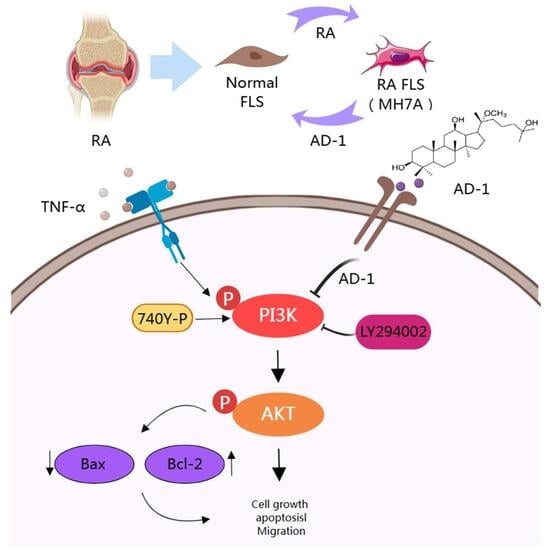
Ginsenoside Derivative AD-1 Suppresses Pathogenic Phenotypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Modulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
Abstract
Highlights
- Network pharmacology identified that the key pathway for AD-1 in treating RA is PI3K/AKT.
- AD-1 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion and promotes apoptosis of MH7A cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
- AD-1 is a potential drug for treating RA, providing experimental evidence for the application of traditional Chinese medicine in the clinical treatment of RA.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Potential Targets of AD-1
2.3. Identification of RA-Related Gene Targets
2.4. Target Prediction of AD-1 Against RA
2.5. Network Analysis of Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI)
2.6. Molecular Docking Verification
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.8. Chemicals
2.9. Cell Culture
2.10. Cell Viability Assay
2.11. 5-Ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) Incorporation Assay
2.12. Colony Formation Assay
2.13. Migration and Invasion Assay
2.14. Apoptosis Assay
2.15. RABC Database Analysis
2.16. Western Blot
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. PPI Network Analysis and Screening of Potential Targets of AD-1 Against RA
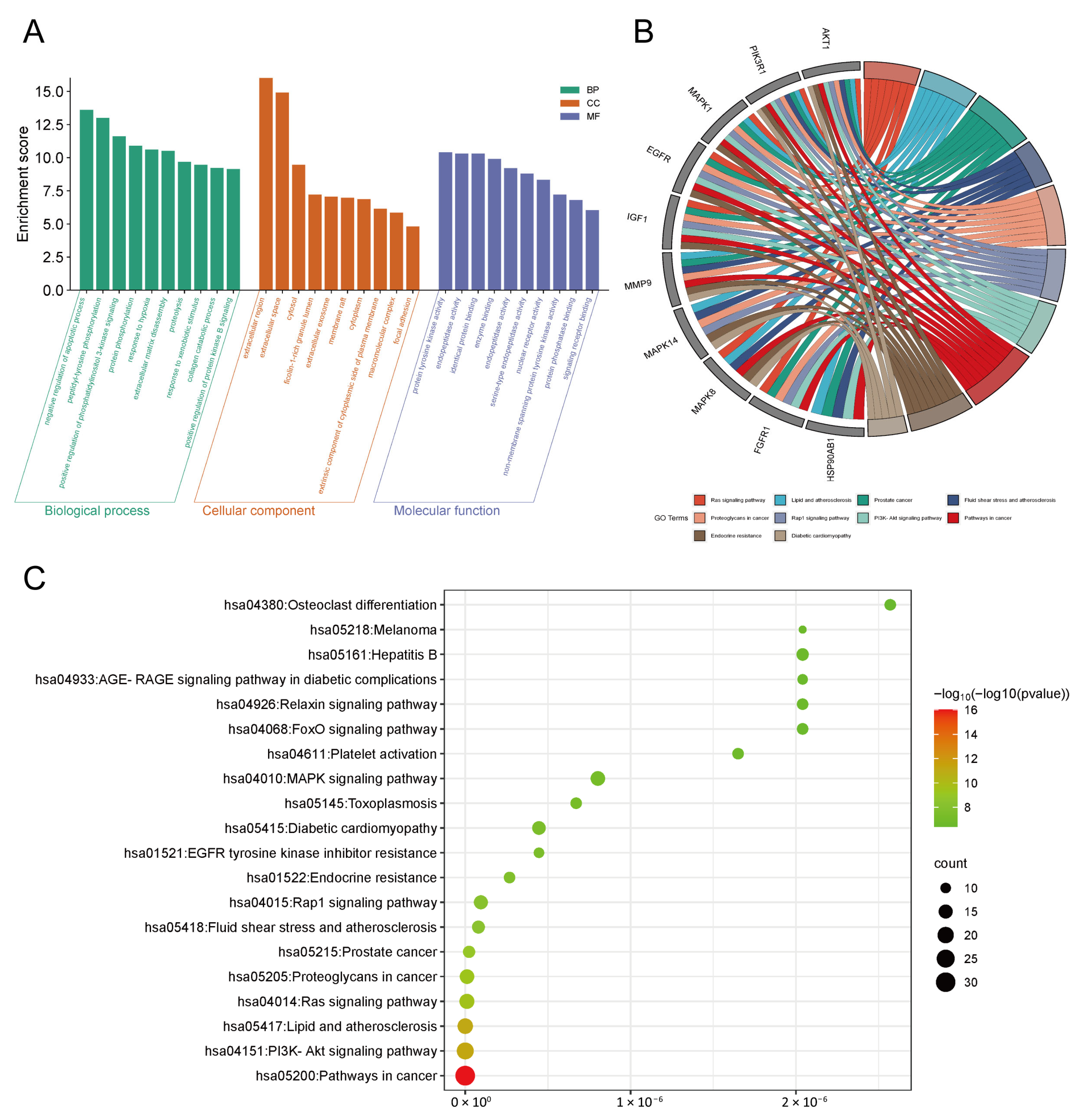
3.2. GO and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
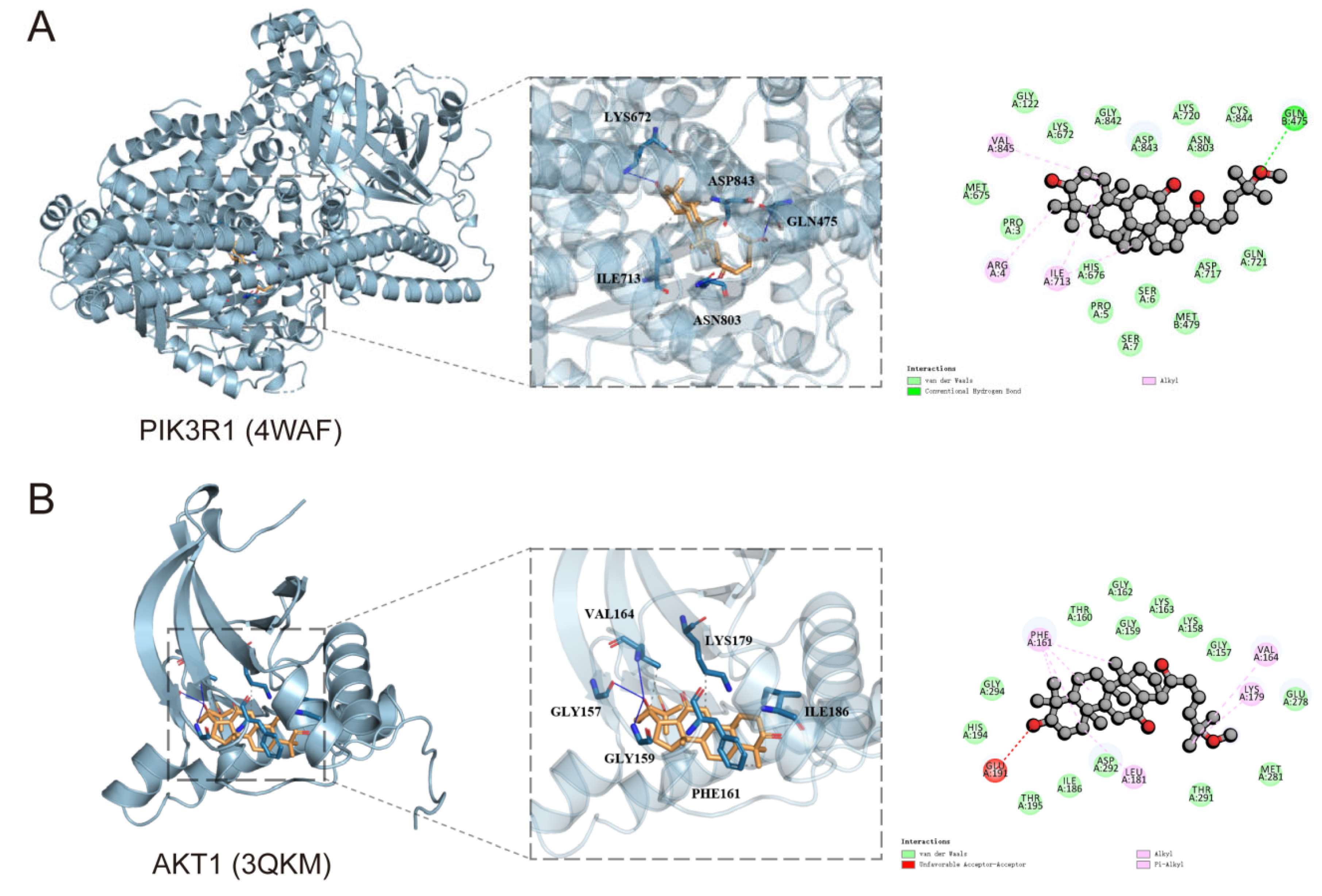
3.3. Molecular Docking Simulation Techniques
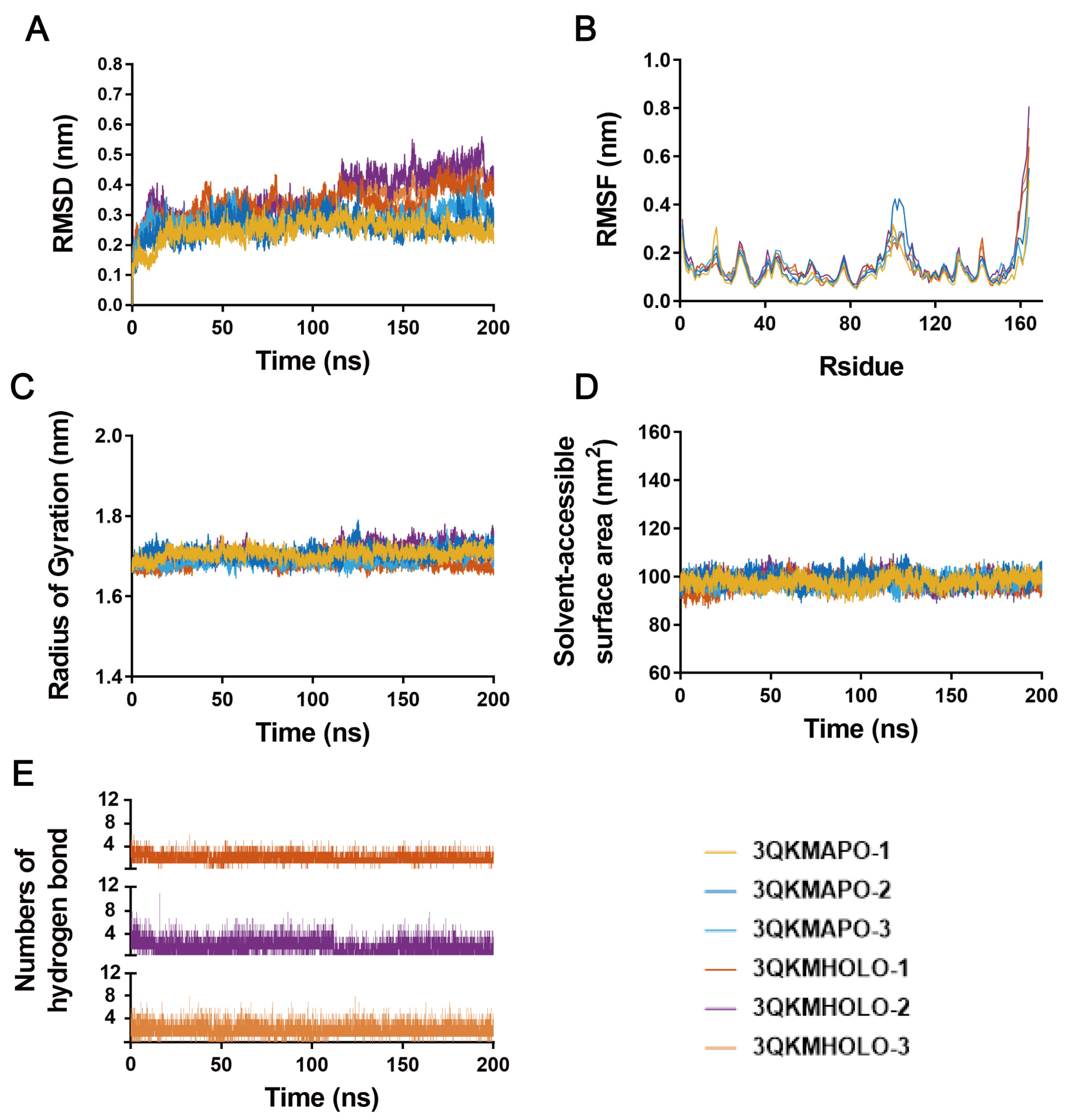
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
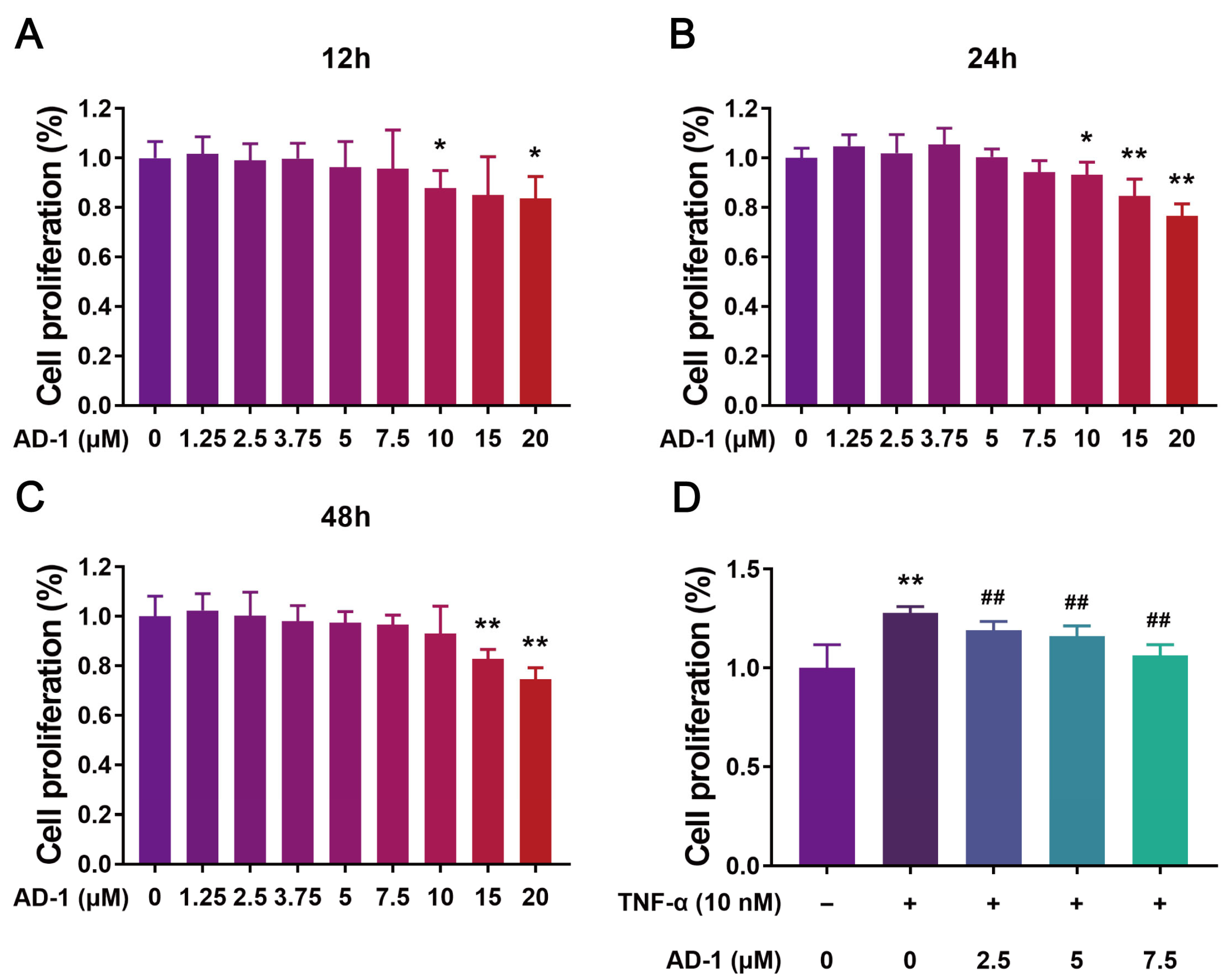
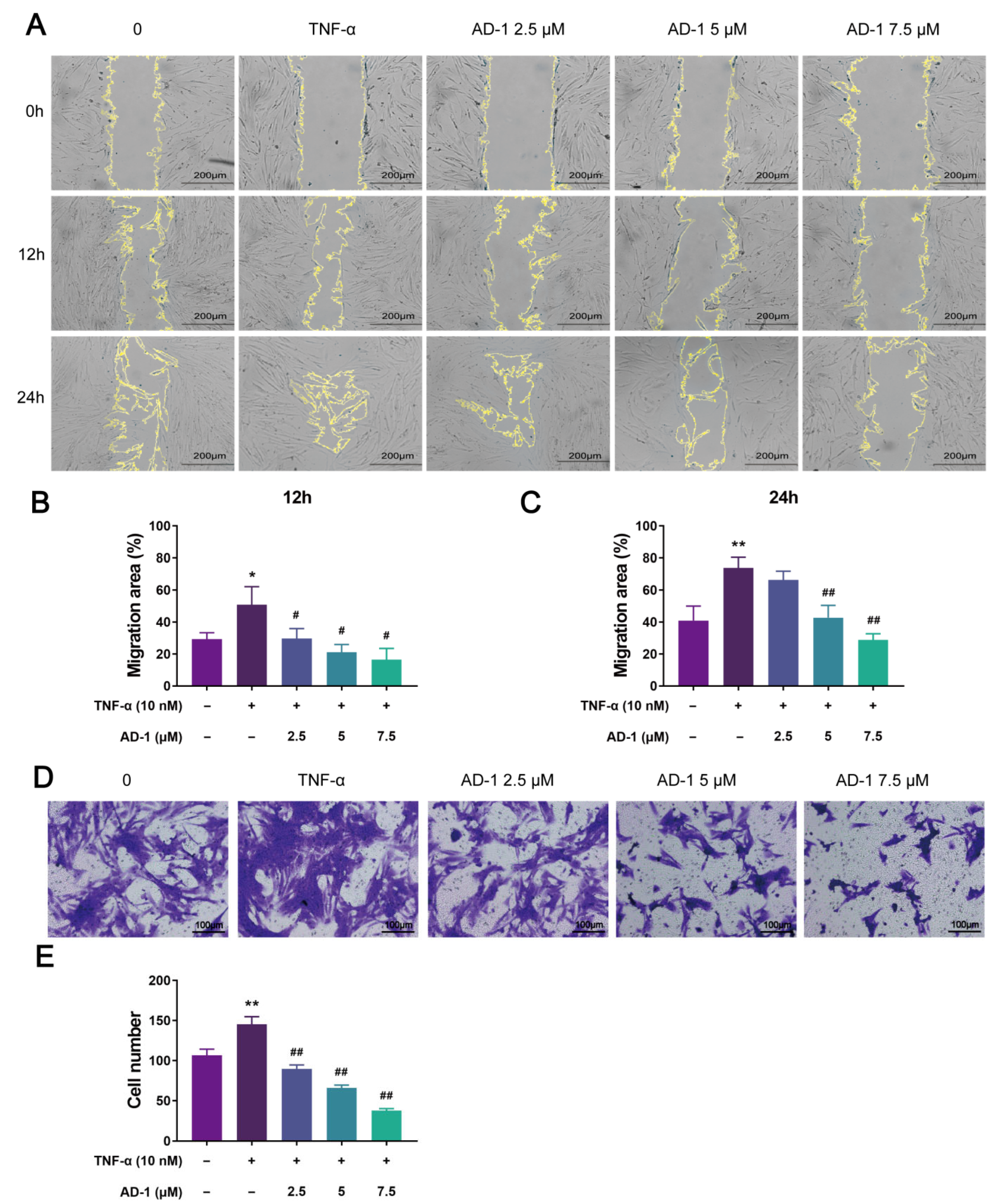
3.5. AD-1 Inhibits Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of MH7A Cells
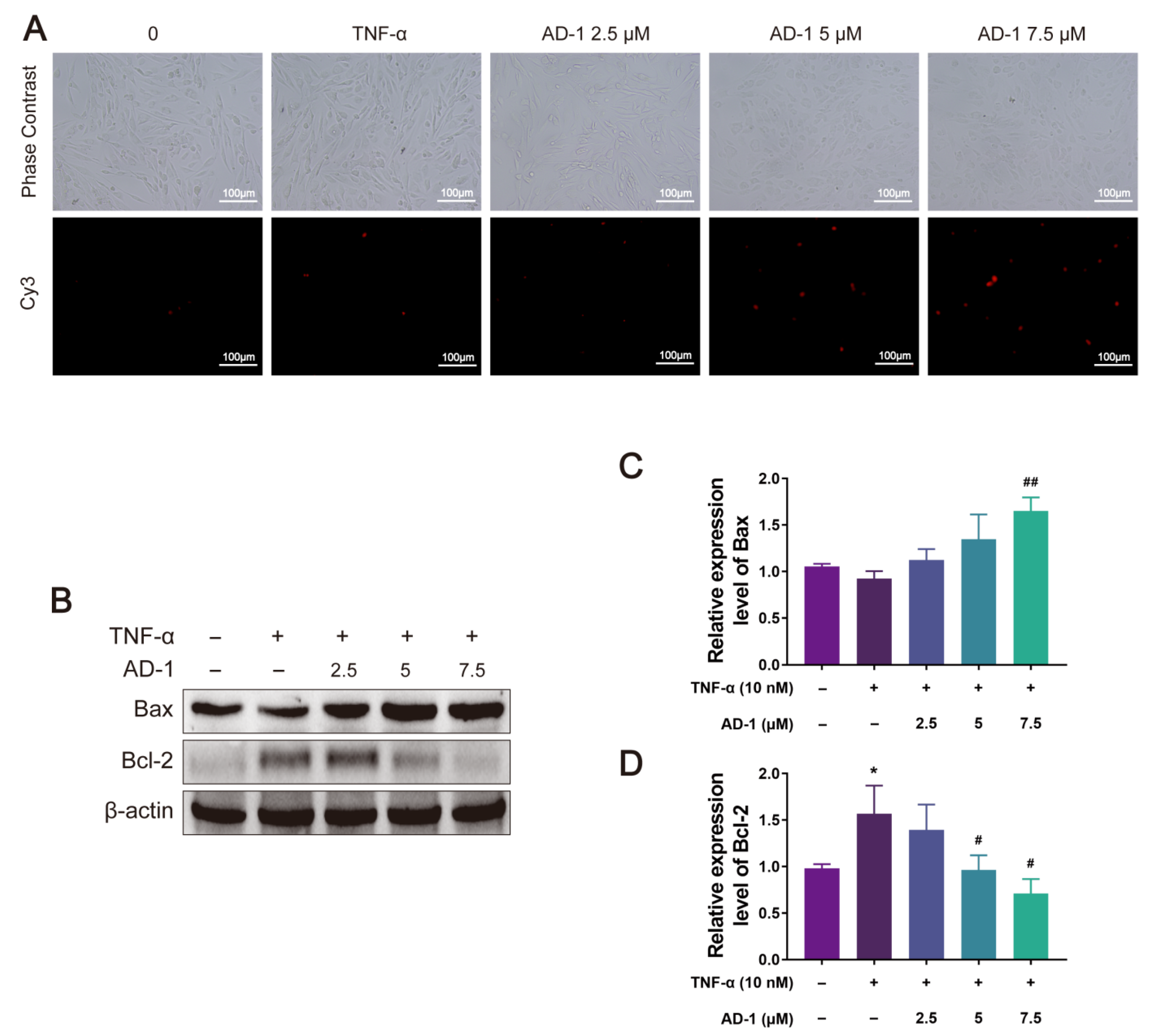
3.6. AD-1 Induced Apoptosis of MH7A Cells
3.7. AD-1 Inhibits the Activation of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in MH7A Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Matteo, A.; Bathon, J.M.; Emery, P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2023, 402, 2019–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, S.A.; Sepriano, A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; van der Heijde, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Verschueren, P.; de Souza, S.; Pope, J.E.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. Efficacy, duration of use and safety of glucocorticoids: A systematic literature review informing the 2022 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Kuroda, T.; Kobayashi, D. Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bergstra, S.A.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Sepriano, A.; Aletaha, D.; Caporali, R.; Edwards, C.J.; Hyrich, K.L.; Pope, J.E.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, H.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Deng, C.J.; Xin, P. Recent advances on signaling pathways and their inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 230, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvano, F.; La Fauci, L.; Lazzarino, G.; Fogliano, V.; Ritieni, A.; Ciappellano, S.; Battistini, N.C.; Tavazzi, B.; Galvano, G. Cyanidins: Metabolism and biological properties. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarpita, S.; Ganesan, R.; Rasool, M. Cyanidin prevents the hyperproliferative potential of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and disease progression via targeting IL-17A cytokine signalling in rheumatoid arthritis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 391, 114917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, F.M.; Dai, Y.; Deng, Y.X.; Shi, K.Y.; Zhu, Z.H.; Liu, X.K.; Ma, X.; Gao, Y.X. Bioinformatics identification based on causal association inference using multi-omics reveals the underlying mechanism of Gui-Zhi-Shao-Yao-Zhi-Mu decoction in modulating rheumatoid arthritis. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Xu, X.Y.; Zhang, H.X.; Hu, Y.Z.; Deng, C.J.; Sun, S.Q.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.G.; Ma, H.X.; Li, X.L. Mechanism investigation of Duhuo Jisheng pill against rheumatoid arthritis based on a strategy for the integration of network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vivo experimental verification. Pharm. Biol. 2023, 61, 1431–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.M.; Song, Y.J.; Hang, M.H.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.Y.; Chen, T.; Xia, M.X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; et al. Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction suppresses inflammation and bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis mice. Chin. Herb. Med. 2024, 16, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, A.; Bungau, S.G. Management of rheumatoid arthritis: An overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Feng, J.; Yang, N.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Qin, Q. Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates angiotensin II-induced myocardial hypertrophy through repressing NLRP3 inflammasome and oxidative stress via modulating SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 98, 107841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.G.; Yang, H.X.; Zhu, C.H.; Deng, J.J.; Fan, D.D. Hypoglycemic effect of ginsenoside Rg5 mediated partly by modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis in diabetic db/db mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.S.; Xie, X.; Yang, Y.Y.; Li, F. Ginsenoside compound K- a potential drug for rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 166, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Song, S.; Yang, X.M.; Jin, G. Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates complete Freund's adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in mice by regulating CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ Treg cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4893–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. In vitro anti-cancer activity and structure-activity relationships of natural products isolated from fruits of Panax ginseng. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Han, L.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hill, D.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R. Isolation, structural determination, and evaluation of the biological activity of 20(S)-25-methoxyl-dammarane-3beta, 12beta, 20-triol [20(S)-25-OCH3-PPD], a novel natural product from Panax notoginseng. Med. Chem. 2007, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.M.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.F.; Piao, H.R.; Zhao, Y.Q. Novel dammarane-type sapogenins from Panax ginseng berry and their biological activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Lu, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y. Determination of 25-OCH3-PPD and the related substances by UPLC-MS/MS and their cytotoxic activity. J. Chromatogr. B. 2016, 1022, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Su, G. Antifibrotic effect of AD-1 on lipopolysaccharide-mediated fibroblast injury in L929 cells and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7650–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Li, F.F.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Jin, D. Integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the effect and mechanism of AD-1 in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1159712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Jia, Y.L.; Lin, X.X.; Zhang, H.Q.; Dong, X.W.; Zhao, J.M.; Shen, J.; Shen, H.J.; Li, F.F.; Yan, X.F.; et al. AD-1, a novel ginsenoside derivative, shows anti-lung cancer activity via activation of p38 MAPK pathway and generation of reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4148–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Y.H.; Wang, S.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Liu, X.F.; Lai, L.H.; Pei, J.F.; Li, H.L. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2017, 45, W356–W360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, K.S.; Shaikh, M.A.J.; Almalki, W.H.; Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Alzarea, S.I.; Imam, S.S.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Singh, S.K.; et al. PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways inhibitors with potential prospects in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Environ. Pathol. Tox. 2022, 41, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhan, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V.; Prilusky, J.; Lancet, D. GeneCards: Integrating information about genes, proteins and diseases. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.L.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W.Z. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, D.C.; Luo, H.T.; Huo, P.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, S.; He, Z.H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Liu, J.J.; Guo, J.C.; et al. KOBAS-i: Intelligent prioritization and exploratory visualization of biological functions for gene enrichment analysis. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2021, 49, W317–W325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.Q.; Song, L.J.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Xie, N.; Yuan, X.M.; Wei, Z.F.; et al. Andrographolide sulfonate alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting glycolysis-mediated activation of PI3K/AKT to restrain Th17 cell differentiation. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2025, 23, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagui, C.; Darden, T.A. Molecular dynamics simulations of biomolecules: Long-range electrostatic effects. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1999, 28, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kr Utler, V.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; Hünenberger, P.H. A fast SHAKE algorithm to solve distance constraint equations for small molecules in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Y. Crystallization-induced dynamic resolution R-epimer from 25-OCH3-PPD epimeric mixture. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1005, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y. New perspective on the metabolism of AD-1 in vivo: Characterization of a series of dammarane-type derivatives with novel metabolic sites and anticancer mechanisms of active oleanane-type metabolites. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 88, 102961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.Z.; Lee, Y.H.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Na, H.K.; Kim, K.O.; Baek, J.H.; Surh, Y.J. ARD1 stabilizes NRF2 through direct interaction and promotes colon cancer progression. Life Sci. 2023, 313, 121217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.W.; Lindstrom, W.; Olson, A.J.; Belew, R.K. Analysis of HIV wild-type and mutant structures via in silico docking against diverse ligand libraries. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 1258–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swargiary, A.; Roy, M.K.; Mahmud, S. Phenolic compounds as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: A docking and molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 41, 3862–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, M.; Miroliaei, M.; Ghanadian, M.; Szumny, A.; Rahimmalek, M. Exploring the inhibitory properties of biflavonoids on alpha-glucosidase; computational and experimental approaches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, Z.; Pan, F.; Jia, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, O.; Wang, C. Construction of an MLR-QSAR Model Based on Dietary Flavonoids and Screening of Natural alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors. Foods 2022, 11, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Kan, R.; Ji, H.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W.; Shuian, D.; Liu, J.; Li, J. Identification of tuna protein-derived peptides as potent SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors via molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.; Nawaz, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, W.; Jiao, Z.; Zhang, Q. Exploring synergistic inhibitory mechanisms of flavonoid mixtures on alpha-glucosidase by experimental analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Pratt, A.G.; Hyrich, K.L. Therapeutic advances in rheumatoid arthritis. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2024, 384, e70856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Ni, T.Y.; Miao, J.R.; Huang, X.Y.; Feng, Z. The role and mechanism of triptolide, a potential new DMARD, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2025, 104, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.M.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.X.; Gong, Z.H.; Du, Y.Y.; Xu, R.T.; Gao, L.; Xu, Q.; Li, N. Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu decoction alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting inflammation by targeting SLPI. Phytomedicine 2025, 139, 156471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, M.; Ma, K.; Pang, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhou, R.; Tang, Z. Anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects of total saponins from Rhizoma Panacis Majoris on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats and rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Phytomedicine 2023, 119, 155021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Tripathi, S.; Tripathi, P.K. Antioxidant and antiarthritic potential of berberine: In vitro and in vivo studies. Chin. Herb. Med. 2023, 15, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Si, M.; Wu, H.; Yan, C.; Wei, W. Ginsenoside metabolite compound K exerts joint-protective effect by interfering with synoviocyte function mediated by TNF-alpha and Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 771, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.S. Ameliorative effects of ginseng and ginsenosides on rheumatic diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. Gender-related differences in pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and excretion of 20(R)-25-methoxyl-dammarane-3beta,12beta,20-triol and its metabolite in rats and anti-ovarian cancer evaluation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 158, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, G.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, X.S.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Y.Q. Antitumor activity of ginseng sapogenins, 25-OH-PPD and 25-OCH3-PPD, on gastric cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, T.T.; McInnes, I.B. Future therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis? Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H.H.H.W. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Sarkar, A.; Maulik, U. Molecular docking study of potential phytochemicals and their effects on the complex of SARS-CoV2 spike protein and human ACE2. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommel, C.; Camps, M.; Ji, H. PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ: Partners in crime in inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and beyond? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Peng, W.; Wei, S.J.; Wei, D.N.; Li, R.L.; Liu, J.; Peng, L.Y.; Yang, S.; Gao, Y.X.; Wu, C.J.; et al. Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu decoction possesses anti-arthritic effects on type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats via suppression of inflammatory reactions, inhibition of invasion & migration and induction of apoptosis in synovial fibroblasts. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Sur, B.J.; Yeom, M.; Lee, B.; Kim, K.S.; Rodriguez, J.P.; Lee, S.; Kang, K.S.; Huh, C.K.; Lee, S.C.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic effects of the ethanolic extract of Aralia continentalis Kitag. in IL-1β-stimulated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and rodent models of polyarthritis and nociception. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, G.; Firestein, G.S. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, J. SUMOylation links metabolic and aggressive phenotype of RA FLS. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, A.W.; Tron, A.E. Recent advances in the development of Mcl-1 inhibitors for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 198, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkenhaug, K. Signaling by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase family in immune cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 675–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruicci, K.M.; Plantinga, P.; Pinto, N.; Khan, M.I.; Stecho, W.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Yoo, J.; Fung, K.; MacNeil, D.; Mymryk, J.S.; et al. Disruption of the RICTOR/mTORC2 complex enhances the response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to PI3K inhibition. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2160–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Tian, F.; Guo, J.L.; Li, X.K.; Ma, L.; Jiang, M.M.; Zhao, J. Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1243820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, B.; King, S.; Suphioglu, C. The Importance of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martinez, M.; Cabail, M.Z. The PI3K/Akt pathway in meta-inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Jin, H.Z.; Jia, W.Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.R.; Xue, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, H.Q. Ermiao San attenuating rheumatoid arthritis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling activate HIF-1α induced glycolysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 345, 119615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Liu, J. The dual anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects of Jianpi Huashi Tongluo prescription on rheumatoid arthritis through inhibiting the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1541314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.Y.; Zhu, M.L.; Li, M.; Cai, J.H.; Rose, P.; Mao, J.C.; Zhu, Y.Z. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene Symbol | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALB | GSTP1 | PIK3CG | HSPA8 | REN | CYP2C9 | MTHFD1 | PIK3R1 | LGALS3 |
| MAPK1 | ADAM17 | ESR1 | PDE4D | FGF1 | JAK3 | VDR | TEK | TGFB2 |
| BMP2 | MAPK8 | SRC | DPP4 | ELANE | NR3C1 | ZAP70 | S100A9 | CTSB |
| AKR1B1 | MMP13 | CDK2 | GSR | HMGCR | MMP2 | DHFR | CTSG | MMP9 |
| TTR | AR | KDR | PLA2G10 | PGF | CTSK | PRKCQ | JAK2 | GSTM1 |
| GC | PPARG | TYMS | SYK | PLA2G2A | PPARA | HSP90AB1 | XIAP | HGF |
| CYP19A1 | MMP3 | DHODH | FGFR1 | PARP1 | IL2 | ACE | CBS | BCL2L1 |
| ITGAL | EGFR | NOS3 | RBP4 | CDK6 | SERPINA1 | CAT | KIT | BTK |
| F2 | MAPK14 | ANXA5 | ESRRA | MMP12 | IGF1 | BPI | HMOX1 | AKT1 |
| CASP3 | WAS | LCK | MMP8 | SOD2 | PADI4 | PPP1CC | CASP1 | |
| Number | Gene Symbol | Uniprot ID | Gene Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SRC | P12931 | Src Proto-Oncogene, Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| 2 | MMP9 | P14780 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 9 |
| 3 | ELANE | P08246 | Elastase, Neutrophil Expressed |
| 4 | SERPINA1 | P01009 | Serpin Family A Member 1 |
| 5 | MAPK8 | P45983 | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 8 |
| 6 | AKT1 | P31749 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 |
| 7 | PIK3R1 | P27986 | Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase Regulatory Subunit 1 |
| 8 | ALB | P02768 | Albumin |
| 9 | KDR | P35986 | Kinase Insert Domain Receptor |
| 10 | GSTP1 | P09211 | Glutathione S-Transferase Pi 1 |
| Targets | PDB | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| PIK3R1 | 4WAF | −8.1 kcal/mol |
| AKT1 | 3QKM | −8.4 kcal/mol |
| Targets (PDB) | PIK3R1 (4WAF) | AKT1 (3QKM) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOLO-1 | HOLO-2 | HOLO-3 | HOLO-1 | HOLO-2 | HOLO-3 | |
| EVDW | −51.97 ± 2.01 | −51.35 ± 4.66 | −53.03 ± 2.23 | −50.25 ± 3.67 | −41.35 ± 6.26 | −45.30 ± 4.10 |
| EELE | −26.40 ± 9.35 | −25.03 ± 4.40 | −18.57 ± 5.79 | −16.69 ± 8.46 | −18.37 ± 6.83 | −17.50 ± 7.20 |
| EGB | 46.48 ± 5.22 | 46.77 ± 5.90 | 44.99 ± 3.55 | 38.46 ± 8.18 | 36.14 ± 5.54 | 37.30 ± 6.00 |
| ESA | −6.72 ± 0.34 | −6.79 ± 0.60 | −6.26 ± 0.46 | −6.73 ± 0.60 | −5.05 ± 0.87 | −5.90 ± 0.75 |
| Bind energy | −38.60 ± 5.56 | −36.39 ± 3.14 | −32.87 ± 4.43 | −35.22 ± 3.20 | −28.63 ± 7.41 | −31.40 ± 4.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Li, F.; Cui, B.; Zhou, Z.; Fang, X.; Huang, S.; Quan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, D. Ginsenoside Derivative AD-1 Suppresses Pathogenic Phenotypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Modulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cells 2025, 14, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201625
Fu Y, Li F, Cui B, Zhou Z, Fang X, Huang S, Quan X, Zhao Y, Jin D. Ginsenoside Derivative AD-1 Suppresses Pathogenic Phenotypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Modulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cells. 2025; 14(20):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201625
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yuan, Fangfang Li, Biao Cui, Zhongyu Zhou, Xizhu Fang, Shengnan Huang, Xingguo Quan, Yuqing Zhao, and Dan Jin. 2025. "Ginsenoside Derivative AD-1 Suppresses Pathogenic Phenotypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Modulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway" Cells 14, no. 20: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201625
APA StyleFu, Y., Li, F., Cui, B., Zhou, Z., Fang, X., Huang, S., Quan, X., Zhao, Y., & Jin, D. (2025). Ginsenoside Derivative AD-1 Suppresses Pathogenic Phenotypes of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Modulating the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Cells, 14(20), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201625