Abstract
Any cancer type is one of the leading death causes around the world. Skin cancer is a condition where malignant cells are formed in the tissues of the skin, such as melanoma, known as the most aggressive and deadly skin cancer type. The mortality rates of melanoma are associated with its high potential for metastasis in later stages, spreading to other body sites such as the lungs, bones, or the brain. Thus, early detection and diagnosis are closely related to survival rates. Computer Aided Design (CAD) systems carry out a pre-diagnosis of a skin lesion based on clinical criteria or global patterns associated with its structure. A CAD system is essentially composed by three modules: (i) lesion segmentation, (ii) feature extraction, and (iii) classification. In this work, a methodology is proposed for a CAD system development that detects global patterns using texture descriptors based on statistical measurements that allow melanoma detection from dermoscopic images. Image analysis was carried out using spatial domain methods, statistical measurements were used for feature extraction, and a classifier based on cellular automata (ACA) was used for classification. The proposed model was applied to dermoscopic images obtained from the PH2 database, and it was compared with other models using accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity as metrics. With the proposed model, values of 0.978, 0.944, and 0.987 of accuracy, sensitivity and specificity, respectively, were obtained. The results of the evaluated metrics show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods for melanoma detection in dermoscopic images.
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
Skin cancer is a disease caused by the abnormal development of cancer cells in any layer of the skin. There are two types of skin cancer, the non-melanoma type and the melanoma type [1,2,3]. Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are non-melanoma malignancies that occur in the epidermis. They present as nodules or nonpainful ulcerated and crusted lesions that do not heal with the passage of time. Their growth is slow, and they rarely metastasize [3,4]. On the other hand, melanoma is the most aggressive skin cancer type; if not diagnosed on time, it is susceptible to invade nearby tissues and spread to other body parts [5]. Hence melanoma is considered as the deadliest form of skin cancer, and early detection is decisive for patient survival. Every year something worrying happens in the world—annual rates of all forms of skin cancer are significantly increased, and melanoma increases rapidly among other cancer forms, particularly affecting the young population [6]. Diagnosis of melanoma is a challenging task due to the similarity in appearance to nonmalignant nevi.
For skin cancer diagnosis, the first step is to obtain a patient medical history; subsequently, a physical examination is performed. If the doctor suspects melanoma, he or she will use a technique called dermoscopy to see the skin more clearly [7]. Dermoscopy consists of using a lens type and a light source, both on the lesion, and obtaining an image of the affected area, which is called a dermoscopic image [8]. The analysis of the dermoscopic image is extremely important in decision making if an invasive method such as biopsy is necessary to be applied or not [8,9,10].
1.2. Related Jobs
Computer Aided Design (CAD) are computer systems that perform the interpretation of a medical image as if it were done by a medical specialist. CADs focused on melanoma detection are a great help for medical specialists in the decision-making process that they carry out in observing a dermoscopic image and is helpful in the pre-diagnosis process in a rapid way [11,12,13]. The first task of a CAD system of this type is to segment the lesions present in dermoscopic images; therefore, there are works that show methodologies that allow lesion segmentation and provide guidelines for their subsequent classification. Some of these works propose methodologies that use fully convolutional network (FCN) and dual path network (DPN) [14]; other works perform segmentation by masks that are manually or automatically performed [15], and others use local binary patterns and clustering using k-means [16]. In this work, segmentation is carried out using spatial domain methods and morphological operators. There are works that perform melanoma detection in dermoscopic images based on clinical diagnostic procedures, such as the ABCD rule. The ABCD rule is a clinical guide to determine when a lesion is a melanoma. This guide consists of looking for specific characteristics that allow detecting the asymmetry (A) of a lesion; the type of border (B) if it is irregular, uneven, or blurred; the color variation (C), with reddish, whitish, and bluish being the most dangerous; and the length of the diameter (D) of the lesion [17]. In [18,19,20,21], different methodologies for melanoma detection use the ABCD rule. Unfortunately, this type of system development is hampered by several challenges, such as the lack of data sets with detailed clinical criteria information, or the subtlety of some diagnostic criteria that makes them difficult to detect. On the other hand, there are works that inspect the lesion, detecting the specific presence of patterns associated with its structure. These methods attempt to detect global patterns that are mainly divided into three categories, such as texture, shape, and color [22,23,24]. In this work, texture descriptors based on statistical measurements are used. In [18], a scoring system based on the ABCD rule, which they call the Total Dermoscopic Score (TDS) for the classification between malignant and benign lesions, is proposed. Other works classify using convolutional neural networks, such as AlexNet and VGG16 [25,26], Support Vector Machines [1,19], or k-NN [27], among others, to classify. In this work, the classification is carried out using a model based on cellular automata proposed by the authors in [28].
The objective of the present work is to develop and implement a classifier algorithm through the use of cellular automata that allows the detection of melanoma-type lesions in dermoscopic images. Cellular automata are simple models to implement and require few computational resources compared to models that make use, for example, of deep learning, such as the AlexNet and VGG16 architectures. On the other hand, with the proposal, concepts from the field of cellular automata could be used and applied to the field of supervised learning through this approach to that of cellular automata.
2. Basic Concepts
2.1. Digital Image
A digital image is a discrete two-dimensional function , where x and y are discrete spatial coordinates in the plane. The breadth of a coordinate pair is called the gray level intensity of the image at that point. An image is represented by a two-dimensional array , where and represent the size of the image (referencing and to height and width of the image, respectively), with (Figure 1) [29].
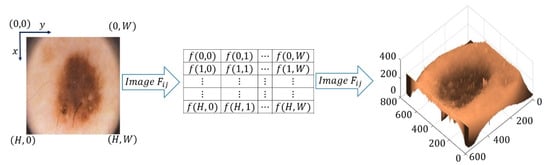
Figure 1.
Definition of an image.
2.2. Mathematical Morphology
The following definitions and theorems correspond to the mathematical morphology [30,31].
Definition 1.
Let. It defines the reflected set ofdenoted for, by:
Definition 2.
Let and. The translation of bydenoted byis defined as:
Definition 3.
Let. The dilation of by, denoted by, is the Minkowski sum ofand, that is:
The setof the above definition is called the structuring element.
Theorem 1.
Let. The following applies:
Definition 4.
Let. The erosion ofby, denoted by, is the Minkowski subtraction ofby, that is:
Theorem 2.
Let. The following applies:
2.3. Cellular Automata
The following definitions correspond to cellular automata [32].
Let be a set of indices. Let be a countable family of closed intervals in , such that the following conditions:
- for some or .
- If , then
- If and are in with , then or .
Definition 5.
Letbe an interval ofwithanda family of closed intervals that satisfy 1, 2, and 3. A 1-dimensional lattice is the set. Ifare families of intervals that meets 1, 2, and 3, then a lattice of dimensionis the set.
Definition 6.
Let. A 1-dimensional lattice is regular iffor each. An n-dimensional lattice is regular iffor.
Definition 7.
Letbe a lattice. A cell or site is an element f; that is, a cell is an element of the formwithfor.
Definition 8.
Letbe a lattice, andis a cell of. A neighborhood of sizeforis the set.
Definition 9.
Let. A cellular automata (CA) is a tuplesuch that:
- 1.
- is a regular lattice.
- 2.
- is a finite set of states.
- 3.
- is a set of neighborhoods that nest as follows:
- 4.
- is a function called the transition function.
Definition 10.
A configuration of the cellular automatais a functionwhich associates to each cell of the latticeat time, a state of.
Ifis a cellular automata and, then the configurationis related withthrough:
Definition 11.
Letandbe two cellular automata. Cellular automata composition of theandin the timeis defined asby the cellular automatawhereandare related as follows:
Definition 12.
Letbe a cellular automata with. Ifand, thendenote the number of cells inwith state.
3. Materials and Methods
This section presents the methodology that detect melanoma in dermoscopic images. The methodology is divided into three modules: image segmentation, feature extraction, and classification.
3.1. Image Segmentation
Segmentation of skin lesions into dermoscopic images was carried out using spatial domain methods. Then, the steps that led the lesion segmentation are shown.
Step 1. To reduce the number of variations in intensity between neighboring pixels, a median filter is applied.
Step 2. The image is binarized using Otsu’s method.
After you apply step 2, the binarized images exhibit additive noise at the corners of the image. To eliminate this noise, the next step is performed.
Step 3. It is considered the circumference that passes through the periphery of the corners of the binarized image taking as its center the coordinate and radius , where . corresponds to the coordinate with the shortest distance that is on the corner’s periphery of the binarized image to the point . Those points that are outside the circumference are removed:
Step 4. Three morphological erosions are applied using Moore’s neighborhood as a structuring element.
Step 5. Three morphological dilations are applied using Moore’s neighborhood as a structuring element.
Step 6. Perform an operation with the color input image.
Figure 2 shows the block diagram that obtains lesion segmentation in the skin from dermoscopic images.
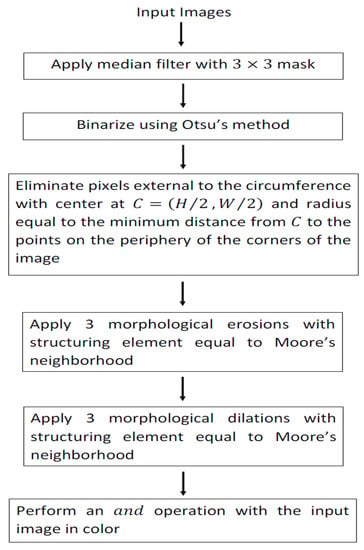
Figure 2.
Block diagram that segments lesions into dermoscopic images.
Figure 3 shows the steps’ application to a dermoscopic image in order to obtain the segmented lesion.
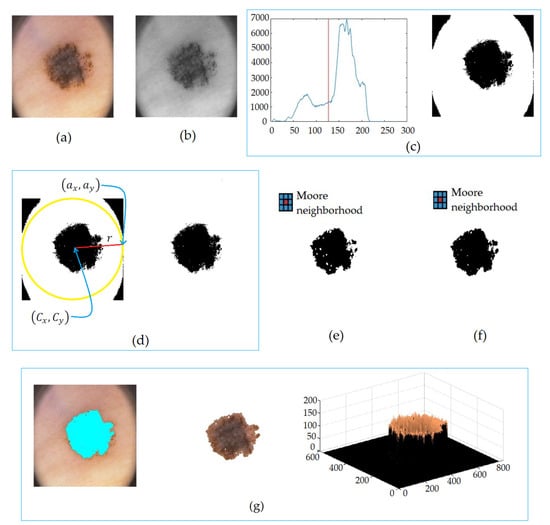
Figure 3.
Lesion segmentation in (a) dermoscopic image, in (b) median filter, in (c) the Otsu method, in (d) corner elimination, in (e) erosions by Moore’s neighborhood, in (f) dilations by Moore’s neighborhood, and in (g) segmented lesion.
3.2. Feature Extraction
To form the pattern of features associated with each image, texture descriptors were used based on 11 statistical measurements shown in Table 1 [33,34]. To perform this, represents the total number of pixels, is the total number of gray levels, is the value of the gray level of the pixel in the image , is the probability that the value of the gray level occurs in the image , is the number of pixels with gray value in the image , is the probability that the gray level occurs in the image and .

Table 1.
Statistical characteristics.
3.3. Classification
An associative model based on cellular automata was used for classification [30]. Associative models are mathematical models whose main objective is to retrieve complete patterns from input patterns. The operation of associative models is divided into two phases: the learning phase—the phase where the associative model is generated, and the recovery phase—the phase where the associative model is operated. During the learning phase, the associative model is constructed from a set of ordered pairs of previously known patterns called the fundamental set. Each pattern that defines the fundamental set is called the fundamental pattern. The fundamental set is represented as follows [35]:
where for with During the recovery phase, the associative model operates with an input pattern to obtain the corresponding output pattern. In this work, we used the associative model based on cellular automata presented in [30]. Then, we present previous definitions and the classifier model in its learning and recovery phase.
Let . Hereinafter, is a cellular automata with initial configuration , defined as follows:
- .
- .
- .
- The transition function is given as follows:
Theorem 3.
The CAwith initial configurationis equivalent to dilating the setbyin the first iteration.
Proof.
If , then by theorem 1, . Therefore, there such that . Since we are dealing with binary images, this means that 1 corresponds as the value of such that ; therefore, then . If then . Since we are dealing with binary images, this means that the neighborhood is formed only by cells with zero values, then , and therefore, . Conversely, if with , then , then there is a cell with the value 1, which is in the vicinity , i.e., there such that and , and is the initial configuration of the CA; therefore, and exists, then , then it follows by theorem 1 that . If with , then , this means that the neighborhood is formed only by cells with values equal to zero, i.e., , then ; therefore, . □
The CA of the previous theorem is called Cellular Dilation (CAD). Let . Hereinafter, is a CA with initial configuration defined as follows:
- .
- .
- .
- The transition function is given as follows:
Theorem 4.
The CAwith initial configurationis equivalent to erode the setbyin the first iteration.
Proof.
If , then by the Theorem 2, because is the set moved by , has to have as many cells with values 1 as ; therefore, therefore . If , then , i.e., there is such that , and this means that there is a cell with value 1 whose value is zero at , then therefore . Conversely, if is a cell with , then , then . If is a cell with , then , and this means that there is a cell in with value zero, and on the other hand, this cell has the value 1 in ; therefore, exists such that therefore, . □
The CA of the previous theorem is called Cell Erosion (CAE).
In what follows, consider the set and the fundamental set with and . The lattice for the CA shall consist of the matrix of size with the first index in . The set is the finite set of states. Let and . Consider the partition of formed by the family of subsets with . Since is a partition of , given , there exists a unique such that . We denote by this single element, i.e., . For example, if , then .
From the above fact, it defines the set of neighborhoods:
Definition 13.
Consider the set. We defined the projection function of the i-th componentasas:
Theorem 5.
If, then.
We define the set .
Consider the CA and with , and , are defined as follows:
and
We define the Associative CA (ACA) in its learning phase as:
The recovery phase for ACA uses the composition of erosions and dilations CA. The algorithm which defines the recovery phase is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1. ACA in recovery phase |
| Input: Fundamental set ; structuring element ; integer value (number of erosions); integer value (number of dilations); pattern to recovery . Output: Recovery pattern .
for do if then if then break end if end if end for end for |
4. Experiments and Results
Dermoscopic images used in this work were obtained from the dermatological service of the Pedro Hispano Hospital in Matosinhos, Portugal. To capture the images, the same conditions were considered through the Tuebinger Mole Analyzer system using a 20× magnification. The images were stored in an 8-bit RGB format with a resolution of pixels. The image bank is made up of melanocyte lesions, including common nevi, atypical nevi, and melanomas. The PH2 database is made up of a total of 200 dermoscopic images developed for research purposes in order to facilitate comparative studies on algorithms for segmentation and classification of dermoscopic images. In this work, 10 images were discarded whose segmentation was not carried out properly due to the lack of sharpness of the images; therefore, in this work, a total of 190 dermoscopic images obtained in the PH2 database [36] were used. The methodology proposed to each of the images was applied to first obtain the segmentation of the binarized lesion (the contour and the image of the lesion in color as shown in Figure 3) then a total of 11 statistical characteristics were extracted (as shown in Table 1), and finally, the classifier model based on cellular automata was applied. Algorithm 1 shows the ACA model in its recovery phase; as a structuring element, the Moore neighborhood was used. The classification of lesions were evaluated using three metrics: sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), and accuracy (ACC). The evaluated metrics are obtained from the confusion matrix and are given by:
where, , , and .
Table 2 shows the values of the confusion matrix, and Table 3 shows a comparison between the proposed model and other works using the SE, SP, and ACC metrics.

Table 2.
Confusion matrix.

Table 3.
Comparison of melanoma diagnosis methods through the accuracy (ACC), sensitivity (SE), and specificity (SP).
Figure 4 shows the ROC plots of the models in Table 3 and the respective area under the curve (AUC).
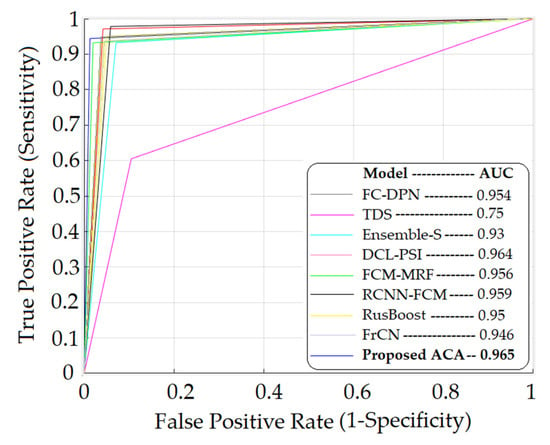
Figure 4.
ROC graph for melanoma detection of different learning methods.
5. Discussion
This paper proposes a methodology that allows the detection of melanoma in dermoscopic images. The methodology consists of three distinguishable stages: segmentation of the lesions, extraction of characteristics, and classification. The segmentation of the lesions was carried out using methods in the spatial domain and morphological operators. For the extraction of characteristics, 11 statistical characteristics shown in Table 1 were used, and for the classification, the ACA model, an associative model based on cellular automata, was used. Table 2 shows the confusion matrix, where it is observed that, out of a total of 190 images considered, the model classified two cases as false positives and two cases as false negatives. This is possibly due to the fact that these cases are on the border classification between the lesions that present melanoma and those that do not, or atypical situations that the model requires to know, or possibly the segmentation process yielded sections of the image that, due to the scarce clarity, classified them erroneously. Table 3 and Figure 4 show the values of the proposed model and its comparison with other models that solve the same problem. Table 3 shows the evaluated metrics considered, which are accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, and Figure 3 also shows the ROC graphs and the areas under the curve. As the results are observed, the value of the sensitivity thrown by the proposed model is by the mean, which is higher than models such as those proposed in [18,37,39,42] but lower than models such as those proposed in [14,38,40,41]. This metric refers to the ability of the model to diagnose lesions that present melanoma adequately. As such, it is a metric that must be improved in the proposed model to obtain better results. However, with respect to the specificity metric, the proposed model yielded superior results to all the models with which it was compared; this metric refers to the ability of the model to diagnose lesions that do not correspond to the presence of melanoma. On the other hand, the proposed model also showed values of higher accuracy than the rest of the models compared, having an accuracy of 0.978. This is also reflected in the area under the ROC curve shown in Figure 4 of the proposed model, which is 0.965 and higher than the area of all the ROC curves compared. The AUC reflects how good the model is to discriminate lesions with the presence and absence of melanoma; the higher its value approaches 1, the greater its discriminative capacity. As can be seen, the proposed model yields competitive results and can be considered for use in the detection of skin diseases that are not necessarily melanoma. The main limitations of this work are due to the amount of images that the PH2 database has, in addition to the fact that the same conditions must be met for the acquisition of the images. It would be convenient to do tests with more dermoscopic images obtained from various conditions that may occur when the images are acquired by specialists who use dermoscopic images for the detection of melanoma. On the part of the classifier, it is limited to structuring elements of the Moore neighborhood form; however, other types of structuring elements can be considered.
6. Conclusions
In this work, a methodology was presented that allows the detection of melanoma in dermoscopic images using a classifier based on cellular automata. The results of the metrics evaluated (sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy) show that the proposed method is more effective than other state-of-the-art methods for the detection of melanoma in dermoscopic images (Table 3).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.-B.; methodology, B.L.-B. and J.C.M.-P.; validation, J.C.M.-P.; investigation, R.F.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.-G. and V.M.S.-G.; writing—review and editing, B.L.-B., R.F.-C., J.C.M.-P., J.C.-G. and V.M.S.-G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
The data sets used are the property of PH2 dataset and were developed for research purposes.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: reference [36]; https://www.fc.up.pt/addi/ph2%20database.html (accessed on 7 December 2021).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Instituto Politécnico Nacional (Secretaría Académica, COFAA, EDD, SIP, ESCOM and CIDETEC) for their financial support to develop this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhen, M.; Tavares, J.M. Effective features to classify skin lesions in dermoscopic images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 84, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Dey, D.; Munshi, S. Optimal selection of features using wavelet fractal descriptors and automatic correlation bias reduction for classifying skin lesión. Biomed. Signal Proccess. Control 2018, 40, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craythorme, E.; Al-Niami, F. Skin cancer. Medicine 2017, 45, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caini, S.; Boniol, M.; Tosti, G.; Magi, S.; Medri, M.; Stanganelli, I.; Palli, D.; Assedi, M.; Del Marmol, V.; Gandini, S. Vitamin D and melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer and prognosis: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Berendt, R.; Jha, N.; Mandal, M. Automatic measurenment of melanoma Depth of invasión in skin hitopathological images. Micron 2017, 97, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Abbad, N.; Faisal, Z. Detection and analysis of skin cancer from skin lesion. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 9046–9052. [Google Scholar]
- Boespflug, A.; Perier-Muzet, M.; Phan, A.; Dhaille, F.; Assouly, P.; Thomas, L.; Petit, A. Dermatoscopia de las lesiones cutáneas no neoplásicas. EMC-Dermatología 2018, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.K.; Ahn, C.S. Dermatoscopy for melanoma and pigmented lesion. Dermatol. Clin. 2012, 30, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos-Hernández, J.F.; Ortiz-Maldondado, A.L.; Minauro-Muñoz, G.G.; Arias-Ceballos, H.; Hernández-Sanjuan, M. Dermoscopy in cutaneous melanoma. Cirugía Y Cir. 2015, 83, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastar, Z.; Lipozencic, J. Significance of dermoscopic in genital dermatoses. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, C.; Celebi, M.E.; Marques, J.S. Development of a clinically oriented system for melanoma diagnosis. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 69, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkashvand, F.; Fartash, M. Automatic segmentation of skin lesion using markov random field. Can. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 3, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Dalila, F.; Zohra, A.; Reda, K.; Hocine, C. Segmentation and classification of melanoma and benign skin lesions. Optik 2017, 140, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, P.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Song, W.; Chen, J. Automatic skin lesion segmentation based on FC-DPN. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 123, 103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahbod, A.; Tschandl, P.; Langs, G.; Ecker, R.; Ellinger, I. The effects of skin lesion segmentation on the performance of dermoscopic image classification. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 197, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.M.M.; Fonseca-Pinto, R.; Paiva, R.P.; Assuncao, P.A.A.; Tavora, L.M.N.; Thomaz, L.A.; Faria, S.M.M. Dermoscopic skin lesión image segmentation based on Local Binary Pattern Clustering: Comparative study. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 59, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigel, D.S.; Russak, J.; Friedman, R. The evolution of melanoma diagnosis: 25 years beyond the ABCDs. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.; Jadhav, M. Analysis of dermoscopic images by using ABCD rule for early detection of skin cancer. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2021, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, L.; Ram, R.; Prakash, S. Designing a Retrieval-Based Diagnostic Aid using Effective Features to Classify Skin Lesión in Dermoscopic Images. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, A.; Hokmabadi, A. Improvement in the diagnosis of melanoma and dysplastic lesions by introducing ABCD-PDT features and a hybrid classifier. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 38, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monisha, M.; Suresh, A.; Bapu, B.R.; Rashmi, M. Classification of malignant melanoma and benign skin lesión by using back propagation neural network and ABCD rule. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 12897–12907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfed, N.; Khelifi, F. Bagged textural and color features for melanoma skin cancer detection in dermoscopic and standar images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 90, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoecker, W.; Wronkiewiecz, M.; Chowdhury, R.; Stanley, R.; Xu, J.; Bangert, A.; Shrestha, B.; Calcara, D.; Rabinovitz, H.; Oliviero, M.; et al. Detection of granularity in dermoscopy images of malignant melanoma using color and texture features. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2011, 35, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathan, S.; Gopalakrishna, K.; Siddalingaswamy, P. Automated detection of melanocytes related pigmented skin lesión: A clinical framework. Biomed. Singal Process. Control 2019, 51, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, J.; Sharif, A.; Gul, N.; Almas, M.; Wasif, M.; Azam, F.; Ahmad, S. Integrated design of deep features fusion for localization and classification of skin cancer. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 131, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Hosseinzadeh, P. A comparative study of deep learning architectures on melanoma detection. Tissue Cell 2019, 58, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganster, H.; Pinz, P.; Rohrer, R.; Wildling, E.; Binder, M.; Kittler, H. Automated melanoma recognition. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna-Benoso, B.; Flores-Carapia, R.; Yáñez-Márquez, C. Associative Memories Based on Cellular Automata: An Application to Pattern Recognition. Appl. Math. Sci. 2013, 7, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, F.; Cheng, S. Adaptative mathematical morphology for Edge linking. Inf. Sci. 2004, 167, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, I. On links between mathematical morphology and rough sets. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 33, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Benoso, B.; Yáñez-Márquez, C.; Figueroa-Nazuno, J.; López-Yañéz, I. Cellular Mathematical Morphology. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sixth Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Aguascalientes, Mexico, 4–10 November 2008; pp. 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Verma, B.; Kumar, K. Neural vs statistical classifier in conjunction with genetic algorithm based feature selection. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2005, 26, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashini, T.S.; Ramalingam, V.; Palanivel, S. Automated assement of breast tissue density in digital mammograms. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2010, 114, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Moreno, R.; Sossa, H.; Gutierrez-Hernández, D.A.; Zamudio, V.; Hernández-Bautista, I.; Valadez-Godínez, S. Novel mathematical modelo f breast cancer diagnostics using an associative pattern classification. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendonca, T.; Ferreira, P.M.; Marques, J.; Marcal, A.R.S.; Rozeira, J. PH2-A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking. In Proceedings of the 35th Internacional Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, M.; Oakley, A.; Bansal, P.; Dancey, D.; Yap, M.H. Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic images with ensemble deep learning methods. IEEE Access 2019, 8, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Kim, J.; Ahn, E.; Kumar, A.; Feng, D.; Fulham, M. Step-wise integration of deep class-specific learning for dermoscopic image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 85, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eltayef, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Detection of melanoma skin cancer in dermoscopic images. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 787, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nida, N.; Irtaza, A.; Javed, A.; Yousaf, M. Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep región based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 124, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajeddin, N.Z.; Asl, B.M. Melanoma recognition in dermoscopic images using lesion’s peripheral región information. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 163, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masni, M.A.; Al-Antari, M.A.; Choi, M.T.; Han, S.M.; Kim, T.S. Skin lesion segmentation in dermoscopic image via deep full resolution convolutional networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 162, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).