CD45 and CD148 Are Critically Involved in Neutrophil Recruitment and Function During Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
2.2. Serum Transfer, Measurement of Ankle Thickness, and Arthritis Scoring
2.3. Chimeric Mice
2.4. Tissue Processing of K/BxN Serum-Induced Mice
2.5. Spectral Flow Cytometry
2.6. Immunohistochemical Staining and Histopathological Scoring
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining and Fluorescence Analysis
2.8. Cytokine Analyses from Synovial Fluid
2.9. Intravital Microscopy
2.10. Soluble ICAM-1- and Fibrinogen-Binding Assay
2.11. Surface Marker Expression upon Stimulation
2.12. Preparation of Plate-Bound Immune Complexes (ICs)
2.13. ROS Production
2.14. LTB4 and IL-1ß Release in Vitro
2.15. Western Blotting
2.16. Statistics
3. Results
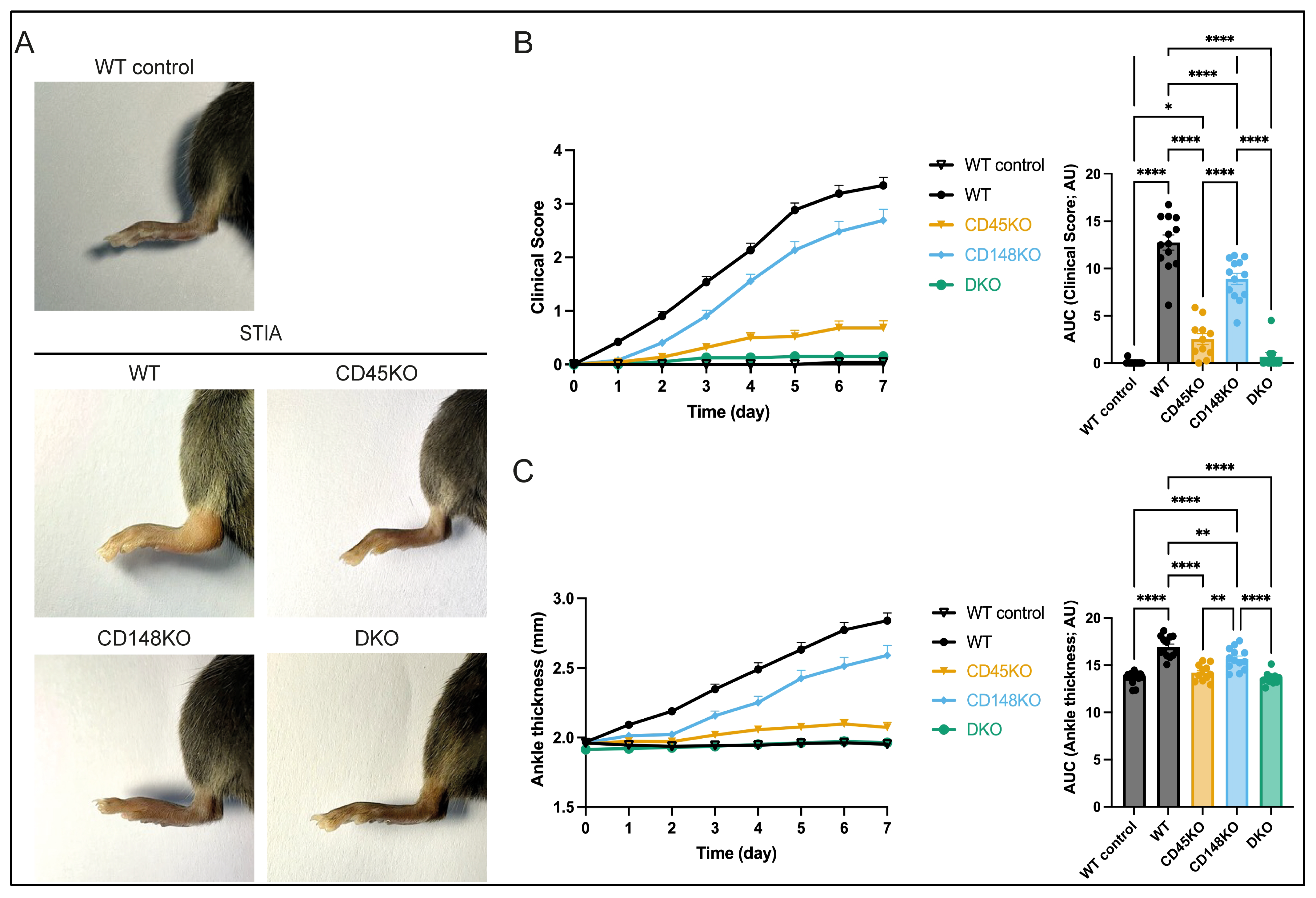
3.1. CD45 and CD148 Are Required for Onset and Progression of Serum Transfer-Induced Arthritis
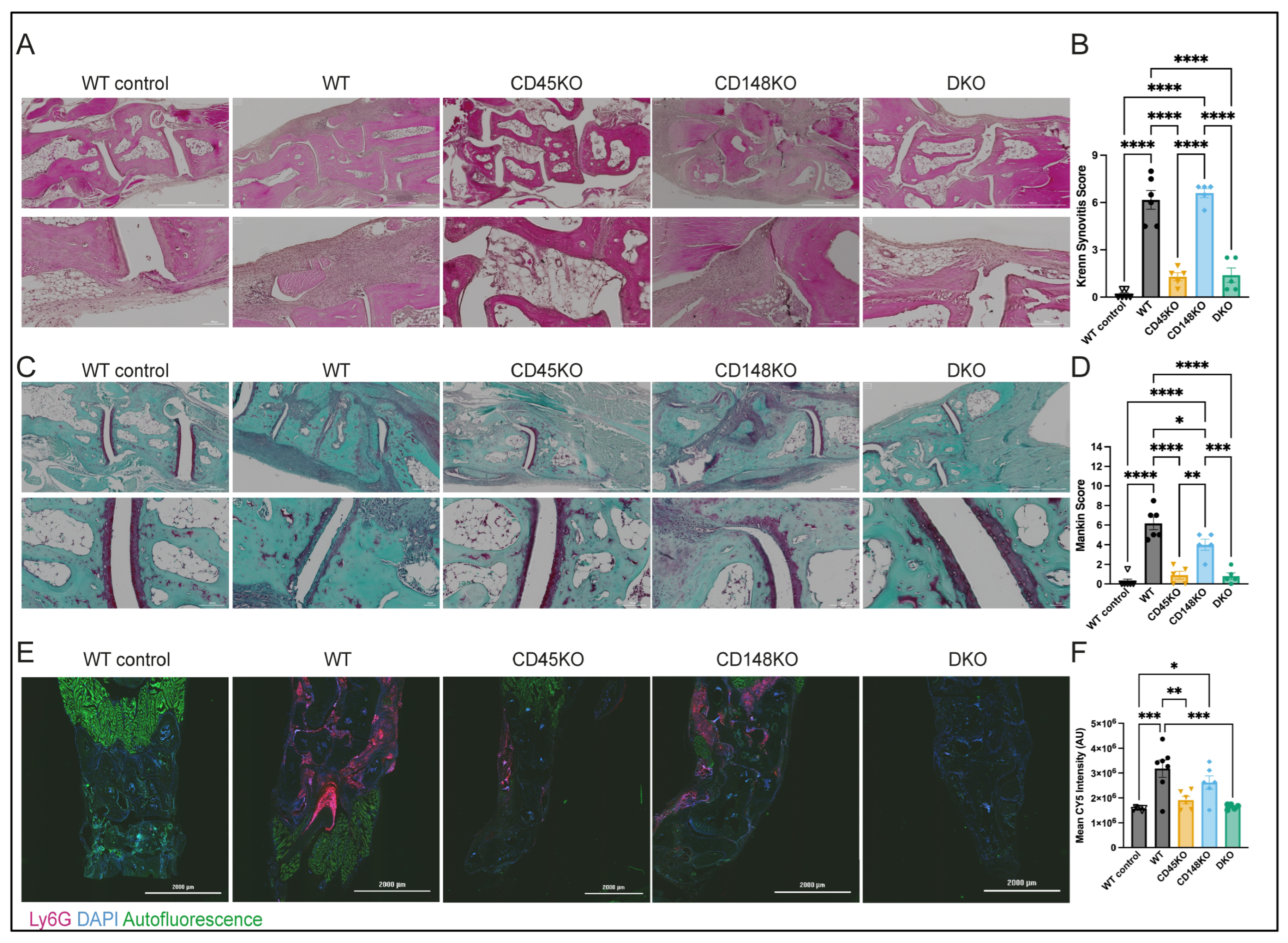
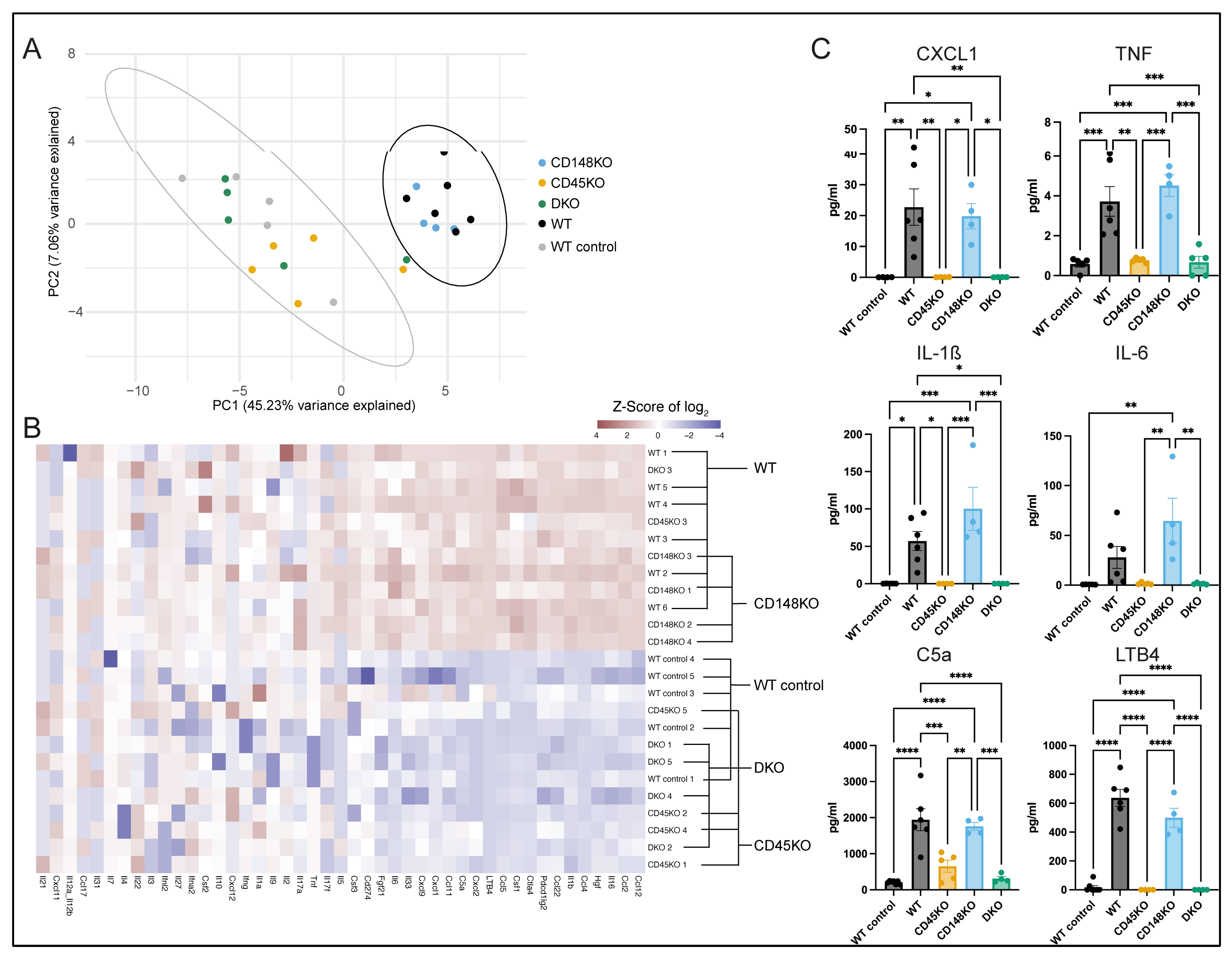
3.2. Presence of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Synovial Fluid During STIA Is Dependent on CD45
3.3. Synovial Fluid of WT and CD148KO Mice Contains High Amounts of Neutrophils with an Activated Proinflammatory Phenotype
3.4. CD45 Deficiency Results in Impaired Neutrophil Recruitment, Differential β2-Integrin Activation, and Affectation of Effector Functions
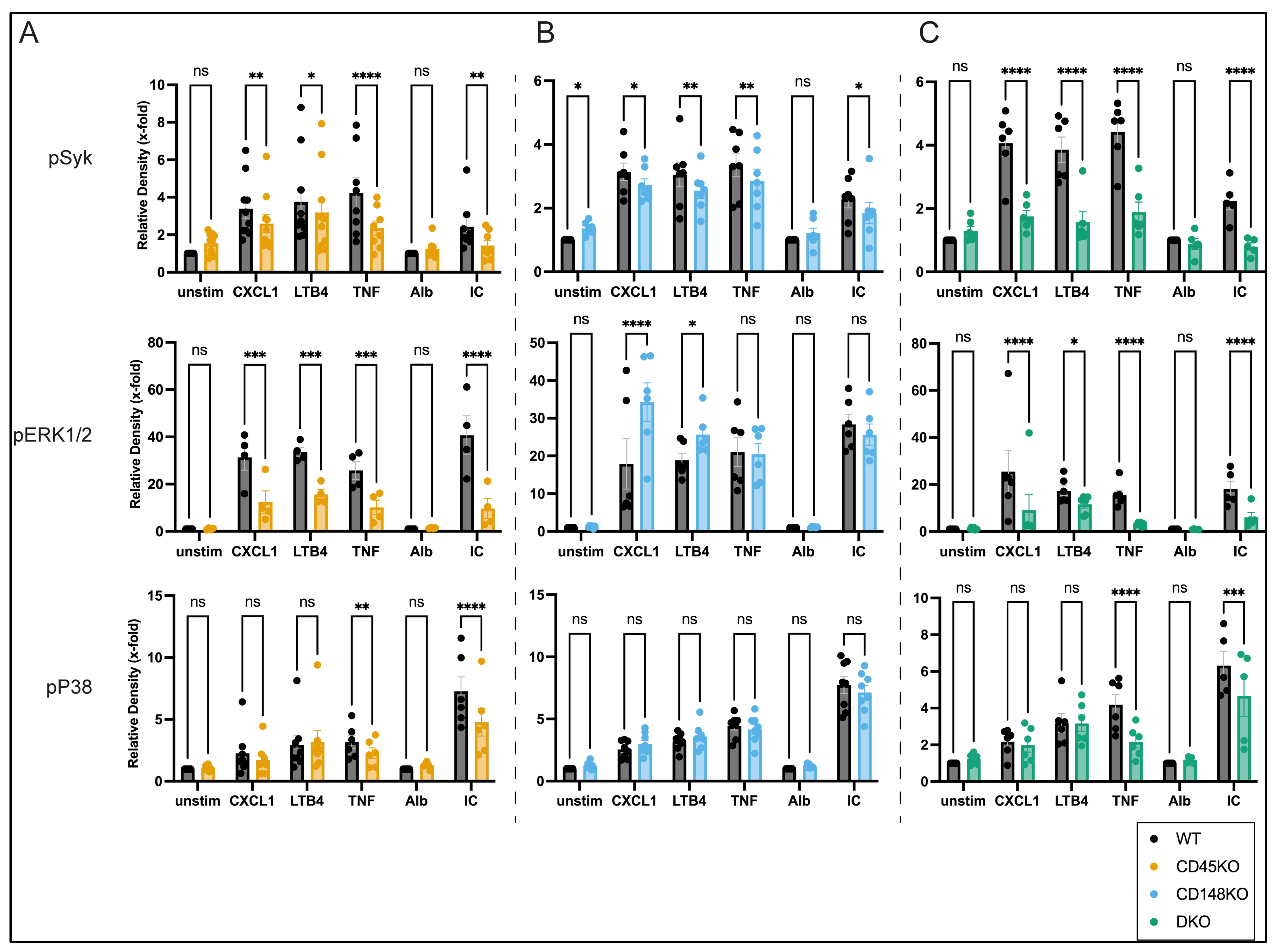
3.5. CD45 and CD148 Have Distinct Regulatory Effects on GPCR- and Fc-Mediated Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD | cluster of differentiation |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| LFA-1 | lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 |
| Mac-1 | Macrophage-1 antigen |
| ICAM | intercellular adhesion molecule |
| LTB4 | Leukotriene B4 |
| KO | knockout |
| DKO | double knockout |
| STIA | serum transfer-induced arthritis |
| PMN | polymorphonuclear neutrophils |
| SF | synovial fluid |
| BM | bone marrow |
| IC | immune complexes |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| SFK | Src family kinases |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| RPTPs | receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases |
References
- Gravallese, E.M.; Firestein, G.S. Rheumatoid Arthritis—Common Origins, Divergent Mechanisms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, L.J.; Kaplan, M.J. Neutrophils in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Breaking Immune Tolerance and Fueling Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wipke, B.T.; Allen, P.M. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monach, P.A.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Chen, M.; Hock, H.; Lee, D.M.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: Critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, M.; Nemeth, T.; Jakus, Z.; Sitaru, C.; Simon, E.; Futosi, K.; Botz, B.; Helyes, Z.; Lowell, C.A.; Mocsai, A. The Src family kinases Hck, Fgr, and Lyn are critical for the generation of the in vivo inflammatory environment without a direct role in leukocyte recruitment. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1993–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Ohmura, K.; Mahmood, U.; Lee, D.M.; Hofhuis, F.M.; Boackle, S.A.; Takahashi, K.; Holers, V.M.; Walport, M.; Gerard, C.; et al. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity 2002, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, Y.; Miyabe, C.; Murooka, T.T.; Kim, E.Y.; Newton, G.A.; Kim, N.D.; Haribabu, B.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Mempel, T.R.; Luster, A.D. Complement C5a Receptor is the Key Initiator of Neutrophil Adhesion Igniting Immune Complex-induced Arthritis. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaaj2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamud, M.; Whitehead, L.; McIntosh, A.; Colella, F.; Roelofs, A.J.; Kusakabe, T.; Dambuza, I.M.; Phillips-Brookes, A.; Salazar, F.; Perez, F.; et al. Recognition and control of neutrophil extracellular trap formation by MICL. Nature 2024, 633, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csepregi, J.Z.; Orosz, A.; Zajta, E.; Kasa, O.; Nemeth, T.; Simon, E.; Fodor, S.; Csonka, K.; Baratki, B.L.; Kovesdi, D.; et al. Myeloid-Specific Deletion of Mcl-1 Yields Severely Neutropenic Mice That Survive and Breed in Homozygous Form. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 3793–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtmann, A.; Germena, G.; Block, H.; Boras, M.; Rossaint, J.; Sundd, P.; Lefort, C.; Fisher, C.I.; Buscher, K.; Gelschefarth, B.; et al. The PSGL-1-L-selectin signaling complex regulates neutrophil adhesion under flow. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2171–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarbock, A.; Abram, C.L.; Hundt, M.; Altman, A.; Lowell, C.A.; Ley, K. PSGL-1 engagement by E-selectin signals through Src kinase Fgr and ITAM adapters DAP12 and FcR gamma to induce slow leukocyte rolling. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futosi, K.; Mocsai, A. Tyrosine kinase signaling pathways in neutrophils. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Ley, K. Protein tyrosine kinases in neutrophil activation and recruitment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 510, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.; Zhou, M.; Mocsai, A.; Lowell, C. Resting murine neutrophils express functional alpha 4 integrins that signal through Src family kinases. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4115–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggon, T.J.; Eck, M.J. Structure and regulation of Src family kinases. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7918–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingley, E. Src family kinases: Regulation of their activities, levels and identification of new pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senis, Y.A.; Mazharian, A.; Mori, J. Src family kinases: At the forefront of platelet activation. Blood 2014, 124, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.A.; Mikhailova, T.; Li, X.; Porter, B.A.; Bah, A.; Kotula, L. Src family kinases, adaptor proteins and the actin cytoskeleton in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Yang, W.; Kontaridis, M.I.; Bivona, T.G.; Wen, G.; Araki, T.; Luo, J.; Thompson, J.A.; Schraven, B.L.; Philips, M.R.; et al. Shp2 regulates SRC family kinase activity and Ras/Erk activation by controlling Csk recruitment. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Hendrickson, W.A. Structural basis for activation of human lymphocyte kinase Lck upon tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature 1996, 384, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Harrison, S.C.; Eck, M.J. Three-dimensional structure of the tyrosine kinase c-Src. Nature 1997, 385, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germena, G.; Volmering, S.; Sohlbach, C.; Zarbock, A. Mutation in the CD45 inhibitory wedge modulates integrin activation and leukocyte recruitment during inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.W.; Brdicka, T.; Katsumoto, T.R.; Lin, J.; Weiss, A. Structurally distinct phosphatases CD45 and CD148 both regulate B cell and macrophage immunoreceptor signaling. Immunity 2008, 28, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.W.; Doan, K.; Park, J.; Chau, A.H.; Zhang, H.; Lowell, C.A.; Weiss, A. Receptor-like tyrosine phosphatases CD45 and CD148 have distinct functions in chemoattractant-mediated neutrophil migration and response to S. aureus. Immunity 2011, 35, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, J.; Nagy, Z.; Di Nunzio, G.; Smith, C.W.; Geer, M.J.; Al Ghaithi, R.; van Geffen, J.P.; Heising, S.; Boothman, L.; Tullemans, B.M.E.; et al. Maintenance of murine platelet homeostasis by the kinase Csk and phosphatase CD148. Blood 2018, 131, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermiston, M.L.; Xu, Z.; Weiss, A. CD45: A critical regulator of signaling thresholds in immune cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 107–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermiston, M.L.; Zikherman, J.; Zhu, J.W. CD45, CD148, and Lyp/Pep: Critical phosphatases regulating Src family kinase signaling networks in immune cells. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 288–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harashima, A.; Suzuki, M.; Okochi, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Motoda, R.; Yoshioka, T.; Orita, K. CD45 tyrosine phosphatase inhibits erythroid differentiation of umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells associated with selective inactivation of Lyn. Blood 2002, 100, 4440–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie-Sasaki, J.; Sasaki, T.; Matsumoto, W.; Opavsky, A.; Cheng, M.; Welstead, G.; Griffiths, E.; Krawczyk, C.; Richardson, C.D.; Aitken, K.; et al. CD45 is a JAK phosphatase and negatively regulates cytokine receptor signalling. Nature 2001, 409, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balavenkatraman, K.K.; Jandt, E.; Friedrich, K.; Kautenburger, T.; Pool-Zobel, B.L.; Ostman, A.; Bohmer, F.D. DEP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase inhibits proliferation and migration of colon carcinoma cells and is upregulated by protective nutrients. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6319–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, J.W.; Baker, J.E.; Weiss, A. Regulated expression of the receptor-like tyrosine phosphatase CD148 on hemopoietic cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2324–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaya, A.; Pirotto, F.; Palou, E.; Autschbach, F.; Del Pozo, V.; Sole, J.; Serra-Pages, C. CD148, a new membrane tyrosine phosphatase involved in leukocyte function. Leuk. Lymphoma 1999, 35, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Singbartl, K.; Ley, K. Complete reversal of acid-induced acute lung injury by blocking of platelet-neutrophil aggregation. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, V.; Morawietz, L.; Burmester, G.R.; Kinne, R.W.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Muller, B.; Haupl, T. Synovitis score: Discrimination between chronic low-grade and high-grade synovitis. Histopathology 2006, 49, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippiello, L.; Hall, D.; Mankin, H.J. Collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 59, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumbe, A.P.; Ramasamy, S.K.; Starsichova, A.; Adams, R.H. Sample preparation for high-resolution 3D confocal imaging of mouse skeletal tissue. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifer, D.R.; Furman, B.D.; Guilak, F.; Olson, S.A.; Brooks, S.C., 3rd; Kraus, V.B. Novel synovial fluid recovery method allows for quantification of a marker of arthritis in mice. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backryd, E.; Tanum, L.; Lind, A.L.; Larsson, A.; Gordh, T. Evidence of both systemic inflammation and neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia patients, as assessed by a multiplex protein panel applied to the cerebrospinal fluid and to plasma. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.C.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Steinberg, O.V.; Wirth, T.; Lauks, S.; Bittner, S.; Schindler, P.; Baranzini, S.E.; Groppa, S.; Bellmann-Strobl, J.; et al. Multiple sclerosis endophenotypes identified by high-dimensional blood signatures are associated with distinct disease trajectories. Sci. Transl. Med. 2024, 16, eade8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, H.; Stadtmann, A.; Van Aken, H.; Hirsch, E.; Wang, D.; Ley, K.; Zarbock, A. Tyrosine kinase Btk regulates E-selectin-mediated integrin activation and neutrophil recruitment by controlling phospholipase C (PLC) gamma2 and PI3Kgamma pathways. Blood 2010, 115, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Lowell, C.A.; Ley, K. Spleen tyrosine kinase Syk is necessary for E-selectin-induced alpha(L)beta(2) integrin-mediated rolling on intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Immunity 2007, 26, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadtmann, A.; Brinkhaus, L.; Mueller, H.; Rossaint, J.; Bolomini-Vittori, M.; Bergmeier, W.; Van Aken, H.; Wagner, D.D.; Laudanna, C.; Ley, K.; et al. Rap1a activation by CalDAG-GEFI and p38 MAPK is involved in E-selectin-dependent slow leukocyte rolling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 2074–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, S.M.; Pick, R.; Brechtefeld, D.; Nussbaum, C.; Kiefer, F.; Sperandio, M.; Walzog, B. Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) is required for LFA-1-mediated neutrophil recruitment during the acute inflammatory response. Blood 2013, 121, 4184–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, C.T.; Rossaint, J.; Moser, M.; Petrich, B.G.; Zarbock, A.; Monkley, S.J.; Critchley, D.R.; Ginsberg, M.H.; Fassler, R.; Ley, K. Distinct roles for talin-1 and kindlin-3 in LFA-1 extension and affinity regulation. Blood 2012, 119, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakus, Z.; Nemeth, T.; Verbeek, J.S.; Mocsai, A. Critical but overlapping role of FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIV in activation of murine neutrophils by immobilized immune complexes. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappenberg, A.; Margraf, A.; Thomas, K.; Bardel, B.; McCreedy, D.A.; Van Marck, V.; Mellmann, A.; Lowell, C.A.; Zarbock, A. L-selectin shedding affects bacterial clearance in the lung: A new regulatory pathway for integrin outside-in signaling. Blood 2019, 134, 1445–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.C.; Kim, N.D.; Sadik, C.D.; Seung, E.; Lan, Y.; Byrne, M.H.; Haribabu, B.; Iwakura, Y.; Luster, A.D. Lipid-cytokine-chemokine cascade drives neutrophil recruitment in a murine model of inflammatory arthritis. Immunity 2010, 33, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uderhardt, S.; Ackermann, J.A.; Fillep, T.; Hammond, V.J.; Willeit, J.; Santer, P.; Mayr, M.; Biburger, M.; Miller, M.; Zellner, K.R.; et al. Enzymatic lipid oxidation by eosinophils propagates coagulation, hemostasis, and thrombotic disease. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2121–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.D.; Haase, C.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) plays an important role in immune complex-mediated arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.H.; Lee, G.; Lee, K.B.; Koh, J.T.; Chun, J.S.; Ryu, J.H. HIF-2alpha-induced chemokines stimulate motility of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and chondrocytes into the cartilage-pannus interface in experimental rheumatoid arthritis mouse models. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, C.; Whiteside, R.; Heras, F.L.; Nesic, D.; Koziol, J.; Grogan, S.P.; Matyas, J.; Pritzker, K.P.; D’Lima, D.D.; Lotz, M.K. Comparison of cartilage histopathology assessment systems on human knee joints at all stages of osteoarthritis development. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzemaekers, M.; Gouwy, M.; Proost, P. Neutrophil chemoattractant receptors in health and disease: Double-edged swords. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.D.; Chou, R.C.; Seung, E.; Tager, A.M.; Luster, A.D. A unique requirement for the leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 for neutrophil recruitment in inflammatory arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lam, B.K.; Kanaoka, Y.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Audoly, L.P.; Austen, K.F.; Lee, D.M. Neutrophil-derived leukotriene B4 is required for inflammatory arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadik, C.D.; Luster, A.D. Lipid-cytokine-chemokine cascades orchestrate leukocyte recruitment in inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 91, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, T.; Futosi, K.; Szilveszter, K.; Vilinovszki, O.; Kiss-Papai, L.; Mocsai, A. Lineage-Specific Analysis of Syk Function in Autoantibody-Induced Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Sitaru, C.; Jakus, Z.; Anderson, K.E.; Damoulakis, G.; Davidson, K.; Hirose, M.; Juss, J.; Oxley, D.; Chessa, T.A.; et al. PI3Kbeta plays a critical role in neutrophil activation by immune complexes. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnich, S.J.; Blanner, P.M.; Hu, L.G.; Shaffer, A.F.; Happa, F.A.; O'Neil, S.; Ukairo, O.; Weiss, D.; Welsh, E.; Storer, C.; et al. Critical role for apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in the development of inflammatory K/BxN serum-induced arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremasco, V.; Graham, D.B.; Novack, D.V.; Swat, W.; Faccio, R. Vav/Phospholipase Cgamma2-mediated control of a neutrophil-dependent murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2712–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, C.D.; Kim, N.D.; Iwakura, Y.; Luster, A.D. Neutrophils orchestrate their own recruitment in murine arthritis through C5aR and FcgammaR signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3177–E3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyabe, Y.; Miyabe, C.; Luster, A.D. LTB(4) and BLT1 in inflammatory arthritis. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 33, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, I.; Rubio-Ponce, A.; Genua, M.; Lusito, E.; Kwok, I.; Fernandez-Calvo, G.; Khoyratty, T.E.; van Grinsven, E.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, S.; Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; et al. Co-option of Neutrophil Fates by Tissue Environments. Cell 2020, 183, 1282–1297.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margraf, A.; Ley, K.; Zarbock, A. Neutrophil Recruitment: From Model Systems to Tissue-Specific Patterns. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasken, S.; Auger, J.L.; Binstadt, B.A. Absence of beta2 integrins impairs regulatory T cells and exacerbates CD4+ T cell-dependent autoimmune carditis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2702–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issekutz, T.B.; Miyasaka, M.; Issekutz, A.C. Rat blood neutrophils express very late antigen 4 and it mediates migration to arthritic joint and dermal inflammation. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, G.M.; Beurskens, F.J.; Martin-Padura, I.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Klickstein, L.B.; Brenner, M.B.; Lee, D.M. Manifestations of inflammatory arthritis are critically dependent on LFA-1. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3668–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaburagi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Nagaoka, T.; Shimada, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Komura, K.; Saito, E.; Yanaba, K.; Takehara, K.; Kadono, T.; et al. The cutaneous reverse Arthus reaction requires intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and L-selectin expression. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2970–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappenberg, A.; Kardell, M.; Zarbock, A. Selectin-Mediated Signaling-Shedding Light on the Regulation of Integrin Activity in Neutrophils. Cells 2022, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakus, Z.; Simon, E.; Balazs, B.; Mocsai, A. Genetic deficiency of Syk protects mice from autoantibody-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwedder, I.; Kurz, A.R.M.; Pruenster, M.; Immler, R.; Pick, R.; Eggersmann, T.; Klapproth, S.; Johnson, J.L.; Alsina, S.M.; Lowell, C.A.; et al. Src family kinase-mediated vesicle trafficking is critical for neutrophil basement membrane penetration. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarantos, M.R.; Zhang, H.; Schaff, U.Y.; Dixit, N.; Hayenga, H.N.; Lowell, C.A.; Simon, S.I. Transmigration of neutrophils across inflamed endothelium is signaled through LFA-1 and Src family kinase. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8660–8669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnen, M.; Leschczyk, C.; Moller, S.; Batel, T.; Klinger, M.; Solbach, W.; Laskay, T. Immobilized immune complexes induce neutrophil extracellular trap release by human neutrophil granulocytes via FcgammaRIIIB and Mac-1. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1954–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, B.; Malik, A.B.; Tang, H.; Yang, T.; Sun, B.; Wang, G.; Minshall, R.D.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Bidirectional regulation of neutrophil migration by mitogen-activated protein kinases. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.R.; Liu, S.; Wu, L.F.; Altschuler, S.J.; Cobb, M.H. Chemoattractant concentration-dependent tuning of ERK signaling dynamics in migrating neutrophils. Sci. Signal 2016, 9, ra122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, T.Z.; Simard, F.A.; Cloutier, A.; Vardhan, H.; Dubois, C.M.; McDonald, P.P. The p38-MSK1 signaling cascade influences cytokine production through CREB and C/EBP factors in human neutrophils. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4299–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heit, B.; Colarusso, P.; Kubes, P. Fundamentally different roles for LFA-1, Mac-1 and alpha4-integrin in neutrophil chemotaxis. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5205–5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.I.; Chen, P.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Tseng, H.H.; Chang, S.H.; Wu, T.S.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Hwang, T.L. Bletinib ameliorates neutrophilic inflammation and lung injury by inhibiting Src family kinase phosphorylation and activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4069–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, A.; Ear, T.; Blais-Charron, E.; Dubois, C.M.; McDonald, P.P. Differential involvement of NF-kappaB and MAP kinase pathways in the generation of inflammatory cytokines by human neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lazarovits, A.; Gao, Z.; Garcia, B.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; Xing, J.J.; White, M.; Zhong, R. Prolongation of xenograft survival using monoclonal antibody CD45RB and cyclophosphamide in rat-to-mouse kidney and heart transplant models. Transplantation 2000, 69, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Takahashi, A.; Manaka, A.; Sato, M.; Osada, H. TU-572, a potent and selective CD45 inhibitor, suppresses IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and murine contact hypersensitivity reactions. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 126, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemecek, E.R.; Matthews, D.C. Antibody-based therapy of human leukemia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2002, 9, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rheinlander, A.; Schraven, B.; Bommhardt, U. CD45 in human physiology and clinical medicine. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, N.; Kanai, T.; Okada, M. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Reactive Oxygen Species: A Review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 3000–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henrotin, Y.E.; Bruckner, P.; Pujol, J.P. The role of reactive oxygen species in homeostasis and degradation of cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Tandel, N.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Tyagi, R.K. Aceclofenac and methotrexate combination therapy could influence Th1/Th17 axis to modulate rheumatoid-arthritis-induced inflammation. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, S.; Tandel, N.; Garg, N.K.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Saini, S.; Sharma, A.; Tyagi, R.K. Co-Delivery of Aceclofenac and Methotrexate Nanoparticles Presents an Effective Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 2149–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heming, J.-N.; Margraf, A.; Najder, K.; Germena, G.; Richter, M.; Cappenberg, A.; Henke, K.; Bardel, B.; Schemmelmann, L.; Oguama, M.; et al. CD45 and CD148 Are Critically Involved in Neutrophil Recruitment and Function During Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice. Cells 2025, 14, 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151169
Heming J-N, Margraf A, Najder K, Germena G, Richter M, Cappenberg A, Henke K, Bardel B, Schemmelmann L, Oguama M, et al. CD45 and CD148 Are Critically Involved in Neutrophil Recruitment and Function During Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice. Cells. 2025; 14(15):1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151169
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeming, Jan-Niklas, Andreas Margraf, Karolina Najder, Giulia Germena, Mathis Richter, Anika Cappenberg, Katharina Henke, Bernadette Bardel, Lena Schemmelmann, Marina Oguama, and et al. 2025. "CD45 and CD148 Are Critically Involved in Neutrophil Recruitment and Function During Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice" Cells 14, no. 15: 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151169
APA StyleHeming, J.-N., Margraf, A., Najder, K., Germena, G., Richter, M., Cappenberg, A., Henke, K., Bardel, B., Schemmelmann, L., Oguama, M., Lindental, P., Amini, W., Sobocik, J., Schett, G., Krönke, G., Block, H., Rossaint, J., Soehnlein, O., & Zarbock, A. (2025). CD45 and CD148 Are Critically Involved in Neutrophil Recruitment and Function During Inflammatory Arthritis in Mice. Cells, 14(15), 1169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151169







