In the original publication [1], the funder “the Graduate Innovation Funding Project of Hebei Medical University, XCXZZS202302” to Boyang Wen was not included. The correct Funding appears below.
- Funding: This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (grant number H2022206085), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 81871524), Postdoctoral Research Project of Hebei Province (grant number 2022005010), and Youth Foundation of Science and Technology Research Project of colleges and Universities of Hebei Province (grant number QN2023219), and the Graduate Innovation Funding Project of Hebei Medical University, (grant number XCXZZS202302).
There was another mistake in Figure 3 as published. The two charts in Figure 3Bb are duplicated. The corrected Figure 3 appears below.
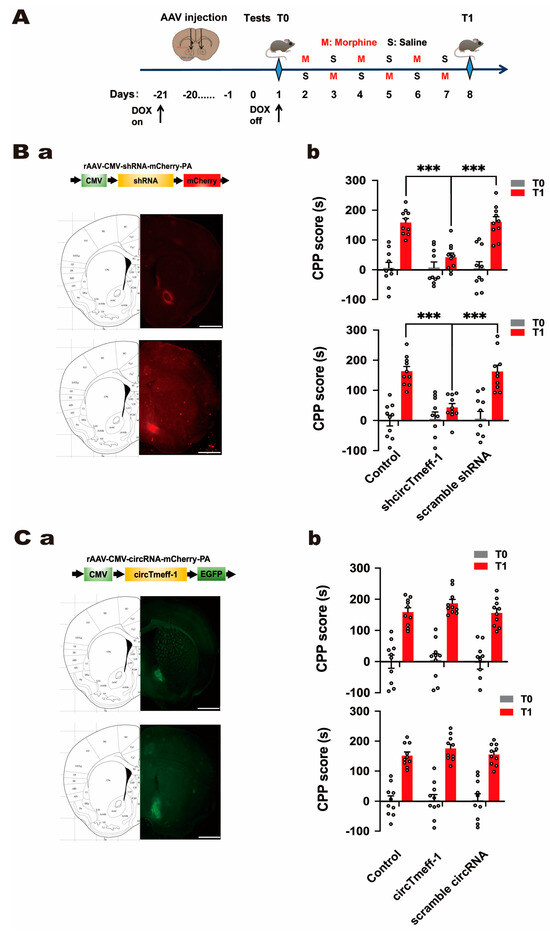
Figure 3.
CircTmeff-1 modulates background-induced memory formation of morphine addiction. (A): a schematic diagram of the timeline of the morphine CPP training program. (B): Reducing circTmeff-1 expression in the NAc inhibits the expression of morphine addiction memory. (a) Schematic diagram of AAV structure used to down-regulate circTmeff-1; mCherry fluorescence location indicated that the injected virus was located in the core or shell of the NAc; scale bar = 1000 µm. (b) Down-regulation of circTmeff-1 in both NAc core and shell inhibited morphine seeking (n = 10 per group), *** p < 0.001. (C): Overexpression of circTmeff-1 in the core and shell of the NAc did not affect the expression of morphine-addicted memory. (a) Schematic diagram of AAV structure used for overexpression of circTmeff-1; EGFP fluorescence location indicated that the injected virus was located in the core or shell of NAc; scale bar = 1000 µm. (b) Overexpression of circTmeff-1 in the core and shell of the NAc had no effect on T1 background-induced morphine seeking (n = 10 per group). EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Yu, H.; Wen, B.; Lu, Y.; Xie, B.; Yu, F.; Zhang, M.; Ma, C.; Cong, B.; Wen, D.; Bi, H. The Role of circTmeff-1 in Morphine Addiction Memory of Mice. Cells 2023, 12, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).