Simple Summary
Radioactive iodine treatment is the oldest targeted therapy for differentiated thyroid cancer. It can be used for normal thyroid remnant ablation (in order to increase the sensitivity and the specificity of the serum marker thyroglobulin), as an adjuvant treatment (in order to improve recurrence-free survival), or to treat radioiodine avid residual disease. Thanks to the use of sensible diagnostic tools, reliable prognostic classifications, and molecular profiling, the indication and modalities of radioiodine treatment are shifting from a one-size-fits-all to a tailored approach. This review provides insights into the most recent and high-quality evidence relating to radioactive iodine treatment.
Abstract
Radioiodine treatment (RAI) represents the most widespread and effective therapy for differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). RAI goals encompass ablative (destruction of thyroid remnants, to enhance thyroglobulin predictive value), adjuvant (destruction of microscopic disease to reduce recurrences), and therapeutic (in case of macroscopic iodine avid lesions) purposes, but its use has evolved over time. Randomized trial results have enabled the refinement of RAI indications, moving from a standardized practice to a tailored approach. In most cases, low-risk patients may safely avoid RAI, but where necessary, a simplified protocol, based on lower iodine activities and human recombinant TSH preparation, proved to be just as effective, reducing overtreatment or useless impairment of quality of life. In pediatric DTC, RAI treatments may allow tumor healing even at the advanced stages. Finally, new challenges have arisen with the advancement in redifferentiation protocols, through which RAI still represents a leading therapy, even in former iodine refractory cases. RAI therapy is usually well-tolerated at low activities rates, but some concerns exist concerning higher cumulative doses and long-term outcomes. Despite these achievements, several issues still need to be addressed in terms of RAI indications and protocols, heading toward the RAI strategy of the future.
1. Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Mortality and Recurrence Risks
Differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) represents the most common endocrine tumor, showing an increasing incidence trend during the last decades [1]. Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is the most common histological subtype [2] and a large number of new cases are related to small and indolent PTC, often found incidentally due to the increased use of diagnostic investigations [3,4]. Despite the steep increase in DTC incidence, the specific five-year-survival rates are about 98% [1] and the related age-adjusted mortality remains stable (about 0.5 per 100,000 per year), with no further expected change according to recent global estimates [4]. The extremely good prognosis of DTC and an increased awareness of the risks of treatments possibly resulting in life-long quality of life (QoL) impairment, has promoted a wide revision of diagnostic and management strategies [2]. This management shift is reflected in the recently observed decrease in indolent tumors (PTC ≤ 1.0 cm and localized disease) incidence in the United States (14.5 vs. 13.48 per 100,000 person-years in 2014 and 2018, respectively) [5] with a stable rate of loco-regional and advanced DTC [5]. In Europe, a similar trend emerged from the French registries, where a decrease in microcarcinomas and a slight, but constant, increase in larger DTC (>40 mm) diagnoses were observed [6].
The upfront therapeutic approach for DTC classically relies on surgery followed by radioiodine (RAI) treatment. The recourse to RAI has deeply changed throughout DTC history, evolving from a “one-size-fits-all” approach to a more selective choice. In fact, the observation of RAI effectiveness in reducing DTC recurrences and mortality initially promoted its use for all cases, irrespective of the disease extension and recurrence risks [7]. At that time, it was considered impossible to carry out adequately powered randomized trials in lower-risk thyroid cancer due to their indolent nature and the relative rarity of the disease. Two European academic studies, the ESTIMABL [8] and the HiLo [9] trial broke this paradigm, paving the way for an evidence-based approach for lower-risk DTCs.
Moreover, observational data on large cohorts found no survival benefit for lower stage patients (corresponding to patients at lower risk) treated with or without RAI [10], and several retrospective works highlighted the good prognosis of small and localized DTC, treated or not treated with RAI, questioning the paradigm of indiscriminate RAI use [11].
Accurate disease risk stratification can assist in the selection of the patients who may benefit from RAI therapy. Two key factors need to be addressed in patients’ initial prognostic assessment: the risk of death, provided by the TNM stage from the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) [12], and the risk of disease recurrence, based on the American Thyroid Association (ATA) [2] guidelines. These two classifications complement each other since the AJCC staging only predicts long-term mortality—usually very low for DTC—and is not designed to predict tumor recurrence; while ATA classification provides a valid medium-to-long term stratification for structural recurrent disease [13,14] (Table 1). It is also worth noting that patients with lower-stage DTC (i.e., at low risk of death) can be at high risk of recurrence [13].

Table 1.
AJCC TNM Staging 8th edition [12] and ATA risk classification and RAI recommendation according to ATA 2015 [2].
The ATA risk of recurrence classification includes three categories: (i) low-risk DTC (risk of recurrence being less than 5%); (ii) intermediate-risk (less than or equal to 20%); (iii) high-risk DTC (more than 20%) [2]. Within each class, we should also consider some additional features (e.g., the number or the extent of lymph node involvement, or the histological variant), which provide auxiliary prognostic information. There is quite a uniform consensus on RAI use for two opposing categories of DTC: on one hand, this therapy is considered avoidable for (very) low-risk DTC, i.e., intrathyroidal papillary microcarcinoma (PTMC), with an expected recurrence rate of less than 2% [14,15]; on the other hand, the use of RAI is mandatory for high risk-patients (Table 1) [2], who represent the rare cases burdened by a higher disease-mortality rate. Between these two extremes, we find the largest group of low and intermediate cases (about 70% of all DTC), where the use of radioiodine is still controversial.
2. Radioiodine Treatment Goals
The administration of RAI pursues different objectives. According to the 2015 ATA guidelines [2], the goals of RAI are: (i) ablative, i.e., the destruction of normal thyroidal remnants, in order to simplify follow-up management; (ii) adjuvant, i.e., the destruction of microscopic tumor foci, in order to improve disease-free survival; (iii) therapeutic, where pathological tissue is expected or diagnosed; (iv) to provide a whole-body evaluation by whole-body scan/Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (WBS/SPECT-CT), which can potentially change the initial staging, uncovering loco-regional or distant tumor foci. The 2022 European Consensus statement [16] was signed by four societies involved in thyroid cancer management: i.e., the American Thyroid Association (ATA), the European Thyroid Association (ETA), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, and the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging. Their purpose was to clarify some key points in RAI treatment indications for DTC and a revision of the traditional nomenclature was also proposed. In particular, they suggested replacing the conventional term “ablative RAI”—i.e., the first radioiodine administration—with the general label of “radioiodine therapy”, which includes all of the potential therapeutic goals: ablative, adjuvant, and (consequently) therapeutic [16].
In order to enhance the administration of radioiodine, a significant increase in thyrotropin (TSH) levels is needed to improve cellular uptake. The required and most accepted value of TSH is conventionally set above 30 mU/L [2]. The ways to obtain this value are: by thyroid hormone withdrawal (THW) performed for four weeks, or after a period of liothyronine (LT3), to reduce deep hypothyroidism sides effects (about for 2–3 weeks before a complete THW); or by recombinant human TSH (rhTSH) stimulation. Before rhTSH availability, THW was the standard protocol for RAI preparation. Hypothyroidism subsequent to THW is associated with transient impairment of QoL and cognitive status, general discomfort, and several adverse events, including cardiovascular and renal function deterioration [2,17,18,19,20]. Thereafter, the equivalence of rhTSH and THW for ablation preparation has been suggested by several studies [20,21,22,23], also showing the advantages of rhTSH in terms of preserving QoL [17,20,21,22,23], lower absorbed RAI activity for abdominal organs [24], and the significant reduction of global radiation exposure in sensitive organs, including bone marrow [25].
2.1. Remnant Ablation
As explained above, the most widespread application of radioiodine is the ablation of residual thyroid tissue, also known as radioiodine remnant ablation (RRA), and its therapeutic protocol underwent numerous revisions over time [16,26].
Serum thyroglobulin (Tg) is a tissue-specific rather than a tumor-specific marker, hence the elimination of all normal thyroid remnants renders the interpretation of this serum marker easier. The main purpose of RRA is to simplify follow-up management, enhancing the diagnostic performance of Tg concentration, rather than improving recurrences or survival [27,28]. Another possible goal of RRA is to facilitate the neutralization of anti-Tg antibodies (TgAb), which could produce interferences in Tg measurement resulting in false-negative, or more rarely, in false-positive results rendering the Tg value not interpretable. Two randomized clinical trials (RCT), ESTIMABL1 [8] and HiLo [9] studies, were designed to explore the non-inferiority of low activity (1.1 GBq) vs. the standard high activity (3.7 GBq) of RAI and to compare different RRA preparations for each therapeutic arm, both with THW and rhTSH stimulations (for a total of four comparison groups). The results of the ESTIMABL1 trial [8] showed that, at the eight-month evaluation, a low-ablative activity of 1.1 GBq was equivalent to a higher one, irrespective of the treatment preparation (complete ablation of 91.7% vs. 92.9% of rhTSH and THW, respectively). THW provoked a significant deterioration of quality of life [17] and more cases of lachrymal dysfunction when compared with rhTSH stimulation. Similarly, the HiLo study [9] confirmed the equivalence of low 131I activity (1.1 GBq) vs. the former standard of care. On the whole, the ESTIMABL1 [8] and HiLo [9] trials independently support the use of 1.1 GBq of radioiodine under rhTSH stimulation for RRA in low-, but also intermediate-risk DTC. The equivalence of low radioiodine activity for RRA was also confirmed by several meta-analyses [29,30].
However, patients with very large thyroid remnants might require higher iodine activity to achieve a complete remnant ablation. At this regard, Jin et al. [31] showed that an approach in which the activity of RAI therapy is based on Tg values and on RAI uptake on a diagnostic RAI scan can achieve a better ablation rate compared with a fixed activity. This approach might be appropriate for those subjects with huge residual tissue eventually avoiding the need for repeated RAI treatments.
Follow-Up Tools for DTC Patients Treated with Surgery Alone
Along with RRA refinement strategies, the available follow-up tools have evolved as well. The main allies of DTC management are neck ultrasound (US), and the dosage of Tg and TgAb. The introduction of highly sensitive Tg (hsTg), whose functional sensitivity is about 0.1 or 0.2 ng/mL, allows for the simplification of the follow-up protocol, avoiding the need for stimulated Tg (stTg). In fact, hsTg proved its equivalence in revealing distant metastases compared with stTg, even in patients without RRA [32,33,34,35].
In patients treated with total thyroidectomy alone (i.e., not followed by RAI), small thyroid remnants might persist resulting in low-detectable Tg [32,36,37]. In these cases, a stable or decreasing trend is associated with remission, while a rising trend is highly suspicious of persistent/recurrent disease [14]. The same consideration can be made for TgAb, as we observe in most cases a spontaneous decline [2,38,39]. Nonetheless, at least half of patients will already have an undetectable Tg after 12 months of follow-up [32,36,37], particularly when surgery is performed in an experienced center. As a consequence, the presence of residual traces of Tg or TgAb should not be considered to be an automatic indication for RAI treatment in lower-risk patients.
In addition, neck US provides an accurate evaluation of thyroid bed and loco-regional lymph nodes (LN), limiting the need for WBS or more invasive imaging [40]. The diagnostic accuracy of neck US coupled with cytology and Tg washout measurement in LN is close to 100% [2,41]. A large proportion of ATA low-risk patients (about 60%) [41] can be classified as being in excellent response after surgery (i.e., post-surgical undetectable hsTg < 0.2 ng/mL or stTg values < 1 ng/mL, without TgAb, and an absence of structural disease at US evaluation). In these cases, RRA does not improve disease outcomes [42].
2.2. Adjuvant Treatment
Adjuvant RAI has the purpose to treat (and eventually reveal) microscopic tumor foci, improving disease-free survival. As explained above, the first administration of RAI may encompass both the ablative and adjuvant aims.
2.2.1. Low-Risk Patients
Low-risk patients represent the largest DTC subgroup.
Several retrospective or observational research works have questioned the usefulness of adjuvant RAI in low-risk patients, since no benefit in terms of survival has been proved [10,14,27,28,43].
From this perspective, the updated results of the ESTIMABL1 [44] and HiLo [45] trials found no differences in disease recurrence after RRA within any analyzed subgroup, considering a median follow-up of 5.4 (ESTIMABL1) [44] and 6.5 [45] years, with only the 1.5% and 4.8% rate of abnormal findings for the ESTIMABL1 and HiLo study, respectively. The higher percentage of events in the HiLo study is due to the larger proportion of intermediate-risk patients enrolled in the study (about 40%), [45]. Observational studies with longer follow-up data [46] showed no difference in recurrence rate after 10 years in a DTC series treated for RRA, after both THW and rhTSH stimulation.
On the whole, observational and RCT results suggest not only the effectiveness of the low activity of 1.1 GBq of 131I under rhTSH for RAI therapy, but also the potential futility of adjuvant treatment in a lower-risk setting of DTC patients.
Two RCTs, the ESTIMABL2 Trial [47] in France and IoN trial (NCT01398085) in the United Kingdom, have been designed to explore the effectiveness of RAI vs. no RAI treatment in low-risk patients after surgery. While IoN results are still pending, the ESTIMABL2 results have recently been published [47]. A total of 776 low-risk DTC patients, either pT1am Nx/0 or pT1b Nx/N0, were randomized to postoperative RAI treatment 1.1 GBq under rhTSH stimulation (N = 389) or to follow-up (N = 387). The study was designed to prove the non-inferiority of follow-up when compared with postoperative RAI treatment in the percentage of patients free from events during the three years following randomization. The event was a composite outcome, including any neck US abnormality (confirmed on cytology or Tg washout), the need for subsequent treatment or serum markers abnormalities (any Tg value above 5 ng/mL, or a Tg on LT4 treatment above 1 ng/mL confirmed on two measurements 6 months apart for the RAI treatment group or a Tg on LT4 treatment above 2 ng/mL confirmed on two measurements 6 months apart for the follow-up group; the appearance of TgAb or an increase of >50% of the Tg Ab titers on two consecutive measurements) [47].
The results of the study were positive and demonstrated no difference in the rate of event-free patients in the two groups (95.6% vs. 95.9% of RAI-treated cases and follow-up groups, respectively 90%CI −2.7–2.2) [47]. Biological events were the more common kind of events and structural (abnormal neck US) or functional (abnormal RAI uptake) events occurred in only eight patients (three in the follow-up group and five in the RAI group). Interestingly, serum Tg above three different cutoffs (0.2, 0.5, and 1ng/mL) was associated with more events at 3 years after randomization, but with a statistically significative difference only of the two latter ones [OR = 3.2 (1.4–7.5) and OR = 5.2 (2.0–13.5)] [47]. Finally, no prognostic value of BRAF-mutation was found in the subgroup of the population from which the molecular profile was performed [47]. While waiting for further results from IoN, ESTIMABL2 is the first study to provide strong evidence against the routine use of RAI therapy for low-risk patients, at least on a short-term basis [47].
It is worth noting that with contemporary diagnostic tools, in cases with disease-free status after initial treatment, at least half of the DTC recurrences are observed within 3 years and up to 80% are detected within 5 years of diagnosis [36]. However, the slow-growing attitude of DTC may result in some delayed cancer relapses observed decades after surgery and initial treatments [48,49], and the ESTIMABL2 trial results will need to be confirmed after a longer follow-up of the study population.
2.2.2. Lower-Intermediate Risk Patients
Intermediate-risk DTC represents a very heterogeneous subgroup of DTC, showing variable overlap with low-risk patients in terms of RAI indications and concerns [28,50]. Lower-intermediate risk DTC may be considered as DTC with microscopical extra-thyroidal extension (mETE) and 5LN micro-metastases (in the central compartment), but not extrathyroidal invasion, aggressive histology, clinically evident N1 (cN1), lateral neck or mediastinal LN involvement (N1b) [2,51]. For this subset of patients, the risk of recurrence ranges from between 5% and 10%, but it drops to less than 4% if an excellent response is achieved after initial treatment, even in cases with additional risk features [26,52,53]. As a result, the systematic use of adjuvant RAI is controversial in this category [50,53].
The limited utility of RAI in reducing cancer mortality [54] or improving prognosis was observed in several retrospective or observational series [55,56,57]. For instance, Hay et al. [58] analyzed a large cohort of low-risk PTC followed at the Rochester Mayo Clinic, covering a long time span of six decades. The patients were classified as low-risk according to MACIS score <6 (a prognostic score calculated as follows: 3.1 (if aged less than or equal to 39 years) or 0.08 × age (if aged greater than or equal to 40 years), +0.3 × tumor size (in centimeters), +1 (if incompletely resected), +1 (if locally invasive), +3 (if distant metastases present)). It is worth noting that, unlike the ATA risk classification, MACIS is more of a survival rather than a recurrence prognostication tool. This population includes low and intermediate patients according to the ATA risk stratifications [58]. The authors observed no benefit in terms of 20-year mortality and recurrence rates in their population comparing patients undergoing and not undergoing RAI treatment. Interestingly, during the most recent twelve years (1995–2014), the authors found in 740 N1 patients a significantly higher regional recurrence rate for the groups who performed RAI rather than surgery alone (p = 0.007) [58]. A possible interpretation of the worse outcome in RAI-treated N1 low-risk patients is the number of metastatic LN on surgical reports: the higher the number of metastatic LN, the higher the probability that patients received RAI (p < 0.001), thus indirectly selecting a subset of more aggressive tumors [58]. This same paradox effect was found by other authors and disappears when a propensity matching is performed [10].
Further conflicting data can be found in the literature. A large retrospective analysis by Kim et al. of 8297 intermediate-risk patients [59] failed to prove that RAI reduced the risk of loco-regional recurrence (HR = 0.852, p = 0.413), even in cases with additional negative features, such as larger tumor size, multifocality, mETE, lymph node metastases, and BRAF mutations. A longitudinal study of 470 PTC patients with mETE N0 or Nx found no significant difference in terms of a structural incomplete response at 1 year in patients treated with or without RAI [60], which was consistent with the results of a retrospective study with a smaller population but a longer follow-up period (median 7 years) [61]. Another study, based on the SEER registry showed some benefits in disease-specific survival, but only in particular subgroups, i.e., male gender (p = 0.005), age > 45 years (p < 0.001), and larger tumors (p = 0.007) [62]. On the other side, Ruel et al. [63] observed a better OS with a 29% chance of decreased risk of death (HR = 0.71; CI 95% 0.62–0.82, p = 0.001) in intermediate-risk patients undergoing adjuvant treatment (excluding aggressive variants and multiple primaries) on a large sample of 21 870 DTCs from the National Cancer Database. The authors found the same results even in younger patients (HR = 0.64; CI 95%:0.45–0.92, p = 0.016) [63]. Considering RAI activity, lower iodine protocols have been proposed for intermediate-risk patients with mainly lower risk features, but controversial results are available [53,64,65,66,67] (Table 2) and different practices can be observed according to each centers’ experience.

Table 2.
Overview of studies considering lower RAI activity in intermediate-risk patients with mainly lower risk features.
2.2.3. Selective Use of Adjuvant RAI in Low and Lower-Intermediate Risk, According to Ongoing Risk Classification
ATA guidelines suggest taking into account several clinical factors for the decision to administer RAI, such as the biochemical and radiological post-operative status of the patient, the quality of post-operative tools (Tg concentration, and neck US), the experience of the thyroid surgeons, and patients’ opinions.
Based on these premises, evidence from the literature advocates more and more a wait-and-see attitude in low and lower-intermediate-risks DTC, where delayed treatment does not seem to affect the final outcome, while effectively stratifying the recurrence risk and thus reducing the rate of unnecessary RAI [50,51,68,69]. Conversely, emerging structural or biochemical incomplete responses might arouse suspicions even in formerly low-risk patients, supporting additional adjuvant treatment in these selected cases [51,70,71]. The results of the available studies are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Selected use of RAI in intermediate-risk patients after ongoing risk stratifications.
The INTERMEDIATE trial (NCT04290663) is an RCT that is enrolling lower-intermediate DTCs that is ongoing in France. The aim is to compare a systematic RAI treatment with 3.7 GBq of 131I after rhTSH vs. RAI treatment indication guided by postoperative results (serum Tg values and diagnostic RAI scintigraphy, all patients having normal neck US at study entry). While waiting for higher quality results, the actual evidence is in favor of a careful selection of intermediate-risk DTC to be eligible for adjuvant RAI, notably for those with lower-risk features.
2.2.4. Higher-Intermediate and High Risk
A global agreement is observed in favor of RAI treatment for both higher-intermediate risk and high-risk patients [2,10].
Higher-intermediate risk includes patients with aggressive histology, or extensive lymph node involvement, i.e., >5 metastatic LN, lateral neck metastases, cN1, the presence of ≥3 LN metastases with extranodal extension. In these cases, the risk of recurrence is ≥20% (Table 1).
Considering specific features, some aggressive variants of PTC—i.e., insular, tall cell (TCV), or diffuse sclerosing (DSV) variants—have a recognized worse prognostic role, irrespective of tumor size or other histological factors [72,73]. The five-year survival rate observed was 87.5% and 80.6% for DSV and TCV, respectively, while RAI therapy resulted in effectively reducing mortality (p = 0.026) [72]. Insular variant and poorly-differentiated thyroid cancer (PDTC) are rare and aggressive types of DTC, with frequent LN and distant metastatic involvement and a ten-year survival of 50% or less [74]. In these cases, adjuvant RAI therapy is usually recommended even if the benefits remain controversial; some studies have reported some benefits [75,76]. A large retrospective SEER analysis found a longer overall survival after RAI treatment (p = 0.001), even without improving the cancer-specific survival (p = 0.083) [77].
The preferred RAI activity for these higher-risk classes is usually ≥3.7 GBq, while the treatment preparation mainly relies on THW [16]. However, the most effective protocols are still debated, with several studies showing variable results, according to different preparations and RAI activities.
Considering the timing of RAI administration in higher-risk categories, Yu et al. observed that early RAI therapy (within 3 months) was associated with less biochemical incomplete responses, but it had no influence on the rate of structural disease recurrence [78] while Kim et al. found no such difference within 6 months of surgery [79].
In summary, adjuvant RAI is recommended in all higher-risk patients based on observational evidence demonstrating advantages in recurrences and survival rates. The best RAI administration protocol has not yet been fully identified [80]. Some studies support the higher activity (averagely 3.7–5.55 GBq) of iodine, and THW is the preparation of reference.
2.3. Therapeutic RAI
Therapeutic RAI refers to radioiodine administration for persistent/recurrent disease or distant metastases. Loco-regional metastases (i.e., LN metastases and the thyroid bed) are the most frequent sites of recurrence (20–30% of all cases) [81] and, in these cases, patients are often referred for surgery. Distant metastases are rare (<10%) and the most frequently involved organs are the lungs and the bones. RAI therapy is the favored starting approach for metastatic DTC [2]. All metastatic DTC cases should be discussed in a multidisciplinary tumor board. The presence of bulky or threatening metastatic sites should lead us to consider focal treatments (e.g., surgery, interventional radiology, and radiotherapy) as an alternative, or in association with RAI therapy, as well as in the case of single or oligo metastatic disease, in order to limit repeated RAI administrations.
Repeated therapeutic activities are administrated (every 3, 6, or 12 months) until a complete response is obtained or refractory disease occurs [50,82,83]. The 10-year disease-specific survival is 92% for those patients who show uptake and respond to RAI treatment, while it drops to 30% and 10% for the patients who do not achieve a complete response to RAI despite uptake and those who do not uptake RAI, respectively [84]. Predictors of a good response to RAI usually are: younger age, iodine avid metastases, a small metastatic disease burden, well-differentiated histology, and lower Tg values at the first RAI treatment [81,84,85,86,87,88,89]. In contrast, the presence of PDTC, bone metastases, macronodular lung lesions, and the absence of RAI uptake are independent predictors of RAI failure and worse prognosis [86,90,91].
Unfortunately, even in the presence of significative RAI uptake, disease progression can occur in favor of RAI refractory disease, as observed in follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC) [81], and RAS mutated tumors [92].
Miliary lung metastases, sometimes evident only on WBS without radiologic evidence of disease, along with younger age groups (<40 years), have a better response after RAI therapies, allowing for a 10-year survival rate of 90.9% vs. 68.9% and 30.6% for patients with detectable subcentimetric or larger metastases, respectively [93].
Bone metastases are the second-most-frequent metastatic site. Up to 13% of patients will develop bone lesions [94] and they represent a negative prognostic factor, reducing patients’ overall survival and quality of life, due to pain or skeletal complications [86,94,95]. In almost 32% of cases, patients may achieve a complete response with a combination of RAI and loco-regional treatments [96,97], which significantly improves the overall survival (7.7 years vs. 3.9 years, for combined therapies and RAI alone, respectively) [96]. However, according to a multicenter survey, up to 37.1% of patients will show harmful or fatal skeletal events [98]. Favorable prognostic factors are younger age (<45 years old) and less than three metastases [94]. In particular, cases where only RAI uptake at WBS scans is detectable, without corresponding lesions on conventional radiologic studies, have the highest chance of a complete response [95,99].
In the event of metastatic disease, higher RAI activity (≥3.7 GBq) is necessary to produce a therapeutic effect and two approaches can be used: fixed doses or dosimetry protocols. An empiric fixed RAI activity between 3.7–7.4 GBq is the most frequently used strategy, as this approach is easier and represents a good compromise in terms of effectiveness and adverse events. However, empiric doses ignore the individual radioiodine kinetics and safety concerns have been raised as fixed activities often exceed the maximum tolerated dose in older subjects, even in cases with normal renal function [100]. On the other hand, the dosimetry approach is based on the assessment of the lesions’ radioiodine uptake and bone marrow tolerance, respecting the “as high as safely administrable” rule [101]. Dosimetry is supposed to provide advantages in several situations: from limited loco-regional disease to advanced stages, where tumor burden can be measured by conventional radiologic tools; in younger patients, where lower activities may be equally effective, as well as desirable; or also in disseminated lung metastases, in order to prevent lung fibrosis [101]. However, dosimetry requires more time and resources, along with specific skills and the administration of low 124Iodine activities to test lesions’ iodine metabolism, which could also result in stunning the metastases, reducing the final effectiveness of the therapeutic RAI [101,102,103]. It is worth noting that the activity administered at each RAI course is usually greater with the dosimetry approach than with the empiric approach. Despite the theoretical advantages of dosimetry, Deandreis et al. [104] found no differences in terms of survival, comparing patients who underwent fixed doses (3.7 GBq) or whole-body dosimetry in two major oncological centers. No difference in survival was found after stratifying for the major predictive factors of RAI response (age and metastatic burden) [104]. Interestingly, the patients treated with the dosimetric approach received larger cumulative activities than those treated with fixed activity [cumulative activity 14.8 GBq (range, 1.8–52.5 GBq) at Gustave Roussy vs. 24.2 GBq (range, 2.7–112 GBq) at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (p < 0.01)].
Another issue concerns hormonal preparation, i.e., rhTSH or THW. THW results in a higher uptake and a longer half-life in the metastatic lesions of RAI [105] and can also reveal more metastatic foci [106].
However, due to the well-known drawbacks and potential health risks of THW, rhTSH has been explored as an alternative protocol for metastatic patients [107]. Some studies showed benefits and the same effectiveness of rhTSH preparation compared with THW [108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115]. However, most of these cohorts are small and retrospective, and the follow-up of the patients treated with rhTSH is most often significantly shorter than that of the patients treated after THW, preventing any reliable conclusions (Table 4). A systematic review confirmed rhTSH and THW equivalence for ablative purposes, while the authors found insufficient data to conclude the same in a metastatic framework [116]. THW is still the standard preparation for therapeutic RAI administration for patients with distant metastases and rhTSH should be considered to be an alternative option only in rare cases in which THW is contraindicated.

Table 4.
Overview of studies exploring rhTSH preparation for therapeutic radioiodine treatment in patients with distant metastases.
Figure 1 summarizes the indications for RAI therapy considering both dynamic risk assessment and 18FDG-PET information.
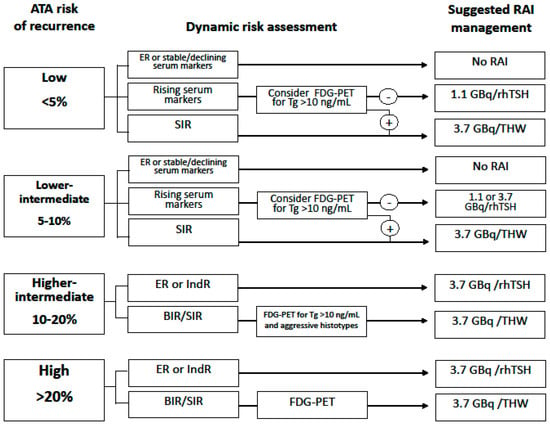
Figure 1.
Indications for RAI therapy considering both dynamic risk assessment and 18FDG-PET information. Abbreviations: RAI, radioiodine; ATA, American Thyroid Association; FDG-PET, fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography; Tg, thyroglobulin; rhTSH, human recombinant thyroid stimulating hormone; THW, thyroid hormone withdrawal; ER, excellent response; SIR, structural incomplete response; BIR, biochemical incomplete response; IndR, indeterminate response.
3. Pediatric DTC
DTC in the pediatric and adolescent populations represents a rare disease with a higher rate of local and distant metastatic disease compared with adult DTCs [117]. Despite the aggressive presentation [117,118,119,120,121,122], pediatric DTCs are the most RAI-sensitive cancers, and a cure can be achieved in up to 52% of the cases [121]. These young patients have similar recurrence rates but lower specific mortality rates than adults in studies with long follow-up periods [117,118,119,120,122], and the rare cases of cancer-related deaths occur at an adult age [117].
Overall, RAI treatment after bilateral thyroid surgery is associated with an improved outcome [123]. The activity of RAI to be administered is calculated according to the body weight of the young patient (1–1.5 mCi/Kg) and the preferred preparation method is THW, although some experiences with rhTSH report non-inferior results [124]. Multiple RAI treatment courses are often necessary to obtain complete disease remission, and in a retrospective analysis of 125 children, 22% of patients required three or more RAI courses [120]. Considering metastatic cases, the cumulative RAI activity ranges from an average of 11.98 GBq to a maximum activity of 22.2 GBq, according to surveys [121,125], although Pires et al. found no therapeutic benefit after 14.8 GBq of iodine administration in their cohort of 118 patients [126]. Interestingly, some delayed responses to RAI were observed in pediatric patients with lung metastases on simple surveillance after repeated RAI treatments [127] supporting a less frequent RAI treatment schedule in these patients. Due to the more aggressive therapeutic approach applied to pediatric DTC, several concerns about iodine safety have arisen over time, notably regarding fertility and additional oncological risks.
4. Side Effects of RAI
Even if RAI therapy is universally considered a safe and well-tolerated treatment [14], some side effects are possible. In fact, in addition to the thyroid gland, the presence of sodium/iodine symporter (NIS) has been shown in several organs, allowing significant iodine uptake, but also leading to an increased susceptibility to adverse events (AEs) during RAI treatments [128]. The most frequently involved non-thyroidal tissues are the salivary and nasolacrimal glands, but potential toxicity on gastrointestinal tissues, bone marrow, and gonads has also been described during the course of succeeding radioiodine administrations [128,129,130,131,132,133]. The real incidence of RAI-related AEs varies, according to the studies and the detection methods. The risk of any RAI-related toxicities increases with the increasing cumulative administered activity of RAI [134,135,136], even if few reliable data are available about the rate of AEs after very high RAI doses. However, potential AEs may develop anyway, even after one RAI treatment or low activity administration, according to individual susceptibility.
The most common chronic side effects are summarized in Table 5.

Table 5.
Summary of radioiodine side effects.
Although extremely rare, the onset of RAI-related second malignancies represents a controversial and feared late AE. Growing concerns have risen especially for younger DTC patients, due to the more aggressive therapeutic approaches applied and the long life expectancy. A study based on a SEER large sample of 27050 pediatric DTC patients showed that the risk of second neoplasms appeared concrete for both hematologic (RR = 1.51; CI 95: 1.08 to 2.01)—including leukemia (RR = 1.92; CI 95:1.04 to 3.56)—and solid cancers (RR = 1.47; CI 95: 1.24 to 1.74)—including breast cancer (RR = 1.46; CI 95: 1.10 to 1.95) [157]. Younger DTC survivors of ≥20 years disclosed the greater risks of secondary neoplasms, and RAI-related cancers were estimated to be 6% and 14% for solid and hematologic tumors, respectively [157]. Another SEER-based study showed a higher rate of second breast cancer in younger DTC patients who performed RAI therapy compared with both non-RAI-treated patients (HR 1.65; CI 95: 1.33–2.05, p < 0.001) and the general population (HR 1.21; CI 95:1.02–1.44, p < 0.05) [158]. However, breast cancer risk remains controversial and the above results have not been confirmed in a large and focused metanalysis of 200247 DTC patients treated with or without radioiodine [159]. Similarly, Kim et al. [160] performed a propensity-score analysis on a wide retrospective multicenter sample of 24318 patients, including RAI-treated and non-RAI-treated subjects, concluding that there was an absence of significant risk of the occurrence of second tumors.
Considering the high rate of salivary gland AEs, several preventive strategies have been investigated in pre-clinical and clinical settings [131,161]. Pre-clinical studies explored the efficacy of various agents, including antioxidants (i.e., Vitamin E) and nutraceutics (i.e., Curcuma longa, Ocimum sanctum, and zinc), showing potential benefits in non-human subject tests [161]. A clinical trial analyzing the influence of Vitamin C on salivary glands’ iodine absorption found only limited effects, irrespective of the moment of administration during RAI therapy [162]. Similarly, pilocarpine, a parasympathomimetic drug stimulating salivary glands, did not prove to provide any substantial advantages, with potential severe toxicities in selected categories, i.e., patients with asthma or cardiac diseases [161]. Amifostine, a supposed salivary gland radioprotector, showed potential effectiveness in two clinical trials [163,164], but failed to confirm the same results in a systematic review [116], and its tolerance and costs further limited its application in clinical practice [161]. The potential benefits of sialagogues agents, such as lemon candies and lemon juices, have been reported thanks to the increase in salivary function and, thus, in iodine washout [161]. However, some concerns emerged after evidence of a higher rate of AEs in early lemon candy eaters (<24 h after iodine administration), due to the concurrent rise in blood flow to the glands, which potentially increased iodine uptake and retention [165]. This event, also named the “rebound effect”, has not been definitely proven [166,167], but the timing of sialagogue administration remains controversial, as well as potential rebounds during the first 24 h after iodine delivery [161,166,168].
5. RAI Refractoriness
5.1. Definition and Prognostic Factors
Iodine refractoriness implies the loss of effective radioiodine uptake and the absence of a therapeutic effect of RAI treatment. The clinical evidence of refractory disease corresponds to a biological tumor change, due to the critical reduction or the loss of specific iodine transporters and other fundamental proteins involved in iodine metabolism.
According to the ATA guidelines, RAI refractoriness is defined by: (i) the absence of any RAI uptake in known metastatic sites; (ii) the loss of RAI uptake after former evidence of RAI uptake; (iii) the presence of a heterogeneous uptake with the presence of RAI-avid and non-RAI-avid metastases; or (iv) the evidence of disease progression after a significative RAI uptake within 6 to 12 months of the last RAI treatment [2]. In line with this definition, cases labeled as RAI refractory should not undergo further treatment, due to their ineffectiveness [2]. Several experts have tried to refine the definition of RAI refractoriness, proposing additional features [169], such as the evidence of 18FDG-PET avid-metastases [170] or a cumulative dose exceeding an activity of 22.2 GBq (600 mCi) [169]. Another scenario that can be assimilated with that of RAI refractory disease is that of locally advanced and unresectable DTCs; these patients have an overall survival similar to RAI refractory patients and should be treated accordingly [171].
Overall, patients fulfilling the definition of RAI refractory disease will not achieve cure with RAI treatment alone but sometimes can obtain some benefit from further RAI, and these cases should be discussed in a case-by-case fashion in expert multidisciplinary boards.
In the event of discordant RAI-avid and RAI refractory metastases, patients formally fit the definition of refractoriness, but they may still achieve some benefits from a combination of RAI and other therapeutic strategies [169]. It is worth noting that the overall prognosis of the patient is driven by the less-differentiated foci of disease (i.e., those that do not uptake RAI) and the treatment of these sites should be prioritized. Even if 18FDG-PET uptake is associated with worse OS, regardless of the RAI uptake status [172,173], some responses to RAI can be observed in patients with distant metastases that show both 18FDG-PET and RAI uptake [174].
Several clinical and molecular features have been associated with a worse outcome in DTC patients and the emergence of RAI refractoriness. Considering clinical features, older age has been traditionally associated with a worse DTC prognosis, since the elderly carry an increased risk of metastatic disease [175] and of refractory DTC [84]. In RAI refractory patients, an age of >60 years-old (HR = 8.498, CI 95:1.555–46.427, p = 0.0135) and the male gender (HR = 5.435, CI 95:1.261–23.256, p = 0.0231) negatively affected patients’ survival [176]. However, Saie et al. [177] observed a reduction in the overall survival (4.65 years, 95% CI: 2.04–5.68, p = 0.0008) only in patients older than 75 years, while they failed to prove an association between age and progression-free survival in their cohort. Other reports did not confirm the negative prognostic role of age in PDTCs, even considering different thresholds [178].
Luo et al. [179] found that the presence of gross ETE, aggressive histology, BRAF-V600E, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) promoter mutations were related to the occurrence of refractory DTC. As stated above, aggressive histotypes usually develop distant metastases and develop RAI refractoriness [73,81]. Histology is also associated with RAI uptake, with FTC and Hürtle cell carcinoma (HCC) showing opposing abilities in iodine concentration, but the same higher rate of progression after RAI [81]. Patients with a gross disease burden, with larger pulmonary or bone metastases, usually do not benefit from RAI treatment and most often have refractory phenotypes [91,93,95].
Considering the molecular signature of refractory DTC, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway—mainly BRAF mutations and the TERT promoter molecular alterations—is most frequently involved in DTC tumorigenesis and development of RAI refractoriness [180]. The most frequent mutation in PTCs is BRAF-V600E, found in up to 60% of PTC [181]. The BRAF mutation causes the uncontrolled activation of the MAPK pathway and is associated with a more aggressive phenotype and a less favorable outcome [182]. Moreover, BRAF mutated tumors have a less-differentiated phenotype with the downregulation of iodine metabolism genes, such as NIS and thyroperoxidase (TPO) [183,184] resulting in a decreased or absent radioiodine uptake and the loss of RAI sensitivity [92]. TERT promoter mutations are considered to be a late event in DTC carcinogenesis and are often found in more aggressive histological types, such as PDTC [185] and anaplastic thyroid cancer [186]. The BRAF and TERT duet is associated with a poor outcome [182,187].
Refractory tumors have an enhanced expression of glucose transporters, such as GLUT1 [188,189]. This change is reflected in the occurrence of 18FDG-PET avid-metastases and is associated with iodine refractoriness, aggressive disease, and poor outcome [170,190,191].
The role of oxidative stress is also recognized in thyroid cancer carcinogenesis and RAI refractoriness [192]. Indeed, the redox status of the cells influences the expression of the NIS [193]. In BRAF-mutated tumors, an increased expression of NOX4 is observed via a TGF-beta-SMAD3-dependent pathway and plays a role in NIS repression [194]. This phenomenon might be due to epigenetic modifications as it has been demonstrated to be reversible [192].
5.2. Strategies to Overcome RAI-Refractoriness
As stated above, the RAI refractory phenotype implies the loss of fundamental cellular proteins involved in iodine uptake and metabolism. Over recent decades, growing attention to the molecular landscape of refractory tumors has driven research into mechanisms underlying refractoriness, allowing initial attempts to restore iodine sensitivity, with variable results. The earliest molecular pathways explored in this framework have been those of retinoid acid (RA) receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ɣ (PPAR ɣ), but with disappointing results [195].
The main breakthrough in this framework was provided by the finding of MAPK signaling as the pathway that was the most frequently involved in the refractoriness process [196,197]. The major trigger of the MAPK pathway is represented by BRAF-V600E [181,185,197], a leading mutation that, by activating the downstream kinases MEK and ERK, produces an uncontrolled stimulation, resulting in a downregulation of iodine metabolism genes, such as NIS and TPO [183,184,196,197,198]. The more recent attempts to stimulate the redifferentiation process have been built around these molecular steps, finding through the selective BRAF and MEK inhibitors the pivotal therapeutic agents [196,197]. The first anti-MEK agent used in clinical practice was selumetinib, which was administrated to a cohort of 24 iodine refractory patients with variable molecular status (RAS, BRAF mutated, or wild-type) [199]. Of the 20 evaluable subjects, five had a partial RECIST response and three had a stable disease, with RAS-mutated patients being better responders [199]. During the following years, other studies focused on specific BRAF inhibitors and on the combination of BRAF and MEK inhibitors. In the former case, small cohorts of BRAF-V600E mutated refractory DTC [200,201,202] have been treated with dabrafenib or vemurafenib alone, finding a rate of objective response ranging from 20 to 50%. The results of these series are listed in Table 6.

Table 6.
Overview of published or ongoing studies on redifferentiation with anti-MEK or anti-BRAF drugs.
A histological drug-induced change was evidenced in a patient harboring the BRAF-K601E mutation and treated for 8 weeks with trametinib ± dabrafenib [207]. In this case, the biopsy following the target therapies treatment showed a more differentiated pattern and a reduced mitotic rate, compared to the initial histology. Moreover, the patient developed overt hyperthyroidism and a metabolic response on 18FDG-PET [207].
Further insights into molecular changes during redifferentiation therapies have emerged over time. As previously reported [208], the inhibition of the MAPK pathway by anti-ERK agents induced the overexpression of the HER3 receptor, which reduced the effects of these drugs. Lapatinib, a HER3 inhibitor, proved to prevent this mechanism, improving the MAPK inhibitor effectiveness and paving the way for this therapeutic combination. A pilot study by Tchekmedyian et al. [206] explored the combination of vemurafenib and a monoclonal antibody anti-HER3 (CDX-3379), due to the supposed reduction of the anti-BRAF inhibition provided by the rebound of tyrosine kinase erbB-3 (HER3). The authors [206] observed two partial responses (PR) and two progressive diseases (PD) in a series of six BRAF-V600E-mutated patients and confirmed the interest of further investigations, including these combinations [206].
Considering the promising results of MAPK inhibitors, several trials are ongoing worldwide, in order to find an effective redifferentiation protocol. MERAIODE (NCT03244956) is a multicenter interventional trial, promoted by the French network TUTHYREF, and aimed to explore the effectiveness of trametinib (anti-MEK) alone in the event of RAS-mutated DTC or a combination of dabrafenib (anti-BRAF) and trametinib, in case of BRAF-V600E-mutated DTC. After the differentiation protocol, patients with restored iodine sensitivity undergo RAI treatment at the fixed activity of 5.55 Gbq after rhTSH stimulation. Preliminary results in 21 BRAF-mutated patients showed PR in 38% (95% CI 18–61), SD in 52% (95% CI 30–74) and PD in 10% (95% CI 1–30). The tumor control rate was 90% and objective responses were observed in 38% of cases, with no patients experiencing adverse events of grade 4 or 5 [205]. The preliminary results of the 10 evaluable patients of the RAS cohort were less promising with only two PR and seven SD [209].
Other trials with similar interventions from Japan (NCT04554680) and the United States (NCT02152995) are actually ongoing in BRAF-V600E or RAS-mutated DTC patients. The former is aimed at exploring the combination of dabrafenib and trametinib after one or four weeks of therapy in a five-subject population; the latter explores the anti-MEK trametinib after four weeks of therapy, in a cohort of thirty-four patients. The results of these studies are pending.
6. Concluding Remarks
Radioiodine represents the oldest therapeutic approach for DTC and the only one capable of obtaining a complete remission at the metastatic stage. However, despite the long tradition of its use, RAI strategies still have several unsolved issues.
Indications for RAI therapy mostly rely on the ATA recurrence risk stratification, which provides an estimate of the risk of persistent or recurrent disease after thyroid cancer surgery. This system is complex due to the numerous items to be taken into account and can be hard to apply in real life practice. To achieve a fine-tuned selection for ablative, adjuvant or therapeutic RAI and to overcome the present limitations of the ATA stratifications, ongoing assessments with serum Tg and TgAb assessment and neck US may be considered. Furthermore, RAI protocols and timing are not standardized, resulting in a variety of behaviors according to single-center practice. In this light, focused studies are needed to fill these gaps of evidence and improve our practice.
An improved risk-based selection of patients and the growing availability of high-quality data have led to a more accurate definition of candidates for ablative RAI and the most effective protocols for lower-risk patients. In most cases, very low and low-risk patients may safely avoid systematic RAI therapy, and eventually be selected for a low-dose protocol, as supported by the ESTIMABLE1, HiLO, and ESTIMABLE2 RCTs [8,9,47]. The intermediate-risk category still appears to be too heterogeneous to draw univocal and comprehensive indications for RAI treatment. Splitting this category into lower- and higher-intermediate-risk might help to refine the therapeutic indications in this group and a post-surgical workup is likely to improve RAI decisions. The results of the IoN and Intermediate RCT will probably shed light on these issues.
Adjuvant RAI is performed in patients who do not clearly show any evidence of disease, and so, a variable proportion of them are likely to be overtreated. In this light, high-risk patients are good candidates for adjuvant RAI, but a tailored approach is required for most of the other risk classes, where the recurrences are rarer [2,16]. On the other hand, the high-risk class still lacks high-quality evidence, which is partially ascribed to the rarity of these patients and the optimal treatment schedule is yet to be established.
Some safety issues are still awaiting clarification. Prevention strategies are urgently needed for frequent RAI AEs, such as xerostomia and salivary gland impairment. On the other hand, due to the unclear risks of RAI-related second cancers, further insights are required and greater caution should be exercised regarding the long-term safety of iodine.
Finally, despite broad progress in terms of knowledge about and protocols for tumor redifferentiation, several issues are still unresolved. Patient selection still needs to be fine-tuned, along with the whole molecular pathway underlying the refractory phenotype. Further molecular alterations and relative targetable drugs should be explored and larger randomized trials are needed. Moreover, the optimal schedule for redifferentiation and the ideal sequence with other available therapeutic options, such as tyrosine-kinase inhibitors, has yet to be established.
In conclusion, RAI therapy still represents a cornerstone of DTC treatment. A tailored approach according to the risk features of patients and their tumors has led to a progressive refinement of therapeutic strategies, optimizing RAI indications and patients selection. Several questions remain unanswered and high-quality studies are needed to further clarify the future RAI strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.S. and L.L; writing—review and editing L.L., C.S., D.H., C.D., S.M., J.H., A.A.G., E.B., I.B. and J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
L.L. has participated in the BAYER, EISAI and IPSEN tumor boards, has received honoraria from EISAI, Lilly and support for attending a meeting from Novartis AAA. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thyroid Cancer—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/thyro.html (accessed on 11 May 2022).
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccarella, S.; Dal Maso, L.; Laversanne, M.; Bray, F.; Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S. The Impact of Diagnostic Changes on the Rise in Thyroid Cancer Incidence: A Population-Based Study in Selected High-Resource Countries. Thyroid 2015, 25, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzato, M.; Li, M.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Singh, D.; La Vecchia, C.; Vaccarella, S. The Epidemiological Landscape of Thyroid Cancer Worldwide: GLOBOCAN Estimates for Incidence and Mortality Rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megwalu, U.C.; Moon, P.K. Thyroid Cancer Incidence and Mortality Trends in the United States: 2000–2018. Thyroid 2022, 32, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, M.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Delafosse, P.; Schvartz, C.; Guizard, A.-V. FRANCIM network Progression of Incidence and Estimate of Net Survival from Papillary Thyroid Cancers Diagnosed between 2008 and 2016 in France. Ann. Endocrinol. 2020, 81, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferri, E.L.; Young, R.L.; Oertel, J.E.; Kemmerer, W.T.; Page, C.P. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: The Impact of Therapy in 576 Patients. Medicine 1977, 56, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumberger, M.; Catargi, B.; Borget, I.; Deandreis, D.; Zerdoud, S.; Bridji, B.; Bardet, S.; Leenhardt, L.; Bastie, D.; Schvartz, C.; et al. Strategies of Radioiodine Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, U.; Harmer, C.; Yap, B.; Wadsley, J.; Clarke, S.; Moss, L.; Nicol, A.; Clark, P.M.; Farnell, K.; McCready, R.; et al. Ablation with Low-Dose Radioiodine and Thyrotropin Alfa in Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1674–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonklaas, J.; Sarlis, N.J.; Litofsky, D.; Ain, K.B.; Bigos, S.T.; Brierley, J.D.; Cooper, D.S.; Haugen, B.R.; Ladenson, P.W.; Magner, J.; et al. Outcomes of Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Following Initial Therapy. Thyroid 2006, 16, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klain, M.; Ricard, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Baudin, E.; Schlumberger, M. Radioiodine Therapy for Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29 (Suppl. 2), S479–S485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-40617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lamartina, L.; Grani, G.; Arvat, E.; Nervo, A.; Zatelli, M.C.; Rossi, R.; Puxeddu, E.; Morelli, S.; Torlontano, M.; Massa, M.; et al. 8th Edition of the AJCC/TNM Staging System of Thyroid Cancer: What to Expect (ITCO#2). Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, L7–L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamartina, L.; Durante, C.; Filetti, S.; Cooper, D.S. Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Radioiodine Remnant Ablation: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1748–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Attard, M.; Torlontano, M.; Ronga, G.; Monzani, F.; Costante, G.; Ferdeghini, M.; Tumino, S.; Meringolo, D.; Bruno, R.; et al. Identification and Optimal Postsurgical Follow-Up of Patients with Very Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4882–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, F.; Fuhrer, D.; Elisei, R.; Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Luster, M.; Schlumberger, M.; Smit, J.W. 2022 ETA Consensus Statement: What Are the Indications for Post-Surgical Radioiodine Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer? Eur. Thyroid J. 2022, 11, e210046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borget, I.; Bonastre, J.; Catargi, B.; Déandréis, D.; Zerdoud, S.; Rusu, D.; Bardet, S.; Leenhardt, L.; Bastie, D.; Schvartz, C.; et al. Quality of Life and Cost-Effectiveness Assessment of Radioiodine Ablation Strategies in Patients with Thyroid Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III ESTIMABL Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, G.; Croce, L.; Sparano, C.; Petrone, L.; Sforza, A.; Maggi, M.; Chiovato, L.; Rotondi, M. Thyroid and heart, a clinically relevant relationship. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 2535–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niri, T.; Horie, I.; Ando, T.; Kawahara, H.; Ueda, M.; Eto, M.; Sako, A.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Nakao, T.; Nakashima, Y.; et al. Renal function and plasma renin activity as potential factors causing hyperkalemia in patients with thyroid carcinoma undergoing thyroid hormone withdrawal for radioactive iodine therapy. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Yun, M.J.; Nam, K.H.; Chung, W.Y.; Soh, E.-Y.; Park, C.S. Quality of Life and Effectiveness Comparisons of Thyroxine Withdrawal, Triiodothyronine Withdrawal, and Recombinant Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Administration for Low-Dose Radioiodine Remnant Ablation of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Thyroid 2010, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, F.; Ladenson, P.W.; Schlumberger, M.; Driedger, A.; Luster, M.; Kloos, R.T.; Sherman, S.; Haugen, B.; Corone, C.; Molinaro, E.; et al. Radioiodine Ablation of Thyroid Remnants after Preparation with Recombinant Human Thyrotropin in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Results of an International, Randomized, Controlled Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianelli, M.; Todino, V.; Graziano, F.M.; Panunzi, C.; Pace, D.; Guglielmi, R.; Signore, A.; Papini, E. Low-Activity (2.0 GBq; 54 MCi) Radioiodine Post-Surgical Remnant Ablation in Thyroid Cancer: Comparison between Hormone Withdrawal and Use of RhTSH in Low-Risk Patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïeb, D.; Sebag, F.; Cherenko, M.; Baumstarck-Barrau, K.; Fortanier, C.; Farman-Ara, B.; De Micco, C.; Vaillant, J.; Thomas, S.; Conte-Devolx, B.; et al. Quality of Life Changes and Clinical Outcomes in Thyroid Cancer Patients Undergoing Radioiodine Remnant Ablation (RRA) with Recombinant Human TSH (RhTSH): A Randomized Controlled Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campennì, A.; Amato, E.; Laudicella, R.; Alibrandi, A.; Cardile, D.; Pignata, S.A.; Trimarchi, F.; Ruggeri, R.M.; Auditore, L.; Baldari, S. Recombinant Human Thyrotropin (RhTSH) versus Levo-Thyroxine Withdrawal in Radioiodine Therapy of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients: Differences in Abdominal Absorbed Dose. Endocrine 2019, 65, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, L.; Duntas, L.H. Management of Endocrine Disease: The Role of RhTSH in the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Pros and Cons. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R133–R145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Tala, H.; Shah, J.; Leboeuf, R.; Ghossein, R.; Gonen, M.; Brokhin, M.; Omry, G.; Fagin, J.A.; Shaha, A. Estimating Risk of Recurrence in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer after Total Thyroidectomy and Radioactive Iodine Remnant Ablation: Using Response to Therapy Variables to Modify the Initial Risk Estimates Predicted by the New American Thyroid Association Staging System. Thyroid 2010, 20, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawka, A.M.; Brierley, J.D.; Tsang, R.W.; Thabane, L.; Rotstein, L.; Gafni, A.; Straus, S.; Goldstein, D.P. An Updated Systematic Review and Commentary Examining the Effectiveness of Radioactive Iodine Remnant Ablation in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 457–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, W.; Fung, C.H.; Chang, J.T.; Waxman, A.; Braunstein, G.D. The Effectiveness of Radioactive Iodine for Treatment of Low-Risk Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Analysis of the Peer-Reviewed Literature from 1966 to April 2008. Thyroid 2010, 20, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardarli, I.; Weidemann, F.; Aboukoura, M.; Herrmann, K.; Binse, I.; Görges, R. Longer-Term Recurrence Rate after Low versus High Dose Radioiodine Ablation for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Low and Intermediate Risk Patients: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, D.L.; Ryan, E.J.; Davey, M.G.; Quinn, A.J.; Heath, D.P.; Garry, S.J.; Boland, M.R.; Young, O.; Lowery, A.J.; Kerin, M.J. Radioiodine Remnant Ablation for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2021, 147, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ruan, M.; Cheng, L.; Fu, H.; Liu, M.; Sheng, S.; Chen, L. Radioiodine Uptake and Thyroglobulin-Guided Radioiodine Remnant Ablation in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Trial. Thyroid 2019, 29, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, C.; Borget, I.; Troalen, F.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Deandreis, D.; Hartl, D.; Lumbroso, J.; Chougnet, C.N.; Baudin, E.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Ultrasensitive Serum Thyroglobulin Measurement Is Useful for the Follow-Up of Patients Treated with Total Thyroidectomy without Radioactive Iodine Ablation. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabashi, C.C.D.; Kasamatsu, T.S.; Crispim, F.; Yamazaki, C.A.; Camacho, C.P.; Andreoni, D.M.; Padovani, R.P.; Ikejiri, E.S.; Mamone, M.C.O.M.; Aldighieri, F.C.; et al. Basal Serum Thyroglobulin Measured by a Second-Generation Assay Is Equivalent to Stimulated Thyroglobulin in Identifying Metastases in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Low or Intermediate Risk of Recurrence. Eur. Thyroid J. 2014, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashat, L.; Orlov, S.; Orlov, D.; Assi, J.; Salari, F.; Walfish, P.G. Serial post-surgical stimulated and unstimulated highly sensitive thyroglobulin measurements in low- and intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma patients not receiving radioactive iodine. Endocrine 2016, 54, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosario, P.W.; Mourão, G.F.; Calsolari, M.R. Can the Follow-up of Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma of Low and Intermediate Risk and Excellent Response to Initial Therapy Be Simplified Using Second-Generation Thyroglobulin Assays? Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 85, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, C.; Montesano, T.; Torlontano, M.; Attard, M.; Monzani, F.; Tumino, D.; Costante, G.; Meringolo, D.; Bruno, R.; Trulli, F.; et al. Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Time Course of Recurrences During Postsurgery Surveillance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angell, T.E.; Spencer, C.A.; Rubino, B.D.; Nicoloff, J.T.; LoPresti, J.S. In Search of an Unstimulated Thyroglobulin Baseline Value in Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients Not Receiving Radioactive Iodine Ablation. Thyroid 2014, 24, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayson, S.E.; Chan, C.M.; Haugen, B.R. Tailoring the Approach to Radioactive Iodine Treatment in Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, T125–T140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, A.; Latrofa, F.; Torregrossa, L.; Piaggi, P.; Gambale, C.; Faranda, A.; Ricci, D.; Agate, L.; Molinaro, E.; Basolo, F.; et al. Changing Trend of Thyroglobulin Antibodies in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Treated with Total Thyroidectomy without 131I Ablation. Thyroid 2018, 28, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamartina, L.; Grani, G.; Durante, C.; Filetti, S. Recent Advances in Managing Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. F1000Research 2018, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filetti, S.; Durante, C.; Hartl, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Locati, L.; Newbold, K.; Papotti, M.; Berruti, A. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1856–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, F.A.; Flux, G.; Giovanella, L.; van Nostrand, D.; Muylle, K.; Luster, M. Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients Potentially Benefitting from Postoperative I-131 Therapy: A Review of the Literature of the Past Decade. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schvartz, C.; Bonnetain, F.; Dabakuyo, S.; Gauthier, M.; Cueff, A.; Fieffé, S.; Pochart, J.-M.; Cochet, I.; Crevisy, E.; Dalac, A.; et al. Impact on Overall Survival of Radioactive Iodine in Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumberger, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Catargi, B.; Deandreis, D.; Zerdoud, S.; Bardet, S.; Rusu, D.; Godbert, Y.; Buffet, C.; Schvartz, C.; et al. Outcome after Ablation in Patients with Low-Risk Thyroid Cancer (ESTIMABL1): 5-Year Follow-up Results of a Randomised, Phase 3, Equivalence Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbi, H.-M.; Mallick, U.; Wadsley, J.; Newbold, K.; Harmer, C.; Hackshaw, A. Recurrence after Low-Dose Radioiodine Ablation and Recombinant Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (HiLo): Long-Term Results of an Open-Label, Non-Inferiority Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, E.; Giani, C.; Agate, L.; Biagini, A.; Pieruzzi, L.; Bianchi, F.; Brozzi, F.; Ceccarelli, C.; Viola, D.; Piaggi, P.; et al. Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Who Underwent Radioiodine Thyroid Remnant Ablation with Low-Activity 131I after Either Recombinant Human TSH or Thyroid Hormone Therapy Withdrawal Showed the Same Outcome after a 10-Year Follow-Up. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboulleux, S.; Bournaud, C.; Chougnet, C.N.; Zerdoud, S.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Catargi, B.; Cao, C.D.; Kelly, A.; Barge, M.-L.; Lacroix, L.; et al. Thyroidectomy without Radioiodine in Patients with Low-Risk Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzaferri, E.L.; Jhiang, S.M. Long-Term Impact of Initial Surgical and Medical Therapy on Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Cancer. Am. J. Med. 1994, 97, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamartina, L.; Handkiewicz-Junak, D. Follow-up of Low Risk Thyroid Cancer Patients: Can We Stop Follow-up after 5 Years of Complete Remission? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, D1–D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, I.J.; Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G.; Palmer, F.L.; Di Lorenzo, M.M.; Grewal, R.K.; Larson, S.M.; Tuttle, R.M.; Shaha, A.; Shah, J.P. The Results of Selective Use of Radioactive Iodine on Survival and on Recurrence in the Management of Papillary Thyroid Cancer, Based on Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center Risk Group Stratification. Thyroid 2013, 23, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grani, G.; Lamartina, L.; Alfò, M.; Ramundo, V.; Falcone, R.; Giacomelli, L.; Biffoni, M.; Filetti, S.; Durante, C. Selective Use of Radioactive Iodine Therapy for Papillary Thyroid Cancers with Low or Lower-Intermediate Recurrence Risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 106, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llamas-Olier, A.E.; Cuéllar, D.I.; Buitrago, G. Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Risk Factors for Early Recurrence in Patients with Excellent Response to Initial Therapy. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, P.W.; Furtado, M.D.S.; Mourão, G.F.; Calsolari, M.R. Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma at Intermediate Risk of Recurrence According to American Thyroid Association Criteria Can Be Reclassified as Low Risk When the Postoperative Thyroglobulin Is Low. Thyroid 2015, 25, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, N. Postoperative Radioactive Iodine-131 Ablation Is Not Necessary among Patients with Intermediate-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Population-Based Study. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, I.D.; McConahey, W.M.; Goellner, J.R. Managing Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Insights Gained from the Mayo Clinic’s Experience of Treating 2512 Consecutive Patients during 1940 through 2000. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2002, 113, 241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lundgren, C.I.; Hall, P.; Dickman, P.W.; Zedenius, J. Influence of Surgical and Postoperative Treatment on Survival in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2007, 94, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podnos, Y.D.; Smith, D.D.; Wagman, L.D.; Ellenhorn, J.D.I. Survival in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer Is Not Affected by the Use of Radioactive Isotope. J. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 96, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, I.D.; Kaggal, S.; Iniguez-Ariza, N.M.; Reinalda, M.S.; Wiseman, G.A.; Thompson, G.B. Inability of Radioiodine Remnant Ablation to Improve Postoperative Outcome in Adult Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 1727–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Woo, J.-W.; Lee, J.H.; Park, I.; Choe, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.S. Radioactive Iodine Ablation May Not Decrease the Risk of Recurrence in Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forleo, R.; Grani, G.; Alfò, M.; Zilioli, V.; Giubbini, R.; Zatelli, M.C.; Gagliardi, I.; Piovesan, A.; Ragni, A.; Morelli, S.; et al. Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension in Predicting 1-Year Outcomes: A Longitudinal Multicenter Study of Low-to-Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (ITCO#4). Thyroid 2021, 31, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.-W.; Ahn, Y.-E.; Chung, W.-S.; Choi, H.-J.; Suh, Y.J. Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Node Negative Papillary Thyroid Cancer with Capsular Invasion Only: Results of a Large Retrospective Study. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 12, e167–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Wei, T. The Benefits of Radioactive Iodine Ablation for Patients with Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, E.; Thomas, S.; Dinan, M.; Perkins, J.M.; Roman, S.A.; Sosa, J.A. Adjuvant Radioactive Iodine Therapy Is Associated with Improved Survival for Patients with Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, L.; Powell, C.; Pratt, B.; Harrington, K.; Nutting, C.; Harmer, C.; Newbold, K. Long-Term Outcomes Following Low-Dose Radioiodide Ablation for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.M.; Kim, W.G.; Kim, T.Y.; Jeon, M.J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Song, D.E.; Hong, S.J.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, W.B. Effects of Low-Dose and High-Dose Postoperative Radioiodine Therapy on the Clinical Outcome in Patients with Small Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Having Microscopic Extrathyroidal Extension. Thyroid 2014, 24, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.H.; Kong, E.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; Cho, I.H.; Chun, K.A.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C. Clinical outcomes of low-dose and high-dose postoperative radioiodine therapy in patients with intermediate-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2017, 38, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pérez, A.M.; García-Alemán, J.; Molina-Vega, M.; Sebastián Ochoa, A.; Pérez García, P.; Mancha Doblas, I.; Tinahones, F.J. Efficacy of Low-Dose Radioiodine Ablation in Low- and Intermediate-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Retrospective Comparative Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, A.; Gambale, C.; Torregrossa, L.; Piaggi, P.; Bianchi, F.; Valerio, L.; Viola, D.; Agate, L.; Molinaro, E.; Materazzi, G.; et al. Delayed 131-i first treatment after surgery has no impact on the median term outcome of patients with intermediate risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocr. Pract. 2020, 26, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahimpasic, T.; Nixon, I.J.; Palmer, F.L.; Whitcher, M.M.; Tuttle, R.M.; Shaha, A.; Patel, S.G.; Shah, J.P.; Ganly, I. Undetectable Thyroglobulin after Total Thyroidectomy in Patients with Low- and Intermediate-Risk Papillary Thyroid Cancer—Is There a Need for Radioactive Iodine Therapy? Surgery 2012, 152, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S.; Soundararajan, R.; Garg, A.; Chopra, S.; Bal, C. Intermediate-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Patients Who Were Surgically Ablated do Not Need Adjuvant Radioiodine Therapy: Long-Term Outcome Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2016, 84, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleira, E.; Peñaloza, M.A.; Jerkovich, F.; Bueno, F.; Pitoia, F. Dynamic risk allows us to adequately select patients with differentiated thyroid cancer who do not require radioiodine treatment. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazaure, H.S.; Roman, S.A.; Sosa, J.A. Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Incidence, Characteristics and Predictors of Survival among 43,738 Patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.S.; Luu, M.; Barrios, L.; Chen, I.; Melany, M.; Ali, N.; Patio, C.; Chen, Y.; Bose, S.; Fan, X.; et al. Incidence and Mortality Risk Spectrum across Aggressive Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.-W.; Lee, C.-H.; Chen, J.-Y.; Tseng, L.-M.; Yang, A.-H. Insular Thyroid Carcinoma: Collective Analysis of Clinicohistologic Prognostic Factors and Treatment Effect with Radioiodine or Radiation Therapy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2006, 203, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.M.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Brierley, J.; Shin, J.; Randolph, G.W. An Evidence-Based Review of Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiagarajan, S.; Yousuf, A.; Shetty, R.; Dhar, H.; Mathur, Y.; Nair, D.; Basu, S.; Patil, A.; Kane, S.; Ghosh-Laskar, S.; et al. Poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma (PDTC) characteristics and the efficacy of radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy as an adjuvant treatment in a tertiary cancer care center. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zou, Q.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Y. Postoperative Radioiodine Therapy Impact on Survival in Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Population-Based Study. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2022, 43, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, X.; Ji, Y.; Tan, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; He, Y.; Wang, R. Delayed Initial Radioiodine Adjuvant Therapy Does Affect Biochemical Response in Intermediate- to High-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 743310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Han, M.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, W.G.; Kim, I.J.; Ryu, J.-S.; Kim, W.B.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, B.H. Impact of Delayed Radioiodine Therapy in Intermediate-/High-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 91, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Ahuja, S.; Avram, A.M.; Bernet, V.J.; Bourguet, P.; Daniels, G.H.; Dillehay, G.; Draganescu, C.; Flux, G.; Führer, D.; et al. Controversies, Consensus, and Collaboration in the Use of 131I Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Joint Statement from the American Thyroid Association, the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the European Thyroid Association. Thyroid 2019, 29, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões-Pereira, J.; Mourinho, N.; Ferreira, T.C.; Limbert, E.; Cavaco, B.M.; Leite, V. Avidity and Outcomes of Radioiodine Therapy for Distant Metastasis of Distinct Types of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3911–e3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.P.; Greening, W.P.; McCready, V.R.; Shaw, H.J.; Harmer, C.L. Radioiodine Treatment of Metastatic Thyroid Carcinoma: The Royal Marsden Hospital Experience. Br. J. Radiol. 1984, 57, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacini, F.; Cetani, F.; Miccoli, P.; Mancusi, F.; Ceccarelli, C.; Lippi, F.; Martino, E.; Pinchera, A. Outcome of 309 Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Treated with Radioiodine. World J. Surg. 1994, 18, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durante, C.; Haddy, N.; Baudin, E.; Leboulleux, S.; Hartl, D.; Travagli, J.P.; Caillou, B.; Ricard, M.; Lumbroso, J.D.; De Vathaire, F.; et al. Long-Term Outcome of 444 Patients with Distant Metastases from Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Benefits and Limits of Radioiodine Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, N.K.; Min, Y.-K.; Kim, S.W.; Chung, J.H. Prognostic Implications of Radioiodine Avidity and Serum Thyroglobulin in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma with Distant Metastasis. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.H.-H.; Wong, K.P.; Cheung, C.Y.; Wan, K.Y.; Lo, C.-Y. Evaluating the Prognostic Factors Associated with Cancer-Specific Survival of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Presenting with Distant Metastasis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammori, M.; Fukumori, T.; Sugishita, Y.; Hoshi, M.; Shimizu, K.; Yamada, T. Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy for Distantly Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (DTC) in Juvenile versus Adult Patients. Endocr. J. 2015, 62, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, D.; Levy, S.; Tsvetov, G.; Gorshtein, A.; Slutzky-Shraga, I.; Akirov, A.; Robenshtok, E.; Shimon, I.; Benbassat, C.A. Long-Term Outcomes and Prognostic Factors in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Distant Metastases. Endocr. Pract. 2017, 23, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreissl, M.C.; Janssen, M.J.R.; Nagarajah, J. Current Treatment Strategies in Metastasized Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, M.M.; Ghossein, R.; Tuttle, R.M. Time Course and Predictors of Structural Disease Progression in Pulmonary Metastases Arising from Follicular Cell–Derived Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, W.G.; Park, S.; Kwon, H.; Jeon, M.J.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, W.B. Growth Kinetics of Macronodular Lung Metastases and Survival in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Thyroid 2017, 27, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, M.M.; Dominguez, J.M.; Grewal, R.K.; Larson, S.M.; Ghossein, R.A.; Tuttle, R.M.; Fagin, J.A. Clinical Outcomes and Molecular Profile of Differentiated Thyroid Cancers with Radioiodine-Avid Distant Metastases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E829–E836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-J.; Qiu, Z.-L.; Shen, C.-T.; Wei, W.-J.; Luo, Q.-Y. Pulmonary Metastases in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Efficacy of Radioiodine Therapy and Prognostic Factors. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muresan, M.M.; Olivier, P.; Leclère, J.; Sirveaux, F.; Brunaud, L.; Klein, M.; Zarnegar, R.; Weryha, G. Bone Metastases from Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Demura, S.; Shinmura, K.; Yokogawa, N.; Shimizu, T.; Tsuchiya, H. Current Management of Bone Metastases from Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Gomes Lima, C.J.; Moreau, S.L.; Kulkarni, K.; Zeymo, A.; Burman, K.D.; Wartofsky, L.; Van Nostrand, D. Improved Survival After Multimodal Approach with 131I Treatment in Patients with Bone Metastases Secondary to Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2019, 29, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannin, A.; Lamartina, L.; Moutarde, C.; Djennaoui, M.; Lion, G.; Chevalier, B.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Deschamps, F.; Hadoux, J.; Baudin, E.; et al. Bone Metastases from Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Heterogenous Tumor Response to Radioactive Iodine Therapy and Overall Survival. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazziotti, G.; Formenti, A.M.; Panarotto, M.B.; Arvat, E.; Chiti, A.; Cuocolo, A.; Dottorini, M.E.; Durante, C.; Agate, L.; Filetti, S.; et al. Real-Life Management and Outcome of Thyroid Carcinoma-Related Bone Metastases: Results from a Nationwide Multicenter Experience. Endocrine 2018, 59, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robenshtok, E.; Farooki, A.; Grewal, R.K.; Tuttle, R.M. Natural History of Small Radioiodine-Avid Bone Metastases That Have No Structural Correlate on Imaging Studies. Endocrine 2014, 47, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.M.; Leboeuf, R.; Robbins, R.J.; Qualey, R.; Pentlow, K.; Larson, S.M.; Chan, C.Y. Empiric Radioactive Iodine Dosing Regimens Frequently Exceed Maximum Tolerated Activity Levels in Elderly Patients with Thyroid Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 1587–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Verburg, F.A.; Hänscheid, H.; Luster, M. Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Therapy for Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 31, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassmann, M.; Reiners, C.; Luster, M. Dosimetry and Thyroid Cancer: The Individual Dosage of Radioiodine. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, R161–R172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, M.; Garcez, K. Prospects for Personalised Treatment of Patients with Radioiodine-Avid Locally Recurrent or Metastatic Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deandreis, D.; Rubino, C.; Tala, H.; Leboulleux, S.; Terroir, M.; Baudin, E.; Larson, S.; Fagin, J.A.; Schlumberger, M.; Tuttle, R.M. Comparison of Empiric Versus Whole-Body/-Blood Clearance Dosimetry—Based Approach to Radioactive Iodine Treatment in Patients with Metastases from Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pötzi, C.; Moameni, A.; Karanikas, G.; Preitfellner, J.; Becherer, A.; Pirich, C.; Dudczak, R. Comparison of Iodine Uptake in Tumour and Nontumour Tissue under Thyroid Hormone Deprivation and with Recombinant Human Thyrotropin in Thyroid Cancer Patients. Clin. Endocrinol. 2006, 65, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nostrand, D.; Khorjekar, G.R.; O’Neil, J.; Moreau, S.; Atkins, F.B.; Kharazi, P.; Mete, M.; Chennupati, S.P.; Burman, K.D.; Wartofsky, L. Recombinant Human Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Versus Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal in the Identification of Metastasis in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with 131I Planar Whole-Body Imaging and 124I PET. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Burman, K.D.; Van Nostrand, D.; Mete, M.; Jonklaas, J.; Wartofsky, L. Potential Use of Recombinant Human Thyrotropin in the Treatment of Distant Metastases in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Pract. 2013, 19, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, F.; Capezzone, M.; Angelini, F.; Taddei, D.; Molinaro, E.; Pinchera, A.; Pacini, F. Radioiodine Treatment of Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Patients on L-Thyroxine, Using Recombinant Human TSH. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 144, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- de Keizer, B.; Brans, B.; Hoekstra, A.; Zelissen, P.M.J.; Koppeschaar, H.P.F.; Lips, C.J.M.; van Rijk, P.P.; Dierckx, R.A.; de Klerk, J.M.H. Tumour Dosimetry and Response in Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Using Recombinant Human Thyrotropin before Radioiodine Therapy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tala, H.; Robbins, R.; Fagin, J.A.; Larson, S.M.; Tuttle, R.M. Five-Year Survival Is Similar in Thyroid Cancer Patients with Distant Metastases Prepared for Radioactive Iodine Therapy with Either Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal or Recombinant Human TSH. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; Burman, K.D.; Van Nostrand, D.; Mete, M.; Jonklaas, J.; Wartofsky, L. Radioiodine Treatment of Metastatic Thyroid Cancer: Relative Efficacy and Side Effect Profile of Preparation by Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal versus Recombinant Human Thyrotropin. Thyroid 2012, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagar, I.; Schwarzbartl-Pevec, A.A.; Vidergar-Kralj, B.; Horvat, R.; Besic, N. Recombinant Human Thyrotropin-Aided Radioiodine Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Thyroid Res. 2012, 2012, 670180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, D.; Kaisar, S.; Awasare, S.; Kamaldeep; Abhyankar, A.; Basu, S. Examining Recombinant Human TSH Primed 131I Therapy Protocol in Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Comparison with the Traditional Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal Protocol. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Ho, K.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Tseng, J.-R.; Yang, L.-Y.; Lin, K.-J.; Cheng, J.-C.; Liou, M.-J. Feasibility of Recombinant Human TSH as a Preparation for Radioiodine Therapy in Patients with Distant Metastases from Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Comparison of Long-Term Survival Outcomes with Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Lima, C.J.; Chittimoju, S.; Wehbeh, L.; Dia, S.; Pagadala, P.; Al-Jundi, M.; Jhawar, S.; Tefera, E.; Mete, M.; Klubo-Gwiezdzinska, J.; et al. Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Survival Is Unaffected by Mode of Preparation for 131I Administration. J. Endocr. Soc. 2022, 6, bvac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, G.; Zuo, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, F. Recombinant Human Thyrotropin (RhTSH) Aided Radioiodine Treatment for Residual or Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 2010, CD008302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, I.D.; Johnson, T.R.; Kaggal, S.; Reinalda, M.S.; Iniguez-Ariza, N.M.; Grant, C.S.; Pittock, S.T.; Thompson, G.B. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC) in Children and Adults: Comparison of Initial Presentation and Long-Term Postoperative Outcome in 4432 Patients Consecutively Treated at the Mayo Clinic During Eight Decades (1936–2015). World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.R.; Zhuge, Y.; Perez, E.A.; Koniaris, L.G.; Lew, J.I.; Sola, J.E. Pediatric Thyroid Carcinoma: Incidence and Outcomes in 1753 Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 156, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busó, M.N.; Burillo, A.G.; Perdigó, M.S.; Mora, P.G.; de Ferrater, M.B.; Borrós, G.C.; Álvarez, C.S.; Conesa, J.C. Long-Term Follow-up of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma in Children and Adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 33, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thankamony, P.; Nirmal, G.; Chandar, R.; Nair, A.K.R.; Veeramoni Iyer Mriduladevi, P. Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma in Children: A Retrospective Analysis of 125 Pediatric Cases from a Single Institution in India. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapuppo, G.; Hartl, D.; Fresneau, B.; Hadoux, J.; Breuskin, I.; Baudin, E.; Rigaud, C.; Guerlain, J.; Ghuzlan, A.A.; Leboulleux, S.; et al. Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in Children and Adolescents: Long Term Outcome and Risk Factors for Persistent Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Shang, X.; Huang, D.; Liu, M.; Zong, L. Incidence and Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer in Children: Based on the SEER Database. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Wloch, J.; Roskosz, J.; Krajewska, J.; Kropinska, A.; Pomorski, L.; Kukulska, A.; Prokurat, A.; Wygoda, Z.; Jarzab, B. Total Thyroidectomy and Adjuvant Radioiodine Treatment Independently Decrease Locoregional Recurrence Risk in Childhood and Adolescent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Gawlik, T.; Rozkosz, J.; Puch, Z.; Michalik, B.; Gubala, E.; Krajewska, J.; Kluczewska, A.; Jarzab, B. Recombinant Human Thyrotropin Preparation for Adjuvant Radioiodine Treatment in Children and Adolescents with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 173, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, K.; Nagahama, M.; Kitagawa, W.; Ohkuwa, K.; Uruno, T.; Matsuzu, K.; Suzuki, A.; Tomoda, C.; Hames, K.Y.; Akaishi, J.; et al. Distant Metastasis in Pediatric and Adolescent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Clinical Outcomes and Risk Factor Analyses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3981–e3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, B.P.; Alves, P.A.G.; Bordallo, M.A.; Bulzico, D.A.; Lopes, F.P.P.L.; Farias, T.; Dias, F.; Lima, R.A.; Santos Gisler, I.C.; Coeli, C.M.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Early and Long-Term Remission in Pediatric Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: The Role of Sex, Age, Clinical Presentation, and the Newly Proposed American Thyroid Association Risk Stratification System. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biko, J.; Reiners, C.; Kreissl, M.C.; Verburg, F.A.; Demidchik, Y.; Drozd, V. Favourable Course of Disease after Incomplete Remission on 131I Therapy in Children with Pulmonary Metastases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: 10 Years Follow-Up. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhiang, S.M.; Sipos, J.A. Na+/I− Symporter Expression, Function, and Regulation in Non-Thyroidal Tissues and Impact on Thyroid Cancer Therapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, T167–T177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Scipioni, A.; Durante, C.; Ferretti, E.; Gandini, L.; Maggisano, V.; Paoli, D.; Verrienti, A.; Costante, G.; Lenzi, A.; et al. Expression and Localization of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter (NIS) in Testicular Cells. Endocrine 2011, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashnehsaz, M.; Takavar, A.; Izadyar, S.; Zakariaee, S.S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Paydar, R.; Geramifar, P. Gastrointestinal Side Effects of the Radioiodine Therapy for the Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Two Days after Prescription. World J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 15, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.C.; Marchal, F.; Angelos, P.; Bernet, V.; Boucai, L.; Buchholzer, S.; Burkey, B.; Eisele, D.; Erkul, E.; Faure, F.; et al. Salivary and Lacrimal Dysfunction after Radioactive Iodine for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: American Head and Neck Society Endocrine Surgery Section and Salivary Gland Section Joint Multidisciplinary Clinical Consensus Statement of Otolaryngology, Ophthalmology, Nuclear Medicine and Endocrinology. Head Neck 2020, 42, 3446–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco-Eizaguirre, G.; Santisteban, P.; De la Vieja, A. The Complex Regulation of NIS Expression and Activity in Thyroid and Extrathyroidal Tissues. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, T141–T165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chung, C.-H.; Lin, L.-F.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-F.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chien, W.-C. Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Thyroid Cancer Patients Increases the Risk of Long-Term Gastrointestinal Disorders: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, R.K.; Larson, S.M.; Pentlow, C.E.; Pentlow, K.S.; Gonen, M.; Qualey, R.; Natbony, L.; Tuttle, R.M. Salivary Gland Side Effects Commonly Develop Several Weeks after Initial Radioactive Iodine Ablation. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, S.C.; Peeters, R.P.; Ronckers, C.M.; Links, T.P.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; van Dijkum, E.J.M.N.; van Rijn, R.R.; van der Pal, H.J.H.; Neggers, S.J.; Kremer, L.C.M.; et al. Intermediate and Long-Term Adverse Effects of Radioiodine Therapy for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma—A Systematic Review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrueco, A.S.; Galán, F.G.; Rueda, I.A.; Coello, J.M.S.; Dorado, M.P.B.; Aubá, J.M.V.; Escanciano, M.E.; Jiménez, L.L.; Fernández, I.M.; Español, C.C. Incidence and risk factors for radioactive iodine-induced sialadenitis. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2020, 140, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, C.; Bader, J.B.; Schaefer, A.; Finke, C.; Kirsch, C.M. Intermediate and long-term side effects of high-dose radioiodine therapy for thyroid carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 1998, 39, 1551–1554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solans, R.; Bosch, J.A.; Galofré, P.; Porta, F.; Roselló, J.; Selva-O’Callagan, A.; Vilardell, M. Salivary and lacrimal gland dysfunction (sicca syndrome) after radioiodine therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2001, 42, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zettinig, G.; Hanselmayer, G.; Fueger, B.; Hofmann, A.; Pirich, C.; Nepp, J.; Dudczak, R. Long-Term Impairment of the Lacrimal Glands after Radioiodine Therapy: A Cross-Sectional Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 1428–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.J. Iodine-131 Therapy and Nasolacrimal Duct Obstructions: What We Know and What We Need to Know. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 32, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Fonseca, F.L.; Yamanaka, P.K.; Kato, J.M.; Matayoshi, S. Lacrimal System Obstruction After Radioiodine Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas: A Prospective Comparative Study. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, N.S.; Buatti, J.M.; Tewfik, H.H.; Pagedar, N.A.; Anderson, C.M.; Watkins, J.M. Radioiodine Ablation Following Thyroidectomy for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Literature Review of Utility, Dose, and Toxicity. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, H.H.; Creutzig, H. Salivary gland scintigraphy after radio-iodine therapy. Functional scintigraphy of the salivary gland after high dose radio-iodine therapy (author’s transl). Rofo Fortschr. Geb. Rontgenstrahlen Nukl. 1976, 125, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrand, D.; Neutze, J.; Atkins, F. Side Effects of “Rational Dose” Iodine-131 Therapy for Metastatic Well-Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 1986, 27, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Wang, S.J. Short-Term Hazards of Low-Dose Radioiodine Ablation Therapy in Postsurgical Thyroid Cancer Patients. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1996, 21, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, E.; Skoknic, V.; Majlis, S.; Tala, H.; Silva, C.; Castillo, E.; Whittle, C.; Niedmann, J.P.; González, P. Radioiodine-Induced Salivary Gland Damage Detected by Ultrasonography in Patients Treated for Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Radioactive Iodine Activity and Risk. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, L.A.; duCret, R.P.; Mariash, C.N. Local Reactions to Radioiodine in the Treatment of Thyroid Cancer. Am. J. Med. 1991, 90, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinuya, S.; Hwang, E.H.; Ikeda, E.; Yokoyama, K.; Michigishi, T.; Tonami, N. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome Caused by Iodine-131 Therapy for Metastatic Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Nucl. Med. 1997, 38, 1831. [Google Scholar]
- Dorn, R.; Kopp, J.; Vogt, H.; Heidenreich, P.; Carroll, R.G.; Gulec, S.A. Dosimetry-Guided Radioactive Iodine Treatment in Patients with Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Largest Safe Dose Using a Risk-Adapted Approach. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 451–456. [Google Scholar]
- Bourcigaux, N.; Rubino, C.; Berthaud, I.; Toubert, M.E.; Donadille, B.; Leenhardt, L.; Petrot-Keller, I.; Brailly-Tabard, S.; Fromigué, J.; de Vathaire, F.; et al. Impact on Testicular Function of a Single Ablative Activity of 3.7 GBq Radioactive Iodine for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, C.; de Vathaire, F.; Dottorini, M.E.; Hall, P.; Schvartz, C.; Couette, J.E.; Dondon, M.G.; Abbas, M.T.; Langlois, C.; Schlumberger, M. Second Primary Malignancies in Thyroid Cancer Patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.P.; Chen, J.; Hitchcock, Y.J.; Szabo, A.; Shrieve, D.C.; Tward, J.D. The Risk of Second Primary Malignancies up to Three Decades after the Treatment of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka, A.M.; Thabane, L.; Parlea, L.; Ibrahim-Zada, I.; Tsang, R.W.; Brierley, J.D.; Straus, S.; Ezzat, S.; Goldstein, D.P. Second Primary Malignancy Risk after Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid 2009, 19, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.M.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, B.I.; Song, H.-C.; Yoon, J.-K.; Won, K.S.; Kim, S.-M.; Cho, I.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Incidence Rate and Factors Associated with the Development of Secondary Cancers after Radioiodine Therapy in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebestreit, H.; Biko, J.; Drozd, V.; Demidchik, Y.; Burkhardt, A.; Trusen, A.; Beer, M.; Reiners, C. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Youth Treated with Radioiodine for Juvenile Thyroid Cancer and Lung Metastases after Chernobyl. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Bertagna, F.; Panarotto, M.B.; Giubbini, R. Early and Late Adverse Effects of Radioiodine for Pediatric Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqual, E.; Schonfeld, S.; Morton, L.M.; Villoing, D.; Lee, C.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Kitahara, C.M. Association Between Radioactive Iodine Treatment for Pediatric and Young Adulthood Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Risk of Second Primary Malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Qi, X.; Zhu, H.; Yang, G.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Q.; Yang, Q. Association of Radioiodine for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Second Breast Cancer in Female Adolescent and Young Adult. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 805194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, C.; Klain, M.; Cantoni, V.; Green, R.; Piscopo, L.; Volpe, F.; Maurea, S.; Petretta, M.; Cuocolo, A. Risk of Primary Breast Cancer in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Undergoing Radioactive Iodine Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bang, J.-I.; Boo, D.; Kim, B.; Choi, I.Y.; Ko, S.; Yoo, I.R.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Joo, Y.; et al. Second Primary Malignancy Risk in Thyroid Cancer and Matched Patients with and without Radioiodine Therapy Analysis from the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3547–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noaparast, Z.; Hosseinimehr, S.J. Radioprotective Agents for the Prevention of Side Effects Induced by Radioiodine-131 Therapy. Future Oncol. 2013, 9, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Kuang, A.; Huang, R.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, R. Influence of Vitamin C on Salivary Absorbed Dose of 131I in Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blind, Controlled Trial. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohuslavizki, K.H.; Klutmann, S.; Brenner, W.; Mester, J.; Henze, E.; Clausen, M. Salivary Gland Protection by Amifostine in High-Dose Radioiodine Treatment: Results of a Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 3542–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohuslavizki, K.H.; Klutmann, S.; Jenicke, L.; Kröger, S.; Buchert, R.; Mester, J.; Clausen, M. Salivary Gland Protection by S-2-(3-Aminopropylamino)-Ethylphosphorothioic Acid (Amifostine) in High-Dose Radioiodine Treatment: Results Obtained in a Rabbit Animal Model and in a Double-Blind Multi-Arm Trial. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 1999, 14, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakada, K.; Ishibashi, T.; Takei, T.; Hirata, K.; Shinohara, K.; Katoh, S.; Zhao, S.; Tamaki, N.; Noguchi, Y.; Noguchi, S. Does Lemon Candy Decrease Salivary Gland Damage after Radioiodine Therapy for Thyroid Cancer? J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrand, D. Sialoadenitis Secondary to 131I Therapy for Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, K.; Van Nostrand, D.; Atkins, F.; Mete, M.; Wexler, J.; Wartofsky, L. Does Lemon Juice Increase Radioiodine Reaccumulation within the Parotid Glands More than If Lemon Juice Is Not Administered? Nucl. Med. Commun. 2014, 35, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein Hesselink, E.N.; Brouwers, A.H.; de Jong, J.R.; van der Horst-Schrivers, A.N.A.; Coppes, R.P.; Lefrandt, J.D.; Jager, P.L.; Vissink, A.; Links, T.P. Effects of Radioiodine Treatment on Salivary Gland Function in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Prospective Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nostrand, D. Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Time to Update the Classifications. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Brose, M.; Elisei, R.; Leboulleux, S.; Luster, M.; Pitoia, F.; Pacini, F. Definition and Management of Radioactive Iodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamartina, L.; Godbert, Y.; Nascimento, C.; Do Cao, C.; Hescot, S.; Borget, I.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Hartl, D.; Hadoux, J.; Pottier, E.; et al. Locally Unresectable Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Outcomes and Perspectives. Endocrine 2020, 69, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, R.J.; Wan, Q.; Grewal, R.K.; Reibke, R.; Gonen, M.; Strauss, H.W.; Tuttle, R.M.; Drucker, W.; Larson, S.M. Real-Time Prognosis for Metastatic Thyroid Carcinoma Based on 2-[18F]Fluoro-2-Deoxy-d-Glucose-Positron Emission Tomography Scanning. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deandreis, D.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Leboulleux, S.; Lacroix, L.; Garsi, J.P.; Talbot, M.; Lumbroso, J.; Baudin, E.; Caillou, B.; Bidart, J.M.; et al. Do Histological, Immunohistochemical, and Metabolic (Radioiodine and Fluorodeoxyglucose Uptakes) Patterns of Metastatic Thyroid Cancer Correlate with Patient Outcome? Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengensatzproduktion, S.; Stückle, D. Abstracts. Eur. Thyroid J. 2017, 6, 23–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, A.; Kudo, T.; Kihara, M.; Higashiyama, T.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Miya, A. Relationship of Biochemically Persistent Disease and Thyroglobulin-Doubling Time to Age at Surgery in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr. J. 2013, 60, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Miyauchi, A.; Ito, M.; Yabuta, T.; Masuoka, H.; Higashiyama, T.; Fukushima, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Kihara, M.; Miya, A. Prognosis and Prognostic Factors of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma after the Appearance of Metastasis Refractory to Radioactive Iodine Therapy. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saïe, C.; Wassermann, J.; Mathy, E.; Chereau, N.; Leenhardt, L.; Tezenas du Montcel, S.; Buffet, C. Impact of Age on Survival in Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 184, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fouchardière, C.; Decaussin-Petrucci, M.; Berthiller, J.; Descotes, F.; Lopez, J.; Lifante, J.-C.; Peix, J.-L.; Giraudet, A.-L.; Delahaye, A.; Masson, S.; et al. Predictive Factors of Outcome in Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 92, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, B.; Liao, T.; Wang, Y. Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Characteristics Correlating to the Occurrence of Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 549882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Yun, C.; Zhang, W. The Genetic Duet of BRAF V600E and TERT Promoter Mutations Predicts the Poor Curative Effect of Radioiodine Therapy in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3470–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Integrated Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Cell 2014, 159, 676–690. [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Alzahrani, A.S.; Carson, K.A.; Shong, Y.K.; Kim, T.Y.; Viola, D.; Elisei, R.; Bendlová, B.; Yip, L.; Mian, C.; et al. Association between BRAF V600E Mutation and Recurrence of Papillary Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, C.; Puxeddu, E.; Ferretti, E.; Morisi, R.; Moretti, S.; Bruno, R.; Barbi, F.; Avenia, N.; Scipioni, A.; Verrienti, A.; et al. BRAF Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas Inhibit Genes Involved in Iodine Metabolism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 2840–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anekpuritanang, T.; Uataya, M.; Claimon, A.; Laokulrath, N.; Pongsapich, W.; Pithuksurachai, P. The Association Between Radioiodine Refractory in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma, Sodium/Iodide Symporter Expression, and BRAF V600E Mutation. OncoTargets Ther. 2021, 14, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirrò, E.; Martorana, F.; Romano, C.; Vitale, S.R.; Motta, G.; Di Gregorio, S.; Massimino, M.; Pennisi, M.S.; Stella, S.; Puma, A.; et al. Molecular Alterations in Thyroid Cancer: From Bench to Clinical Practice. Genes 2019, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jannin, A.; Escande, A.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Blanchard, P.; Hartl, D.; Chevalier, B.; Deschamps, F.; Lamartina, L.; Lacroix, L.; Dupuy, C.; et al. Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma: An Update. Cancers 2022, 14, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Bishop, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, T.; Ladenson, P.W.; Xing, M. Mortality Risk Stratification by Combining BRAF V600E and TERT Promoter Mutations in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Genetic Duet of BRAF and TERT Promoter Mutations in Thyroid Cancer Mortality. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönberger, J.; Rüschoff, J.; Grimm, D.; Marienhagen, J.; Rümmele, P.; Meyringer, R.; Kossmehl, P.; Hofstaedter, F.; Eilles, C. Glucose Transporter 1 Gene Expression Is Related to Thyroid Neoplasms with an Unfavorable Prognosis: An Immunohistochemical Study. Thyroid 2002, 12, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabellus, F.; Nagarajah, J.; Bockisch, A.; Schmid, K.W.; Sheu, S.-Y. Glucose Transporter 1 Expression, Tumor Proliferation, and Iodine/Glucose Uptake in Thyroid Cancer with Emphasis on Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, L.N.; Iravani, A.; Nhung, N.T.; Hanh, N.T.M.; Hutomo, F.; Son, M.H. Relationship between Clinicopathologic Factors and FDG Avidity in Radioiodine-Negative Recurrent or Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi Rizzini, E.; Repaci, A.; Tabacchi, E.; Zanoni, L.; Vicennati, V.; Cavicchi, O.; Pagotto, U.; Morganti, A.G.; Fanti, S.; Monari, F. Impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT on Clinical Management of Suspected Radio-Iodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (RAI-R-DTC). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, R.A.E.; Buffet, C.; Leboulleux, S.; Dupuy, C. Oxidative Stress in Thyroid Carcinomas: Biological and Clinical Significance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R131–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppin, C.; Arturi, F.; Ferretti, E.; Russo, D.; Sacco, R.; Tell, G.; Damante, G.; Filetti, S. Transcriptional Regulation of Human Sodium/Iodide Symporter Gene: A Role for Redox Factor-1. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouzi, N.; Cailloux, J.; Cazarin, J.M.; Knauf, J.A.; Cracchiolo, J.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Hartl, D.; Polak, M.; Carré, A.; El Mzibri, M.; et al. NADPH Oxidase NOX4 Is a Critical Mediator of BRAFV600E-Induced Downregulation of the Sodium/Iodide Symporter in Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Ahn, B.-C. Molecular Mechanisms of Radioactive Iodine Refractoriness in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Impaired Sodium Iodide Symporter (NIS) Expression Owing to Altered Signaling Pathway Activity and Intracellular Localization of NIS. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6251–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffet, C.; Wassermann, J.; Hecht, F.; Leenhardt, L.; Dupuy, C.; Groussin, L.; Lussey-Lepoutre, C. Redifferentiation of Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Cancers. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, R113–R132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamartina, L.; Anizan, N.; Dupuy, C.; Leboulleux, S.; Schlumberger, M. Redifferentiation-Facilitated Radioiodine Therapy in Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, T179–T191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aashiq, M.; Silverman, D.A.; Na’ara, S.; Takahashi, H.; Amit, M. Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Cancer: Molecular Basis of Redifferentiation Therapies, Management, and Novel Therapies. Cancers 2019, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.L.; Grewal, R.K.; Leboeuf, R.; Sherman, E.J.; Pfister, D.G.; Deandreis, D.; Pentlow, K.S.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Haque, S.; Gavane, S.; et al. Selumetinib-Enhanced Radioiodine Uptake in Advanced Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, S.M.; McFadden, D.G.; Palmer, E.L.; Daniels, G.H.; Wirth, L.J. Redifferentiation of Iodine-Refractory BRAF V600E-Mutant Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Cancer with Dabrafenib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huillard, O.; Tenenbaum, F.; Clerc, J.; Goldwasser, F.; Groussin, L. Restoring Radioiodine Uptake in BRAF V600E-Mutated Papillary Thyroid Cancer. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, L.A.; Sherman, E.J.; Baxi, S.S.; Tchekmedyian, V.; Grewal, R.K.; Larson, S.M.; Pentlow, K.S.; Haque, S.; Tuttle, R.M.; Sabra, M.M.; et al. Vemurafenib Redifferentiation of BRAF Mutant, RAI-Refractory Thyroid Cancers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, T.; Waguespack, S.G.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Elbanan, M.; Vu, T.; Dadu, R.; Sherman, S.I.; Amit, M.; Santos, E.B.; Zafereo, M.; et al. Targeted Therapy in Advanced Thyroid Cancer to Resensitize Tumors to Radioactive Iodine. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, A.; Solomon, B.; Pattison, D.A.; Jackson, P.; Ravi Kumar, A.; Kong, G.; Hofman, M.S.; Akhurst, T.; Hicks, R.J. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Inhibition for Redifferentiation of Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: An Evolving Protocol. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leboulleux, S.; Cao, C.D.; Zerdoud, S.; Attard, M.; Bournaud, C.; Benisvy, D.; Taieb, D.; Bardet, S.; Terroir-Cassou-Mounat, M.; Betrian, S.; et al. MERAIODE: A Redifferentiation Phase II Trial with Trametinib and Dabrafenib Followed by Radioactive Iodine Administration for Metastatic Radioactive Iodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with a BRAFV600E Mutation (NCT 03244956). J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, A876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekmedyian, V.; Dunn, L.; Sherman, E.; Baxi, S.S.; Grewal, R.K.; Larson, S.M.; Pentlow, K.S.; Haque, S.; Tuttle, R.M.; Sabra, M.M.; et al. Enhancing Radioiodine Incorporation in BRAF-Mutant, Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Cancers with Vemurafenib and the Anti-ErbB3 Monoclonal Antibody CDX-3379: Results of a Pilot Clinical Trial. Thyroid 2022, 32, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leboulleux, S.; Dupuy, C.; Lacroix, L.; Attard, M.; Grimaldi, S.; Corre, R.; Ricard, M.; Nasr, S.; Berdelou, A.; Hadoux, J.; et al. Redifferentiation of a BRAFK601E-Mutated Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patient with Dabrafenib and Trametinib Treatment. Thyroid 2019, 29, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Conde, C.; Ruiz-Llorente, S.; Dominguez, J.M.; Knauf, J.A.; Viale, A.; Sherman, E.J.; Ryder, M.; Ghossein, R.A.; Rosen, N.; Fagin, J.A. Relief of Feedback Inhibition of HER3 Transcription by RAF and MEK Inhibitors Attenuates Their Antitumor Effects in BRAF-Mutant Thyroid Carcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboulleux, S.; Benisvy, D.; Taieb, D.; Attard, M.; Bournaud, C.; Terroir, M.; Ghuzlan, A.A.; Lamartina, L.; Schlumberger, M.J.; Godbert, Y.; et al. 1743MO MERAIODE: A Redifferentiation Phase II Trial with Trametinib Followed by Radioactive Iodine for Metastatic Radioactive Iodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with a RAS Mutation. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).