Methylation Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Data Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
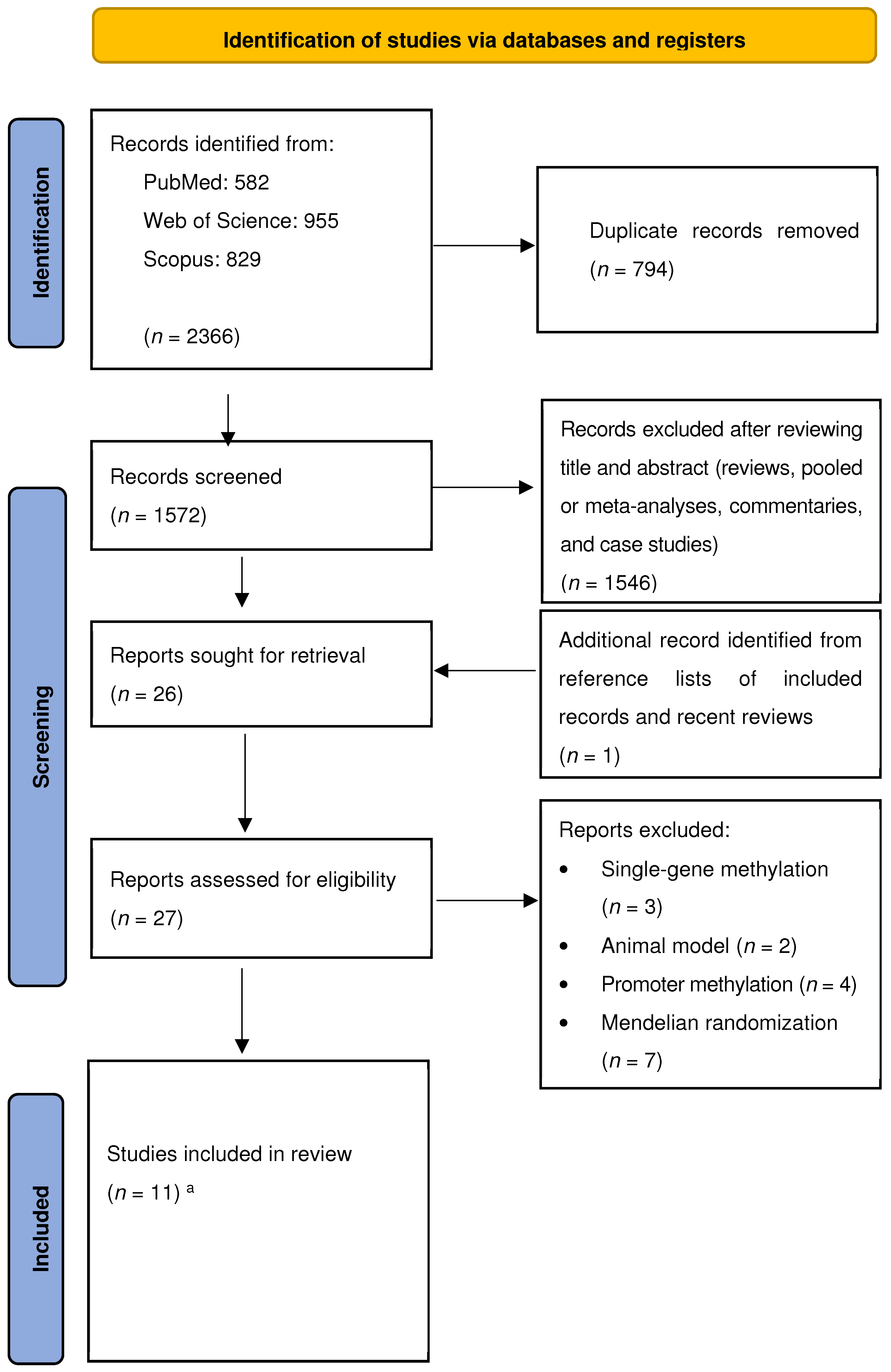
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics and Quality Assessment
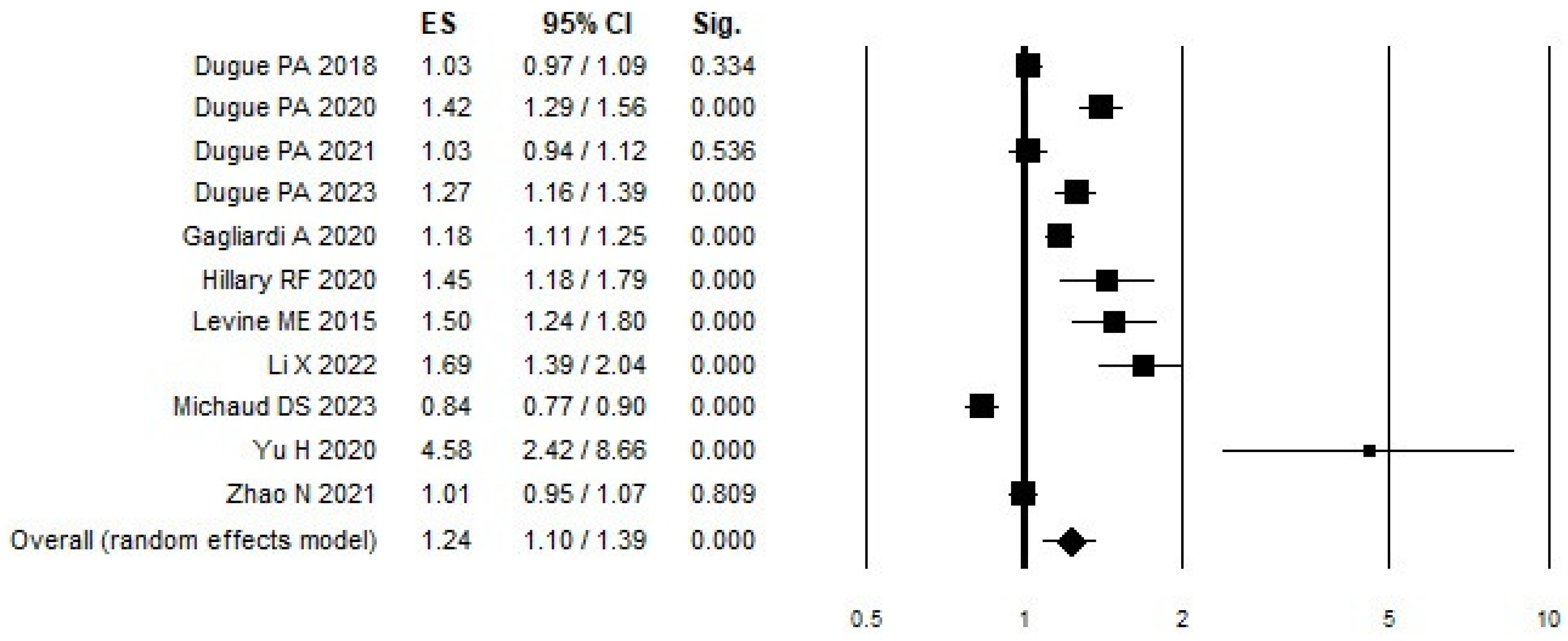
3.3. Meta-Analysis of DNAm
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of DNAm
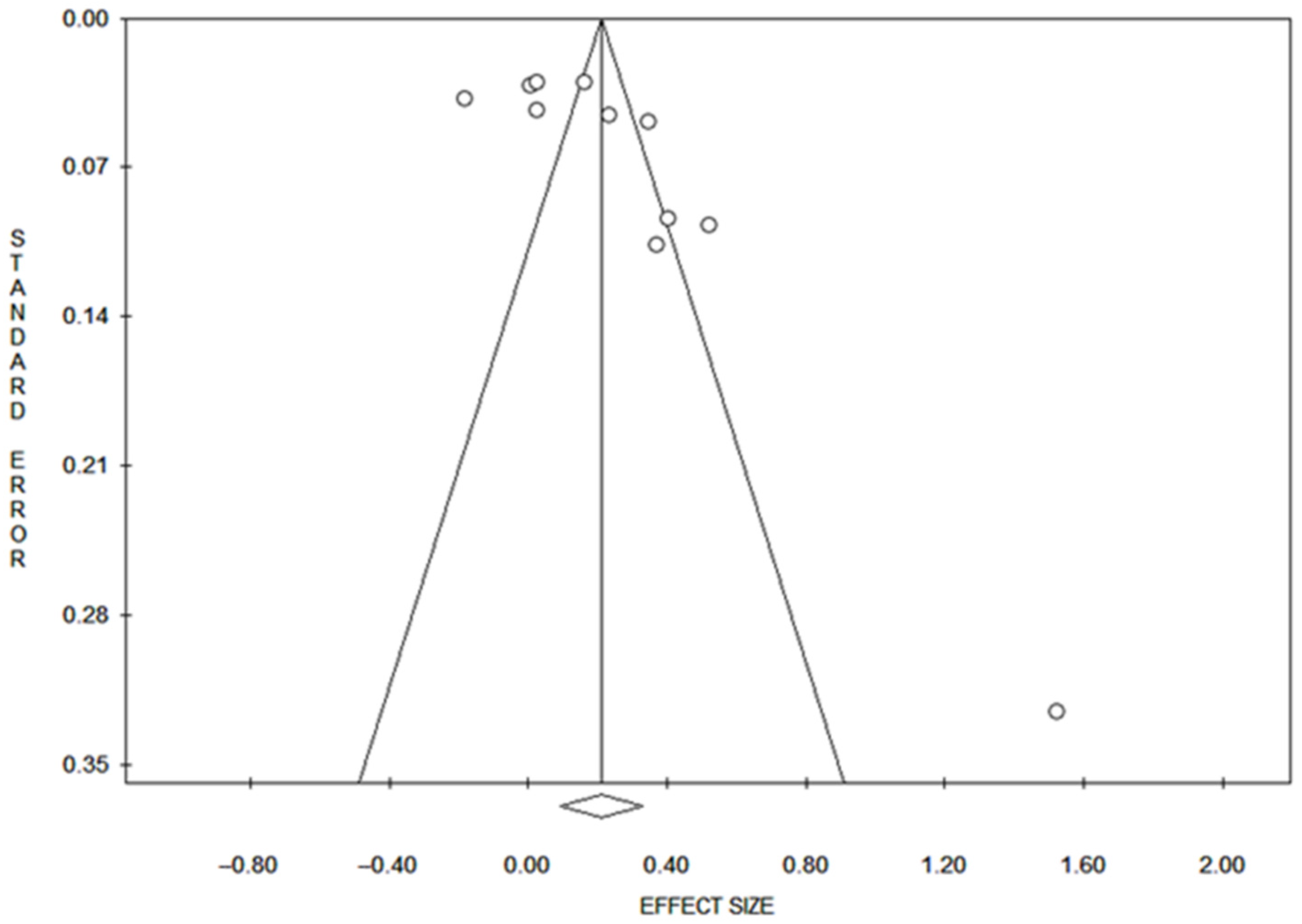
3.5. Publication Bias of DNAm
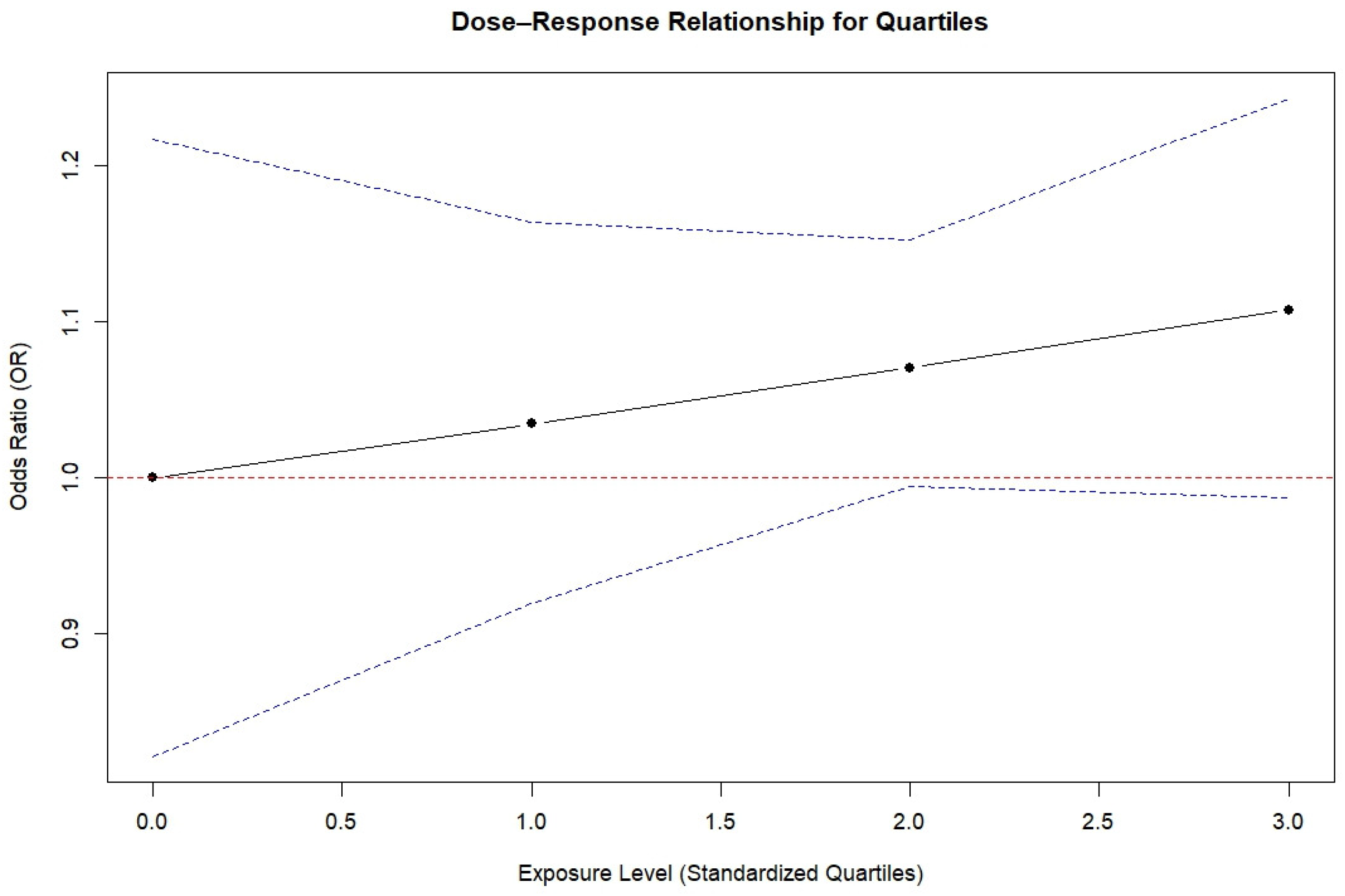
3.6. Dose–Response
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/en/dataviz/pie?mode=cancer&group_populations=1&types=0 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Chiavarini, M.; Rosignoli, P.; Sorbara, B.; Giacchetta, I.; Fabiani, R. Benzene Exposure and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Human Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jemal, A.; Center, M.M.; DeSantis, C.; Ward, E.M. Global Patterns of Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates and Trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The Effect of Advances in Lung-Cancer Treatment on Population Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiani, R.; La Porta, G.; Cavoli, L.L.; Rosignoli, P.; Chiavarini, M. Adherence to Data-Driven Dietary Patterns and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, L.L.; Teutsch, S.; Johnson, M. Lung Cancer Screening with Sputum Cytologic Examination, Chest Radiography, and Computed Tomography: An Update for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.J.; Van Der Aalst, C.M.; De Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, P.S.; Callahan, K.E.; Medina, H.N.; Koru-Sengul, T.; Kobetz, E.N.; Gomez, S.L.; Lopes, G.d.L. Lung cancer in never smokers: Distinct population-based patterns by age, sex, and race/ethnicity. Lung Cancer 2022, 174, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; Chiavarini, M.; Rosignoli, P.; Giacchetta, I. Leucocyte Telomere Length and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Cancers 2024, 16, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazi, S.; Dadzadi, M.; Sahafnejad, Z.; Allahverdi, A. Epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. Medcomm 2023, 4, e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The Epigenomics of Cancer. Cell 2007, 128, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenson, V.V. DNA methylation as a universal biomarker. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.; Chen, T.; Hung, C.; Wen, C.; Lin, R.; Lee, H.; Wang, Y. Characterization of a multiple epigenetic marker panel for lung cancer detection and risk assessment in plasma. Cancer 2007, 110, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Leung, D.; Thrush, K.; Zhao, W.; Ratliff, S.; Tanaka, T.; Schmitz, L.L.; Smith, J.A.; Ferrucci, L.; Levine, M.E. Underlying features of epigenetic aging clocks in vivo and in vitro. Aging Cell 2020, 19, 13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Robertson, N.A.; Wang, T.; Havas, A.; Ideker, T.; Adams, P.D. DNA Methylation Clocks in Aging: Categories, Causes, and Consequences. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.H.; Marioni, R.E.; Colicino, E.; Peters, M.J.; Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Tsai, P.C.; Roetker, N.S.; Just, A.C.; Demerath, E.W.; Guan, W.; et al. DNA methylation-based measures of biological age: Meta-analysis predicting time to death. Aging 2016, 8, 1844–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambatipudi, S.; Horvath, S.; Perrier, F.; Cuenin, C.; Hernandez-Vargas, H.; Le Calvez-Kelm, F.; Durand, G.; Byrnes, G.; Ferrari, P.; Bouaoun, L.; et al. DNA methylome analysis identifies accelerated epigenetic ageing associated with postmenopausal breast cancer susceptibility. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Bandinelli, S.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Li, Y.; et al. An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2018, 10, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wong, A.; Kuh, D.; Paul, D.S.; Rakyan, V.K.; Leslie, R.D.; Zheng, S.C.; Widschwendter, M.; Beck, S.; Teschendorff, A.E. Correlation of an epigenetic mitotic clock with cancer risk. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Dobersch, S.; Romero-Olmedo, A.J.; Barreto, G. Epigenetics in lung cancer diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgkouranidou, I.; Liloglou, T.; Lianidou, E.S. Lung Cancer Epigenetics: Emerging Biomarkers. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Joyce, B.T.; Colicino, E.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Dai, Q.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Kibbe, W.A.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Blood Epigenetic Age may Predict Cancer Incidence and Mortality. eBioMedicine 2016, 5, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresovich, J.K.; Xu, Z.; O’brien, K.M.; Weinberg, C.R.; Sandler, D.P.; Taylor, J.A. Epigenetic mortality predictors and incidence of breast cancer. Aging 2019, 11, 11975–11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugué, P.-A.; Bassett, J.K.; Wong, E.M.; Joo, J.E.; Li, S.; Yu, C.; Schmidt, D.F.; Makalic, E.; Doo, N.W.; Buchanan, D.D.; et al. Biological Aging Measures Based on Blood DNA Methylation and Risk of Cancer: A Prospective Study. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2020, 5, pkaa109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillary, R.F.; Stevenson, A.J.; McCartney, D.L.; Campbell, A.; Walker, R.M.; Howard, D.M.; Ritchie, C.W.; Horvath, S.; Hayward, C.; McIntosh, A.M.; et al. Epigenetic measures of ageing predict the prevalence and incidence of leading causes of death and disease burden. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ni, W.; Yao, Y.; Just, A.; Heiss, J.; Wei, Y.; Gao, X.; Coull, B.A.; Kosheleva, A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. DNA methylation-based biomarkers of age acceleration and all-cause death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and cancer in two cohorts: The NAS, and KORA F4. eBioMedicine 2021, 63, 103151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durso, D.F.; Bacalini, M.G.; Sala, C.; Pirazzini, C.; Marasco, E.; Bonafé, M.; Valle, Í.F.D.; Gentilini, D.; Castellani, G.; Faria, A.M.C.; et al. Acceleration of leukocytes’ epigenetic age as an early tumor and sex-specific marker of breast and colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23237–23245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis Of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 134, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. (n.d.). Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Orsini, N.; Bellocco, R.; Greenland, S. Generalized Least Squares for Trend Estimation of Summarized Dose–response Data. Stata J. Promot. Commun. Stat. Stata 2006, 6, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, S. Dose-response and trend analysis in epidemiology: Alternatives to categorical analysis. Epidemiology 1995, 6, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cochrane Collaboration ®. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; The Cochrane Collaboration ®: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating Characteristics of a Rank Correlation Test for Publication Bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Dugué, P.-A.; Nøst, T.H.; Southey, M.C.; Buchanan, D.D.; Schmidt, D.F.; Makalic, E.; Hodge, A.M.; English, D.R.; Doo, N.W.; et al. Stochastic Epigenetic Mutations Are Associated with Risk of Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, and Mature B-cell Neoplasms. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 2026–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.E.; Hosgood, H.D.; Chen, B.; Absher, D.; Assimes, T.; Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of blood predicts future onset of lung cancer in the women’s health initiative. Aging 2015, 7, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugué, P.; Bassett, J.K.; Joo, J.E.; Jung, C.; Wong, E.M.; Moreno-Betancur, M.; Schmidt, D.; Makalic, E.; Li, S.; Severi, G.; et al. DNA methylation-based biological aging and cancer risk and survival: Pooled analysis of seven prospective studies. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Raut, J.R.; Schöttker, B.; Holleczek, B.; Zhang, Y.; Brenner, H. Individual and joint contributions of genetic and methylation risk scores for enhancing lung cancer risk strati-fication: Data from a population-based cohort in Germany. Clin. Epigenetics 2020, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Ruan, M.; Koestler, D.C.; Lu, J.; Salas, L.A.; Kelsey, K.T.; Platz, E.A.; Michaud, D.S. Methylation-derived inflammatory measures and lung cancer risk and survival. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugué, P.-A.; Hodge, A.M.; Wong, E.M.; Joo, J.E.; Jung, C.-H.; Hopper, J.L.; English, D.R.; Giles, G.G.; Milne, R.L.; Southey, M.C. Methylation marks of prenatal exposure to maternal smoking and risk of cancer in adulthood. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Schöttker, B.; Holleczek, B.; Brenner, H. Associations of DNA methylation algorithms of aging and cancer risk: Results from a prospective cohort study. eBioMedicine 2022, 81, 104083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugué, P.A.; Yu, C.; Hodge, A.M.; Wong, E.M.; Joo, J.E.; Jung, C.H.; Southey, M.C. Methylation scores for smoking, alcohol consumption, and body mass index and risk of seven types of cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, D.S.; Chung, M.; Zhao, N.; Koestler, D.C.; Lu, J.; Platz, E.A.; Kelsey, K.T. Epigenetic age and lung cancer risk in the CLUE II prospective cohort study. Aging 2023, 15, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Kim, W.J. DNA Methylation Markers in Lung Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinsky, S.A.; Nikula, K.J.; Palmisano, W.A.; Michels, R.; Saccomanno, G.; Gabrielson, E.; Baylin, S.B.; Herman, J.G. Aberrant methylation of p16 INK4a is an early event in lung cancer and a potential biomarker for early diagnosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11891–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joehanes, R.; Just, A.C.; Marioni, R.E.; Pilling, L.C.; Reynolds, L.M.; Mandaviya, P.R.; Guan, W.; Xu, T.; Elks, C.E.; Aslibekyan, S.; et al. Epigenetic Signatures of Cigarette Smoking. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.L.; Stevenson, A.J.; Hillary, R.F.; Walker, R.M.; Bermingham, M.L.; Morris, S.W.; Clarke, T.-K.; Campbell, A.; Murray, A.D.; Whalley, H.C.; et al. Epigenetic signatures of starting and stopping smoking. eBioMedicine 2018, 37, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshawarz, A.; Joehanes, R.; Guan, W.; Huan, T.; DeMeo, D.L.; Grove, M.L.; Fornage, M.; Levy, D.; O’connor, G. Longitudinal change in blood DNA epigenetic signature after smoking cessation. Epigenetics 2022, 17, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R115, Erratum in Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannum, G.; Guinney, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Hughes, G.; Sadda, S.; Klotzle, B.; Bibikova, M.; Fan, J.-B.; Gao, Y.; et al. Genome-wide Methylation Profiles Reveal Quantitative Views of Human Aging Rates. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Wilson, J.G.; Reiner, A.P.; Aviv, A.; Raj, K.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Li, Y.; Stewart, J.D.; et al. DNA methylation GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging 2019, 11, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartling, L.; Milne, A.; Hamm, M.P.; Vandermeer, B.; Ansari, M.; Tsertsvadze, A.; Dryden, D.M. Testing the Newcastle Ottawa Scale showed low reliability between individual reviewers. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oremus, M.; Oremus, C.; Hall, G.B.C.; McKinnon, M.C.; ECT & Cognition Systematic Review Team. Inter-rater and test–retest reliability of quality assessments by novice student raters using the Jadad and Newcastle–Ottawa Scales. BMJ Open 2012, 2, e001368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, S.; Erhart, W.; Brosch, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; Von Schönfels, W.; Ahrens, M.; Heits, N.; Bell, J.T.; Tsai, P.C.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Obesity accelerates epigenetic aging of human liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15538–15543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Raisky, J.; Ratliff, S.M.; Liu, J.; Kardia, S.L.; Turner, S.T.; Mosley, T.H.; Zhao, W. Intrinsic and extrinsic epigenetic age acceleration are associated with hypertensive target organ damage in older African Americans. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author, Year, Reference | Cohort 1, Location | Study Design | DNAm Measure 2 | N | Age (M: Mean, Mdn: Median) | Sex (% Male) | Race (% White) | BMI (%, M: Mean, Mdn: Median [kg/m2] < 25) | Type of LC 3 | Smoking Status (% Never) | Matched or Adjusted Variables | NOS 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Michaud DS, 2023 [52] | CLUE II, USA | Nested case–control | Epigenetic Age AA_Hannum, AA_Horvath, AA_Pheno, IEAA_Hannum, IEAA_Horvath, IEAA_Pheno | Cases: 208 Controls: 208 | Cases: 58.3 (M) Controls: 55.9 (M) | Cases: 45.7 Controls: 45.7 | NA | Cases: 26.0 (M) Controls: 26.2 (M) | LC (NSCLC: 74%) | Cases: 10.6 Controls: 10.6 | Batch effects, BMI, smoking predicted years | 8 |
| Dugue PA, 2023 [51] | MCCS, Australia | Nested case–control | SMOKING Smk-233, Smk-1061. BMI BMI-1109, BMI-85. ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION Alc-450, Alc-459 | Cases: 327 Controls: 327 | Cases: 61 (Mdn) Controls: 61 (Mdn) | Cases: 61 Controls: 61 | NA | Cases: 27 (M) Controls: 27 (M) | LC | Cases: 46 Controls: 48 | Smoking details, physical activity, diet quality, education, SES, alcohol consumption, BMI | 9 |
| Li X, 2022 [50] | ESTHER, Germany | Cohort study; FU: 17 years | Epigenetic Age AgeAccelPheno, AgeAccelPheno Methylation Score MRscore-8CpGs | Cases: 207 Controls: 205 | Cases: 63.2 (M) Controls: 62.5 (M) | Cases: 63.8 Controls: 42.9 | NA | Cases: 23.7 (%) Controls: 31.2 (%) | LC | Cases: 30.4 Controls: 49.5 | Age, sex, leukocyte composition, batch, educational level, smoking status, alcohol consumption, BMI, diabetes status | 8 |
| Dugue PA, 2020 [27] | MCCS, Australia | Nested case–control | Epigenetic Age PhenoAge, GrimAge | Cases: 327 Controls: 327 | Cases: 61 (Mdn) Controls: 61 (Mdn) | Cases: 69.3 Controls: 69.3 | NA | Cases: 27 (Mdn) Controls: 27 (Mdn) | LC | Cases: 45.8 Controls: 45.8 | Age, sex, country of birth, sample type, smoking information, BMI, height, alcohol consumption, physical activity, dietary quality, socioeconomic status, education | 8 |
| Dugue PA, 2021 [49] | MCCS, Australia | Nested case–control | MATERNAL SMOKING MS-568, MS-19, MS-15, MS-28, MS-17 ADULT SMOKING AS-233, AS-56, AS-1061 | Cases: 327 Controls: 327 | Cases: 61 (Mdn) Controls: 61 (Mdn) | Cases: 61 Controls: 61 | NA | NA | LC | Cases: 48 Controls: 46 | Smoking information, alcohol consumption, BMI, physical activity, dietary quality, education, socioeconomic status, height | 8 |
| Zhao N, 2021 [48] | CLUE I-II, USA | Nested case–control | mdNLR; CRP Score 1, 2, 3. | Cases: 208 Controls: 208 | Cases: 59 (Mdn) Controls: 56 (Mdn) | Cases: 45.7 Controls: 45.7 | Cases: 98.6 Controls: 100 | NA | LC (all LC and NSCLC) | Cases: 10.6 Controls: 10.6 | Age, sex, smoking status, BMI, batch effects, predicted pack-years smoked, cell proportions | 9 |
| Hillary RF, 2020 [28] | GS, Scotland | Cohort | DunedinPoAm | Cases: 4450 Controls: 2578 | Cases: 51.4 (M) Controls: 50 (M) | Cases: 43.7 Controls: 38.6 | NA | Cases: 26.8 (M) Controls: 27.2 (M) | LC | NA | Age, sex, alcohol consumption, BMI, deprivation, education, smoking | 8 |
| Yu H, 2020 [47] | ESTHER, Germany | Nested case–control | Methylation Risk Score MRS | Cases: 143 Controls: 1460 | Cases: 63.7 (M) Controls: 61.8 (M) | Cases: 62.9 Controls: 44.0 | NA | NA | LC | Cases: 12.1 Controls: 49.7 | Batch, leukocyte composition, age, sex, smoking status, pack-years | 9 |
| Gagliardi A, 2020 [44] | EPIC, Italy | Nested case–control | LogSEM model 4; LogSEM model EPIC, LogSEMmodel(TTD) ≤ 5 y, 5–10 y, >10 y | Cases: 556 Controls: 556 | Cases: 53.7 (M) Controls: 53.5 (M) | Cases and controls: 31 | NA | NA | LC | Cases: 43 Controls: 49 | Age, sex smoking, BMI, dietary quality, alcohol intake, physical activity, education, Horvath DNAmAge epigenetic AA, DNAmGrimAge, epigenetic AA | 9 |
| MCCS, Australia | Nested case–control | LogSEM model 4; LogSEM model MCCS, LogSEMmodel(TTD) ≤ 5 y, 5–10 y, > 10 y | Cases: 3482 Controls: 3482 | Cases: 59.1 (M) Controls: 58.9 (M) | Cases and controls: 61 | NA | NA | LC | Cases: 46 Controls: 48 | Age, sex smoking, BMI, dietary quality, alcohol intake, physical activity, education, Horvath DNAmAge epigenetic AA, DNAmGrimAge, epigenetic AA | 9 | |
| NOWAC, Norway | Nested case–control | LogSEM model 4; LogSEM model NOWAC, LogSEMmodel(TTD) ≤ 5 y, 5–10 y, > 10 y | Cases: 316 Controls: 316 | Cases and Controls: 55.9 (M) | Cases and Controls: 0 | NA | NA | LC | Cases: 26 Controls: 38 | Age, sex smoking, BMI, dietary quality, alcohol intake, physical activity, education, Horvath DNAmAge epigenetic AA, DNAmGrimAge, epigenetic AA | 9 | |
| Dugue AP, 2018 [46] | MCCS, Australia | Nested case–control | Epigenetic Age AA_Hannum, AA_Horvath, IEAA_Hannum, IEAA_Horvath, EEAA. | Cases: 332 Controls: 332 | Cases: 59.5 (M) Controls: 59.4 (M) | Cases and Controls: 64 | NA | Cases: 37.0 (%) Controls: 28.0 (%) | LC | Cases and Controls: 12 | BMI, smoking, alcohol intake, diet quality, physical activity, socioeconomic status education, age, sex, ethnicity | 8 |
| Levine ME, 2015 [45] | WHI, USA | Case–control | Epigenetic Age IEAA by age: All ages, 50–59, 60–69, 70+. IEAA by smoking status: Current, Former, Never. | Cases: 43 Controls: 1986 | 65.34 (M: Cases + Controls) | Cases: 0 Controls: 0 | NA | NA | LC | 54.4 (M: Cases + Controls) | Age, race/ethnicity, CHD status, pack-years, smoking status | 7 |
| Combined Risk Estimate a | Test of Heterogeneity | Publication Bias | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N b | Value (95% CI) | Q | I2 % | p | p (Egger Test) | p (Begg Test) | |
| ALL (11 articles) | 111 | 1.24 (1.10–1.39) | 163.95 | 93.90 | 0.00 | 0.032 | 0.07 |
| ALL (Case–control study) | 104 | 1.05 (0.99–1.11) | 350 | 70.57 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.14 |
| ALL (Cohort study) | 7 | 1.61 (1.36–1.90) | 7.01 | 14.42 | 0.32 | 0.012 | 0.18 |
| Smoking status | |||||||
| CURRENT | 7 | 1.60 (1.43–1.79) | 2.65 | 0.00 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.042 |
| PAST | 7 | 1.58 (1.42–1.77) | 4.11 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.09 | 0.19 |
| Follow-up | |||||||
| ≤5 | 3 | 1.46 (1.08–1.98) | 4.92 | 59.36 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| 5–10 | 3 | 1.20 (1.06–1.36) | 1.27 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| ≤10 | 20 | 1.06 (0.93–1.21) | 16.92 | 82.27 | 0.001 | 0.46 | 0.50 |
| >10 | 17 | 0.99 (0.85–1.16) | 12.97 | 76.87 | 0.005 | 0.94 | 0.50 |
| Group of indicators | |||||||
| 7 indicators 1 | 23 | 1.04 (0.95–1.14) | 64.89 | 66.1 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.96 |
| 4 indicators 2 | 14 | 1.12 (0.96–1.30) | 55.52 | 76.58 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.70 |
| AA_Hannum | 3 | 0.93 (0.74–1.16) | 4.19 | 52.28 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.60 |
| AA_Horvath | 3 | 0.95 (0.86–1.05) | 1.97 | 0.00 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.60 |
| AA_Pheno | 5 | 1.18 (0.95–1.48) | 12.10 | 66.94 | 0.017 | 0.59 | 0.33 |
| AA_Grim | 3 | 1.97 (1.57–2.47) | 1.14 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.60 |
| 3 indicators 3 | 8 | 0.96 (0.89–1.04) | 4.05 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.026 | 0.14 |
| IEAA_Hannum | 3 | 0.95 (0.79–1.14) | 2.83 | 29.28 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.12 |
| IEAA_Horvath | 3 | 0.97 (0.87–1.08) | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.046 | 0.12 |
| Type of indicators | |||||||
| Hannum (AA + IEAA) | 6 | 0.95 (0.85–1.08) | 7.02 | 28.77 | 0.22 | 0.023 | 0.19 |
| Horvath (AA + IEAA) | 6 | 0.96 (0.89–1.03) | 2.64 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.023 | 0.13 |
| Pheno (AA + IEAA) | 7 | 1.09 (0.91–1.31) | 16.73 | 64.13 | 0.010 | 0.68 | 0.88 |
| Grim (AA) | 3 | 1.97 (1.57–2.47) | 1.14 | 0.00 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolcini, J.; Chiavarini, M.; Firmani, G.; Brennan, K.J.M.; Cardenas, A.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Barbadoro, P. Methylation Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040690
Dolcini J, Chiavarini M, Firmani G, Brennan KJM, Cardenas A, Baccarelli AA, Barbadoro P. Methylation Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(4):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040690
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolcini, Jacopo, Manuela Chiavarini, Giorgio Firmani, Kasey J. M. Brennan, Andres Cardenas, Andrea A. Baccarelli, and Pamela Barbadoro. 2025. "Methylation Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 4: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040690
APA StyleDolcini, J., Chiavarini, M., Firmani, G., Brennan, K. J. M., Cardenas, A., Baccarelli, A. A., & Barbadoro, P. (2025). Methylation Biomarkers of Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(4), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040690







