8,29]. The hydrocarbon content of the springs makes the waters reducing, and as a result, the dissolved sulphate within the spring water is reduced to H2S. The removal of SO4 from solution means that the Hit-Kubaysa springs are depleted in this species compared to the other Abu Jir springs (Figure 7), also shown by the much higher Cl/SO4 weight ratio of the Hit-Kubaysa springs (2–10) [8,10,49] compared to the regional rainfall, the groundwater within the carbonate aquifers, and the spring water unaffected by SO4 reduction (0.4–0.5) [9,10,11,45,46,47,49]. The high nitrate levels in the springs were most likely released by degradation of the organic matter, as crude oils generally contain up to 1 weight % N in compounds, such as pyridines and amines [60], and elevated nitrate levels are typical of oil field brines [29]. The hydrocarbons within the Hit-Kubaysa springs have probably seeped upwards from underlying Jurassic–Cretaceous or Oligocene oil and gas reservoirs [61], driven by the lower density of the oil than the surrounding groundwater (0.85–0.95 g/cc compared to 1 g/cc for pure water). The oil in the springs is the same type as that from the East Baghdad field [49]. The seepage at Hit-Kubaysa is presumably occurring beneath the Abu Jir lineament along subvertical faults (Figure 5), which may be flower structures that have reached the surface [28]; this is the only location along the Abu Jir lineament where deep-seated faults penetrate to the surface. Hussien and Gharbie [12] proposed that deep groundwater (oilfield brine) is seeping upwards along with hydrocarbons at the Hit-Kubaysa springs, and there is good evidence for this. The salinity of the spring water increases to the east towards the Abu Jir lineament [12,29], resulting in a linear trend on the Piper plot (Figure 6), and probably reflecting an increasing contribution of oilfield brine. The maximum temperature of the springs around Hit (34 °C; Table 1), is ~10 °C warmer than the average air temperatures (21–24 °C), so this suggests that the springs are rising from at least 500 m depth; the geothermal gradient in the area is ~20°C/km [62]. The underlying oil reservoirs are at much greater depths [11], indicating that the brines are rising sufficiently slowly that their temperature has partially equilibrated with the aquifer temperature at shallower depths. The hydrocarbons and sulphurous content of the Hit-Kubaysa springs (Figure 5) are considered useful for bathing therapy for the treatment of inflammatory joint disease and psoriatic disease [29].
The above discussion shows that the species in the spring waters were derived either from rainfall, rock–water interaction within the aquifers, or, in the case of some Hit-Kubaysa springs, oilfield brines. Al Dahaan [10] and al Dahan et al. [11] hypothesised that there was also a contribution of connate seawater originally deposited with the marine carbonates of the aquifers. However, the aquifer carbonates are strongly cemented and lack any significant original granular porosity where the connate groundwater could have been stored. In any case, the maximum groundwater ages on the Arabian Peninsula are only 20,000–30,000 years [44,50], indicating that any connate seawater was flushed from the aquifers long ago. Furthermore, the stable isotope composition of the springs (Figure 9) is consistent with an origin entirely from rainfall. The stable isotope composition of seawater is around 0 for both δ18O and δ2H, and although there is one spring sample with stable isotope values close to this, it has undergone considerable evaporation [7]. The spring samples plot on the evaporation trends (Figure 9), because the spring flow rates are mostly slow enough to allow for significant evaporation soon after the spring water has reached the surface. Groundwater stable isotope data from nearby wells within the carbonate aquifers are mostly located to the right of the Local Meteoric Water Line (LMWL), indicating some evaporation during recharge. A few data lie to the left of the LMWL; this groundwater could have been recharged under a previous wetter climate, e.g., the relatively wet ‘Pluvial Period’ from 9500 to 5000 years ago [44,50].
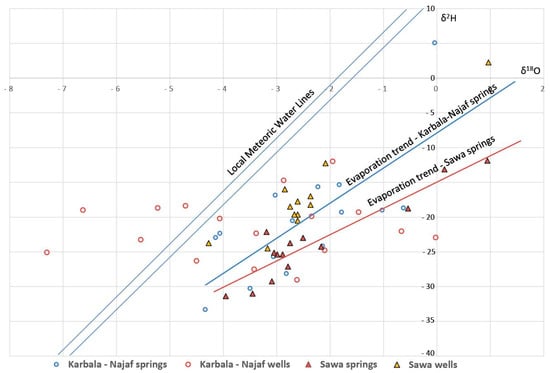
Figure 9.
Stable isotope data for some Abu Jir springs; groundwater data from nearby wells shown for comparison; data from refs. [7,48].

Figure 8.
Groundwater spring at Hit showing floating spongy bitumen (see Figure 1 for location).
4. Conclusions
A detailed study of the Abu Jir springs, using existing data and satellite mapping, has allowed for a reassessment of the hydrogeology and hydrochemistry of these springs, including the reasons for their existence in such an arid area. They lie along the 520 km-long NW-SE Abu Jir lineament that coincides with the boundary between the Mesopotamian Plain and the Arabian Desert plateau. This lineament is not a fault but the western depositional margin of a foreland basin infilled by the floodplain sediments of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. The springs discharge from the gently east-dipping Neogene Umm er Radhuma-Dammam aquifer system, which is composed of carbonates and has karstic permeability. Spring locations along the Abu Jir lineament occur where conduit flow in the carbonate aquifer intersects the ground surface at the break in slope between the Mesopotamian Plain and Desert plateau, or where it is forced to the surface by overlying aquitards, either Neogene marls or Quaternary floodplain sediments. Recharge to the aquifer system occurs across the Arabian Desert plateau and is facilitated by rapid infiltration through karst depressions, such that karst porosity is the primary enabler of groundwater recharge. Annual recharge for the Neogene carbonates is significant (estimated 130–500 million m3), despite the very low rainfall and high evaporation, and is sufficient to maintain spring flow along the Abu Jir lineament. However, excessive extraction for agriculture will negatively impact spring flow, and active management of groundwater extraction rates is needed for the long-term sustainability of the springs. The hydrochemistry of the springs shows high SO4 concentrations (originating from the dissolution of wind-blown gypsum in the rainfall) and depletion in Ca and K relative to the rainfall, probably due to plant uptake as the rainfall infiltrates through the soils, despite the sparse vegetation on the desert plateau. There is little evidence of limestone dissolution in the spring chemistry, even though the groundwater feeding the springs travels through a carbonate aquifer. The springs at Hit-Kubaysa contain tar, high levels of H2S, and a component of oilfield brine; the presence of hydrocarbons makesthe water reducingand converts the dissolved SO4 to H2S. The tar and brine have seeped upwards along faults from underlying oil and gas reservoirs; this is the only location along the Abu Jir lineament where deep-seated faults penetrate to the surface.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, J.J. and R.J.F.; methodology, J.A.W.; investigation, J.A.W. and R.J.F.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.W. and R.J.F.; writing—review and editing, J.A.W., R.J.F. and J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the reported results can be obtained upon request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Comments from two anonymous reviewers substantially improved this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Altaweel, M.; Marsh, A.; Jotheri, J.; Hritz, C.; Fleitmann, D.; Rost, S.; Lintner, S.F.; Gibson, M.; Bosomworth, M.; Jacobson, M.; et al. New Insights on the Role of Environmental Dynamics Shaping Southern Mesopotamia: From the Pre-Ubaid To the Early Islamic Period. Iraq 2019, 81, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissakian, V.K.; Mohammad, B.S. Geology of Iraqi Western Desert: Stratigraphy. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. Spec. Issue 2007, 51–124. [Google Scholar]
- Thabit, J.M.; Al-yasi, A.I.; Al-shemmari, A.N. Estimation of Hydraulic Parameters and Porosity from Geoelectrical Properties for Fractured Rock Quifer in Middle Dammam Formation at Bahr. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. 2014, 10, 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, S.A.; Al-Ansari, N.; Abdullah, T. Groundwater Hydrology in Iraq. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 10, 155–197. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhlif, H.N.; Rabeea, R.; Hussien, B.M. Characterization of the Groundwater within Regional Aquifers and Suitability Assessment for Various Uses and Purposes-Western Iraq. Baghdad Sci. J. 2021, 18, 0670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dulaimi, A.M.S.; Al-Kubaisi, Q.Y. Hydrochemistry and Water Quality Index of Groundwater in Abu-Jir Village in Al-Anbar, Western Iraq. Iraqi Geol. J. 2022, 55, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Maliki, A.; Kumar, U.S.; Falih, A.H.; Sultan, M.A.; Al-Naemi, A.; Alshamsi, D.; Arman, H.; Ahmed, A.; Sabarathinam, C. Geochemical Processes, Salinity Sources and Utility Characterization of Groundwater in a Semi-Arid Region of Iraq through Geostatistical and Isotopic Techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awadh, S.M.; Al-Ghani, S.A. Assessment of Sulfurous Springs in the West of Iraq for Balneotherapy, Drinking, Irrigation and Aquaculture Purposes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dahaan, S.A.J.M.; Hussain, H.M.; Al-Ansari, N.; Knutson, S. Hydrochemistry of Springs, Najaf Area, Iraq. J. Environ. Hydrol. 2015, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dahaan, S.A.J.M. Origin and source of springs, west Iraq. J. Kufa-Phys. 2014, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dahaan, S.A.M.; Alabidi, A.J.; Al-Ansari, N.; Knutsson, S. Relationship between Selected Hydrochemical Parameters in Springs of Najaf Province, Iraq. Engineering 2015, 7, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussien, B.M.; Gharbie, M.A. Hydrogeochemical Evaluation of the Groundwater Within Abu Jir Fault Zone, Hit–Kubaisa Region, Central Iraq. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. 2010, 6, 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Casana, J.; Jackson, C. The CORONA Atlas Project: Orthorectification of CORONA Satellite Imagery and Regional-Scale Archaeological Exploration. In Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space, 5; Comer, D.C., Harrower, M.J., Eds.; Springer Science Business and Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, G.; Donoghue, D.; Beck, A.; Galiatsatos, N. CORONA Satellite Photography: An Archaeological Application from the Middle East. Antiquity 2002, 76, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, A. Arabia Deserta; The American Geographical Society: New York, NY, USA, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller, H. Qualitative Evaluation of Groundwater Resources. In Methods and Techniques of Groundwater Investigations and Development; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.F.; Webb, J.A.; Jacobsen, G.E.; Chisari, R.; Dresel, P.E. Biomass Uptake and Fire as Controls on Groundwater Solute Evolution on a Southeast Australian Granite: Aboriginal Land Management Hypothesis. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4099–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drever, J.I. The Geochemistry of Natural Waters, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, G.; Hughes, M. The Use of Environmental Chloride and Tritium to Estimate Total Recharge to an Unconfined Aquifer. Soil Res. 1978, 16, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.F.; Webb, J.A.; Jacobsen, G.; Chisari, R.; Dresel, P.E. A groundwater recharge perspective on locating tree plantations within low-rainfall catchments to limit water resource losses. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1107–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, A.M.; Lark, R.M.; Taylor, R.G.; Abiye, T.; Fallas, H.C.; Favreau, G.; Goni, I.B.; Kebede, S.; Scanlon, B.; Sorensen, J.P.R.; et al. Mapping Groundwater Recharge in Africa from Ground Observations and Implications for Water Security. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 034012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, S.Y. Stratigraphy of the Mesopotamia Plain. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. 2011, 4, 47–82. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulnaby, W. Structural Geology and Neotectonics of Iraq, Northwest Zagros. In Tectonic and Structural Framework of the Zagros Fold-Thrust Belt; Saein, A.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 53–73. ISBN 978-0-12-815048-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sissakian, V.K. Geological Evolution of the Iraqi Mesopotamia Foredeep, Inner Platform and near Surroundings of the Arabian Plate. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 72, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladwani, N.S.; Alenezi, A.; Diab, A. Investigation of the Cretaceous Total Petroleum System Using Wireline Logs, Core, and Geochemical Data in Bahrah Field, Northern Basin, Kuwait. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2023, 13, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissakian, V.K.; Fouad, S.F.A. Geological Map of Iraq, Scale 1: 1,000,000. Iraqi Bull. Geol. Min. 2015, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey and Arabian American Oil Company. Geologic Map of the Arabian Peninsula. Washington, D.C., U.S.A. 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadithi, A.A.; Salih, E.M. Behavior of Abu-Jir Fault Zone in Al-Thirthar Valley and near Habbaniya Lake Areas–Comparative Study Using Seismic Reflection Sections. J. Univ. Anbar Pure Sci. 2017, 11, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dulaymie, A.S.; Hussien, B.M.; Gharbi, M.A.; Mekhlif, H.N. Balneological Study Based on the Hydrogeochemical Aspects of the Sulfate Springs Water (Hit-Kubaiysa Region), Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2013, 6, 801–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, S. Contribution to the Structure of the Abu-Jir Fault Zone, West Iraq. Iraqi Geol. J. 1999, 32, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Benischke, R.; Fuchs, G.; Weissensteiner, V. Speleological Investigations in Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of Speleology, La Chaux-de-Fonds, Geneva, Switzerland, 10–17 August 1997; International Union of Speleology: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Waltham, T. Asia, Southwest. In Encyclopedia of Caves and Karst Science; Gunn, J., Ed.; Fitzroy Dearborn: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 114–116. [Google Scholar]
- Barwary, A.M.; Slewa, N.A. Geological Map of Karbala Quadrangle, Sheet NI-38-14; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Barwary, A.M.; Slewa, N.A. Geological Map of Al-Najaf Quadrangle, Sheet NH-38-2; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Deikran, D.B.; Mahammad, S.M. Geological Map of Baghdad Quadrangle, Sheet NI-38-10; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sissakian, V.K.; Youkhanna, R.Y. Geological Map of Al-Birreet Quadrangle, Sheet NH-38-1; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sissakian, V.K.; Zwaid, Q.A.; Mohammad, S.M. Geological Map of Al-Ramadi Quadrangle, Sheet NI-38-9; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdi, A.H.; Youkhanna, R.Y. Geological Map of Shithatha Quadrangle, Sheet NI-38-13; State Establishment of Geological Survey and Mining: Baghdad, Iraq, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zubedi, A.S.; Thabit, J.M. Use of 2D Azimuthal Resistivity Imaging in Delineation of the Fracture Characteristics in Dammam Aquifer within and out of Abu-Jir Fault Zone, Central Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, F.H. Porosity and Permeability of Karst Carbonate Rocks along an Unconformity Outcrop: A Case Study from the Upper Dammam Formation Exposure in Kuwait, Arabian Gulf. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abadi, A.M.; Shahid, S. Spatial Mapping of Artesian Zone at Iraqi Southern Desert Using a GIS-Based Random Forest Machine Learning Model. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-ESCWA and BGR. Inventory of Shared Water Resources in Western Asia; United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia; Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe: Beirut, Lebanon, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, R.D. Fossil Water or Renewable Resource: The case for one Arabian aquifer. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Marit. Energy 1994, 106, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, R.; Dirks, H.A. Hydrogeological Overview of the Upper Mega Aquifer System on the Arabian Platform. Hydrogeol. J. 2024, 32, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadh, S.A. The Atmospheric Pollution of Baghdad City, Iraq. In Proceedings of the 3rd Scientific Conference College of Science, University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq, 24–26 March 2009; pp. 1727–1740. [Google Scholar]
- Handy, A.H.; Tucker, R.A. Rainfall Quality at Selected Sites in Saudi Arabia. Water Research and Study Division; Publication No. 2; Ministry of Agriculture and Water, Water Resources Development Department: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 1984; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Michelsen, N.; Reshida, M.; Siebert, C.; Knoller, K.; Wiese, S.M.; Rausch, R.; Al-Saud, M.; Schuth, C. Isotopic and Chemical Composition of Precipitation in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Chem. Geol. 2015, 413, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.K.; Ajeena, A.R. Assessment of Interconnection between Surface Water and Groundwater in Sawa Lake Area, Southern Iraq, Using Stable Isotope Technique. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadh, S.M.; Ali, K.K.; Alazzawi, A.T. Geochemical Exploration Using Surveys of Spring Water, Hydrocarbon and Gas Seepage, and Geobotany for Determining the Surface Extension of Abu-Jir Fault Zone in Iraq: A New Way for Determining Geometrical Shapes of Computational Simulation Models. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 124, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, I.; Rausch, R.; Keim, B.; Al-Saud, M.; Schüth, C. Surface and Subsurface Conceptual Model of an Arid Environment with Respect to Mid- and Late Holocene Climate Changes. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrood, M.J.; Hussein, H.M. A Preliminary Ecological Analysis of Spring Water in Al-Shanafiyah District, Al-Qadisiyah Province, Southern Iraq. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 790, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennetts, D.A.; Webb, J.A.; Stone, D.J.M.; Hill, D.M. Understanding the Salinisation Process for Groundwater in an Area of South-Eastern Australia, Using Hydrochemical and Isotopic Evidence. J. Hydrol. 2006, 323, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imo, T.; Amosa, P.; Latu, F.; Vaurasi, V.; Ieremia, R. Chemical Composition of Rainwater at Selected Sites on Upolu Island, Samoa. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2021, 11, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.A.; White, S. Karst in Deserts. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 6, p. 397406. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, J.F. Mineral Salts Absorption in Plants; Pergamon: London, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Mengel, K.; Kirkby, E.A. Principles of Plant Nutrition; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, R.O.; Golding, D.L. Controls on Groundwater Chemistry in Subalpine Catchments in the Southern Interior of British Columbia. J. Hydrol. 1997, 201, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, K.L.; West, J.; Berner, R.A. Solute Flux and Mineral Mass Balance Approaches to the Quantification of Plant Effects on Silicate Weathering. Am. J. Sci. 2000, 300, 539–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.; Webb, J. The Importance of Unsaturated Zone Biogeochemical Processes in Determining Groundwater Composition, Southeastern Australia. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, G.H.C.; Rao, Y.; De Klerk, A. Nitrogen Removal from Oil: A Review. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 14–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, B.M.; Rabeea, M.A.; Farhan, M.M. Characterization and Behavior of Hydrogen Sulfide Plumes Released from Active Sulfide-Tar Springs, Hit, Iraq. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, J.K.; Steinshouer, D.; Lewan, M.D. Petroleum Generation and Migration in the Mesopotamian Basin and Zagros Fold Belt of Iraq: Results from a Basin-Modeling Study. GeoArabia 2004, 9, 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).