Abstract
The present study evaluated different sludge-reduction mechanisms in the oxic-settling-anaerobic (OSA) process in terms of their effects on methane productivity by anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Two different layouts were investigated for the sludge return from an anaerobic side-stream reactor (ASSR) to the anoxic (scheme A) or the aerobic (scheme B) reactor of a pre-denitrification plant. Biochemical methane-potential (BMP) assays performed on the excess sludge revealed that scheme A promoted an overall increase of methane production in the OSA (20 mLCH4 gVSS−1d−1, +19%), although compared with a control CAS plant a significant decrease in the excess sludge production (31%) was obtained. Operating conditions in scheme A caused the occurrence of cell lysis and EPS hydrolysis, thereby increasing the biodegradability of sludge. In contrast, scheme B favoured the occurrence of uncoupling and a maintenance metabolism that did not involve sludge hydrolysis. Consequently, despite a higher reduction of excess sludge (82%), a significant decrease in methane productivity in the OSA (4 mLCH4 gVSS−1d−1, −41%) was observed. Based on the results, implementing the OSA process may allow high levels of methane production by anaerobic digestion to be maintained if specific sludge-reduction mechanisms are triggered in the waterline, also raising the possibility of co-digestion with other feedstocks.
1. Introduction
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) produce sewage sludge as a byproduct of water treatment processes. Specifically, sludge production in biological treatment is due to the growth of heterotrophic and autotrophic bacteria, accumulation of inert solids contained in the raw wastewater, and accumulation of endogenous residue [1]. To maintain steady state conditions, the excess sludge must be regularly discharged from the system (usually from secondary clarifiers). Thereafter, the excess sludge is subjected to specific treatments in the sludge-handling units, including thickening, digestion, and dewatering, before being subject to disposal according to the current environmental regulations. Due to the potential contamination of soil and water, disposal of sludge could potentially be harmful to the ecosystem [2]. Moreover, sludge management has a significant impact in economic terms, since it can account for up to approximately 40–60% of the entire operating costs of a WWTP [3].
The large amounts of sludge produced and the requirement to implement reuse or recovery in compliance with the current European and national legislation, as well as the impending shift towards the principles of a circular economy, are crucial factors contributing to the urgency of solving critical issues relating to sewage sludge [4].
In accordance with the waste hierarchy established by Directive 2018/851/EC, prevention (e.g., waste minimization techniques), reuse (e.g., agronomic use), recycling (e.g., matter recovery), other recovery (e.g., energy recovery), and disposal (e.g., incineration or landfilling) should be carried out in this precise order [5]. Therefore, minimizing excess sludge is considered a priority to solve the sewage-sludge problem and reduce the operating costs of WWTPs. According to reports in the technical literature, several chemical-physical (e.g., ultrasound, ozonation, thermal treatments, etc.), or biological processes as well as their mutual integration, have been successfully applied to achieve reduction of excess sludge [2,6]. Among these, the oxic settling anaerobic (OSA) method is a biological-based process that has been proven very effective in reducing excess sludge production, while involving less economic impact on plants’ operating costs compared with other processes [7,8]. It involves the modification of a conventional activated sludge (CAS) scheme by inserting an anaerobic side-stream reactor (ASSR) in the return activated sludge (RAS) line [9]. Due to sludge holding under anaerobic fasting conditions, uncoupling metabolism, cell lysis, and destructuration of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) occur, thereby limiting biomass growth and excess sludge production [10].
Alongside strategies for sludge minimization, the valorization of sludge through energy recovery represents a widely established practice in WWTPs. In this context, energy recovery from excess sludge by anaerobic digestion (AD) is the most common strategy for excess sludge valorization. AD entails the biological degradation of organic matter under absence of oxygen with a subsequent conversion of chemical energy in organic carbon into biogas [11]. AD is generally implemented in large WWTPs (>100,000 PE) instead of aerobic stabilization, since the higher capital costs due to the larger volume and higher complexity of the digestion facilities are compensated by lower operational costs related to biogas valorization.
Resource utilization of sludge is an effective way to avoid secondary pollution. Sludge-based ceramsite can achieve the stabilization of heavy metals and reduce pollution by heavy metals in the environment [12]. Indeed, implementing excess sludge minimization strategies in a WWTP with anaerobic digestion could be detrimental for achieving high methane production rates. The lower amount of excess sludge that is daily transferred to the sludge line could decrease up to 40–60% when implementing the OSA process [10], thereby reducing the overall biogas obtainable by AD. Nevertheless, the literature review reveals that some of the key mechanisms that are responsible of sludge minimization in the OSA process (e.g., cell lysis, EPS destructuration) are usually implemented as a pre-treatment stage before anaerobic digestion in order to increase the biogas production rate. The most frequently used pretreatment methods for sewage sludge, such as thermal and ultrasonic treatments or ozonation, are based on the principle of bacterial cell-wall disintegration. Cellular lysis leads to the release of intracellular organic matter that becomes more easily usable by anaerobic microorganisms [13]. Accordingly, the methane production rate by AD might increase [14]. Therefore, the implementation of the OSA process under specific operating conditions could theoretically enhance specific methane production by anaerobic digestion. Consequently, this effect could counterbalance the reduction of excess sludge available for anaerobic digestion. Nonetheless, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, very limited literature is available on this topic [15].
Considering the above discussion, this study was aimed at assessing the side effects of OSA process implementation in the water-handling units of a pilot WWTP for achieving minimization of excess sludge, in terms of methane production by anaerobic digestion in the sludge line. In more detail, different sludge-reduction mechanisms (e.g., cell lysis, EPS destructuration, uncoupling metabolism, maintenance metabolisms) were induced in the ASSR, and their effects in terms of biochemical methane potential (BMP) of the excess sludge were assessed. The experimental results are supported by an economic analysis aimed at establishing whether implementation of the OSA process in a large WWTP is a cost-effective solution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Description
The experimental activity was carried out in two identical pilot plants, one in which the OSA process was implemented and the other as control, namely control-CAS. The comparison between OSA and control-CAS was explored in a previous study to which readers are referred for further details [16]. Briefly, both plants were configured according to a pre-denitrification scheme, involving an anoxic reactor (23 L) followed by an aerobic reactor (23 L) and an internal recirculation circuit. In the OSA plant, an ASSR with hydraulic retention time (HRT) from 8 to 12 h was inserted into the RAS line from the clarifier to the biological reactors. Two plant layouts were studied, namely schemes A and B, involving sludge recirculation from the ASSR to the anoxic reactor (scheme A) or the aerobic reactor (scheme B) of the main line. The aim was to expose biomass to prolonged non-aerobic (anaerobic/anoxic) or prolonged famine conditions in schemes A and B, respectively, to induce different stressors and mechanisms of sludge reduction. The excess sludge was discharged daily from the bottom of the clarifiers to maintain a constant total suspended solids (TSS) concentration in the reactors. Biomethane potential assays were performed on these samples to assess the effects of the OSA process and specifically of the sludge-minimization mechanisms on the methane yield achievable from anaerobic digestion. Figure 1 depicts the plants’ configurations.
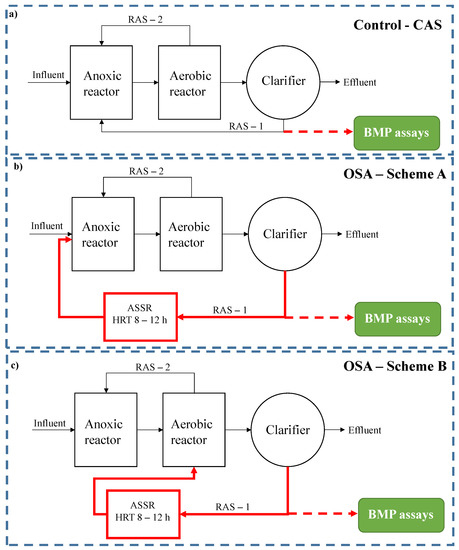
Figure 1.
Layouts of the (a) control-CAS and (b,c) OSA plants according to scheme A and scheme B.
2.2. Experimental Campaign Set-Up
Experiments were divided into five periods, namely period 1 (P1), period 2 (P2), period 3 (P3), period 4 (P4) and period 5 (P5). Different HRTs (8–12 h) in the ASSR were tested in both schemes A and B. The plants were fed with real wastewater collected downstream of the screening and grit-removal unit of a municipal WWTP. The average chemical oxygen demand (COD) concentration was 732 mg L−1. The wastewater was stored in a refrigerated tank to prevent biological reactions, without removing the suspended settleable solids. Thus, the excess sludge discharged from the secondary clarifiers included also primary sludge. As discussed above, the excess sludge was discharged daily from the clarifiers of both plants to maintain TSS concentrations of approximately 3 gTSS L−1. As a result, the sludge-retention time (SRT) was not controlled and was calculated by means of mass balance between the biomass growth yield and the amount withdrawn as excess sludge or effluent total suspended solids. The food to microorganisms (F/M) ratio results were close to 0.20 gCOD gTSS−1 d−1 in the CAS, on average, whereas in the OSA the ratio was slightly lower because of the higher volume due to the ASSR. Table 1 summarizes the main operating conditions (Table 1).

Table 1.
Main operating conditions of CAS and OSA during the experiment.
2.3. Analytical Methods
All the chemical-physical analyses, including total and volatile suspended solid (VSS) concentrations, suspended settleable solids, and COD, were performed according to standard methods [17]. The extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and the soluble microbial products (SMP) were extracted using a heating method [18]. Specifically, first the SMP and the loosely bound EPS were obtained by centrifuging an activated sludge sample at 5000 rpm for 5 min and filtering the supernatant with 0.22 µm membrane. Then, the same sample was re-suspended with deionized water and heated in a water-bath at 80 °C for 10 min to allow solubilization of the flocs-bound EPS. The sample was then centrifuged at 7000× g rpm for 10 min at 4 °C and the supernatant filtered with 0.22 µm membrane to obtain the tightly bound EPS. The EPS were extracted following the above-described method and were related to the TSS concentration of the sample. Then, the concentrations of carbohydrates and proteins were determined according to the literature [19,20], using bovine serum albumin and glucose as standards, respectively.
2.4. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Assays
BMP assays were performed at the end of each experimental period after the steady state condition of excess sludge reduction was attained. In each period, the BMP assays were performed on the excess sludge from the OSA and CAS plants. Each BMP assay was carried out at an inoculum to substrate ratio (ISR) equal to 5, based on the VSS concentration [21]. Sludge samples collected from a bench scale anaerobic digester operating under mesophilic conditions (T = 35 °C) were used as inoculum for each of the BMP assays. The anaerobic inoculum was cultivated using a mixture of acetate and trace elements to enhance the growth of methanogenic bacteria [22]. The TSS concentration of the inoculum ranged from 5.32–7.12 gTSS L−1, while the ratio between VSS and TSS was approximately 0.65.
All the assays were performed using glass bottles with a working volume of 500 mL. The excess sludge from OSA or CAS were mixed with inoculum to a final volume of 400 mL, thus the headspace volume was 100 mL. Before starting the assays, each bottle was fluxed with nitrogen gas, to limit the free oxygen availability. The samples were mixed using a magnetic stirrer for 1 h adding an external COD supply (as acetate), to remove nitrate resulting from uncomplete denitrification.
The above tests were carried out in triplicate including a blank, which indicated the productivity of the inoculum. In all the assays, pH was set close to 7.5. The BMP reactors were placed within a thermostatic chamber under controlled temperature (35 °C) after being sealed and connected to a Tedlar bag in which the produced biogas was collected. The volume of biogas accumulated within the bags was measured every 2–3 days. A liquid-displacement method, with an alkaline solution (2% NaOH) as barrier was used to measure the methane volume accumulated into the Tedlar bags. The BMP assays continued until the accumulated methane production reached a steady value. The methane production level in the BMP assay was related to the VSS concentration (mLCH4 gVSS−1).
2.5. Modeling of Methane Production and Calculations
A first-order rate model was employed to interpolate the cumulative methane production obtained from the BMP assays (Equation (1)):
where P(t) is the methane production at a generic time, Ptot is the cumulative value of methane produced at the end of BMP, k is the rate of methane production, and t is the time.
The solver function of Excel (MS Office) was used to estimate Ptot and k, by minimizing the sum square of errors between the experimental data obtained from BMP assays and the results of the model.
The maximum methane production yield, namely Pmax (mLCH4 gVSS−1d−1), was estimated as the product between the Ptot and k obtained from the model (Equation (2)):
To assess daily methane production, namely PCH4 (mLCH4 d−1), Pmax obtained in the BMP assays of OSA and CAS was multiplied by the respective daily excess sludge production on a dry basis (Equation (3)):
where ΔXSS is the excess sludge produced from the OSA and CAS plants (gVSS d−1).
2.6. Economic Analysis
To assess if the implementation of the OSA process represents a cost-effective solution, an economic analysis was carried out based on costs related to OSA implementation, sludge disposal, and methane generation. Referring to OSA implementation, it was assumed that the additional cost for WWTP management was related to the energy necessary for the ASSR mixing. Thus, the capital cost for the construction of a new tank was not considered, since it was supposed that existing disused facilities could be retrofitted to implement the OSA process [23].
Specifically, the economic analysis was aimed at assessing the overall increase or decrease of management costs (ASSR operations, sludge disposal, and methane generation) depending on the different process scenarios investigated in this study, from P1 to P5. To this scope, reference was made to a WWTP with a potential of 100,000-person equivalent (PE), with a layout similar to that in the present study. The overall daily excess sludge production was calculated by assuming the same specific production as the CAS plant in this study. The cost of ASSR operation was considered according to the electric energy necessary for a mixing system with the capacity to ensure a specific mixing power of 10 W per m3 of the ASSR. This was calculated as the product of the HRT of the ASSR in each experimental period and the sludge recirculation flowrate, the latter assumed equal to 80% of the influent flow rate of the simulated plant. The cost of electricity was assumed as EUR 11.82 kWh−1 in line with the mean electric energy price for industrial consumers in Europe [24].
Specific cost for sludge disposal was estimated as the average cost in EU countries, equal to EUR 0.190 per kg of dewatered sludge, assuming landfilling as disposal method [24]. The residual humidity of the sludge was assumed to be 75%, according to EU regulations [25].
Referring to methane production, its impact on the WWTP economy was calculated by multiplying the sale price of methane by the percentage increase or decrease of daily methane production in the scenario without OSA implementation. That price was assumed equal to 0.24 € m−3 [24] on the basis of the selling price of natural gas, and reduced to 10 c€ m−3 to take into account the costs of biogas upgrading [26].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Efficiency of Excess Sludge Minimization and Insights on Mechanisms Involved
A previous study provided a specific focus on the minimization of excess sludge, its impact on nutrient removal, and the mechanisms of sludge reduction in the OSA plant [16].
Briefly, the average daily amount of excess sludge produced in the CAS plant varied during each experimental period, depending on the characteristics of the raw wastewater. The excess sludge production in the OSA plant was lower in all the investigated configurations compared with the control plant. Specifically, the sludge production was lowered by approximately 15% (P1), 31% (P2), 40% (P3), 26% (P4), and 41% (P5), thereby suggesting that the OSA process resulted in higher or lower efficiency of sludge reduction depending on the different operating conditions and configurations implemented. Figure 2 reports the average daily sludge production on a dry basis obtained in the OSA and CAS plants in each period.
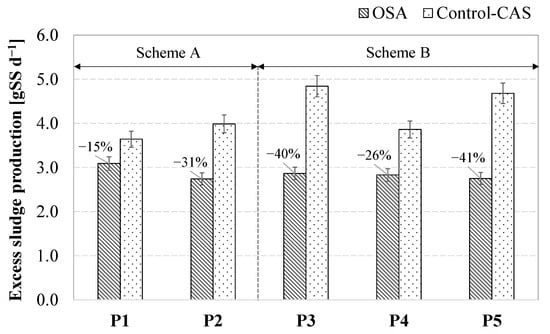
Figure 2.
Excess sludge production in OSA and CAS plants during the experiment (bars indicate standard deviation).
The highest reduction efficiencies were obtained when the OSA plant was operated according to scheme B (P3 and P5), whereas scheme A (P1 and P2) determined lower sludge minimization. Therefore, at equal HRT in the ASSR (P2 vs. P3, P5), more extensive substrate deficiency (scheme B) was observed to be a greater stressor for biomass than a longer oxygen lack (scheme A) [16]. Therefore, a double-growth limitation strategy consisting of prolonged substrate limitation after sufficient retention under anaerobic conditions enabled more extensive minimization of excess sludge. Indeed, it is likely that the internal ATP restoration in the mainstream reactor was lower in scheme B than scheme A because of the lower organic carbon availability in the aerobic reactor compared to the anoxic [27].
Primary sludge accounted for approximately 50–60% of the overall sludge production in the CAS plant (Table 2). Contrarily, its incidence in the sludge of the OSA plant was significantly higher, between 65–95%. This was because mechanisms of excess sludge minimization occurring in the OSA process affected only the production of biological solids, referring to the conversion of the organic substrate into bio-solids [28]. Therefore, the primary sludge was predominant in the excess sludge produced by the OSA plant.

Table 2.
Summary of the main possible mechanisms involved in excess sludge minimization during each period, and percentage of primary sludge in the sludge produced by OSA and CAS.
Uncoupling and maintenance metabolisms were found to be the main mechanisms allowing minimization of excess sludge when scheme B was implemented. Indeed, a long-term lack of substrate in the anaerobic environment forced bacteria to reduce their metabolic activity and dissociated catabolism from anabolism. This resulted in lower production of excess sludge and a consequent increase of the SRT in the water line from 8 days to 12 days on average [29]. The lower biomass yield was attributed to the reduced ATP availability of heterotrophic bacteria in the OSA system, under which conditions the energy produced by catabolism was insufficient to produce new biomass since it was partially used for restoration of internal energy [29,30].
In contrast, scheme A induced cell lysis and destructuration of the extracellular matrix as the main mechanisms, although the uncoupling metabolism continued to have a marginal effect on the process [31]. According to other studies, the increase of anaerobic HRT promoted the onset of bacterial lysis and increased EPS destructuration [31,32].
Therefore, prolonged exposure to unaerated conditions caused by the sludge cycling between the ASSR and the anoxic reactor in scheme A was responsible for cell lysis, confirmed by the increase of the soluble microbial product in the bulk [32].
3.2. Methane Production Yield in Excess Sludge from OSA and CAS
For each experimental period, BMP assays were carried out on the excess sludge from OSA and CAS after steady state conditions in terms of sludge reduction efficiency were achieved. Figure 3 shows the cumulative specific methane production obtained in each of the assays. The maximum methane production rate was determined by fitting the cumulative methane production data to the model reported in Equation (1). A good agreement between the experimental data and model (R2 > 0.97) was obtained in all the assays. The cumulative data of methane obtained in the assays of OSA and CAS sludge were reduced according to the methane generated in the inoculum assay and related to the VSS concentration in the sludge sample.
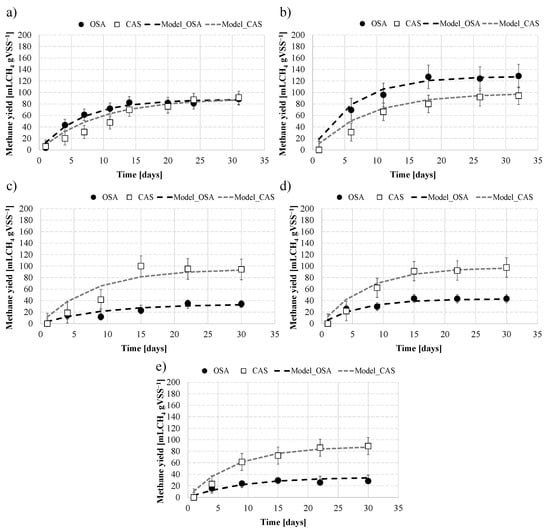
Figure 3.
(a–e) Cumulative methane production obtained from the excess sludge of OSA and CAS plants, in Periods 1–5 (bars indicate standard deviation).
In Period 1 (Figure 3a) BMP trends were in the OSA and CAS were fairly similar and the final cumulative methane yields obtained after 30 days were comparable in both samples, resulting in close to 80 mLCH4 gVSS−1. The sludge from the OSA plant resulted in a slightly higher methane production rate in the early test period. The k factor obtained from the methane production model in the OSA assay was equal to 0.156 d−1, whereas in the CAS it was approximately 0.11 d−1.
The methane production in the OSA assay showed a significant increase in Period 2 (Figure 3b). Indeed, the cumulative methane yield in the CAS was comparable to that obtained in the previous period, resulting in close to 90 mLCH4 gVSS−1, whereas in the OSA it increased up to 120 mLCH4 gVSS−1, thereby showing an increase of approximately 40% compared with the control system. In addition, faster kinetics of methane production were attained in the OSA. The methane-production model indicated k values of 0.16 d−1 in the OSA and 0.12 d−1 in the CAS, thus confirming the faster kinetics of methane production obtained in the BMP assay of the OSA in Period 2.
In Periods 3 (Figure 3c), 4 (Figure 3d), and 5 (Figure 3e), methane yields noticeably decreased in the BMP assays of the OSA. The maximum methane yield was obtained in Period 4 (40 mLCH4 gVSS−1), and lower values were observed in Period 3 and Period 5 (20 mLCH4 gVSS−1). Overall, the methane yields were approximately 75% lower than those obtained in the BMP assays in the CAS (92 mLCH4 gVSS−1). Similarly, the kinetics of methane production reduced considerably. The k factor obtained from the model was close to 0.11 d−1 on average, whereas that of the CAS was in line with the values obtained in Period 1 and Period 2 (0.13 d−1).
Overall, the maximum methane production rate, obtained by multiplying the cumulative methane volume by the k factor, was higher in the OSA during Period 1 and Period 2, whereas a considerable decrease was noticed from Period 3 onwards (Figure 4). The maximum methane rates obtained by the excess sludge from the OSA plant were equal to 14 mLCH4 gVSS−1d−1 and 20 mLCH4 gVSS−1d−1 in Period 1 and Period 2, respectively, resulting in daily increases in methane production of 27% and 41% compared with CAS. Contrarily, decreased methane production in the range 49–69% was observed in Period 3 (−69%), Period 4 (−49%), and Period 5 (−66%).
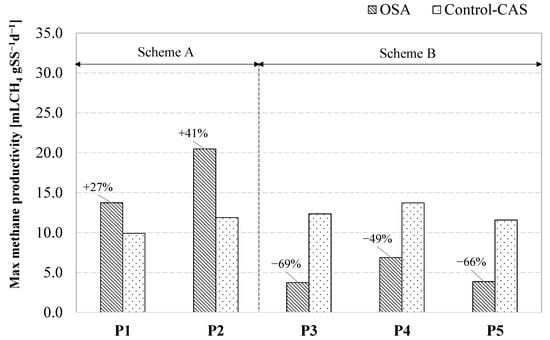
Figure 4.
Maximum methane productivity obtained in the BMP assays of the OSA and CAS during the experiment.
The methane production yields and rates obtained in the control system were comparable with those reported in previous studies on excess sludge composed of both primary and biological sludge in similar proportions (50% v/v) [33,34].
In general, the results obtained in the BMP assays of the OSA samples indicated that implementation of the ASSR resulted in an increased methane production rate only when it was operated according to scheme A. In contrast, implementation of ASSR according to scheme B caused a considerable decrease of the methane production by AD. In this respect, very little published information is available about the effect of ASSR installation in a WWTP. In a previous study, the authors observed an increase in the BMP of excess sludge from an ASSR operating with an HRT of 2 days under mesophilic conditions [15]. In that study, the ASSR was inserted in the activated sludge return line of a CAS system consisting of a primary clarifier followed by an aeration basin and a secondary clarifier. The authors reported that the reduction of biological sludge obtained by implementing the ASSR increased the ratio between the primary and the biological sludge in the anaerobic digester, thereby resulting in higher methane productivity. Indeed, other studies confirmed that the methane production from AD increased when the ratio of biological sludge and primary sludge was lower than 40% [35].
In the present study, however, the ratio between the primary and biological sludge had no clear effect on methane production. Specifically, the excess sludge from the OSA plant was characterized by a higher fraction of primary sludge compared with that of the control plant, which was on average close to 70% with a maximum of 95% in Period 3, whereas in the CAS it was on average close to 55%. However, in the present study, clarification of wastewater before the biological treatment was not foreseen. Consequently, the primary sludge fed to the biological reactors underwent a stabilization process, resulting in a decrease of the organic content to approximately only 30%. For this reason, it is possible that the effect of the higher percentage of primary sludge in the excess sludge from the OSA plant did not entail a corresponding increase in methane production.
Another reason why the OSA process could involve an increase of methane productivity is related to the higher bacterial diversity of the ASSR sludge compared with the activated sludge of the control system [36]. Park and co-authors [15] supposed that the sludge from a mesophilic ASSR contained key anaerobic communities, thus the addition of this sludge to anaerobic digesters provided anaerobic seed that enhanced the speed of anaerobic digestion.
Nevertheless, although a specific microbiological characterization of sludge was not carried out in this study, it was assumed that the composition of the microbial community did not affect the methane productivity. When the ASSR was operated under the same HRT (8–12 h) according to schemes A and B, a substantial difference in methane productivity was observed. It should be noted that 12 h of anaerobic HRT is not considered sufficient to achieve a significant enrichment of methanogenic bacteria in sludge [37]. Therefore, the different methane production yields and rates were probably related to the different operating conditions in the plants during the experiments, hence the modification of bacterial metabolism and the physical properties of sludge that occurred in the ASSR. Methane productivity was well correlated with the exposure time to unaerated conditions in the water line of the OSA plant (Figure 5).
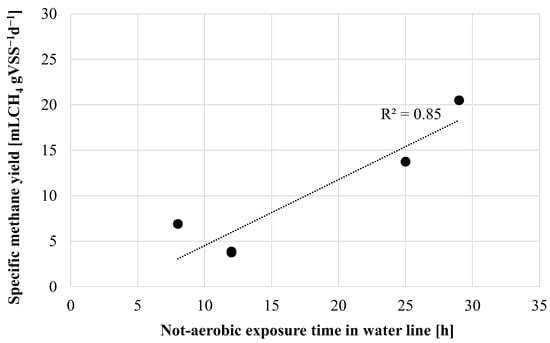
Figure 5.
Correlation between the methane productivity and the exposure time to anaerobic conditions.
The above results suggest that, at equal HRT in the ASSR, when the sludge cycled from the ASSR to the anoxic reactor in scheme A the methane productivity was higher than scheme B where the sludge was instead recycled to the aerobic reactor. A possible explanation could be related to the establishment of hydrolytic processes due to long-term exposure under unaerated conditions. A previous study suggested that under unaerated starvation conditions only the concentration of intracellular low-molecular-weight compounds decreased, while no significant changes were noted for cellular protein, lipids, polysaccharides, or nucleic acids [38]. In contrast, under aerobic starvation significant degradation of exopolymers occurred. Accordingly, prolonged starvation under aerobic conditions (scheme B) reduced the amount of organic matter available for anaerobic digestion, thereby reducing methane productivity.
It should be also considered that when operating with the same plant layout, methane productivity increased with the HRT in the ASSR. Nevertheless, HRT of higher than 12 h in the ASSR was not implementable, at least under the conditions of the present study, due to significant worsening of the effluent quality from the OSA plant.
3.3. Insights of ASSR Operating Conditions on Methane Production
The results obtained from the BMP assays indicated that the operating conditions of schemes A and B in the OSA plant involved a noticeable increase or decrease in methane production by AD. Based on the results discussed in the previous sections, it was noted that the implementation of the OSA process, and more specifically the change in plant layout (scheme A or scheme B), involved a noticeable modification in the bacterial metabolism and the physical properties of the sludge, because of the establishment of different phenomena all contributing to excess sludge minimization.
In more detail, the different operating conditions in schemes A and B had remarkable impacts on the physical characteristics of the sludge in the OSA plant. Figure 6 shows the COD concentrations in the supernatant of the ASSR, as well as the average concentrations of the SMP (as sum of proteins and carbohydrates).
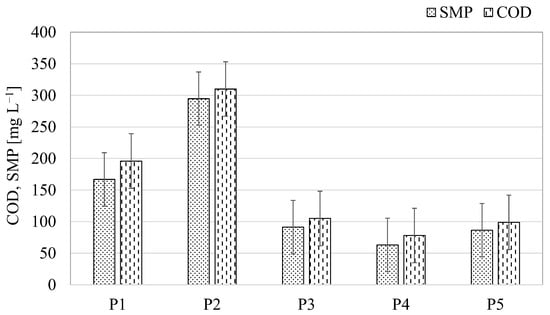
Figure 6.
Concentrations of COD and SMP in the supernatant of the ASSR during the experiment.
The results shown in Figure 6 indicate that in Period 1 and Period 2 the concentrations of SMP in the supernatant of the ASSR were on average equal to 160 mg L−1 and 290 mg L−1, respectively. These results were considerably higher than those obtained in Period 3, Period 4, and Period 5, which had an average value close to 80 mg L−1. Similarly, the COD concentrations were higher in Period 1 and Period 2 (195 mg L−1 and 310 mg L−1, respectively) compared with the other periods (72 mg L−1, on average), thus confirming the higher concentration of organic matter in the supernatant of the ASSR when scheme A was implemented in the OSA plant. These results confirmed that long-term exposure to unaerated starvation conditions increased the concentration of proteins and carbohydrates in the bulk [38].
The sludge cycling according to scheme A promoted a long-term exposure under unaerated conditions, since the sludge from the ASSR was recirculated to the anoxic reactor. Because of this, cell lysis and EPS destructuration were triggered as the main mechanisms of sludge reduction. Indeed, in Period 1 and Period 2 noticeable increases of soluble microbial products and endogenous decay rates of autotrophic and heterotrophic bacteria were observed, suggesting the occurrence of both phenomena [16]. This indicated that prolonged exposure of the sludge under unaerated conditions promoted bacterial cell lysis and the release of biodegradable compounds in the bulk, thereby increasing the biodegradability of the excess sludge [39].
Consequently, this resulted in higher methane productivity as observed in the BMP assays of the OSA sludge samples. It is known that sludge hydrolysis is the rate-limiting step in the AD process, therefore sludge pretreatment is generally carried out with the aim of promoting solubilization and hydrolysis of particulate organic matter [40]. The various pretreatment methods (e.g., alkaline treatment, ozonation, thermal hydrolysis, etc.) act by disrupting sludge cells and solubilizing EPS, thus increasing the biodegradability of the sludge [41]. Previous research demonstrated the possibility of increasing methane production in anaerobic digestion by 30–40% by using thermal alkali and ozone pre-treatment of sludge [42]. Other advanced pretreatments including microwave treatment, ultrasonication, high-pressure homogenization, and electrokinetic disintegration enabled additional methane production up to 100%, while involving high energy requirements (>30 kWh m−3, 14 MJ kgTS−1) [43]. Consequently, many of the above techniques are financially expensive and several raise environmental concerns (CO2 generation, high management costs, etc.) [44]. In this study, it was observed that the insertion of an ASSR according to scheme A produced similar effects to these expensive technologies in terms of specific methane productivity increment (20–40%), while ensuring a noticeable energy saving.
In contrast, scheme B promoted different sludge-reduction mechanisms, mainly attributable to uncoupling and maintenance metabolisms. Consequently, EPS hydrolysis and cell lysis were minimized. In previous studies, it was noted that prolonged aerobic starvation conditions were more favorable to induce maintenance metabolism, rather than EPS and cell hydrolysis [45,46]. Therefore, sludge hydrolysis was not observed when scheme A was implemented.
Overall, if on the one hand scheme A in the OSA plant involved less reduction of excess sludge compared with scheme B, on the other hand it promoted higher methane productivity because the same sludge-reduction mechanisms promoted an increase of sludge biodegradability that was favorable for AD.
3.4. Economic Impact of OSA on Plant Operational Costs
The present study demonstrated that the insertion of an ASSR into a conventional activated sludge system realized according to a pre-denitrification layout for biological nitrogen removal can substantially decrease the amount of sludge to be disposed of, and increase or decrease the methane productivity if a specific plant configuration is implemented. This might be an interesting opportunity for medium or large WWTPs where AD is used for stabilization of excess sludge and sludge disposal is one of the main operating costs.
Considering that the OSA process could easily be implemented in the plant layout by retrofitting existing holding tanks for ASSR, from an economic point of view the effects of such plant modification could influence sludge-disposal costs and the economic benefit deriving from methane generation from AD [46].
Overall, based on the results discussed in the previous sections, scheme A resulted in the highest increase of methane production (+19%) and most effective minimization of excess sludge (−31%) when the ASSR was operated with 12 h of HRT (P2). In contrast, the implementation of scheme B while operating with the same HRT in the ASSR (12 h) involved a decrease of both sludge production (−82%) and methane productivity (−41%) (Figure 7).
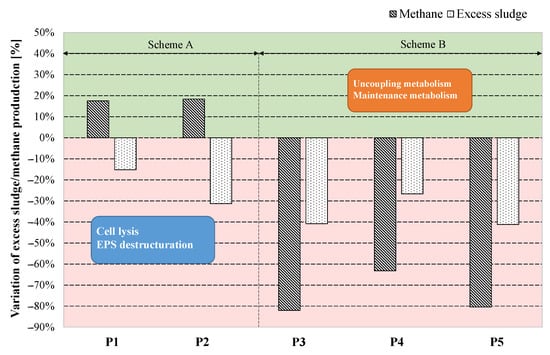
Figure 7.
Overall effects of the OSA process on excess sludge minimization and methane productivity during the experiment.
The cost effectiveness of this intervention according to scheme A or scheme B was assessed by means of economic analysis. The analysis referred to a WWTP with a potential of 100,000 PE. Based on the current costs for sludge management and disposal, biogas upgrading, and the selling price of methane, estimations were calculated for the increase and decrease of management costs (ASSR operations, sludge disposal, and methane generation) depending on the different process scenarios investigated in this study, from P1 to P5. Results are reported in Figure 8.
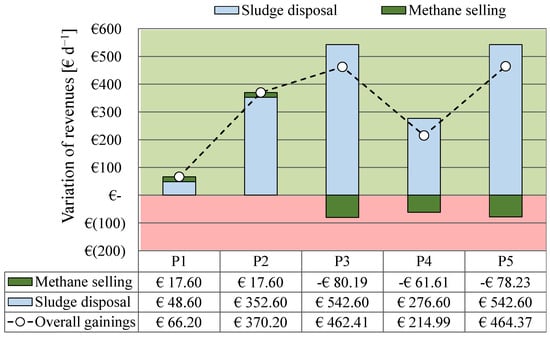
Figure 8.
Variation of revenues related to sludge disposal cost and methane production ( positive variation,
positive variation,  negative variation).
negative variation).
 positive variation,
positive variation,  negative variation).
negative variation).
The implementation of the OSA process resulted in a positive change in the revenue related to sludge disposal costs in all the investigated scenarios. In more detail, the greatest revenues were obtained in Period 3 and Period 5 (+550 EUR d−1) when the lowest sludge production was achieved. On the other hand, the variation of revenues was negative related to the methane sales price only when scheme B was implemented (−75 EUR d−1), because of the decrease in methane productivity.
The overall gain was positive in all the periods, indicating that OSA implementation could be a cost-effective solution for retrofitting WWTP. In this specific case, the highest revenues were achieved when scheme B was implemented (+350 ± 150 EUR d−1 on average), whereas scheme A resulted in a lower benefit (+200 ± 150 EUR d−1) overall. The above results suggest that the cost effect of OSA implementation is strictly related to the unit costs of sludge disposal and methane sales. These costs are highly variable and subject to frequent market fluctuations depending on different regional, national, or international scenarios. Policies aimed at the reuse of sludge could significantly reduce its disposal costs, and economic subsidies could boost the methane sale price. Therefore, the above analysis could result in different results if significant variations of the above costs were to occur. Specifically, if the incidence of the methane sales price is greater than that of sludge disposal, scheme A is the best solution for WWTP retrofitting. In contrast, scheme B could provide greater economic benefit from the reduction of sludge requiring disposal of, while allowing use of the AD for co-digestion facilities.
In addition, it should be remarked that the kinetics of methane production increased when scheme A was implemented, and simultaneously the quantity of sludge fed to the AD was decreased. From an operational point of view, this can increase the potential of exiting digesters because of the lower quantity of sludge fed daily to the digester and the faster kinetics, which may allow for digestion with external organic feedstocks.
4. Conclusions
The present study evaluated OSA process implementation in a CAS system under two different plant layouts in terms of its effects on the methane productivity achievable by anaerobic digestion of the excess sludge. The BMP assays showed that operation of the OSA plant in which the sludge was subjected to prolonged long-term exposure under anaerobic/anoxic conditions in the water line (scheme A) promoted increases of methane productivity and kinetic activity (20–40%), despite the reduction in the amount of excess sludge produced. The results demonstrated that under such conditions, cell lysis and EPS hydrolysis occurred, thereby improving sludge biodegradability and methane production. In contrast, prolonged starvation under anaerobic/aerobic conditions (scheme B) induced different metabolic pathways for minimization of excess sludge (uncoupling and maintenance metabolism) that caused a significant decrease in methane production (−80%). Therefore, retrofitting a WWTP with the OSA may allow high performances in methane production by anaerobic digestion to be maintained if specific sludge-reduction mechanisms are triggered in the water line. Moreover, the faster process kinetics and lower quantities of sludge to be managed might enhance the potential of a conventional anaerobic digester and make it suitable for co-digestion with other feedstocks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F.C., D.D.T. and F.D.M.; methodology, S.F.C. and F.D.M.; software, S.F.C. and D.D.T.; validation, S.F.C., D.D.T., M.T. and G.V.; formal analysis, S.F.C. and F.D.M.; investigation, S.F.C. and F.D.M.; resources, M.T. and G.V.; data curation, S.F.C. and D.D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F.C. and F.D.M.; writing—review and editing, D.D.T., M.T. and G.V.; visualization, M.T. and G.V.; supervision, M.T. and G.V.; project administration, M.T. and G.V.; funding acquisition, M.T and G.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR, Italy)—Project PON Ricerca e Innovazione 2014–2020—FSE REACT-EU—Azione VI (D.M. 1062/2021)—project title: BIOFEEDSTOCK—Sviluppo di Piattaforme Tecnologiche Integrate per la Valorizzazione di Biomasse Residuali—project code: ARS01_00985 – CUP: B66C18000320005.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available on request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Sara Mulone, Manuela Russo Tiesi, and Lilly Tortorici for their valuable contribution during pilot plant operations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Foladori, P.; Andreottola, G.; Ziglio, G. Sludge Reduction Technologies in Wastewater Treatment Plants; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2010; ISBN 9781843392781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, R.; Cao, K.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, J.; Xian, G. Zero excess sludge wastewater treatment with value-added substances recovery using photosynthetic bacteria. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, A.U.A.; Sorour, M.T.; Aly, S.A. Cost analysis of activated sludge and membrane bioreactor WWTPs using CapdetWorks simulation program: Case study of Tikrit WWTP (middle Iraq). Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 4659–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Torretta, V. What Advanced Treatments Can Be Used to Minimize the Production of Sewage Sludge in WWTPs? Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Frattarola, A.; Carnevale Miino, M.; Padovani, S.; Katsoyiannis, I.; Torretta, V. Legislation for the Reuse of Biosolids on Agricultural Land in Europe: Overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebian, S.; Borghei, S.M.; Torkaman, M.; Goudarzi, H.H. Influence of ultrasonic cell disintegration on excess sludge reduction in a Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iaconi, C.; De Sanctis, M.; Altieri, G.V. Full-scale sludge reduction in the water line of municipal wastewater treatment plant. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Combination of the OSA process with thermal treatment at moderate temperature for excess sludge minimization. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semblante, G.U.; Hai, F.I.; Bustamante, H.; Guevara, N.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Biosolids reduction by the oxic-settling-anoxic process: Impact of sludge interchange rate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.J.; Stuart, B.; Kumar, S. Investigation of Anaerobic Digestion of the Aqueous Phase from Hydrothermal Carbonization of Mixed Municipal Solid Waste. Biomass 2021, 1, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Sheng, L. Preparation of ceramsite from municipal sludge and its application in water treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Andreottola, G. Sludge reduction by an anaerobic side-stream reactor process: A full-scale application. Environ. Chall. 2021, 2, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; You, X. Impact of hydrothermal pre-treatment on the anaerobic digestion of different solid–liquid ratio sludges and kinetic analysis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19104–19113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Capua, F.; Spasiano, D.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F.; Fratino, U.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. High-solid anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Chon, D.-H.; Brennan, A.; Eom, H. Investigation of sludge reduction and biogas generation in high-rate anaerobic side-stream reactors for wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1829–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Carabillò, M.; Cosenza, A.; De Marines, F.; Di Trapani, D.; Traina, F.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Insights on mechanisms of excess sludge minimization in an oxic-settling-anaerobic process under different operating conditions and plant configurations. Chemosphere 2022, 312, 137090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0875532356. [Google Scholar]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A.G. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuBois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P.J.; Ergas, S.J.; Mihelcic, J.R.; Hobbs, S.R. Effect of Substrate to Inoculum Ratio on Bioenergy Recovery from Food Waste, Yard Waste, and Biosolids by High Solids Anaerobic Digestion. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, W.; Lia, A. Essential Role of Trace Elements in Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanza, R.; Cortesi, A.; De Arana-Sarabia, M.E.; Gallo, V.; Vasiliadou, I.A. Oxic settling anaerobic (OSA) process for excess sludge reduction: 16 months of management of a pilot plant fed with real wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G.; Olsson, G. Energy Issues in Sustainable Urban Wastewater Management: Use, Demand Reduction and Recovery in the Urban Water Cycle. Sustainability 2020, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2000/60/EC The European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32000L0060 (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- De Rosa, M. Economic assessment of producing and selling biomethane into a regional market. Energy Environ. 2020, 31, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Polonio, E.; Fernández-Navarro, J.; Alonso-Molina, J.L.; Amorós-Muñoz, I.; Bes-Piá, A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Changes in the process performance, sludge production and microbial activity in an activated sludge reactor with addition of a metabolic uncoupler under different operating conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-S.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.-P. Sludge reduction based on microbial metabolism for sustainable wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semblante, G.U.; Hai, F.I.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; You, S.-J.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Sludge cycling between aerobic, anoxic and anaerobic regimes to reduce sludge production during wastewater treatment: Performance, mechanisms, and implications. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 155, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudoba, P.; Morel, A.; Capdeville, B. The case of both energetic uncoupling and metabolic selection of microorganisms in the OSA activated sludge system. Environ. Technol. 1992, 13, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fida, Z.; Price, W.E.; Pramanik, B.K.; Dhar, B.R.; Kumar, M.; Jiang, G.; Hai, F.I. Reduction of excess sludge production by membrane bioreactor coupled with anoxic side-stream reactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 281, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, V.; Bansal, A.; Jha, M.K. Investigation of activated sludge characteristics and their influence on simultaneous sludge minimization and nitrogen removal from an advanced biological treatment for tannery wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.H.; Kotova, P.; Shaw, C.; Hong, Y.; Chang, S. Impacts of Temperature and Solids Retention Time, and Possible Mechanisms of Biological Hydrolysis Pretreatment on Anaerobic Digestion. Water 2020, 12, 3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Assay Method for Anaerobic Digestion Research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaveli, F.; Petala, M.; Tsiridis, V.; Darakas, E. Enhanced Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Primary Sewage Sludge. Water 2021, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Chon, D.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, C. Investigation of bacterial community in activated sludge with an anaerobic side-stream reactor (ASSR) to decrease the generation of excess sludge. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4292–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yue, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Ning, X. Effects of bioporous carriers on the performance and microbial community structure in side-stream anaerobic membrane bioreactors. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslev, P.; King, G.M. Aerobic and anaerobic starvation metabolism in methanotrophic bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Dai, X. Perspective on enhancing the anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Dai, X.; Dai, L. Enhancing Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge by Solid–Liquid Separation via Isoelectric Point Pretreatment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14774–14784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G.; Jin, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, M.; Xu, X. Effect of alkaline addition on anaerobic sludge digestion with combined pretreatment of alkaline and high pressure homogenization. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 168, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Dagnew, M. Enhancing biomethane production and phosphorus recovery from CEPT sludge through a low temperature thermal alkali and ozonation pretreatment processes. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 5, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Gievers, F.; Vance, C.; Magnolo, F.; Murphy, F.; Goi, D. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge pretreatment for biogas production: From laboratory tests to full-scale applicability. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 322, 129056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; De Oliveira, T.S.; Di Trapani, D.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Simultaneous sludge minimization, biological phosphorous removal and membrane fouling mitigation in a novel plant layout for MBR. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 259, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, V.; Bansal, A.; Jha, M.K. Minimization of excess bio-sludge and pollution load in oxic-settling-anaerobic modified activated sludge treatment for tannery wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).