Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Toxins | Variants | Toxin producing cyanobacterial genera | Toxic mechanism | Health effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcystin | Over 85 variants | Anabaena, Anabaenopsis, Aphanizomenon, Merismopedia, Microcystis, Oscillatoria, Phormidium, Synechococcus and Planktothrix | Hepatotoxic, inhibits eukaryotic protein phosphatases | Gastrointestinal, liver inflammation, and hemorrhage and liver failure leading to death, pneumonia, dermatitis |
| Nodularin | 8 variants | Nodularia and Nostoc | Hepatotoxic, inhibits eukaryotic protein phosphatases | Gastrointestinal, liver inflammation, and hemorrhage and liver failure leading to death, pneumonia, dermatitis |
| Cylindrospermopsin | 3 variants, Cylindrospermopsin 7-epicylindrospermopsin 7-deoxycylindrospermopsin | Cylindrospermopsis, Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Oscillatoria, Raphidiopsis, Umezakia and Sphaerospermopsis | Hepatotoxic, cytotoxic, neurotoxic; inhibition of glutathione synthesis, protein synthesis and cytochrome P450 | Gastrointestinal, liver inflammation and hemorrhage, pneumonia, dermatitis |
| Anatoxin-a | 3 variants, Anatoxin-a, homoanatoxin-a Anatoxin-a(s) | Anabaena, Aphanizomenon and Oscillatoria | Neurotoxic, mimics the neurotransmitter acetylcholine | Tingling, burning, numbness, drowsiness, incoherent speech, respiratory paralysis leading to death |
| Saxitoxin | 20 variants | Anabaena Aphanizomenon, Cylindrospermopsis, Lyngbya, Planktothrix, Raphidiopsis and Scytonema | Neurotoxic, blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels | Tingling, burning, numbness, drowsiness, incoherent speech, respiratory paralysis leading to death |
2. Microcystins (MCs) & Nodularins (NODs)
2.1. Synthesis and Regulation
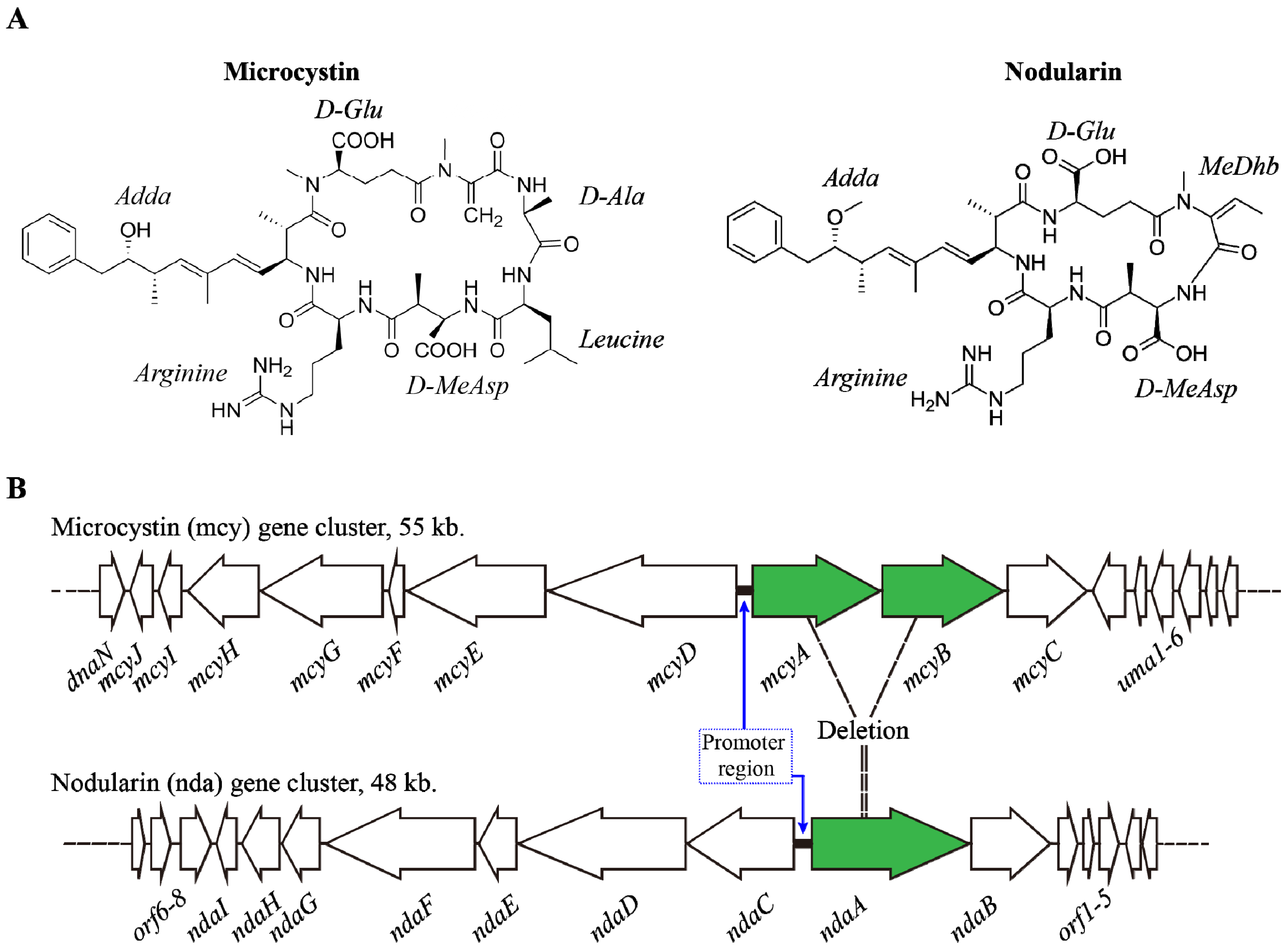
2.2. Environmental Factors Regulating MCs Synthesis
2.3. Environmental Regulation of Nodularin
3. Cylindrospermopsin
3.1. Characteristics
3.2. Structure and Toxicity
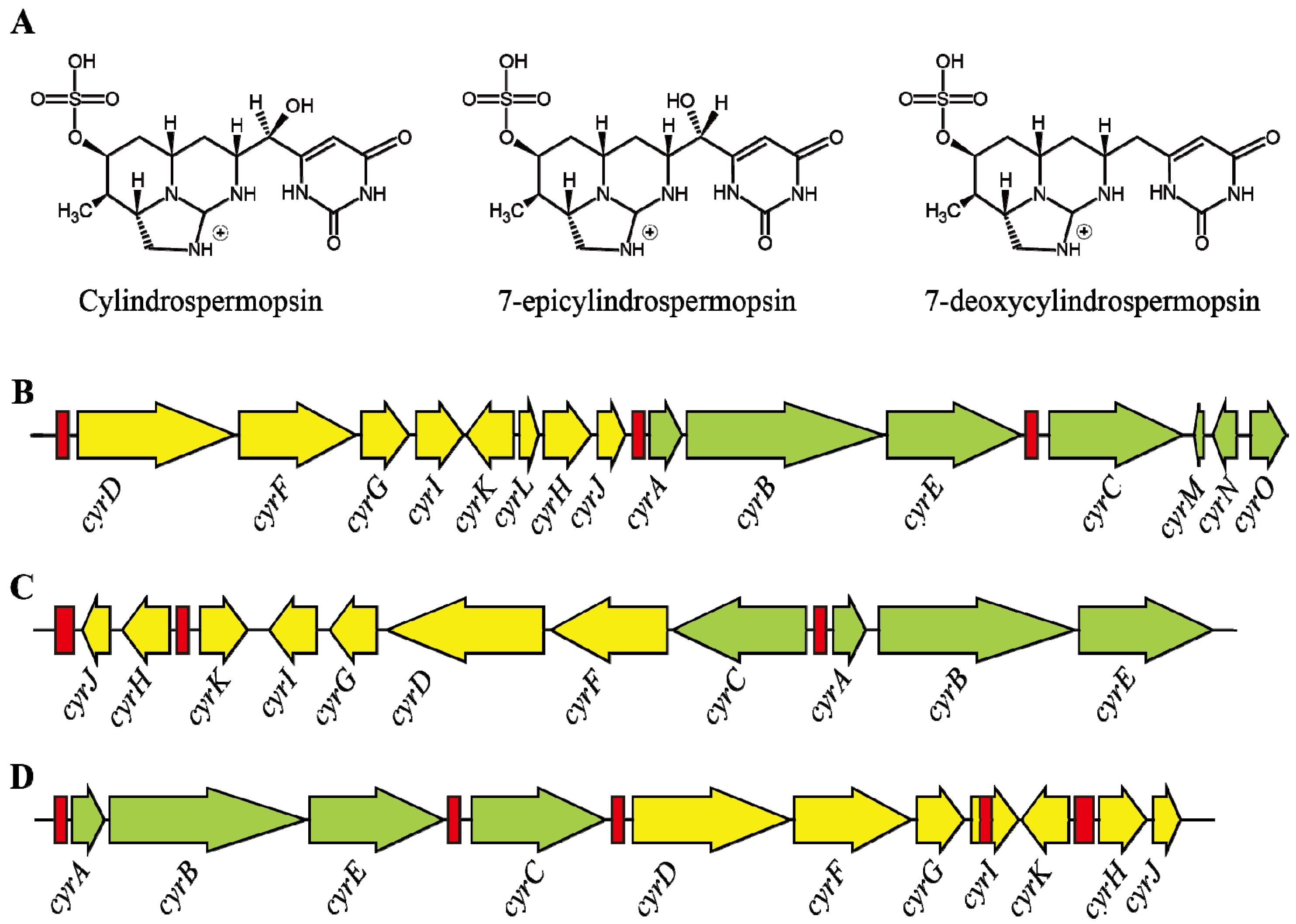
3.3. Transcription of Cylindrospermopsin Synthetase Gene
3.4. Role of Environmental Factors in CYN Production
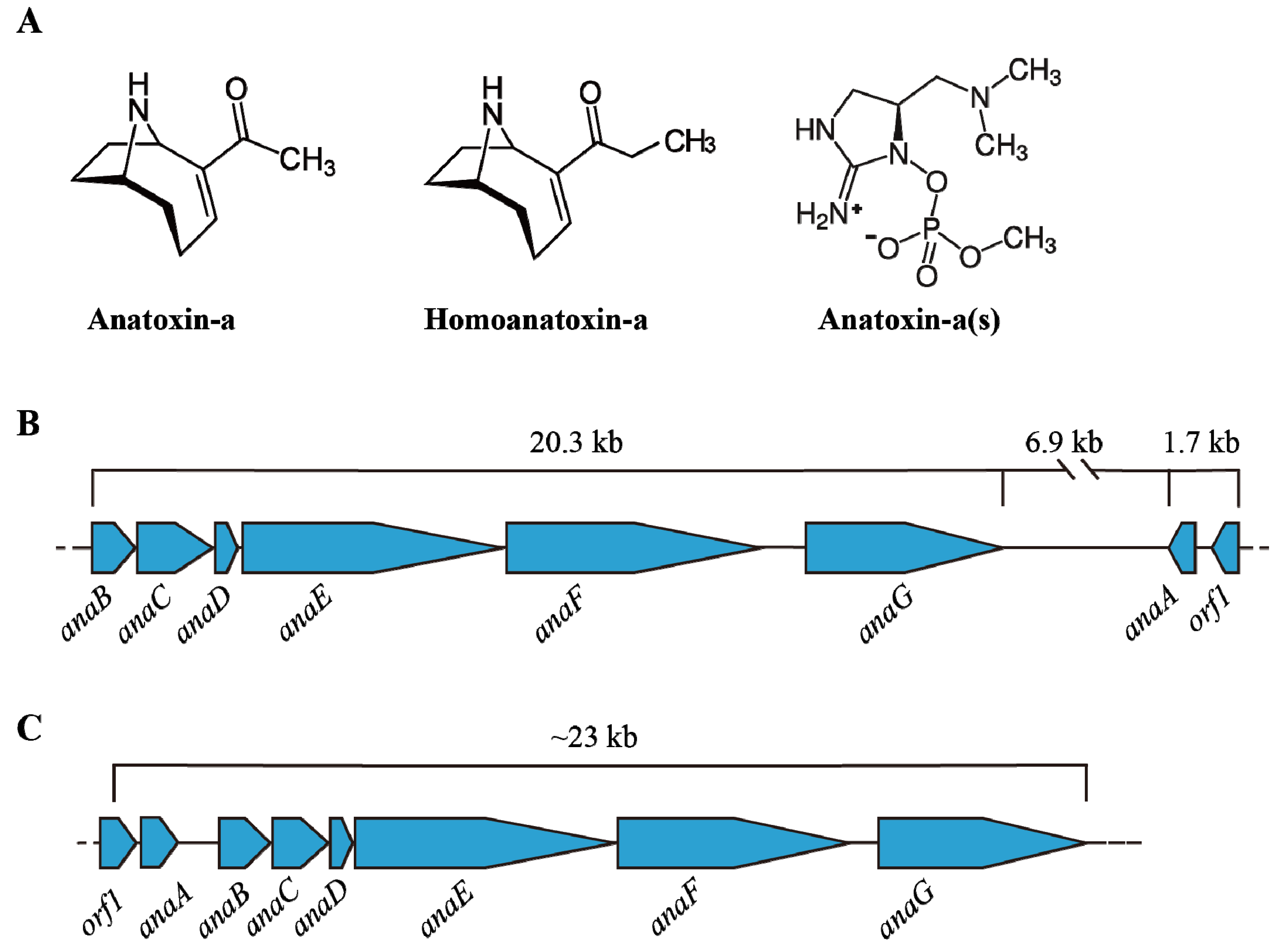
4. Anatoxins (ATXs)
4.1. Structure and Occurrence of ATXs
4.2. Transcription of Ana Cluster
4.3. Environmental Impact on ATX
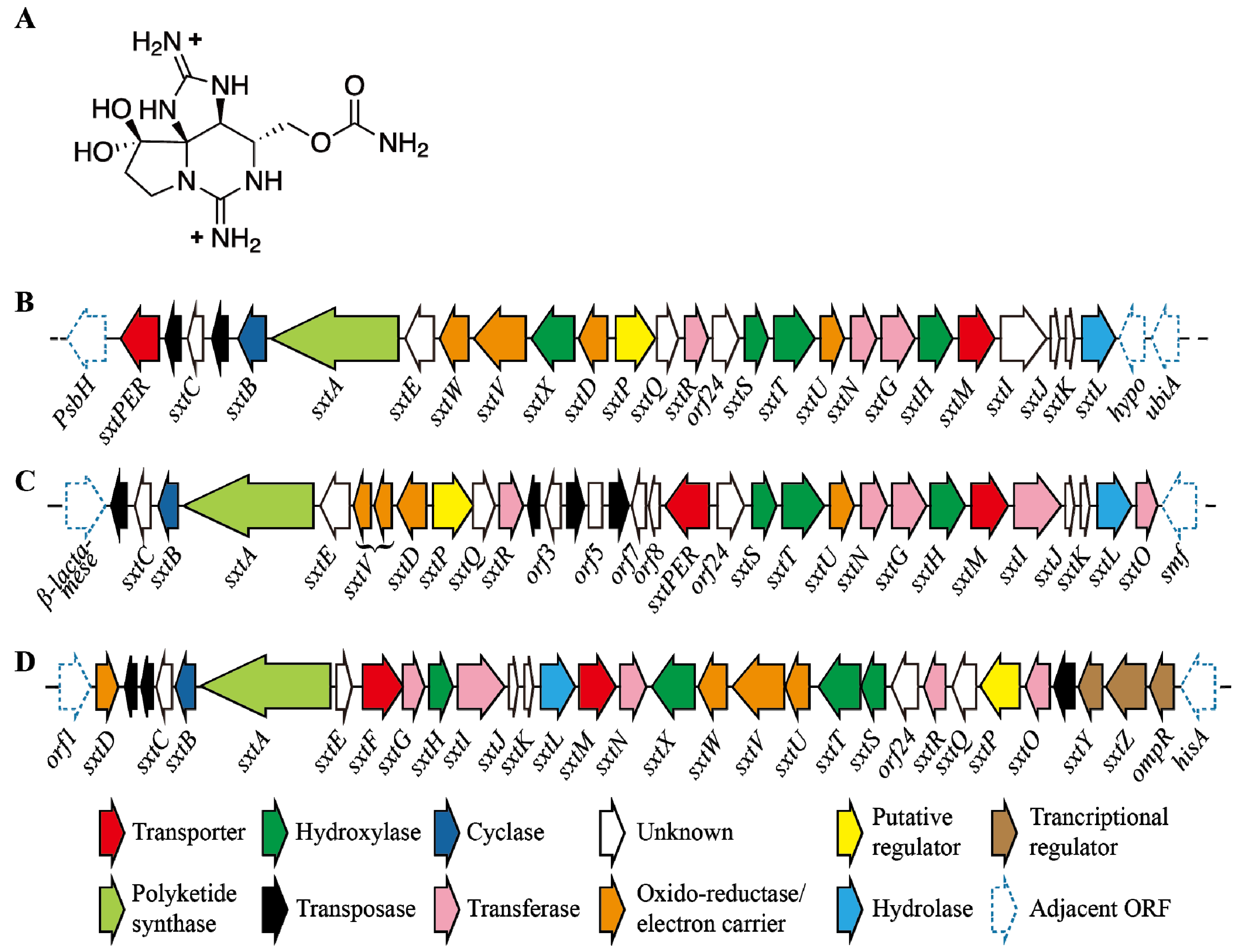
5. Saxitoxin
5.1. Structure and Toxicity of STXs
5.2. Regulation of STX Production
5.3. Impact of Environmental Factors
| Toxin | Gene cluster | Up regulating factors | Down regulating factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCs | mcy | active photosynthesis | FurA |
| N-limitation | |||
| more nitrate | |||
| NtcA | |||
| FurA | |||
| RcaA | |||
| 2-OG | |||
| high light intensity | |||
| NODs | nda | Nitrogen fixation | Ammonia supplementation high salinity high inorganic nitrogen |
| NtcA | |||
| Phosphate starvation | |||
| light stress | |||
| high temperature | |||
| CYNs | cyr/aoa | lack on fixed N source | Ammonia as N-source high light intensity (initially) phosphate limitation |
| phosphate limitation | |||
| high light intensity | |||
| (more incubation) | |||
| ATXs | ana | N-starvation | High temperature |
| sub optimal light | |||
| sub optimal temperature | |||
| green algal extract | |||
| (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii) | |||
| STXs | stx | High light intensity | High Nitrogen Dark conditions |
| High temperature | |||
| sub optimal temperature | |||
| Extracellular salt (NaCl) |
6. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoll, A.H. Cyanobacteria and Earth History. In The Cyanobacteria: Molecular Biology, Genomics, and Evolution; Herrero, A., Flores, E., Eds.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2008; p. 484. [Google Scholar]
- Schopf, J.W. The Fossil Record: Tracing the Roots of the Cyanobacterial Lineage. In The Ecology of Cyanobacteria; Whitton, B., Potts, M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 13–35. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, M.M.; Li, Z.; Effler, T.C.; Hauser, L.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Comparative metagenomics of toxic freshwater Cyanobacteria bloom communities on two continents. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkanen, S.; Pulina, S.; Engstrom-Ost, J.; Lehtiniemi, M.; Lehtinen, S.; Brutemark, A. Climate change and eutrophication induced shifts in northern summer plankton communities. PLoS One 2013, 8, e66475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.A. Is the future blue-green? A review of the current model predictions of how climate change could affect pelagic freshwater cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, S.; Mougin, C.; Bouaicha, N. Cyanobacterial toxins: Modes of actions, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops. Chemosphere 2014, 96, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.Y.; Liang, S.; Lee, J. Toxin-producing cyanobacteria in freshwater: A review of the problems, impact on drinking water safety, and efforts for protecting public health. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, A.; Harel, M.; Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Hadas, O.; Sukenik, A.; Dittmann, E. The languages spoken in the water body (or the biological role of cyanobacterial toxins). Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 138:1–138:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaebernick, M.; Neilan, B.A. Ecological and molecular investigations of cyanotoxin production. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilan, B.A.; Pearson, L.A.; Muenchhoff, J.; Moffitt, M.C.; Dittmann, E. Environmental conditions that influence toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, L.; Mihali, T.; Moffitt, M.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1650–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, M.T.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Allelopathy in freshwater cyanobacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 35, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, P.N.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Allelopathic activity of cyanobacteria on green microalgae at low cell densities. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinteich, J.; Wood, S.A.; Kupper, F.C.; Camacho, A.; Quesada, A.; Frickey, T.; Dietrich, D.R. Temperature-related changes in polar cyanobacterial mat diversity and toxin production. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Drakare, S.; Bertilsson, S.; Pernthaler, J.; Peura, S.; Rofner, C.; Simek, K.; Yang, Y.; Znachor, P.; Lindstrâm, E.S. Unveiling distribution patterns of freshwater phytoplankton by a next generation sequencing based approach. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Brett, M.T.; Muller-Solger, A.; Goldman, C.R. Climatic forcing and primary productivity in a subalpine lake: Interannual variability as a natural experiment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosten, S.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Bécares, E.; Costa, L.S.; van Donk, E.; Hansson, L.-A.; Jeppesen, E.; Kruk, C.; Lacerot, G.; Mazzeo, N.; et al. Warmer climates boost cyanobacterial dominance in shallow lakes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Farnsley, S.E.; LeCleir, G.R.; Layton, A.C.; Satchwell, M.F.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Boyer, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W. The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuiper-Goodman, T.; Falconer, I.; Fitzgerald, J. Human Health Aspects. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E & FN Spon Publishers: London, UK, 1999; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- Van Apeldoorn, M.E.; van Egmond, H.P.; Speijers, G.J.; Bakker, G.J. Toxins of cyanobacteria. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2007, 51, 7–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W.W. Health effects of toxin-producing cyanobacteria: “The CyanoHAB”. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2001, 7, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilliges, Y.; Kehr, J.-C.; Meissner, S.; Ishida, K.; Mikkat, S.; Hagemann, M.; Kaplan, A.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. The cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin binds to proteins and increases the fitness of Microcystis under oxidative stress conditions. PLoS One 2011, 6, e17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmayer, R. The toxic cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain 152 produces highest amounts of microcystin and nostophycin under stress conditions. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.J.; Dietrich, D.R. Pathological and biochemical characterization of microcystin-induced hepatopancreas and kidney damage in carp (Cyprinus carpio). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2000, 164, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.J.; Altheimer, S.; Cattori, V.; Meier, P.J.; Dietrich, D.R.; Hagenbuch, B. Organic anion transporting polypeptides expressed in liver and brain mediate uptake of microcystin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochimsen, E.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; An, J.; Cardo, D.M.; Cookson, S.T.; Holmes, C.E.; Antunes, M.B.; Filho, D.A.D.; Lyra, T.M.; Barreto, V.S.T. Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Sun, H.; Xie, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, N.; Yan, W.; Li, G. The role of apoptosis in MCLR-induced developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 149, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermeyer, T.J.; Schmieder, P.; Kurmayer, R. Isolation of Microcystins from the Cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens Strain No80. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2014, 4, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Incharoensakdi, A. The cyanotoxin-microcystins: Current overview. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.M.; Wannicke, N. Climate change and regulation of hepatotoxin production in Cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neilan, B.A.; Pearson, L.A.; Moffitt, M.C.; Mihali, K.T.; Kaebernick, M.; Kellmann, R.; Pomati, F. The genetics and genomics of cyanobacterial toxicity. In Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms: State of the Science and Research Needs; Hudnell, H.K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 417–452. [Google Scholar]
- Kaasalainen, U.; Fewer, D.P.; Jokela, J.; Wahlsten, M.; Sivonen, K.; Rikkinen, J. Cyanobacteria produce a high variety of hepatotoxic peptides in lichen symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5886–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaasalainen, U.; Fewer, D.P.; Jokela, J.; Wahlsten, M.; Sivonen, K.; Rikkinen, J. Lichen species identity and diversity of cyanobacterial toxins in symbiosis. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Characterization of the nodularin synthetase gene cluster and proposed theory of the evolution of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6353–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexova, R.; Haynes, P.; Ferrari, B.; Neilan, B. Comparative protein expression in different strains of the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, 3749–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Kuhajek, J.M.; Winton, M.; Phillips, N.R. Species composition and cyanotoxin production in periphyton mats from three lakes of varying trophic status. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 79, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouhiainen, L.; Vakkilainen, T.; Siemer, B.L.; Buikema, W.; Haselkorn, R.; Sivonen, K. Genes coding for hepatotoxic heptapeptides (microcystins) in the cyanobacterium Anabaena strain 90. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christiansen, G.; Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin biosynthesis in Planktothrix: Genes, evolution, and manipulation. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaebernick, M.; Dittmann, E.; Börner, T.; Neilan, B.A. Multiple alternate transcripts direct the biosynthesis of microcystin, a cyanobacterial. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, H.P.; Pearson, L.A.; Neilan, B.A. NtcA from Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 is autoregulatory and binds to the microcystin promoter. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4362–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexova, R.; Fujii, M.; Birch, D.; Cheng, J.; Waite, T.D.; Ferrari, B.C.; Neilan, B.A. Iron uptake and toxin synthesis in the bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa under iron limitation. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1064–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Olman, V.; Mao, F.; Xu, Y. Comparative genomics analysis of NtcA regulons in cyanobacteria: Regulation of nitrogen assimilation and its coupling to photosynthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5156–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque, I.; Vazquez-Bermudez, M.F.; Paz-Yepes, J.; Flores, E.; Herrero, A. In vivo activity of the nitrogen control transcription factor NtcA is subjected to metabolic regulation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 236, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasubramanian, T.S.; Wei, T.F.; Oldham, A.K.; Golden, J.W. Transcription of the Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 ntcA gene: Multiple transcripts and NtcA binding. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuniyoshi, T.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Lopez-Gomollon, S.; Valladares, A.; Bes, M.T.; Fillat, M.F.; Peleato, M.L. 2-oxoglutarate enhances NtcA binding activity to promoter regions of the microcystin synthesis gene cluster. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 3921–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermilova, E.V.; Forchhammer, K. PII signaling proteins of cyanobacteria and green algae. New features of conserved proteins. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 60, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-X.; Jiang, Y.-L.; He, Y.-X.; Chen, Y.-F.; Teng, Y.-B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.-C.; Zhou, C.-Z. Structural basis for the allosteric control of the global transcription factor NtcA by the nitrogen starvation signal 2-oxoglutarate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12487–12492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, A.; Muro-Pastor, A.; Flores, E. Nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, B.M.; Jones, G.J.; Orr, P.T. Cellular microcystin content in N-limited Microcystis aeruginosa can be predicted from growth rate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkilen, H.; Gjølme, N. Toxin production by Microcystis aeruginosa as a function of light in continuous cultures and its ecological significance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Downing, T.G.; Meyer, C.; Gehringer, M.M.; van de Venter, M. Microcystin content of Microcystis aeruginosa is modulated by nitrogen uptake rate relative to specific growth rate or carbon fixation rate. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, T.G.; Sember, C.S.; Gehringer, M.M.; Leukes, W. Medium N:P ratios and specific growth rate comodulate microcystin and protein content in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 and M. aeruginosa UV027. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 49, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, E.; Martin-Luna, B.; Vela, L.; Bes, M.T.; Peleato, M.L.; Fillat, M. Microcystin-LR synthesis as response to nitrogen: Transcriptional analysis of the mcyD gene in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonk, L.; van de Waal, D.B.; Slot, P.; Huisman, J.; Matthijs, H.C.; Visser, P.M. Amino acid availability determines the ratio of microcystin variants in the cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Lürling, M.; van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; Huisman, J. The ecological stoichiometry of toxins produced by harmful cyanobacteria: An experimental test of the carbon-nutrient balance hypothesis. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Finke, J.F.; Vournazou, V.; Immers, A.K.; Kardinaal, W.E.A.; Tonk, L.; Becker, S.; van Donk, E.; Visser, P.M.; et al. Reversal in competitive dominance of a toxic versus non-toxic cyanobacterium in response to rising CO2. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnichen, S.; Long, B.M.; Petzoldt, T. Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa: Direct regulation by multiple environmental factors. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horst, G.P.; Sarnelle, O.; White, J.D.; Hamilton, S.K.; Kaul, R.B.; Bressie, J.D. Nitrogen availability increases the toxin quota of a harmful cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Res. 2014, 54, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monchamp, M.-E.; Pick, F.R.; Beisner, B.E.; Maranger, R. Nitrogen forms influence microcystin concentration and composition via changes in cyanobacterial community structure. PLoS One 2014, 9, e85573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Song, L.; Sedmak, B. UVB Radiation as a potential selective factor favoring microcystin producing bloom forming cyanobacteria. PLoS One 2013, 8, e73919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaebernick, M.; Neilan, B.A.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. Light and the transcriptional response of the microcystin biosynthesis gene cluster. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3387–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonk, L.; Visser, P.M.; Christiansen, G.; Dittmann, E.; Snelder, E.O.; Wiedner, C.; Mur, L.R.; Huisman, J. The microcystin composition of the cyanobacterium Planktothrix agardhii changes toward a more toxic variant with increasing light intensity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5177–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, A.; Axelsson, R.; Lindberg, P.; Troshina, O.Y.; Wünschiers, R.; Lindblad, P. Cloning and characterisation of a hyp gene cluster in the filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. strain PCC 73102. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 201, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, E.; Martin-Luna, B.; Bes, M.T.; Fillat, M.; Peleato, M.L. An active photosynthetic electron transfer chain required for mcyD transcription and microcystin synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, R.R.; Downing, T.G. A growth advantage for microcystin production by Microcystis PCC7806 under high light. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deblois, C.P.; Juneau, P. Relationship between photosynthetic processes and microcystin in Microcystis aeruginosa grown under different photon irradiances. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, E.; Martin-Luna, B.; Vela, L.; Bes, M.T.; Fillat, M.F.; Peleato, M.L. Iron availability affects mcyD expression and microcystin-LR synthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, M.M.; Adler, L.; Roberts, A.A.; Moffitt, M.C.; Mihali, T.K.; Mills, T.J.T.; Fieker, C.; Neilan, B.A. Nodularin, a cyanobacterial toxin, is synthesized in planta by symbiotic Nostoc sp. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1834–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur-Marzec, H.; Meriluoto, J.; Plinski, M.; Szafranek, J. Characterization of nodularin variants in Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, S.; Valladares, A.; Flores, E.; Herrero, A. Transcription activation by NtcA in the absence of consensus NtcA-binding sites in an anabaena heterocyst differentiation gene promoter. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2939–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasson, S.; Vintila, S.; Sivonen, K.; El-Shehawy, R. Expression of the nodularin synthetase genes in the Baltic Sea bloom-former cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena strain AV1. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vintila, S.; El-Shehawy, R. Ammonium ions inhibit nitrogen fixation but do not affect heterocyst frequency in the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena strain AV1. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3704–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, S.; Fastner, J.; Dittmann, E. Microcystin production revisited: Conjugate formation makes a major contribution. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vob, B.; Bolhuis, H.; Fewer, D.P.; Kopf, M.; Moke, F.; Haas, F.; El-Shehawy, R.; Hayes, P.; Bergman, B.; Sivonen, K.; et al. Insights into the physiology and ecology of the brackish-water-adapted cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena CCY9414 based on a genome-transcriptome analysis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e60224. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtimaki, J.; Moisander, P.; Sivonen, K.; Kononen, K. Growth, nitrogen fixation, and nodularin production by two baltic sea cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schembri, M.; Neilan, B.; Saint, C. Identification of genes implicated in toxin production in the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmouz, R.; Chapuis-Hugon, F.; Mann, S.; Pichon, V.; Mejean, A.; Ploux, O. Biosynthesis of cylindrospermopsin and 7-epicylindrospermopsin in Oscillatoria sp. strain PCC 6506: Identification of the cyr gene cluster and toxin analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4943–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.I.; Ohtani, I.; Iwamoto, K.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, M.F.; Watanabe, M.; Terao, K. Isolation of cylindrospermopsin from a cyanobacterium Umezakia natans and its screening method. Toxicon 1994, 32, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banker, R.; Carmeli, S.; Hadas, O.; Teltsch, B.; Porat, R.; Sukenik, A. Identification of cylindrospermopsin in Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Cyanophyceae) isolated from lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt-Oliveira, M.D.C.; Piccin-Santos, V.; Kujbida, P.; Moura, A.D.N. Cylindrospermopsin in Water Supply Reservoirs in Brazil Determined by Immunochemical and Molecular Methods. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2011, 3, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.; Davis, T.; Muenchhoff, J.; Pratama, R.; Jex, A.; Burford, M.; Neilan, B. Comparative genomics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains with differential toxicities. BMC Genomics 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, C.; Ikuko, M.; Runnegar, M. Cylindrospermopsin: A potent hepatotoxin from the blue-green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 7941–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoof, L.; Berg, K.; Rapala, J.; Lahti, K.; Lepist, L.; Metcalf, J.; Codd, G.; Meriluoto, J. First observation of cylindrospermopsin in Anabaena lapponica isolated from the boreal environment (Finland). Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 21, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.; Pearson, L.; Davis, T.; Burford, M.; Orr, P.; Neilan, B. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones, is climate change responsible? Water Res. 2012, 46, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnear, S. Cylindrospermopsin: A decade of progress on bioaccumulation research. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 542–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banker, R.; Carmeli, S.; Werman, M.; Teltsch, B.; Porat, R.; Sukenik, A. Uracil moiety is required for toxicity of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin cylindrospermopsin. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2001, 62, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banker, R.; Teltsch, B.; Sukenik, A.; Carmeli, S. 7-Epicylindrospermopsin, a toxic minor metabolite of the cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon ovalisporum from Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Brittain, S.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Liu, Y.; Watanabe, M.M. First report of the cyanotoxins cylindrospermopsin and deoxycylindrospermopsin from Raphidiopsis curvata (Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briand, J.-F.; Jacquet, S.; Bernard, C.; Humbert, J.-F. Health hazards for terrestrial vertebrates from toxic cyanobacteria in surface water ecosystems. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiswell, R.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Eaglesham, G.; Smith, M.J.; Norris, R.L.; Seawright, A.A.; Moore, M.R. Stability of cylindrospermopsin, the toxin from the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: Effect of pH, temperature, and sunlight on decomposition. Environ. Toxicol. 1999, 14, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormer, L.; Cirés, S.; Carrasco, D.; Quesada, A. Cylindrospermopsin is not degraded by co-occurring natural bacterial communities during a 40-day study. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Yu, G.; Sano, T.; Pan, Q.; Li, R. Molecular basis and phylogenetic implications of deoxycylindrospermopsin biosynthesis in the cyanobacterium Raphidiopsis curvata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runnegar, M.T.; Xie, C.; Snider, B.B.; Wallace, G.A.; Weinreb, S.M.; Kuhlenkamp, J. In vitro hepatotoxicity of the cyanobacterial alkaloid cylindrospermopsin and related synthetic analogues. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 67, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humpage, A.R.; Fontaine, F.; Froscio, S.; Burcham, P.; Falconer, I.R. Cylindrospermopsin genotoxicity and cytotoxicity: Role of cytochrome P-450 and oxidative stress. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2005, 68, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froscio, S.M.; Humpage, A.R.; Burcham, P.C.; Falconer, I.R. Cylindrospermopsin induced protein synthesis inhibition and its dissociation from acute toxicity in mouse hepatocytes. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runnegar, M.T.; Kong, S.-M.; Zhong, Y.-Z.; Ge, J.-L.; Lu, S.C. The role of glutathione in the toxicity of a novel cyanobacterial alkaloid cylindrospermopsin in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 201, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runnegar, M.T.; Kong, S.-M.; Zhong, Y.-Z.; Lu, S.C. Inhibition of reduced glutathione synthesis by cyanobacterial alkaloid cylindrospermopsin in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, C.; Harvey, M.; Briand, J.; Biré, R.; Krys, S.; Fontaine, J. Toxicological comparison of diverse Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii strains: Evidence of liver damage caused by a French C. raciborskii strain. Environ. Toxicol. 2003, 18, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Preliminary evidence for in vivo tumour initiation by oral administration of extracts of the blue green alga Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii containing the toxin cylindrospermopsin. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, E.; Zehr, R.; Gage, M.; Humpage, A.R.; Falconer, I.R.; Marr, M.; Chernoff, N. The cyanobacterial toxin, cylindrospermopsin, induces fetal toxicity in the mouse after exposure late in gestation. Toxicon 2007, 49, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saker, M.; Neilan, B.; Griffiths, D. Two morphological forms of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) isolated from Solomon Dam, Palm Island, Queensland. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byth, S. Palm Island mystery disease. Med. J. Aust. 1980, 2, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stuken, A.; Jakobsen, K. The cylindrospermopsin gene cluster of Aphanizomenon sp. strain 10E6: Organization and recombination. Microbiology 2010, 156, 2438–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihali, T.K.; Kellmann, R.; Muenchhoff, J.; Barrow, K.D.; Neilan, B.A. Characterization of the gene cluster responsible for cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenchhoff, J.; Siddiqui, K.S.; Poljak, A.; Raftery, M.J.; Barrow, K.D.; Neilan, B.A. A novel prokaryotic L-arginine:glycine amidinotransferase is involved in cylindrospermopsin biosynthesis. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3844–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalev-Malul, G.; Lieman-Hurwitz, J.; Viner-Mozzini, Y.; Sukenik, A.; Gaathon, A.; Lebendiker, M.; Kaplan, A. An AbrB-like protein might be involved in the regulation of cylindrospermopsin production by Aphanizomenon ovalisporum. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.W.; Orr, P.T.; Boyer, G.L.; Burford, M.A. Investigating the production and release of cylindrospermopsin and deoxy-cylindrospermopsin by Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii over a natural growth cycle. Harmful Algae 2014, 31, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, M.L.; Neilan, B.A. Varied diazotrophies, morphologies, and toxicities of genetically similar isolates of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (nostocales, cyanophyceae) from Northern Australia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stucken, K. Physiogenomics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Raphidiopsis brookii with Emphasis on Cyanobacterial Evolution, Nitrogen Control and Toxin Biosynthesis. In Faculty of Biology and Chemistry; University of Bremen: Bremen, Germany, 2010; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Bacsi, I.; Vasas, G.; Suranyi, G.; M-Hamvas, M.; Mathe, C.; Toth, E.; Grigorszky, I.; Gaspar, A.; Toth, S.; Borbely, G. Alteration of cylindrospermopsin production in sulfate- or phosphate-starved cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon ovalisporum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Yosef, Y.; Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Viner-Mozzini, Y.; Kaplan, A. Enslavement in the water body by toxic Aphanizomenon ovalisporum, inducing alkaline phosphatase in phytoplanktons. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burford, M.A.; Davis, T.W.; Orr, P.T.; Sinha, R.; Willis, A.; Neilan, B.A. Nutrient-related changes in the toxicity of field blooms of the cyanobacterium, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, P.T.; Rasmussen, J.P.; Burford, M.A.; Eaglesham, G.K.; Lennox, S.M. Evaluation of quantitative real-time PCR to characterise spatial and temporal variations in cyanobacteria, Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszynska) Seenaya et Subba Raju and cylindrospermopsin concentrations in three subtropical Australian reservoirs. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Al-Shehri, A.M. Assessment of cylindrospermopsin toxin in an arid Saudi lake containing dense cyanobacterial bloom. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyble, J.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W. Effects of light intensity on cylindrospermopsin production in the cyanobacterial HAB species Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormans, M.; Lengronne, M.; Brient, L.; Duval, C. Cylindrospermopsin accumulation and release by the benthic cyanobacterium Oscillatoria sp. PCC 6506 under different light conditions and growth phases. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 92, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Shi, J.; Yang, S. The effect of pyrogallic acid on growth, oxidative stress, and gene expression in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). Ecotoxicology 2013, 22, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadel-Six, S.; Iteman, I.; Peyraud-Thomas, C.; Mann, S.; Ploux, O.; Mejean, A. Identification of a polyketide synthase coding sequence specific for anatoxin-a-producing Oscillatoria cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4909–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivonen, K.; Jones, G. Cyanobacterial Toxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; WHO E & FN Spon Publishers: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Osswald, J.; Rellan, S.; Gago, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Toxicology and detection methods of the alkaloid neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria, anatoxin-a. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 1070–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, W.; Gorham, P.; Biggs, D. Two laboratory case studies on the oral toxicity to calves of the freshwater cyanophyte (blue-green alga) Anabaena flos-aquae NRC-44-1. Can. Vet. J. 1977, 18, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, A.; Bober, B.; Lechowski, Z.; Bialczyk, J. Determination of anatoxin-a stability under certain abiotic factors. Harmful Algae 2013, 28, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, N. The toxins of cyanobacteria. Sci. Am. 1994, 270, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.A.; Selwood, A.I.; Rueckert, A.; Holland, P.T.; Milne, J.R.; Smith, K.F.; Smits, B.; Watts, L.F.; Cary, C.S. First report of homoanatoxin-a and associated dog neurotoxicosis in New Zealand. Toxicon 2007, 50, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, P.; Carmichael, W.W.; An, J.; Moestrup, O. Detection of an anatoxin-a(s)-like anticholinesterase in natural blooms and cultures of cyanobacteria/blue-green algae from Danish lakes and in the stomach contents of poisoned birds. Toxicon 1997, 35, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Scrimgeour, C.M.; Codd, G.A. Identification of anatoxin-A in benthic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and in associated dog poisonings at Loch Insh, Scotland. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duy, T.N.; Lam, P.K.; Shaw, G.R.; Connell, D.W. Toxicology and risk assessment of freshwater cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in water. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 163, 113–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merel, S.; Clement, M.; Thomas, O. State of the art on cyanotoxins in water and their behaviour towards chlorine. Toxicon 2010, 55, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Otero, P.; Alfonso, A.; Ramos, V.; Vasconcelos, V.; Araoz, R.; Molgo, J.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Detection of anatoxin-a and three analogs in Anabaena spp. cultures: New fluorescence polarization assay and toxin profile by LC-MS/MS. Toxins 2014, 6, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala-Ylinen, A.; Kana, S.; Wang, H.; Rouhiainen, L.; Wahlsten, M.; Rizzi, E.; Berg, K.; Gugger, M.; Sivonen, K. Anatoxin-a synthetase gene cluster of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain 37 and molecular methods to detect potential producers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7271–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méjean, A.; Mann, S.; Maldiney, T.; Vassiliadis, G.; Lequin, O.; Ploux, O. Evidence that biosynthesis of the neurotoxic alkaloids anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a in the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria PCC 6506 occurs on a modular polyketide synthase initiated by L-proline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7512–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peary, J.A.; Gorham, P.R. Influence of light and temperature on growth and toxin production by Anabaena flos-aquae. J. Phycol. 1966, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Bhaskar, A.S.B.; Rao, P.V.L. Growth characteristics and toxin production in batch cultures of Anabaena flos-aquae: Effects of culture media and duration. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapala, J.; Sivonen, K.; Luukkainen, R.; Niemelä, S. Anatoxin-a concentration in Anabaena and Aphanizomenon under different environmental conditions and comparison of growth by toxic and non-toxic Anabaena-strains—A laboratory study. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumke-Vogt, C.; Mailahn, W.; Rotard, W.; Chorus, I. A highly sensitive analytical method for the neurotoxin anatoxin-a, using GC-ECD, and first application to laboratory cultures. Phycologia 1996, 35, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapala, J.; Sivonen, K. Assessment of environmental conditions that favor hepatotoxic and neurotoxic Anabaena spp. strains cultured under light limitation at different temperatures. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araoz, R.; Nghiem, H.O.; Rippka, R.; Palibroda, N.; de Marsac, N.T.; Herdman, M. Neurotoxins in axenic oscillatorian cyanobacteria: Coexistence of anatoxin-a and homoanatoxin-a determined by ligand-binding assay and GC/MS. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearns, K.D.; Hunter, M.D. Green algal extracellular products regulate antialgal toxin production in a cyanobacterium. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 2, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, M.; Dagostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strichartz, G. Structural determinants of the affinity of saxitoxin for neuronal sodium channels. Electrophysiological studies on frog peripheral nerve. J. Gen. Physiol. 1984, 84, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Salata, J.J.; Bennett, P.B. Saxitoxin is a gating modifier of HERG K+ channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 121, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Sheets, M.; Ishida, H.; Li, F.; Barry, W.H. Saxitoxin blocks L-type ICa. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, B.; Shaw, G.R.; Morrall, J.; Senogles, P.; Woods, T.; Papageorgiou, J.; Kapralos, C.; Wickramasinghe, W.; Davis, B.; Eaglesham, G. Chlorination for degrading saxitoxins (paralytic shellfish poisons) in water. Environ. Technol. 2003, 24, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.J.; Negri, A.P. Persistence and degradation of cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish poisons (PSPs) in freshwaters. Water Res. 1997, 31, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Mihali, T.; Jeon, Y.; Pickford, R.; Pomati, F.; Neilan, B. Biosynthetic intermediate analysis and functional homology reveal a saxitoxin gene cluster in cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4044–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuken, A.; Campbell, R.; Quesada, A.; Sukenik, A.; Dadheech, P.; Wiedner, C. Genetic and morphologic characterization of four putative cylindrospermopsin producing species of the cyanobacterial genera Anabaena and Aphanizomenon. J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Liebe, K.; Murillo, A.A.; Krock, B.; Stucken, K.; Fuentes-Valdes, J.J.; Trefault, N.; Cembella, A.; Vasquez, M. Reassessment of the toxin profile of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3 and function of putative sulfotransferases in synthesis of sulfated and sulfonated PSP toxins. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plominsky, Á.M.; Soto-Liebe, K.; Vásquez, M. Optimization of 2D-PAGE protocols for proteomic analysis of two nonaxenic toxin-producing freshwater cyanobacteria: Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii and Raphidiopsis sp. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K.; Nagasawa, K.; Oshima, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Synthesis and identification of proposed biosynthetic intermediates of saxitoxin in the cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis (TA04) and the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Axat-2). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 3016–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihali, T.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. Characterisation of the paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis gene clusters in Anabaena circinalis AWQC131C and Aphanizomenon sp. NH-5. BMC Biochem. 2009, 10, 8:1–8:13. [Google Scholar]
- Chislock, M.F.; Sharp, K.L.; Wilson, A.E. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii dominates under very low and high nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios. Water Res. 2014, 49, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunes, J.S.; de la Rocha, S.; Giroldo, D.; Silveira, S.B.D.; Comin, R.; Bicho, M.D.S.; Melcher, S.S.; Sant’anna, C.L.; Vieira, A.A.H. Release of carbohydrates and proteins by a subtropical strain of Raphidiopsis brookii (cyanobacteria) able to produce saxitoxin at three nitrate concentrations. J. Phycol. 2009, 45, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B.A. Biochemical characterization paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis in vitro. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, R.L.; Santos, M.E.V.D.; Pacheco, A.B.F.; Azevedo, S.M.F.D.O.E. Effects of light intensity and light quality on growth and circadian rhythm of saxitoxins production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria). J. Plankton Res. 2009, 31, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.; Vera, D.; Lagos, N.; Garcia, C.; Vasquez, M. The effect of temperature on growth and production of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins by the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii C10. Toxicon 2004, 44, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, E.; Pereira, P.; Franca, S. Production of paralytic shellfish toxin Aphanizomenon sp. LMECYA 31 (Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomati, F.; Rossetti, C.; Manarolla, G.; Burns, B.P.; Neilan, B.A. Interactions between intracellular Na+ levels and saxitoxin production in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii T3. Microbiology 2004, 150, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Boopathi, T.; Ki, J.-S. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production. Toxins 2014, 6, 1951-1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6071951
Boopathi T, Ki J-S. Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production. Toxins. 2014; 6(7):1951-1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6071951
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoopathi, Thangavelu, and Jang-Seu Ki. 2014. "Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production" Toxins 6, no. 7: 1951-1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6071951
APA StyleBoopathi, T., & Ki, J.-S. (2014). Impact of Environmental Factors on the Regulation of Cyanotoxin Production. Toxins, 6(7), 1951-1978. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins6071951





