Analysis of the Triggering and Maintenance Mechanisms of a Record-Breaking Warm-Sector Extreme-Rainfall Process in Front of an Upper-Level Trough in Tianjin, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Introduction
3. Overview of the Rainfall Event
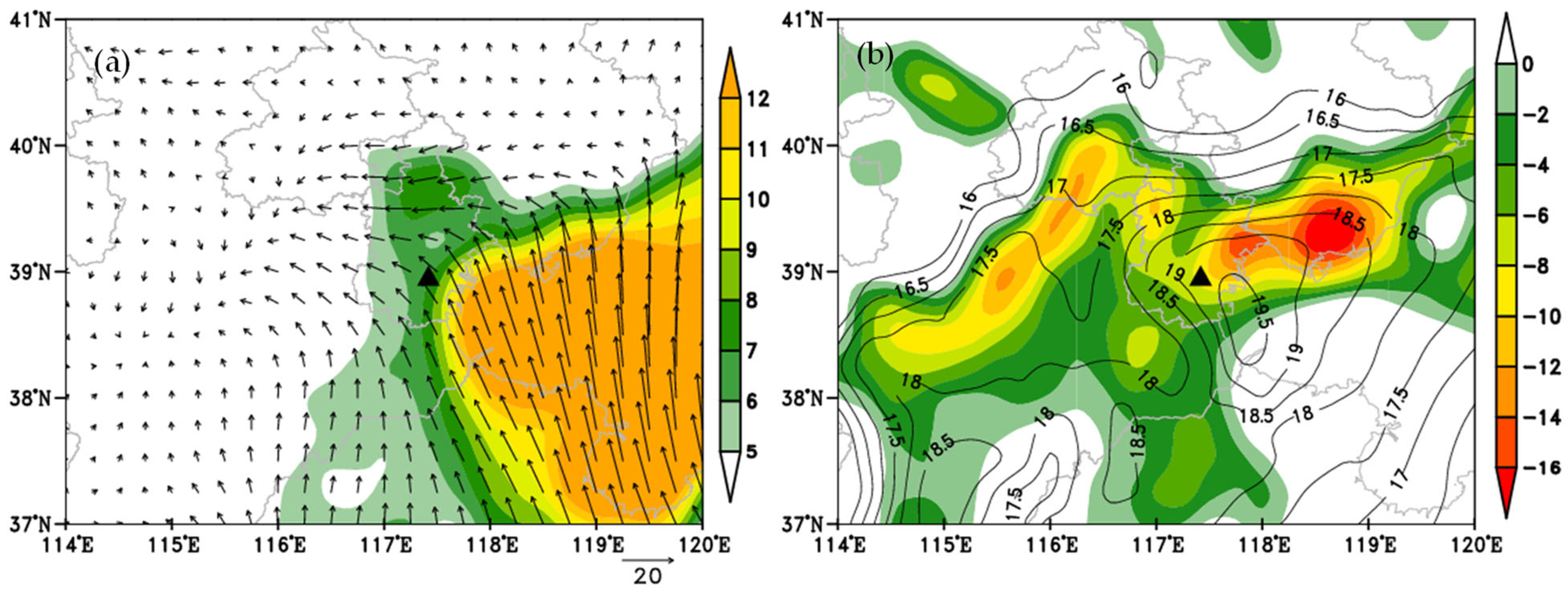
4. Analysis of Circulation Situation
5. Occurrence and Development of Mesoscale Convective Systems
5.1. Occurrence and Development of Local Heavy Rainfall Clusters
5.2. Evolution Characteristics of the Meso-γ-Scale Convective System
5.3. Development Mechanisms of the Convective System
5.4. Water Vapor Characteristics
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, X.; Ye, L.; Xin, Q.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, F.; Nerantzaki, S.D.; Papalexiou, S.M. Extreme Precipitation in China: A Review on Statistical Methods and Applications. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 163, 104144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Ingram, W. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.S.; He, N.; Wang, G.R.; Chen, M.X.; Liao, X.N.; Wang, H. Preliminary analysis on synoptic configuration evolvement and mechanism of a torrential rain occurring in Beijing on 21 July 2012. Torr. Rain Dis. 2012, 31, 218–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y. Impact of Interaction between Metropolitan Area and Shallow Lake on Daily Extreme Precipitation over Eastern China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, C. Characteristics of concurrent precipitation and wind speed extremes in China. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2021, 32, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doswell, C.A., III; Brooks, H.E.; Maddox, R.A. Flash Flood Forecasting: An Ingredients-Based Methodology. Weather Forecast. 1996, 11, 560–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.N.; Ni, Y.Q.; He, N.; Song, Q.Y. Analysis of the synoptic-scale dynamic process causing the extreme moisture environment in the “7.21” heavy rain case. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 71, 997–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, K.-M.; Zhou, Y.P.; Wu, H.-T. Have tropical cyclones been feeding more extreme rainfall? J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D23113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.Y. Heavy Rainfalls in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 1–225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.Y.; Zhao, S.X.; Zhou, X.P.; Ji, L.R.; Sun, S.Q.; Gao, S.T.; Zhang, Q.Y. The research progress of the synoptic meteorology and synoptic forecast. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 27, 451–467. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Q.H.; Ding, Z.; Wu, M.Y. Statistical analysis of typhoon heavy rainfall in North China. Meteorol. Mon. 2005, 31, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.H.; Qi, L.L.; Zhao, S.X. A study on mesoscale convective systems of the severe heavy rainfall in North China by “9608” typhoon. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2006, 64, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Sun, J.S.; He, N.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, J. A study on the mechanism for the vortex system evolution and development during the torrential rain event in North China on 20 July 2016. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2017, 75, 685–699. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.X.; Sun, J.H.; Lu, R.; Fu, S. Analysis of the 20 July 2016 unusual heavy rainfall in North China and Beijing. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.L.; Lin, Y.H.; Zhao, P.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Kang, H.; Ding, Y. The Beijing extreme rainfall of 21 July 2012: “Right results” but for wrong reasons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1426–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, D.L. Initiation and organizational modes of an extreme-rain-producing mesoscale convective system along a Mei-Yu front in East China. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Wu, M.W.; Ren, F.M.; Li, J.; Wong, W.K. Synoptic situations of extreme hourly precipitation over China. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 8703–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Hu, S.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Ye, L.; Li, H.; Xia, F.; Gao, L. Multiscale Perspectives on an Extreme Warm-Sector Rainfall Event over Coastal South China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Liu, X.; Pu, Y.; Li, H.; Xia, F.; Xu, B. Contrasts in the Evolution and Microphysical Features of Two Convective Systems during a Heavy Rainfall Event along the Coast of South China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. Heavy Rain in South China during Pre-Flood Season; Guangdong Science and Technology Press: Guangzhou, China, 1986; pp. 94–95. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.F.; Chen, T.; Kong, Q. A review of studies on prefrontal torrential rain in South China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2016, 27, 559–569. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xue, J.S.; Yan, H. The impact of physics parameterization schemes on mesoscale heavy rainfall simulation. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2003, 6, 203–218. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.D.; Zhao, S.X.; Sun, J.H. A study of circumstances of meso-β-scale systems of strong heavy rainfall in warm sector ahead of fronts in South China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 988–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Li, Z.C.; Xiao, Z.N. Comparison analysis of South China front and warm-area heavy rain systems in June 2006. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2008, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.X.; Sun, J.H.; Fu, S.M. Comparison of Synoptic Circulation Characteristics in Different Types of Warm-Sector Heavy Rainfall Events over South China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2021, 26, 359–373. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Bian, S.F.; Yu, X.D.; Cui, Y.Y. Comparative analysis of CINRAD SA doppler radar product in three local torrential rains in the West of Beijing. Meteorol. Mon. 2009, 35, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Lv, W.Q.; Yu, C.; Li, S.Q.; Yang, S.N.; Zhu, W.J.; Gong, Y. Analysis of a forecast failure case of warm sector torrential rainfall in North China. Meteorol. Mon. 2018, 44, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, L.Y.; Li, S.Q.; Xu, J. A review of the warm-sector rainstorms in China. Torr. Rain Dis. 2019, 38, 483–493. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.Z.; Lv, J.J.; Xu, C.Y. Fluctuation characteristics of Tianjin rainstorm in late July 2012. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 37, 613–622. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, B.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, H.W.; Wang, X.Y. The spatial and temporal distributions of warm sector rainfall and frontal rainfall for the torrential rain event in Beijing on 21 July 2012. Torr. Rain Dis. 2017, 36, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Xing, N.; Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Zhai, L.; Jing, H.; Guo, J. A study on the warm-sector torrential rainfall during 15–16 July 2018 in Beijing area. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2020, 78, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Mechanisms for the isolated convections triggered by the sea breeze front and the urban heat Island. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2021, 133, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X. Mesoscale Observational Analysis of Isolated Convection Associated with the Interaction of the Sea Breeze Front and the Gust Front in the Context of the Urban Heat Humid Island Effect. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, S.N.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Discussion on the formation of a warm sector torrential rain case in North China. Meteorol. Mon. 2014, 40, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; He, Q.Y.; Liu, B.X.; Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Y.W. Analysis on the mesoscale characteristics of a local rainstorm event under a typical circulation situation in Tianjin. Torr. Rain Dis. 2018, 37, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.H.; Chen, H.; He, Q.Y.; Lin, X.M.; Zhang, H. Influence of easterly winds from west coast of Bohai sea on local heavy rainfall in Tianjin. Meteorol. Mon. 2019, 45, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; YI, X.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Xu, M. The Thermal and Dynamic Environmental Field Analysis of a Meso-γ Scale Short-Time Rainstorm in Tianjin. Meteorol. Mon. 2021, 47, 398–411. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.Y.; Wei, J. The westward, northward advance of the subtropical high over the West Pacific in Summer. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2006, 17, 513–525. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Thépaut, J.N. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyi, D.N.; He, L.F.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, S. Fine observation characteristics and thermodynamic mechanisms of extreme heavy rainfall in Henan on 20 July 2021. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2022, 33, 1–15. [Google Scholar]














Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, N.; Lin, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of the Triggering and Maintenance Mechanisms of a Record-Breaking Warm-Sector Extreme-Rainfall Process in Front of an Upper-Level Trough in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050808
Chen H, Wang Y, Wei Y, Zhang N, Lin X, Yang Y, Zhang Y. Analysis of the Triggering and Maintenance Mechanisms of a Record-Breaking Warm-Sector Extreme-Rainfall Process in Front of an Upper-Level Trough in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(5):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050808
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Hong, Yanchun Wang, Yinghua Wei, Nan Zhang, Xiaomeng Lin, Yang Yang, and Yuqing Zhang. 2023. "Analysis of the Triggering and Maintenance Mechanisms of a Record-Breaking Warm-Sector Extreme-Rainfall Process in Front of an Upper-Level Trough in Tianjin, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 5: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050808
APA StyleChen, H., Wang, Y., Wei, Y., Zhang, N., Lin, X., Yang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Analysis of the Triggering and Maintenance Mechanisms of a Record-Breaking Warm-Sector Extreme-Rainfall Process in Front of an Upper-Level Trough in Tianjin, China. Atmosphere, 14(5), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14050808





