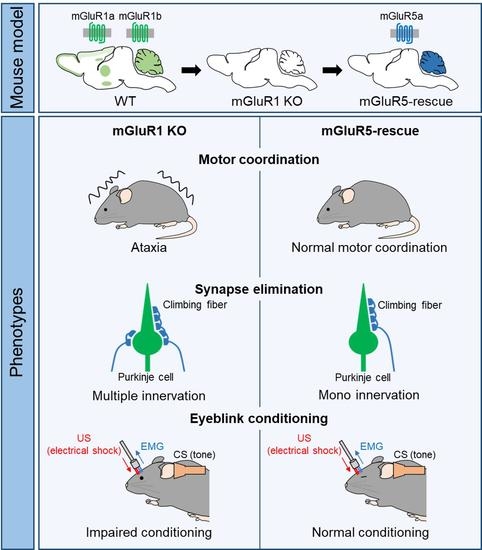
mGluR5 Is Substitutable for mGluR1 in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells for Motor Coordination, Developmental Synapse Elimination, and Motor Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Generation of Transgenic Mice
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.5. Preparation of Synaptosomal Fraction and Coimmunoprecipitation
2.6. Rotarod Test and Footprints
2.7. Delay Eyeblink Conditioning
2.8. Electrophysiological Recording
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Generation of mGluR5-Rescue Mice
3.2. Normal Motor Coordination in mGluR5-Rescue Mice
3.3. Normal Regression of Multiple CF Innervation in PCs of mGluR5-Rescue Mice
3.4. Recovered Performance of Eyeblink Conditioning as a Motor Learning in mGluR5-Rescue Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakanishi, S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science 1992, 258, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu. Rev. Pharm. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abe, T.; Sugihara, H.; Nawa, H.; Shigemoto, R.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13361–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto, R.; Nakanishi, S.; Mizuno, N. Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) in the central nervous system: An in situ hybridization study in adult and developing rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 322, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catania, M.V.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Testa, C.M.; Standaert, D.G.; Penney, J.B., Jr.; Young, A.B. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are differentially regulated during development. Neuroscience 1994, 61, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notartomaso, S.; Nakao, H.; Mascio, G.; Scarselli, P.; Cannella, M.; Zappulla, C.; Madonna, M.; Motolese, M.; Gradini, R.; Liberatore, F.; et al. mGlu1 Receptors Monopolize the Synaptic Control of Cerebellar Purkinje Cells by Epigenetically Down-Regulating mGlu5 Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Notartomaso, S.; Aronica, E.; Storto, M.; Battaglia, G.; Vieira, E.; Gatti, S.; Bruno, V.; Biagioni, F.; Gradini, R.; et al. Switch in the expression of mGlu1 and mGlu5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in the cerebellum of mice developing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and in autoptic cerebellar samples from patients with multiple sclerosis. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notartomaso, S.; Zappulla, C.; Biagioni, F.; Cannella, M.; Bucci, D.; Mascio, G.; Scarselli, P.; Fazio, F.; Weisz, F.; Lionetto, L.; et al. Pharmacological enhancement of mGlu1 metabotropic glutamate receptors causes a prolonged symptomatic benefit in a mouse model of spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiba, A.; Kano, M.; Chen, C.; Stanton, M.E.; Fox, G.D.; Herrup, K.; Zwingman, T.A.; Tonegawa, S. Deficient cerebellar long-term depression and impaired motor learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell 1994, 79, 377–388. [Google Scholar]
- Kano, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Kurihara, H.; Watanabe, M.; Inoue, Y.; Aiba, A.; Tonegawa, S. Persistent multiple climbing fiber innervation of cerebellar Purkinje cells in mice lacking mGluR1. Neuron 1997, 18, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichise, T.; Kano, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Yanagihara, D.; Nakao, K.; Shigemoto, R.; Katsuki, M.; Aiba, A. mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells essential for long-term depression, synapse elimination, and motor coordination. Science 2000, 288, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Fujimichi, R.; Araishi, K.; Kawahara, S.; Kano, M.; Aiba, A.; Kirino, Y. mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells is required for normal association of temporally contiguous stimuli in classical conditioning. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 2416–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiba, A.; Chen, C.; Herrup, K.; Rosenmund, C.; Stevens, C.F.; Tonegawa, S. Reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation and context-specific deficit in associative learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell 1994, 79, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdick, J.; Smeyne, R.J.; Mann, J.R.; Zackson, S.; Morgan, J.I. A promoter that drives transgene expression in cerebellar Purkinje and retinal bipolar neurons. Science 1990, 248, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, H.; Nakao, K.; Kano, M.; Aiba, A. Metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype-1 is essential for motor coordination in the adult cerebellum. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 57, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Whiteley, M.; Felsenfeld, G. A 5’ element of the chicken beta-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 1993, 74, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Kushiya, E.; Yamasaki, M.; Fukaya, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Simon, M.I.; Sakimura, K.; Kano, M.; Watanabe, M. Gq protein alpha subunits Galphaq and Galpha11 are localized at postsynaptic extra-junctional membrane of cerebellar Purkinje cells and hippocampal pyramidal cells. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, Y.; Miyata, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Tabata, T.; Kishimoto, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Kase, D.; Kassai, H.; Nakao, K.; Hirata, T.; et al. The synaptic targeting of mGluR1 by its carboxyl-terminal domain is crucial for cerebellar function. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2702–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, T.; Kumada, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Furukawa, T.; Aiba, A.; Conquet, F.; Saga, Y.; Fukuda, A. Guidepost neurons for the lateral olfactory tract: Expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 and innervation by glutamatergic olfactory bulb axons. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1559–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Oku, I.; Nishigawa, A.; Nishimoto, A.; Kirino, Y. Impaired long-trace eyeblink conditioning in a Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 506, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, H.; Kishimoto, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Kitamura, K.; Yamasaki, M.; Nakao, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kano, M.; Kirino, Y.; Aiba, A. mGluR1 in cerebellar Purkinje cells is essential for the formation but not expression of associative eyeblink memory. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minakami, R.; Iida, K.; Hirakawa, N.; Sugiyama, H. The expression of two splice variants of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in the rat brain and neuronal cells during development. J. Neurochem. 1995, 65, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, C.; van den Pol, A.N.; O’Malley, K.L. Enhanced early developmental expression of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 in rat brain: Protein, mRNA splice variants, and regional distribution. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 367, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi-Yamaguchi, Y.; Furuichi, T. The Homer family proteins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Munguba, H.; Gutzeit, V.A.; Singh, D.R.; Kristt, M.; Dittman, J.S.; Levitz, J. Defining the Homo- and Heterodimerization Propensities of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werthmann, R.C.; Tzouros, M.; Lamerz, J.; Augustin, A.; Fritzius, T.; Trovo, L.; Stawarski, M.; Raveh, A.; Diener, C.; Fischer, C.; et al. Symmetric signal transduction and negative allosteric modulation of heterodimeric mGlu1/5 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kano, M. Functional differentiation of multiple climbing fiber inputs during synapse elimination in the developing cerebellum. Neuron 2003, 38, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, S.; Tsutsumi, R.; Kohara, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Okada, M. Control of calcium oscillations by phosphorylation of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature 1996, 383, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, C.; Gomeza, J.; Brabet, I.; Curry, K.; Bockaert, J.; Pin, J.P. Molecular, functional, and pharmacological characterization of the metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 splice variants: Comparison with mGluR1. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 3970–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mion, S.; Corti, C.; Neki, A.; Shigemoto, R.; Corsi, M.; Fumagalli, G.; Ferraguti, F. Bidirectional regulation of neurite elaboration by alternatively spliced metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5) isoforms. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2001, 17, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, R.; Kassai, H.; Sakai, Y.; Schonherr, S.; Fukaya, M.; Schwarzer, C.; Sakagami, H.; Nakao, K.; Aiba, A.; Ferraguti, F. New Features on the Expression and Trafficking of mGluR1 Splice Variants Exposed by Two Novel Mutant Mouse Lines. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Control | mGluR5-Rescue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average | SEM | Average | SEM | t-Test vs. Control | |
| CR amplitude (%) | 204.81 | 30.1 | 248.98 | 41.07 | 0.4 |
| CR onset latency (ms) | 48.05 | 2.3 | 48.13 | 3.06 | 0.98 |
| UR amplitude (%) | 263.5 | 58.52 | 287.75 | 60.75 | 0.78 |
| startle response (%) | 6.05 | 2.35 | 5.17 | 3.08 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harbers, M.; Nakao, H.; Watanabe, T.; Matsuyama, K.; Tohyama, S.; Nakao, K.; Kishimoto, Y.; Kano, M.; Aiba, A. mGluR5 Is Substitutable for mGluR1 in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells for Motor Coordination, Developmental Synapse Elimination, and Motor Learning. Cells 2022, 11, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132004
Harbers M, Nakao H, Watanabe T, Matsuyama K, Tohyama S, Nakao K, Kishimoto Y, Kano M, Aiba A. mGluR5 Is Substitutable for mGluR1 in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells for Motor Coordination, Developmental Synapse Elimination, and Motor Learning. Cells. 2022; 11(13):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132004
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarbers, Maria, Harumi Nakao, Takaki Watanabe, Kyoko Matsuyama, Shoichi Tohyama, Kazuki Nakao, Yasushi Kishimoto, Masanobu Kano, and Atsu Aiba. 2022. "mGluR5 Is Substitutable for mGluR1 in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells for Motor Coordination, Developmental Synapse Elimination, and Motor Learning" Cells 11, no. 13: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132004
APA StyleHarbers, M., Nakao, H., Watanabe, T., Matsuyama, K., Tohyama, S., Nakao, K., Kishimoto, Y., Kano, M., & Aiba, A. (2022). mGluR5 Is Substitutable for mGluR1 in Cerebellar Purkinje Cells for Motor Coordination, Developmental Synapse Elimination, and Motor Learning. Cells, 11(13), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11132004