Abstract
This study revises the δ18O and δ2H status of Lake Baikal. The mean values of δ18O and δ2H varied from −15.9 to −15.5‰ and from −123.2 to 122.2‰, respectively, for the past 30 yr. The isotopic composition of the lake remained more ‘‘light” compared to the regional precipitation and rivers inflows. The isotopic composition of the lake has begun to change since ca.1920 after the Little Ice Age; however, Lake Baikal still has not reached the isotopically steady state in the present. The calculated composition of the steady-state should be −12.3‰ for δ18O and −103.6‰ for δ2H. If regional climate parameters do not change dramatically, Lake Baikal will reach these values in ca. 226 yr. Based on isotopic fingerprints of the upper (0 to 150 m) and near-bottom layers (ca. 150 m from the bottom floor), the renewal in the southern and central basins of Lake Baikal has occurred recently compared to the northern Baikal basin, and the size of the mixing-cell of downwelling is close to 30 km.
1. Introduction
Lake Baikal is the largest and the most ancient lake in the world. Its size of 632 km in length and 1.642 km in depth assumes a long hydrological history and residence time. The watershed of the lake is approximately 557.000 km2 and covers Northern Mongolia and East Siberia. Tributaries of Lake Baikal flow over landscapes of steppe, boreal taiga, permafrost, and mountains. The main tributaries of the lake are the Selenga (~25.57 to 29.43 km3 yr−1, ~50% of the total annual inflow), Upper Angara (~8.37 to 8.56 km3 yr−1, ~12% of the total annual inflow), and Barguzin (~3.71 to 3.9 km3 yr−1, ~6% of the total annual inflow) rivers [1]. Table 1 shows monthly hydrological parameters of Lake Baikal when the maximum inflow and evaporation occur in June and December, respectively. Outflow through the Angara River is stable (~5 km3 month−1) during the year. Although Lake Baikal is located in the Baikal Rift Zone, the groundwater input is <4.5% of the total water input [2].
One of the most fundamental questions for any deep lake is the mechanism of the rate of deep-water renewal via exchange with surface water. Simple indicators of the renewal for Lake Baikal are the changes in temperature and oxygen concentration at the water interface near the bottom [3]. Seasonal convection in Lake Baikal occurs in two time spans: spring and late autumn when the temperature of the surface layers are below 4 °C and colder than the deep layer [4,5,6]. When the temperature of the surface layer equals that of the deep layer, deep convection must stop.
The renewal inferred from isotopic methods was estimated 30 or more years ago. Thus, based on the content of CFC-11 and CFC-12 in Lake Baikal in 1988, only about 12.5% of the renewal of deep waters occurred each year in the 20th century [6].
Rates of the renewal of deep water with surface water deduced from volume-weighted mean 3H-3He ages below 250 m depth are about 10% yr−l in the southern and central basins and 15% yr−l in the northern basin [7].
Westerlies (transfer from the North Atlantic), the Arctic Oscillation, the East Asian monsoon, and the winter Siberian High form the climate in East Siberia. Specifically, the Westerlies are forced to move northwards during warm seasons due to the following factors: (i) the northward shift of the atmospheric circulation cells driven by Earth’s tilt and (ii) the expansion and the northward shift of the Azores high-pressure system [8]. Moreover, during the warm season, the well-developed East Asia low-pressure system extends to the southeast of Siberia, and “lures” the westerlies to move further eastwards, enhancing the warm-season domination of the westerlies [9]. At present, 70% of the annual precipitation in East Siberia is recorded during warm seasons when heavy but rare rain occurs due to the Asian monsoon [10]. This pattern indicates that the atmospheric circulation of the northwesterly wind direction is dominant in the area of Lake Baikal. In winter, the Siberian High occupies East Siberia and blocks the penetration of moisture from the oceans to continental Asia.
Changes in climate and the atmospheric water cycle are known to leave an imprint on the isotopic composition of different water reservoirs. Therefore, the investigation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopic characteristic can be useful for the hydrological reconstruction of water bodies [11]. However, isotopic investigations of the area around Lake Baikal and its watershed are still rare. In Siberia, the contribution from recycled water mainly controls the isotopic composition of summer precipitation [12]. On other hand, air temperature mainly affects the isotopic composition of regional precipitation, and no significant correlations were obtained for precipitation amount and relative humidity [13,14].

Table 1.
Hydrological and isotopic characteristics of the water balance of Lake Baikal.
Table 1.
Hydrological and isotopic characteristics of the water balance of Lake Baikal.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.13 | 0.33 | 4.88 | 0.55 | 0.82 | −17.8 | −28.16 | −216.34 | −18.36 | −139.76 |
| 2 | 0.85 | 0.2 | 4.32 | 0.06 | 0.76 | −14.4 | −25.31 | −199.11 | −17.37 | −132.96 |
| 3 | 0.93 | 0.24 | 5.08 | 0.23 | 0.65 | −6.4 | −20.73 | −161.14 | −16.57 | −126.37 |
| 4 | 2.5 | 0.58 | 4.82 | 0.77 | 0.56 | 2.5 | −14.92 | −113.98 | −15.39 | −116.76 |
| 5 | 7.74 | 0.91 | 4.54 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 10.2 | −13.31 | −103.39 | −15.27 | −115.93 |
| 6 | 11.71 | 1.61 | 4.46 | 0.12 | 0.67 | 15.4 | −11.25 | −93.09 | −14.99 | −114.46 |
| 7 | 11.09 | 2.58 | 4.82 | 0.17 | 0.74 | 18.3 | −9.89 | −78.05 | −14.44 | −109.97 |
| 8 | 10.46 | 2.2 | 5.08 | 0.94 | 0.78 | 15.8 | −9.71 | −74.97 | −14.49 | −110.03 |
| 9 | 8.29 | 1.39 | 5.02 | 1.77 | 0.76 | 9.1 | −14.13 | −106.36 | −15.30 | −115.81 |
| 10 | 5.23 | 0.7 | 5.18 | 2.85 | 0.73 | 1.8 | −20.98 | −157.25 | −16.15 | −122.10 |
| 11 | 2.18 | 0.86 | 5.31 | 3.42 | 0.79 | −7.6 | −25.51 | −191.26 | −18.33 | −138.30 |
| 12 | 1.49 | 0.86 | 5.39 | 3.33 | 0.85 | −15.3 | −27.53 | −212.21 | −19.90 | −152.10 |
1—Month, 2—Inflow (km3), 3—Precipitation (km3), 4—Outflow (km3), 5—Evaporation (km3), 6—Humidity, a.u (0–1), 7—Mean air temperatures (°C), 8—Mean regional δ18O precipitation (‰), 9—Mean regional δ2H precipitation (‰), 10—Weighted mean δ18O Input (‰), 11—Weighted mean δ2H Input (‰). Values of Inflow, precipitation, outflow via the Angara River were according to [14], humidity and mean air temperatures 1995-2020 were taken from NOAA data-set www.ncdc.noaa.gov (accessed on 26 November 2021) and grid model from http://climate.geog.udel.edu (accessed on 26 November 2021), bulk annual δ of river inflow was used as −15.5‰ for δ18O and −117.4‰ for δ2H [5].
The isotopic study of Lake Baikal was performed only in 1991 and 1992, which revealed that Lake Baikal was in a transit status and did not reach a steady-state isotopic composition (isotopic equilibrium with inflowing water) [2]. Based on this estimation, Lake Baikal will reach its steady-state in 780 yr [2]. However, this estimation results from the calculations of the isotopic values in the starting composition of the inflow [2]. In our study, the initial isotopic composition of Lake Baikal and the inflow (1991 and 1992 yrs.) used in calculations were known that it improves to estimate the isotopic evolution of the Lake Baikal.
Lake Baikal is an ecosystem with endemic flora and fauna, and we can assume that changes in the isotopic composition of the lake will have a prolonged effect on the life cycles of its biota. For example, there are different oxygen isotopic fractionations between the δ18O bulk water and the δ18O incorporated bulk of inorganic orthophosphate at the biogeochemical cycle of phosphorus [15,16]. Thus, nucleic acids account for 76% (wt.) of Porg in cells and are widespread in aquatic and sedimentary environments. Therefore, we expect that the process of the Pinorganic regeneration from nucleic acids can exert a significant impact on the δ18OP values of dissolved inorganic phosphate in natural waters, sediments, and soils. For example, there is a linear trend between the O isotope values of Pinorganic released by Escherichia coli-synthesized enzymes and ambient water [17].
There have been no isotopic studies of Lake Baikal for the past 30 yr. However, the climate of the Earth has been significantly changing over the past decades [18], and these changes can affect the atmospheric circulation and hydrological regime of lakes [19]. For example, wind mixing of water layers in Lake Baikal is an effective trigger for their renewal [2]. However, regional wind activity has reduced for the past decade [3], and it could cause a decrease in the renewal of the lake.
For the past decade, the shallow zone of Lake Baikal has been under intensive anthropogenic eutrophication (excess nutrient enrichment from human activity) [20,21]. Thus, another aspect of the renewal of Lake Baikal can be the influx of polluted water from the shallow zone into the deep zone, and isotopic fingerprints can indicate this process.
In general, for the past decades, significant changes in the environment have occurred on global and regional scales, and it seems that a response of the isotopic status of Lake Baikal to these changes needs actualization. This study aimed to estimate the isotopic changes of Lake Baikal for the past 30 yr and search for isotopic fingerprints of vertical mixing between the upper and bottom water layers of the lake.
2. Methods
Eight vertical stations from the surface to the bottom of Lake Baikal and several surface samples were studied (Figure 1). The water samples were collected from 4 to 9 June 2021 (the first cycle of deep convection in Lake Baikal) from the board of the R/V “Vereshagin”.
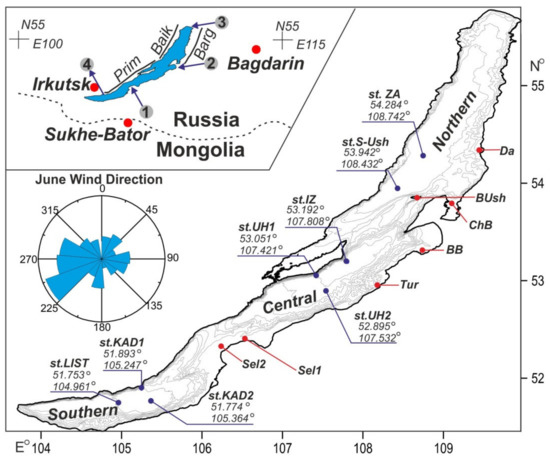
Figure 1.
A sketch shows the location of points of isotopic samples. The upper panel—isotopic composition of regional precipitation from weather stations—Irkutsk, Bagdarin, and Sukhe-Bator [12,13,14,22]. Numbers into grey circles are 1, 2, and 3—inflow via Selenga, Bargyzin, and Upper Angara Rivers, respectively. 4—outflow via the Angara River. Prim, Baik, and Barg—Primorsky, Baikalsky, and Barguzinsky Ridges, respectively. The bottom panel is Lake Baikal, grey lines—isobaths countered at 200 m [23]. Blue circles are stations of vertical profiles of temperatures, oxygen concentration, and isotopic composition from the surface to the bottom. Red circles—surface samples.
The isotopic values of δ18O and δ2H in Lake Baikal were detected by a Picarro L2130i (CRDS). The accuracies of these measurements were 0.1 and 0.4‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively. Two international standards, USGS-47 (δ18O −19.8 ± 0.02‰, δ2H −150.2 ± 0.5‰) and GRESP (δ18O −33.4 ± 0.04‰, δ2H −258.0 ± 0.4‰), were used for calibration. Deuterium excess was calculated as d-excess = δ2H‰ − δ18O‰ × 8.
The isotopic composition of regional precipitation collected from 1971 to 2017 was based on samples from weather stations Irkutsk [14,22], Bagdarino [12], and Sukhe-Bator [13].
An SBE-25 CTD probe (SeaBird, Bellevue, WA, USA) and a Rinko III (JFE Advantech Co., Kawasaki, Japan) were used to measure temperature (accuracy: ±0.002 °C) and the concentration of oxygen (DO) by with a resolution of 0.2 mg L−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Southern Basin of Lake Baikal
The temperature profiles can be divided into three zones. The upper zone (0 to 145 m) is characterized by a transition of water temperatures from 2.4 to 3.6 °C. The temperature gradually decreased to 3.38 °C in the middle zone (145–150 to 1150 m). In the bottom zone (1150–1450 m), the temperature drastically decreased to 3.3 °C (Figure 2). The distribution of oxygen through the deep layers closely corresponds to temperature profiles. The DO varied from 13.5 to 9.5 mg L−1. The LIST station showed the highest oxygen concentration compared to the KAD1 and KAD2. The location of zones in the oxygen profile was identical to temperature zones (Figure 2). However, these changes in the bottom layer were most significant at LIST and KAD1.
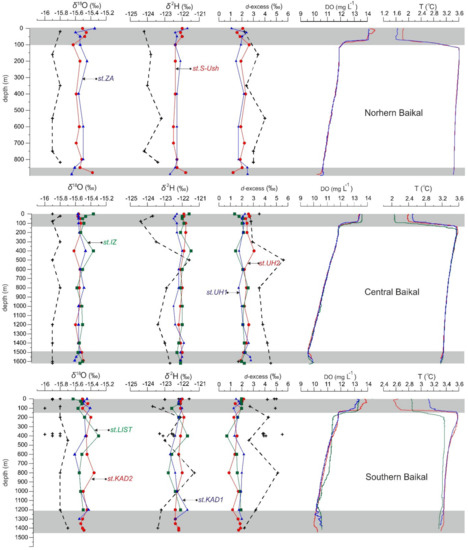
Figure 2.
Vertical profiles showing the distribution of δ18O, δ2H, d-excess, temperatures, and oxygen concentrations along stations from Figure 1. Black lines and symbols (+) are the distribution of δ18O, δ2H, d-excess in June 1991–1922 [2]. Gray areas define the vertical zonation of the water column.
The mean values of δ18O and δ2H for LIST, KAD1, and KAD2 were similar and ranged from −15.3 to −15.6‰ and from −121.7 ± 0.1 to −122.4 ± 0.3‰, respectively. The upper and bottom zones had the minimum offsets between layers and stations in the δ18O and δ2H compositions (Figure 2). In the middle zone, these offsets could increase to 0.17‰ and 0.75‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively.
3.2. The Central Basin of Lake Baikal
At the stations (UH1, UH2, and IZ) of the central basin of Lake Baikal, there are also three zones with different temperatures, oxygen concentration, δ18O, and δ2H. The temperature profiles of the stations were uniform and smooth. The temperature in the upper zone (0 to 150 m) ranged from 2 to 3.6 °C, whereas, in the 0–80 m layer, it ranged from 2 to 2.4 °C. This 0–80 m layer was colder than the upper layer in the southern basin. The temperature gradually decreased from 3.6 to 3.2 °C in the middle zone (150 to 1500 m). Temperature changes were insignificant (around 0.05 °C) in the bottom zone (1500–1620 m). The DO varied from 13.58 to 9 mg L−1 in the upper and middle zones, while oxygen concentration increased to 9.9 mg L−1 in the bottom zone. In general, the station IZ was enriched in the oxygen of ca. 0.5 mg L−1 compared to stations UH1 and UH2 in the upper zone.
The isotopic composition along all stations ranged from −15.3 to −15.6‰ and from −121.5 to −122.5‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively. Overall, offsets in the isotopic composition between layers at the stations were 0.05‰ and 0.2‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively. Obviously, the main abiotic factors (temperature and oxygen concentration) of the central basin were more homogeneous than in the southern part.
3.3. The Northern Basin of Lake Baikal
The temperatures of the uppermost layer (0 to 70 m) ranged from 1.6 to 1.8 °C, and the thickness of the upper cold zone (1.6 to 3.6 °C) was short (100 m). The temperature gradually decreased to 3.4 °C at a depth of 890 m (Figure 2). There was no change in temperature at the bottom layer. The DO concentration varied from 14 to 11.2 mg L−1 in the upper 100 m layer. The concentration gradually decreased to 10 mg L−1 at a depth of 870 m. However, in the bottom zone (870 to 896 m), it sharply decreased to 9.5 mg L−1 (Figure 2).
Oxygen isotope values along the depth ranged from −15.3 to −15.6‰, δ2H accounted for −121.7 to −122.5‰. Offsets in the isotopic composition between layers at the stations and the stations were 0.07‰ and 0.18‰ for δ18O and δ2H, respectively. The most significant offsets occurred in the upper (0 to 100 m) and bottom (870 to 896 m) zones.
3.4. Isotopic Composition of the Surface Water
The values of δ18O and δ2H between stations ranged from −15.3 to −15.6‰, and δ2H from −121.6 to −123.0‰ (Figure 3). However, stations Sel (δ18O −15.7‰; δ2H −120.3‰) and BB (δ18O −17.05‰; δ2H −130.3‰) showed the most contrasting values with other surface stations. Cluster analysis constructed on δ18O, δ2H, Local Meteoric Water Line (LMWL), and d-excess indicates no difference in isotopes between southern, central, and northern basins of Lake Baikal. For example, there is a cluster close to the southern basin (KD2), northern basin (BUsh), and Chevyrkuy Bay-ChB (Figure 3).
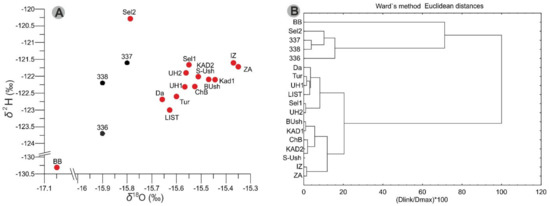
Figure 3.
Panel (A)—isotopic composition of the surface water in Lake Baikal at June 2021 (red circles) and June 1991–1992 (black circles, No. 336, 337 and 338) from [2]. Panel (B)—the result of cluster analysis notes that there is no difference between the southern, central, and northern Baikal (see Figure 1) in the isotopic composition of the surface water.
3.5. Isotopic Characteristics of Inflow in Precipitation, Rivers and the Lake
To estimate the regional isotopic composition of precipitation, we used data from stations Irkutsk (70 km from Lake Baikal), Bagdarin (near the watershed of the Barguzin River) and Sukhe-Bator (the watershed of the Selenga River, Mongolia) collected in 1971, 1990, from 1996 to 2000, and from 2012 to 2017 [12,13,14,22]. The isotopic composition of the Baikal tributaries was taken from Seal and Shanks [2]. Groundwater input in Lake Baikal is <4.5% of the total net flux, and it cannot cardinally change the isotopic proportion in the lake [2].
The seasonal means of regional precipitation for δ18O and δ2H, respectively, amount to −27‰ and −209.2‰ in winter, −16.3‰ and −126.2‰ in spring, −10.3‰ and −82.0‰ in summer, and −20.2‰ and −151.6‰ in autumn (Figure 4). Figure 5 shows that regional precipitations are close to Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL), although they are isotopically lighter. Rivers inflow also shows offset from GMWL. The annual rivers inflow is −15.5‰ for δ18O and −117.4‰ for δ2H [2]. The isotopic composition of Lake Baikal is close to the precipitation of Irkutsk, whereas the δ18O and δ2H compositions of some surface samples were close to ones for Bagdarin and Irkutsk (Figure 5). In general, the isotopic composition of Lake Baikal is “lighter” compared to regional precipitation and rivers inflow. On the other hand, vapor from Lake Baikal should deplete the isotopic composition of precipitation in Irkutsk, and this influence of the lake increases in autumn when evaporation is the maximum. This feature of Irkutsk most likely explains the isotopic difference with Bagdarin.
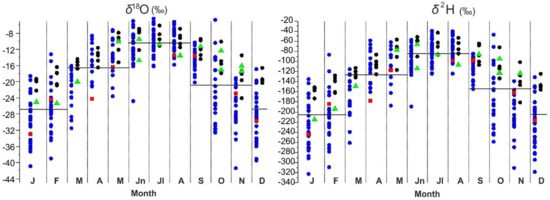
Figure 4.
Monthly isotopic characteristics of regional precipitation. Blue circles—Irkutsk at 2012–2017, black circles—Bagdarin at 1996–2000, red circles—Sukhe-Bator 2002–2003, green triangles—Irkutsk at 1971, 1990. Horizontal black lines—seasonal means isotopic values.
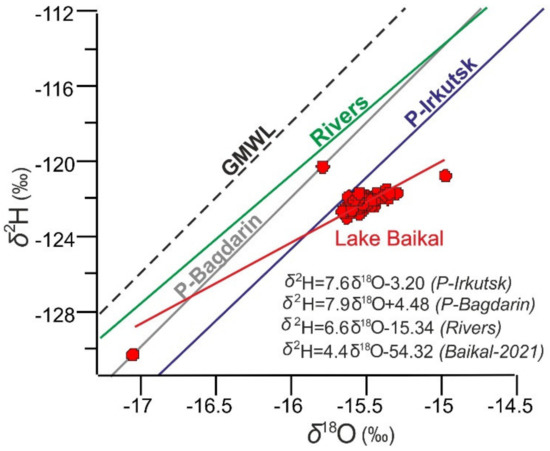
Figure 5.
Line regressions of oxygen and hydrogen isotopic composition of regional precipitation (Irkutsk—blue, Bagdarin—grey), rivers inflow—green, and Lake Baikal—red. GMWL—Global Water Meteoric Line (δ2H = 8 × δ18O + 10).
Notably, the isotopic composition of regional precipitation from April to September is more isotopically heavy compared to the lake composition (Figure 2 and Figure 4). A similar disproportion in the isotopic composition of the lake, precipitation, and rivers inflow was also observed in 1991 and 1992 [2]. Most likely, this evidences that Lake Baikal is in a transient state with respect to the isotopic characteristics of its water budget.
3.6. Isotopic Composition in 1991, 1992, and 2021
Inputs from precipitation, rivers inflow, and groundwater fluxes form the water balance of Lake Baikal, whereas outputs mainly occur as effluents through the Angara River (the southern basin) and evaporation. Figure 6 shows that the maximum inflow to Lake Baikal occurs from June to August, while evaporation begins to gradually increase from September and prevails over the inflow from November to December. In 1991 and 1992, Lake Baikal was characterized by the mean values of δ18O and δ2H accounting for −15.9‰ and −123.2‰, respectively. However, at present, these values are −15.5‰ (δ18O) and −122.2 ‰ (δ2H).
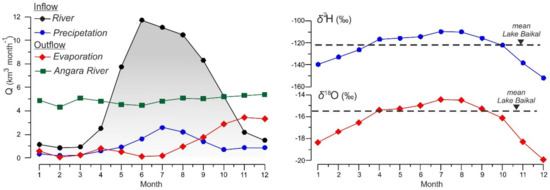
Figure 6.
(Left) pane—seasonal variation in the hydrological balance of Lake Baikal. (Right) pane—weight average season isotopic characteristic (red and blue curves) of inflow into Lake Baikal, and the mean values of δ18O and δ2H (black dashed lines) for the lake.
It is widely acknowledged that there is a clear positive relationship between rising in air and ocean temperature and enrichment of precipitation in heavy oxygen and hydrogen isotopes e.g., [11]. In Russia and the Baikal region, the temperature rises by +0.45 °C every 10 years and by +0.34 °C every 10 years, respectively [24]. Based on this trend, the shift in air temperature of the Baikal region is approximately +1.02 °C for the past 30 years. The δ18O/T gradient for weighted mean monthly precipitation in the Lake Baikal region ranges from 0.36 to 0.50‰ per °C [2,14]. Thus, we can assume that the revealed changes in the isotopic characteristics of Lake Baikal occurred due to the increase in δ18O and δ2H in regional precipitation with the global warming during the past decades. However, there is no significant difference in monthly offsets of regional isotopic values of precipitation for 1971 and 1990, from 1996 to 2000, and from 2012 to 2017 (Figure 5), and Lake Baikal is still isotopically depleted compared to precipitation. In this regard, modern isotope values of rivers inflow are most likely close to those in 1991 and 1992 (−15.5‰ for δ18O and −117.4‰ for δ2H) reported by Seal and Shanks [2]. Moreover, surface samples from Barguzin Bay and the Selenga Delta show the isotopic composition and d-excess ~6‰ close to those for the Selenga and Barguzin rivers in 1991 and 1992.
The outflow through the Angara River is the same during the year. However, the net inputs are close to the equal net outputs, so there is no net change in the volume of the lake (Table 1). Furthermore, the Angara River discharges water from the lake’s depth of 0 to 50 m. Ultimately, the outflow through the Angara River should not result in an isotopic change in the composition of the lake.
Seal and Shanks [2] suggested that the “light” isotopic water of Lake Baikal formed during the Little Ice Age.
According to Equation (1) from Gonfiantini [25], we estimated the change in the isotopic composition of the lake − with the time span of one month:
where is the initial isotopic composition of the lake in the previous month, and is the steady-state isotopic composition that the lake approaches as ; —the total monthly inflow (km3) into the lake; V—the volume of Lake Baikal (km3). The steady-state isotopic composition, is given by Gonfiantini [25] and Gat [26] as Equation (2):
where (evaporation/inflow); is the temporal slope from Gibson et al., (2016) [4]; —the limiting factor for isotope enrichment from Gonfiantini [25], and —amount-weighted isotopic composition of the total monthly inflow. This calculation began with June 1992 when was −15.9‰ for δ18O and −123.2‰ for δ2H; δ of monthly precipitation was as shown in Table 1, and the bulk annual δ of rivers inflows was used, −15.5‰ for δ18O and −117.4‰ for δ2H [2].
These calculations indicate that changes in the isotopic composition of Lake Baikal in time can be described as (R2 = 0.99), (R2 = 0.99) where is the number of months (Figure 7). The calculated data on the shift in the isotopic values from June 1992 to June 2021 (348 months) were as follows: δ18O = −15.44‰ and δ2H = −120.69 ‰. These calculated and the measured mean values (−15.5‰ for δ18O and −122.2‰ for δ2H) are very close, and these regression models can be used to calculate a time when Lake Baikal will be in steady-state isotopic composition. According to Equation (2), the mean annual values of should be close to −12.36‰ for δ18O and −103.64‰ for δ2H. If regional climate parameters do not change dramatically, Lake Baikal will reach these values in ca. 226 yr.
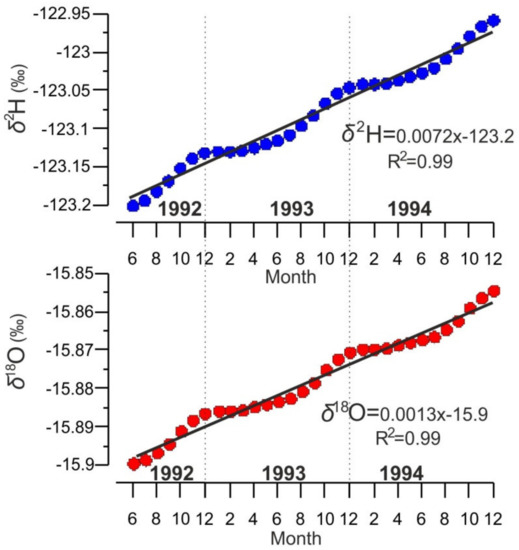
Figure 7.
The example of changes in δ18O and δ2H in a month scale, when June 1992 was the beginning for calculation Equations (1) and (2).
In Lake Baikal, the residence time of water is about 330 yr, and that of trace elements is 94 to 320 yr [27]. Based on the found line regressions of time estimates of the steady-state isotopic composition, we can assume that the lake has begun to change in an isotopic transient state since ca. 1920. The global climate transition from the Little Ice Age to the Recent Warming might trigger this change in Lake Baikal. According to many reconstructions of global surface temperatures for the Northern Hemisphere, a transition from the Little Ice Age to the Recent Warming was characterized by a sharp increase in the annual temperature that occurred ca. 1850 to 1860 [28,29,30]. However, records from East Siberia revealed that significant changes in climate parameters, vegetation, and lake bio-productivity were not intense until 1900 [30]. It seems that a regional climate passed fully to the Recent Warming of 1900 to 1920. Most likely, the found changes in the isotopic composition of the lake are rather due to the changes in the water balance and gradual replacement of the water body formed until 1920 by modern influxes than to climate changes occurring in the recent decades.
3.7. Renewal of Lake Baikal
Figure 2 clearly indicates that the upper layer from 100 to 150 m is colder and enriched in oxygen compared to the underlying water layers. Ultimately, thermal stratification and storm forced this cold layer to sink to the bottom because it is denser than the surrounding water masses [6,31]. A fingerprint of this vertical mixing is temperature and oxygen “anomalies” in the near-bottom layer. The estimated mean residence times for layers >250 m in the southern, central, and north basins range from 11 to 17 yr, from 10 to 18, and from 6.2 to 11 yr, respectively [6,7,32]. According to this vertical mixing mechanism, the upper and bottom layers could be younger than the “core” of the lake. The identified changes in the isotopic composition (Figure 2) at the interface of 100 to 150 m from the bottom-most likely have this origin. Notably, the vertical water exchange does not occur every year. For instance, between 2005 and 2012, the mixing in the southern, central, and northern basins occurred with frequencies of 65, 50, and 45% yr−1, respectively [33].
The determined d-excess for the bottom interfaces is uniform between stations and the parts of Lake Baikal. In this regard, it seems that the d-excess can be a marker of the time span between the formations of the upper and the near-bottom layers. For example, there is no significant offset in the d-excess for the southern basin, and it can be evidence that these bottom layers are formed by one generation of downwelling. On the contrary, in the central basin, UH1 located 3 km from the coast shows offset of d-excess in ca. 1‰ from the pelagic stations UH2 and IZ. The maximum offset (1.5‰) in the d-excess of the bottom layers was determined in the northern basin (Figure 2).
The average distance between the stations with offsets in d-excess in the near-bottom layers is 30 km (Figure 1). Based on this distance, the size of the mixing-cell of downwelling is close to 30 km. Additionally, the d-excess of the upper (0 to 150 m) and bottom layers of the southern basin are very close. It most likely elucidates that vertical renewal of water in the south basin is more frequent than in other parts of Lake Baikal. The northwesterly wind dominates in the Baikal region [34]. Thus, frequent renewal of the southern basin can be due to more intensive wind-induced convection. The central and northern basins are partially shielded from wind penetration by Primorsky, Baikalsky, and Barguzin Ridges.
In general, the identified renewal in the southern and central basins might have occurred recently compared to the northern basin. Moreover, the bottom interface in the northern basin was maximally depleted in the concentration of oxygen over vertical profiles and vice-versa in the southern and central basins (Figure 2). Time without renewal of water at the bottom of the lake was characterized by the deficiency of DO due to organic matter oxidation in bottom sediments.
The value of stable isotopes analysis can be used in qualitative analysis of water sources in a water treatment context [35,36]. Settlements located around the shoreline of Lake Baikal do not have water treatment stations, or these stations operate incorrectly without quality treatment of wastewater [37]. Ultimately, wastewater inflows to the shallow zone of the lake with groundwater. Noteworthy is that domestic water is enriched in heavy isotopes of ~0.12 to 4 ‰ for δ18O [38,39]. The number of tourists visiting Lake Baikal used to be approximately 1.8 M yr−1 before the COVID-19 pandemic. Hence, we can assume that wastewater could enrich the shallow zone with heavy δ18O. This study does not present pelagic samples with “anomalously heavy” δ18O. However, in the future, the δ18O and δ2H composition of the Lake Baikal shallow zone should be studied in detail.
4. Conclusions
We studied the distribution of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes, temperatures and oxygen concentrations in Lake Baikal as hydrological proxies in June 2021. Thus, a 30-year gap in the study of δ18O and δD has been filled. We have revealed that current values of δ18O (−15.5 ‰) and δ2H (−122.2‰) are “heavier” by 0.5 and 1‰ compared to those in 1991 and 1992. Based on the evolution of the isotopic composition of the lake from June 1992 to June 2021 with a time span of one month, we have calculated a line regression model for the change in the isotopic composition per unit of time. Isotopic values in 2021 are still lower than the calculated isotopic composition of the steady-state (−12.3‰ for δ18O and −103.6‰ for δ2H). Therefore, Lake Baikal most likely has not yet reached the isotopically steady state. This study revealed that the lake has begun to change since ca.1920 and will reach the isotopically steady-state in ca. 226 yr. Gradual replacement of the water body formed until 1920 by modern influxes explains well the identified shifts in isotopic composition.
The closeness of the calculated and measured δ18O and δ2H values demonstrates the relevance of used equations to estimate the isotopic status of large lakes.
There are offsets in temperatures and oxygen concentrations in the 100 to 150 m near-bottom water interface from the overlapping water layers. The δ18O and δ2H fingerprints have been first used to substantiate a vertical mixing in the uppermost (0 to ca.150 m) and near-bottom layers. It seems that the vertical renewal of water in the southern basin of Lake Baikal is more frequent than in other parts of the lake. The size of the mixing-cell of downwelling is close to 30 km.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—A.F.; methodology—A.F. and O.S.; fieldwork, sampling, temperature and oxygen measurements—R.G., V.B., M.S. and V.D.; writing—original draft A.F.; project administration—A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation, the grant No. 075-15-2020-787 for implementation of Major scientific projects on priority areas of scientific and technological development (the project «Fundamentals, methods and technologies for digital monitoring and forecasting of the environmental situation on the Baikal natural territory»).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author Fedotov A. mix@lin.irk.ru.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Papina T.S.—Institute for Water and Environmental Problems SB RAS (Barnaul, Russia) for help in the isotopic investigation and the crew of R/V “Vereshchagin” for fieldwork made on Lake Baikal.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Potemkina, T.G.; Potemkin, V.L. Actual inflow of riverine sediment load into Lake Baikal: Main tributaries—The Selenga, Upper Angara, and Barguzin Rivers (Russia). Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 1, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, R.R.; Shanks, W.C. Oxygen and hydrogen isotope systematics of Lake Baikal, Siberia: Implications for paleoclimate studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Verbolov, V.I. Water temperature and circulation. In Lake Baikal: Evolution and Biodiversity; Kozhova, O.M., Izmest’eva, L.R., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 26–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Granin, N.G.; Zhdanov, A.A. Deep ventilation of Lake Baikal waters due to spring thermal bars. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1993, 38, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Sizova, L.N.; Troitskaya, E.S. Heat balance of Lake Baikal and the relationship of its ice-thermal and water regime with global atmospheric circulation in the Northern Hemisphere during the modern period. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F.; Carmack, E.C.; Koropalov, V.M. Deep-water renewal and biological production in Lake Baikal. Nature 1991, 349, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, R.; Hofer, M.; Kipfer, R.; Peeters, F.; Imboden, D.M.; Baur, H.; Shimaraev, M.N. Distribution of helium and tritium in Lake Baikal. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 10, 12823–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bridgman, B.H.; Oliver, J.E. The Global Climate System: Patterns, Processes, and Teleconnections; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Aizen, E.M.; Aizen, V.B.; Melack, J.M.; Nakamura, T.; Ohta, T. Precipitation and atmospheric circulation patterns at mid-latitudes of Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaziy, G.I. (Ed.) Atlas of Lake Baikal; Roskartografiya: Moscow, Russia, 1993.
- Gibson, J.J.; Birks, S.J.; Yi, Y. Stable isotope mass balance of lakes: A contemporary perspective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 131, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, N.; Yoshida, N.; Inoue, G.; Chayanova, E.A. Modern isotope climatology of Russia: A first assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D03102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Tsujimura, M.; Oyunbaatar, D.; Davaa, G. Isotopic variation of precipitation over eastern Mongolia and its implication for the atmospheric water cycle. J. Hydrol. 2007, 333, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostrova, S.S.; Meyer, H.; Fernandoy, F.; Werner, M.; Tarasov, P.E. Moisture origin and stable isotope characteristics of precipitation in southeast Siberia. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, J.R.; Vennemann, T.W.; McKenzie, W.F. Effects of speciation on equilibrium fractionations and rates of oxygen isotope exchange between (PO4) aq and H2O. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2003, 67, 3135–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Blake, R.E. Oxygen isotope signature of Pi regeneration from organic compounds by phosphomonoesterases and photooxidation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3957–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Blake, R.E. Compound- and enzyme-specific phosphodiester hydrolysismechanisms revealed by δ18O of dissolved inorganic phosphate: Implications for marine P cycling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3782–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V.P., Zhai, A., Pirani, S.L., Connors, C., Péan, S., Berger, N., Caud, Y., Chen, L., Goldfarb, M.I., Gomis, M., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; in press.
- Sharma, S.; Richardson, D.C.; Woolway, R.I.; Imrit, M.A.; Bouffard, D.; Blagrave, K.; Daly, J.; Filazzola, A.; Granin, N.; Korhonen, J.; et al. Loss of ice cover, shifting phenology, and more extreme events in northern hemisphere lakes. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2021JG006348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.A. Coastal zone of the world’s great lakes as a target feld for interdisciplinary research and ecosystem monitoring: Lake Baikal (East Siberia). Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 1, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadeboncoeur, Y.; Moore, M.V.; Stewart, S.D.; Chandra, S.; Atkins, K.S.; Baron, J.S.; Bouma-Gregson, K.; Brothers, S.; Francoeur, S.N.; Genzoli, L.; et al. Blue waters, green bottoms: Benthic filamentous algal blooms are an emerging threat to clear lakes worldwide. BioScience 2021, 71, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency). Statistical treatment of data on environmental isotopes in precipitation. IAEA Tech. Rep. Ser. 1992, 331, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- De Batist, M.; Canals, M.; Sherstyankin, P.; Alekseev, S.; The INTAS Project 99-1669 Team. A New Bathymetric Map of Lake Baikal. 2002. Available online: https://dataservices.gfz-potsdam.de/SDDB/showshort.php?id=escidoc:76692 (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- IGCE Roshydromet. A Report on Climate Features on the Territory of Russian Federation in 2016; Frolov, A.V., Ed.; Roshydromet Press: Moscow, Russia, 2017. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Gonfiantini, R. Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Fritz, P., Fontes, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1986; Volume 3, pp. 113–168. [Google Scholar]
- Gat, J.R. Stable Isotopes of fresh and saline lakes. In Physics and Chemistry of Lakes; Lerman, A., Imboden, D., Gat, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 139–166. [Google Scholar]
- Falkner, K.K.; Church, M.; Measures, C.I.; Le Baron, G.; Thouron, D.; Jeandel, C.; Stordal, M.C.; Gill, G.A.; Mortlock, R.; Froelich, P.; et al. Minor and trace element chemistry of Lake Baikal, its tributaries and surrounding hot springs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luterbacher, J.; Dietrich, D.; Xoplaki, E.; Grosjean, M.; Wanner, H. European seasonal and annual temperature variability, trends and extremes since 1500. Science 2004, 303, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osborn, T.J.; Briffa, K.R. The spatial extent of 20th century warmth in the context of the past 1200 years. Science 2006, 311, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedotov, A.P.; Trunova, V.A.; Enushchenko, I.V.; Vorobyeva, S.S.; Stepanova, O.G.; Petrovskii, S.K.; Melgunov, M.S.; Zvereva, V.V.; Krapivina, S.M.; Zheleznyakova, T.O. A 850-year record climate and vegetation changes in East Siberia (Russia), inferred from geochemical and biological proxies of lake sediments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 7297–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, R.; Kipfer, R.; Peeters, F.; Piepke, G.; Imboden, D.M.; Shimaraev, M.N. Processes of deep-water renewal in Lake Baikal. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 841–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peeters, F.; Kipfer, R.; Hohmann, R.; Hofer, M.; Imboden, D.M.; Kodenev, G.G.; Khodzher, T. Modeling transport rates in Lake Baikal: Gas exchange and deep water renewal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2973–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Domysheva, V.M.; Gnatovskii, R.Y.; Blinov, V.V.; Sakirko, M.V. The influence of deep convection on aeration of the bottom zone in Baikal. Geogr. Nat. Resour. 2016, 37, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, L.P. Transfer of Moisture over the Territory of the USSR; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1978. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kracht, O.; Gresch, M.; Gujer, W. A stable isotope approach for the quantification of sewer infiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5839–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieroza, M.; Baker, A.; Bridgeman, J.; Boomer, I. Stable isotopic composition of raw and treated water. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers. Water Manag. 2014, 167, 414–429. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshkin, O.A.; Moore, M.V.; Kulikova, N.N.; Tomberg, I.V.; Malnik, V.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Troitskaya, E.S.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Sinyukovich, V.N.; Zaitseva, E.P.; et al. Groundwater contamination by sewage causes benthic algal outbreaks in the littoral zone of Lake Baikal (East Siberia). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilperoort, R.P.S.; Meijer, H.A.J.; Flamink, C.M.L.; Clemens, F.H.L.R. Changes in isotope ratios during domestic wastewater production. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bondt, K.; Seveno, F.; Petrucci, G.; Rodriguez, F.; Joannis, C.; Claeys, P. Potential and limits of stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to detectparasitic water in sewers of oceanic climate cities. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 18, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).