Abstract
Prion diseases are fatal, chronic, and incurable neurodegenerative diseases caused by pathogenic forms of prion protein (PrPSc) derived from endogenous forms of prion protein (PrPC). Several case–control and genome-wide association studies have reported that the M129V polymorphism of the human prion protein gene (PRNP) is significantly associated with susceptibility to sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD). However, since some case–control studies have not shown these associations, the results remain controversial. We collected data that contain the genotype and allele frequencies of the M129V single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the PRNP gene and information on ethnic backgrounds from sporadic CJD patients. We performed a meta-analysis by collecting data from eligible studies to evaluate the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD. We found a very strong association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD using a meta-analysis for the first time. We validated the eligibility of existing reports and found severe heterogeneity in some previous studies. We also found that the MM homozygote is a potent risk factor for sporadic CJD compared to the MV heterozygote in the heterozygote comparison model (MM vs. MV, odds ratio = 4.9611, 95% confidence interval: 3.4785; 7.0758, p < 1 × 10−10). To the best of our knowledge, this was the first meta-analysis assessment of the relationship between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD.
1. Introduction
Prion diseases are chronic, lethal, and malignant neurodegenerative diseases caused by toxic forms of prion protein (PrPSc) derived from benign prion protein (PrPC), which is encoded by the prion protein gene (PRNP) [1,2,3,4,5]. In humans, prion diseases are classified into three types: sporadic, genetic, and acquired. The most common type of human prion disease is sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD), which accounts for approximately 85% of all CJD cases. Genetic forms of human prion disease, accounting for 10–15% of all CJD cases, occur due to germline mutations of the PRNP gene. These forms include fatal familial insomnia (FFI) with the D178N-129M genotype; Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS) with P102L, A117V, and F198S mutations; and genetic CJD, including the G114V, D178N-129V, V180I, E200K, and V210I mutations. Acquired forms of human prion disease account for less than 1% of all CJD cases, including iatrogenic CJD, kuru, and variant CJD, which are caused by consuming meat from bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)-affected cattle [6,7,8,9,10]. However, the cause of sporadic CJD has not been elucidated thus far.
In previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS), the locus of the PRNP gene was found to be extremely related to susceptibility to sporadic CJD [11,12]. Several case–control studies using fine mapping have also identified that the nonsynonymous polymorphism at codon 129 of the PRNP gene is significantly associated with susceptibility to sporadic CJD [10,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. However, the control populations used in several case–control studies were not in a Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) and showed severe heterogeneity in the value of association [15,19,20,22,24]. In addition, the genotype and allele distributions of the M129V SNP were not shown to be related to vulnerability to sporadic CJD in the Brazilian population, and the allele distribution of the M129V single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) was not found to be associated with the susceptibility to sporadic CJD in several other case–control studies [13,15,18,19,23]. Furthermore, since some studies have provided information only on sporadic CJD patients, an association test was not available in those studies [23,25]. Thus, a comprehensive evaluation of the association between polymorphisms of the PRNP gene at codon 129 and susceptibility to sporadic CJD is needed in quality-checked and quantitatively synthesized studies.
To evaluate the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD, we collected data on the genotype and allele frequencies of the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and information on ethnic backgrounds from sporadic CJD patients. The information on matched-control populations was supplemented from the 1000 Genomes Project and used for an association analysis. Then, we performed a meta-analysis by collecting data from eligible studies to evaluate the association of the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene with susceptibility to sporadic CJD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
A literature search was performed in the PubMed database to identify studies relating to the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene from sporadic CJD patients. The following search terms were used: “PRNP”, “prion”, “CJD”, or “Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease” combined with “SNP” or “polymorphism” or “susceptibility” (the last search update was performed on 8 March 2021). We also supplemented our search by screening reference lists of all the relevant studies, including original articles and reviews. Irrelevant studies were excluded after the initial screening of titles and abstracts. Eligible studies met the following inclusion criteria: (1) relating to the association between the M129V SNP and sporadic CJD; (2) being a cohort or case–control study; (3) containing genetic information on the M129V SNP of sporadic CJD patients; (4) having full text available; and (5) being published in English. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) animal studies; (2) case reports; and (3) insufficient genotype data.
2.2. Association Analysis
We collected 13 studies that contained the genotype and allele frequencies of the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene in sporadic CJD patients and information on their ethnic background. Information on matched control populations, including Caucasian and East Asian populations, was obtained from the 1000 Genome Project. Comparison of the genotype and allele frequencies between sporadic CJD patients and control populations was analyzed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Statistical significance was measured by p-values obtained using the χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test. The HWE test was performed using Haploview version 4.2 (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, USA).
2.3. Meta-Analysis
The strength of the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD was estimated in a meta-analysis. The pooled odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated based on additive (M vs. V), recessive (MM vs. MV + VV), dominant (MM + MV vs. VV), and over-dominant (MV vs. MM + VV) genetic models and homozygote (MM vs. VV) and heterozygote (MM vs. MV and MV vs. VV) comparisons. Heterogeneity was evaluated by the p-value and I2 value. Fixed and random effect models were selected to calculate the pooled odds ratios according to the value of the I2 test. Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s weighted regression methods. A meta-analysis was conducted using the meta package of the R program (https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 14 August 2021)).
3. Results
3.1. Investigation of the Association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP Gene and Susceptibility to Sporadic CJD in Each Group
We searched 278 research articles using the search terms “PRNP”, “prion”, “CJD”, or “Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease” combined with “SNP” or “polymorphism” or “susceptibility” (the last search update was performed on 8 March 2021) in PubMed. After excluding duplicate and irrelevant articles, a total of 13 relevant studies were extracted from the databases based on our inclusion and exclusion criteria.
To identify an association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD, we performed an association analysis between sporadic CJD patients and matched control populations, including Caucasian and East Asian populations obtained from the 1000 Genomes Project. Except for two groups, Salvatore et al. 1994 and Croes et al. 2004, the genotype frequencies of the control population of all groups tested were in HWE. Except for one group, Martins 2007, the genotype frequencies of M129V of the PRNP gene exhibited a strong association (p < 0.05) with susceptibility to sporadic CJD in all groups tested (Table 1). Except for five groups—Palmer et al. 1991, Croes et al. 2004, Martins et al. 2007, Bishop et al. 2009, and Kobayashi et al. 2015—the allele frequencies of the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene also showed a strong association (p < 0.05) with the vulnerability of sporadic CJD in all groups tested.

Table 1.
Comparison of the genotype and allele frequencies of M129V in the prion protein gene (PRNP) between sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) patients and matched control populations (CTL) in previous studies.
3.2. Evaluation of the Association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP Gene and Susceptibility to Sporadic CJD by Meta-Analysis
First, we performed a meta-analysis with all 13 groups tested and found severe heterogeneity and publication bias induced by Doh-ura et al. 1991, Salvatore et al. 1994, Croes et al. 2004, Jeong et al. 2005 and Bishop et al. 2009 (data not shown). Except for the five studies listed, a total of eight studies showing the association between the M129V SNP and susceptibility to sporadic CJD were included in this meta-analysis (Table 1, shaded blocks). In total, 3290 sporadic CJD patients and 3415 controls were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals were calculated based on additive, recessive, dominant, and over-dominant genetic models and homozygote and heterozygote comparisons. Heterogeneity among the collected studies was tested using the p-value and I2 value (Table 2). According to the I2 value of these studies with no heterogeneity, we used fixed (<50%) and random (>50%) models for the meta-analysis.

Table 2.
Meta-analysis of the association between M129V of the prion protein gene (PRNP) and susceptibility to sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD).
Our data revealed an association between the risk of sporadic CJD and the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene in the additive model (odds ratio = 1.7698, 95% confidence interval: 1.6068; 1.9494, p < 0.0001), recessive model (odds ratio = 3.1556, 95% confidence interval: 2.5163; 3.9574, p < 0.0001, dominant model (odds ratio = 0.6722, 95% confidence interval: 0.5569; 0.8114, p < 0.001), over-dominant model (odds ratio = 0.2088, 95% confidence interval: 0.1483; 0.2939, p < 0.0001), and heterozygote comparisons (MM vs. MV, odds ratio = 4.9611, 95% confidence interval: 3.4785; 7.0758, p < 0.0001; MV vs. VV, odds ratio = 0.2256, 95% confidence interval: 0.1810; 0.2811, p < 0.0001). However, no significant association was found in the homozygote comparison (odds ratio = 1.1906, confidence interval: 0.9788; 1.4483, p = 0.5666). To examine potential publication bias, Egger’s tests were performed, and publication bias was not observed in this meta-analysis (p > 0.1). The details of the outcomes are shown in Table 2. The most significant association was observed in the heterozygote comparison (MM vs. MV), followed by the recessive model and additive model. Forest plots of the heterozygote comparison (MM vs. MV), recessive model, and additive model are drawn in Figure 1.
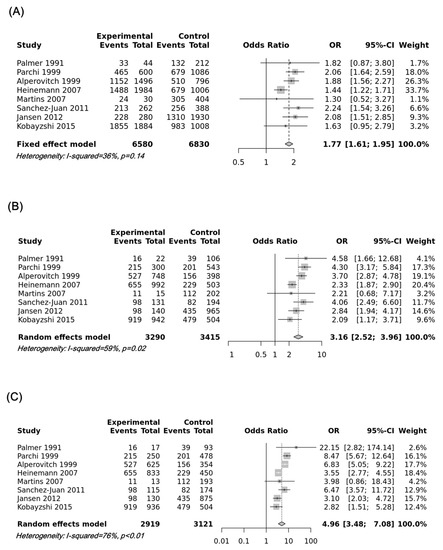
Figure 1.
(A) Forest plot of the association between the M129V single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) in the additive model (M vs. V). (B) The forest plot for the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD in the recessive model (MM vs. MV + VV). (C) The forest plot for the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD in the heterozygote comparison (MM vs. MV).
4. Discussion
In the present study, we evaluated the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD using a meta-analysis. To do so, we validated the eligibility of each study and identified that several studies were not suitable due to HWE violation and significant heterogeneity (Table 1). We performed a meta-analysis on qualifying studies and identified a significant association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD in all genetic models, except for the homozygote comparison (Table 2). Notably, the strongest association was found in the heterozygote comparison (MM vs. MV). In previous studies, heterozygosity at codon 129 of the human PRNP gene was found to be related to the resistance of human prion diseases. Sporadic CJD patients and kuru with the MV genotype at codon 129 of the human PRNP gene showed later disease onset and longer incubation time [28,29,30]. In addition, human PrP transgenic mice with the MV genotype at codon 129 of the human PRNP gene showed a prolonged incubation period [27,31,32]. These studies indicated that the heterozygote comparison model showed a correlation with the pathomechanism of prion diseases according to the genotypes of PRNP polymorphisms at codon 129.
After the validation of previous case–control studies, we found that the remaining studies were primarily composed of Caucasian populations (75%, Table 1). Since the number of case–control studies in East Asia and South America is not sufficient to evaluate the susceptibility to sporadic CJD by meta-analysis, further case–control studies are highly desirable in various countries and ethnic backgrounds. In addition, two studies in the Korean and Japanese populations showed severe heterogeneity and were excluded from the current meta-analysis (Table 1). The data in the Japanese population [22] and the Korean population [24] showed a low odds ratio (0.37) and an extremely high odds ratio (17.78) in the heterozygote comparison model (MM vs. MV, data not shown), respectively. However, there was no remarkable difference in the incidence of sporadic CJD between the two countries. Thus, these results indicate that another genetically susceptible factor may be involved in susceptibility to sporadic CJD. Previous studies have shown that codon 129 polymorphism of the human PRNP gene in the Asian population has rarely been found in sporadic CJD patients, and the heterozygote of this SNP has been considered to have a resistant effect. Thus, the further estimation of the effect of the M129V SNP combined with the genotype and allele frequencies of the E219K SNP on susceptibility to sporadic CJD is needed in future studies. In addition, to date, since GWAS has not been conducted in the Asian population thus far, a large-scale GWAS consisting of a coalition of Asian countries may be necessary in order to discover novel genetic factors related to susceptibility to sporadic CJD in the Asian population. Furthermore, because the CJD patients used in this study were not subdivided based on the PrPSc banding pattern into subtypes, including MM1, MM2, MV1, MV2, VV1, and VV2, a further analysis conducted according to these subtypes would be highly desirable in the future. In addition, since the present meta-analysis was performed with a relatively small number of a total of 13 studies, a further analysis using a larger number of studies would be highly desirable in the future.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we identified a strong association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD using a meta-analysis for the first time. We validated the eligibility of previous case–control studies and found severe heterogeneity in some previous case–control studies. In addition, we found that the heterozygote comparison model (MM vs. MV) showed the highest risk of susceptibility to sporadic CJD in the meta-analysis. MM homozygote is an especially potent risk factor of sporadic CJD compared to MV heterozygote. To the best of our knowledge, this was the first meta-analysis assessment of the association between the M129V SNP of the PRNP gene and susceptibility to sporadic CJD.
Author Contributions
Y.-C.K. and B.-H.J. conceived and designed the experiment. Y.-C.K. performed the experiments. Y.-C.K. and B.-H.J. analyzed the data. Y.-C.K. and B.-H.J. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Yong-Chan Kim was supported by the BK21 Plus Program in the Department of Bioactive Material Sciences. This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1A6A1A03015876, 2021R1A6A3A010864). This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C1013213). This work was supported by the NRF (National Research Foundation of Korea) Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2019-Fostering Core Leaders of the Future Basic Science Program/Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on reasonable request. Requests may be made to bhjeong@jbnu.ac.kr.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Prusiner, S.B. The prion diseases. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manix, M.; Kalakoti, P.; Henry, M.; Thakur, J.D.; Menger, R.; Guthikonda, B.; Nanda, A. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Updated diagnostic criteria, treatment algorithm, and the utility of brain biopsy. Neurosurg. Focus 2015, 39, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigurdson, C.J.; Bartz, J.C.; Glatzel, M. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Prion Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prion biology and diseases. Harvey Lect. 1991, 87, 85–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Budka, H. Molecular Pathology of Human Prion Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 976–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.-H.; Kim, Y.-S. Genetic Studies in Human Prion Diseases. J. Korean Med Sci. 2014, 29, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gambetti, P.; Cali, I.; Notari, S.; Kong, Q.; Zou, W.-Q.; Surewicz, W.K. Molecular biology and pathology of prion strains in sporadic human prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 121, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, S.; Mead, S.; Collinge, J. Genetics of Prion Disease. Top. Curr. Chem. 2011, 305, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperovitch, A.; Zerr, I.; Pocchiari, M.; Mitrova, E.; Cuesta, J.D.P.; Hegyi, I.; Collins, S.; Kretzschmar, H.; van Dujin, C.; Will, R. Codon 129 prion protein genotype and sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1999, 353, 1673–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, S.; Uphill, J.; Beck, J.; Poulter, M.; Campbell, T.; Lowe, J.; Adamson, G.; Hummerich, H.; Klopp, N.; Rückert, I.-M.; et al. Genome-wide association study in multiple human prion diseases suggests genetic risk factors additional to PRNP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 21, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, E.; Hummerich, H.; Viré, E.; Uphill, J.; Dimitriadis, A.; Speedy, H.; Campbell, T.; Norsworthy, P.; Quinn, L.; Whitfield, J.; et al. Identification of novel risk loci and causal insights for sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2020, 19, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Teruya, K.; Matsuura, Y.; Shirai, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Yamada, M.; Mizusawa, H.; Mohri, S.; Kitamoto, T. The influence of PRNP polymorphisms on human prion disease susceptibility: An update. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 130, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parchi, P.; Giese, A.; Capellari, S.; Brown, P.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.; Windl, O.; Zerr, I.; Budka, H.; Kopp, N.; Piccardo, P.; et al. Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.T.; Pennington, C.; Heath, C.A.; Will, R.G.; Knight, R.S.G. PRNP variation in UK sporadic and variant Creutzfeldt Jakob disease highlights genetic risk factors and a novel non-synonymous polymorphism. BMC Med Genet. 2009, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-Juan, P.; Bishop, M.T.; Croes, E.A.; Knight, R.S.; Will, R.G.; Van Duijn, C.M.; Manson, J.C. A polymorphism in the regulatory region of PRNPis associated with increased risk of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. BMC Med Genet. 2011, 12, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinemann, U.; Krasnianski, A.; Meissner, B.; Varges, D.; Kallenberg, K.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Grasbon-Frodl, E.M.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Zerr, I. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Germany: A prospective 12-year surveillance. Brain 2007, 130, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, V.R.; Gomes, H.R.; Chimelli, L.; Rosemberg, S.; Landemberger, M.C. Prion diseases are undercompulsory notification in Brazil: Surveillance of cases evaluated by biochemicaland/or genetic markers from 2005 to 2007. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2007, 1, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Croes, E.A.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; Bertoli-Avella, A.M.; Rademaker, T.; Vergeer-Drop, J.; Dermaut, B.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Wientjens, D.P.; Hofman, A.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; et al. Polymorphisms in the prion protein gene and in the doppel gene increase susceptibility for Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 12, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, M.; Genuardi, M.; Petraroli, R.; Masullo, C.; D’Alessandro, M.; Pocchiari, M. Polymorphisms of the prion protein gene in Italian patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Hum. Genet. 1994, 94, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinge, J.; Palmer, M.; Dryden, A. Genetic predisposition to iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet 1991, 337, 1441–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh-Ura, K.; Kitamoto, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Tateishi, J. CJD discrepancy. Nature 1991, 353, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.S.; Dryden, A.J.; Hughes, J.T.; Collinge, J. Homozygous prion protein genotype predisposes to sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Nature 1991, 352, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, N.-H.; Jin, J.-K.; Kim, J.-I.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.-S. Association of sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease with homozygous genotypes at PRNP codons 129 and 219 in the Korean population. neurogenetics 2005, 6, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, C.; Parchi, P.; Capellari, S.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Schuur, M.; Strammiello, R.; Corrado, P.; Bishop, M.T.; Van Gool, W.A.; Verbeek, M.M.; et al. Human Prion Diseases in The Netherlands (1998–2009): Clinical, Genetic and Molecular Aspects. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croes, E.A.; Dermaut, B.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Broeck, M.V.D.; Cruts, M.; Breteler, M.M.B.; Hofman, A.; van Broeckhoven, C.; van Duijn, C.M. Early cognitive decline is associated with prion protein codon 129 polymorphism. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, A.; Asano, M.; Mohri, S.; Kitamoto, T. Cross-sequence Transmission of Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Creates a New Prion Strain. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30022–30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Will, R.G.; Ironside, J.W. Sporadic and Infectious Human Prion Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 7, a024364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Brown, P.; Cervenáková, L.; Garruto, R.M.; Alpers, M.P.; Gajdusek, D.C.; Goldfarb, L.G. Increased Susceptibility to Kuru of Carriers of thePRNP129 Methionine/Methionine Genotype. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uttley, L.; Carroll, C.; Wong, R.; Hilton, D.A.; Stevenson, M. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: A systematic review of global incidence, prevalence, infectivity, and incubation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e2–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asante, E.A.; Linehan, J.M.; Desbruslais, M.; Joiner, S.; Gowland, I.; Wood, A.L.; Welch, J.; Hill, A.F.; Lloyd, S.E.; Wadsworth, J.D.; et al. BSE prions propagate as either variant CJD-like or sporadic CJD-like prion strains in transgenic mice expressing human prion protein. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6358–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korth, C.; Kaneko, K.; Groth, D.; Heye, N.; Telling, G.; Mastrianni, J.; Parchi, P.; Gambetti, P.; Will, R.; Ironside, J.; et al. Abbreviated incubation times for human prions in mice expressing a chimeric mouse-human prion protein transgene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4784–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).