Genetic and Genomic Diversity in a Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) Germplasm Collection and Adaptability to Mediterranean Climate Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. Molecular Analysis
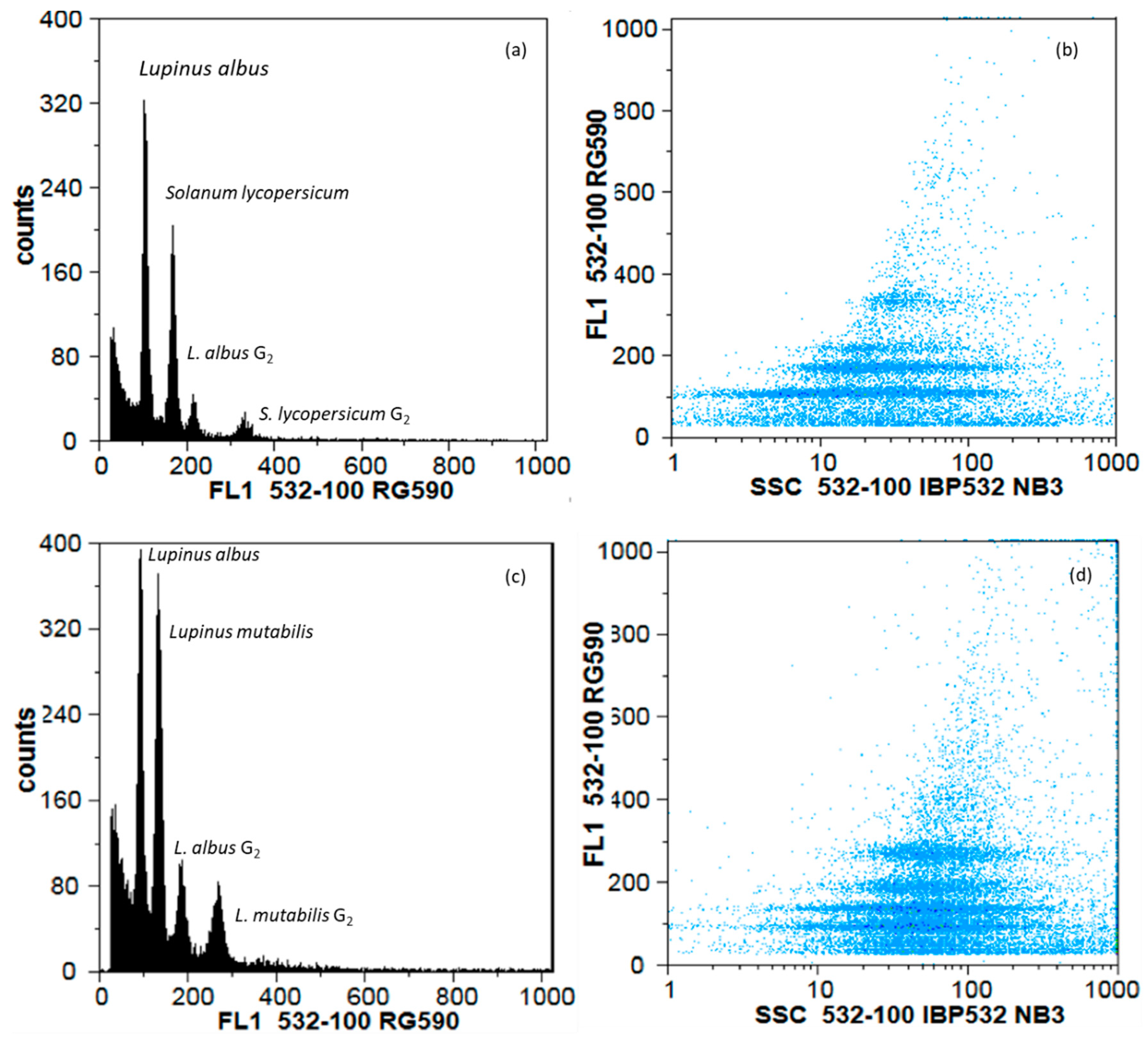
2.4. Flow Cytometry
3. Results
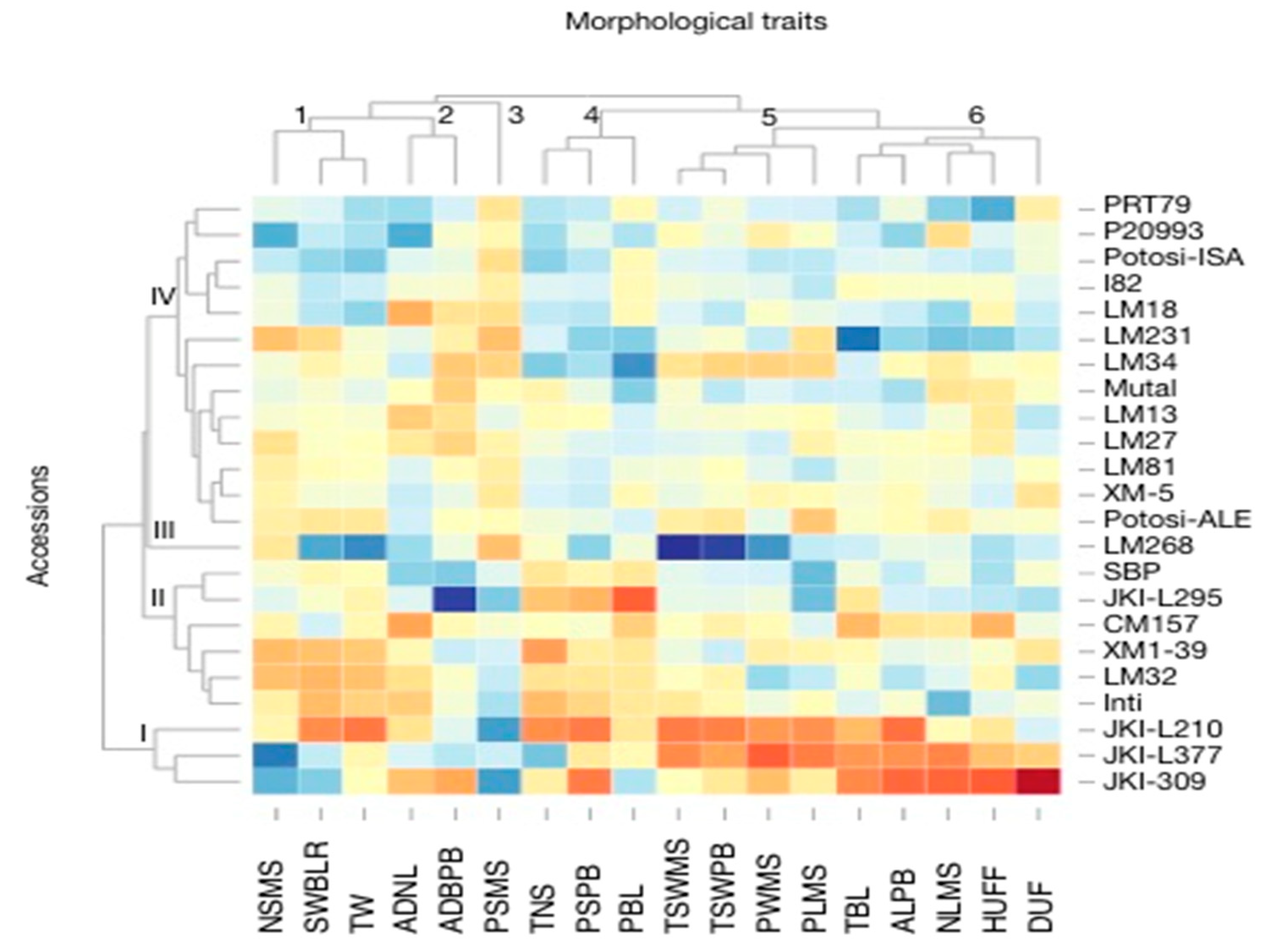
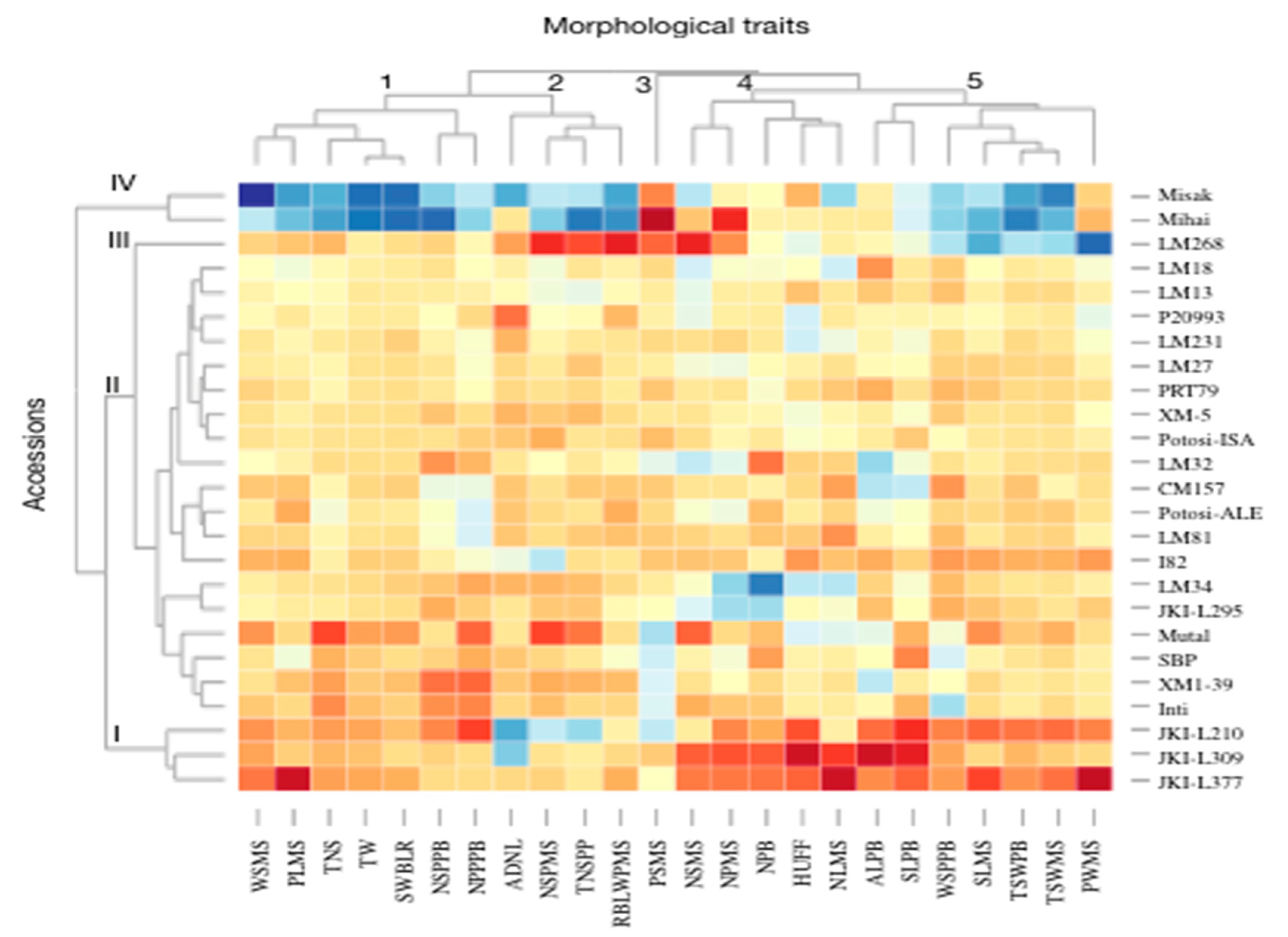
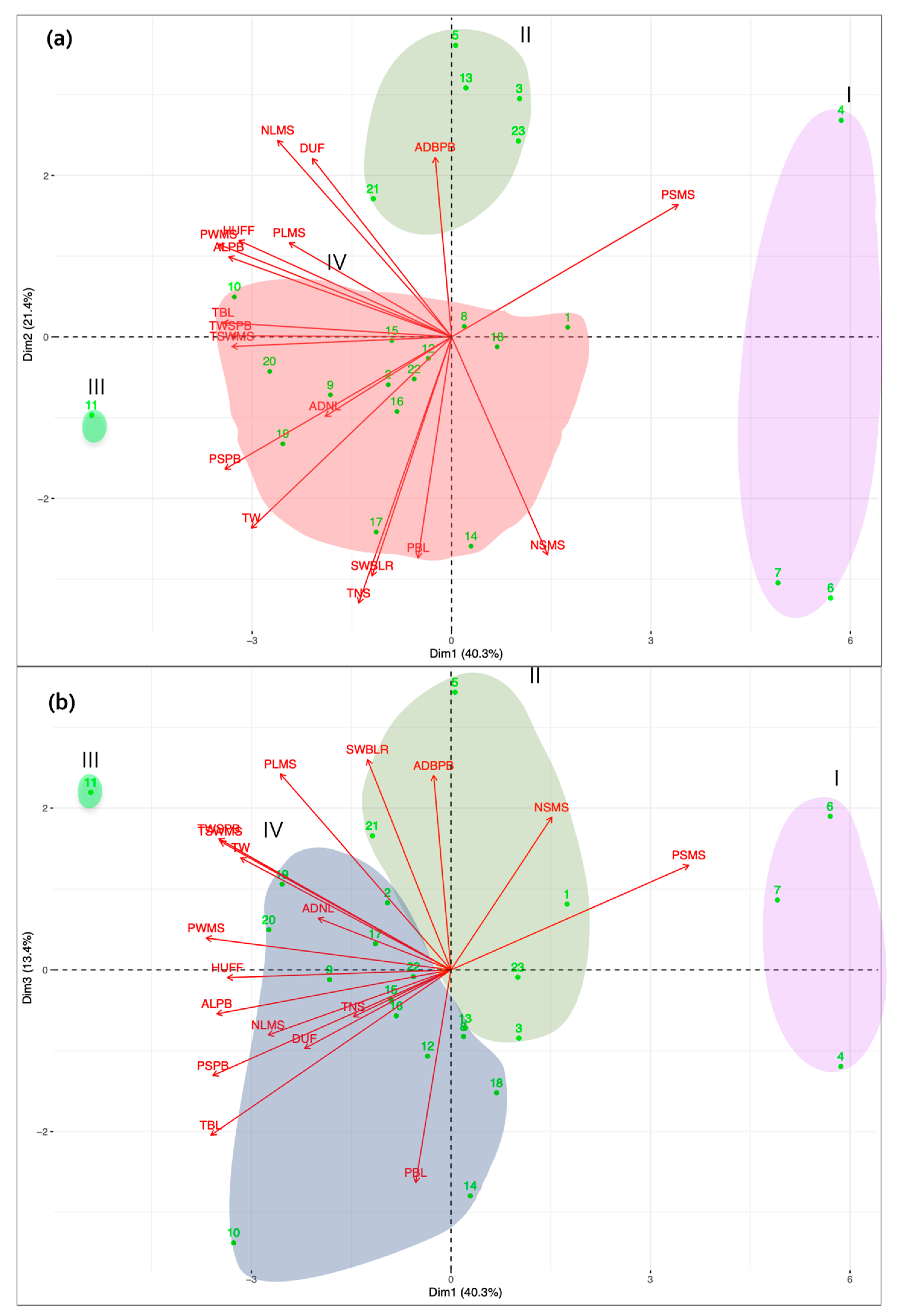
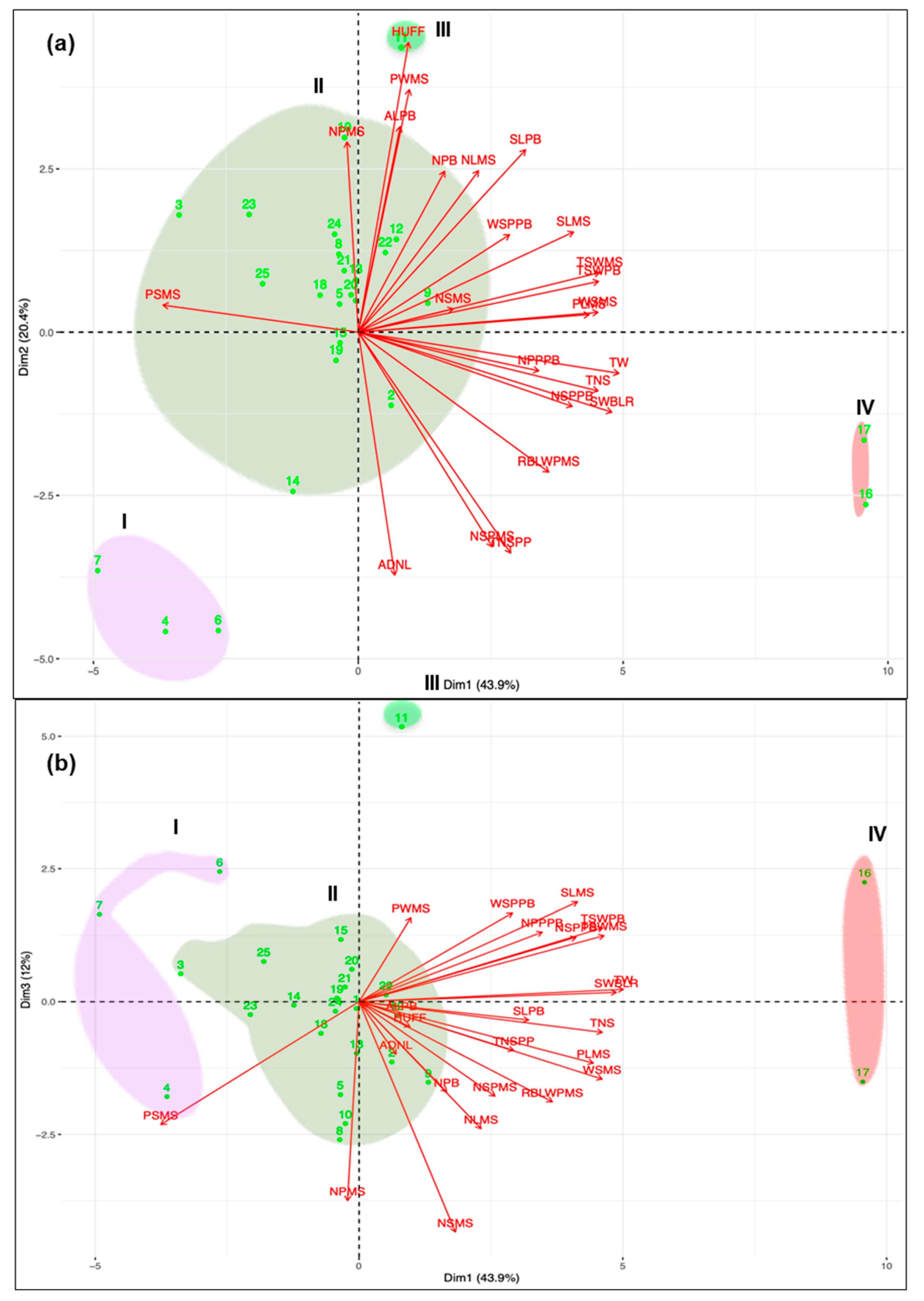
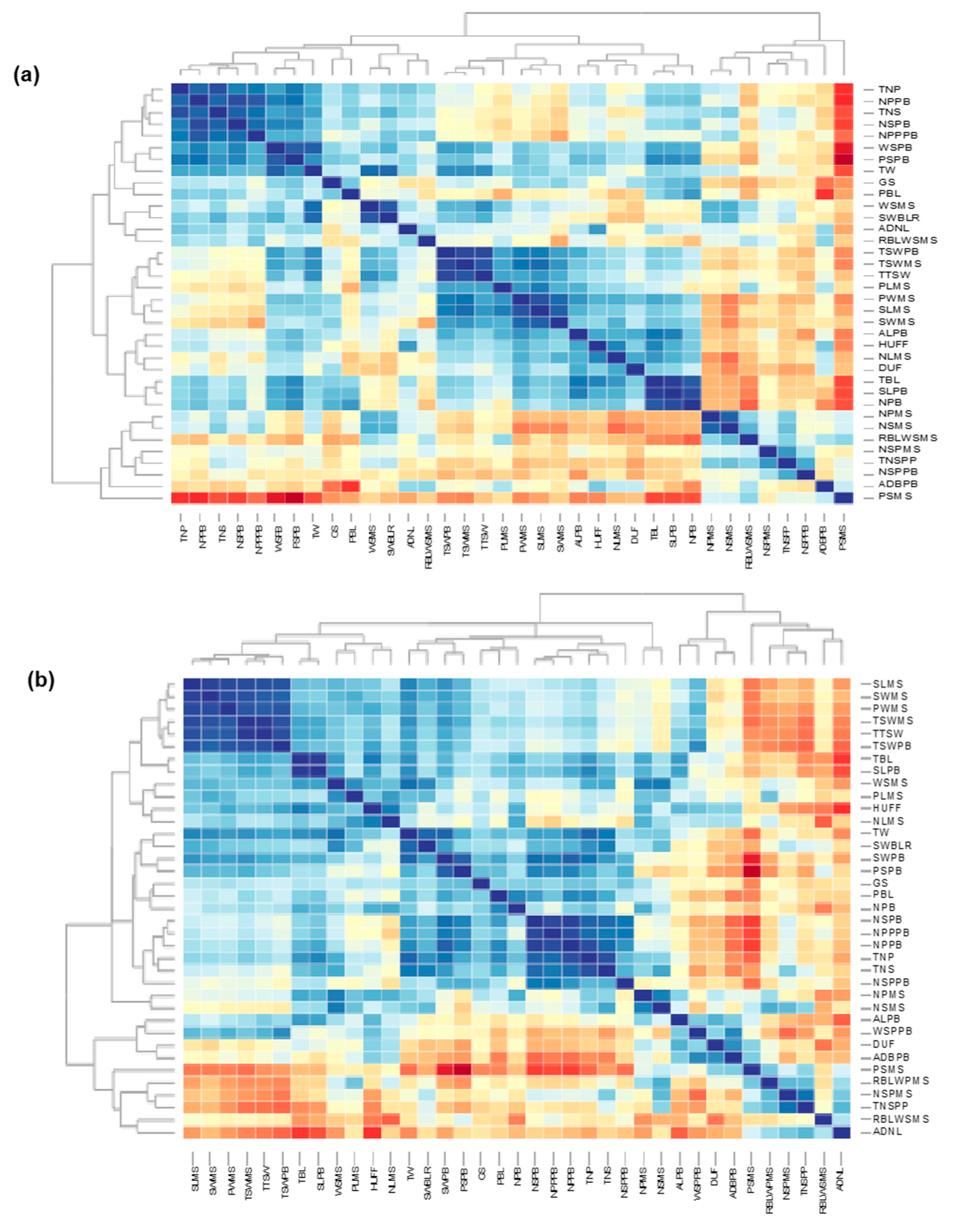
3.1. Morphological Characterization and Genetic Parameters among Accessions
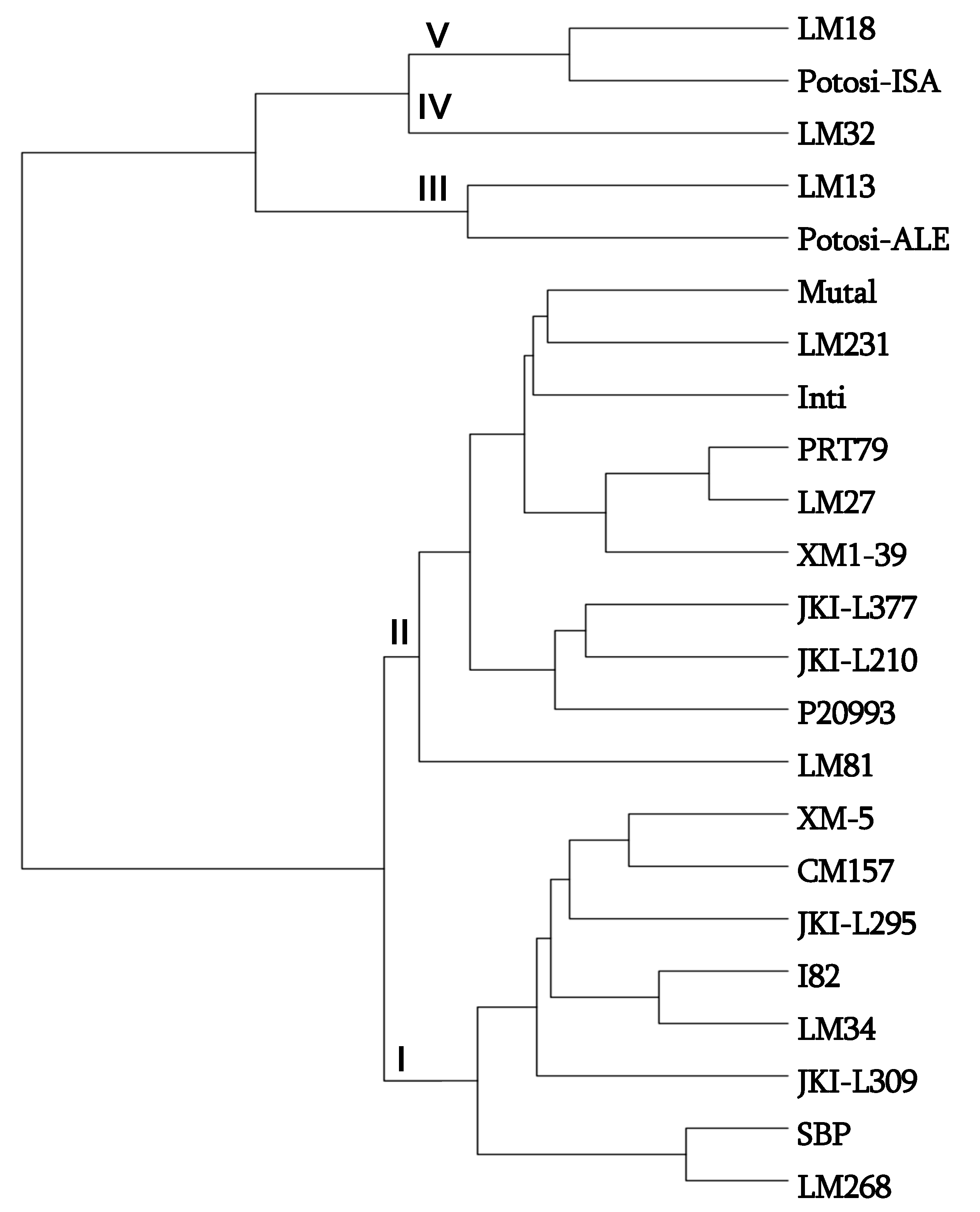
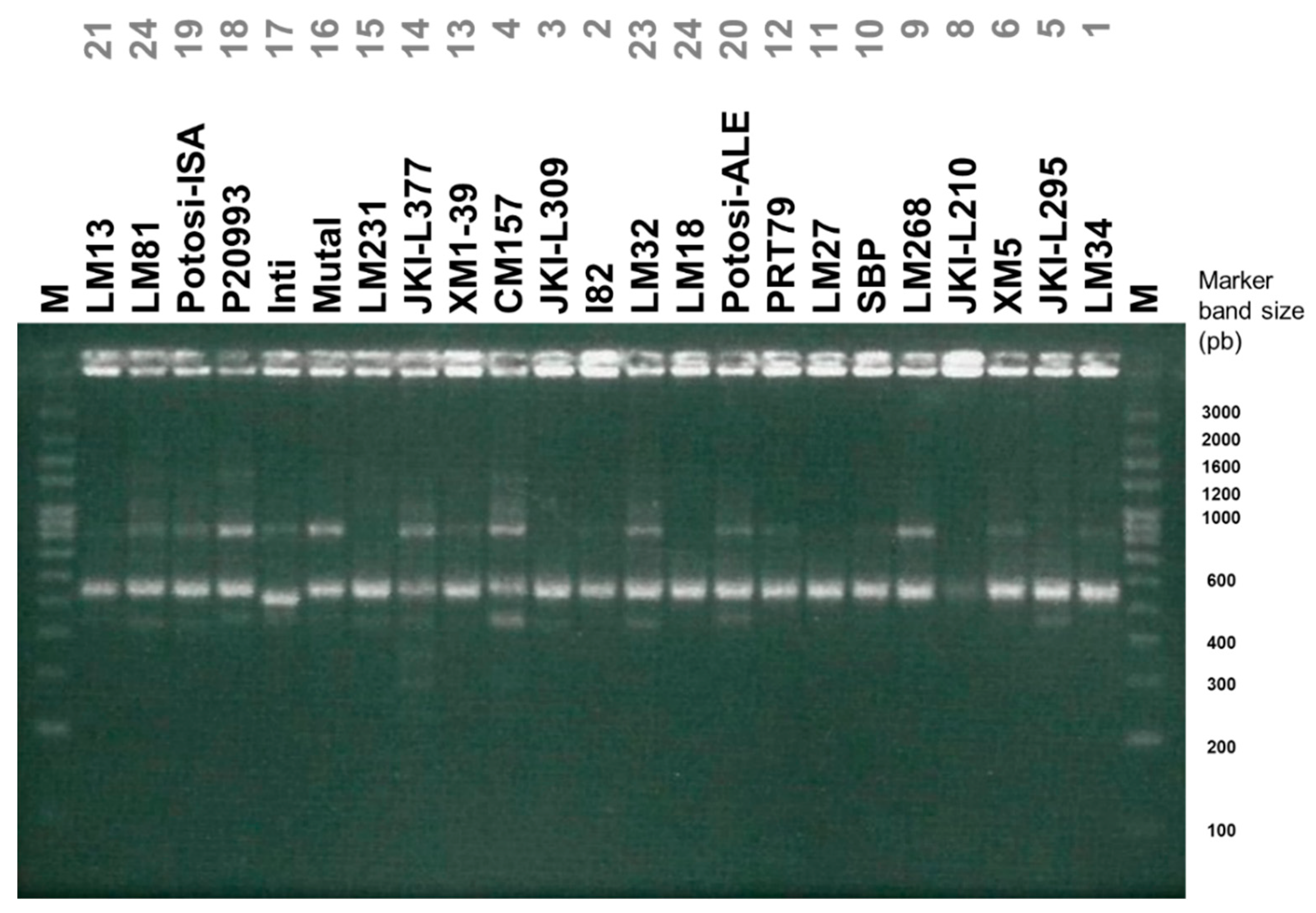
3.2. Diversity Assessed by Molecular Markers
3.3. Diversity Assessed by Genomic Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eastwood, R.J.; Drummond, C.S.; Schifino-Wittmann, M.T.; Hughes, C.E. Diversity and evolutionary history of lupins insights from new phylogenies. In Lupins for Health and Wealth. Proceedings of the 12th International Lupin Conference, Fremantle, Australia, 14–18 September 2008; Palta, J.A., Berger, J.B., Eds.; International Lupin Association: Canterbury, New Zealand, 2008; pp. 346–354. [Google Scholar]
- Gladstones, J.S. Lupins of the Mediterranean Region and Africa; Western Australian Department of Agriculture and Food: Kensington, Australia, 1974; Volume 26, pp. 1–48.
- Gladstones, J.S. Present situation and potential of Mediterranean/African Lupinus for crop production. In Proceedings of the Third International Lupin Conference, La Rochelle, France, 4–8 June 1984; pp. 18–37. [Google Scholar]
- Bellido, L.L.; Garcia, M.F. El Altramuz; Ministerio de Agricultura y Alimentación: Córdoba, Spain, 1991.
- Caligari, P.D.S.; Römer, P.; Rahim, M.A.; Huyghe, C.; Neves-Martins, J.; Sawicka-Sienkiewicz, E.J. The Potential of Lupinus mutabilis as a crop In Linking Research and Marketing Opportunities for Pulses in the 21st Century; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 34, pp. 569–574. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, S.E.; Mujica, A. El Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) y sus parientes silvestres. Bot. Econ. Andes Cent. 2006, 28, 458–482. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M. Quinolizidine alkaloids. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry, 8th ed.; Waterman, P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1993; pp. 197–239. [Google Scholar]
- Wink, M.; Meißner, C.; Witte, L. Patterns of quinolizidine alkaloids in 56 species of the genus Lupinus. Phytochemistry 1995, 38, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Larenas, F.E.; Linnemann, A.R.; Nout, M.J.R.; Koziol, M.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Lupinus mutabilis: Composition, uses, toxicology, and debittering. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1454–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borek, S.; Ratajczak, W.; Ratajczak, L. Regulation of storage lipid metabolism in developing and germinating lupin (Lupinus spp.) seeds. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2015, 37, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés, E.; Peralta, E.; Álvarez, M. Recetario Chochos en Su Punto; INIAP Santa Catalina: Quito, Ecuador, 2003; p. 43. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.M.N.; Talhinhas, P.; De Sousa, R.B. Yield and seed chemical composition of Lupinus mutabilis in Portugal. Rev. Ciênc. Agrar. 2016, 39, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.N.; Ferreira, R.B.; Teixeira, A.R. Seed Proteins ofLupinus mutabilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3821–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galek, R.; Sawicka-Sienkiewicz, E.; Zalewski, D.; Stawiński, S.; Spychała, K. Searching for low alkaloid forms in the Andean lupin (Lupinus mutabilis) collection. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2017, 53, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Flores, L.A.; Ruivemkamp, G.; Jongerden, J. Plant breeding and social rationality: The unintended effects of the release of a lupino seed (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) in Ecuador. Antípod. Rev. Antropol. Arqueol. 2016, 26, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Atchison, G.W.; Nevado, B.; Eastwood, R.J.; Contreras-Ortiz, N.; Reynel, C.; Madriñán, S.; Filatov, D.A.; Hughes, C.E. Lost crops of the Incas: Origins of domestication of the Andean pulse crop tarwi, Lupinus mutabilis. Am. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 1592–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galek, R.A.; Kozak, B.; Biela, A.; Zalewski, D.; Sawicka- Sienkiewicz, E.; Spychała, K.; Stawiń;ski, S. Seed coat thickness differentiation and genetic polymorphism for Lupinus mutabilis Sweet breeding. Turk. J. Field Crops 2016, 21, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, R. El Cultivo y la Utiliziación del Lupinus mutabilis Sweet; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Ge, X.; Gong, X.; Hao, G.; Zheng, S. ISSR Variation in the Endemic and Endangered Plant Cycas guizhouensis (Cycadaceae). Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almajali, D.; Abdel-Ghani, A.H.; Migdadi, H. Evaluation of genetic diversity among Jordanian fig germplasm accessions by morphological traits and ISSR markers. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 147, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.A.; Ghada, B.; Laila, E.; Hafid, A.; Bouchaib, K.; Amel, S.-H. Use of morphological traits and microsatellite markers to characterize the Tunisian cultivated and wild figs (Ficus carica L.). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 59, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Garcia-Gonzalez, C.; Tous, J.; Rovira, M. Genetic diversity revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers in hazelnut germplasm from northern Spain. Plant Breed. 2010, 129, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.-Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, P.-P.; Xiao, W.-J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, S.; Zhou, P.; Chang, H.-P.; He, Z.; Hu, R.; et al. Genetic diversity revealed by morphological traits and ISSR markers in 48 Okras (Abelmoschus escullentus L.). Physiol. Mol. Boil. Plants 2015, 21, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elameen, A.; Larsen, A.; Klemsdal, S.S.; Fjellheim, S.; Sundheim, L.; Msolla, S.; Masumba, E.; Rognli, O.A. Phenotypic diversity of plant morphological and root descriptor traits within a sweet potato, Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam., germplasm collection from Tanzania. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 2011, 58, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnotta, M.A.; Mondini, L.; Codianni, P.; Fares, C. Agronomical, quality, and molecular characterization of twenty Italian emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccon) accessions. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 2009, 56, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.C.; Tanksley, S.D. RFLP analysis of phylogenetic relationships and genetic variation in the genus Lycopersicon. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1990, 80, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, E.F.; Rahimmalek, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Ehtemam, M.H. Genetic structure and diversity of ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi) populations based on molecular, morphological markers, and volatile oil content. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 92, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpana, D.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, T.K.; Senthil, K.; Lee, Y.S. Assessment of genetic diversity among varieties of mulberry using RAPD and ISSR fingerprinting. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 134, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanijajiva, O. Genetic variability among durian (Durio zibethinus Murr.) cultivars in the Nonthaburi province, Thailand detected by RAPD analysis. J. Agric. Technol. 2011, 7, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Zietkiewicz, E.; Rafalski, A.; Labuda, D. Genome Fingerprinting by Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR)-Anchored Polymerase Chain Reaction Amplification. Genomics 1994, 20, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oney, S.; Tabur, S. Genome size and morphological variation in Brachypodium distachyon along altitudinal levels. Pak. J. Bot. 2018, 50, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, G.; Dzhambazova, T.; Moyankova, D.; Georgieva, D.; Michova, A.; Djilianov, D.; Möller, M. Morphological variation, genetic diversity and genome size of critically endangered Haberlea (Gesneriaceae) populations in Bulgaria do not support the recognition of two different species. Plant Syst. Evol. 2014, 300, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheidai, M.; Afshar, F.; Keshavarzi, M.; Talebi, S.-M.; Noormohammadi, Z.; Shafaf, T. Genetic diversity and genome size variability in Linum austriacum (Lineaceae) populations. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2014, 57, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, K.; Chang, D.; Bai, S.; Shen, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Ploidy Level and DNA Content of Erianthus arundinaceus as Determined by Flow Cytometry and the Association with Biological Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Taliaferro, C.M.; Bai, G.H.; Martin, D.L.; Anderson, J.A.; Anderson, M.P.; Edwards, R.M. Genetic Analyses of Chinese Accessions by Flow Cytometry and AFLP Markers. Crops Sci. 2006, 46, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermayer, R.; Świecicki, W.K.; Greilhuber, J. Flow Cytometric Determination of Genome Size in some Old World Lupinus Species (Fabaceae). Plant Biol. 1999, 1, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos-Arias, M.C.; Jiménez, J.E.; Vilca-Machaca, L.S. Analysis of Genetic Variability among thirty accessions of Andean Lupin (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) using ISSR molecular markers. Sci. Agropecu. 2015, 6, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galek, R.; Kozak, B.; Sawicka-Sienkiewicz, E.; Zalewski, D.; Nowosad, K. Searching for the most useful genotypes of Lupinus mutabilis sweet for breeding purpose. Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ. 2017, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smithm, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements—FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998.
- Talhinhas, P.; Leitão, J.; Martins, J. Collection of Lupinus angustifolius L. germplasm and characterisation of morphological and molecular diversity. Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBPGR. Lupin Descriptors; IBPGR: Rome, Italy, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Conover, W.J.; Iman, R.L. Rank Transformations as a Bridge between Parametric and Nonparametric Statistics. Am. Stat. 1981, 35, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Mazid, M.; Rafii, M.; Hanafi, M.M.; Rahim, H.; Shabanimofrad, M.; Latif, M.A. Agro-morphological characterization and assessment of variability, heritability, genetic advance and divergence in bacterial blight resistant rice genotypes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 86, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhinhas, P.; Neves-Martins, J.; Leitão, J. AFLP, ISSR and RAPD markers reveal high levels of genetic diversity among Lupinus spp. Plant Breed. 2003, 122, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, D.; Rajpal, V.R.; Raina, S.N.; Sasanuma, T.; Sasakuma, T. Assaying polymorphism at DNA level for genetic diversity diagnostics of the safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) world germplasm resources. Genetica 2009, 135, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.K.; Chabane, K.; Hendre, P.S.; Aggarwal, R.K.; Graner, A. Comparative assessment of EST-SSR, EST-SNP and AFLP markers for evaluation of genetic diversity and conservation of genetic resources using wild, cultivated and elite barleys. Plant Sci. 2007, 173, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Agrawal, V. Assessment of genetic diversity, population structure and sex identification in dioecious crop, Trichosanthes dioica employing ISSR, SCoT and SRAP markers. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolezel, J.; Sgorbati, S.; Lucretti, S. Comparison of three DNA fluorochromes for flow cytometric estimation of nuclear DNA content in plants. Physiol. Plant. 1992, 85, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.D.; Smith, J.B. Nuclear DNA Amounts in Angiosperms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 1976, 274, 227–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Doležel, J.; Santos, C. Two New Nuclear Isolation Buffers for Plant DNA Flow Cytometry: A Test with 37 Species. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležel, J.; Bartoš, J. Plant DNA Flow Cytometry and Estimation of Nuclear Genome Size. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doležel, J.; Bartoš, J.; Voglmayr, H.; Greilhuber, J. Nuclear DNA content and genome size of trout and human. Cytometry 2003, 51, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhinhas, P. Caracterização de Germoplasma do Género Lupinus, Avaliação da Resistência à Antracnose e Estudos da Diversidade e Taxinomia do Agente Causal (Colletotrichum Acutatum Simmonds ex Simmonds). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Técnica de Lisboa, Lisboa, Portugal, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, A.; Huyghe, C.; Rahim, M.A.; Roemer, P.; Neves-Martins, J.M.; Sawicka-Sienkiewicz, E.; Caligari, P.D.S. Effects of genotype and environment on architecture and flowering time of indeterminate Andean lupins (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1998, 49, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, N.A.; Kosev, V.I. Analysis of Character Association of Quantitative Traits in Lupinus Species. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, J.; Buirchell, B.; Cowling, W. Relationship between morphological variation and geographical origin or selection history in Lupinus pilosus. Plant Breed. 2006, 115, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.W.; Robinson, H.F.; Comstock, R.E. Estimates of Genetic and Environmental Variability in Soybeans. Agron. J. 1955, 47, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Q.A.; Tariq, K.; Iftikhar, A.; Nazir, A.; Muhammad, A.; Muhammad, F.; Muhammad, U. Estimation of heritability and selection response for some yield traits in F3 populations of wheat. Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci. 2017, 9, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, G.; Tesfaye, K.; Bekele, E. Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) analysis of wild and cultivated rice species from Ethiopia. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 5048–5059. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Z.; Mori, N.; Kawamura, M.; Ishii, T.; Yoshida, S.; Ikegami, M.; Takumi, S.; Nakamura, C. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of Japanese sake-brewing rice as revealed by AFLP and nuclear and chloroplast SSR markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1586–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirinos-Aria, M.C.; Jiménez, J.E. Transference of some microsatellite molecular markers from Fabaceae family to Andean Lupin (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet). Sci. Agropecu. 2015, 6, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussell, J.D.; Waycott, M.; Chappill, J.A. Arbitrarily amplified DNA markers as characters for phylogenetic inference. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2005, 7, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Saha, S.; Bandyopadhyay, T.K.; Ghosh, P. Efficiency of ISSR marker for characterization of Cymbopogon germplasms and their suitability in molecular barcoding. Plant Syst. Evol. 2014, 301, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykut Tonk, F.; Tosun, M.; Ilker, E.; Istipliler, D.; Tatar, O. Evaluation and comparison of ISSR and RAPD markers for assessment of genetic diversity in triticale genotypes. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Grativol, C.; Lira-Medeiros, C.D.F.; Hemerly, A.S.; Ferreira, P.C.G. High efficiency and reliability of inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) markers for evaluation of genetic diversity in Brazilian cultivated Jatropha curcas L. accessions. Mol. Boil. Rep. 2010, 38, 4245–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiyeva, S.V.; Akparov, Z.I.; Hasanov, N.A.; Mustafayeva, Z.P.; Hajiyev, E.S.; Mammadov, A.T.; Izzatullayeva, V.I.; Babayeva, S.M.; Sharifova, S.S.; Mammadov, A.M.; et al. ISSR Analysis of Variability of Cultivated Form and Varieties of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) from Azerbaijan. Russ. J. Genet. 2018, 54, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamare, A.; Rao, S.R. Efficacy of RAPD, ISSR and DAMD markers in assessment of genetic variability and population structure of wild Musa acuminata colla. Physiol. Mol. Boil. Plants 2015, 21, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.L.; Cheng, X. Genetic diversity and a population structure analysis of accessions in the Chinese cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] germplasm collection. Crop J. 2017, 5, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Gituru, R.W.; Juntawong, N.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L. Genetic diversity and classification of Nelumbo germplasm of different origins by RAPD and ISSR analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2010, 125, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganowska, B.; Wolko, B.; Śliwińska, E.; Kaczmarek, Z. Nuclear DNA Content Variation and Species Relationships in the Genus Lupinus (Fabaceae). Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, A.L.; Biradar, D.P.; Nelson, R.L.; McCloskey, R.; Yeater, K.M. Documenting Intraspecfic Genome Size Variation in Soybean. Crops Sci. 2004, 44, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, M.F.; Poggio, L.; Cámara-Hernández, J.; González, G.E. Intra-specific variation in genome size in maize: Cytological and phenotypic correlates. AoB Plants 2015, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kerstetter, R.A.; Michael, T.P. Evolution of Genome Size in Duckweeds (Lemnaceae). J. Bot. 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Ramos, M.A. Satellite DNA in Plants: More than Just Rubbish. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 146, 153–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, D.A. Evolution of genome size: New approaches to an old problem. Trends Genet. 2001, 17, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Ramos, M.A. Satellite DNA: An Evolving Topic. Genes 2017, 8, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, C.A. Mechanisms and Control of Rapid Genomic Changes in Flax. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y. Genome Size Unaffected by Variation in Morphological Traits, Temperature, and Precipitation in Turnip. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.M.; Moles, A.T.; Leitch, I.J.; Bennett, M.D.; Dickie, J.B.; Knight, C.A. Correlated evolution of genome size and seed mass. New Phytol. 2007, 173, 422–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
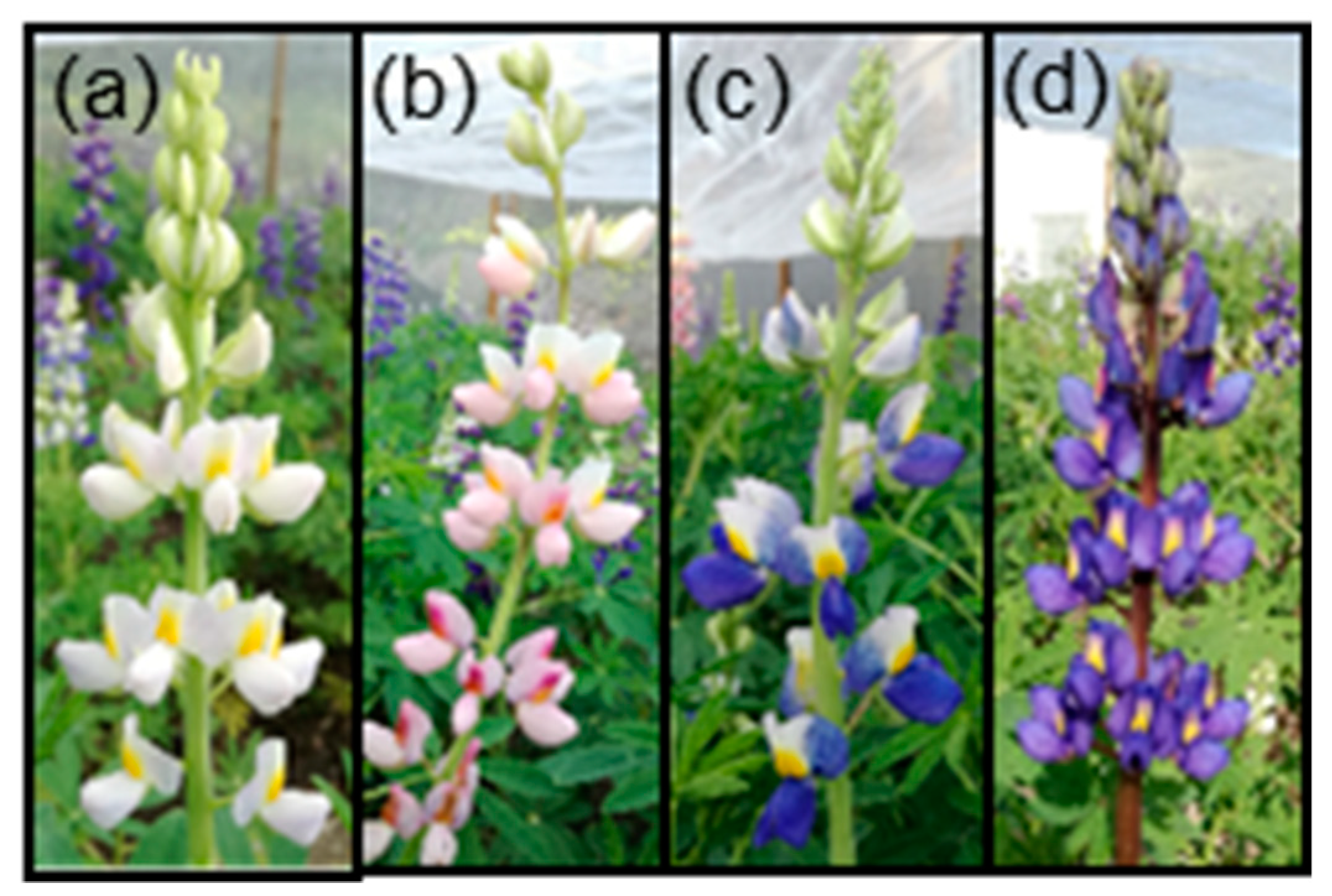


| Acronym | Trait 1 | Method (unit) |
|---|---|---|
| DUF | Days from sowing until flowering 3 | Counting (nr 4) |
| NLMS | Number of leaves on the main stem | Counting (nr) |
| HUFF | Height up to first flower | Metric meas. 5 (cm) |
| ADNL | Average distance between leaves | = HUFF/NLMS (cm) |
| NPMS | Number of pods on the main stem | Counting |
| PLMS | Pod length on the main stem | Metric meas. (cm) |
| PWMS | Pod width on the main stem | Metric meas. (cm) |
| RBLWPMS | Ratio length-width of pods on the main stem | = PLMS/PWMS (dim. 6) |
| NSMS | Number of seeds on the main stem | Counting (nr) |
| SLMS | Seed length on the main stem 2 | Metric meas. (cm) |
| SWMS | Seed width on the main stem | Metric meas. (cm) |
| RBLWSMS | Ratio length-width of seed on the main stem 2,3 | = SLMS/SWMS (dim.) |
| NSPMS | Number of seed per pod on the main stem | Counting (nr) |
| WSMS | Weight of seeds on the main stem | Weighting (g) |
| TSWMS | Thousand seeds weight on the main stem 2 | = WSMS/NSMS*1000 (g) |
| NPB | Number of primary branches | Counting (nr) |
| ADBPB | Average distance between primary branches 2,3 | = HUFF/NPB (cm) |
| SLPB | Sum of the length of primary branches | Metric meas. (cm) |
| ALPB | Average length of primary branches | = SLPB/NPB (cm) |
| PBL | Proportion of leaves with branches 2,3 | = NPB/NLMS (%) |
| NPPB | Number of pods on primary branches 2 | Counting (nr) |
| NSPB | Number of seeds on primary branches 2 | Counting (nr) |
| NSPPB | Number of seeds per pod on primary branches | = NSPB/NPPB (nr) |
| NPPPB | Number of pods per primary branch | = NPPB/NPB (nr) |
| WSPB | Weight of seeds on primary branches 2 | Weighting (g) |
| WSPPB | Thousand seeds weight per primary branches | Weighting (g) |
| TSWPB | Thousand seeds weight on primary branches | = WSPB/NSPB × 1000 (g) |
| TBL | Total branch length | = SLPB+ HUFF |
| TNP | Total number of pods 2 | Counting (nr) |
| TNS | Total number of seeds | Counting (nr) |
| TNSPP | Total number of seeds per pod | = TNS/TNP (nr) |
| TW | Total seed weight | Weighing (g) |
| PSMS | Percentage of seed weight on the main stem | = WSMS/TW (%) |
| PSPB | Percentage of seed weight on primary branches 3 | = WSPB/TW (%) |
| TTSW | Total thousand seeds weight | = TW/TNS × 1000 (g) |
| SWBLR | Seed weight/total branch length ratio | = TW/TBL × 100 (g/m) |
| Accession | SFC 2 | DUF 3 | NLMS | HUFF | NPB | SLPB | PBL | TBL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JKI-L309 | D | 80.8 a | 12.9 a | 40.0 a | 2.8 abc | 81.9 a | 21.6 efgh | 122.0 a |
| JKI-L377 | B | 92.8 b | 12.8 a | 47.7 bc | 2.7 ab | 87.2 a | 19.9 cde | 137.7 ab |
| MUTAL | A | 93.5 b | 14.8 b | 60.0 gh | 3.3 efg | 152.0 h | 22.8 efgh | 213.1 i |
| JKI-L210 | C | 96.4 c | 15.8 def | 50.0 bcd | 3.0 cde | 89.1 a | 19.1 bc | 142.2 bc |
| LM13 | C | 97.7 cd | 16.5 fg | 53.0 cdef | 3.9 ijk | 132.0 cdefg | 23.3 efghi | 185.6 efgh |
| LM81 | C | 97.8 cd | 15.2 bcd | 54.3 cdef | 3.3 cdef | 127.0 bcdef | 21.7 defgh | 182.4 defgh |
| JKI-L295 | A | 98.6 cd | 16.2 f | 60.7 fgh | 2.6 a | 114.1 b | 16.3 a | 175.2 def |
| LM268 | A | 98.8 cd | 16.3 f | 60.9 gh | 3.6 hij | 133.3 defgh | 22.2 efgh | 194.2 fghi |
| PRT79 | C | 98.8 cd | 17.4 hi | 65.1 hi | 3.5 hij | 136.2 efgh | 20.4 cde | 202.3 ghi |
| I82 | D | 99.9 cd | 15.9 def | 52.4 cde | 3.4 fghi | 115.8 bc | 21.2 def | 169.0 de |
| LM34 | D | 100.1 cd | 15.2 bcd | 50.9 bcd | 3.7 hijk | 124.5 bcde | 24.3 i | 175.6 de |
| Potosi-ALE | C | 100.3 cd | 15.0 b | 53.6 cde | 3.5 fghi | 134.2 bcdef | 23.4 fghi | 188.7 efgh |
| LM27 | A | 100.4 cd | 15.9 cdef | 55.8 efgh | 3.5 fghi | 125.3 bcdef | 21.9 defgh | 181.7 efgh |
| Potosi-ISA | C | 100.5 cd | 16.7 fg | 58.9 efgh | 3.4 fghi | 118.5 bcd | 20.7 cde | 177.5 def |
| LM18 | C | 100.5 cd | 17.7 ghi | 54.6 defg | 3.7 hij | 127.8 bcdef | 20.8 cde | 182.5 defg |
| CM157 | C | 100.6 cd | 15.4 bcde | 49.1 bcd | 3.0 bcd | 111.4 b | 18.6 bc | 160.7 cd |
| XM-5 | B | 101.2 cd | 16.4 fg | 58.5 efgh | 3.5 fghi | 125.0 bcdef | 21.3 defg | 184.1 efgh |
| LM32 | C | 101.6 d | 16.2 ef | 53.7 cdef | 3.4 fgh | 125.3 bcdef | 21.5 def | 179.6 defg |
| LM231 | C | 102.4 d | 18.0 i | 64.8 hi | 4.6 k | 163.2 gh | 25.5 ghi | 229.4 hi |
| P20993 | B | 102.6 d | 15.1 bc | 55.3 defg | 3.6 ghij | 125.1 bcdef | 23.5 hi | 180.4 defg |
| INTI | C | 102.6 cd | 17.7 i | 68.9 i | 3.3 def | 147.0 fgh | 18.6 b | 218.7 i |
| SBP | C | 103.0 d | 16.0 f | 58.6 efgh | 3.2 def | 119.7 bcdef | 19.7 bcd | 179.4 defgh |
| XM1-39 | C | 103.4 d | 16.2 f | 54.6 defg | 3.1 def | 110.3 bc | 18.7 bc | 166.4 de |
| Mihai | 97.6 cd | 16.6 fgh | 42.6 ab | 3.7 hijk | 122.1 bcdef | 22.5 defgh | 164.7 cde | |
| Misak | 98.6 cd | 18.8 j | 38.2 a | 3.8 jk | 120.7 bcdefg | 20.4 cde | 158.9 cd | |
| p-value 4 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| p-value 5 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.020 | 0.000 | |
| p-value 6 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Accession | TNP 2 | TNS | TNSPP | TTSW | PSMS | PSPB | TW | SWBLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JKI-L210 | 11.5 a | 36.6 ab | 3.3 fg | 101.4 a | 87.8 | 12.2 | 3.7 a | 1.3 a |
| INTI | 13.7 a | 37.4 ab | 2.7 bcd | 154.0 cd | 74.6 | 25.4 | 5.7 b | 2.3 ef |
| XM1-39 | 13.9 ab | 36.1 ab | 2.8 bcd | 180.4 jkl | 78.1 | 21.9 | 6.3 b | 1.3 a |
| JKI-L377 | 19.8 cdef | 61.3 cde | 3.0 ef | 103.7 a | 72.2 | 27.8 | 6.3 b | 3 def |
| JKI-L309 | 16.1 bc | 49.2 cd | 3.1 efg | 159.7 ef | 72.2 | 27.8 | 7.8 c | 3.1 fg |
| SBP | 16.8 cd | 43.6 bc | 2.6 bc | 188.7 lm | 77.0 | 23.0 | 8.0 cd | 1.7 abc |
| LM32 | 22.1 efg | 56.7 def | 2.7 bcd | 150.8 cde | 67.3 | 32.7 | 8.4 cde | 1.1 ab |
| Potosi-ALE | 25.0 gh | 62.2 efg | 2.6 b | 182.7 bc | 59.1 | 40.9 | 8.4 cdef | 1.5 abcd |
| LM34 | 24.9 gh | 67.9 fg | 2.7 bcde | 131.6 b | 55.0 | 45.0 | 8.5 cde | 1.6 abcd |
| JKI-L295 | 18.0 cde | 48.0 cd | 2.7 bcd | 188.4 m | 80.3 | 19.7 | 9.0 def | 2.2 bcdef |
| LM231 | 22.9 fgh | 59.9 def | 2.6 bcd | 169.4 fgh | 56.2 | 43.8 | 9.5 cdef | 1.5 abcd |
| MUTAL | 19.2 def | 52.2 cd | 2.8 bcd | 184.7 lm | 67.2 | 32.8 | 9.6 def | 3.3 g |
| LM81 | 23.1 gh | 63.1 fg | 2.9 bcde | 157.8 ef | 57.7 | 42.3 | 9.7 fghi | 1.8 abcde |
| LM13 | 22 fgh | 57.5 def | 2.7 bcd | 179.0 ijk | 70.3 | 29.7 | 9.9 efgh | 1.8 abcde |
| XM-5 | 23.8 gh | 59.7 def | 2.6 bc | 170.1 ghi | 61.2 | 38.8 | 9.9 defg | 1.9 abcde |
| CM157 | 23.0 gh | 64.9 efg | 2.8 cde | 157.3 def | 61.6 | 38.4 | 10.0 fghij | 2.1 abcdef |
| LM27 | 23.0 efg | 62.0 def | 2.8 bcde | 178.4 ghijk | 64.1 | 35.9 | 10.5 fghij | 1.8 abcde |
| PRT79 | 22.5 gh | 62.8 fg | 2.8 de | 177.6 hijk | 58.3 | 41.7 | 11.1 ghijk | 2.1 abcde |
| P20993 | 24.8 hi | 67.7 g | 2.8 bcde | 168.9 fg | 58.0 | 42.0 | 11.1 ijk | 2.1 abcdef |
| I82 | 21.8 efg | 64.5 fg | 3.1 efg | 175.4 ghij | 62.5 | 37.5 | 11.2 ghijk | 2.2 def |
| Potosi-ISA | 23.7 gh | 64.3 fg | 3.1 bcde | 184.0 klm | 55.7 | 44.3 | 11.5 jk | 2.3 bcdef |
| LM18 | 23.2 gh | 66.1 efg | 2.9 def | 190.5 lm | 52.1 | 47.9 | 12.6 hijk | 2.2 cdef |
| LM268 | 22.1 gh | 50.5 cd | 2.2 a | 289.2 n | 40.9 | 59.1 | 13.8 k | 2.7 abcdef |
| Mihai | 25.7 hi | 101.2 h | 4.0 h | 370.7 n | 28.8 | 71.1 | 36.7 l | 23.3 abcde |
| Misak | 28.8 i | 98.0 h | 3.4 g | 381.5 n | 45.0 | 54.9 | 37.2 l | 22.9 abcde |
| p-value 3 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| p-value 4 | 0.040 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.969 | 0.756 | 0.004 | 0.000 |
| p-value 5 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Traits | Average | Phenotypic Variance | Genotypic Variance | PCV 1 | GCV 2 | H 2,3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | 2016/17 | 2017/18 | |
| TSWMS | 184.15 | 10.94 | 1368.99 | 1779.1 | 1368.82 | 1599.4 | 20.09 | 21.91 | 20.09 | 20.77 | 1 | 0.9 |
| TSWPB | 156 | 3.04 | 1423.64 | 1562.07 | 1423.39 | 1466.89 | 24.19 | 24.64 | 24.18 | 23.88 | 1 | 0.94 |
| TTSW | 158.29 | 177.98 | 1145.83 | 1561.49 | 1113.07 | 1339.14 | 21.39 | 22.20 | 21.08 | 20.56 | 0.97 | 0.86 |
| DUF | 87.67 | 3.04 | 17.21 | 23.25 | 16.59 | 10.85 | 4.73 | 4.52 | 4.65 | 3.09 | 0.96 | 0.47 |
| WSPPB | 52.29 | 23.32 | 148.79 | 382.43 | 140.77 | 289.57 | 23.33 | 30.14 | 22.69 | 26.22 | 0.95 | 0.76 |
| HUFF | 73.1 | 31.24 | 83.85 | 26.45 | 78.7 | 23.64 | 12.53 | 12.29 | 12.14 | 11.61 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| NLMS | 15.21 | 23.32 | 2.14 | 1.36 | 2 | 1.22 | 9.62 | 7.09 | 9.29 | 6.73 | 0.93 | 0.9 |
| SLMS | 0.95 | 51.2 | 0 | 0.6 | 0 | 0.57 | 6.72 | 8.19 | 6.48 | 7.97 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| PWMS | 1.57 | 7.57 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 7.12 | 8 | 6.75 | 7.83 | 0.9 | 0.96 |
| SWBLR | 4.31 | 192.52 | 1.31 | 0 | 1.17 | 0 | 26.54 | 20.07 | 25.09 | 18.33 | 0.89 | 0.83 |
| TBL | 220.4 | 352.93 | 1183.56 | 421 | 1044.3 | 344.87 | 15.61 | 14.55 | 14.66 | 13.17 | 0.88 | 0.82 |
| ALPB | 46.86 | 10.94 | 17.46 | 27.53 | 15.11 | 22.04 | 8.92 | 14.9 | 8.29 | 13.33 | 0.87 | 0.8 |
| TW | 9.49 | 31.24 | 7.7 | 6391.49 | 6.73 | 6049.35 | 29.24 | 22.65 | 27.33 | 22.04 | 0.87 | 0.95 |
| ADNL | 4.84 | 10.48 | 0.16 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | 8.35 | 9.57 | 7.72 | 8.82 | 0.85 | 0.85 |
| PSMS | 0.66 | 99 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 16.93 | 19.84 | 15.5 | 17.91 | 0.84 | 0.81 |
| PSPB | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 32.29 | 26.56 | 29.56 | 21.14 | 0.84 | 0.63 |
| SLPB | 147.29 | 2.64 | 796.89 | 291.04 | 671.56 | 218.18 | 19.17 | 17.23 | 17.59 | 14.92 | 0.84 | 0.75 |
| NSMS | 31.29 | 0.66 | 48.96 | 38.56 | 40.63 | 25.37 | 22.36 | 19.88 | 20.37 | 16.12 | 0.83 | 0.66 |
| WSMS | 5.69 | 5.54 | 1.82 | 2.76 | 1.52 | 2.3 | 23.74 | 29.96 | 21.66 | 27.39 | 0.83 | 0.84 |
| WSPB | 4.19 | 3.6 | 2.68 | 2.72 | 2.19 | 2.19 | 39.08 | 45.87 | 35.36 | 41.15 | 0.82 | 0.8 |
| ADBPB | 25.11 | 3.56 | 12.34 | 14.96 | 9.59 | 10.17 | 13.99 | 22.22 | 12.33 | 18.32 | 0.78 | 0.68 |
| NPMS | 9.67 | 7.94 | 3.85 | 2.44 | 2.98 | 1.88 | 20.29 | 14.9 | 17.84 | 13.09 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| NPB | 3.12 | 3.03 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 13.18 | 13.41 | 11.52 | 12.25 | 0.76 | 0.84 |
| NPPPB | 3.11 | 1.39 | 0.67 | 0.81 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 26.38 | 29.55 | 22.9 | 23.77 | 0.75 | 0.65 |
| PBL | 0.21 | 1.27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11.77 | 17.57 | 10.18 | 13.96 | 0.75 | 0.63 |
| TNS | 62.05 | 3.56 | 191.54 | 140.03 | 142.42 | 104.68 | 22.3 | 23.11 | 19.23 | 19.98 | 0.74 | 0.75 |
| NSPB | 26.83 | 0.41 | 72.78 | 77.2 | 52.66 | 51.89 | 31.8 | 37.68 | 27.05 | 30.89 | 0.72 | 0.67 |
| NPPB | 10.09 | 0.18 | 8.17 | 13.53 | 5.77 | 10.18 | 28.32 | 33.64 | 23.8 | 29.18 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| TNP | 21.62 | 64.89 | 22.19 | 20.2 | 15.86 | 15.97 | 21.79 | 22.64 | 18.42 | 20.13 | 0.71 | 0.79 |
| PLMS | 6.96 | 9.46 | 0.25 | 7.88 | 0.17 | 7.87 | 7.17 | 29.04 | 5.93 | 29.65 | 0.68 | 1 |
| RBLWSMS | 1.28 | 19.85 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.66 | 4.81 | 2.13 | 0 | 0.64 | 0.45 |
| SWMS | 0.75 | 160.41 | 0 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.36 | 7.29 | 8.1 | 5.48 | 7.88 | 0.57 | 0.95 |
| RBLWPMS | 4.46 | 141.02 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 5.6 | 6.61 | 4.06 | 6.13 | 0.53 | 0.86 |
| TNSPP | 2.98 | 10.48 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 9.1 | 11.59 | 6.55 | 10.5 | 0.52 | 0.82 |
| NSPPB | 2.74 | 4.64 | 0.18 | 6.04 | 0.08 | 2.37 | 15.5 | 30.97 | 10.04 | 19.41 | 0.42 | 0.39 |
| NSPMS | 3.48 | 1.52 | 0.21 | 0.2 | 0 | 0.14 | 13.28 | 14.87 | 0.67 | 12.17 | 0 | 0.67 |
| Primer | Bands | PB | MB | PB (%) | MB (%) | PIC | EMR | RP | MI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVH(TG)7 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 50 | 50 | 0.23 | 2 | 13.58 | 0.46 |
| GA8YT | 6 | 1 | 5 | 16.66 | 83.33 | 0.71 | 0.16 | 5 | 0.11 |
| AG8YT | 6 | 1 | 5 | 16.66 | 83.33 | 0.72 | 0.16 | 4.58 | 0.12 |
| GT8YC | 4 | 3 | 1 | 75 | 25 | 0.24 | 2.25 | 6.42 | 0.54 |
| AG8YC | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 100 | 0.58 | 0 | 6 | 0.00 |
| AG8YG | 8 | 2 | 6 | 25 | 75 | 0.48 | 0.5 | 10.33 | 0.24 |
| Total | 37 | 11 | 26 | ||||||
| Minimum | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 25 | 0.23 | 0 | 4.58 | 0 |
| Maximum | 8 | 4 | 6 | 50 | 100 | 0.72 | 2.25 | 13.58 | 0.54 |
| Mean | 6.16 | 1.83 | 4.33 | 30.55 | 69.44 | 0.49 | 0.85 | 7.65 | 0.24 |
| Accession | Genome Size (Mbp) | H.G. 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average | StDev 1 | ||
| SBP | 1897.3 | 18.4 | a |
| XM1-39 | 1907.3 | 17.0 | a |
| JKI-L378 | 1938.0 | 49.0 | ab |
| Prt-79 | 1957.4 | 16.2 | ab |
| JKI-L377 | 1961.4 | 16.3 | ab |
| Mutal | 1967.6 | 121.6 | abc |
| JKI-L295 | 1969.0 | 11.8 | abc |
| JKI-L210 | 1973.6 | 26.9 | bcd |
| LM13 | 1975.7 | 118.4 | bcd |
| JKI-L309 | 1979.7 | 37.6 | bcd |
| LM231 | 1984.1 | 100.4 | cd |
| LM18 | 1986.4 | 54.6 | cde |
| XM5 | 2009.1 | 20.1 | cde |
| P-20993 | 2021.5 | 22.8 | cde |
| Potosi-ISA | 2024.3 | 36.1 | cde |
| Potosi-ALE | 2024.8 | 19.3 | cde |
| LM27 | 2027.7 | 23.9 | cde |
| LM32 | 2040.9 | 17.9 | de |
| CM157 | 2040.9 | 43.8 | de |
| I82 | 2041.6 | 10.9 | de |
| Inti | 2058.1 | 23.9 | ef |
| LM268 | 2078.9 | 10.1 | f |
| LM81 | 2080.2 | 13.1 | f |
| LM34 | 2083.2 | 17.3 | f |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guilengue, N.; Alves, S.; Talhinhas, P.; Neves-Martins, J. Genetic and Genomic Diversity in a Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) Germplasm Collection and Adaptability to Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Agronomy 2020, 10, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010021
Guilengue N, Alves S, Talhinhas P, Neves-Martins J. Genetic and Genomic Diversity in a Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) Germplasm Collection and Adaptability to Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Agronomy. 2020; 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuilengue, Norberto, Sofia Alves, Pedro Talhinhas, and João Neves-Martins. 2020. "Genetic and Genomic Diversity in a Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) Germplasm Collection and Adaptability to Mediterranean Climate Conditions" Agronomy 10, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010021
APA StyleGuilengue, N., Alves, S., Talhinhas, P., & Neves-Martins, J. (2020). Genetic and Genomic Diversity in a Tarwi (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) Germplasm Collection and Adaptability to Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Agronomy, 10(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010021





