Abstract
Straw returning is an environmentally friendly method to improve soil health and agricultural productivity by reusing organic waste products. However, fields are often also treated with inorganic fertilizers, and the effect of the interaction between phosphate fertilizer application and straw return on crop yield remains unclear. Therefore, a full-factorial, two-year field experiment was conducted on sweet corn (NARC-16 in late 2021 and Kashmeri-19 in early 2022) to explore how crop yield may be optimized by combining straw return with efficient phosphate fertilization. The experiment involved the application of DAP, SSP, and NP (three different types of phosphates) and the application of crop waste byproducts, namely the residual stover left after sorghum and maize harvesting. We compared control fields with no crop waste or phosphate addition (CR0 and PS0) to experimental plots treated with various phosphates and straw return. Growth parameters such as days to emergence, tasseling, silking and maturity, emergence rate (emergence m−2), height of plant, number of leaves, leaf area per plant, and yield were evaluated, and the influence of the treatment on the economic value of crops was estimated. Phosphorus and straw return were applied at rates of 90 kg per hectare and 5 tons per hectare, respectively. The best P-crop straw combination treatment involved DAP (90 kg ha−1) with the incorporation of 5 tons’ ha−1 of maize straw, which resulted in delayed tasseling (50 days), early silking (68 days), taller plants (178 cm), improved thousand-grain weight (233 g), maximum biological yield (11,349 kg ha−1) and grain yield (3760 kg ha−1). The application of DAP with maize straw return resulted in the highest plant height, biological yield, and grain yield of sweet corn during the second year of the experiment, despite the first year’s yield being influenced by a natural disaster. This combined management strategy (using either DAP or crop residuals) was found to have a more a favorable cost–benefit ratio (BCR) efficiency. In conclusion, increasing the use of crop residuals can help reduce the expensive application of synthetic mineral fertilizers like SSP and NP, while significantly increasing sweet corn production and improving profit margins. Considering the importance of environmental friendliness and sustainable agriculture, the combined use of DAP and straw return is considered a viable method.
1. Introduction
Sweet corn (Zea mays var. saccharata, var. rugosa) is a genetically distinct maize type with a high sugar content in the kernels due to a variation that alters the conversion of sugar to starch during maturation [1]. This sweet corn crop is genetically different from field simple corn crop, but not in terms of organization or taxonomic classification [2]. The use of sweet corn and its residuals have dramatically increased worldwide over the last thirty years. The main products are the sweet corn pericarp and its endosperm tissue. Since the endosperm contains both sugar and starch, it has a syrupy flavor until it matures and becomes drier than other corn forms [3]. Sweet corn is a profitable crop due to its higher market value compared to other common corn varieties. However, successful production requires proper management and marketing. Strong market linkages and a solid understanding of consumer preferences can help farmers maximize their income from sweet corn production. Effective management practices include choosing suitable varieties, timely planting and harvesting, and implementing pest and disease control measures. Management can make an important difference in the profit margins of maize production, and optimizing yield necessitates optimizing management—particularly in the form of fertilization.
Phosphorus (P) is an essential macronutrient necessary for plant growth and development, as it is involved in various physiological processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and energy transfer [4]. It is vital for the production of nucleic acids, phospholipids, and ATP, which are necessary for cell division, DNA replication, and energy storage and transfer [3]. P is considered the second most important nutrient after nitrogen for enhancing crop production [5], and an adequate supply of P is necessary for proper root development, plant growth, and an optimal crop yield. Without adequate P, plants may experience stunted growth, reduced yield, and lower quality produce [6]. P has a significant effect on the physiological traits of crops, including leaf area, plant height, leaf production per plant, and disease tolerance [7]. Moreover, it aids in the rapid formation and expansion of roots, enhancing crop tolerance to agricultural diseases [8]. However, P deficiency in soils is a widespread issue that limits crop production and global food security [9]. Thus, the use of P fertilizers is essential to replenish P levels in soils and meet the nutritional demands of crops [3]. Nevertheless, recent studies have shown that excessive P addition does not increase light-saturated photosynthesis rates or growth rates of understory plants. In fact, P addition significantly decreases the survival rate of seedlings and has been shown to reduce species richness and density of understory plants. Furthermore, excessive P addition can have negative impacts on surface water and increase the production of ozone-harming chemicals that disrupt the functioning of biological systems [10]. Additionally, excessive P can run off into nearby bodies of water, leading to an overgrowth of algae and pathogenic bacteria that reduce oxygen levels in the water and make it unsafe for drinking or recreation [11]. Therefore, it is crucial to determine the current P levels in the soil, the adequate P levels needed by the crop, and the amount of fertilizer that should be applied to the soil to meet the crop’s optimal P needs before suggesting a P fertilizer. These results emphasize the need to consider the effects of P addition not only on individual plants but also on the functioning and diversity of plant communities [12].
One option for mitigating our reliance on inorganic phosphorus fertilizers is the integration of crop waste residuals to improve soil nutrient quality. Plants can obtain a variety of nutrients through recycling by using crop waste [13]. Crop leftovers preserve the biological and physical qualities of the soil and shield it from soil and water degradation [14]. The remaining plant material aids in nutrient recycling [13]. Generally, the husk of maize or sorghum residuals are largely recycled as animal feed or returned to the soil as a natural fertilizer. The remaining straw is typically burned in the open air [15]. However, the incorporation of agricultural residues containing organic nitrogen or other natural substances as a substitute for fertilizer has been shown to improve soil fertility, heat, bulk density, progressive growth, humidity, hydraulic properties, and ultimately increase crop production while reducing our reliance on synthetic fertilizers [16]. Ideally, this management design can improve biomass production, humification of biomass back into the soil, deep-C movement into the earth through bioturbation, deep root system development, and organomineral structure formation, ultimately improving soil fertility [17]. In experiments where organic waste and inorganic nutrients have been applied together, the combinatorial effect is greater than the positive influence of each separate component [18]. In many agricultural countries, the accumulation of agricultural waste has been carelessly managed, which can have an impact on grain yields [19,20]. An appropriate amount of plant waste helps to protect plants from habitation, increases leaf area and chlorophyll concentration, and significantly increases yield when compared to the total amount of returning stover [21].
Application of organic nutrient sources can lessen reliance on pricey chemical P fertilizers, either by releasing organic acids to solubilize preserved insoluble soil P or by replacing them with cost-effective and environmentally friendly natural P sources like agricultural crop wastes. Previous research has shown that applying phosphorus sources together with plant residues like sarson and sesbania together can improve soil quality [22]. Similarly, joint applications of sugarcane filter mud (SFM) [23], and chicken manure [24] have been shown to crop brassica residues, and household waste have all been shown to have a positive impact on plant growth and yield. However, no one has yet evaluated the joint and combinatorial influence of phosphorus and crop stover application in the form of mulch (henceforth, straw return). The purpose of this study was to evaluate whether a combination of phosphorus sources and crop residues could be efficient for the enhancement, development and yield of sweet corn. To accomplish this, we conducted an experiment on a small plot of land and examined the potential benefits of this approach. We hypothesized that this approach could be a more cost-effective substitute which reduces our reliance on artificial expensive fertilizers. One of the top phosphate-producing nations is Brazil, which generated 5.5 million metric tons of phosphate in 2021, less than it did in 2020 (6 million metric tons).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
The present study employed a factorial design with three replications over a two-year period to investigate the effects of two factors: phosphates and plant stover. The first factor comprised three different types of phosphates—triple superphosphate (SSP), ammonium phosphate (NP), and diammonium phosphate (DAP). The second factor examined the influence of crop residue on the experimental outcomes, namely stover residue from sorghum and from maize. The experiment was constructed as a random complete block design to reduce any potential bias. The crop residues, sorghum and maize, with different C/N ratios (70:1 and 19:1), respectively, were applied at a rate of 5 tons per hectare to the field before sowing. A free treatment plot was included as a control for comparison. The experimental design consisted of plots that were 4 × 5 m in size, wherein row-row space of plants was 0.75 m and plant–plant space of crop was 0.25 m. The crop straw was first chopped and then left in the field for one month and incorporated into the soil. The application rates were based on the mean data of the crops and recommendations from previous studies conducted by [25,26,27]. The characteristics of experimental soil are shown in Table 1. The specific meteorological data from March to November is supported in Figure 1.

Table 1.
Physiochemical properties of the soil used in this experiment.
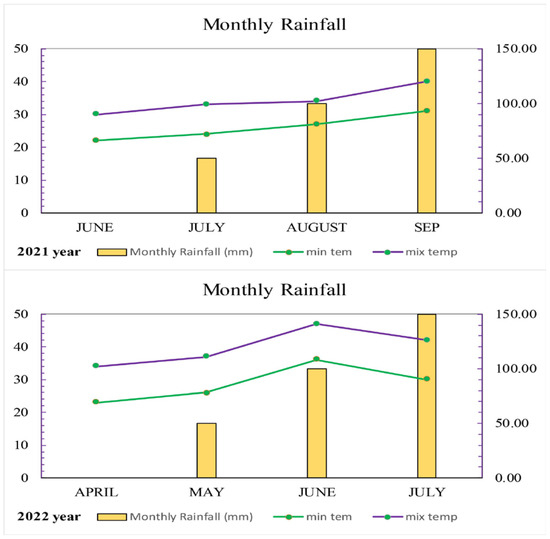
Figure 1.
The climatic data of the experimental site in 2021 and 2022.
The field received a recommended dose of 90 kg P2O5 per hectare for both years based on previous research conducted by [28,29,30]. The field was plowed twice using both a cultivator and a rotavator. Both crop straw of corn residue and sorghum residue were applied to the field before one month in chopped form on the basis of arranged plots, while in case of synthetic fertilizer the different phosphorus sources were applied to the field before sowing. In addition, 150 kg N per hectare was supplied from the source of urea DAP (46% N). The N (18%) and NP (22%) contents in DAP were subtracted from the final calculation. No potassium fertilizer was added during the experiment. The two sweet corn verities used was Kashmeri-19 and NARC-16. NARC-16 variety was sown on June 2021, while Kashmeri-19 variety was sown on April 2022; the seeds were sown using a drill machine at a sowing depth of 5 cm and a recommended rate of 25 kg per hectare with appropriate row spacing. Irrigation was applied as needed in accordance with the crop’s requirements and prevailing weather conditions. Hand hoeing was used to physically remove weeds, while knee-height thinning was utilized to achieve optimal plant spacing. After a maturation period of 90 days, the crop was harvested. The kernels had a milky appearance, were tender, and contained approximately 70–75% water. The ears were fully formed and surrounded by compact, green husk leaves. All agronomic practices were uniformly applied across all experimental units to ensure the reliability and comparability of the results.
2.2. Sample Collection and Calculation
Figure 2 shows data related to phonological and growth parameters, such as emergence per square meter, tassels, silk, leaves in plant, leaf area in plants, tallness of the plant, and maturity of the plant. Additionally, trials were conducted to observe sweet corn yield. Emergence data were obtained by calculating the number of days from sowing to the date on which 80% of seedlings emerged from the soil. Similarly, emergence per meter data were calculated by taking into account that there are five plants in a one-meter row in different places in each subfield, changing it into a field of m2, and then determining the mean [31]. Tassel was determined by calculating the number of days between seeding and the day 50% of plants started to generate tassels, while silk was determined by calculating the number of days from sowing to the date on which 50% of plants produced silk.
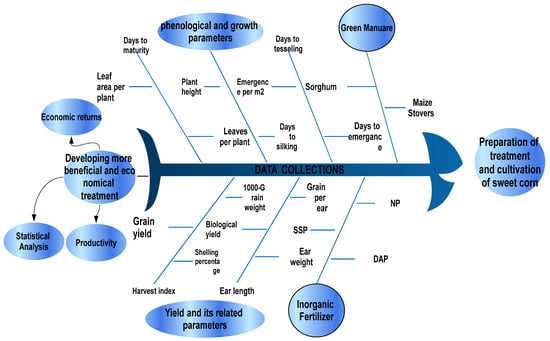
Figure 2.
Green Manuarin sorghum and maize stovers and phosphorus fertilizer on the parameters of sweet corn.
To calculate the number of leaves per plant, five random plants were selected, and the number of leaves per plant was counted. The mean was then determined for each field plot. The leaf area of the plant was calculated in Equation (1) by multiplying the length and width of the leaf with a correction factor (CF = 0.75) using [32] the following formula:
Crop height, days to maturity, ear weight, ear length, grains in ear, and grain weight (in grams) were collected systematically. To measure the height of the plant, five plants were randomly selected from each treatment field, and their heights were measured from the base to the tip of the tassel using a measuring tape. The days to maturity of the plants were determined by calculating the number of days from the date of sowing to the date when 80% of the plants in each field reached maturity.
The weight of the ears was calculated in grams by weighing the husk-less corn on a weighing scale. In addition, the length of the ears was determined by selecting five random plants in each plot and measuring their length using a measuring scale. The average ear length was calculated by taking the mean of all measurements.
To calculate the data concerning seeds per ear, ten ears were chosen at random and shelled. The number of seeds per ear were counted. Mean number of seeds per ear was determined by calculating the mean of these ten ears. Finally, the weight of 1000 seeds (in grams) were measured by weighing 1000 seeds from different locations in each field using an electronic balance.
Figure 2 shows the complete details of parameters for sweet corn crop to measure the biological yield; four central rows were harvested from each plot, and the harvested crop was sun-dried and weighed using a spring balance. The yield was then calculated using Equation (2), and the results are expressed in kilograms per hectare (kg ha−1) following the method described by [33]. Furthermore, the grain yield and harvest index for each treatment were calculated using Equations (3) and (4), respectively, as reported by [29]. The shelling percentage was determined by randomly selecting ten ears from each plot, weighing the ears and cobs, and then using Equation (5), as explained by [34].
where row-to-row distance is indicated by the symbol R − R.
2.3. Economic Analysis
To analyze the influence of management on gross revenue, net revenue, and benefit–cost ratio (BCR), we used Equation (6), which considered the cost of on-field activities such as land preparation, the cost of workers, water supply, and other costs, including costs of seeds, urea, phosphorus fertilizers, plant remains, marketing, and transportation.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The collected data were analyzed using Statistix 8.1 software (Tallahassee, FL, USA). Means of phonological and growth parameters, yield and yield components in different treatments were tested for normality and homogeneity, and the differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA (LSD test) at the 0.05 probability level. Each year of experimental results was analyzed separately. Significant differences at p < 0.05 are indicated by different letters. Furthermore, to assess economic aspects we followed conventional analysis metrics laid out in CYMMIT [35].
3. Result
3.1. Phonological and Growth Parameter
The supplementation of phosphorus (P) or crop waste have a no significant (p > 0.05) influence on the emergence of sweet corn in both the experiments for 2021 and 2022 (Figure 3A). However, the application of P and agricultural waste also show no significant (p > 0.05) impact on the emergence per square meter in different plots (Figure 3B). Tasseling and silking in sweet corn was significantly (p < 0.05) affected by the application of P or crop straw in both years.
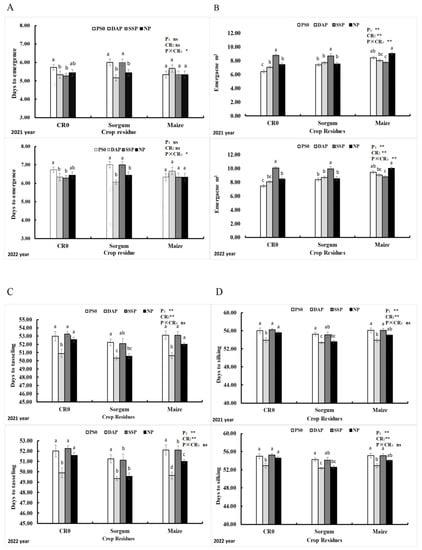
Figure 3.
Data for 2021 and 2022 on day to emergence (A) and emergence m2 (B) tassel (C) and silking (D) of sweet corn afflicted by the treatment of P and CR. Vertical bars represent the mean value. Capped bars above represent the standard error of three replicates. A different lower-case letter indicates significant differences among the treatments via the LSD test at p < 0.05. Note: significant at p < 0.05 *; p < 0.01 **; ns, non-significant. Phosphorus sources (P) and crop residues (CR). In total, 90 kg ha−1 of phosphorus and 5 tons’ ha−1 of crop waste were supplied, respectively. CR0 control, no application of crop waste; PS0 control, no supplication of P; SSP, triple superphosphate; NP, ammonium phosphate; DAP, diammonium phosphate.
Interestingly, the 2021 data related to phosphorus sources revealed that a lower number of days to tasseling was recorded in DAP plots (50 days) compared to SSP, NP, and the control plots, which required more days to tasseling (53 days). Similar data were observed for maize residues, where the non-treated crop took more days to tassel, while the crop treated with maize residues reached tasseling earlier (50 days). However, in 2022, non-treated crops had the highest number of tassels (53 days) compared to crops treated with SSP (52 days) and NP (51 days), with DAP supplementation resulting in the lowest number of tassels (50 days). Additionally, the application of crop waste significantly affected the number of tassels in sweet corn. The application of 5 tons per hectare of maize straw produced the highest number of tassels in sweet corn crop (52 days) (Figure 3).
The days to silking in sweet corn for both years were significantly affected by P sources or crop waste (p < 0.05). During 2021, less data regarding days to silking were recorded in DAP plots followed by SSP, NP, and the control plots, with the control plots taking the most days to silk. In terms of applying maize residues, less days were required for silking (53 days) compared to sorghum residues, while the non-treated crop took the longest time to reach the silking stage (56 days).
In 2022, we found that the highest number of days to silking (57) occurred in non-treated plots and sweet corn treated with SSP and NP. However, a decrease in silking time (54) was observed in sweet corn treated with DAP 90 kg per hectare. Furthermore, our study found that silking took the longest to occur (57 days) in sweet corn treated with agricultural waste, followed by the use of maize stover (56 days) and sorghum stover (55 days) (Figure 3D).
Regarding P application, the highest number of leaves per plant (12 leaves) was observed for the application of 90 kg DAP ha−1, followed by NP (12 leaves) and SSP (11 leaves), and untreated crops showed a lower number of leaves per plant (11). We also observed that straw from maize waste improved leaf per crop rates (12 leaves) compared to straw from sorghum wastes (Figure 4A). A taller crop was reported in 2022 than 2021 (Figure 4B). Among the different P sources, the highest plant height (178 cm) was observed under DAP application, followed by NP (178 cm) and SSP (165 cm). The non-treated plot height was always shorter (153 cm). When considering the different crop residues, the use of maize waste resulted in the tallest crops (172 cm), while the non-treated crops had a smaller height (159 cm). Among the different P sources, the highest leaf area per plant (6144 cm2) was observed in DAP, followed by NP (5643 cm2) and SSP (5253 cm2). Crops from the control fields had an average of smaller leaf area per plant. Similarly, regarding the different crop residues, the application of maize waste resulted in the largest leaf area per plant (6464 cm2), followed by sorghum residue (5580 cm2), while the non-treated crops had a smaller leaf area per plant (4405 cm2) (Figure 4C). The non-treated field matured latest (93 days) in 2022 and took over 100 days to mature in 2021. In comparison, plants treated with 90 kg SSP (or NP) matured quicker (92 days and 91 days, respectively, per hectare). The application of DAP resulted in an even shorter maturity period (89 days). Regarding the different crop residues, the control crops required the most days to reach maturity (92 days), while the use of sorghum residues resulted in a shorter maturity period (90 days) (Figure 4D). Our results also indicated that the number of leaves per plant, height, and maturity of the crops was significantly influenced by P application of 90 kg per hectare or plant residues of 5 tons per hectare (p < 0.05).
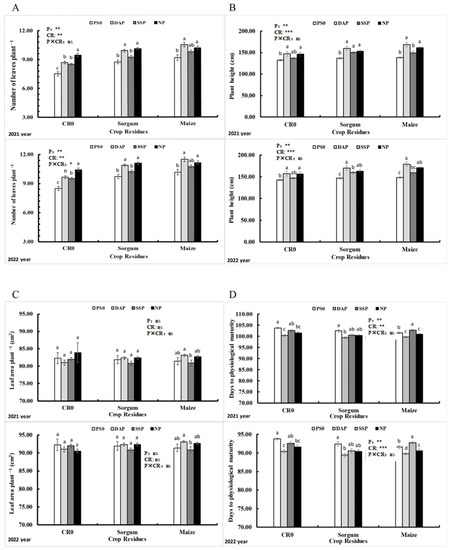
Figure 4.
Number of leaves per plant (A), height of the plant (B), leaf area of the plant (C), and days to maturity of the plant (D) of 2021 and 2022 sweet corn affected by the treatment of phosphorus and crop wastes. Vertical bars represent the mean value. Capped bars above represent the standard error of three replicates. A different lower-case letter indicates significant differences among the treatments via LSD test at p < 0.05. Note: phosphorus sources (P) and crop residues (CR). *: significant at p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ns: non-significant. In total, 90 kg ha−1 of phosphorus and 5 tons’ ha−1 of crop waste were supplied, respectively. CR0 control, no application of crop waste; PS0 control, no supplication of P; SSP, triple superphosphate; NP, ammonium phosphate; DAP, diammonium phosphate.
3.2. Yield and Yield Components
In 2022, among the various P application regimens, the DAP treatment at a depth of 15 cm resulted in the longest corn ears compared to the to the PS0 treatment at a depth of 10 cm. Additionally, when compared to the treatment with CR0 treatment at a depth of 11 cm, the return of straw also had a significant impact on ear length. Specifically, the treatment involving the application of 5 tons per hectare of maize wastes resulted in 14 cm ear length, while the treatment with sorghum wastes yielded 13 cm ear length (Figure 5A).
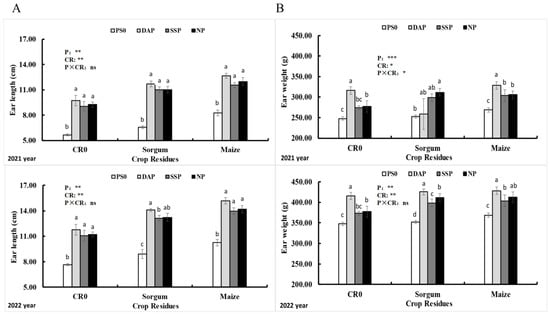
Figure 5.
Length of the ear (A) and weight of the ear (B) of sweet corn of 2021 and 2022 as affected by the treatment of phosphorus and crop wastes. Vertical bars represent the mean value. Capped bars above represent the standard error of three replicates. A different lower-case letter indicates significant different among the treatments via LSD test at p < 0.05. In total, 90 kg ha−1 of phosphorus and 5 tons’ ha−1 of crop waste were supplied, respectively. Note: phosphorus sources (P) and crop Residues (CR). *: significant at p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ns: non-significant. CR0 control, no application of crop waste; PS0 control, no supplication of P; SSP, triple superphosphate; NP, ammonium phosphate; DAP, diammonium phosphate.
Another important parameter for sweet corn crop is ear weight, which also showed variations in 2021. The highest ear weight of 328 g was observed when using 90 kg per hectare of DAP along with the application of 5 tons per hectare of maize residues. In contrast, the control plots for both applications recorded lower ear weights of 247 g for DAP and 268 g for maize residues.
In 2022, the DAP treatment resulted in the heaviest corn ears, weighing 429 g compared to the other treatments: PS0 (366.2 g), single superphosphate (SSP) (404 g), and nitrogen–phosphorus (NP) (401 g). Furthermore, the application of maize straw resulted in the highest ear weight of 411 g, surpassing the non-treated crop weight of 382 g (Figure 5B). The results of the analysis of variance indicated a significant effect of both P fertilizer and straw return on both ear length and weight (p < 0.05).
In 2022, compared to the PS0 (295), the DAP treatment resulted in the highest number of seeds per ear (321), follow by NP (313) and SSP (306). Compared to the CR0 control (277), maize straw return resulted in the highest number of seeds per ear (328), though sorghum straw also improved seed number compared to the control (320) (Figure 6A).
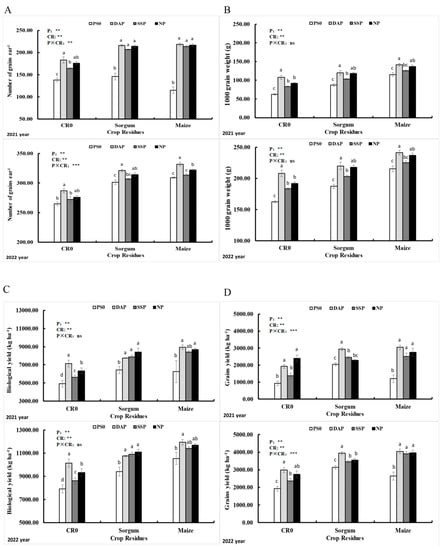
Figure 6.
Numbers of per ear seeds (A) 1000-weight seeds, (B) biological output, (C) seeds output, (D) of sweet corn of 2021 and 2022 as affected by the treatment of phosphorus and crop wastes. Vertical bars represent the mean value. Capped bars above represent the standard error of three replicates. A different lower-case letter indicates significant differences among the treatments via the LSD test at p < 0.05. Note: phosphorus sources (P) and crop residues (CR). **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ns: non-significant. In total, 90 kg ha−1 of phosphorus and 5 tons’ ha−1 of crop waste were supplied, respectively. CR0 control, no application of crop waste; PS0 control, no supplication of P; SSP, triple superphosphate; NP, ammonium phosphate; DAP, diammonium phosphate.
In the case of 1000-seed weight of 2021, more data was seen when using DAP and maize residue (141 g) and less data was seen in control plots like DAP. In 2022, we found that the 1000-seed weight of sweet corn kernels was influenced by both P application and crop waste (Figure 6B). Our results showed that compared to PS0 control (198 g), the DAP treatment was the highest in 1000-seed weight of sweet corn (233 g), followed by NP (225 g). Compared to the CR0 control (196 g), we saw a similar influence of straw return, and the application of maize straw resulted in the highest 1000-seed weight (239 g), followed by the application of sorghum straw (217 g).
Yields were all higher in 2022 than in 2021. During 2021, the data on biological yield were reported using treatment of DAP and maize straw, resulting in data for (8947 kg per hectare) and minimum data were seen from the non-treated crop group. In comparison, less data was available for 2021 than 2022. Same data were seen in 2021 and 2022 for seed yield of the crop for sweet corn. Less data was seen from the control crop of crop residues (1203 kg per hectare) and phosphorus sources (924 kg ha−1) and more output of the crop was seen from the application of both DAP and maize residue sources for seed yield (3047 kg per hectare).
In 2022, among the P sources, the highest biological yield of sweet corn 11,349 kg ha−1 and grains yield 3760 kg ha−1 were obtained from DAP treatment which was increased by 26.63% and 41.03%, respectively, as compared to the PS0 control group. The application of maize residue resulted in the highest biological yield of 11,177 kg ha−1 and grains yield of 3760 kg ha−1, which was increased by 22.77% and 44.39%, respectively, as compared to the CR0 control (Figure 6C,D).
The 2021 experiment on sweet corn crop showed that control plots for both the application of phosphorus sources and crop residues had a lower shelling percentage (54% and 57%, respectively). On the other hand, higher shelling percentages were observed when using both treatments of DAP and maize straw (64%). In 2022, compared to the untreated plots (77%), the highest shelling percentage (84%) was achieved with the application of DAP, followed by NP (81%) and SSP (79%); the application of maize and sorghum wastes resulted in the highest shelling percentage of 81% and 80.1%, respectively. Highest amount of harvest index was reported in 2022 in the Kashmeri variety while less amount was reported in 2021 for the NARC variety using the same treatments (Figure 7A). Compared to the untreated plots (29.3), higher result concerning HI (32.9%) was achieved with the application of DAP treatment, follow by NP (32.4%) and SSP (31.8%). And compared to the untreated plots (28.4%), the use of sorghum wastes resulted in the highest harvest index of 33.4% followed by 33.0% with the application of maize waste (Figure 7B).
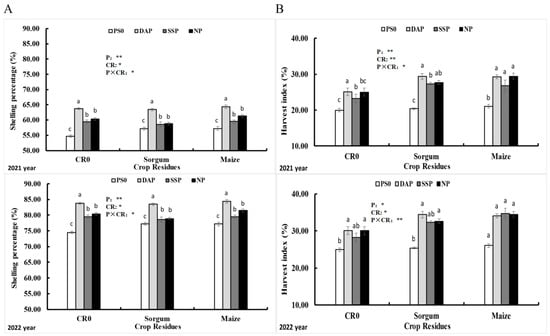
Figure 7.
Selling percentage (A) and harvest index (B) of sweet corn affected by the treatment of phosphorus and crop wastes. Vertical bars represent the mean value. Capped bars above represent the standard error of three replicates. A different lower-case letter indicates significant differences among the treatments via the LSD test at p < 0.05. Note: phosphorus sources (P) and crop residues (CR). *: significant at p < 0.05. **: p < 0.01; ns: non-significant. In total, 90 kg ha−1 of phosphorus and 5 tons’ ha−1 of crop waste were supplied, respectively. CR0 control, no application of crop waste; PS0 control, no supplication of P; SSP, triple superphosphate; NP, ammonium phosphate; DAP, diammonium phosphate.
3.3. Economic Survey
This study examined the costs and benefits associated with using different crop residues and P sources for sweet corn production. Table 2 shows that the costs of activities such as plowing, planting seeds, and watering were consistent across all treatments, and only the expenses associated with applying crop residues and P sources varied across experimental treatments. The results indicated that the use of 5 ton ha−1 of maize plus 90 kg N-P per hectare led to increased gross income of USD 800.18 ha−1 and the greatest net return of USD 560.13 ha−1. Economic analysis revealed that the benefit−cost-ratio (B-C-R) varied across different management choices, with the application of 5 tons of maize straw per hectare plus 90 kg N-P per hectare producing the greatest B-C-R (3.33), followed by the supplementation using 5 tons of maize straw per hectare and 90 kg of S-S-P per hectare, which generated a B-C-R of 3.27.

Table 2.
Economic investigation of the impact of incorporating straw of the crop with synthetic P on the efficiency of sweet corn grown under irrigation during the spring of 2022 in Peshawar, Pakistan.
4. Discussion
Our research findings indicate that based on the two years of experimental data, sweet maize emergence of the seed, different growth stages of the crop and yield are generally improved when phosphorus was applied. The outcome was further enhanced when maize and sorghum crop residues were added. This can be attributed to the fact that crop residues contain a significant amount of organic matter, which plays a crucial role in improving soil structure, fertility, and microbial activity. The addition of crop residues increased the availability of phosphorus in the soil by breaking down the chemical bonds between the nutrients and soil particles [11,12,19,36]. However, in the first year of our project, a natural disaster occurred which caused heavy rain and flooding. This resulted in lodging of the crop, which may have influenced our final results, including certain yield parameters such as ear weight, ear length, number of seeds per ear, 1000-seed weight, biological yield, seed yield, shelling percentage, and harvest index. In general, the improvements in management were most notable in the second year, compared to the first year even when a natural disaster caused lodging, affecting ear weight, ear length, biological yield, grain yield, harvest index, and shelling percentage.
P deficiency negatively affects maize morphogenesis and physiological mechanisms, leading to decreased biomass and the manifestation of P deficiency-related symptoms [37]. Crop residues contain various macronutrients and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, which can be slowly released into the soil through decomposition [38]. The addition of crop waste enhances soil composition, water-holding ability, and nutrient retention, which can positively impact plant growth and development [39,40]. Additionally, organic matter provides a food source for soil microorganisms, and in turn facilitates nutrient cycling and uptake by sweet maize. These results highlight the importance of soil management practices that focus on improving soil health and organic matter content to achieve sustainable crop production [41,42].
Our results demonstrated that tasseling, silking, and maturity in sweet corn were significantly affected by P supplementation and crop waste with residual stover from either sorghum or maize. This could be attributed to enhanced uptake of P from the soil, leading to improved growth and developmental stages of the crop. This is consistent with other research that shows sweet corn responds favorably to P supplementation, resulting in better performance [43,44,45]. Crop residues can help retain soil moisture by reducing water evaporation from the soil surface. This can be especially beneficial during dry spells when water availability is limited, as sufficient moisture is crucial for proper tasseling and silking in maize.
However, our results are consistent with other experiments suggesting that P and crop waste supplementation have no substantial influence on the emergence per square meter and on days to emergence of sweet corn [46,47,48]. Generally, this is assumed to be the influence of ontogeny: crop residues may be unavailable in the early stages of sowing and planting when plants rely more intensely on internal nutrients within the seed.
Furthermore, the results indicate that P sources and crop residues can significantly impact the number of leaves in the crop, area of a single leaf, crop height, and the length of the maturation period of sweet corn, with certain treatments resulting in larger leaf area and shorter maturity periods. The highest number of leaves per plant was observed with the application of 90 kg DAP/ha, with a maximum plant height of 178 cm. This information is consistent with a host of other studies that have shown that phosphorus fertilizers improve the growth and development of sweet corn crops, generally by increasing leaf area during the growth period, often leading to a shorter period of maturation and earlier yield [49,50]. Ref. [51] found that a higher leaf area index enhances a crop’s ability to intercept, absorb, and utilize radiant energy, leading to a faster rate of photosynthesis and greater accumulation of dry matter in the crops. In essence, increased nutrient availability allows for the production of larger leaf area which ultimately improves crop yield and plant health.
Ear weight (429 g) and length (average of 15 cm) were significantly affected by phosphorus addition (90 kg/ha) and also by the straw of the crop which was provided to the field using 5 tons/hectare. These results are consistent with other research [22,23,52], which also demonstrated that DAP and crop residues resulted in a greater ear weight and increased ear length.
This could result from the nitrogen and phosphorus in DAP and crop residues, which can enhance plant vegetative growth by stimulating protein production essential for cell growth and division as well as root development, improving plants’ ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. This, in turn, promotes the formation of larger and heavier ears in sweet corn.
Although environmental factors, such as the growing season, climate conditions, water availability, and soil conditions, all play a role in corn yields [53], research indicates that the use of phosphorus and crop residues can have a more significant impact on crop yield [54]. Phosphorus and crop residues provide essential nutrients, improve soil health, increase water availability to roots, and result in better root growth and nutrient uptake, ultimately leading to higher crop yields compared to the influence of environmental factors alone [55].
The present study’s results suggest that the application of P sources and crop residues had a significant impact on the yield and quality of sweet corn. Specifically, the application of 90 kg DAP and 5 tons per hectare of maize stover resulted in the highest number of seeds per ear, the highest 1000-seed weight, and overall largest biological yield, particularly in comparison to the poor seed yield observed in the non-treated crops because DAP contains 46 percent of phosphorus which helps in the root and fruit development of the crops, while maize straw contains different nitrogen content and potassium which is available to the crop after its decomposition. Our findings are consistent with earlier studies by [56], which observed that seed yield improved with synthetic and organic supplementation. Ref. [57] showed that the application of residues-rich soil significantly increased seed productivity of crops compared to non-treatment plots.
Moreover, these findings are consistent with past studies that have reported the positive impact of P application and crop residue on the yield and quality of seed in maize [58,59,60]. Refs. [61,62] presented similar results, showing that crops responded better to higher doses of P, and that the highest 1000-seed weight was observed in fields treated with high amounts of P compared to plots with no or low application of treatment.
The higher yield of grains per ear observed in certain crops may be attributed to the role of phosphorus (P), which can stimulate root system growth and improve water and nutrient acquisition. The subsequent increase in nutrient uptake can then readily translocate toward developing spikes, enhancing grain production [63]. Additionally, a suitable application of P may also promote rapid vegetative growth and increase the plant’s ability to intercept solar radiation, leading to a greater number of grains per ear [30].
The findings of this study suggest that the use of appropriate P supplication and straw of the crop can significantly enhance the shelling percentage and harvest index of sweet corn. The highest shelling percentage and harvest index was observed in plots treated with 90 kg DAP per hectare and 5 tons of sorghum waste per hectare, respectively. The results also indicate that there was no significant interaction between P application and crop waste. The enhancement in shelling percentage and harvest index of sweet corn may be attributed to an improvement in the ear’s quantity of seeds and increased 1000-seed weight resulting from enhanced application of P doses. Previous research has shown that a higher number of shelling percentage and harvest index of crops resulted from the implementation of higher doses of P and enhanced single or combined supplication of P levels [64,65,66,67].
5. Conclusions
The utilization of by-products generated from agro-industry can enhance the sustainability of agro-ecosystems. However, it is crucial to assess their suitability as alternatives or supplements to chemical fertilizers. For example, crop straw contains various nutrients and its usage can also help protect the environment from volatile toxic gases emitted by chemical fertilizers. In this two-year study, we investigated the effects of crop straws like sorghum or maize and phosphorus on sweet maize growth and production. According to the findings, the application of DAP at a rate of 90 kg per hectare combined with 5 tons per hectare of maize waste provided the greatest enhancement in sweet corn. However, the performance of the crop in the first year was not satisfactory, but its growth stages were acceptable. Despite this, when comparing yields in 2022, we found that supplementing fields with both DAP and maize waste was the most cost-effective way to improve sweet maize yields. The application of organic remedies obtained as agricultural crop byproducts is a way of integrating organic material into agro-ecosystems using a less expensive, more readily available source of nutrients. The recycling of these waste materials significantly reduces fertilization costs and mitigates concerns with inorganic P addition. Thus, coupling crop waste with inorganic P fertilizer is highly advised to enhance sweet corn performance under the agro-climatic conditions of Peshawar. Further studies are needed to evaluate the combinatorial influence of other management strategies, such as the effects of other nutrients, effects on different varieties of the same species, and the physical parameters that should be studied alongside crop performance and soil fertility, including soil structure, nutrient cycling, water availability, pH, and microbial diversity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.U. and P.F.; Methodology, J.U. and S.C.; Software, A.A.; Validation, J.U., S.C. and Y.R.; Formal analysis, J.U. and N.M.K.; Investigation, J.U. and M.N.U.R.; Resources, Y.R.; Data curation, P.F.; Writing—original draft, J.U.; Writing—review & editing, P.F.; Visualization, J.U.; Supervision, P.F.; Project administration, Y.R.; Funding acquisition, Y.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Project of Sanya Yazhou Bay Science and Technology City, Grant No.: SCKJ-JYRC-2022-94 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32160750).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Shevkani, K. Maize: Composition, bioactive constituents, and unleavened bread. In Flour and Breads and Their Fortification in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 111–121. [Google Scholar]
- Banotra, M.; Sharma, B.C.; Nandan, B.; Arya, V.M.; Kumar, R.; Verma, A.; Shah, I.A.; Gupta, V. Yield, Quality and Economics of different Sweet Corn (Zea mays L. Var. Saccharata) Cultivars at different Planting and Harvesting Dates under Shiwalik Foothills of J&K. Indian J. Ecol. 2017, 44, 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.H.; Khalil, S.K.; Nigar, S.; Khalil, I.; Haq, I.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.Y. Phenology and yield of sweet corn landraces influenced by planting dates. Sarhad J. Agric 2009, 25, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, R.B.; Zhang, X. Phosphorus use efficiency in agricultural systems: A comprehensive assessment through the review of national scale substance flow analyses. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, O.; Keshavarz-Afshar, R.; Jahanzad, E.; Battaglia, M.L.; Luo, Y.; Sadeghpour, A. Effect of wheat cover crop and split nitrogen application on corn yield and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimpour, S.I.; Khavazi, K.; Nadian, H.; Besharati, H.; Miransari, M. Enhancing phosphorous availability to canola (“Brassica napus” L.) using P solubilizing and sulfur oxidizing bacteria. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 4, 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Asim, M.; Hussain, Q.; Ali, A.; Farooq, S.; Khan, R.; Shah, S.A.A. Responses of maize to different levels and sources of phosphorus application. Pure Appl. Biol. 2017, 6, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Muhammad, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, A.; Khattak, A.M.; Saljoqi, A.R. Wheat yield and phosphorus uptake as affected by rock phosphate added with different organic fertilizers. Ciência Técnica Vitivinícola J. 2015, 30, 90–100. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, H.; Fatima, R.; Sharma, A.; Mathur, S. Enhancement of applicability of rock phosphate in alkaline soils by organic compost. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, R. Paradoxically Vicious Cycle of Agriculture Pollution: A Contextual Bibliographical Review for Prospective Agenda. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 3068–3075. [Google Scholar]
- Pierzynski, G.M.; Logan, T.J. Crop, soil, and management effects on phosphorus soil test levels: A review. J. Prod. Agric. 1993, 6, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Chen, H.; Gurmesa, G.A.; Gundersen, P.; Ellsworth, D.S.; Gilliam, F.S.; Wang, C.; Zhu, F.; Ye, Q.; Mo, J. Negative effects of long-term phosphorus additions on understory plants in a primary tropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizito, S.; Luo, H.; Lu, J.; Bah, H.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Role of nutrient-enriched biochar as a soil amendment during maize growth: Exploring practical alternatives to recycle agricultural residuals and to reduce chemical fertilizer demand. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.K.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, B.; Singh, A.P. Long-term effect of crop residues and zinc fertilizer on crop yield, nutrient uptake and fertility build-up under rice-wheat cropping system in calciorthents. J. Indian Soc. soil Sci. 2010, 58, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Croce, S.; Wei, Q.; D’Imporzano, G.; Dong, R.; Adani, F. Anaerobic digestion of straw and corn stover: The effect of biological process optimization and pre-treatment on total bio-methane yield and energy performance. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1289–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K.G.; Misra, A.K.; Hati, K.M.; Bandyopadhyay, K.K.; Ghosh, P.K.; Mohanty, M. Rice residue-management options and effects on soil properties and crop productivity. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2004, 2, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, A.; Xu, H.; Shao, X.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Murphy, D. V Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in relation to soil particle-size fractions after 32 years of chemical and manure application in a continuous maize cropping system. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titab, D.; Shri, R.; Nand, R. Effect of long term application inorganic fertilizers and manure on yields, nutrients uptake and grain quality of wheat under rice-wheat cropping system in a Mollisols. Pantnagar J. Res. 2011, 9, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Luo, Z.Z.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, R.Z.; Li, G.D.; Cai, L.Q.; Xie, J.H. Effects of stubble management on soil fertility and crop yield of rainfed area in Western Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 256312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Wei, J.G.; Li, J.; Feng, S.F.; Li, Z.F.; Jiang, G.M.; Lucas, M.; Wu, G.L.; Ning, T.Y. Anaerobic fermentation technology increases biomass energy use efficiency in crop residue utilization and biogas production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4588–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunna, S.; Sinath, P.; Makara, O.; Mitchell, J.; Fukai, S. Effects of straw mulch on mungbean yield in rice fields with strongly compacted soils. Field Crops Res. 2011, 124, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, J.; Shah, S.; Mihoub, A.; Jamal, A.; Saeed, M.F.; Székely, Á.; Radicetti, E.; Salman, M.; Caballero-Calvo, A. Assessing the Effect of Combining Phosphorus Fertilizers with Crop Residues on Maize (Zea Mays L.) Productivity and Financial Benefits. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Inamullah; Jamal, A.; Mihoub, A.; Saeed, M.F.; Radicetti, E.; Ahmad, I.; Naeem, A.; Ullah, J.; Pampana, S. Composting Sugarcane Filter Mud with Different Sources Differently Benefits Sweet Maize. Agronomy 2023, 13, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlina, N.; Rahim, S.E.; Hawayanti, E. Utilization of Organic Fertilizer on Sweet Corn (Zea mays saccharata Sturt) Crop at Shallow Swamp Land. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 97, 1103. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, K.; Shah, S.N.M.; Ali, A.; Zaheer, S.; Wahid, F.; Khan, A.; Shah, M.; Bibi, S.; Majid, A. Effects of humic acid and crop residues on soil and wheat nitrogen contents. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Akbar, H. Integrated management of crop residue and N fertilizer for wheat production. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 2015–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, T.; Khan, H.; Noor, M.A.; Ghoneim, A.; Wang, X.; Sher, A.; Nasir, M.; Basahi, M.A. Effects of potassium on phenological, physiological and agronomic traits of maize (Zea mays L.) under high nitrogen nutrition with optimum and reduced irrigation. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 7079–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Amanullah; Jamal, A.; Mihoub, A.; Farooq, O.; Farhan Saeed, M.; Roberto, M.; Radicetti, E.; Zia, A.; Azam, M. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizers with organic supplements increased wheat productivity and profitability under limited and assured irrigation regimes. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.F.; Jamal, A.; Muhammad, D.; Shah, G.M.; Bakhat, H.F.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, S.; Ihsan, F.; Wang, J. Optimizing phosphorus levels in wheat grown in a calcareous soil with the use of adsorption isotherm models. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, A.; Fawad, M. Effectiveness of phosphorous fertilizers in wheat crop production in Pakistan. J. Hortic. Plant Res. 2019, 5, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, M.; Khan, G.D.; Khalil, S.K. Emergence in wheat as affected by different tillage implements and soil compaction levels. Sarhad J. Agric 2014, 30, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Musa, U.T.; Usman, T.H. Leaf area determination for maize (Zea mays L.), okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) crops using linear measurements. J. Biol. Agric. Healthc. 2016, 6, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ramadhan, M.N. Yield and yield components of maize and soil physical properties as affected by tillage practices and organic mulching. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 7152–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwudi, U.P.; Kutu, F.R.; Mavengahama, S. Heat stress effect on the grain yield of three drought-tolerant maize varieties under varying growth conditions. Plants 2021, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliba, A.R.; Verkuijl, H.; Mwangi, W.M.; Moshi, A.J.; Chilagane, A.; Kaswende, J.S.; Anandajayasekeram, P. Adoption of Maize Production Technologies in Eastern Tanzania; CIMMYT: El Batan, Mexico, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, C.Y. Predicting Stages of Sweet Corn (Zea mays L.) Development1. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1974, 99, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Yang, K.; Pan, G.; Rong, T. The effects of low phosphorus stress on morphological and physiological characteristics of maize (Zea mays L.) landraces. Agric. Sci. China 2007, 6, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanbi, W.B.; Togun, A.O. Productivity and Influence of maize stover compost on Growth, Yield and Nutrient Uptake of Amaranth. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Qu, P.; Wei, Z. Impacts of crop residues on soil health: A review. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X. A meta-analysis of the effects of crop residue return on crop yields and water use efficiency. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhong, S.; Su, L.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Effect of biofertilizer for suppressing Fusarium wilt disease of banana as well as enhancing microbial and chemical properties of soil under greenhouse trial. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 93, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lv, J.L.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.H.; Xi, H.; Kou, C.L.; He, Z.C.; Shen, A.L. Long-term decomposed straw return positively affects the soil microbial community. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah, A.; Zakirullah, M. Timing and rate of phosphorus application influence maize phenology, yield and profitability in Northwest Pakistan. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. H. Bot. 2010, 1, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.K.; Khan, S.; Rahman, A.; Khan, A.Z.; Khalil, I.H.; Amanullah, W.S.; Mohammad, F.; Nigar, S.; Zubair, M.; Parveen, S. Seed priming and phosphorus application enhance phenology and dry matter production of wheat. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Turk, M.A.; Tawaha, A.-R.M. Impact of seeding rate, seeding date, rate and method of phosphorus application in faba bean (Vicia faba L. minor) in the absence of moisture stress. BASE 2002, 6, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, Y.; Subasi, I.; Katar, D.; Kodas, R.; Keyvanoglu, H. Effect of Different Levels of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on The Yield and Yield Component of False Flax (Camelina sativa L.) CRANTZ. Anadolu Tarim Bilim. Derg. 2014, 29, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Khan, S.; Fahad, S.; Faisal, S.; Hussain, S.; Ali, S.; Ali, A. Effect of different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus on the phenology and yield of maize varieties. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.J.; Ye, D.L.; Su, D.; Li, F.; Zheng, C.Y.; Wu, L.Q. Effects of phosphorus application on phosphorus uptake and utilization of sweet corn. Acta Agron. Sin. 2021, 47, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrurrozi, F.; Muktamar, Z.; Sudjatmiko, S.; Chozin, M.; Setyowati, N. Phosphorus Uptakes and Yields of Sweet Corn Grown under Organic Production System. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Manila, Philippines, 18–21 October 2018; Volume 347, p. 12006. [Google Scholar]
- Onasanya, R.O.; Aiyelari, O.P.; Onasanya, A.; Oikeh, S.; Nwilene, F.E.; Oyelakin, O.O. Growth and yield response of maize (Zea mays L.) to different rates of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in southern Nigeria. World J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 5, 400–407. [Google Scholar]
- Varatharajan, T.; Choudhary, A.K.; Pooniya, V.; Dass, A.; Meena, M.C.; Gurang, B.; Harish, M.N. Influence of different integrated crop management modules on growth indices and productivity of pigeonpea in semi-arid north Indian plains. Ann. Agric. Res. New Ser. 2018, 39, 398–405. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, G.; Khan, A.A.; Inamullah, A.R.; Fayyaz, H.; Naz, G.; Nawaz, H.; Ali, I.; Raza, H.; Amin, J.; Ali, S. Impact of phosphorus and potassium levels on yield and yield components of maize. Pure Appl. Biol. 2017, 6, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motazedian, A.; Kazemeini, S.A.; Bahrani, M.J. Sweet corn growth and GrainYield as influenced by irrigation and wheat residue management. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massawe, P.I.; Mrema, J. Effects of different phosphorus sources and application rates on soils residual N and P in the rice field. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2018, 8, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, H.; Vandana; Sharma, S.; Pandey, R. Phosphorus nutrition: Plant growth in response to deficiency and excess. In Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 171–190. [Google Scholar]
- Maqsood, M.; Abid, A.M.; Iqbal, A.; Hussain, M.I. Effect of variable rate of nitrogen and phosphorus on growth and yield of maize (golden). Online J. Biol. Sci. 2001, 1, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, M.; Bakht, J.; Jan, M.T.; Shah, Z. Soil C and N dynamics and maize (Zea may L.) yield as affected by cropping systems and residue management in North-western Pakistan. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 94, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.S.; Ali, M.M.; Naveed, M.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Shafique, M.W.; Ali, H.M.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Ghareeb, R.Y.; Feng, G. Co-application of organic amendments and inorganic P increase maize growth and soil carbon, phosphorus availability in calcareous soil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 949371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, K.; Wasaya, A.; Rehman, H.U.; Yasir, T.A.; Farooq, O.; Imran, M.; Ikram, R.M.; Nazeer, R.; Zahoor, F.; Yonas, M.W. Integrated phosphorus nutrient sources improve wheat yield and phosphorus use efficiency under sub humid conditions. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfanullah, H.A.; Hussain, A.A.I.; Khan, M.W.; Ahmadzai, M.D. Yield and yield attributes of maize (Zea mays L.) as affected by detasseling and potassium fertilization. Pure Appl. Biol. 2017, 6, 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, M.; Saeed, A.; Nisar, M.; Mian, I.A.; Afzal, M. Effect of potassium rates and sources on the growth performance and on chloride accumulation of maize in two different textured soils of Haripur, Hazara division. Sarhad J. Agric. 2011, 27, 415–422. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, T.; Gul, R.; Munsif, F.; Jalal, F.; Hussain, Z.; Noreen, N.; Khan, H.; Nasiruddin, K.H. Effect of different phosphorus levels on the yield and yield components of maize. Sarhad J. Agric. 2011, 27, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, M.F.; Ahmadzai, M.D.; Liaqat, W.; Ahmad, H.; Rehan, W. Effect of poultry manure and phosphorous on phenology, yield and yield components of wheat. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 3751–3760. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad Alias, M.U.; Ullah, E.; Warraich, E.A. Effects of different phosphorus levels on the growth and yield of two cultivars of maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2003, 4, 632–634. [Google Scholar]
- Amanullah; Asif, M.; Malhi, S.S.; Khattak, R.A. Effects of phosphorus fertilizer source and plant density on growth and yield of maize in Northwestern Pakistan. J. Plant Nutr. 2009, 32, 2080–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah; Khan, A. Phosphorus and compost management influence maize (Zea mays) productivity under semiarid condition with and without phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.; Abbasi, M.K.; Khaliq, A. Effect of different phosphorus sources on the growth, yield, energy content and phosphorus utilization efficiency in maize at Rawalakot Azad Jammu and Kashmir, Pakistan. J. Plant Nutr. 2013, 36, 1915–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).