Simple Summary
Breast cancer is widespread globally and significantly affects patients’ well being. e-Health solutions are rapidly increasing, offering support for patients’ mental health and quality of life. This systematic review includes 27 randomized studies with a total of 2898 patients, which evaluated the effects of e-Health interventions on mental health and quality of life in breast cancer patients. The results show a significant reduction in anxiety and depression and an improvement in quality of life, but no significant effect on reducing distress.
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The prevalence of breast cancer (BC) is significant globally. The malignancy itself and the related treatments have a considerable impact on patients’ overall well-being. The adoption of e-health solutions for patients is increasing rapidly worldwide, since these innovative tools hold significant potential to positively impact the mental health and quality of life (QoL) of BC patients. However, their overall impact is still being explored, and further understanding and analysis are required. This review paper aims to present, quantify, and summarize the cumulative available randomized evidence on the state of the art of supportive interventions delivered via e-health applications for patients’ mental health and QoL before, during, and after BC treatment. Methods: A systematic review was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines in the Scopus and PubMed databases on 7 November 2024 to identify studies that utilized internet-based interventions in BC patients. The inclusion criteria were as follows: adult men and women (aged > 18 years) diagnosed with breast cancer (BC) who received patient-directed e-health interventions, compared to standard care or control interventions. The studies had to focus on outcomes such as quality of life (QoL), anxiety, depression, and distress, and be limited to randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The PRISMA-P guidelines were followed. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk-of-bias (RoB) tool for randomized controlled trials. Results: A total of 27 randomized studies, involving 2898 patients, were included in this systematic review. The e-health interventions significantly affected patients’ anxiety (SMD = −0.80; 95% CI: −1.33 to −0.27; p < 0.01; and I2 = 94%), depression (SMD = −0.74; 95% CI: −1.40 to −0.09; p = 0.026; and I2 = 95%) and QoL (SMD = 0.65; 95% CI: 0.27 to 1.04; p < 0.01; and I2 = 90%) but had no significant effect on distress (SMD = −0.78; 95% CI: −1.93 to 0.37; p = 0.184; and I2 = 95%). Conclusions: This study showed that e-health interventions can improve QoL, reduce anxiety, and decrease depression in adult BC patients. However, no noticeable impact on reducing distress levels was observed. Additionally, given the diversity of interventions, these results should be interpreted with caution. To determine the optimum duration, validate different intervention approaches, and address methodological gaps in previous studies, more extensive clinical studies are needed.
1. Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common type of cancer, commonly diagnosed in women, although it can occur in men [1]. It poses a significant health burden globally, with over 2 million new cases diagnosed in 2022 [2]. It is also one of the leading causes of death in women worldwide, despite its downward trend, particularly in developed countries. This highlights the importance of advancing BC management, with a focus on enhancing early detection methods and developing more effective treatment options [3].
Currently, therapeutic options for BC encompass surgical interventions, chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy [4]. The evolution of novel treatments and therapies has notably improved the survival of BC patients. Approximately 70% of patients experience an increase in life expectancy of more than five years, while 40% experience an increase of more than ten years. Moreover, for 15% of patients, life expectancy extends by over twenty years [5]. However, it is well recognized that patients’ mental health and QoL are typically impacted by BC treatment and its sequelae, and some of them can be lifelong [6]. Thus, the transition from the “cancer struggle” to “regular life” for survivors mandates that they first deal with the adverse effects of cancer therapy [7]. Therefore, as survival rates have improved considerably [5], the mitigation of cancer therapy-related adverse effects is crucial to improving QoL. The management of QoL, in its physical and psychological components, will result in improved treatment efficacy and prognosis [8].
E-health refers to the use and application of digital technologies (e.g., internet, mobile devices, wearables, software tools, etc.) that support healthcare delivery for improved disease monitoring, management, and QoL [9]. The rapid improvements and increasing accessibility of these technologies have driven the widespread adoption of e-health interventions in cancer care, enabling, among others, patient engagement and communication with healthcare experts throughout the healthcare delivery continuum [10]. Currently, there are several studies showing that e-health interventions may have a positive effect on cancer patients’ physical, psychological, and social functioning, as well as their self-efficacy, QoL, mental well-being, depression, and anxiety [5,11,12,13]. Nonetheless, the overall impact of e-health interventions on patients’ mental health and QoL is not yet clear, largely due to the variability in study designs, intervention types, and outcome measures used in existing research, and this variability presents a significant challenge in conducting comprehensive reviews to accurately estimate their overall effectiveness.
To address this challenge, we performed a systematic review with the aim of quantifying and summarizing the available randomized evidence on the use of supportive interventions delivered via e-health on patients’ mental health and QoL.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
The PubMed and Scopus databases were systematically scrutinized from inception up to 7 November 2024 for eligible studies. This study was registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews.
To identify relevant studies for this review, a Boolean string consisting of several relevant keywords was generated. The following string was applied: “((quality of life) AND (mental health AND ((mental OR emotional OR psychological OR social) AND well-being) OR mental disorder OR depression OR anxiety) AND (breast cancer) AND (e-health OR electronic health OR information and communication technolog* OR ICT OR m-health OR mobile health OR digital health OR mobile OR internet OR web OR online OR digital OR remote OR smartphone OR application OR app OR e-coach))”. This string was developed so that the search of each database only identified studies relevant to the topic, thereby ensuring consistency and comprehensiveness in the search process. For a study to be considered for inclusion in our analysis, it had to meet the predefined inclusion criteria listed in Table 1. In addition, the study had to be published in English, and the full text had to be available. The inclusion criteria were determined using the PICOS framework [14].

Table 1.
Inclusion criteria for studies.
2.2. Data Extraction
The papers retrieved were subsequently handled with an automated tool (Zotero 6.0.36, Corporation for Digital Scholarship, Vienna, VA, USA), which was used to remove duplicate entries. The remaining articles were then independently screened for title and abstract by each of the two reviewers who participated in the study selection process. Potentially eligible articles were then assessed in full text by the same reviewers independently once again. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion or, if necessary, with the involvement of a third reviewer.
The data from the remaining studies were extracted by two independent reviewers according to the PRISMA guidelines.
A predefined data extraction sheet was used to collect information from each study. The focus was on evaluating changes in anxiety, depression, quality of life, and distress before and after the intervention involving e-health applications. Studies that did not report outcomes for any of these categories were excluded from the current analysis. Data extraction was performed independently by two authors, and the accuracy of the extracted data was verified by a third author. For each study, we extracted information regarding the authors, publication year, ID, sample size, cancer and therapy information, intervention type, duration of the intervention, study design, outcomes of interest, and a summary of the results.
2.3. Risk of Bias and Quality Assessment
Two independent reviewers assessed the quality of the included studies using the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool, a commonly used method for assessing the risk of bias in various study designs, including randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [15]. The quality of each study was evaluated in the following domains: adequate sequence generation, allocation concealment, adequate blinding of patients and personnel, adequate blinding of outcome assessors, incomplete outcome data assessment, and selective reporting bias [16].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
We performed a meta-analysis using RStudio software (version 4.3.1; R Core Team, 2023) with the ‘meta’ and ‘metafor’ packages. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals were used for the outcomes, measured as the mean and standard deviation. A random-effects model was employed to account for potential differences in samples and interventions across the included studies. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic [17]. Values of 0–25%, 25–50%, and 50–100% were considered to indicate low, moderate, and substantial heterogeneity, respectively [18]. Moreover, subgroup analyses were performed based on the mode of e-health intervention (Web, mobile applications, other), as well as the duration of the intervention (less than 12 weeks and 12 weeks or more). Small study effects, indicative of publication bias, were assessed by visual inspection of funnel plots and Egger’s test [19]. This assessment was performed only for analyses that included 10 or more studies, and a p-value < 0.1 was considered indicative of small study effects.
3. Results
A total of 1488 records were identified following the search of Scopus and PubMed. After title and abstract screening, 109 publications were identified as potentially eligible (Figure 1). Following detailed screening, our systematic review retained a total of 27 studies focusing on e-health interventions targeting mental health and QoL in BC patients.
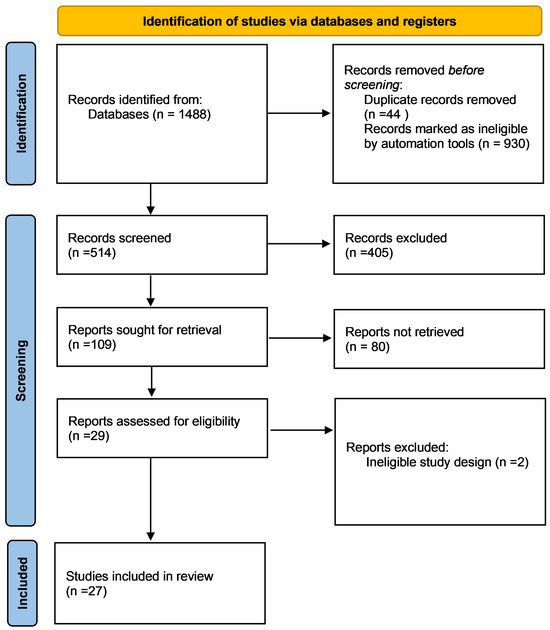
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
All the studies included in the final analysis focused on adult patients and cancer survivors aged 18 years or older. All the studies included were RCTs specifically targeting patients diagnosed with BC. The sample size ranged from 35 to 363 patients. Five studies had a sample size of less than 50 patients, twelve between 50 and 100 patients, while the remaining studies had a sample size of more than 100 patients. In total, (i) patients in 10 studies had a mean age between 50 and 60 years, patients in 1 study had a mean age of over 60 years, and patients in the remaining studies had a mean age of 50 years or younger; (ii) the publications were from 2018 onward: nine studies were published in 2024, two studies in 2023, three studies in 2022, two studies in 2021, four studies in 2020, three studies in 2019, and four studies in 2018; and (iii) the majority (13/27) were conducted in Asia, followed by seven, four, and three in Europe, America, and Australia, respectively.
The included studies had different intervention durations, ranging from 3 to 24 weeks, and different e-health tools were used. Notably, the majority of studies (16/27) used mHealth apps [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37], while the remaining studies used web applications [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46].
The main characteristics and findings of the studies included are summarized in Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 2.
Studies on e-health interventions in cancer patients.

Table 3.
Studies on e-health interventions in cancer patients.

Table 4.
Studies on e-health interventions in cancer patients.
3.2. Risk of Bias Within Studies
We used the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool to assess the quality of the included studies. Of the 27 included studies, only three RCTs met all the requirements to be considered as having a low risk of bias. Of the 27 included studies, 24 (89%) had an appropriate sequence generation process, while only 13 used allocation concealment. Most of the studies (81.5%) did not blind their patients or professionals, or it was unclear whether blinding was used, resulting in a high or unclear risk of bias. Thirteen studies (48%) implemented blinding of outcome assessors. Twenty studies (74%) were judged as posing a low risk of incomplete outcome data.
Altogether, 21 (78%) studies were considered as having a low risk of reporting bias. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the results of the quality assessment of the included studies using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool.
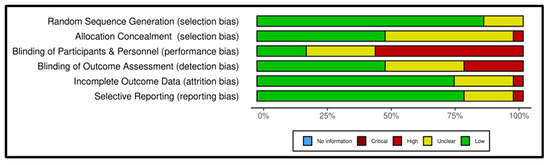
Figure 2.
Risk-of-bias graph.
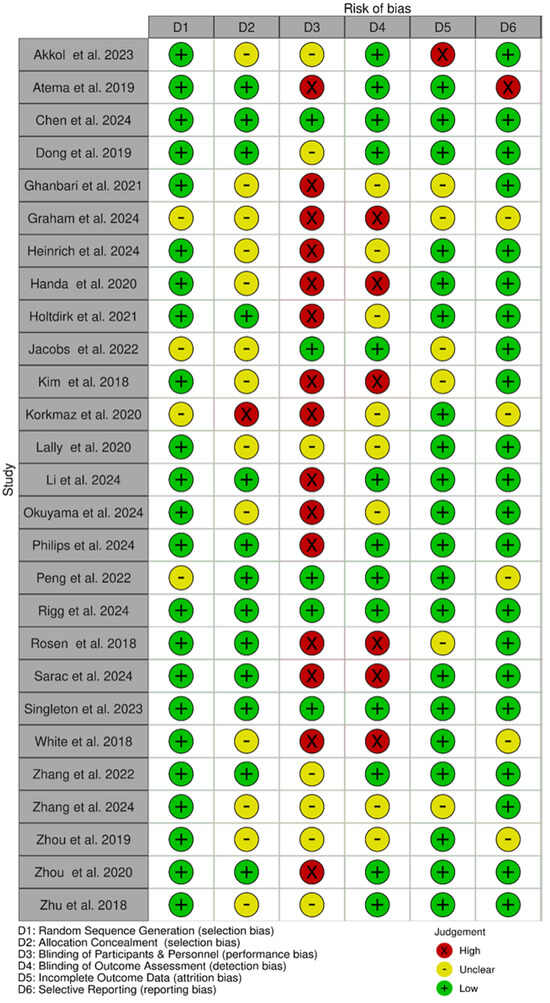
Figure 3.
Risk-of-bias summary [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46].
3.3. Intervention Outcomes
3.3.1. Anxiety
Nineteen studies [20,22,23,24,25,27,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,45,46] provided data on anxiety for a total of 2060 patients. Heterogeneity testing showed I2 = 94%, indicating high heterogeneity among the studies. The results of the analysis showed that the anxiety levels of the control group were higher than those of the intervention group (SMD = −0.80; 95% CI: −1.33 to −0.27; p < 0.01; and I2 = 94%) (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
Forest plots—effects of e-health interventions on anxiety, presented by method of intervention (web application: p = 0.083; mobile application: p = 0.019; other: p = 0.142) [20,22,23,24,25,27,30,31,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,45,46]. SD, standard deviation; SMD, standardized mean difference. The “Other” category includes two studies that used virtual reality-based interventions and one study that used a wearable-based intervention.
The subgroup analysis based on the delivery method showed that studies using web-based interventions (n = 6) [38,39,40,41,45,46] yielded an SMD of −0.11 (95% CI: −0.24 to 0.01; p = 0.083; and I2 = 0%), while studies using mobile-based interventions (n = 10) [20,22,23,24,27,30,31,33,34,35] showed a statistically significant SMD of −0.96 (95% CI: −1.76 to −0.15; p = 0.019; and I2 = 96%) (Figure 4). The subgroup analysis based on the intervention duration showed a statistically significant decrease in anxiety in the intervention group for both categories, with studies with a duration of less than 12 weeks (n = 5) [20,22,30,35,46] showing an SMD of −0.95 (95% CI: −1.69 to −0.21; p = 0.011; and I2 = 90%), and studies lasting 12 weeks or more (n = 14) [23,24,25,27,31,33,34,36,37,38,39,40,41,45] showing an SMD of −0.75 (95% CI: −1.45 to −0.06; p = 0.033; and I2 = 94%) (Supplementary Figure S1). It is important to note that low scores on the anxiety scales correspond to a lower level of anxiety.
3.3.2. Depression
Sixteen studies [20,23,24,25,27,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,45,46] involving 1741 patients reported depression outcomes. The meta-analysis results showed that patients receiving e-health interventions reported lower levels of depression compared to the control group and that this difference was statistically significant (SMD −0.74; 95% CI −1.40 to −0.09; p = 0.026; and I2 = 95%). The heterogeneity test showed a substantial I2 = 95%, indicating high heterogeneity among the studies (Figure 5).
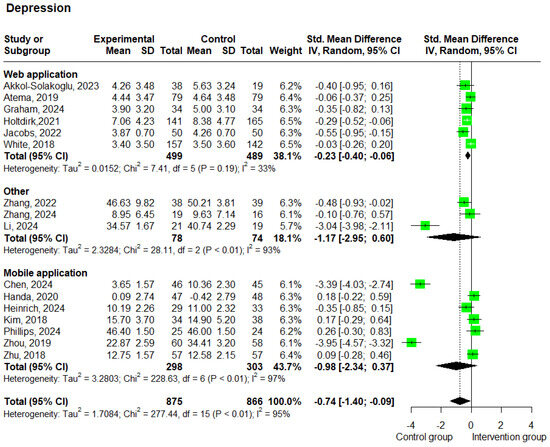
Figure 5.
Forest plots—effects of e-health interventions on depression, presented by method of intervention (web application: p = 0.008; mobile application: p = 0.155; other: p = 0.195) [20,23,24,25,27,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,45,46]. SD, standard deviation; SMD, standardized mean difference. The “Other” category includes two studies that used virtual reality-based interventions and one study that used a wearable-based intervention.
The subgroup analysis based on the delivery method showed that studies using web-based interventions (n = 6) [38,39,40,41,45,46] yielded a statistically significant SMD of −0.23 (95% CI: −0.40 to −0.06; p = 0.008; and I2 = 33%), while studies using mobile-based interventions (n = 7) [20,23,24,27,33,34,35] reported an SMD of −0.98 (95% CI: −2.34 to 0.37; p = 0.155; and I2 = 97%) (Figure 5). Furthermore, the subgroup analysis based on the intervention duration revealed that studies with a duration of less than 12 weeks (n = 3) [20,35,46] showed an SMD of −1.19 (95% CI: −3.35 to 0.96; p = 0.278; and I2 = 97%), while studies lasting 12 weeks or more (n = 13) [23,24,25,27,33,34,36,37,38,39,40,41,45] showed an SMD of -0.64 (95% CI: −1.31 to 0.04; p = 0.065; and I2 = 94%) (Supplementary Figure S2). Additionally, it is important to note that low scores on the depression scales correspond to a lower level of depression.
3.3.3. QoL
A total of 19 studies [20,21,25,26,28,29,30,31,32,33,35,36,37,39,41,42,44,45,46] reported data on QoL. These studies included 1,706 patients and showed substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 90%). Compared to the control group, the analysis of patients receiving e-health interventions showed better QoL, and this difference was statistically significant (SMD: 0.65; 95% CI: 0.27 to 1.04; p < 0.01; and I2 = 90%) (Figure 6).
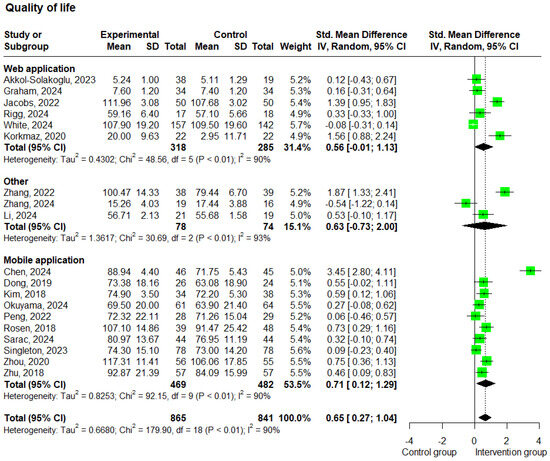
Figure 6.
Forest plots—effects of e-health interventions on QoL, presented by method of intervention (web application: p = 0.052; mobile application: p = 0.017; other: p = 0.364) [20,21,25,26,28,29,30,31,32,33,35,36,37,39,41,42,44,45,46]. SD, standard deviation; SMD, standardized mean difference. The “Other” category includes two studies that used virtual reality-based interventions and one study that used a wearable-based intervention.
The subgroup analysis based on the delivery method showed that studies using web-based interventions (n = 6) [39,41,42,44,45,46] yielded an SMD of 0.56 (95% CI: −0.01 to 1.13; p = 0.052; and I2 = 90%), while studies using mobile-based interventions (n = 10) [20,21,26,28,29,30,31,32,33,35] reported a statistically significant SMD of 0.71 (95% CI: 0.12 to 1.29; p = 0.017; and I2 = 90%) (Figure 6). Furthermore, the subgroup analysis based on the intervention duration in QoL studies revealed that studies with a duration of less than 12 weeks (n = 7) [20,29,30,35,42,44,46] showed a statistically significant SMD of 1.00 (95% CI: 0.15 to 1.86; p = 0.022; and I2 = 93%), while studies lasting 12 weeks or more (n = 12) [21,25,26,28,31,32,33,36,37,39,41,45] showed a statistically significant SMD of 0.46 (95% CI: 0.10 to 0.81; p = 0.012; and I2 = 87%) (Supplementary Figure S3). Moreover, higher scores on the QoL scales indicate a higher level of QoL for the patients.
3.3.4. Distress
A total of nine studies [20,24,30,36,37,38,43,44,47] reported data on distress. These studies included 746 patients and showed substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 95%). Compared to the control group, the analysis showed that the e-health intervention did not have a statistically significant impact on the intervention group (SMD: −0.78; 95% CI −1.93 to 0.37; p = 0.184; and I2 = 95%) (Figure 7).
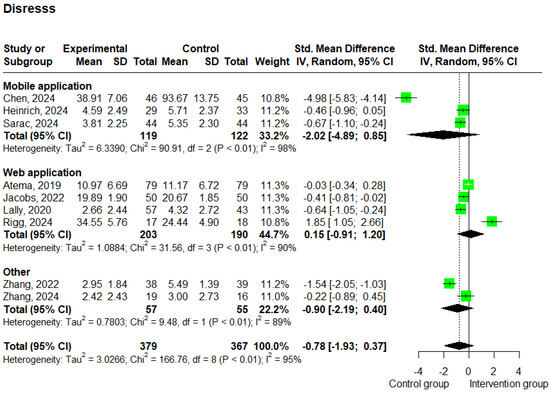
Figure 7.
Forest plots—effects of e-health interventions on distress, presented by method of intervention (web application: p = 0.783; mobile application: p = 0.168; other: p = 0.173) [20,24,30,36,37,38,43,44,47]. SD, standard deviation; SMD, standardized mean difference. The “Other” category includes two studies that used virtual reality-based interventions (p = 0.1734).
The subgroup analysis based on the delivery method showed that studies using web-based interventions (n = 3) [38,41,43,44] yielded an SMD of 0.15 (95% CI: −0.91 to 1.20; p = 0.783; and I2 = 90%), while studies using mobile-based interventions (n = 3) [20,24,30] reported an SMD of −2.02 (95% CI: −4.89 to 0.85; p = 0.168; and I2 = 98%) (Figure 7). Furthermore, the subgroup analysis based on the intervention duration revealed that studies with a duration of less than 12 weeks (n = 3) [20,30,44] showed an SMD of −1.26 (95% CI: −5.16 to 2.63; p = 0.52; and I2 = 99%), while studies lasting 12 weeks or more (n = 6) [24,36,37,38,43,47] showed a statistically significant SMD of −0.54 (95% CI: −0.96 to −0.12; p = 0.011; and I2 = 81%) (Supplementary Figure S4). Additionally, it is important to note that low scores on the distress scales correspond to a lower level of distress.
Moreover, visual inspection of the funnel plots and Egger’s test analyses [19] indicated no significant publication bias. This assessment was performed only for anxiety, depression, and quality of life, as the number of studies included in each of these fields was 10 or more (Supplementary Figures S5–S7). A p-value < 0.1 was considered indicative of small study effects.
4. Discussion
Global adoption of new technologies and their rapid growth in popularity have had an important impact on patient care management, bringing exciting potential as well as significant challenges. Patients who have severe or chronic disorders frequently receive digital support at home in order to prevent, manage, and ameliorate disease symptoms and adverse treatment effects. Additionally, real-time remote interactions reduce the effort of attending hospital visits and reduce treatment delays and travel costs. Access to cancer treatment is improved by using e-health approaches, particularly for patients who live in remote areas, have difficulties traveling, or prefer to communicate from home [48]. Furthermore, it is important to mention that COVID-19 was a key contributor to the rapid adoption of e-health technologies, permanently integrating online medical services into the healthcare system and changing the way care is provided [49].
Alongside e-health interventions, artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming cancer care, offering an opportunity for significant improvements in both patient survival and quality of life [50]. Future AI-enhanced tools could provide clinicians with quick, cost-effective, and globally accessible solutions, helping match patients with the most appropriate treatments while simultaneously reducing potential negative impacts. AI methods will be able to integrate multiple data sources, such as patient-generated health data (PGHD) and electronic health records (EHRs), for personalized treatment recommendations and prediction of outcomes [51]. This precision-based approach could strengthen clinical decision-making, reduce time for treatment, and deliver personalized care tailored to each patient’s needs [52]. In addition, large language models (LLMs) have shown potential for classifying and predicting complex interactions, such as chemotherapy-induced toxicity, which could enhance patient monitoring and reduce treatment complications [53]. As AI technology evolves and becomes increasingly integrated into medicine, it holds the potential to further enhance cancer management, offering even more impressive outcomes for patient survival and well-being [54]. AI has significantly enhanced diagnostic capacities through data analysis and machine learning algorithms, increasing the accuracy of disease diagnosis and decreasing diagnostic errors [55].
According to our analysis, the experimental group’s anxiety symptoms were lower than those of the control group. The moderate effect, demonstrated by the SMD value of −0.80, indicates the efficacy of experimental interventions. Although the confidence range is quite broad (ranging from −1.33 to −0.27), it was still below zero, indicating that the experimental group derived significant benefits. The statistical significance of the result was confirmed by the low value of p (<0.01). This result should be interpreted with caution, as there was significant heterogeneity between studies (indicated by the high value of I2 = 94%), which raises the possibility that variables such as study design, demographics, or the variety of interventions used may have played a role in the credibility of the results observed. Moreover, the subgroup analysis based on the method of intervention delivery revealed that only mobile applications managed to reach statistical significance. Mobile applications have been extensively used in the literature because they offer ‘accessibility, convenience, and adaptability’, ‘patient-centeredness’, ‘data insights’, and ‘efficiency and effectiveness’ [56].
As with anxiety, the experimental group’s SMD score for depression symptoms was −0.74, indicating a substantial decrease in this symptom through the use of e-health support. The experimental group performed better because the confidence interval was negative, and it spanned from −1.40 to −0.09. The statistical significance of the outcome was confirmed by the p-value < 0.01. Again, the heterogeneity between the studies was high (I2 = 95%), which must be considered when interpreting the results, as various variables likely affected the findings. The subgroup analysis based on the method of intervention delivery confirmed that only web applications reached statistical significance in the context of depression. Furthermore, the literature confirms that web applications can reduce the burden of chronic mental illness and improve patient outcomes [57].
With an SMD value of 0.65, the experimental intervention was linked to a small but not negligible and statistically significant (p value < 0.01) improvement in the overall QoL. The positive impact of the intervention is indicated by the confidence interval (0.27 to 1.04) being above zero. However, an I2 score of 90% suggests high heterogeneity between the studies, which raises questions regarding the uniformity and comparability of the results across the studies.
The intervention reduced distress (SMD = −0.78), but the effect was unclear due to the wide confidence interval, which included zero (−1.93 to 0.37). Although the pattern generally favored the experimental group, it did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.184). Extreme heterogeneity was indicated by the very high I2 value of 95%, which suggests that variables like demographics, intervention techniques, or measuring instruments may have had a considerable impact on the outcomes. Also, it has to be considered that distress in cancer care is a multifactorial dimension, and the measures to quantify it may focus on different subdimensions [58,59].
The subgroup analyses showed that mobile-based interventions were more effective than web-based ones for anxiety and QoL, while only web-based interventions showed a significant effect on depression. Additionally, the subgroup analyses revealed that both short-term (less than 12 weeks) and long-term (12 weeks or more) interventions significantly improved quality of life and reduced anxiety in patients, with the best results observed in interventions shorter than 12 weeks, highlighting the importance of the intervention duration. Notably, the duration of the intervention also played an important role in distress, as patients receiving e-health interventions reported significantly lower distress than the control group after a longer duration (12 weeks or more) of intervention.
Furthermore, it is important to note that most subgroups had high levels of heterogeneity, indicating differences in the populations and study designs.
Notably, four of the five studies [27,35,36,44], whose findings indicated no beneficial effect on specific psychological factors, involved patients with metastatic cancer, a population that faces serious psychological difficulties as a result of the disease’s advanced stage. These studies’ lack of effectiveness may have been due to the group’s increased psychological stress, which makes improvement challenging through interventions that only address some of their psychological demands. The fifth study [23] used the Breast Cancer Patient Support System app for side-effect management by tracking symptoms during chemotherapy. While it offered some assistance, it was not enough to improve patients’ psychological well-being, which requires more comprehensive and intensive interventions.
To the best of our knowledge, this study marks a milestone as one of the pioneering efforts to systematically examine the impact of e-health interventions on the mental health and QoL of patients with BC. The findings of this systematic review highlight the importance of e-health interventions in improving the mental health and QoL of BC patients. The analysis of 27 RCTs, with a total sample size of 2898 patients, shows that e-health interventions can significantly reduce anxiety and depression while helping to improve QoL. Furthermore, these results align with earlier systematic reviews that suggest e-health interventions can enhance the mental health and QoL of BC patients [60,61]. Conversely, it is noteworthy that the e-health interventions failed to reduce the distress that BC patients were experiencing. However, the high heterogeneity (I2 > 85%) of the findings underscores the need for further standardization in e-health interventions, even with the favorable impact. Comparing interventions that differ in duration, frequency, and structure, as well as in how they monitor results, is challenging and makes determining their overall efficacy and interpretation extremely difficult. Furthermore, it is difficult to define the specific variables that lead to the most significant patient outcomes, since there are no generally recognized criteria. An integrated approach to intervention planning and implementation is required to increase the reliability of future studies.
Limitations
This study has certain limitations: (i) The search strategy was limited to studies published in English. (ii) There was diversity in the frequency, content, and delivery formats of e-health interventions. (iii) In some studies, the number of patients included was small, which raises concerns about the reliability and generalizability of the results. (iv) The effectiveness of each intervention may have been affected by a possible low level of patient adherence. It is essential to acknowledge these limitations and putative influencing factors as reasons for the surprisingly non-positive results for the many studied domains. Therefore, to define the optimal type and regimen of e-health intervention, high-quality RCTs are needed.
5. Conclusions
E-health support has been shown to significantly improve QoL and reduce anxiety and depression in BC patients. These results imply that e-health interventions have been at least to some extent successful and beneficial. Considering the decades-long dominance of traditional treatments and supportive care management, these e-health intervention outcomes are more than encouraging for the future of medical care. Additionally, the reasons for the moderate effectiveness of some e-health interventions need to be further analyzed, including potential biases, implementation issues, and methodological weaknesses that may impact the results.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers17111780/s1, Figure S1: Forest plots showing the effects of e-Health interventions on anxiety, presented by intervention duration (less than 12 weeks: p = 0.011; 12 weeks or more: p = 0.033); Figure S2: Forest plots showing the effects of e-Health interventions on depression, presented by intervention duration (less than 12 weeks: p = 0.278; 12 weeks or more: p = 0.065); Figure S3: Forest plots showing the effects of e-Health interventions on quality of life (QoL), presented by intervention duration (less than 12 weeks: p = 0.022; 12 weeks or more: p = 0.012); Figure S4: Forest plots showing the effects of e-Health interventions on distress, presented by intervention duration (less than 12 weeks: p = 0.52; 12 weeks or more: p = 0.011); Figure S5: Funnel plot of publication bias on anxiety. The result of Egger’s test (p = 0.003) indicates the presence of small study effects, as suggested by the asymmetry in the plot; Figure S6: funnel plot of publication bias on depression. The result of Egger’s test (p = 0.037) indicates the presence of small study effects, as suggested by the asymmetry in the plot; Figure S7: Funnel plot of publication bias on QoL. The result of Egger’s test (p = 0.032) indicates the presence of small study effects, as suggested by the asymmetry in the plot.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.M., P.F., E.I.G., G.K. and K.M. (Kostas Marias); Methodology: A.M., P.F. and E.I.G.; Validation: A.M. and E.I.G.; Formal Analysis: A.M. and P.F.; Investigation: A.M. and E.I.G.; Data Curation: A.M., P.F. and E.I.G.; Writing—Original Draft: A.M. and P.F.; Visualization: A.M.; Supervision: K.K.N. and D.I.F.; Writing—Review and Editing: P.F., G.K., E.I.G., D.M., K.K.N., A.C., K.K., D.T., K.M. (Ketti Mazzocco), A.A. (Alexia Alexandraki), E.K., Y.G., A.P., A.A. (Athos Antoniades), C.B., V.B., E.M., K.M. (Kostas Marias), M.T. and D.I.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Athos Antoniades and Cameron Brown were employed by the company Stremble Ventures Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| App | Application |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| E-health | Electronic health |
| HRQoL | Health-related quality of life |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| PICOS | Population, Intervention, Comparator, Outcomes, Study Design |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis |
| QoL | Quality of life |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| PGHD | Patient-generated health data |
| EHRs | Electronic health records |
References
- “Breast Cancer|Breast Cancer Information & Overview”. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer.html (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Zahwe, M.; Bendahhou, K.; Eser, S.; Mukherji, D.; Fouad, H.; Fadhil, I.; Soerjomataram, I.; Znaor, A. Current and future burden of female breast cancer in the Middle East and North Africa region using estimates from GLOBOCAN 2022. Int. J. Cancer 2025, 156, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Swinnen, J.; Li, Y.; Ni, Y. A Review on Curability of Cancers: More Efforts for Novel Therapeutic Options Are Needed. Cancers 2019, 11, 11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gong, J.; Li, Q. The application of eHealth in cancer survivorship care: A review of web-based dyadic interventions for post-treatment cancer survivors and caregivers. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 9, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emre, N.; Yılmaz, S. Sleep quality, mental health, and quality of life in women with breast cancer. Indian J. Cancer 2024, 61, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.G.; George, A.; Vidyasagar, M.S.; Mathew, S.; Nayak, S.; Nayak, B.S.; Shashidhara, Y.; Kamath, A. Quality of Life among Cancer Patients. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2017, 23, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Hu, C.-H.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zhou, J.-S.; Wang, S.-X.; Liu, M.-D.; Qiu, Z.-H.; Deng, C.; Ma, F.; Xia, C.-F.; et al. Association between pretreatment emotional distress and immune checkpoint inhibitor response in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogerd, E.A.; Arts, T.; Engelen, L.J.; van de Belt, T.H. ‘What Is eHealth’: Time for An Update? JMIR Res. Protoc. 2015, 4, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penedo, F.J.; Oswald, L.B.; Kronenfeld, J.P.; Garcia, S.F.; Cella, D.; Yanez, B. The increasing value of eHealth in the delivery of patient-centred cancer care. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e240–e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitonga, I.; Desmond, D.; Duda, N.; Maguire, R. Impact of connected health interventions on psychological wellbeing and quality of life in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychooncology 2022, 31, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q. A critical literature review of dyadic web-based interventions to support cancer patients and their caregivers, and directions for future research. Psychooncology 2020, 29, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, R. The effectiveness of E-health interventions promoting physical activity in cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapter 8: Assessing Risk of Bias in a Randomized Trial. Available online: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/archive/v6.2/chapter-08 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) Tool | Cochrane Methods. Available online: https://methods.cochrane.org/risk-bias-2 (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qin, Y.; Chaimongkol, N. Effectiveness of a phone-based support program on self-care self-efficacy, psychological distress, and quality of life among women newly diagnosed with breast cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, 71, 102643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yi, X.; Gao, D.; Gao, Z.; Huang, S.; Chao, M.; Chen, W.; Ding, M. The effects of the combined exercise intervention based on internet and social media software (CEIBISMS) on quality of life, muscle strength and cardiorespiratory capacity in Chinese postoperative breast cancer patients: A randomized controlled trial. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2019, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, E.; Yektatalab, S.; Mehrabi, M. Effects of Psychoeducational Interventions Using Mobile Apps and Mobile-Based Online Group Discussions on Anxiety and Self-Esteem in Women with Breast Cancer: Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2021, 9, e19262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, S.; Okuyama, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakamura, S.; Kato, Y. Effectiveness of a Smartphone Application as a Support Tool for Patients Undergoing Breast Cancer Chemotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 20, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, R.; Schilling, G.; Wojtyna, E.; Arnold, D.; Geisler, M.; Kley, S.; Grudzinski, P.; Księżak, M.; Schoenfelder, T. Effects of Mobile Application-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy on Psychological Outcomes in Women Treated for Breast Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial in Germany. Psycho-Oncology 2024, 33, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sang, D.; Gong, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Yu, J.; Kong, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Improving physical and mental health in women with breast cancer undergoing anthracycline-based chemotherapy through wearable device-based aerobic exercise: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1451101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, H.; Takada, F.; Taira, N.; Nakamura, S. A randomized trial of the impact of symptom monitoring using an electronic patient-reported outcome app on health-related quality of life in postmenopausal breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant endocrine therapy. Breast Cancer 2024, 31, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M.; Starikovsky, J.; Solk, P.; Desai, R.; Reading, J.M.; Hasanaj, K.; Wang, S.D.; Cullather, E.; Lee, J.; Song, J.; et al. Feasibility and preliminary effects of the Fit2ThriveMB pilot physical activity promotion intervention on physical activity and patient reported outcomes in individuals with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 208, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Cao, X.; Li, M. Effects of an online mindfulness-based intervention on Fear of Cancer Recurrence and quality of life among Chinese breast cancer survivors. Complement Ther. Clin. Pr. 2022, 49, 101686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, K.D.; Paniagua, S.M.; Kazanis, W.; Jones, S.; Potter, J.S. Quality of life among women diagnosed with breast Cancer: A randomized waitlist controlled trial of commercially available mobile app-delivered mindfulness training. Psycho-Oncology 2018, 27, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraç, F.S.; İlhan, S.E.; Kutun, S.; Kutlutürkan, S. The Effect of Informative Mobile App Use on Anxiety, Distress, and Quality of Life of Women with Breast Cancer. Eur. J. Breast Health 2024, 20, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.C.; Raeside, R.; Partridge, S.R.; Hyun, K.K.; Tat-Ko, J.; Sum, S.C.M.; Hayes, M.; Chow, C.K.; Thiagalingam, A.; Maka, K.; et al. Supporting women’s health outcomes after breast cancer treatment comparing a text message intervention to usual care: The EMPOWER-SMS randomised clinical trial. J. Cancer Surviv. 2023, 17, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Guo, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; An, J.; Li, J.; et al. Benefits of a WeChat-based multimodal nursing program on early rehabilitation in postoperative women with breast cancer: A clinical randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2020, 106, 103565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ebert, L.; Liu, X.; Wei, D.; Chan, S.W.-C. Mobile breast cancer e-support program for chinese women with breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy (Part 2): Multicenter randomized controlled trial. JMIR MHealth UHealth 2018, 6, 9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Li, X. Effects of cyclic adjustment training delivered via a mobile device on psychological resilience, depression, and anxiety in Chinese post-surgical breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Shin, H.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, Y.I.; Han, D.H. A Mobile Game for Patients with Breast Cancer for Chemotherapy Self-Management and Quality-of-Life Improvement: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pang, Y.; He, Y.; You, M.; Tang, L. Feasibility of online managing cancer and living meaningfully (CALM) in Chinese patients with metastatic breast cancer: A pilot randomized control trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, S.; Wang, M.; Yin, X.; Bi, Z.; Jing, Y.; Cheng, H. The Impact of VR-CALM Intervention Based on VR on Psychological Distress and Symptom Management in Breast Cancer Survivors. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atema, V.; van Leeuwen, M.; Kieffer, J.M.; Oldenburg, H.S.; van Beurden, M.; Gerritsma, M.A.; Kuenen, M.A.; Plaisier, P.W.; Cardozo, A.M.L.; van Riet, Y.E.; et al. Efficacy of Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Treatment-Induced Menopausal Symptoms in Breast Cancer Survivors: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, C.D.; Ellison, R.; Hall, L.H.; Clark, J.; McNaught, E.; Green, S.M.C.; Wilkes, H.; Robson, G.; Lorentz, I.; Holmes, L.; et al. A pilot randomised controlled trial of acceptance and commitment therapy for medication decision-making and quality of life in women with breast cancer: The ACTION trial. Psycho-Oncology 2024, 33, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtdirk, F.; Mehnert, A.; Weiss, M.; Mayer, J.; Meyer, B.; Bröde, P.; Claus, M.; Watzl, C. Results of the Optimune trial: A randomized controlled trial evaluating a novel Internet intervention for breast cancer survivors. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Post, K.; Massad, K.; Horick, N.K.; Walsh, E.A.; Cohn, J.; Rapoport, C.S.; Clara, A.J.; Antoni, M.H.; Safren, S.A.; et al. A telehealth intervention for symptom management, distress, and adherence to adjuvant endocrine therapy: A randomized controlled trial. Cancer 2022, 128, 3541–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, S.; Iyigun, E.; Tastan, S. An Evaluation of the Influence of Web-Based Patient Education on the Anxiety and Life Quality of Patients Who Have Undergone Mammaplasty: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Cancer Educ. 2020, 35, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lally, R.M.; Kupzyk, K.A.; Bellavia, G.; Hydeman, J.; Gallo, S.; Helgeson, V.S.; Erwin, D.; Mills, A.C.; Brown, J.K. CaringGuidanceTM after breast cancer diagnosis eHealth psychoeducational intervention to reduce early post-diagnosis distress. Support Care Cancer 2020, 28, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, A.; Kemp, E.; Koczwara, B.; Butow, P.; Girgis, A.; Hulbert-Williams, N.J.; Kaambwa, B.; Long, R.; Schofield, P.; Turner, J.; et al. Feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary efficacy of a self-directed online psychosocial intervention for women with metastatic breast cancer: Finding My Way-Advanced. Support Care Cancer 2024, 32, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, V.; Farrelly, A.; Pitcher, M.; Hill, D. Does access to an information-based, breast cancer specific website help to reduce distress in young women with breast cancer? Results from a randomised trial. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2018, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkol-Solakoglu, S.; Hevey, D. Internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy for depression and anxiety in breast cancer survivors: Results from a randomised controlled trial. Psycho-Oncology 2023, 32, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Ream, M.E.; Pensak, N.; Nisotel, L.E.; Fishbein, J.N.; MacDonald, J.J.; Buzaglo, J.; Lennes, I.T.; Safren, S.A.; Pirl, W.F.; et al. Patient experiences with oral chemotherapy: Adherence, symptoms, and quality of life. JNCCN J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle-Lindrud, S. State of eHealth in Cancer Care: Review of the Benefits and Limitations of eHealth Tools. CJON 2020, 24, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wosik, J.; Fudim, M.; Cameron, B.; Gellad, Z.F.; Cho, A.; Phinney, D.; Curtis, S.; Roman, M.; Poon, E.G.; Ferranti, J.; et al. Telehealth transformation: COVID-19 and the rise of virtual care. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2020, 27, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Yan, Q. Artificial intelligence empowered digital health technologies in cancer survivorship care: A scoping review. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 9, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Woods, N.; Jordan; Starren, J. The role of artificial intelligence for the application of integrating electronic health records and patient-generated data in clinical decision support. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2024, 2024, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Zhang, L.; Tong, Z. Application progress of artificial intelligence in tumor diagnosis and treatment. Front. Artif. Intell. 2025, 7, 1487207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Sarrias, O.; Martínez del Prado, M.P.; Sala Gonzalez, M.Á.; Azcuna Sagarduy, J.; Casado Cuesta, P.; Figaredo Berjano, C.; Galve-Calvo, E.; López de San Vicente Hernández, B.; López-Santillán, M.; Nuño Escolástico, M.; et al. Leveraging Large Language Models for Precision Monitoring of Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicities: A Pilot Study with Expert Comparisons and Future Directions. Cancers 2024, 16, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, R.; Arunkumar, S.; Jayaraj, V.; Sivasamy, A. Healthcare’s new Frontier: AI-driven early cancer detection for improved well-being. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 115331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nori, L.P.; Lohitha, M.; Vadapalli, R.R.; Bonthagarala, B.; Nagineni, S.R.; Kalidindi, V.R. Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Impact of AI on Precision Medicine. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2025, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, M.; Azar, G. A systematic review of reviews on the advantages of mHealth utilization in mental health services: A viable option for large populations in low-resource settings. Camb. Prism. Glob. Ment. Health 2024, 11, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, K.G.; Uzun, S.; Emirza, E.G. The effectiveness of telemedicine applications in mental health services: A meta-analysis study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 194, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distress-the 6th Vital Sign-PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21980246/ (accessed on 5 February 2025).
- Nelson, H.D.; Pappas, M.; Cantor, A.; Haney, E.; Holmes, R. Risk Assessment, Genetic Counseling, and Genetic Testing for BRCA-Related Cancer in Women: Updated Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2019, 322, 666–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dong, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S. Effect of telehealth interventions on anxiety and depression in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Telemed. Telecare 2024, 30, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Chen, C.; Ren, W.; Hu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, Q. Effect of electronic health (eHealth) on quality of life in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 14252–14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).