Smart and Biodegradable Polymers in Tissue Engineering and Interventional Devices: A Brief Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Relevance and Methodology
3. Trends and Advances in Smart and Biodegradable Materials
3.1. Shape Memory Polymers
3.2. Tissue Engineering
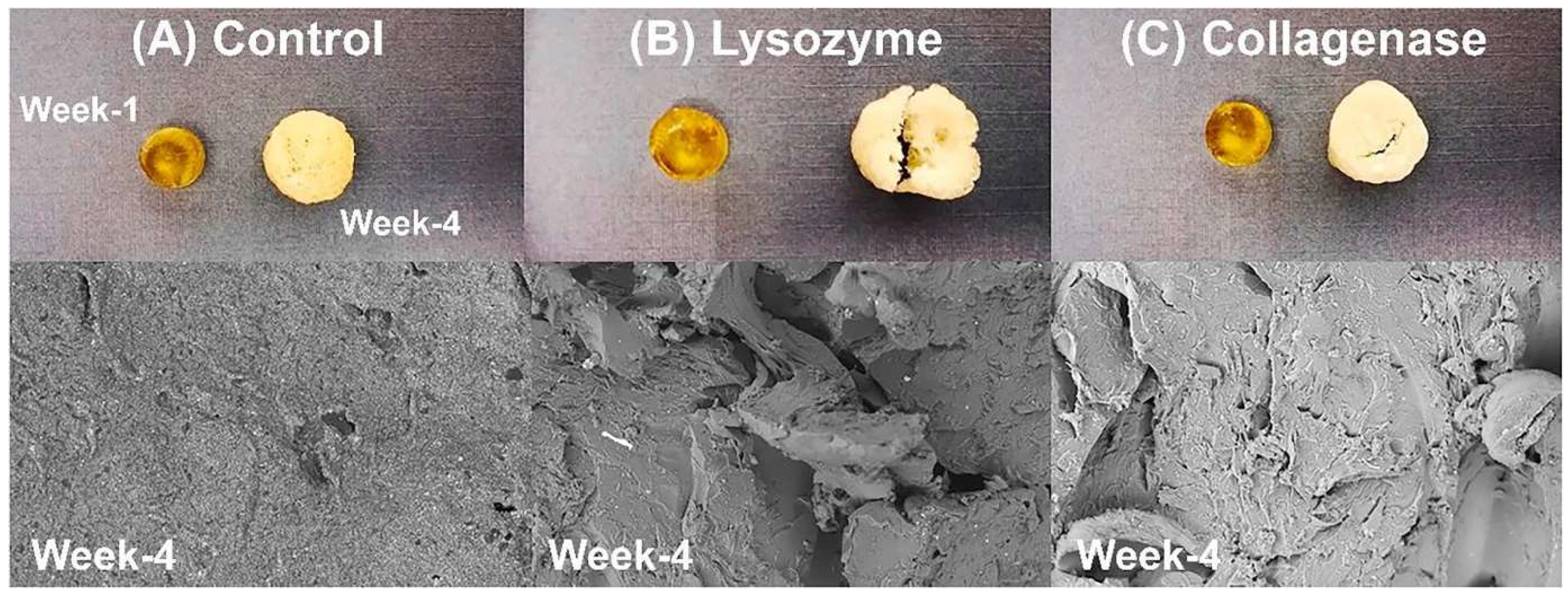
3.3. Degradable Synthetic Polymers Drug Delivery and Bone Repair
3.4. On-Demand Degradable Polymer
3.5. Aniline-Based Biomaterials
3.6. Inorganic Biomaterials
- Bioinert materials—such as aluminium oxide, zirconia, titanium, and its alloys—do not chemically interact with surrounding tissue. They are typically employed in load-bearing implants, for instance, bone-support devices and hip prosthesis femoral heads.
- Bioactive materials—like bioglasses and glass-ceramics—form direct bonds with living tissue and have been used to fill minor bone defects and periodontal irregularities.
- Bioresorbable materials—including calcium phosphates (CaPs), calcium phosphate cements (CPCs), calcium carbonates, and calcium silicates—undergo gradual resorption in vivo, eventually being replaced by natural bone.
- Functionalization via Ionic Doping
- The 3D Scaffolds in TERM
- Nutrient transport to support cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation,
- Structural cues for cell attachment, growth, and migration,
- Mechanical stability,
- Controlled degradation without toxicity or inflammation.
- Applications of Inorganic Biomaterials
3.7. Natural Polymers
4. Mechanisms and Design Principles of SMPs
4.1. Thermally Activated SMPs
4.2. Light-Activated SMPs
4.3. pH-Sensitive SMPs
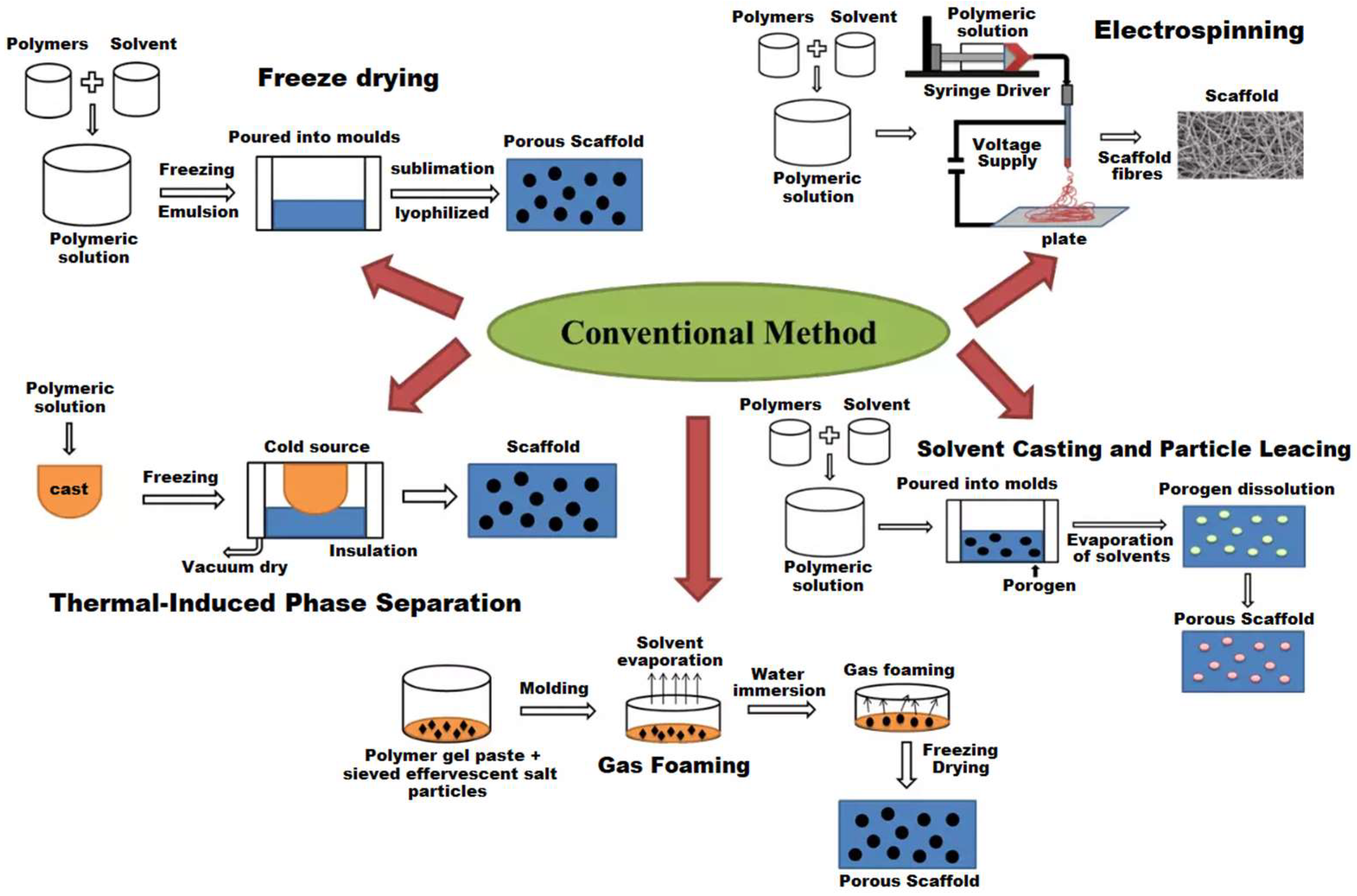
5. Methods for Creating Polymer Scaffolds
6. Available Biodegradable Devices
7. Discussion
8. Future Directions and Outlook
9. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral organoids model human brain development and microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaraju, S.M.; Shen, Y.; Elele, E.; Khusid, B.; Eshghinejad, A.; Li, J.; Jaffe, M.; Arinzeh, T.L. Three-dimensional piezoelectric fibrous scaffolds selectively promote mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Biomaterials 2017, 149, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipskas, J.; Deep, K.; Yao, W. Robotic-assisted 3D bioprinting for repairing bone and cartilage defects through a minimally invasive approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallaev, R. Advances in Materials with Self-Healing Properties: A Brief Review. Materials 2024, 17, 2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mura, S.; Nicolas, J.; Couvreur, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Cambre, J.N.; Sumerlin, B.S. Future perspectives and recent advances in stimuli-responsive materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 278–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, D.; Younes, H. Biodegradable PEO/PLA block copolymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1988, 22, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendlein, A.; Kelch, S. Shape-memory polymers as stimuli-sensitive implant materials. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2005, 32, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toncheva, A.; Paneva, D.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone) membranes containing antimicrobial agents for wound dressing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3556–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Chen, S.; Ma, J.; Dong, C.; Banerjee, H.; Laperrousaz, S.; Piveteau, P.L.; Meng, Y.; Leng, J.; Sorin, F. Multimaterial Shape Memory Polymer Fibers for Advanced Drug Release Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; He, R.; Deng, G.; Peng, Z.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; He, X.; et al. Cryogenic 3D Printing of w/o Pickering Emulsions Containing Bifunctional Drugs for Producing Hierarchically Porous Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds with Antibacterial Capability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Jacob, A. Techniques in scaffold fabrication process for tissue engineering applications: A review. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarin, M.; Todesco, M.; Fontanella, C.G.; Morlacco, A.; Dal Moro, F.; Bagno, A. Hybrid Materials for Tissue Repair and Replacement: Another Frontier in Biomaterial Exploitation Focusing on Cardiovascular and Urological Fields. Processes 2023, 11, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunja, N.J.; Athanasiou, K.A. Biodegradable materials in arthroscopy. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2006, 14, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Cheong, N.; He, Z.; Zhang, T. Application of Hydroxyapatite Composites in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginebra, M.P.; Espanol, M.; Maazouz, Y.; Bergez, V.; Pastorino, D. Bioceramics and bone healing. EFORT Open Rev. 2018, 3, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, A.V.; Islamov, S.R.; Ignatyev, K.V.; Mardashov, D.V. Laboratory Studies of Polymer Compositions for Well-Kill under Increased Fracturing. Perm J. Pet. Min. Eng. 2020, 20, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecen, B.; Hassan, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.S. Smart Biomaterials in Biomedical Applications: Current Advances and Possible Future Directions. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, 2200550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Shape Memory Polymers and Their Composites in Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 97, 864–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayyoub, T.; Maksimkin, A.V.; Filippova, O.V.; Tcherdyntsev, V.V.; Telyshev, D.V. Shape Memory Polymers as Smart Materials: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowiak, J.; Klekiel, T.; Będziński, R. Biodegradable Polymers in Biomedical Applications: A Review—Developments, Perspectives and Future Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socci, M.C.; Rodríguez, G.; Oliva, E.; Fushimi, S.; Takabatake, K.; Nagatsuka, H.; Felice, C.J.; Rodríguez, A.P. Polymeric Materials, Advances and Applications in Tissue Engineering: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, T.; Vadivel, G.; Ramasamy, B.; Murugesan, G.; Sebaey, T.A. Biodegradable Conducting Polymer-Based Composites for Biomedical Applications—A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcerak-Woźniak, A.; Dzwonkowska-Zarzycka, M.; Kabatc-Borcz, J. A Comprehensive Review of Stimuli-Responsive Smart Polymer Materials—Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Materials 2024, 17, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Husseiny, H.M.; Mady, E.A.; El-Dakroury, W.A.; Doghish, A.S.; Tanaka, R. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: Smart State of-the-Art Platforms for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1174075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Chen, Z.W.; Xie, Z.F.; Wang, S.S.; Xie, Y.M.; Zhang, Z.W. Recent Development of Biodegradable Occlusion Devices for Intra-Atrial Shunts. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimanzadeh, H.; Rolfe, B.; Bodaghi, M.; Jamalabadi, M.; Zhang, X.; Zolfagharian, A. Sustainable Robots 4D Printing. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2023, 7, 2300289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hua, D.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-Based Stimuli-Responsive Materials for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 4, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Tsai, Y.L.; Lin, S.H.; Hsu, S.H. Smart Polymers for Cell Therapy and Precision Medicine. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, L.G.; Savi, M.A. Medical Applications of Shape Memory Alloys. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2003, 36, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Maparathne, S.; Chinwangso, P.; Lee, T.R. Review of Shape-Memory Polymer Nanocomposites and Their Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, W.M. Mechanisms of the multi-shape memory effect and temperature memory effect in shape memorypolymers. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Cohen, D.J. Are Drug-Eluting Stents Cost-Effective? It Depends on Whom You Ask. Circulation 2006, 114, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, G.M.; Small, W., IV; Wilson, T.S.; Benett, W.J.; Matthews, D.L.; Hartman, J.; Maitland, D.J. Fabrication and In Vitro Deployment of a Laser Activated Shape Memory Polymer Vascular Stent. Biomed. Eng. Online 2007, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, G.M.; Wilson, T.S.; Small, W., IV; Hartman, J.; Benett, W.J.; Matthews, D.L.; Maitland, D.J. Thermomechanical properties, collapse pressure, and expansion of shape memory polymer neurovascular stent prototypes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 90B, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffington, S.L.; Sadeghifar, H.; Meenach, S.A.; Lannutti, J.J. Enzymatically triggered shape memory polymers. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Hu, J.; Huang, H.; Han, J.; Hu, H. Study of Multi-Functional Electrospun Composite Nanofibrous Mats for Smart Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebara, M. Shape-memory polymers for mechanobiology. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 014804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, W., IV; Wilson, T.S.; Buckley, P.R.; Benett, W.J.; Loge, J.M.; Hartman, J.; Maitland, D.J. Prototype fabrication and preliminary in vitro testing of a shape memory endovascular thrombectomy device. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, B.; Wu, H.; Liang, Y.; Ma, P.X. Injectable antibacterial conductive nanocomposite cryogels with rapid shape recovery for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wei, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. 3D Printing of Shape Memory Poly(d,l-Lactide-Co-Trimethylene Carbonate) by Direct Ink Writing for Shape-Changing Structures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neffe, A.T.; Hanh, B.D.; Steuer, S.; Lendlein, A. Polymer networks combining controlled drug release, biodegradation, and shape memory capability. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3394–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Ahmed, M.F.; Li, Y.; Bejoy, J.; Zeng, C.; Li, Y. PCL PDMS PCL Copolymer Based Microspheres Mediate Cardiovascular Differentiation from Embryonic Stem Cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2017, 23, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, D.; Hosseinnezhad, R.; Bondarenko, V.; Morawiec, J.; Vozniak, I.; Galeski, A. Shape Memory Polymer Foam Based on Nanofibrillar Composites of Polylactide/Polyamide. Molecules 2024, 29, 5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, M.; Paknejad, Z.; Rad, M.R.; Motamedian, S.R.; Eghbal, M.J.; Nadjmi, N.; Khojasteh, A. Polymeric Scaffolds in Tissue Engineering: A Literature Review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Wu, B.; Su, Y.; Sun, T.; Guo, X. Recent Advances in the Application of Natural and Synthetic Polymer-Based Scaffolds in Musculoskeletal Regeneration. Polymers 2022, 14, 4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, J.S.; Labhade, S.D.; Chitlange, S.S.; Mahadevan, S. Biopolymer Conjugated Protein-Based Hydrogel Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Application. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2020, 17, 284–316. [Google Scholar]
- Gunther, S.B.; Graham, J.; Norris, T.R.; Ries, M.D.; Pruitt, L. Wear in polyethylene components of hip and knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2002, 17, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsomboon, K.; Oyen, M.L. Composite electrospun gelatin fiber–alginate gel scaffolds for mechanically robust tissue engineered cornea. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 21, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeong, W.Y.; Chua, C.K.; Leong, K.F.; Chandrasekaran, M. Rapid prototyping in tissue engineering: Challenges and potential. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ke, J.; Zhang, L. Antibacterial polymers in biomedical applications. In Racing for the Surface: Antimicrobial and Interface Tissue Engineering; Li, B., Moriarty, T.F., Webster, T., Xing, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- Donnaloja, F.; Jacchetti, E.; Soncini, M.; Raimondi, M.T. Mechanosensing at the nanoscale: From single molecule force sensing to cell mechanosensitivity. Polymers 2020, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciola, C.R.; Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L. Implant infections: Adhesion, biofilm formation and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Wang, Y.; Grainger, D.W. Elevated cytokine responses from polymeric biomaterials: The role of DAMPs and immunological profiles. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Bioactive inorganic/organic nanocomposites for wound healing. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; De la Hoz Siegler, H. Evolution of Hybrid Hydrogels: Next-Generation Biomaterials for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Gels 2024, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björninen, M.; Gilmore, K.; Pelto, J.; Seppänen Kaijansinkkö, R.; Kellomäki, M.; Miettinen, S.; Wallace, G.; Grijpma, D.; Haimi, S. Electrically Stimulated Adipose Stem Cells on Polypyrrole-Coated Scaffolds for Smooth Muscle Tissue Engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Sun, B.; Mo, X. Electrospun Polypyrrole-Coated Polycaprolactone Nanoyarn Nerve Guidance Conduits for Nerve Tissue Engineering. Front. Mater. Sci. 2018, 12, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.F.; Wang, Y.G.; Cheng, L.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.D.; Peng, J. Preparation of Polypyrrole Embedded Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Nerve Tissue Engineering. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanjanizadeh Ezazi, N.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Shatalin, Y.V.; Nadal, E.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Kemell, M.; Correia, A.; Hirvonen, J.; Santos, H.A. Conductive Vancomycin Loaded Mesoporous Silica Polypyrrole Based Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelmi, A.; Zhang, J.; Cieslar Pobuda, A.; Ljunngren, M.K. Electroactive 3D Materials for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–12 March 2015; Bar Cohen, Y., Ed.; SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 9430, p. 94301T. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, R.B.; Swain, M.V. A Critical Review of Dental Implant Materials with an Emphasis on Titanium versus Zirconia. Materials 2015, 8, 932–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toncheva, A.; Khelifa, F.; Paint, Y.; Voué, M.; Lambert, P.; Dubois, P.; Raquez, J.M. Fast IR-actuated shape-memory polymers using in situ silver nanoparticle-grafted cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29933–29942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raphael, B.; Khalil, T.; Workman, V.L.; Smith, A.; Brown, C.P.; Streuli, C.; Saiani, A.; Domingos, M. 3D Cell Bioprinting of Self-Assembling Peptide-Based Hydrogels. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asti, A.; Gioglio, L. Natural and Synthetic Biodegradable Polymers: Different Scaffolds for Cell Expansion and Tissue Formation. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2014, 37, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Huang, Y.Y.; Sharma, S.K.; Carroll, J. Biphasic dose response in low level light therapy—An update. Dose-Response 2011, 9, 602–618. [Google Scholar]
- Gkogkos, A.S.; Karoussis, I.K.; Prevezanos, I.D.; Marcopoulou, K.E.; Kyriakidou, K.; Vrotsos, I.A. Effect of Nd:YAG Low Level Laser Therapy on Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Int. J. Dent. 2015, 2015, 258941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, U.; Concagh, D.; Core, L.; Kuang, Y.; You, C.; Pham, Q.; Zugates, G.; Busold, R.; Webber, S.; Merlo, J.; et al. The Development of Bioresorbable Composite Polymeric Implants with High Mechanical Strength. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnavi, S.; Saravanan, U.; Arthi, N.; Bhuvaneshwar, G.S.; Kumary, T.V.; Rajan, S.; Verma, R.S. Biological and Mechanical Evaluation of a Bio-Hybrid Scaffold for Autologous Valve Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizik, D.G.; Hermiller, J.B.; Kereiakes, D.J. The ABSORB Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffold: A Novel, Fully Resorbable Drug-Eluting Stent: Current Concepts and Overview of Clinical Evidence. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 86, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Li, L.; Shi, J.P.; Li, Z.A.; Yang, J.Q. Mechanical characterization of 3D printed multi-morphology porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds based on triply periodic minimal surface architectures. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Gong, Y.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Klämpfl, F.; Freund, S.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Laser beam melting 3D printing of Ti6Al4V based porous structured dental implants: Fabrication, biocompatibility analysis and photoelastic study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holten, C.H. Lactic Acid: Properties and Chemistry of Lactic Acid and Derivatives; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1971; 566p, ISBN 3527253440. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, D.; Younes, H.; Marom, G. Amorphous and Crystalline Morphologies in Glycolic Acid and Lactic Acid Polymers. Polymer 1987, 28, 2018–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezwada, R.S.; Jamiolkowski, D.D.; Lee, I.-Y.; Agarwal, V.; Persivale, J.; Trenka-Benthin, S.; Erneta, M.; Suryadevara, J.; Yang, A.; Liu, S. Monocryl Suture, a New Ultra-Pliable Absorbable Monofilament Suture. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.A.; Heller, J.; Gurny, R. Bioerodible Polymers for Ocular Drug Delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1998, 15, 381–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelberg, I.; Kohn, J. Physico-mechanical properties of degradable polymers used in medical applications: A comparative study. Biomaterials 1991, 12, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nho, Y.-C.; Park, J.-S.; Lim, Y.-M. Preparation of Poly(acrylic acid) Hydrogel by Radiation Crosslinking and Its Application for Mucoadhesives. Polymers 2014, 6, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Vora, L.K.; Wang, J.; Sabri, A.H.B.; Graham, A.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Poly(acrylic acid)/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Microarray Patches for Continuous Transdermal Delivery of Levodopa and Carbidopa: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hari, S.K.; Gauba, A.; Shrivastava, N.; Tripathi, R.M.; Jain, S.K.; Pandey, A.K. Polymeric micelles and cancer therapy: An ingenious multimodal tumor-targeted drug delivery system. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2023, 13, 135–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Thouas, G.A.; Chen, Q.Z. Biodegradable Soft Elastomers: Synthesis/Properties of Materials and Fabrication of Scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 8229–8242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Webb, A.R.; Pickerill, S.J.; Hageman, G.; Ameer, G.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Poly(Diol Citrate) Biodegradable Elastomers. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, D.; Nair, P.; Kim, H.K.W.; Yang, J. Citrate-Based Biodegradable Injectable Hydrogel Composites for Orthopedic Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Yang, J.; Kodali, P.; Koh, J.; Ameer, G.A. A Citric Acid-Based Hydroxyapatite Composite for Orthopedic Implants. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5845–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Yang, D. Excess molar enthalpies of binary mixtures for (tributyl phosphate + methanol/ethanol) at 298.15 K. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2006, 85, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, E.S.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Fabrication and characterization of hydrophilic poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend cell scaffolds by melt-molding particulate leaching method. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
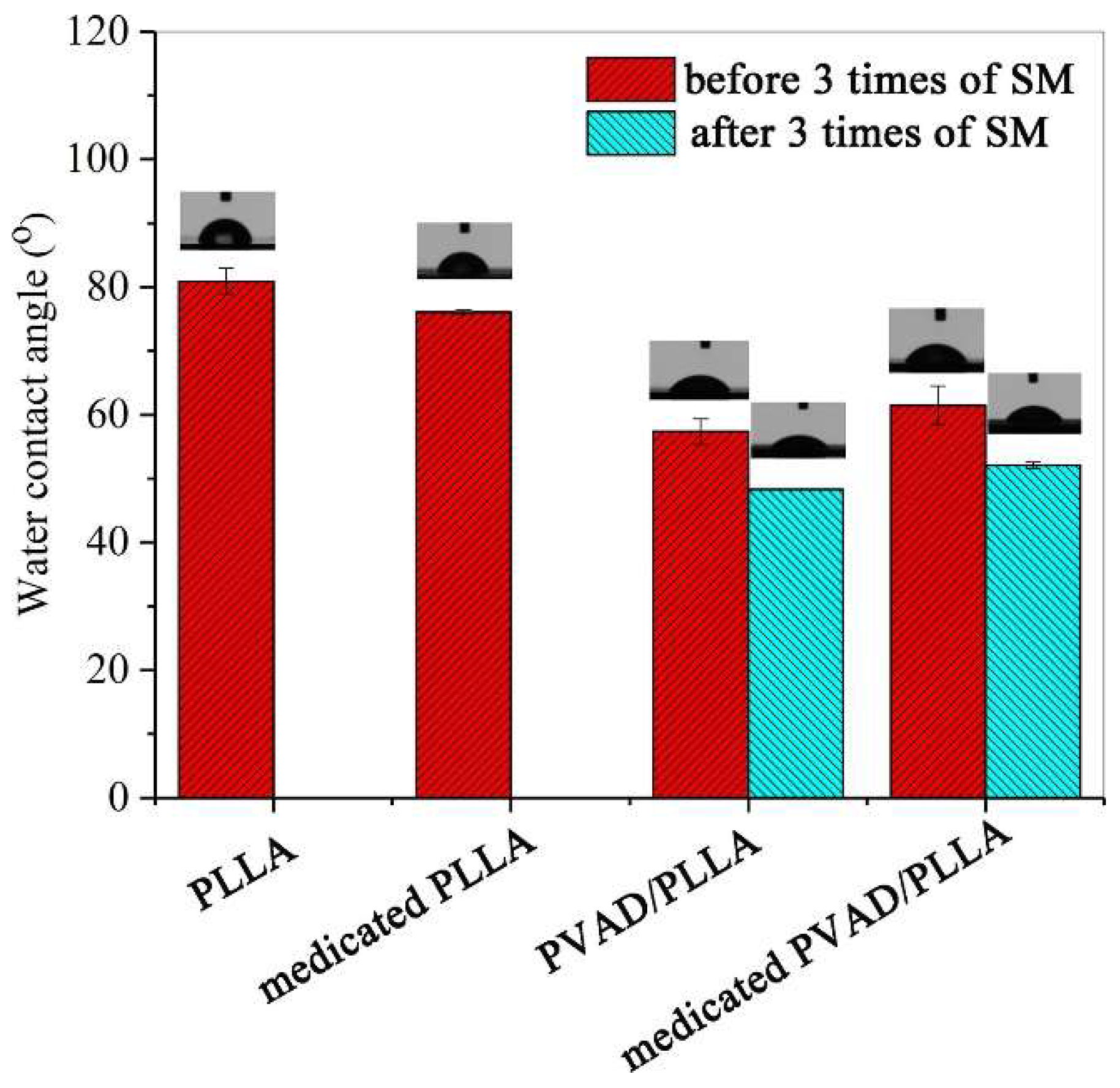
- Ren, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Qu, R.; Xu, H.; Song, X. A Drug-Loaded Amphiphilic Polymer/Poly(L-Lactide) Shape-Memory System. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Q.; Long, H.; Hu, K.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Wei, X.; Suo, J.; et al. Development of chitosan/gelatin hydrogels incorporating biphasic calcium phosphate nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, P.-Y.; Kim, Y.-K.; Jeong, K.-I.; Park, J.-C.; Choi, Y.-J. Influence of bone morphogenetic protein and proportion of hydroxyapatite on new bone formation in biphasic calcium phosphate graft: Two pilot studies in animal bony defect model. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.-P.; Silva-Correia, J.; Oliveira, M.B.; Vilela, C.; Pereira, H.; Sousa, R.A.; Mano, J.F.; Oliveira, A.L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Bilayered silk/silk-nanoCaP scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering: In vitro and in vivo assessment of biological performance. Acta Biomater. 2015, 12, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.-P.; Silva-Correia, J.; Correia, C.; Caridade, S.G.; Fernandes, E.M.; Sousa, R.A.; Mano, J.F.; Oliveira, A.L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Bioactive macro/micro porous silk fibroin/nano-sized calcium phosphate scaffolds with potential for bone-tissue-engineering applications. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochicchio, B.; Barbaro, K.; De Bonis, A.; Rau, J.V.; Pepe, A. Electrospun poly(d,l-lactide)/gelatin/glass-ceramics tricomponent nanofibrous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Mayer, J.; Wintermantel, E.; Leong, K.W. Biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, F.; Ferri, M.; Morelli, A.; Dipaola, L.; Latini, G. Perspectives on Alternatives and Additives to Phthalate Plasticized PVC in Medical Devices. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1067–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, A.D.; Spintig, T.; Kallage, I.; Müller, W.-D. Flexural Behavior of PEEK Materials for Dental Application. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Xiang, D.; Wang, S.; Liao, Z.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Peng, Z. In vitro wear study of PEEK and CFRPEEK against UHMWPE for artificial cervical disc application. Tribol. Int. 2018, 122, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ma, S.; Wu, Y.; Lee, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Adaptive control in lubrication, adhesion, and hemostasis by Chitosan–Catechol–pNIPAM. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3599–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, K.; Ali Khan, S.; Murtaza, G.; Sohail, M.; Azizullah; Manan, A.; Afzal, A. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels as Potential Biomaterials for Colonic Delivery of Oxaliplatin. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Ma, Y.; Hou, C.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, C.; Pan, H.; Lu, W.W.; Liu, W. 3D-printed high strength bioactive supramolecular polymer/clay nanocomposite hydrogel scaffold for bone regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
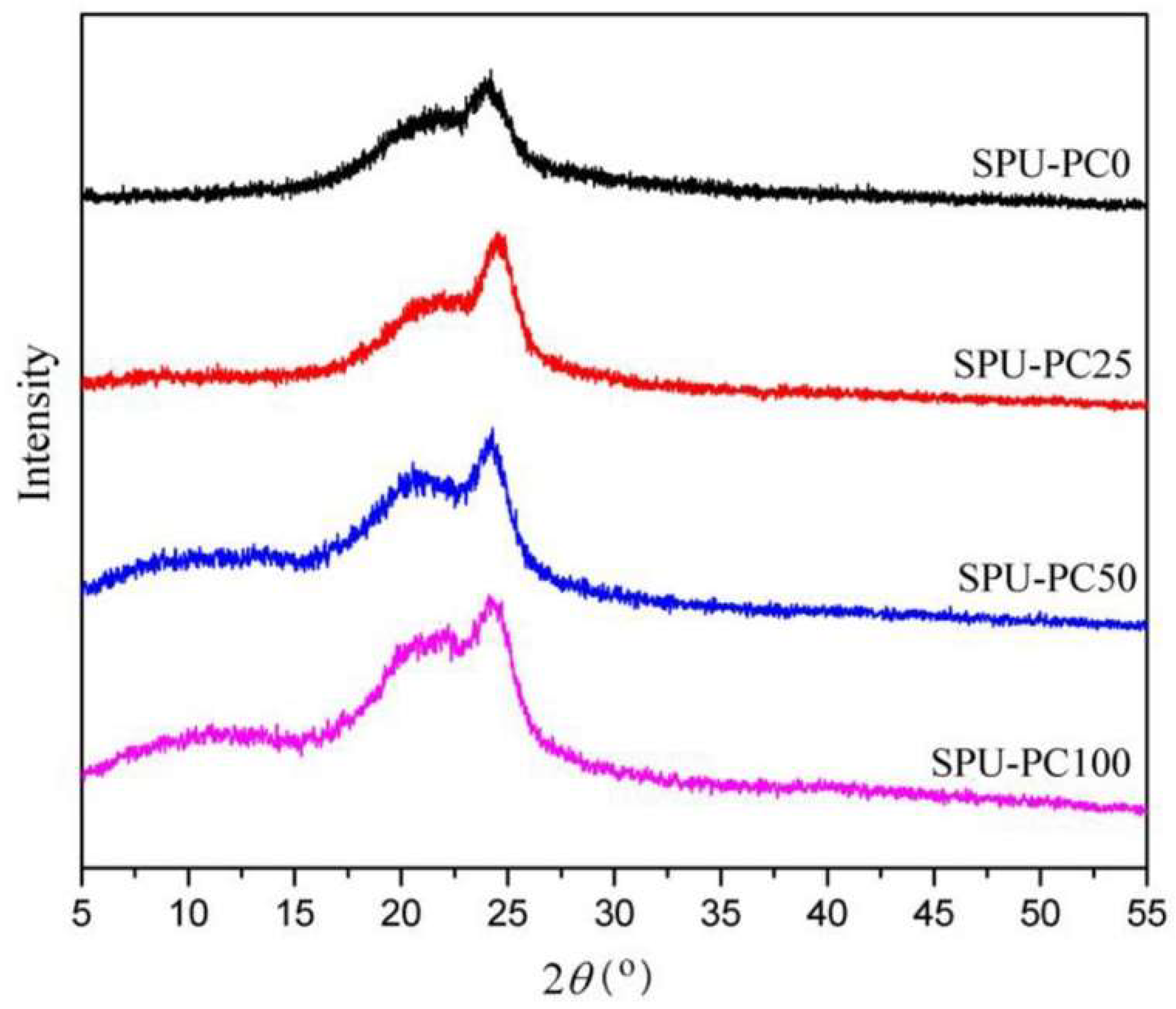
- Wang, Y.-J.; Jeng, U.-S.; Hsu, S.-H. Biodegradable Water-Based Polyurethane Shape Memory Elastomers for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergenrother, P.M. The Use, Design, Synthesis, and Properties of High-Performance/High-Temperature Polymers: An Overview. High Perform. Polym. 2003, 15, 3–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Bull, J.L.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Transport of Nitric Oxide (NO) in Various Biomedical-Grade Polyurethanes: Measurements and Modeling Impact on NO Release Properties of Medical Devices. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.C.; Meyerhoff, M.E.; Siedlecki, C.A. Blood Coagulation Response and Bacterial Adhesion to Biomimetic Polyurethane Biomaterials Prepared with Surface Texturing and Nitric Oxide Release. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zolotarskaya, O.; Ashraf, K.M.; Wen, X.; Ohman, D.E.; Wynne, K.J. Surface Characterization, Antimicrobial Effectiveness, and Human Cell Response for a Biomedical-Grade Polyurethane Blended with Mixed-Soft-Block PTMO-Quat/PEG Copolyoxetane Polyurethane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 20699–20714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castel, N.; Soon-Sutton, T.; Deptula, P.; Flaherty, A.; Parsa, F.D. Polyurethane-Coated Breast Implants Revisited: A 30-Year Follow-Up. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2015, 42, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Davim, J.P. The Design and Manufacture of Medical Devices; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 115–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildgruber, M.; Lueg, C.; Borgmeyer, S.; Karimov, I.; Braun, U.; Kiechle, M.; Meier, R.; Koehler, M.; Ettl, J.; Berger, H. The Role of Image-Guided Biopsy in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 59, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, P.; Small, W.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.; Maitland, D.J.; Wilson, T.S. Low-Density Biodegradable Shape memory Polyurethane Foams for Embolic Biomedical Applications. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bil, M.; Jurczyk-Kowalska, M.; Kopeć, K.; Heljak, M. Study of Correlation between Structure and Shape-Memory Effect/Drug-Release Profile of Polyurethane/Hydroxyapatite Composites for Antibacterial Implants. Polymers 2023, 15, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, J.Y.; Hou, T.Y.; Shih, M.F.; Talsma, H.; Hennink, W.E. Polyurethane-Based Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 450, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Knight, P.T.; Mather, P.T. Tailored Drug Release from Biodegradable Stent Coatings Based on Hybrid Polyurethanes. J. Control. Release 2009, 137, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowinger, M.B.; Barrett, S.E.; Zhang, F.; Williams, R.O., III. Sustained Release Drug Delivery Applications of Polyurethanes. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucińska-Lipka, J. Polyurethanes Crosslinked with Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) as Slowly Degradable and Hydrophilic Materials of Potential Use in Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2018, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liang, D.; He, X.; Li, J.; Tan, H.; Li, J.; Fu, Q.; Gu, Q. The Degradation and Biocompatibility of pH-Sensitive Biodegradable Polyurethanes for Intracellular Multifunctional Antitumor Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucinska-Lipka, J.; Gubanska, I.; Janik, H.; Pokrywczynska, M.; Drewa, T. L-Ascorbic Acid Modified Poly(Ester Urethane)s as Suitable Candidates for Soft Tissue Engineering Applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 97, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucińska-Lipka, J.; Gubanska, I.; Skwarska, A. Microporous Polyurethane Thin Layer as a Promising Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2017, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipka, J.K.; Lewandowska, I.G.A.; Pokrywczynska, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Antibacterial Polyurethanes Modified with Cinnamaldehyde as Potential Materials for Wound Dressings. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2955–2976. [Google Scholar]
- Heureux, L.; Fricain, J.-C.; Catros, S.; Le Nihouannen, D. Characterization of Printed PLA Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Jing, X.; Yu, E.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Turng, L.-S. Manipulating the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Polycaprolactone Hybrid Small-Diameter Vascular Scaffolds Fabricated via Electrospinning Using an Assembled Rotating Collector. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 78, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Sun, L.; Guo, J.; Yao, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, D. Enhancement in Mechanical Properties and Cell Activity of Polyurethane Scaffold Derived from Gastrodin. Mater. Lett. 2018, 228, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.P.; Sell, S.A.; Boland, E.D.; Simpson, D.G.; Bowlin, G.L. Nanofiber Technology: Designing the Next Generation of Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, S.; Gong, Y. Improved Biocompatibility of Phosphorylcholine End-Capped Poly(Butylene Succinate). Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Xu, J.; Teng, J.; Jia, Q.; Wang, X. Facile Preparation of Medical Segmented Poly(Ester-Urethane) Containing Uniformly Sized Hard Segments and Phosphorylcholine Groups for Improved Hemocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudiño-Rivera, J.; Medellín-Rodríguez, F.J.; Ávila-Orta, C.; Palestino-Escobedo, A.G.; Sánchez-Valdés, S. Structure/Property Relationships of Poly(L-Lactic Acid)/Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites. J. Polym. 2013, 2013, 729061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsa, R.; Tudorachi, N.; Vasile, C.P. Poly(α-Hydroxy Acids) in Biomedical Applications: Synthesis and Properties of Lactic Acid Polymers. e-Polymers 2010, 10, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulery, B.D.; Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biomedical Applications of Biodegradable Polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 832–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liechty, W.B.; Kryscio, D.R.; Slaughter, B.V.; Peppas, N.A. Polymers for Drug Delivery Systems. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2010, 1, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, N.V. Smart Polymers Are in the Biotech Future. BioProcess Int. 2006, 4, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Galaev, I.; Mattiasson, B. Smart Polymers and What They Could Do in Biotechnology and Medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, S.W. Saccharide Effect on the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermo-Sensitive Polymers. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.). Board on Chemical Sciences and Technology. Polymer Science and Engineering: The Shifting Research Frontiers; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 1994.
- Liu, P.; Jimaja, S.; Immel, S.; Thomas, C.; Mayer, M.; Weder, C.; Bruns, N. Mechanically triggered on-demand degradation of polymers synthesized by radical polymerizations. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, F.; Klaiber, M.; Franzreb, M.; Bräse, S.; Lahann, J. On Demand Light-Degradable Polymers Based on 9,10-Dialkoxyanthracenes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hoogenboom, R. X-ray-Induced Photodegradation of Hydrogels by the Incorporation of X-ray-Activated Long Persistent Luminescent Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 20273–20283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Png, Z.M.; Wang, C.G.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Lee, J.J.C.; Surat’man, N.E.; Tan, Y.L.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Tan, B.H.; Xu, J.W.; et al. Stimuli-Responsive Structure-Property Switchable Polymer Materials. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2023, 8, 1097–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Choi, B.; Yu, B.; Li, W.; Matsumoto, M.M.; Harris, K.R.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Larson, A.C.; Mouli, S.K.; Kim, D.H. On-Demand Degradable Embolic Microspheres for Immediate Restoration of Blood Flow during Image-Guided Embolization Procedures. Biomaterials 2021, 265, 120408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Bei, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; et al. Selenide-Linked Polydopamine-Reinforced Hybrid Hydrogels with on-Demand Degradation and Light-Triggered Nanozyme Release for Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomater. Res. 2023, 27, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulchandani, N.; Narayan, R. Redesigning Carbon–Carbon Backbone Polymers for Biodegradability–Compostability at the End-of-Life Stage. Molecules 2023, 28, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsuffi, B.; Siqueira, G.; Nyström, G.; Titotto, S.; Magrini, T.; Daraio, C. Programmable Multi-Responsive Nanocellulose-Based Hydrogels with Embodied Logic. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2409864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklavčič, D.; Pavšelj, N.; Hart, F.X. Electric Properties of Tissues. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering; Akay, M., Ed.; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, V.; Alvarez-Perez, M.A.; Borriello, A.; Napolitano, T.; Ambrosio, L. Conductive PANi/PEGDA macroporous hydrogels for nerve regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ge, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Electroactive nanofibrous biomimetic scaffolds by thermally induced phase separation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6119–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Albertsson, A.-C. Facile Synthesis of Degradable and Electrically Conductive Polysaccharide Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2601–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Faul, C.F.J. Aniline Oligomers—Architecture, Function and New Opportunities for Nanostructured Materials. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Mouser, D.J.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Geissler, S.; Chow, J.K.; Nguy, L.; Kim, J.M.; Schmidt, C.E. Biodegradable Electroactive Polymers for Electrochemically-Triggered Drug Delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6809–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Abidian, M.R. Conducting Polymers for Neural Prosthetic and Neural Interface Applications. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7620–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Kampstra, K.L.; Abidian, M.R. High-Performance Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Biosensors for Detection of Biomolecules. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5068–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Morshed, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Baharvand, H.; Kiani, S.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Application of conductive polymers, scaffolds and electrical stimulation for nerve tissue engineering. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2011, 5, e17–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidez, P.R.; Li, S.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; Venancio, E.C.; Wei, Y.; Lelkes, P.I. Polyaniline, an electroactive polymer, supports adhesion and proliferation of cardiac myoblasts. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2006, 17, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo-Corrales, L.; Latorre-Esteves, M.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E. Scaffold design for bone regeneration. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 15–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasbi Rad, A.; Ali, N.; Kotturi, H.S.R.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Smay, J.; Vashaee, D.; Tayebi, L. Conducting scaffolds for liver tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 4169–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihardja, S.S.; Sievers, R.E.; Lee, R.J. The effect of polypyrrole on arteriogenesis in an acute rat infarct model. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4205–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, M.; Nozaki, H.; Kaji, H.; Kitazume, T.; Kobayashi, N.; Ishibashi, T.; Abe, T. Electrodeposition of anchored polypyrrole film on microelectrodes and stimulation of cultured cardiac myocytes. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharibi, R.; Yeganeh, H.; Rezapour-Lactoee, A.; Hassan, Z.M. Stimulation of Wound Healing by Electroactive, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Polyurethane/Siloxane Dressing Membranes: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24296–24311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y. Nano-hydroxyapatite surfaces grafted with electroactive aniline tetramers for bone-tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touri, R.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Sadeghian, Z.; Bizari, D.; Mozafari, M. Use of carbon nanotubes to reinforce 45S5 bioglass-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 465086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Man, Y.; Li, L. Electrical Stimuli Improve Osteogenic Differentiation Mediated by Aniline Pentamer and PLGA Nanocomposites. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Non-Cytotoxic Conductive Carboxymethyl-Chitosan/Aniline Pentamer Hydrogels. React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 82, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Hu, J.; Lang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lelkes, P.I.; MacDiarmid, A.G.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Electroactive and Biodegradable ABA Block Copolymer of Polylactide and Aniline Pentamer. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.R.; Fisher, J.; Matthews, J.B.; Stone, M.H.; Ingham, E. Effect of size and dose on bone resorption activity of macrophages by in vitro clinically relevant ultra high molecular weight polyethylene particles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 53, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashi, M.; Baghbani, F.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mobasheri, H.; Kowsari, E. Green synthesis of degradable conductive thermosensitive oligopyrrole/chitosan hydrogel intended for cartilage tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Rivers, T.J.; Hudson, T.W.; Collier, J.H. Modification of Electroactive Biomaterials for Neural Engineering Applications. ACS Symp. Ser. 2003, 832, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Kamra, M.; Roy, S.; Muniyappa, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sasor, A. Novel Oligopyrrole Carboxamide Based Nickel(II) and Palladium(II) Salens, Their Targeting of Human G-Quadruplex DNA, and Selective Cancer Cell Toxicity. Chem.–Asian J. 2016, 11, 2542–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, C.D.; Booth, M.A.; Mawad, D.; Armgarth, A.; Nielsen, C.B.; Stevens, M.M. Synthesis of Hetero-Bifunctional, End-Capped Oligo-EDOT Derivatives. Chem 2017, 2, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Shadrin, I.Y.; Lam, J.; Xian, H.-Q.; Snodgrass, H.R.; Bursac, N. Tissue-engineered cardiac patch for advanced functional maturation of human ESC-derived cardiomyocytes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5813–5820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Khattab, A.; Islam, M.A.; Abou Hweij, K.; Zeitouny, J.; Waters, R.; Sayegh, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Paul, A. Injectable hydrogels for cardiac tissue repair after myocardial infarction. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.H.; Cho, J.Y. Myocardial tissue engineering using electrospun nanofiber composites. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Morshed, M.; Memic, A.; Hassan, S.; Webster, T.J.; Marei, H.E.-S. Nanoparticles in tissue engineering: Applications, challenges and prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5637–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciocci, M.; Mochi, F.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Giovanni, E.; Prosposito, P.; Francini, R.; De Matteis, F.; Reshetov, I.; Casalboni, M.; Melino, S.; et al. Scaffold in Scaffold Potential to Induce Growth and Differentiation of Cardiac Progenitor Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotenuto, F.; Teodori, L.; Maccari, A.M.; Delbono, L.; Orlando, G.; Di Nardo, P. Turning regenerative technologies into treatment to repair myocardium injuries. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2704–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotenuto, F.; Manzari, V.; Di Nardo, P. Cardiac Regeneration: The Heart of the Issue. Curr. Transpl. Rep. 2021, 8, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
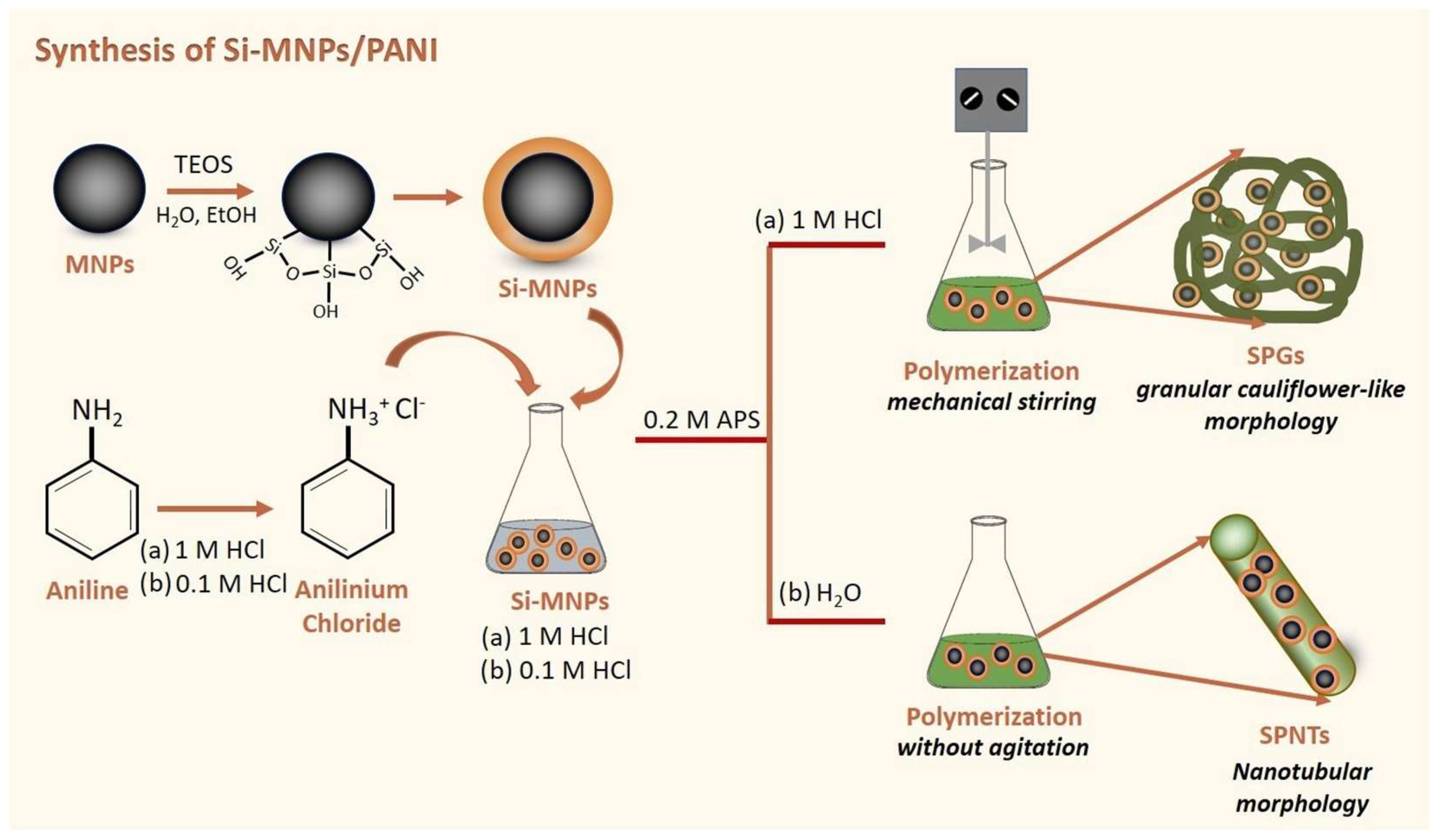
- Lalegül Ülker, Ö.; Murat, Y. Magnetic and electrically conductive silica coated iron oxide/polyaniline nanocomposites for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi Soflou, R.; Nejati, S.; Karkhaneh, A. Electroactive and antioxidant injectable in situ forming hydrogels with tunable properties by polyethylenimine and polyaniline for nerve tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, B. Electroactive 3D Scaffolds Based on Silk Fibroin and Water Borne Polyaniline for Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1700147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, A.; Vyas, C.; Cooper, G.; Qulub, F.; Suratman, R.; Mahyuddin, A.I.; Dirgantara, T.; Bartolo, P. 3D Printing of Polycaprolactone–Polyaniline Electroactive Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2020, 13, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.H.; Park, S.H.; Woo, S.I. Binary and Ternary Doping of Nitrogen, Boron, and Phosphorus into Carbon for Enhancing Electrochemical Oxygen Reduction Activity. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 7084–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, D.N.; Lee, S.J.; Timsina, R.; Qiu, X.; Castro, N.J.; Zhang, L.G. Development of 3D printable conductive hydrogel with crystallized PEDOT:PSS for neural tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, A.G.; Puetzer, J.L.; Armgarth, A.; Littmann, E.; Stavrinidou, E.; Giannelis, E.P.; Malliaras, G.G.; Stevens, M.M. Highly porous scaffolds of PEDOT:PSS for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017, 62, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Jian, N.; Qu, K.; Xu, J.; Zhao, X. Pure PEDOT:PSS hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daculsi, G.; Laboux, O.; Malard, O.; Weiss, P. Current state of the art of biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohner, M. Calcium orthophosphates in medicine: From ceramics to calcium phosphate cements. Injury 2000, 31 (Suppl. S4), 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.H.; Alves, A.; Ferreira, B.M.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reys, L.L.; Ferreira, R.J.F.; Sousa, R.A.; Silva, S.S.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. Materials of marine origin: A review on polymers and ceramics of biomedical interest. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 276–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Costa, S.; Leonor, I.; Malafaya, P.; Mano, J.; Reis, R. Novel hydroxyapatite/carboxymethylchitosan composite scaffolds prepared through an innovative “autocatalytic” electroless coprecipitation route. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 88, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Kotobuki, N.; Tadokoro, M.; Hirose, M.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L.; Ohgushi, H. Ex vivo culturing of stromal cells with dexamethasone-loaded carboxymethylchitosan/poly(amidoamine) dendrimer nanoparticles promotes ectopic bone formation. Bone 2010, 46, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piña, S.; Ferreira, J. Brushite-forming Mg-, Zn- and Sr-substituted bone cements for clinical applications. Materials 2010, 3, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoaia, G.; Mocanu, A.; Vida-Simiti, I.; Jumate, N.; Bobos, L.D.; Soritau, O.; Tomoaia-Cotisel, M. Silicon effect on the composition and structure of nanocalcium phosphates: In vitro biocompatibility to human osteoblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 37, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Arcos, D. Silicon substituted hydroxyapatites: A method to upgrade calcium phosphate based implants. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, N.; Otuzbir, A.; Pekşen, C.; Kiremitçi, A.; Doğan, A. A silver ion-doped calcium phosphate-based ceramic nanopowder-coated prosthesis increased infection resistance. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; Kijkowska, R.; Bautista, C.; Retino, M.; LeGeros, J.P. Magnesium incorporation in apatites: Effect of CO3 and F. J. Dent. Res. 1996, 75, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Piña, S.; Canadas, R.F.; Jiménez, G.; Perán, M.; Marchal, J.A.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Biofunctional ionic-doped calcium phosphates—Silk fibroin composites for bone tissue engineering scaffolding. Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Yu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Leng, H.; Yang, X.; Cai, Q. Improving Bone Regeneration with Composites Consisting of Piezoelectric Poly(L-Lactide) and Piezoelectric Calcium/Manganese Co-Doped Barium Titanate Nanofibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 234, 109734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorrez, L.; Shansky, J.; Wang, L.; Fast, L.; VandenDriessche, T.; Chuah, M.; Mooney, D.; Vandenburgh, H. Growth, differentiation, transplantation and survival of human skeletal myofibers on biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, A.J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Bioactive ceramics: From bone grafts to tissue engineering. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 11116–11131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S.; Ahmed, I.; Parsons, A.J.; Rudd, C.D.; Walker, G.S.; Scotchford, C.A. Investigating the use of coupling agents to improve the interfacial properties between a resorbable phosphate glass and polylactic acid matrix. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 28, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Li, K.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Hao, Y. Pore functionally graded Ti6Al4V scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. Mater. Des. 2019, 168, 107643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolos, E.; Ruys, A. Biomimetic coating on porous alumina for tissue engineering: Characterisation by cell culture and confocal microscopy. Materials 2015, 8, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieralli, S.; Kohal, R.J.; Jung, R.E.; Vach, K.; Spies, B.C. Clinical outcomes of zirconia dental implants: A systematic review. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 96, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Kocagöz, S.; Arnholt, C.; Huet, R.; Ueno, M.; Walter, W.L. Advances in zirconia toughened alumina biomaterials for total joint replacement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 31, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chocholata, P.; Kulda, V.; Babuska, V. Fabrication of Scaffolds for Bone-Tissue Regeneration. Materials 2019, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, L.-C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive Glass and Glass-Ceramic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials 2010, 3, 3867–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, I.A.M.; Ribeiro, R.F.; Francischone, C.E.; De Mattos, M.G.C. In vitro comparative analysis of the fit of gold alloy or commercially pure titanium implant-supported prostheses before and after electroerosion. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 92, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowley, A.; Woodward, B. A Healthy Future: Platinum in Medical Applications Platinum Group Metals Enhance the Quality of Life of the Global Population. Platin. Met. Rev. 2011, 55, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, M.A.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouet, C.; Leriche, A.; Hampshire, S.; Kashani, M.; Stamboulis, A.; Iafisco, M.; Tampieri, A. Advances in Ceramic Biomaterials; Palmero, P., Cambier, F., De Barra, E., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Pathak, L.; Vyas, P. Biobased polymers of plant and microbial origin and their applications—A review. Biotechnol. Sustain. Mater. 2024, 1, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, J.; Silva, G.; Azevedo, H.; Malafaya, P.; Sousa, R.; Silva, S.; Reis, R. Natural origin biodegradable systems in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Present status and some moving trends. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 999–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malafaya, P.B.; Silva, G.A.; Reis, R.L. Natural-origin polymers as carriers and scaffolds for biomolecules and cell delivery in tissue engineering applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.K.; Jin, Y.G.; Rha, S.J.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, J.H. Biochemical characteristics of four marine fish skins in Korea. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Geng, X.; Li, W.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Review on Application Progress of Marine Collagen Cross-Linking Modification in Bone Repairs. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, C.M.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels in healthcare: From static to dynamic material microenvironments. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dutt, D.; Kaur, P.; Singh, H.; Mishra, N.C. Microfibrous paper scaffold for tissue engineering application. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2020, 31, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Xing, T.L.; Yin, R.X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, S.M.; Zhang, W.J. Three-dimensional bioprinting is not only about cell-laden structures. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2016, 19, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenry, W.C.L.; Loh, K.P.; Lim, C.T. When stem cells meet graphene: Opportunities and challenges in regenerative medicine. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohil, S.V.; Brittain, S.; Kan, H.M.; Drissi, H.; Rowe, D.; Nair, L.S. Evaluation of enzymatically crosslinked injectable glycol chitosan gel. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5511–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.C.; Salgado, C.L.; Sahu, A.; Garcia, M.P.; Fernandes, M.H.; Monteiro, F.J. Preparation and characterization of collagen-nanohydroxyapatite biocomposite scaffolds by cryogelation method for bone tissue engineering applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2013, 101A, 1080–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.; Reinwald, Y.; Bhat, S. Cryogels: Freezing unveiled by thawing. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Sakthivel, K.; Mohamed, M.G.A.; Boras, E.; Shin, S.R.; Kim, K. Designing Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA)-Based Bioinks for Visible Light Stereolithographic 3D Biofabrication. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, M.; de Ruijter, M.; Beirne, S.; Villette, C.C.; Ito, K.; Wallace, G.G.; Malda, J. Multitechnology Biofabrication: A New Approach for the Manufacturing of Functional Tissue Structures? Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkaron, W.; Almansoori, A.; Balázsi, C.; Balázsi, K. A Critical Review of Natural and Synthetic Polymer-Based Biological Apatite Composites for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Karlioti, G.; Kalamas, T.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Vlachopoulos, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, D.N. Poly(lactic Acid): A Versatile Biobased Polymer for the Future with Multifunctional Properties—From Monomer Synthesis, Polymerization Techniques and Molecular Weight Increase to PLA Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, F.; Zhang, A.; Cheng, F.; Cui, L.; Liu, J.; Xia, Y. Biodegradable Polymeric Architectures via Reversible Deactivation Radical Polymerizations. Polymers 2018, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Gaddala, R.; Thomas, S.; Schumacher, J.; Schönherr, H. Green Synthesis of Polymer Materials via Enzyme- Initiated RAFT Polymerization. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Serpe, M.J. Stimuli-Responsive Polymers and Their Applications. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Tan, R.Y.H. NIR-Induced Photothermal-Responsive Shape Memory Polyurethane for Versatile Smart Material Applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24265–24286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessini, V.; Salaris, V.; Oliver-Cuenca, V.; Tercjak, A.; Fiori, S.; López, D.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Thermally-Activated Shape Memory Behavior of Biodegradable Blends Based on Plasticized PLA and Thermoplastic Starch. Polymers 2024, 16, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrukh, A.; Nayab, S. Shape Memory Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2024, 10, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpfer, J.R.; Rowan, S.J. Thermo-, Photo-, and Chemo-Responsive Shape-Memory Properties from Photo-Cross-Linked Metallo-Supramolecular Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12866–12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smola-Dmochowska, A.; Śmigiel-Gac, N.; Kaczmarczyk, B.; Sobota, M.; Janeczek, H.; Karpeta-Jarząbek, P.; Kasperczyk, J.; Dobrzyński, P. Triple-Shape Memory Behavior of Modified Lactide/Glycolide Copolymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, M.; Razzaq, M.Y.; Lendlein, A. Multifunctional Shape-Memory Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3388–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchi, K.A.; Pantoja, M.; Cakmak, M. Shape Memory Ionomers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Skallevold, H.E.; Srimaneepong, V.; Marya, A.; Shah, P.K.; Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Sapkota, J. Shape Memory Polymeric Materials for Biomedical Applications: An Update. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.J.; Lih, E.; Choi, J.; Joung, Y.K.; Ahn, D.J.; Han, D.K. Shape-Memory Effect by Specific Biodegradable Polymer Blending for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, P.; Schäfer, H.; Jubsilp, C.; Rimdusit, S.; Koschek, K. Thermosetting Shape Memory Polymers and Composites Based on Polybenzoxazine Blends, Alloys and Copolymers. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonés, A.; Peponi, L.; Fiori, S.; Lieblich, M. Effect of the Addition of MgO Nanoparticles on the Thermally-Activated Shape Memory Behavior of Plasticized PLA Electrospun Fibers. Polymers 2022, 14, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisar, J.; Pummerova, M.; Drohsler, P.; Masar, M.; Sedlarik, V. Changes in the Thermal and Structural Properties of Polylactide and Its Composites During a Long-Term Degradation Process. Polymers 2025, 17, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X. Role of Entropy-Enthalpy Competition on the Thermochemically Driven Shape Memory Effect in Amorphous Polymer Films. Materials 2025, 18, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Qin, B.; Wang, K.; Xie, T.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Polydopamine Coated Shape Memory Polymer: Enabling Light Triggered Shape Recovery, Light Controlled Shape Reprogramming and Surface Functionalization. Chem. Sci. 2016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; Liu, P.; Xu, Y.; Guan, Q.; You, Z. Near-Infrared Light Triggered the Shape Memory Behavior of Polydopamine-Nanoparticle-Filled Epoxy Acrylate. Polymers 2023, 15, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, M.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Chang, Y.-W.; Jang, K.S. Near-Infrared Light-Responsive Shape Memory Polymer Fabricated from Reactive Melt Blending of Semicrystalline Maleated Polyolefin Elastomer and Polyaniline. Polymers 2021, 13, 3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, K.; Wang, B.; Hu, P. Thermo- and PH-Sensitive Shape Memory Polyurethane Containing Carboxyl Groups. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.Y.H.; Lee, C.S.; Pichika, M.R.; Cheng, S.F.; Lam, K.Y. PH Responsive Polyurethane for the Advancement of Biomedical and Drug Delivery. Polymers 2022, 14, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, W.; Yu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. Recent Development of pH-Responsive Polymers for Cancer Nanomedicine. Molecules 2019, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katari, R.S.; Peloso, A.; Orlando, G. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Semantic considerations for an evolving paradigm. Adv. Surg. 2014, 48, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.J.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, J.H.; Chiang, S.F.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, K.Y. Fabrication of porous biodegradable polymer scaffolds using a solvent merging/particulate leaching method. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 59, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.; Bahrampourian, R.; Patel, A.; Mequanint, K. Fabrication of highly porous tissue-engineering scaffolds using selective spherical porogens. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2010, 20, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, G.; Clarke, J.; Picard, F.; Riches, P.; Jia, L.; Han, F.; Li, B.; Shu, W. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 278–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashaswini, Y.D.; Prabhu, A.; Anil, S.; Venkatesan, J. Preparation and characterization of dexamethasone loaded sodium alginate-graphene oxide microspheres for bone tissue engineering. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, H. Controlled freezing and freeze drying: A versatile route for porous and micro-/nano-structured materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, K.; Thomas, C.H.; Healy, K.E.; Nuber, G. A novel method to fabricate bioabsorbable scaffolds. Polymer 1995, 36, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.C.; Haider, A.; Choi, Y.R.; Kang, I.K. Nanofibrous Scaffolds in Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Res. 2014, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papež, N.; Pisarenko, T.; Ščasnovič, E.; Sobola, D.; Ţălu, Ş.; Dallaev, R.; Částková, K.; Sedlák, P. A Brief Introduction and Current State of Polyvinylidene Fluoride as an Energy Harvester. Coatings 2022, 12, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Functional Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 1392–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.T.; Kim, J.F.; Wang, H.H.; Di Nicolo, E.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Understanding the NIPS effect during the fabrication of microporous PVDF membranes via TIPS. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Turng, L.S. Fabrication of porous synthetic polymer scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Cell. Plast. 2014, 51, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, T. Techniques for fabrication and construction of three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusakov, D.; Menner, A.; Bismarck, A. High-Performance Polymer Foams by Thermally Induced Phase Separation. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, 2000110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMaio, E.; Mensitieri, G.; Iannace, S.; Nicolais, L.; Li, W.; Flumerfelt, R.W. Structure optimization of polycaprolactone foams by using mixtures of CO2 and N2 as blowing agents. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Yoon, J.J.; Park, T.G. A novel fabrication method of macroporous biodegradable polymer scaffolds using gas foaming salt as a porogen additive. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Che, X. Biofabrication of Tissue Scaffolds. Adv. Biomater. Sci. Biomed. Appl. 2013, 12, 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Barbetta, A.; Rizzitelli, G.; Bedini, R.; Pecci, R.; Dentini, M. Porous gelatin hydrogels by gas-in-liquid foam templating. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1785–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbetta, A.; Gumiero, A.; Pecci, R.; Bedini, R.; Dentini, M. Gas-in-liquid foam templating as a method for the production of highly porous scaffolds. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 3188–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, R.A.; France, R.M.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Howdle, S.M. Supercritical fluid technologies and tissue engineering scaffolds. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, N.; Sudin, I.; Ngadiman, N.H.A.; Ishak, M.S.A. A Comprehensive Review of Biopolymer Fabrication in Additive Manufacturing Processing for 3D-Tissue-Engineering Scaffolds. Polymers 2022, 14, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace Varghese, M.; Thomas, A.; Rupesh, S.; Sameer, K.M.; Joseph, D.; Mathew, T.A.; George Thomas, N. Fabrication Techniques for Scaffolds Applied in Regenerative Medicine. In Novel Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesvoranan, O.; Anup, A.; Hixon, K.R. Current Concepts and Methods in Tissue Interface Scaffold Fabrication. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyachandran, D.; Cerruti, M. Glass, Ceramic, Polymeric, and Composite Scaffolds with Multiscale Porosity for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishani, M.; Shin, W.Y.; Suhaimi, H.; Sambudi, N.S. Development of Scaffolds from Bio-Based Natural Materials for Tissue Regeneration Applications: A Review. Gels 2023, 9, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, P.D.; Vaquette, C.; Farrugia, B.L.; Dargaville, T.R.; Brown, T.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Electrospinning and Additive Manufacturing: Converging Technologies. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharibshahian, M.; Salehi, M.; Beheshtizadeh, N.; Kamalabadi-Farahani, M.; Atashi, A.; Nourbakhsh, M.S.; Alizadeh, M. Recent Advances on 3D-Printed PCL-Based Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1168504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Man, L.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Y.-G.; Zhu, X.X. Programmable Polymers with Shape Memory for Biomedical Applications. Program. Mater. 2023, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Ashfaq Ahmed, M.; Jalal, A.H.; Siddiquee, I.; Adury, R.Z.; Hossain, G.M.M.; Pala, N. Recent Progress and Challenges of Implantable Biodegradable Biosensors. Micromachines 2024, 15, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, F.; Xu, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L. Recent Progress on Smart Hydrogels for Biomedicine and Bioelectronics. Biosurface Biotribol. 2022, 8, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.J.; Hildick-Smith, D.; De Giovanni, J.V.; Duke, C.; Hillis, W.S.; Morrison, W.L.; Jux, C. BioSTAR Evaluation Study (BEST): A Prospective, Multicenter, Phase I Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Feasibility, Efficacy, and Safety of the BioSTAR Bioabsorbable Septal Repair Implant for the Closure of Atrial-Level Shunts. Circulation 2006, 114, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jux, C.; Bertram, H.; Wohlsein, P.; Bruegmann, M.; Paul, T. Interventional Atrial Septal Defect Closure Using a Totally Bioresorbable Occluder Matrix: Development and Preclinical Evaluation of the BioSTAR Device. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavčnik, D.; Wright, K.C.; Wallace, S. Monodisk: Device for percutaneous transcatheter closure of cardiac septal defects. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1993, 16, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavčnik, D.; Takulve, K.; Uchida, B.T.; Pavčnik Arnol, M.; VanAlstine, W.; Keller, F.; Rösch, J. Biodisk: A new device for closure of patent foramen ovale: A feasibility study in swine. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 75, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigler, M.; Söderberg, B.; Schmitt, B.; Mellmann, A.; Bernhard, J. Carag bioresorbable septal occluder (CBSO): Histopathology of experimental implants. EuroIntervention 2018, 13, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Shi, P.; Zheng, X.; Hongxin, L.; Li, Z.; Lv, M.; Wang, H. Echocardiographic characteristics of transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale with Mallow biodegradable occluder: A single-center, phase III clinical study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 945275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong-Hong, D.; Tang, Y.D.; Wu, W.; Venkatraman, S.S.; Boey, F.; Lim, J.; Yip, J. Fully biodegradable septal defect occluder—A double umbrella design. Catheter Cardiovasc. Interv. 2010, 76, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yip, J.; Tang, Y.D.; Khoo, V.; Kong, J.F.; Duong-Hong, D.; Boey, F.; Venkatraman, S.S. A novel biodegradable septal defect occluder: The “Chinese Lantern” design, proof of concept. Innovations 2011, 6, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.J.; Peng, K.M.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Liu, K.S.; Chung, H.T.; Chen, J.K. Novel biodegradable polycaprolactone occlusion device combining nanofibrous PLGA/collagen membrane for closure of atrial septal defect. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.F.; Huang, X.M.; Cao, J.; Hu, J.Q.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, H.B.; Li, Z.F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Qin, Y.W.; et al. Animal experimental study of the fully biodegradable atrial septal defect (ASD) occluder. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 735989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.F.; Wang, S.S.; Zhang, Z.W.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, X.M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, D. A novel-design poly-L-lactic acid biodegradable device for closure of atrial septal defect: Long-term results in swine. Cardiology 2016, 135, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Pan, X. A novel totally biodegradable device for effective atrial septal defect closure: A 2-year study in sheep. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2018, 31, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, Y.; Berman, D.P.; Kurobe, H.; Kelly, J.M.; Iwaki, R.; Blum, K.; Toshihiro, S.; Harrison, A.; Cheatham, J.P.; Shinoka, T. Pre-clinical evolution of a novel transcatheter bioabsorbable ASD/PFO occluder device. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2022, 43, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, B.; Xie, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Initial Clinical Experience with the Biodegradable AbsnowTM Device for Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defect: A 3-Year Follow-Up. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2021, 2021, 6369493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xie, H.; Shao, H.; Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Lan, B.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. A Prospective, Single-Center, Phase I Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Value of Transesophageal Echocardiography in the Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale with a Novel Biodegradable Occluder. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 849459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargav, D. Bioresorbable Scaffolds: Current Evidence in the Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, KE01–KE04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda-Castillo, S.A.; Stiles, A.M.; Bohnstedt, B.N.; Lee, H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, C.-H. Shape Memory Polymer-Based Endovascular Devices: Design Criteria and Future Perspective. Polymers 2022, 14, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Wu, B.M.; Dunn, J.C.Y. Accelerating Vascularization in Polycaprolactone Scaffolds by Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Tissue Eng.-Part A 2011, 17, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, C.V.; Gonçalves, V.; da Silva, M.C.; Bañobre-López, M.; Gallo, J. PLGA-Based Composites for Various Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belousov, A.; Lushpeev, V.; Sokolov, A.; Sultanbekov, R.; Tyan, Y.; Ovchinnikov, E.; Shvets, A.; Bushuev, V.; Islamov, S. Experimental Research of the Possibility of Applying the Hartmann–Sprenger Effect to Regulate the Pressure of Natural Gas in Non-Stationary Conditions. Processes 2025, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Zhang, F.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Shape Memory Polymer Composites: 4D Printing, Smart Structures, and Applications. Research 2023, 6, 0234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; Wu, H.; Lin, X.; Cai, L. Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel Dressing for Wound Healing. APL Mater. 2025, 13, 010601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Cai, D.; Liao, P.; Su, J.W.; Deng, H.; Vardhanabhuti, B.; Ulery, B.D.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, J. 4D Printing of Shape-Memory Polymeric Scaffolds for Adaptive Biomedical Implantation. Acta Biomater. 2021, 122, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, D.; Cao, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Li, Z.; He, W.; Ju, J.; Zhang, Y. 4D Printing of Shape Memory Vascular Stent Based on ΒCD-g-Polycaprolactone. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavkovic, V.; Palic, N.; Milenkovic, S.; Zivic, F.; Grujovic, N. Thermo-Mechanical Characterization of 4D-Printed Biodegradable Shape-Memory Scaffolds Using Four-Axis 3D-Printing System. Materials 2023, 16, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; An, R.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Yu, D.; Zhu, X. Self-Healing Hydrogels: Mechanisms and Biomedical Applications. MedComm 2025, 6, e70181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harito, C.; Utari, L.; Putra, B.R.; Yuliarto, B.; Purwanto, S.; Zaidi, S.Z.J.; Bavykin, D.V.; Marken, F.; Walsh, F.C. Review—The Development of Wearable Polymer-Based Sensors: Perspectives. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Du, X.; Long, Y.; Zheng, H. Biodegradable Polymeric Materials for Flexible and Degradable Electronics. Front. Electron. 2022, 3, 985681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, J.B.; Raut, P.; Kumar, S. Organic Electronics in Biosensing: A Promising Frontier for Medical and Environmental Applications. Biosensors 2023, 13, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Comparison Review (Title, Year, Journal) | Limitations of That Review | Strengths of the Current Review |
|---|---|---|
| Kurowiak et al., “Biodegradable Polymers in Biomedical Applications: A Review” (2023, IJMS) [22]. |
|
|
| Socci et al., “Polymeric Materials, Advances and Applications in Tissue Engineering: A Review” (2023, Bioengineering) [23]. |
|
|
| Khan et al., “Biodegradable Conducting Polymer-Based Composites for Biomedical Applications: A Review” (2024, Polymers) [24]. |
|
|
| Balcerak-Woźniak et al., “A Comprehensive Review of Stimuli-Responsive Smart Polymer Materials” (2024, Materials) [25]. |
|
|
| El-Husseiny et al., “Stimuli-responsive Hydrogels: Smart State-of-the-Art Platforms for Cardiac Tissue Engineering” (2023, Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.) [26]. |
|
|
| Li et al., “Recent Development of Biodegradable Occlusion Devices for Intra-Atrial Shunts” (2024, Rev. Cardiovasc. Med.) [27]. |
|
|
| Sustainable Robots 4D Printing (2023, Adv. Sustainable Systems)—Soleimanzadeh et al. [28]. |
|
|
| Bio-based stimuli-responsive materials for biomedical applications (2023, Materials Advances)—Ma et al. [29]. |
|
|
| Fabrication Method | Advantages | Limitations and Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Solvent Casting and Particulate Leaching (SC/PL) | Simple, low-cost, tunable porosity (50–90%), controllable pore size (5–600 µm) [268,269]. | Limited scaffold thickness (<3–4 mm), poor interconnectivity; use of toxic solvents that may leave residues and compromise biocompatibility; inconsistent reproducibility |
| Gas Foaming | Solvent-free porosity creation (~85%), suitable for hydrophilic/hydrophobic polymers [270]. | Poor mechanical properties, non-uniform pores, often closed external surfaces, often poor pore interconnectivity. Long processing times: saturation and depressurization cycles may require days, which is impractical for rapid prototyping |
| Thermally Induced Phase Separation (TIPS) | High pore interconnectivity, uniform porosity, suitable for thermoplastics [271]. | Complex, user-sensitive process; long freeze-drying time; limited macropore size (~100–200 µm); specialized equipment needed |
| Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization) | High porosity (>90%), homogenous porous network, preserves bioactive agents (no heating) [272]. | Energy-intensive and costly, slow processing, often small and irregular pores |
| Electrospinning | Economical, simple, flexible, produces ECM-like nanofibers with controllable diameters [273]. | Low throughput; frequent nozzle clogging; uses toxic solvents; weak mechanical strength; difficult to form true 3D structures and achieve uniform cell distribution |
| Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing: FDM, SLA, SLS, Bioprinting) | High architecture control; reproducible; custom geometries; room-temperature or cell-compatible printing [274]. | Limited resolution for micro/nano-pores; restricted material choices; some techniques require heat or UV (potential cytotoxicity); high equipment cost |
| Device (Manufacturer) | Design/Working Principle and Polymer Role | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioSTAR (NMT Medical, Boston, MA, USA) [279]. | Self-expanding double-disc nitinol frame (MP35N alloy, non-degradable) covered by a biodegradable acellular porcine-derived type-I collagen membrane. After deployment, the collagen layer fuses to the septum and is gradually absorbed (90–95% by ~24 months), allowing native tissue ingrowth. (The device was also heparin-coated to reduce thrombosis.) |
|
|
| Double BioDisk (Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA) [280]. | Two connected nitinol rings (double-disc) covered with a bioabsorbable porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS) membrane. The self-expanding device centers itself in the defect and can be redeployed. The SIS (styrene-isoprene-styrene) polymer membrane acts as a temporary barrier and promotes tissue growth. |
|
|
| Carag CSBO (CARAG AG, Baar, Switzerland) [282]. | Self-centering double-disc occluder with a PLGA bioresorbable polymer frame and two polyester fabric covers. (PLGA = poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) copolymer.) The frame degrades in vivo (begins ~6 mo, gone by ~18–24 mo). X-ray markers (platinum/Phynox) are incorporated for visibility. |
|
|
| Pancy® Occluder (Shanghai, China) [283]. | Double-disc PDO (polydioxanone) frame with interleaving PET membrane and degradable nylon suture. (PDO is a bioabsorbable polymer.) The discs self-expand to seal the PFO. In animal tests, the PDO framework began dissolving at ~3 mo and was mostly gone by 6 mo. |
|
|
| Double-Umbrella Occluder [284]. | Fully biodegradable double-umbrella design for PFO: two self-expanding umbrella-shaped discs of PCL (polycaprolactone) coated with a PLC (poly(L-lactide–co–ε-caprolactone)) film, plus eight symmetrical PLC spokes. A stretchable stem fixes the left disc on septum; right disc seals the defect. |
|
|
| Chinese Lantern (CL) [285]. | Fully biodegradable device: “lantern” structure with soft polymer “head/waist/tail” films (blends of PLC/PCL) and a structural skeleton (wires) also of PLC/PCL blends. A pull-fold mechanism deploys the device; the waist length is adjustable to septal anatomy. Made radio-opaque by added (unspecified) radiopacifier. |
|
|
| PCL-PLGA/Collagen Occluder [286]. | Novel biodegradable ASD occluder: micro-injection-molded PCL scaffold (frame) with electrospun PLGA/collagen nanofiber membrane covering. Double-disc shape mimics Amplatzer device. PCL (semi-crystalline polymer) provides elasticity and shape memory, while PLGA/collagen film acts as a barrier and promotes cell adhesion. |
|
|
| Fully Biodegradable ASD Occluder (improved Amplatzer, 2012) [287] | Double-disc device (Amplatzer-like) with PDO monofilament frame (0.298 mm thick) and PLA (polylactic acid) membranes. Tantalum markers embedded for X-ray. Compressed for catheter delivery and self-expands on release. (PDO frame is elastic yet bioabsorbable.) |
|
|
| Absnow™ PLLA Occluder (Lifetech, China) [291]. | Fully bioabsorbable double-disc device: 0.15 mm PLLA wire mesh skeleton bonded to PLLA membranes on both discs and waist. Novel locking/unlocking handle allows device shape control during deployment. Seven platinum-iridium markers for visibility. Available in 6–32 mm sizes. |
|
|
| Memosorb® PFO Occluder (Shanghai, China) [289]. | Evolved from an earlier PLA-based occluder. Current design is fully biodegradable double-disc: PDO monofilament framework with PLLA membranes. Delivered via novel sheath/pusher with internal cable; “waist” formed by pentagonal skeleton between discs (improves fit in complex septa). |
|
|
| BAO (Bioabsorbable ASD/PFO) [290]. | First-generation biodegradable occluder: symmetric double-disc with 20 mm (left)/15 mm (right) discs and 5 mm waist, made of PLCL (poly(lactide–co–ε-caprolactone)) and 15.2 µm PGA fiber. A 0.9 mm nitinol spring gives X-ray visibility. After poor initial fit, 2nd-gen removed PGA, thickened PLCL fibers, added PLCL knit layer, and lengthened waist to 7 mm. |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dallaev, R. Smart and Biodegradable Polymers in Tissue Engineering and Interventional Devices: A Brief Review. Polymers 2025, 17, 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141976
Dallaev R. Smart and Biodegradable Polymers in Tissue Engineering and Interventional Devices: A Brief Review. Polymers. 2025; 17(14):1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141976
Chicago/Turabian StyleDallaev, Rashid. 2025. "Smart and Biodegradable Polymers in Tissue Engineering and Interventional Devices: A Brief Review" Polymers 17, no. 14: 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141976
APA StyleDallaev, R. (2025). Smart and Biodegradable Polymers in Tissue Engineering and Interventional Devices: A Brief Review. Polymers, 17(14), 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17141976






