Abstract
Swine manure is widely used for ameliorating red soil acidification, but little information is available about its effect on N2O emissions. To explore the effects, a 35-day incubation experiment was conducted with two soils under different fertilization history: chemical fertilizers only (F) and combination of chemical fertilizers with swine manure (M). The treatments included no fertilizer (control), 100% N from urea (M0), and urea plus swine manure, which supplied 20% (M20), 40% (M40), 60% (M60), and 100% (M100) of total N. Soil N2O emission rates, pH, exchangeable acidity, mineral N species, dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen, microbial biomass carbon, and their inner relationships were examined. The N2O emission rates markedly increased following the treatments, reached peaks before day 2, and thereafter decreased sharply to the level of the control by day 25, 25, 23, 15, and 9 in F soil and by day 25, 25, 23, 19, and 11 in M soil for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. As swine manure application rate increased, the cumulative N2O emissions of F soil decreased significantly, while, for M soil, there was no significant difference among M0, M20, M40, and M60 treatments, which were higher than the M100 treatment. At the end of incubation, soil pH in F and M soils followed the order M0 < M20 < M40 < M60 < control < M100 and vice versa for exchangeable Al3+ and acidity. F soil had relatively higher NH4+-N concentration in M0 treatment and higher NO3−-N concentrations in M0 and M20 treatments than M soil. Soil pH and NH4+-N had the greatest relative contribution to N2O emissions. Overall, this study indicates that partial chemical N replacement by swine manure could effectively mitigate N2O emissions from acidic red soil primarily because of mineral N immobilization and alleviated red soil acidification. Thus, swine manure has the potential to co-ameliorate red soil acidification and N2O emission. Further research is needed to determine the effect of swine manure on N2O emission reductions under field conditions and the overall benefit in effective N management.
1. Introduction
Nitrous oxide (N2O), as a potent greenhouse gas, has received great attention due to its atmospheric longevity (about 120 years) and global warming potential (273 times that of CO2 on a per-molecule basis over a 100-year period) [1]. The main source of anthropogenic N2O is agriculture, accounting for 60% of the global N2O emissions due to overuse of nitrogen fertilizers for food production [2]. Acidic soil comprises approximately one-third of the global ice-free land area, and it is the hotspot of global N2O emissions [3,4]. In China, most acidic soil is distributed in the red soil region. Overuse of chemical nitrogen fertilizer has intensified red soil acidification, which seriously limits crop growth in the region [5]. Swine manure rich in alkalinity is widely used for preventing red soil acidification, in addition to introducing a large amount of carbon and other nutrients [6,7,8]. Swine manure’s effect on red soil N2O emissions is not fully understand.
N2O is produced primarily via microbial nitrification and denitrification processes. Swine manure is rich in easily degradable organic carbon, such as soluble organic carbon and volatile fatty acids, which could effectively alleviate the denitrification inhibition caused by the insufficient supply of carbon substrates, which is conducive to promoting N2O production [9,10]. The input of unstable organic materials accompanied with manure could create a more anoxic soil environment and favor N2O production from the denitrification process [11]. In addition, soil pH is recognized as an important factor influencing N2O production by altering microbial-driven N-cycling processes [12,13,14]. For example, Cheng et al. [15] found that organic fertilizer increased acidic red soil N2O emissions due to the soil pH elevation, which reduced the relative proportion of N2O emissions caused by heterotrophic nitrification, but this might be masked by the increase in overall N2O emissions stimulated by carbon input. The effect of pH stimulation on the rate of autotrophic nitrification and NO3− accumulation, as well as the increase in carbon availability, further facilitated the denitrification process [16].
However, opposite results have been obtained regarding the effect of organic fertilizer application on N2O emissions. Li et al. [17] showed that, compared with chemical fertilizer, organic fertilizer amendment could significantly reduce N2O emissions. The possible reasons are that the soil N2O emissions were mainly from the chemical fertilizer nitrogen, rather than the mineralization and transformation of organic matter, while the available nitrogen in the soil after the addition of organic fertilizer was lower than that after inorganic fertilizer treatments [18,19]. Thus, the addition of organic N relative to chemical N could slow the mineralization of soil N for nitrification and denitrification; thus, it had the potential to depress the N losses of N2O. Considerable field investigations have shown that decreasing the amount of chemical fertilizer input and replacing it with organic fertilizer (e.g., manure) could substantially reduce soil N2O emissions [17,18,19]. However, the measurements affected by partial chemical N replacement by manure were not consistent due to substitution rates and soil properties.
The contributions of various combinations of swine manure-N with urea-N and of soil improvement from manure amendment to N2O emissions are not fully clear. The purpose of this study was to determine the potential effects of swine manure as amendment for alleviating red soil acidification on N2O emissions and N transformation processes in comparison with chemical fertilizers only. Therefore, a 35-day incubation experiment was designed to investigate the effect of the proportion gradients of different swine manure to replace chemical nitrogen fertilizer on the acidity of red soil and N2O emissions. Our hypothesis was that the increase in swine manure substitution ratio could effectively mitigate red soil acidification and reduce N2O emissions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
Soils (0–20 cm) used in the study were collected in February 2022 from two different fertilization plots of a long-term (13 years) field experiment located at the Red Soil Experimental Station (26°45′12″ N, 111°52′32″ E, with an altitude of 120 m above sea level) of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Qiyang City, Hunan Province, China. The field experiment was conducted in September 2009, and the cropping system was single spring maize. The fertilization treatments included chemical N, P, and K fertilizers without manure (F), and chemical NPK plus swine manure at 60% of the total N supply (M). The total N application rate was 225 kg N ha−1 year−1. Urea (CH4N2O) (46.6% N) was used as the chemical N fertilizer source. Superphosphate (Ca(H₂PO4)2) (12.5% P2O5) and potassium chloride (KCl) (60.0% K2O) were applied at 33 kg P ha−1 year−1 and 62 kg K ha−1 year−1 to both treatments. All fertilizers were applied to the soil together. Lime (CaO) (71.5% Ca) was applied at rate of 1500 kg ha−1 for F treatment at the end of 2019 due to severe red soil acidification from chemical fertilizers. The study area is a subtropical humid monsoon climate, and the details can be found in Cai et al. [8]. The soil is Ferralic Cambisol according to the FAO or World Soil Classification and derived from quaternary red earth. The soil texture is clay, and the main clay mineral is kaolin. Surface soils (0–20 cm) were collected, air-dried, ground, and sieved to pass through a 2.0-mm sieve for incubation experiment.
The swine manure used for incubation experiment was collected from local farmyards and air-dried. For achieving uniform treatment, the swine manure was ground, sieved to pass through a 2.0-mm sieve, and thoroughly mixed before incubation experiment. Selected chemical properties of the soils and the swine manure are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Selected chemical properties of the soils and the swine manure.
2.2. Experimental Design and Incubation Procedure
Two soils (F and M) were respectively set up with 6 treatments: (1) no fertilizer (Control), (2) 100% chemical fertilizer nitrogen (M0), (3) 20% N from manure and 80% N from chemical N (M20), (4) 40% N from manure and 60% N from chemical N (M40), (5) 60% N from manure and 40% N from chemical N (M60), and (6) 100% N from manure (M100). An amount of air-dried soil equivalent to 1.5 kg of oven-dried soil was weighed in a sterilized glass bottle (2500 mL volume capacity) for 36 duplicates. These soil samples were moistened to 60% water holding capacity by DI water. The bottles were pre-incubated in a constant-temperature and -humidity incubator (HSP-350B Kuntian, Shanghai, China) at 25 ± 1 °C for 21 days to recover microbial activity. The urea and manure were added to reach the final treatment rates, respectively. The soil, urea, and manure were thoroughly mixed, and the soil water content was adjusted to 20% (w/w), equivalent to 80% of water holding capacity (25%, w/w). Then, the bottles continued to incubate for 35 days. Each bottle was sealed with PM996 sealing film and was equipped with 30 small pinholes to reduce water loss during gas exchange. During the incubation, the weight of each bottle was recorded every 2 or 3 days to calculate the water lost through evaporation, and DI water was added to soil.
2.3. Gas Sampling and Analysis
Gas samples were collected on days 0, 0.25, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 28, 30, and 35 after adding fertilizers. Prior to gas sampling, the sealing film was removed so that it was in equilibrium with the surrounding air for 30 min, and then the bottle was sealed with a rubber cork with a glass tube (diameter 4.6 mm) at a 120° angle at the top, which connected to a rubber tube and a three-way valve for gas sampling. The gas samples were collected in 12.5 mL vacuum glass bottles with a 30 mL syringe at 0, 1, and 2 h after sealing. The concentrations of N2O were determined using a meteorological chromatograph (Agilent Technologies 7890A, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). The N2O emission rate was calculated by the following formula [20]:
is the N2O emission rate (μg kg−1 h−1), is the N2O density under the standard condition (kg m−3), is the volume of gas in the incubation bottle (m3), is the mass of drying soil in the incubation bottle (kg), is the change in N2O concentration during the sealing time (ppm), is the sealing time (h), and is the incubation temperature (25 °C).
denotes the cumulative N2O emissions (μg kg−1), and and are the N2O emission rates at time and , respectively.
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
Soil samples were collected on days 0, 0.25, 1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 15, 21, 28, and 35 after fertilizer addition. The soil in the incubation bottle was thoroughly mixed with a long-handled stainless-steel weighing spoon before sampling, and then 50 g of soil was taken for soil property analysis. Soil ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) were extracted with 2 mol L−1 KCl and analyzed by a flow injection analyzer (SEAL Auto Analyzer AA3, Norderstedt, Germany) [21]. Soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) was estimated using the chloroform–fumigation–extraction method [22]. Soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) and nitrogen (DON) were extracted with 0.5 mol L−1 K2SO4 solution [23]. MBC, DOC, and DON were analyzed by a total organic carbon analyzer (multi N/C 3100 Analityk Jena, Germany). Soil pH was determined by a pH meter (FE28, Mettler, Toledo, OH, USA) with a mixture of soil and water at a ratio of 1:2.5 (soil-to-water ratio) [24]. For total exchangeable acidity (Al3+ and H+), soils were extracted with 1 mol L−1 KCl, and then titrated with 0.02 mol L−1 NaOH to phenolphthalein endpoint [25].
2.5. Data Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the independent-sample Duncan test were conducted to compare differences in mean N2O emissions and soil properties among different treatments at a significant level of 0.05 by SPSS v. 19.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Pearson correlation analysis was used to calculate correlation coefficients between N2O emissions and soil properties by Origin 2023 (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA). All figures and tables were created using SigmaPlot 10.0 and Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). All the data are presented as the mean plus or minus standard error.
3. Results
3.1. N2O Emission
There were no significant changes in N2O emissions from no fertilizer (control) of the F and M soils throughout the whole incubation period. However, the N2O emission rates of F soil were markedly increased following fertilization and reached the peaks by day 0.25 for M40, M60, and M100 treatments, and by day 1 and day 2 for M20 and M0 treatment, respectively, indicating that the peaks significantly increased with the manure application rate (p < 0.05). For M100 treatment, the N2O emission rates decreased sharply thereafter (p < 0.05), in spite of some fluctuation between 0.58 and 0.77 μg kg−1 h−1 during days 1 to 5, and further decreased to 0.03–0.06 μg kg−1 h−1 after day 9, becoming similar to the control. For M40 and M60 treatments, a further decrease in N2O emission rates was observed by day 15 and 11, respectively (p < 0.05). The second peaks were found by day 7 and 15 for M0 and M20 treatments, respectively, and a further decrease was observed after day 19 (p < 0.05). For M soil, the peaks of N2O emission rates were observed by day 0.25 in all fertilization treatments and decreased sharply (p < 0.05) thereafter to the level of the control by 25, 25, 23, 19, and 11 in M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively (Figure 1).
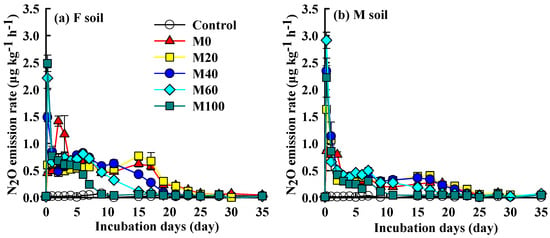
Figure 1.
Change in nitrous oxide emission rates of the red soils after different fertilizations. The initial soils were from two fertilization treatments of a long-term field experiment. (a) F soil N2O emission rate, (b) M soil N2O emission rate. Error bars are the standard error of the mean.
The cumulative N2O emissions showed a significant difference among treatments and soils. As compared with the control, all fertilization treatments significantly increased the cumulative N2O emissions for both soils. For F soil, the cumulative N2O emissions decreased with the increase in manure application rates. At the end of incubation, the highest (282.17 μg kg−1) cumulative N2O emissions were observed in M0 treatment, and the lowest (146.81 μg kg−1) were found in M100 treatment. For M soil, there was no significant difference among M0, M20, M40, and M60 treatments, which were higher than the M100 treatment (Figure 2).
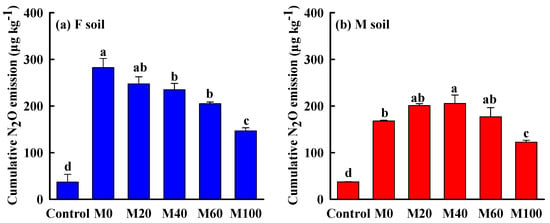
Figure 2.
Change in cumulative N2O emissions of the red soils after different fertilizations. (a) F soil cumulative N2O emission, (b) M soil cumulative N2O emission. Error bars are the standard error of the mean. Different letters indicate a significant (p < 0.05) difference between the treatments and soils.
3.2. Soil pH Change
The changes in soil pH during the study period are shown in Figure 3. Soil pH was significantly affected by application rates of swine manure in both the F and the M soils. Without fertilizer addition (control), the soil pH showed no change throughout the incubation period. As compared with the control, soil pH significantly increased for all fertilization treatments of the two soils at the beginning of the incubation experiment (p < 0.05). Thereafter, F soil pH significantly decreased (p < 0.05) and then stabilized by days 28, 21, 15, 11, and 7, and the stable pH was 4.58, 4.79, 4.99, 5.27, and 5.78 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. In M soil, it took 28, 21, 15, 11, and 5 days to reach the stable pH of 4.63, 4.74, 4.97, 5.25, and 5.81 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. For both soils, the final pH significantly increased with swine manure application rates (p < 0.05), and the M100 treatment had much higher soil pH than the control treatment (p < 0.05). At the end of incubation, the pH of soils followed the order M0 < M20 < M40 < M60 < control < M100, and there was no significant difference between the F and the M soil at the same fertilization application rates in the incubation study.
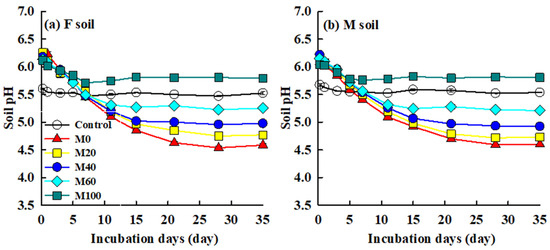
Figure 3.
Change in pH of the red soils after different fertilizations. (a) F soil pH, (b) M soil pH.The initial soils were from two long-term field fertilization treatments. Error bars are the standard error of the mean.
3.3. Soil Exchangeable Acidity
The exchangeable H+ and Al3+ and the acidity differed between the two soils and were also significantly affected by swine manure application rates (Figure 4). After 35-day incubation, the exchangeable H+ and Al3+ and the acidity of the two soils significantly decreased as the swine manure application rate increased. The highest exchangeable H+ was found in the M0 treatment of M soil. As compared to the control, exchangeable H+ increased by 33.33% in the M0 treatment of F soil (p < 0.05), and increased by 51.67% and 26.67% for the M0 and M20 treatments of M soil, respectively (p < 0.05) (Figure 4a,b). The exchangeable H+ of the M0 and M20 treatments of M soil was much higher compared to F soil (p < 0.05).
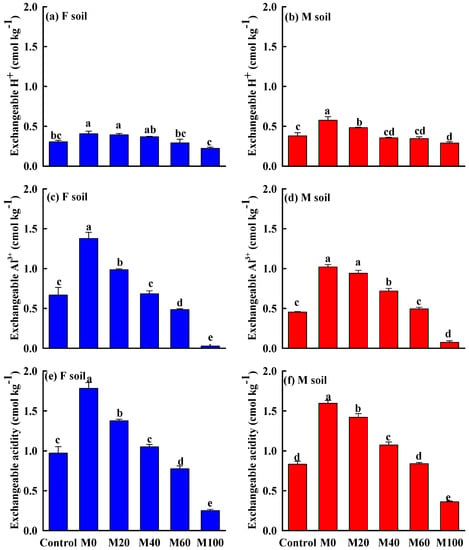
Figure 4.
Change in exchangeable acidity of the red soils after different fertilizations. (a) F soil exchangeable H+, (b) M soil exchangeable H+, (c) F soil exchangeable Al3+, (d) M soil exchangeable Al3+, (e) F soil exchangeable acidity, (f) M soil exchangeable acidity. Error bars are the standard error of the mean. Different letters indicate a significant (p < 0.05) difference between the treatments and soils.
There was the same change trend in exchangeable Al3+ and acidity of the two soils (Figure 4c–f). The highest exchangeable Al3+ and acidity were both observed in M0 of F soil. As compared with the control, the M0 and M20 treatments of F soil increased exchangeable Al3+ and acidity by 46.99–105.60% and 42.01–83.80% (p < 0.05); the M0, M20, and M40 treatments of M soil increased exchangeable Al3+ and acidity by 59.74–126.59% and 29.34–92.29% (p < 0.05). There were no significant differences in exchangeable Al3+ or acidity between the control and M40 for F soil, and between the control and M60 for M soil. The M60 and M100 treatments had much lower concentrations of exchangeable Al3+ and acidity than the control treatment of F soil. For M soil, the lowest exchangeable Al3+ and acidity were observed in the M100 treatment.
3.4. Soil Mineral Nitrogen Change
The changes in soil mineral N species (NH4+-N and NO3−-N) during the 35-day incubation experiment are shown in Figure 5. Soil N species were significantly affected by the application rates of swine manure in both the F and the M soils. Without fertilizer addition (control), NH4+-N and NO3−-N of the two soils showed no change throughout the incubation period. As compared to the control, soil NH4+-N significantly increased for all fertilization treatments of the two soils at the beginning of the incubation experiment (p < 0.05). The peak NH4+-N concentration of both F and M soils decreased as the swine manure application rate increased. Thereafter, the NH4+-N of F soil significantly decreased to the level of the control by days 28, 21, 15, 11, and 7 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. In M soil, it took 28, 21, 15, 11, and 5 days to decrease to the level of the control for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. The concentration of NH4+-N in the M0 treatment of F soil was higher than that from M soil until day 11 (Figure 5a,b).
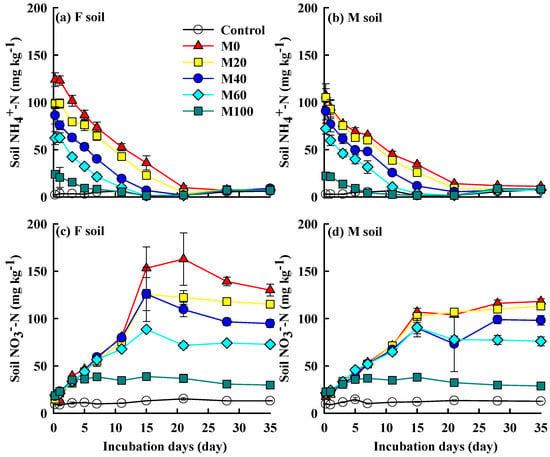
Figure 5.
Change in mineral nitrogen species of the red soils after different fertilizations. (a) F soil NH4+-N, (b) M soil NH4+-N, (c) F soil NO3−-N, (d) M soil NO3−-N. The initial soils were from two long-term field fertilization treatments. Error bars are the standard error of the mean.
A decrease in soil NH4+-N concentration was accompanied by an increase in NO3—N concentration indicating nitrification. Soil NO3—N concentration significantly increased for all fertilization treatments of the two soils following addition and stabilized by days 15, 15, 15, 15, and 3 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively (p < 0.05). The stable NO3−-N concentrations of F soil were 146.3, 120.3, 106.7, 76.8, and 35.0 mg kg−1 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. In M soil, the stable NO3−-N concentrations were 111.3, 108.1, 90.0, 64.7, and 33.3 mg kg−1 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. The stable NO3−-N concentrations of M0 and M20 in F soil were higher than those from M soil at the same fertilization (Figure 5c,d).
3.5. Soil Dissolved Organic Carbon and Nitrogen, and Microbial Biomass Carbon
Soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations increased firstly and then stabilized as the incubation time increase. The increase rates of DOC in F soil were 2.30–3.63 mg kg−1 d−1 in the first 15 days, and slightly decreased in days 15–21. Soil DOC of M40, M60, and M100 treatments were stable at 133.08–152.97 mg kg−1 after day 21, and the concentration increased with the swine manure application rate (p < 0.05). Soil DOC in the control treatment increased by 15.32% in the first 7 days and then stabilized around 124.10 mg kg−1. For M soil, DOC of M20, M40, M60, and M100 increased by 24.40–31.21% as compared with the initial values (p < 0.05), and then decreased slightly after 21 days. The DOC of the control and M0 treatments in the M soil continued to increase throughout the incubation period and increased by 18.14% and 44.85% as compared to initial value. At the end of the incubation experiment, the final concentrations of DOC increased with swine manure application rates (p < 0.05), and the highest was found in the M100 treatment. The soil DOC of F soil was higher than that from M soil for the same fertilization treatments (Figure 6a,b).
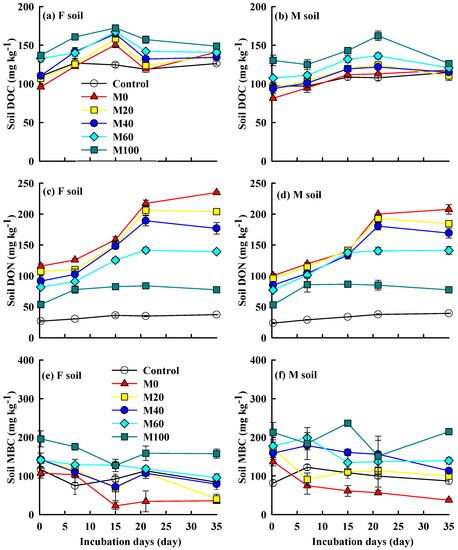
Figure 6.
Changes in DOC, DON, and MBC of the red soils after different fertilizations. (a) F soil DOC, (b) M soil DOC, (c) F soil DON, (d) M soil DON, (e) F soil MBC, (f) M soil MBC. The initial soils were from two long-term field fertilization treatments. Error bars are the standard error of the mean.
There was a similar trend in soil dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) concentrations to DOC concentrations. There were no significant changes in DON concentrations of the control treatment for both F and M soils. DON concentrations in all fertilization treatments for both F and M soils increased first (p < 0.05) and then stabilized by days 21, 21, 21, 21, and 7 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. The highest DON concentrations of F soil were 226.1, 205.1, 183.0, 140.4, and 80.5 mg kg−1 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. In M soil, the stable DON concentrations were 203.8, 188.7, 174.8, 140.8, and 83.7 mg kg−1 for M0, M20, M40, M60, and M100 treatments, respectively. The stable DON concentrations of M0 and M20 in F soil were higher than those from M soil at the same fertilization treatments (Figure 6c,d).
The soil microbial biomass carbon (MBC) content fluctuated greatly and increased with the swine manure application rate. After 35-day incubation, the MBC of M100 was significantly higher than that from other treatments. The soil MBC in M soil was higher than that from F soil for the same fertilization treatments (Figure 6e,f).
3.6. Relationship between N2O Emission and Soil Properties
The N2O emission rate was positively correlated with soil pH, NH4+-N, and MBC, and the correlation coefficients were 0.59, 0.54, and 0.27, respectively (p < 0.001). The N2O emission rate was significantly negatively correlated with soil NO3—N, DON, and DOC, and the correlation coefficients were −0.46, −0.44 (p < 0.001), and −0.18 (p < 0.05), respectively. There was no significant correlation between N2O emission rate and MN (manure nitrogen) (Figure 7a). The results of random forest statistics showed that soil pH had the greatest relative contribution to N2O emissions followed by NH4+-N, while MBC had the lowest impact (Figure 7b).
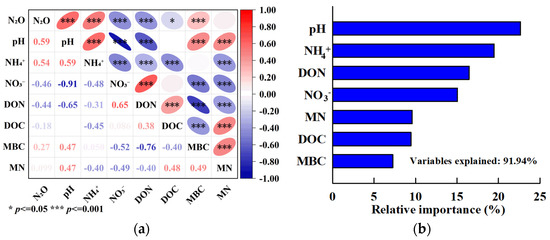
Figure 7.
Relationship and relative contribution of soil properties to N2O emission. (a) Relationship between soil properties and N2O emission, (b) relative importance of soil properties to N2O emission.
4. Discussion
4.1. Difference in N2O Emmision between the Two Soils
The current study showed that the cumulative N2O emissions of M0 and M20 treatments in F soil significantly increased by 23.24–68.25% (p < 0.05) compared with that from M soil (Figure 2). A possible reason was the reduction in soil NH4+-N and NO3−-N due to microbial assimilation from long-term carbon input in M soil [18,19]. In this study, more than 90% N2O of fertilization treatments were released within the first 21 days of incubation period, implying that a substantial amount of N2O was produced through nitrification process. Swine manure as an organic carbon substrate for microbial growth could promote the assimilation of microbial nitrogen, which led to an intense competition for NH4+-N between heterotrophic microorganisms and autotrophic nitrifiers, resulting in a decrease in N2O production [26]. Studies have shown that a combination with organic fertilizers could enhance the microbial immobilization [27,28] and reduce the soil nitrogen availability for N2O production [29]. Bhattacharyya et al. [30] also reported that a combined application of chemical and organic N reduced the conversion of fertilizer N to soil ammonium and nitrate by 20% as compared to chemical fertilizers only. Yao et al. [31] pointed out through meta-analysis that organic fertilizers decreased N2O emissions because of the limitation of the readily available nitrogen substrates.
The N transformation data in the current study also confirmed microbial assimilation as the concentration of NH4+-N in M0 treatment of M soil was lower than that from F soil (Figure 5a,b), and the NO3−-N concentrations of M0 and M20 in M soil were also lower than those from F soil (Figure 5c,d). The M soil with long-term swine manure application history had a relatively higher TOC and C/N ratio than F soil (Table 1), which might stimulate microbial immobilization, and it had reduced N2O production from nitrification compared to F soil. A high proportion of chemical nitrogen fertilizer (M0 and M20) was conducive to promoting the immobilization of nitrogen by microorganisms, thus reducing available nitrogen for nitrification and denitrification and, therefore, N2O emissions [32]. Huang et al. [33] also showed that soil N2O emission had a negative relationship with C/N.
4.2. Partial Chemical N Replacement by Swine Manure Mitigating Red Soil N2O Emission
This study showed that the cumulative N2O emission decreased with the increase in manure application rates, and a significant difference between F and M soils disappeared as the swine manure application rate increased to 40% (M40), 60% (M60), and 100% (M100) of total N (Figure 2). A possible reason is that the soil N2O emissions mainly came from hydrolysis and nitrification of urea-N rather than mineralization and transformation of swine manure-N [18]. In the current study, the relative importance of soil NH4+-N concentration to N2O production was only lower than that of pH (Figure 7). The ammonification of organic N within swine manure was much harder than that of hydrolysis of urea, and partial chemical N replacement by swine manure markedly decreased soil NH4+-N concentration, which substantially reduced the nitrification process, supported by a much lower NO3−-N concentration in swine manure amendment treatments. A decrease in soil NH4+-N showed a lack of nitrification substrate, which resulted in a significant reduction in N2O emissions [19]. The lower soil NH4+-N concentration resulting from an increased swine manure substitution ratio decreased soil N2O emissions at the initial stage. This is consistent with the results reported by Duan et al. [34], where N2O emissions from nitrification in chemical nitrogen treatments were significantly higher than manure treatments.
In addition, the increased swine manure substitution ratio resulting in prevailing anoxic conditions might facilitate dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium [35], resulting in a decrease in soil NO3− concentrations (Figure 5). The N transformation data also suggested that NO3− production through nitrification could have been impeded by O2 limitations in the present study. Under the prevailing reductive soil conditions, denitrifiers might easily assimilate the highly reactive N2O as an electron-acceptor or nitrogen source [36], thus lowering N2O emissions with manure substitution. Xia et al. [37] showed that the combined application of synthetic and organic nitrogen fertilizers promoted the reduction of N2O to N2 during denitrification due to the supply of dissolved organic carbon by organic fertilizer addition.
In addition to a reduction in mineral N, soil pH was one of the most important factors for N2O production, influencing nitrification, nutrient conversion, and microbial community structure in the soil [38,39]. Soil pH increased by 0.13–1.21 units after swine manure amendment (Figure 3). The increase in soil pH could enhance the activity of N2O reductase encoded by nosZ gene, as well as promote the reduction of N2O to N2 [40]. Therefore, N2O production decreased as the swine manure application rate increased (Figure 1). The abundance of N2O-related bacteria might have also increased with the elevation of soil pH [41]; however, more N2O-consuming bacteria could have dominated over the N2O-producing bacteria and then eventually resulted in a net decrease in bacterial N2O emission with more manure addition in this study. Wang et al. [3] also pointed out that, under the same N input, the N2O emissions of acidic soil were higher than those of alkaline soil. Acidic conditions might favor the growth of fungal populations lacking N2O reductase, terminating at N2O. Therefore, the inhibition of N2O reductase activity during bacterial denitrification under low-pH conditions might have been another reason for the high N2O emissions [42]. In this study, the manure rich in alkalinity addition increased the soil pH; therefore, the increased N2O reductase activity decreased the N2O emissions [43]. In addition, higher soil pH might suppress the nitrate reductase activity that converted NO3− into NO2− and then decreased N2O emissions [20].
In the future, it is still necessary to further explore the effects of adding different amounts of swine manure on soil carbon and nitrogen conversion processes and greenhouse gas emissions through isotope tracer technology, and study the community composition, abundance of key nitrogen-related microorganisms, and related enzymes in the process of nitrification and denitrification of red soil by applying organic materials combined with molecular study. This can provide technical support for the efficient use of nitrogen fertilizer in red soil production systems, reduce nitrogen gas loss, leaching loss, and environmental risks, and provide a scientific basis for nutrient management of red soil and improvement of soil cultivated land quality.
5. Conclusions
Our data indicated that partial chemical N replacement by swine manure could effectively mitigate N2O emissions from acidic red soil primarily because of mineral N immobilization and alleviated red soil acidification. Thus, swine manure has the potential to co-ameliorate red soil acidification and N2O emission. Further research is needed to determine the effect of swine manure on N2O emission reductions and related enzymes under field conditions and the overall benefits in effective N management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and H.Z.; methodology, L.Z., M.A.A. and N.A.D.; resources, T.R. and S.W.; data curation, L.Z., J.L. and K.A.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, T.R. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, S.W. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2021FY100504), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD1900605), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-Profit Scientific Institution (1610132020024), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42207398).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pirani, A., Connors, S.L., Péan, C., Berger, S., Caud, N., Chen, Y., Goldfarb, L., Gomis, M.I., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Lu, C.; Canadell, J.G.; Davidson, E.A.; Jackson, R.B.; Arneth, A.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P. Global soil nitrous oxide emissions since the preindustrial era estimated by an ensemble of terrestrial biosphere models: Magnitude, attribution, and uncertainty. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Guo, J.H.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, X.S. Soil pH as the chief modifier for regional nitrous oxide emissions: New evidence and implications for global estimates and mitigation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Tu, X.S.; Chen, Z.X.; Elrys, A.S.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, L.F. A shift from nitrification to denitrification dominated N2O emission in an acidic soil following organic amendment. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, H.M.; He, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, S. Intensified soil acidification from chemical N fertilization and prevention by manure in an 18-year field experiment in the red soil of southern China. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Xu, M.G.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.L.; Gao, S.D. Effectiveness of crop straws, and swine manure in ameliorating acidic red soils: A laboratory study. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2893–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.J.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.L.; Xu, M.G.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Carswell, A.M.; Gao, S.D. Striking a balance between N sources: Mitigating soil acidification and accumulation of phosphorous and heavy metals from manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velthof, G.L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Oenema, O. Nitrous oxide emission from animal manures applied to soil under controlled conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 37, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, S.J.; Zhu, X.Y.; Vereecken, H.; Brüggemann, N. Stimulation of N2O emission by manure application to agricultural soils may largely offset carbon benefits: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4068–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimek, M.; Cooper, J.E. The influence of soil pH on denitrification: Progress towards the understanding of this interaction over the last 50 years. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 53, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M.; Smales, C.L.; Bateman, E.J. Changing pH shifts the microbial source as well as the magnitude of N2O emission from soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.M.; Su, Q.X.; Ma, Y.J.; Valverde-Perez, B.; Domingo-Felez, C.; Jensen, M.M.; Smets, B.F. The pH dependency of N-converting enzymatic processes, pathways and microbes: Effect on net N2O production. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggar, S.; Jha, N.; Deslippe, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Luo, J.; Giltrap, D.L.; Kim, D.-G.; Zaman, M.; Tillman, R.W. Denitrification and N2O:N2 production in temperate grasslands: Processes, measurements, modelling and mitigating negative impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z.J.; Sun, N.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.B.; Chang, S.X.; Xu, M.G.; et al. Contrasting effects of different pH-raising materials on N2O emissions in acidic upland soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavo, P.; Richaume, A.; Lafolie, F. Fate of nitrogen and carbon in the vadose zone: In situ and laboratory measurements of seasonal variations in aerobic respiratory and denitrifying activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 36, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Tang, J.W.; Che, S.G.; Wen, Y.C.; Sun, W.Y.; Zhao, B.Q. Effect of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizer on the Emission of CO2 and N2O from the Summer Maize Field in the North China Plain. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 4381–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.X.; Luo, J.F.; Li, J.; Yu, H.Y.; Fan, J.L.; Liu, D.Y. Effect of long-term compost and inorganic fertilizer application on background N2O and fertilizer-induced N2O emissions from an intensively cultivated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.Y.; Fujii, T.; Morioto, S.; Lin, X.G.; Yagi, K. Population size and specific nitrification potential of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacteria under long-term fertilizer management. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1960–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aamer, M.; Chattha, M.B.; Mahmood, A.; Naqve, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Shaaban, M.; Rasul, F.; Batool, M.; Rasheed, A.; Tang, H.Y.; et al. Rice Residue-Based Biochar Mitigates N2O Emission from Acid Red Soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Cao, G.X.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.Q.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Shen, J.B.; Jiang, R.F.; et al. Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 2016, 537, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Willett, V. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.G. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Agronomy Monographs; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 3 Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.L.; Jin, Y.G.; Yu, K.; Swaney, D.P.; Liu, S.W.; Zou, J.W. Low N2O emissions from wheat in a wheat-rice double cropping system due to manure substitution are associated with changes in the abundance of functional microbes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.Y.; Chen, D.L. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and soil carbon balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Fang, Q.C.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.Q.; Velthof, G.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F.S. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Z.Y.; Abdalla, M.; Xia, L.L.; Zhou, F.; Sun, W.J.; Smith, P. Can cropland management practices lower net greenhouse emissions without compromising yield? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 4657–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Nayak, A.K.; Mohanty, S.; Tripathi, R.; Shahid, M.; Kumar, A.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.B.; Roy, K.S.; Neogi, S.; et al. Greenhouse gas emission in relation to labile soil C, N pools and functional microbial diversity as influenced by 39 years long-term fertilizer management in tropical rice. Soil Till. Res. 2013, 129, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.C.; Wu, X.W.; Bai, H.; Gu, J.X. Nitrous oxide emission and grain yield in Chinese winter wheat–summer maize rotation: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.B.; Song, K.F.; Miao, X.; Huang, Q.; Ma, J.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Paustian, K.; Yan, X.Y.; Xu, H. Nitrous oxide emissions, ammonia volatilization, and grain-heavy metal levels during the wheat season: Effect of partial organic substitution for chemical fertilizer. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 311, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zou, J.W.; Zheng, X.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Xu, X.K. Nitrous oxide emissions as influenced by amendment of plant residues with different C:N ratios. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.P.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, Z.Q. Mechanisms of mitigating nitrous oxide emissions from vegetable soil varied with manure, biochar and nitrification inhibitors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 278, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.B.; Müller, C.; Cai, Z.C. Mechanisms of soil N dynamics following long-term application of organic fertilizers to subtropical rain-fed purple soil in China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 91, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Garcia-Torres, L.; Van Groenigen, J.W.; Vallejo, A. Role of maize stover incorporation on nitrogen oxide emissions in a non-irrigated Mediterranean barley field. Plant Soil 2013, 364, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.L.; Lam, S.K.; Wolf, B.; Kiese, R.; Chen, D.L.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Trade-offs between soil carbon sequestration and reactive nitrogen losses under straw return in global agroecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 5919–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, J.; Almøy, T.; Bakken, L.R. Excessive use of nitrogen in Chinese agriculture results in high N2O/(N2O+N2) product ratio of denitrification, primarily due to acidification of the soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 1685–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gao, Q.; Yan, L. Nitrogen application effect on maize yield, NH3, and N2O emissions in Northeast China by meta-analysis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.P.; Khalid, M.S.; Peng, Q.A.; Xu, X.Y.; Wu, L.; Younas, A.; Bashir, S.; Mo, Y.L.; Lin, S.; et al. Reduction in soil N2O emissions by pH manipulation and enhanced nosZ gene transcription under different water regimes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Roux, X.L.; Wang, C.P.; Gu, Z.K.; An, M.; Nan, H.Y.; Chen, B.Z.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.J.; Du, G.Z.; et al. Identifying response groups of soil nitrifiers and denitrifiers to grazing and associated soil environmental drivers in Tibetan alpine meadows. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Han, Z.Q.; Zheng, F.W.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, S.W.; Li, S.Q.; et al. Biochar reduced soil nitrous oxide emissions through suppressing fungal denitrification and affecting fungal community assembly in a subtropical tea plantation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).