Abstract
Soil erosion can be linked to relative fractional cover of photosynthetic-active vegetation (PV), non-photosynthetic-active vegetation (NPV) and bare soil (BS), which can be integrated into erosion models as the cover-management C-factor. This study investigates the capability of EnMAP imagery to map fractional cover in a region near San Jose, Costa Rica, characterized by spatially extensive coffee plantations and grazing in a mountainous terrain. Simulated EnMAP imagery is based on airborne hyperspectral HyMap data. Fractional cover estimates are derived in an automated fashion by extracting image endmembers to be used with a Multiple End-member Spectral Mixture Analysis approach. The C-factor is calculated based on the fractional cover estimates determined independently for EnMAP and HyMap. Results demonstrate that with EnMAP imagery it is possible to extract quality endmember classes with important spectral features related to PV, NPV and soil, and be able to estimate relative cover fractions. This spectral information is critical to separate BS and NPV which greatly can impact the C-factor derivation. From a regional perspective, we can use EnMAP to provide good fractional cover estimates that can be integrated into soil erosion modeling.
1. Introduction
Monitoring and characterizing the evolution of various terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems on a global scale is the primary aim of the upcoming Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (EnMAP) German hyperspectral satellite mission [1]. In preparation for its launch in 2018, there is a need to assess the capabilities of this satellite to provide useful information for various types of environmental challenges related to human activity and climate change. One such challenge is land degradation, with nearly 19.65 percent of the terrestrial surface worldwide defined as degraded land as of the beginning of the 21st century [2]. One major aspect of land degradation is the loss of top soils due to erosional processes, causing multiple environmental and socio-economic consequences. According to the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations 2014, the definition for soil degradation follows largely the definition of the term land degradation, which is defined as the reduction in the capacity of land to provide ecosystem goods and services securing its function for all beneficiaries of the land. As such, the key objective of this study is to assess the capability of using simulated EnMAP imagery to derive essential land cover information in a regional context, specifically photosynthetic active vegetation (PV), non-photosynthetic active (NPV, including standing dry vegetation and litter) and bare soil (BS, including stones and rocks) fractional cover, that can be integrated into soil erosion models. The region of interest in this study is located west of San Jose, Costa Rica, and comprises a highly fragmented landscape characterized by urban, agricultural areas, and forests in a mountainous terrain.
Where water-driven soil erosion takes place there is commonly an associated loss of soil fertility. In agricultural regions, this negatively affects crop yields forcing farmers to expand agricultural areas or increase the use of fertilizers. Additionally, the eroded nutrients and sediments that travel to areas at lower elevations may cause several off-site effects such as the sedimentation of reservoirs or riverbed filling. This can result in decreased water quality or an increased flood risk [3]. An analysis of the linkage between land use type and soil erosion reveals that the degree and type of soils and vegetation cover from non-existing (e.g., BS) to sparse ground cover (e.g., living and dead grass) to full cover (e.g., forests) is of major importance in the assessment of the potential for soil erosion [4,5,6,7]. Of particular importance are the canopy, surface cover and below surface effects that vegetation has on limiting surface erosion [8]. Soils covered by dense vegetation are often characterized by a higher occurrence of organic carbon, enhanced infiltration, moisture, increased surface roughness and different soil structure/aggregates resulting in better growth conditions for other plants resulting in minimal soil erosion [9,10]. PV forests with dense canopy cover or thick PV grass cover can reduce the kinetic energy of rainfall by increasing interception. Associated root systems can further reduce run-off from loosening of soil particles and subsequent down slope redistribution [11] through physical binding of soil particles [12]. The role of NPV on soil erosion has been widely analyzed, where the occurrence of NPV can also significantly reduce the potential for soil erosion owing to partial canopy cover, loose vegetative cover (e.g., litter, slash, logs) or from existing or dead root systems that provide protection from flowing water [9,10]. As such, soil erosion potential is highest where soils are bare of PV or NPV. In such cases, soil type becomes an important factor as different soil types impact soil erodibility based on their composition, permeability and structure [13], for example fine grained clay rich soils tend to be more resistant to erosion [14].
The linkage between the structural composition of the landscape expressed with PV, NPV and BS types with landform characteristics is well known in soil erosion modeling that allows studying interactions of all parameters determining the type of degradation process. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and the Revised USLE (RUSLE) are empirical models calculating long-term averages of soil loss for a given time period based on soil properties, rainfall, terrain information, vegetation cover, and management type [13,15]. Similar input parameters are needed for the European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM) [9] that has been evaluated for modeling of event-based soil erosion in Costa Rica, Nicaragua and Mexico [16]. As such, there is a need to supply quality information of soil erosion parameters at regional scales that are relevant for land management practices.
Many studies have shown that optical Earth Observation (EO) can be a useful tool to measure landscape components on a large geographical scale. For example, Asner et al. [17] have used this concept for estimating canopy gap fractions and fractional photosynthetic cover to assess land cover change, ecological variability, and biogeochemical processes across the Amazon and bordering Cerrado regions of Brazil. An overview in Guerschman et al. [18] provides a wide range of studies targeting NPV, PV and BS fractional cover mapping using multispectral data like Landsat, ASTER and MODIS. This review has shown the great importance of such inventories due to the long-term availability of such sensors and the accessibility of data. In these studies, model and spectral mixture analysis based methods have been shown to provide useful fractional cover estimates. However, the results presented also highlight issues related to spectral separation of BS and NPV that reduced fractional cover accuracy. For example, Guerschman et al. [18] used NDVI and Cellulose Absorption Index (CAI) to unmix MODIS data which resulted in overall accuracy (RMSE) that was higher for NPV (25%) and BS (26%) compared with PV (17.2%). The results also noted that soil brightness and soil moisture were associated with poor model performance for BS and NPV estimates owing to confusion between NPV and BS due to similar surface reflectances. In Okin et al. [19], a comparison of multiple methods were used to estimate fractional cover of PV, NPV and BS using MODIS data. In general, lower correlations were also found for NPV and BS compared with PV where these results were attributed to the fact that NPV spectrum can be so similar to soils [20]. Low correlation between linear spectral unmixing fractions of non-photosynthetic matter and field measurements due to confusion with the spectrally very similar soil endmembers were also reported in De Asis and Omasa [11]. To better discriminate NPV and BS, Asner and Heidebrecht [21] identified the SWIR spectral wavelength region as more suitable if the spectral coverage (2.0–2.3 µm) is sufficient. Moreover, systems with low spectral resolutions like Landsat TM showed an overestimation of NPV compared to spectrally high resolution systems like AVIRIS [22]. The drawback of limited spectral information available in the short-wave infrared (SWIR) region of existing multispectral EO systems for a reliable differentiation between NPV and BS was also reported by [20,23]. In a comprehensive review targeting EO products for water erosion assessment [5], the authors identified that the accurate assessment of senescent vegetation as a major observation-related gap could be overcome by future satellite missions with improved spectral capabilities. Such seasonal changes can greatly impact the relative fractions of PV and NPV, and thus, must be accurately accounted for in soil erosion modeling [6].
Imaging spectroscopy sensors, commonly referred to as hyperspectral sensors, are characterized by recording the Earth surface by nearly continuous narrow spectral bands that can capture absorption features related to biochemical and geochemical Earth surface characteristics. The importance of imaging spectroscopic techniques and data are considered essential for monitoring of ecosystem function and value [24] and have been used for various soil mapping and soil degradation studies owing to the ability to identify surface materials and quantify surface properties [25,26]. For example, the physical based differentiation of NPV and exposed soil can be carried out due to specific absorption features of cellulose and lignin occurring in the SWIR region of the spectrum [22,27,28]. Additionally, the SWIR region also provides useful information on soil types, in particular the occurrence of clay minerals [29]. The potential of these reflectance characteristics has been successfully harnessed in several studies using airborne hyperspectral data (e.g., [22,30,31]). For example, deconvolving individual pixel spectra into their constituent components using spectral mixture analysis has been shown to be a useful tool to estimate subpixel information on vegetation cover and soil components [24,32]. However, airborne campaigns are not suitable for long-term and large scale operational monitoring of degradation processes because they are expensive and time-consuming. Multi-temporal surveys are also necessary to assess changes in phenology throughout the year that impact the relative abundance of PV vs. NPV [5,6] further making airborne campaigns less cost effective. The first experimental hyperspectral satellite, Hyperion, has provided high spectral resolution data, multi-temporal and spatial coverage for 15 years in addition to its original one-year lifespan. The sensor has been used in numerous studies related to vegetation and soils. For example, Bannari et al. [33] used field spectra in conjunction with Hyperion data to estimate and map crop residual in Saskatchewan, Canada. As shown by Ghosh et al. [34] Hyperion data provided useful spectral information to map salinization severity of irrigated soils and thus, provide useful information on land degradation processes. Wu et al. [35] introduce a methodology to map land degradation in Hengshan Country, China, based on several hyperspectral indices derived from Hyperion data. However, the system has been plagued by issues related to reduced instrumental performance [36,37], and is nearing the end of its lifespan [38]. Thus, moving forward the ability to study soil and landscape degradation processes such as soil erosion, new operational systems that can provide large spatial coverage with multi-temporal and high spectral resolution capabilities are necessary. Upcoming hyperspectral satellite systems such as EnMAP [39], HYSPIRI [40], HISUI [41] and others should be able to provide the required data on an operational basis.
The overall goal of this study is to analyze the potential of the future spaceborne hyperspectral EnMAP mission to estimate essential land cover information for large areas without the need of cost and labor intensive field surveys. The specific objectives are to (1) identify the spectral capabilities of EnMAP to distinguish between PV, NPV and BS, (2) to assess the spatial characteristics of EnMAP to detect large- and small-scale land cover pattern relevant for soil erosion and (3) to demonstrate the potential of EnMAP to automatically assess soil erosion parameters by linking fractional cover estimates from PV, NPV and BS to the RUSLE C-factor. This study makes use of a large scale airborne HyMap hyperspectral survey flown over portions of Costa Rica in 2005 and the EnMAP End-to-End Simulation tool (EeteS) developed at the Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum (GFZ) [42] to generate simulated EnMAP data. The study area south of San Jose, Costa Rica, is dominated by intensively managed crop types like coffee, bananas and grazing land, where soil erosion processes are visible. Fractional cover estimates are derived from the reflectance imagery using a spectral mixture analysis approach, specifically a Multiple End-member Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA) approach. Since no ground truth data were available in this study, plausibility checks concerning the spectral and spatial capabilities of EnMAP have been carried out using the airborne HyMap data. A similar approach was used in Rogge et al. [43] which used airborne data for plausibility checks to assess simulated EnMAP data for geological mapping. Although an independent reference is missing, the detailed qualitative and quantitative comparison of the EnMAP and HyMap results derived using the same methodological approach will give valuable insights into the capacities of the upcoming EnMAP satellite to provide useful information related to estimating soil erosion potential at a regional scale.
2. Study Area
The study was conducted in the province of San Jose and partially in the provinces Heredia and Alajuela located on the western side of Costa Rica (Figure 1). The 900 km2 area is delimited by the extent of the simulated EnMAP imagery and was chosen as the area is known for extensive coffee plantations and grazing in mountainous terrain which may be prone to soil erosion. The densely populated urban area of San Jose is located in the north-east corner of the imagery, but several smaller villages and settlements exist throughout the study area. Coffee plantations and grazing areas span a large portion of the study site with relatively dense occurrences in areas with moderate to high elevations (Figure 2). Agricultural activities are also present adjacent to many rivers that cross the study area. Elevations range from 200–2200 m with slopes as steep as 54 degrees occurring in the highest mountains (Figure 1). The climate is dominated by a tropical wet (May to November) and dry climate (December to April) with annual precipitation averaging between 2000 and 4000 mm and a mean annual temperature of 20.5 degree Celsius in the low elevations to 12–18 degrees Celsius in the mountains. The major soil types in the south of the region are ultisols [44], also known as red clay soils, which are defined as mineral soils without calcareous material and are considered more suitable for tree crop plantations than for the cultivation of food crops. Along the main river valleys of the study site, the dominating soil type is entisols, which are characteristic for landscapes where the soil material is not in place long enough for pedogenic processes to form distinctive horizons. The north of the study site is dominated by two major soil types, namely alfisols and inceptisols. Alfisols are characterized by a clay-enriched subhorizon. In contrast to ultisols, these soils show relatively high natural fertility and they are considered as a relatively important soil type regarding food and fiber productions. In the southern part of the study site, vertisols occur and are characterized as clayey soils which are considered relatively inappropriate for commercial agricultural use.
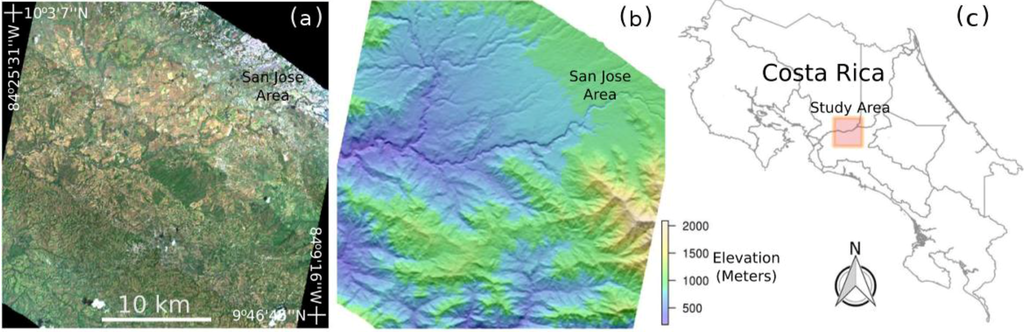
Figure 1.
(a) HyMap RGB true color mosaic of study area (~30 × 30 km) located in central Costa Rica near San Jose; (b) Digital elevation model of the study area; (c) Location within the country.

Figure 2.
Examples of the terrain characteristics of the study area which include extensive coffee plantations and grazing areas in rugged mountainous terrain.
3. Data
3.1. HyMap
Airborne HyMap hyperspectral imagery was provided by the Centre for Earth Observation, University of Alberta, Canada. The total data set consists of 232 hyperspectral flight-lines acquired during a flight period between 1 March and 6 April 2005 and covers approximately 85% of Costa Rica. This time period represents that later stages of the dry season with the area characterized by an abundance of NPV, with PV restricted to irrigated land and river valleys. The HyMap sensor comprises 125 contiguous spectral bands across the reflective solar wavelength region from 0.45–2.5 µm. For the given survey, the data were collected at a spatial resolution between 15.5 and 16.9 m owing to high variability in topography across the country. The data was originally georeferenced and atmospherically corrected by HyVista Corporation. However, owing to radiometric and reflectance inconsistencies between flight-lines the data was reprocessed following a standardized processing chain developed by the German Aerospace Center (DLR) which is integrated into the FP7 EUFAR (European Fleet for Airborne Research) project. Reprocessing included a data quality assessment [45], spectral wavelength calibration [46], georectification [47], rugged terrain atmospheric correction [46], BRDF correction [48], as well as the generation of an image mosaic for the study area (Figure 1). The spatial resolution of the reprocessed data was set to a uniform 15 m pixel size. Of the original bands, 16 were removed from the main water absorption regions near 1.4 and 1.9 µm, with the following wavelength ranges used for subsequent analysis: 0.454–1.310, 1.504–1.785, 2.010–2.445 µm. All of the processing steps used were done such that the highest quality reflectance mosaic could be generated and subsequently, be used to generate a high quality EnMAP simulation.
3.2. EnMAP
The EnMAP satellite will have 242 bands over the 0.420–2.450 µm spectral range at a varying spectral sampling of 0.0065–0.1 µm. Images will have a swath width of 30 km at an approximate ground sampling distance of 30 m. As part of the system’s development, the EnMAP End-to-End Simulation tool (EeteS) was developed at GFZ to provide an accurate simulation of the entire image generation, calibration and processing chain. EeteS is also being used to assist with overall system design, the optimization of fundamental instrument parameters, and the development and evaluation of data pre-processing and scientific-exploitation algorithms [42,49,50]. The reprocessed HyMap reflectance mosaic was used as an input to EeteS to generate an EnMAP-like image of the study area. In the first step the HyMap reflectance data was transformed into raw EnMAP data using a series of forward processing steps that model atmospheric conditions and account for spatial, spectral, and radiometric differences between the two sensors. The software then simulates the full EnMAP image processing chain, including onboard calibration, atmospheric correction and orthorectification to ultimately produce geocoded at-surface reflectance. Simulation parameters were chosen to gain comparable results regarding the HyMap data.
The resulting simulation area is approximately a 30 × 30 km area cropped slightly on the west and east sides as the simulation generated was done such that it followed the actual orbital path of EnMAP. The cropped area to the north and south is caused by the size of the original HyMap mosaic. After the simulation process was completed, 51 bands were removed. These are located within the main water absorption regions near 1.4 and 1.9 µm and within the overlapping region of EnMAPs two spectrometers between 0.905 and 0.980 µm. The resulting wavelength ranges to be used for subsequent analysis were set to match as closely as possible to that used with the HyMap data: 0.450–1.311, 1.499–1.783, 2.007–2.439 µm. As urban areas are not of interest in this study, we have made use of the 12 m pixel Global Urban Footprint (GUF) [51] made available by the DLR to mask these areas independently in both the HyMap and EnMAP imagery.
4. Methodology
4.1. Fractional Cover Estimation
The spatial resolution of airborne or spaceborne hyperspectral imagery can vary significantly (e.g., sub meter to 10s of meters). However, regardless of pixel size, the spectral signature of a given pixel is commonly a mixture, comprising the spectral characteristics of components that lie within the pixel. Based on the physical relationship between subpixel constituents and sensed signal, the proportion of a material in the signal is equal to the ground cover fraction of this material in the pixel, which can thus be quantitatively derived [52]. Assuming that there is no significant amount of multiple scattering, the sensed reflectance value ρ in band j for one image pixel can be approximated as the summation of the individual material reflectance functions ρj,e multiplied by their surface fraction fe within the effective ground-projected instantaneous field of view. Thus,
where δj denotes the residual error term. Furthermore, all fractions should be greater than or equal to zero, and less than or equal to one, and should sum to one. This constrained linear equation is then solved in a least-squares fashion using either singular value decomposition or the pseudoinverse. Key to spectral unmixing are pure spectral signatures, or spectral endmembers, of the various components within a pixel. Thus, for spectral unmixing approaches, the first step is the collection of endmembers before subsequently deconvolving the pixel spectra into its fractional abundances.
The collection of spectral endmembers aims to find the most pure spectral representations of the materials of interest. This can be accomplished by deriving a suite of endmembers that are collected in the field or laboratory, or based on the image data itself. The latter option is used in this study as spectral measurements from the field for the given cover types are not available and would commonly not be available when doing large regional surveys. Representative class spectra were extracted for PV, NPV and BS using the updated spatial spectral endmember extraction tool (SSEE) [53], which was specifically adapted to work with large images or multiple flight-line data sets. A brief overview of the three main steps of SSEE are as follows. The image is first divided into equal sized non-overlapping subset regions where a set of eigenvectors that explain the majority of spectral variance is calculated for each subset via singular value decomposition. In the second step the image data are projected onto the local eigenvectors compiled from all subset regions and those pixels that lie at either extreme of the vectors are retained as candidate endmembers. The third step averages the candidate pixels with all other pixels within a given spatial window that are also spectrally similar based on a minimum spectral angle [54]. SSEE generally finds a larger endmember set compared with other spectral based automated endmember extraction methods. However, many of the additional spectra derived using SSEE comprise spectrally similar, but spatially independent, surface materials. As such, the approach allows for a good representation of the intra-class variability within a given class type and allows for expert knowledge to be integrated in the selection process to select a final endmember set appropriate for a specific application. In this study, the resulting candidate endmembers derived from SSEE were grouped into four main classes PV, NPV BS and other (e.g., urban materials, water). Within each of the PV, NPV, and BS classes, the individual spectra comprise the inter- and intra-class variability necessary for performing MESMA to derive fractional cover estimates.
Since plant species and soil types are normally not constant in one scene, it is unlikely that only one PV, NPV or BS component can adequately represent the spectral variability of its ground cover class, and thus, model the whole image effectively. As such, the MESMA approach was developed where the main concept is to optimize the endmember set for each pixel independently based on the inter- and intra-class variability contained in a multiple endmember set, in this case derived from SSEE. The implementation of the general MESMA approach [55] used in this study is µMESMA, which has been successfully applied for the quantification of fractional ground coverage in semi-arid environments [56,57] and also in the context of soil and mineral mapping (e.g., [31,58]). Within µMESMA, each pixel is modeled by three endmember classes, namely PV, NPV and BS, plus an optional shade component, with one spectrum of each endmember class being used at a time. Spectra related to the fourth class comprising urban and water materials are not used in this approach. All possible combinations of endmembers belonging to the three classes are calculated, and the combination having the smallest modeling error is then selected. This optimized combination for pixel unmixing is defined by the lowest root mean squared error (RMSE), predefined abundance constraints and by the consideration of class specific absorption features of the spectra (e.g., chlorophyll absorption, clay-OH-absorption, or ligno cellulose). The latter being specific to µMESMA. As a result, accurate fractions for each class, and thereby the ground cover fractions, are retrieved for each pixel.
In the context of this study, a first iteration of µMESMA was carried out using the SSEE derived endmember classes for PV, NPV and BS. Subsequently, µMESMA highlights pixel spectra that have a high modeling error as possible additional endmembers, which were then interactively checked and included in the final endmember set. In addition to the endmembers for PV, NPV and BS, a shade component was included. The final abundances where then adjusted for the shade component, and rescaled accordingly.
4.2. C-Factor Analysis
The assessment of soil erosion commonly utilizes predictive models such as the USLE or RUSLE [13,59,60]. As the initial application purpose of USLE was to provide conservationists with a tool supporting decisions on sustainable cropping or management strategies its applications are limited to long-term estimations of annual soil loss. The final outcome from USLE is the soil loss per unit area A and is calculated as:
R is defined as the rainfall-erosivity index. K is the soil erodibility factor, which represents both the susceptibility of soil to erosion and the rate of runoff. The L and S parameters together are defined as the topographic factor LS, which is a product of slope length and slope steepness. The intensity of management and land cover on soil loss is expressed by the crop and management factor C, where this parameter is estimated based on a ratio between erosion rates on BS and under different cropping systems. The consideration of the effectiveness of the plant cover/canopy to reduce energy from rainfall, type of tillage management and organic matter production makes the derivation of this factor rather challenging and to some extent subjective. For RUSLE the C-factor was changed such that it was not tied to agricultural settings [13]. Similar to the C-factor, the conservation practice factor, P, accounts for management practices (e.g., contouring, stripe cropping or terracing) [61].
In this study, one objective is to derive land cover fractions to be used to calculate the C-factor using the airborne and simulated spaceborne hyperspectral datasets. It is considered to be one of the more difficult coefficients to estimate and commonly makes use of ground measurements to derive empirical equations which are not always sufficient to represent the variability in vegetative cover over large geographic areas [6,11]. As such, the use of remote sensing has become an alternative to estimate the C-factor which allows for continuous spatial coverage and multi-temporal analysis of fractional cover.
As proposed by De Asis and Omasa [11] the C-factor using remote sensing imagery is calculated as:
where fractional cover of soil (fC_{BS}) is divided by the degree of vegetative surface cover defined as the sum of abundance values received for PV and non-photosynthetic-active matter (NPM) (fC_{PV} + fC_{NPM}). Note in this work we use NPV instead of NPM, where NPV includes both loose and standing non-photosynthetic-active vegetation. In this context, the C-factor is independent of the imagery used to estimate the cover fractions. However, successful applications of RUSLE in tropical ecosystem, as nicely reviewed by Labrière et al. [7], reinforce the decision to focus on the capabilities of hyperspectral data to derive the C-factor.
Two C-factor fractional cover maps are produced. The first case is based on Equation (3) where PV and NPV are combined in the denominator. In the second case, NPV is combined with BS in the numerator. The rational for these two cases are to highlight the importance of being able to distinguish and separate fractional cover for BS and NPV. In these two cases we assume PV and NPV carry equal weight in the ability to reduce soil erosion.
4.3. Plausibility Check Approach
As ground data were not available, an assessment of EnMAP-derived products was done by comparing them with products derived from the airborne HyMap data which has different spectral and spatial characteristics. The assessment will first consider the endmembers derived from SSEE for both data sets where specific attention is placed on the ability of EnMAP to extract similar endmembers that include important spectral characteristics for discriminating PV, NPV and BS. This is followed by qualitative and quantitative comparisons of spatial and statistical distributions of the fractional estimates for PV, NPV and BS. It is also assessed how MESMA uses the derived endmembers from the two image data sets to calculate fractional cover. This careful comparison will provide insights on the potential and limitations of the EnMAP spaceborne sensor for the given application, in particular how a reduced spatial resolution and lower signal-to-noise ratio influences the proposed workflow.
5. Results
5.1. Endmember Extraction
For the implementation of SSEE, the following key input parameters were used: window size = 24 pixels; SVD threshold = 99% of variance. The HyMap images delivered in total 700 candidate endmember pixels that represent 0.0175 percent of all non-zero pixels within the reflectance image. Of these, 587 pixels represented urban or water surface components, 49 endmembers where detected for PV, 51 for NPV and only 13 pixels for exposed soils. The final libraries consist of 18 spectra for the class PV, 17 for NPV as well as 10 spectra for BS. Furthermore, the 18 PV spectra can be divided based on the shape of the spectra into six sub classes, for NPV four sub classes have been identified and the BS endmembers indicate the occurrence of five different BS sub classes. Figure 3 shows, for clarity only, the mean spectra for each sub class. In the case of EnMAP, having a coarser spatial, but spectrally finer resolution than HyMap, urban or water components are represented with 260 candidate endmembers, PV with 110, NPV 105 and BS with only 13, in total making up 0.0488 percent of all non-zero pixels within the simulated image. For the final library, PV is supported with 20 total spectra and NPV with 16 spectra with each class divided into six and four sub classes, respectively. For the final 13 BS endmembers identified, only three different BS sub classes were determined. For PV and NPV, sub classes derived from the EnMAP data match those sub classes from HyMap. For BS the three sub classes from EnMAP did match three sub classes from the HyMap data, but the two remaining sub classes from HyMap were not accounted for.
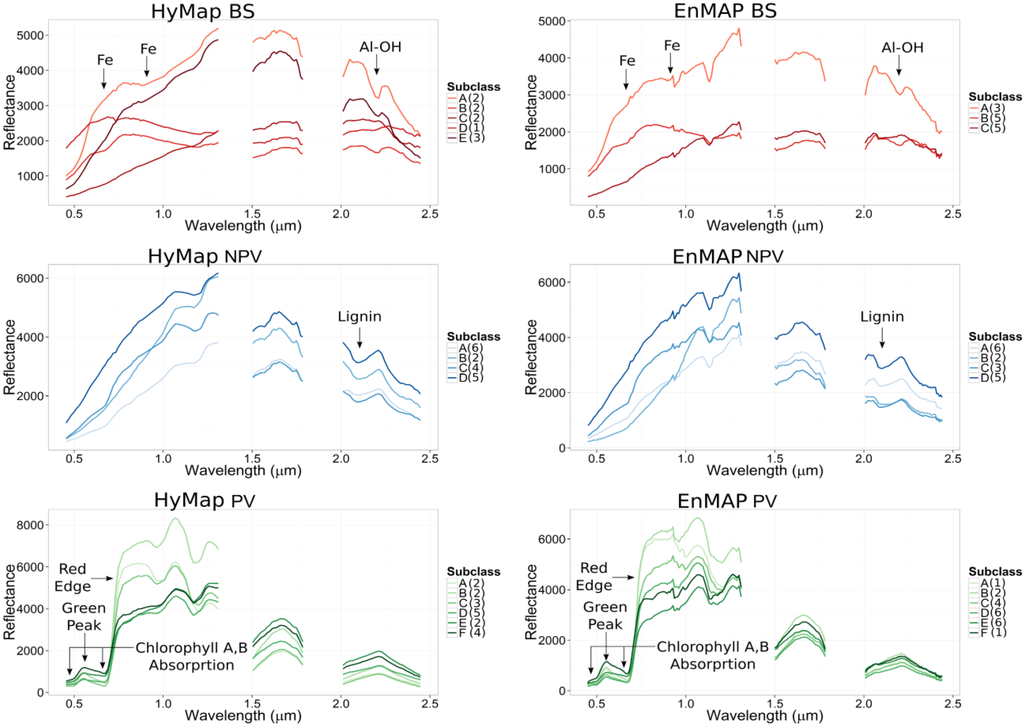
Figure 3.
HyMap and EnMAP PV, NPV and BS classes and sub classes (for clarity only the mean spectra per sub class are shown with the number of spectra per class shown in parenthesis) derived independently from the extracted SSEE candidate endmembers. Arrows highlight key spectral features related to BS, NPV and PV.
Looking at the BS sub classes from both HyMap and EnMAP (Figure 3) we can highlight a number of key features related to the known soils in the area that distinguish them from NPV. Most notably is the diagnostic narrow Al-OH clay feature seen at 2.2 µm in a number of the BS sub classes. The depth of this absorption features does vary for the sub classes indicating the relative abundance of clay minerals is variable in the soils detected. Additionally, broad absorption features in the visible portion of the spectra occur, which can be attributed to iron oxide and iron hydroxide minerals such as goethite (FeOOH) and hematite (Fe2O3), which is consistent with the oxidized red colored soils in the region. Similar features characterize the two additional sub classes detected by HyMap, but in different magnitudes. One BS sub class does not show a distinct clay feature and is characterized by a very low reflectance in the visible portion of the spectra, which may indicate a darker organic rich top soil. With respect to the NPV class spectra one can see that they contain the diagnostic lignin feature found at approximately 2.105 µm that is useful to distinguish from PV in the SWIR. The endmembers representing PV are clearly defined by a green peak at approximately 0.55 µm, Chlorophyll A and B absorption between 0.4 and 0.5 µm and 0.6 and 0.7 µm, and lastly a strong red edge from 0.68–0.73 µm. A detailed assessment of the endmembers is not given here, but the results do indicate that at the 30 m pixel resolution of EnMAP, it is possible to effectively discriminate NPV and PV and extract relatively pure BS spectra with characteristics that are expected for the soils in the area.
5.2. MESMA
The resulting PV, NPV and BS fractional abundance maps for HyMap and EnMAP are shown in Figure 4. Included in Figure 4 are absolute difference images between HyMap and EnMAP results. Visual comparison of MESMA results show high overall similarities in the fractional abundance pattern for all classes, nevertheless on closer inspection results from HyMap display more local-scale spatial distribution and variability of fractional abundances. This result is expected as one pixel of EnMAP is covered by four HyMap pixels. As the overall patterns are similar, a more quantitative analysis of the fractional abundance values in the image as a whole is needed to assess where key differences occur in the results.
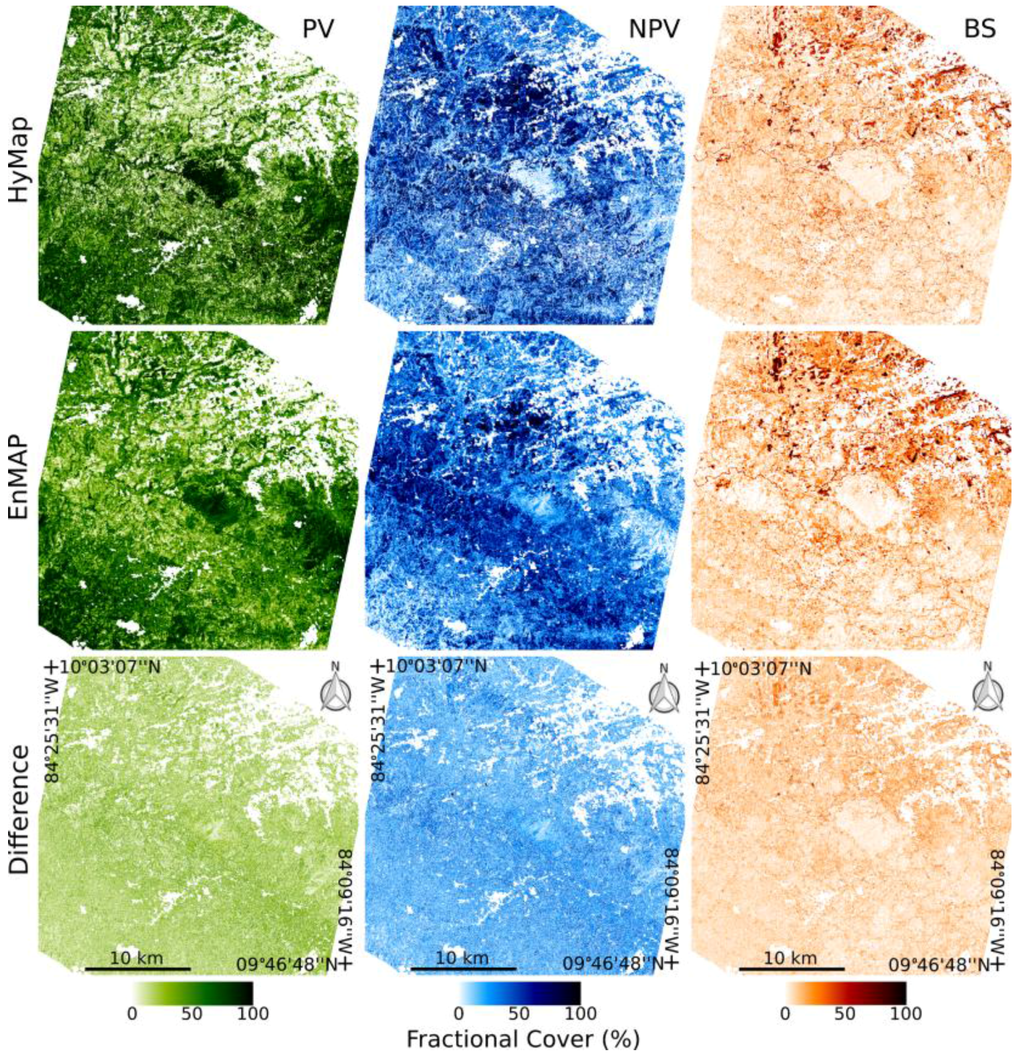
Figure 4.
MESMA fractional cover estimates (%) for PV (green), NPV (blue) and BS (orange) and absolute difference images.
Starting with the class histograms for the full image data for the three classes, one can see overall similarities, but with some notable differences (Figure 5). First, for the BS the best overall match between HyMap and EnMAP can be observed, with only a slight shift in the distribution towards higher fractions. In the case of NPV, considering HyMap values, low to moderate abundance values (25%–50%) are overestimated in the EnMAP imagery, while the opposite case is observed for high abundances (70%–100%). Fractional cover values of PV for EnMAP show a more normal distribution in contrast to HyMap, where the abundance values are almost uniformly distributed, but with an anomalous increase in number of pixels for high abundance values (90%–97%). This increase above 90% may be attributed to higher sub pixel mixing in the 30 m EnMAP pixels. For example, small clusters of trees or even individual trees surrounded by NPV and/or soil may be common in some areas. These may be detectable at the 15 m HyMap data, but mixed within the EnMAP data. However, the cause of this anomalous feature has yet to be determined.
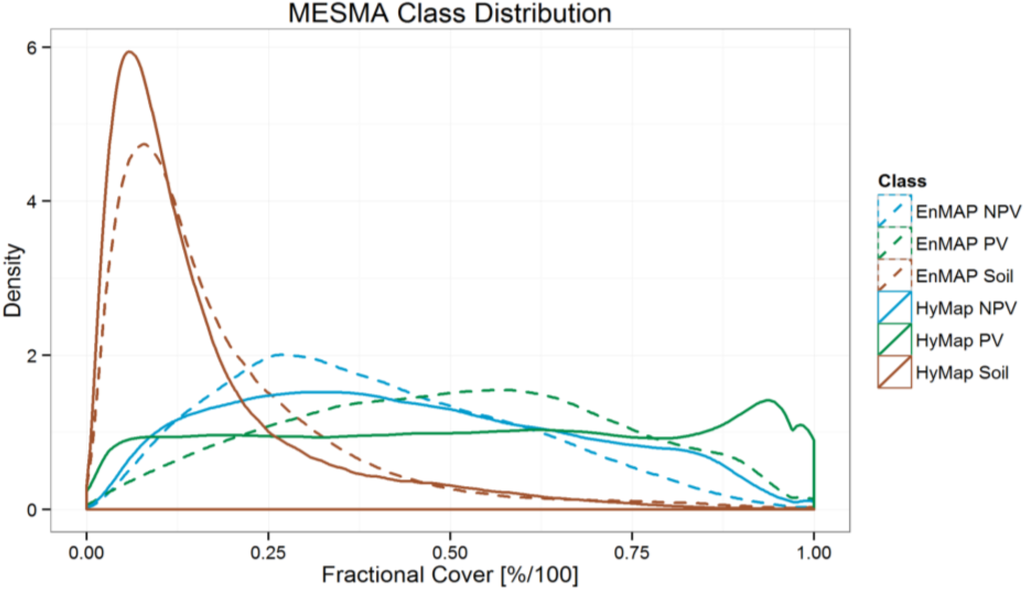
Figure 5.
MESMA fractional cover histograms for HyMap (solid lines) and EnMAP (dotted lines) imagery for PV (green), NPV (blue) and BS (orange).
Next, HyMap and EnMAP results are compared by plotting the pixels of each of the three classes against each of the other classes as density scatter plots (Figure 6) to highlight the mixing relationships between the classes. Once again, the overall patterns are similar between sensors. However, in the scatter plots one can see that the high density areas for the various mixtures between classes for EnMAP are more spread out compared with HyMap. Mixing between PV and NPV is strongly negatively correlated for both data sets. However, differences include a higher proportion of NPV fractions (>80%) mixing with low PV (<20%) for HyMap, whereas this feature is absent from the EnMAP results. Low fractional cover of BS occurs across all values of PV and NPV for HyMap, but for EnMAP this is limited to the 0%–80% range for NPV and 20%–100% for PV. There also appears to be slightly more EnMAP BS pixels in the 20%–40% range mixing with PV and NPV as compared with HyMap. Overall, the mixing relationships show that PV and NPV dominate most pixels and are interchangeable with both showing a similar mixing relationship with BS, which is very limited in the region.
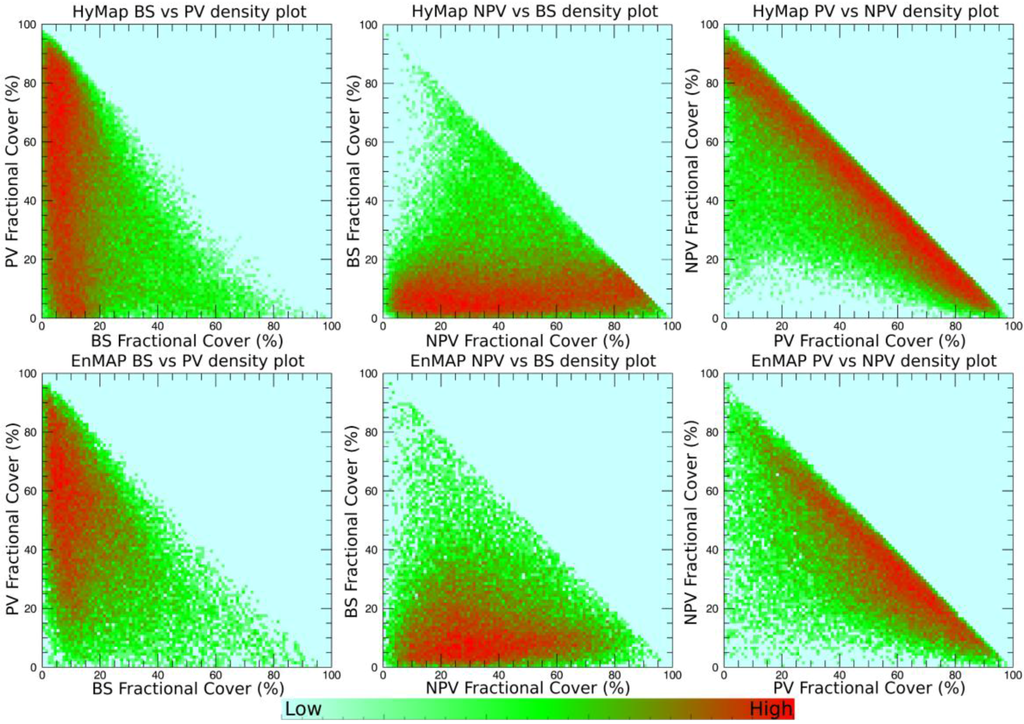
Figure 6.
Density scatterplots showing mixing relationship between the classes BS, PV and NPV fractional cover for HyMap and EnMAP.
To quantitatively assess how similar the calculated fractions between HyMap and EnMAP for a given location are, focus is given on homogeneous regions. This is done to reduce the effects of different pixel sizes along sharp edges and spatial boundaries between different classes. Once homogeneous regions were defined, scatter plots for each class were generated for those pixels and an assessment of correlation was calculated, in this case Pearson R2 (Figure 7). For all three classes, it can be observed visually that there is an overall correlation for all fractional values, which is also indicated by the R2 values. However, it is also evident that there is still a high degree of pixels which deviate from the correlation axis. This indicates that even within homogeneous regions actual fractional abundances can be quite variable. EnMAP commonly under estimates soil fractions, whereas for NPV it overestimates at low fractional values and underestimates at high values. A similar case can be seen for PV. The results further demonstrate that the EnMAP and HyMap results are consistent overall, but local differences can result in significant differences in calculated fractions, even in homogeneous areas. Putting this in perspective to the differences in spatial resolution (a factor of 4 in area) and to the general error margins of spectral unmixing (typically ±10% absolute in cover, see e.g., [21,22,56]), the overall agreement between the two datasets can be considered good.
In the next evaluation of the HyMap and EnMAP results, the actual sub classes used in each pixel to unmix the spectra are considered. Here, the goal is to assess if the MESMA mixing approach consistently uses the same sub classes from both sets of spectral libraries. The comparison of the different endmember sub classes is shown in Figure 8 as a confusion matrix. Again, in this case the focus is on homogeneous regions. For none of the three classes, BS, NPV and PV significant patterns can be observed. Note that for BS there are three sub classes for EnMAP whereas there are five for HyMap. With the exception of HyMap BS sub class E all endmembers are more or less "randomly" substituted with the three EnMAP endmember sub classes. A significant relationship between endmember sub class A from class NPV (45%) for both data sets can be observed underpinning the dominance of spectra belonging to this sub class across the entire study site for both images. The fact that for HyMap a higher diversity of different sub classes has been used by MESMA (C 9.5% and D 11.3%) indicates that MESMA is likely sensitive to the spatial resolution of input images. Both data sets delivered the same corresponding vegetation sub classes, but similar to NPV, one dominant sub class can be identified (D with 22.2%) and most pixels have been modeled for EnMAP with spectra from sub classes D and E (around 78%). Compared to HyMap these two groups are used for approximately 61% of all pixels with fractional cover values for PV, with sub class C and F comprising around 12% and 14%, respectively.
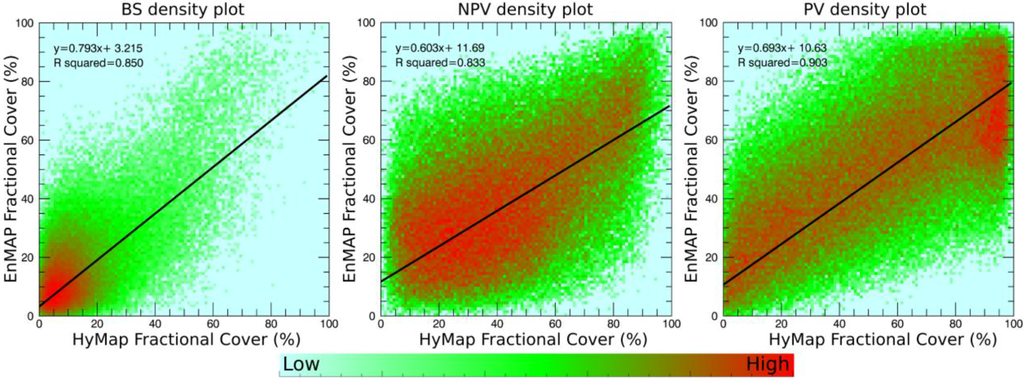
Figure 7.
Density scatterplots of BS, NPV and PV fractional abundance results for EnMAP compared to the HyMap imagery with associated slope, intercepts and calculated R2 values.
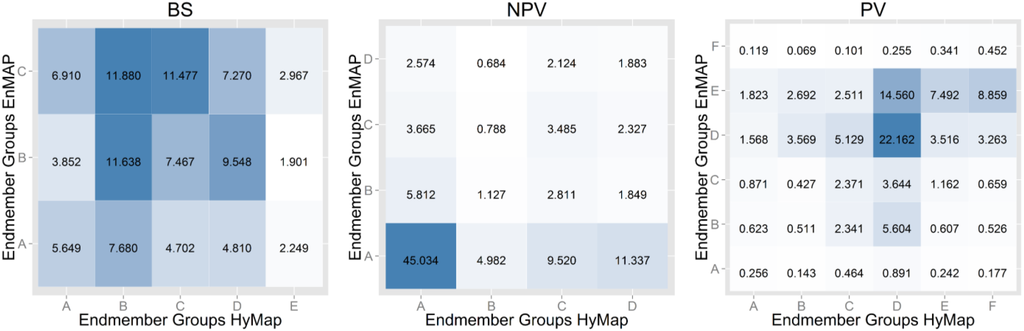
Figure 8.
Endmember sub class confusion matrix for BS, NPV and PV between EnMAP and HyMap imagery. Values given as percentage of pixels.
5.3. C-Factor Analysis
For the analysis of the C-factor derived from HyMap and EnMAP data, the unmixing results (PV, NPV and BS fractional maps) are integrated in Equation (3). Figure 9 shows the results for the full study area for each of the two C-factor cases (see Section 4.2). Similar to the fractional cover estimates the same overall patterns between HyMap and EnMAP for each C-factor case are observed. However, there are notable differences with respect to the two calculated C-factor cases. For example, higher values occur throughout the southern portion of the study area (e.g., arrow (i) and (ii) in Figure 9). These differences are directly attributed to NPV being combined with BS in the second case, which would represent the extreme case where these two classes are not separable based on spectral information. This highlights the importance of considering both PV and NPV when estimating the C-factor, particularly during different periods of the growing season.
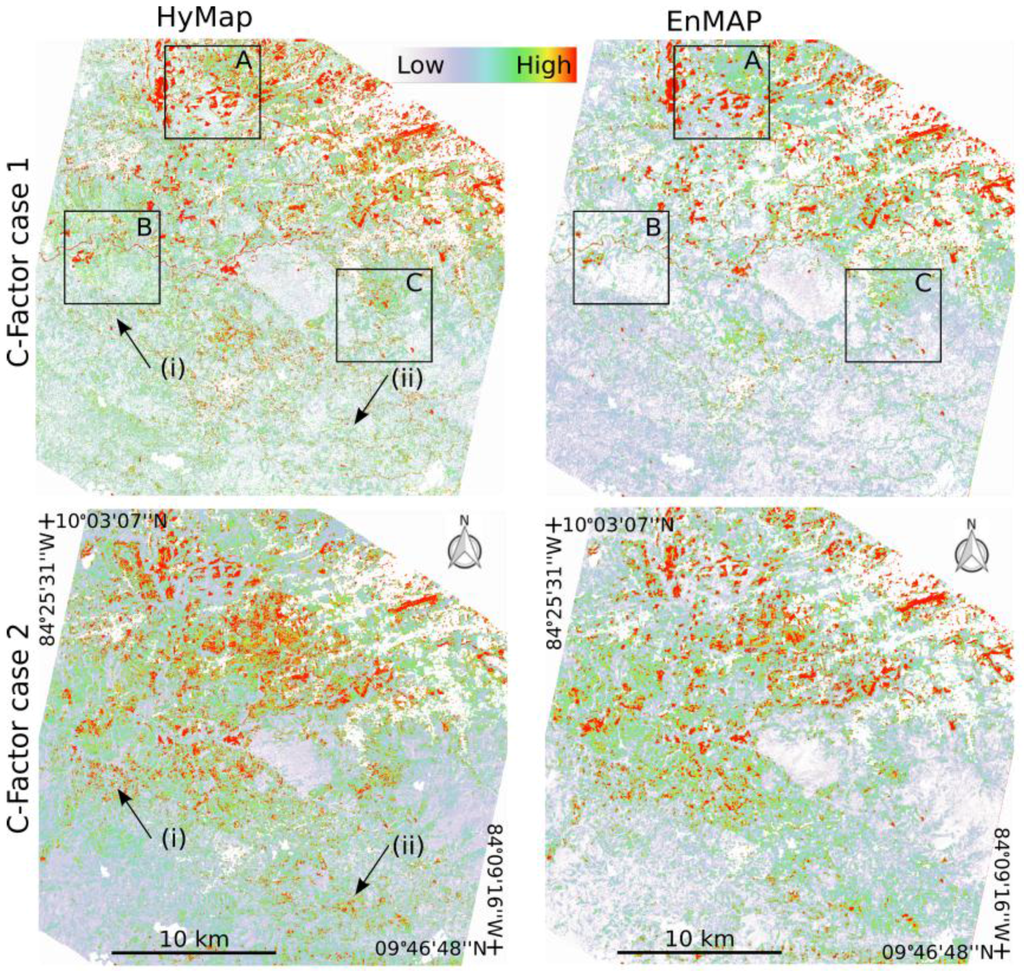
Figure 9.
C-factor case 1 and 2 results for the full study area derived for HyMap and EnMAP. See text for details on arrow descriptions. Boxes 1, 2 and 3 represent zoom windows a, b and c in Figure 10.
With respect to the more optimal case of separating BS and NPV, key differences between HyMap and EnMAP results are visible at a local scale. To highlight these local differences, Figure 10 zooms in on the three different areas shown in Figure 9. The first area (A) is located in an area characterized by large agricultural fields with various degrees of soil exposure. The larger fields are well represented in both the EnMAP and HyMap results with some notable differences (e.g., arrow (i) Figure 9). The major difference between the two outputs are a higher level of spatial detail for HyMap, as expected, but also an overall higher C-factor background. This is also evident in the next two areas (B) and (C). This can be explained by EnMAP underestimating higher fractions of PV and NPV which subsequently result in lower background C-factor values. The second zoom area (B) is characterized by a more hilly terrain with extensive plantations with dense PV vegetation cover mainly occurring in the valleys. Overall, the spatial patterns are similar, but zones with higher C-factor are generally spatially more extensive (e.g., arrow (ii) Figure 9). The last zoom area (C) shows a more rugged mountainous region with differences highlighting narrow paths/roads (e.g., arrow (iii) Figure 9) visible in HyMap but not in EnMAP results.
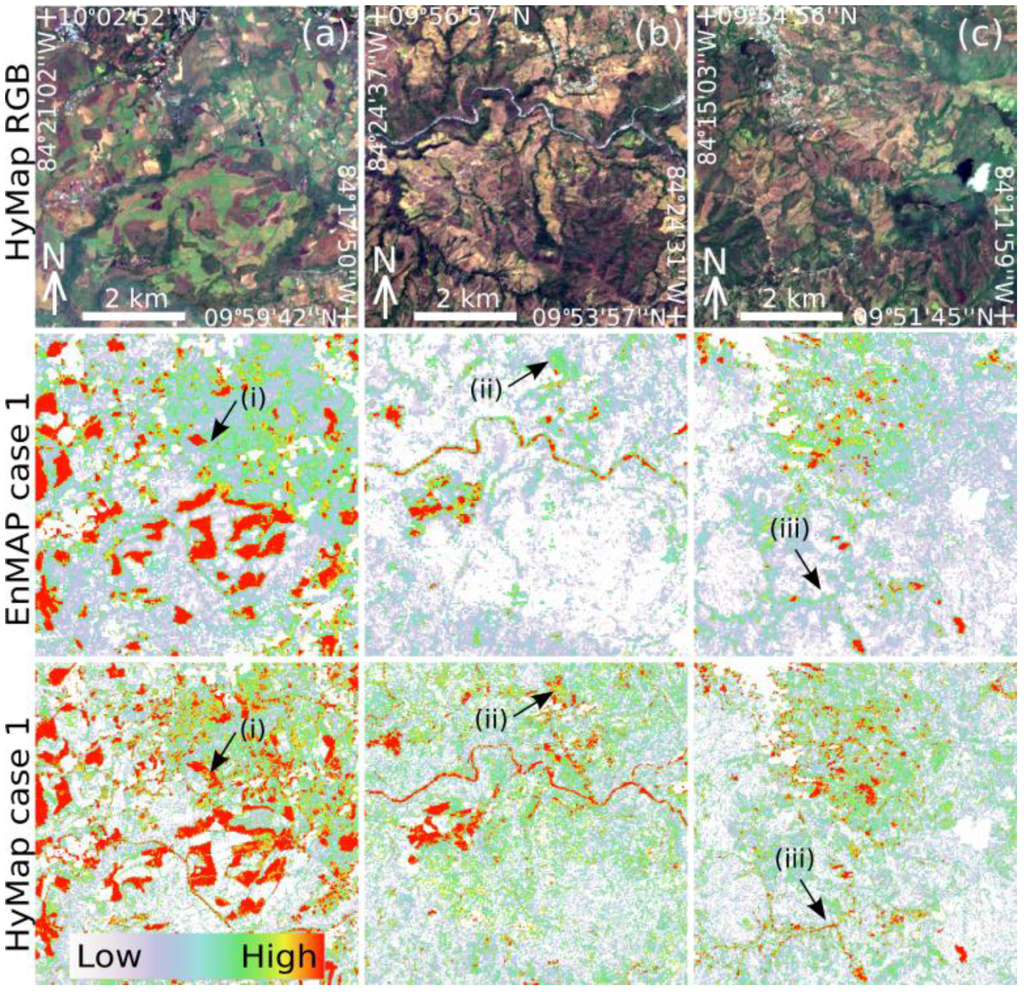
Figure 10.
Zoom areas (a), (b) and (c) highlighting local differences between EnMAP and HyMap C-factor case 1 results. See text for details on zoom areas.
6. Discussion
6.1. EnMAP Simulation Quality
The output from the EeteS simulation software is well tested and understood [42], and as such, the critical factor becomes the input data in the simulator. The generation of the EnMAP simulation involved a great deal of care in building the highest quality mosaic of the airborne HyMap data. Special attention was paid to improving radiometric quality through the assessment of wavelength shifts for individual lines and during the extent of the flight campaign. Through improvements in radiometric quality, important spectral features in the SWIR near 2.10–2.20 µm associated with lignin allowed for improved discrimination of representative NPV and soil spectra from the image data directly. Though the spectral bandwidths of HyMap are about twice as large as for EnMAP, the difference does not impact the ability to discriminate important features of interest (e.g., clay and lignin), which means that this information is transferred to the simulation. The high quality of the resulting mosaic was also evident in that the resulting fractional cover estimates are highly consistent across the HyMap flight-lines which can be attributed to improved radiometric consistency and BRDF correction, although some inconsistency does remain. As such, the differences observed between HyMap and EnMAP results can be attributed to the differences in sensor characteristics rather than issues related to the simulation generation.
6.2. Fractional Cover Estimates
The distribution of significant quantitative differences in fractional cover estimates between HyMap and EnMAP data show over- or underestimation in predicted abundance values. However, qualitative visual comparisons clearly show similar overall distribution of fractional estimations (e.g., spatial patterns, mixing relationships). These results were used to assess if the differences observed were related to spectral and/or spatial differences between the two sensors.
In Thorp et al. [62], Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS) data was used to investigate the effect of spatial and spectral characteristics on MESMA performances for PV, NPV, and BS in semi-arid rangelands with their results showing that MESMA is more sensitive to spectral degradation than spatial degradation. However, the findings of Thorp et al. [62] pointing out a higher sensitivity of MESMA against spectral than spatial range are based on the removal of key spectral ranges (e.g., VIS/NIR, SWIR). In this study the same spectral wavelength ranges for both sets of imagery were used, with only the spectral bandwidths and thus the number of bands changed. Additionally, the spectral features visible in EnMAP are dependent on the original spectral features in the HyMap data, with the exception of noise specific features added during the simulation process. In regards to the results from this study, the higher spectral resolution of EnMAP (242 bands compared to HyMap with 125 bands) on the derivation of relative fractional cover appears to be negligible. The key absorption features characterizing the classes and their associated sub classes were detectable in both EnMAP and HyMap. The applied endmember extraction method derived similar endmember classes for both data sets, with the exception of two additional sub classes for BS extracted from the HyMap data. This indicates that for both the HyMap and EnMAP spatial resolutions, the majority of endmember representatives of PV, NPV and BS occur locally in reasonably large homogeneous regions. Whereas, for the two extra BS sub classes derived from HyMap, pixel size likely influenced their ability to be extracted. Similar conclusions were drawn by Rogge et al. [43], whom considered airborne AISA and simulated EnMAP data for mapping geology, pointing out that the different spatial resolutions (2 and 30 m pixels) was the main reason for important differences in the extracted endmembers.
Results derived for both airborne HyMap and simulated satellite EnMAP imagery produce similar overall spatial patterns and similar quantitative values of fractional coverage. The key differences were found at a local scale, where the distribution of surface materials commonly occurs below that of the 30 m pixel size of EnMAP. This was evident from the class to class scatter plots that highlight slightly different distribution densities and mixing characteristics between classes (Figure 6). For homogeneous regions, one would expect the fractional values to be highly correlated. However, in Figure 7 even for homogeneous regions, a high degree of variance of absolute fractions between the EnMAP and HyMap results exist. Thus, not only are there local differences in spatial distribution and values, there is also an absolute difference between the two data sets.
Increasing pixel size involves a higher degree of surface mixtures within a given pixel. This result is more critical for local studies, where mapping results have to be very precise in respect to the location. A similar conclusion was drawn by Bannari et al. [33] who applied a constrained linear spectral mixture analysis based on the Hyperion data with endmembers collected in the field. This was because the small scale distribution of crop residuals and open soil limited the applicability of image derived endmembers due to the Hyperion’s spatial resolution of 30 m. As seen from the perspective of large scale studies (e.g., regional or national scale), the significant differences in the fractional cover values of HyMap and EnMAP appear as spatially related patterns, thus the areas where high or low values appear are only shifted by a few meters, but the overall distributions are still very similar. Similar results were also shown in Okujeni et al. [63] who used hyperspectral remote sensing data to retrieve vegetation cover, vegetation type, and soil type in areas of low vegetation cover using MESMA. Increased surface mixing in larger pixels also reduces the potential occurrence of extremes, or pure pixels. This is evident in Figure 6 where high values of NPV (>80%) or low PV (<20%) in the HyMap results are not evident for EnMAP. These results again underpin the potential of EnMAP to continue to provide hyperspectral data to the community into the future as Hyperion will not provide data beyond 2015 [38]. Hyperion has shown during its extended lifespan the need to utilize existing methodologies and to stimulate research focusing on generalizing and transferring existing methodologies to other regions. As such, there is a need to ensure the availability of high quality hyperspectral data for future studies.
Another interesting outcome of this study is the use of specific sub classes used within MESMA. With respect to this study, there is not a strong correlation between which sub class was used by EnMAP compared to HyMap data. Additionally, specific sub classes appear to dominate. The latter case may just indicate an overall spatial dominance of a specific sub class, but it may also indicate that specific spectral features in a given sub class dominate the unmixing process. In either case, this presents a potential problem for integrated soil erosion modeling based on different soil and/or vegetation types.
6.3. C-Factor Analysis
As ground data was not available, the C-factor analysis results were assessed quantitatively. Results in Figure 9 and Figure 10 show that areas with high C-factor values are located in distinctive patterns which are similar for both HyMap and EnMAP. However, the patterns are significantly different for the two C-factor cases. For example, in areas in the image where it appears that soil and NPV are dominant, the resulting C-factor is low for case 1. On the other hand, if NPV and soil are combined in the C-factor calculation, these areas result in much higher C-factor values. The two cases used in this study provide two extreme examples where NPV and BS are separable or not and they have subsequent impact on the derived C-factor. The given cases make the assumption that PV and NPV carry equal weight in reducing the potential for soil erosion. However, based on the physical characteristics of PV and NPV, it is apparent that this assumption may not be correct. As such, the C-factor equation used in this analysis could be expanded to include different weights for PV and NPV, which may better reflect the ability of the given cover types to reduce soil erosion. This would be particularly important if seasonality is also taken into account, where relative fractions of PV and NPV can change dramatically. Thus, accurate C-factor calculations require good estimations of PV, NPV and BS cover fractions, which can be improved by taking advantage of the additional spectral information available with the upcoming EnMAP as demonstrated in this work. As C-factor analysis in the context of soil erosion assessments cannot be conducted with a single snapshot in time, phenology needs to be taken into consideration [6]. Thus, the availability of low cost multitemporal hyperspectral data, as presently provided by Hyperion and in the future by EnMAP, is mandatory.
7. Conclusions and Outlook
This work demonstrates the potential of EnMAP to assess selected drivers of soil degradation (e.g., erosion) over vast regions (potentially 30 × 5000 km of imagery per day) based on subpixel classification that can be made available to the scientific community to derive useful information about Earth Surface processes. Thus, it is likely that EnMAP will continue to provide high quality spaceborne hyperspectral data for environmental applications, such as large scale mapping of soil erosion, as existing systems such as Hyperion will be retired. The spectral capabilities of EnMAP were shown to be robust and allowed for extracting quality endmember classes that contain important spectral features related to PV, NPV and BS. As such, good separation of NPV and BS fractional cover is possible resulting in improved C-factor estimates. The coarser spatial resolution of EnMAP (30 m) compared to HyMap (15 m) produces no substantial differences concerning the spatial patterns of fractional abundances and C-factor estimates on a regional scale, although local differences are evident. Additionally, the results demonstrate that the 30 m spatial resolution is sufficient for regional studies when using automated spectral mixture analysis approaches as suggested by other studies. With this technique, reasonable estimates of sub pixel cover fractions can be derived, as long as good spectral representations of ground cover classes are ensured. However, results show either slight over- or underestimations of fractional cover compared to HyMap data. As shown by numerous studies to conduct comprehensive soil erosion modeling, C-factor shall be estimated monthly or at least reflect the seasonal variations. Although this study derives information for a snapshot in time, EnMAP will be a suitable sensor for such studies, since it has a revisit time of up to four days at the Equator and even better at higher latitudes. Given the multitemporal availability of EnMAP data, the presented automated approach is suitable for measuring the variability of essential input parameters for soil erosion modeling that are caused by seasonal variations and management decisions on a short- and midterm basis, but it can also reflect the transformation of a region because of climate influences over the long-term. Overall, the study demonstrates the capability of EnMAP to continue to provide hyperspectral satellite data compared to existing missions with similar sensor properties, and therefore, facilitate a continuation of exiting research focusing on long term monitoring and mapping of various environmental applications. Automated methods developed based on systems like Hyperion are likely to be transferrable to EnMAP data to provide low cost remote sensing products to decision makers. Against this backdrop, the future goal of this study is to expand the existing methodologies to other regions of the HyMap Costa Rica survey data, in particular mapping succession stages of dry tropical forest areas in the Guanacaste region.
Acknowledgments
This work was made possible through the DLR—University of Alberta iTERI HGF initiative. HyMap radiance data and DEM provided by the Center of Earth Observation, University of Alberta, Canada. Level 2 (atmospheric and geometric) correction and the GUF mask was provided by Land Surface Department, DLR, Germany. EnMAP simulation provided by GFZ Postdam, Germany. Additionally we are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments which helped to improve the quality of this paper.
Author Contributions
Sarah Malec, Derek Rogge and Uta Heiden, Martin Wegmann conceived and designed the experiments; Sarah Malec, Derek Rogge, Martin Bachmann performed the experiments; Sarah Malec, Derek Rogge analyzed the data; Derek Rogge, Arturo Sanchez-Azofeifa contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Sarah Malec, Derek Rogge, Uta Heiden, Martin Bachmann wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kaufmann, H.; Segl, K.; Chabrillat, S.; Hofer, S.; Stuffler, T.; Müller, A.; Richter, R.; Schreier, G; Haydn, R; Bach, H. EnMaP a hyperspectral sensor for environmental mapping and analysis (invited paper). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006.
- Eswaran, H.; Lal, R.; Reich, P.F. Land degradation: An overview. In Responses to Land Degradation, Proceedings of the International Conference on Land Degradation and Desertification, New Dehli, India, 2001; Hannam, I.D., Oldeman, L.R., Pening de Vries, F.W.T., Scherr, S.J., Sompatpanit, S., Eds.; Oxford Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Soil erosion assessment and its verification using the universal soil loss equation and geographic information system: A case study at Boun, Korea. Environ. Geol. 2004, 45, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrieling, A. Satellite remote sensing for water erosion assessment. Catena 2006, 65, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Panagopoulos, T. Seasonality of soil erosion under Mediterranean conditions at the Alqueva dam watershed. Environ. Manag. 2014, 54, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bernoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. A universal soil-loss equation to guide conservation farm planning. Trans. Int. Congr. Soil Sci. 1968, 1, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyssels, G.; Poesen, J.; Bochet, E.; Li, Y. Impact of plant root characteristics on resistance of soil to erosion by water: A review. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2005, 29, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Asis, A.M.; Omasa, K. Estimation of vegetation parameter for modeling soil erosion using spectral mixture analysis of Landsat ETM data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.H.; Sotir, R.B. Biotechnical and Soil Bioengineering Slope Stabilization: A Practical Guide for Erosion Control; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Yoder, D.C.; Lightle, D.T.; Dabney, S.M. Universal Soil Loss Equation and Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation, 1st ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsal, I.A. Soil Pollution: Origin, Monitoring and Remediation; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shoshanya, M.; Goldshlegerb, N.; Chudnovskyc, A. Monitoring of agricultural soil degradation by remote-sensing methods: A review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 37, 6152–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veihe, A.; Rey, J.; Quinton, J.N.; Strauss, P.; Sancho, F.M.; Somarriba, M. Modelling of event-based soil erosion in Costa Rica, Nicaragua and Mexico: Evaluation of the Eurosem model. Catena 2001, 44, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Knapp, D.E.; Cooper, A.N.; Bustamante, M.M.C.; Olander, L.P. Ecosystem structure throughout the brazilian amazon from landsat observations and automated spectral unmixing. Earth Interact. 2005, 9, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerschman, J.P.; Scarth, P.F.; McVicar, T.R.; Renzullo, L.J.; Malthus, T.J.; Stewart, J.B.; Rickards, J.E.; Trevithick, R. Assessing the effects of site heterogeneity and soil properties when unmixing photosynthetic vegetation, non-photosynthetic vegetation and BS fractions from Landsat and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.S.; Clarke, K.D.; Lewis, M.M. Comparison of methods for estimation of absolute vegetation and soil fractional cover using MODIS normalized BRDF-adjusted reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 130, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.S. Relative spectral mixture analysis—A multitemporal index of total vegetation cover. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Heidebrecht, K.B. Spectral unmixing of vegetation, soil and dry carbon in arid regions: Comparing multi-spectral and hyperspectral observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Lobell, D.B. A biogeophysical approach for automated SWIR unmixing of soils and vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D. Visible and near infrared reflectance characteristics of dry plant materials. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1775–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustin, S.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Gamon, J.A.; Asner, G.P.; Green, R.O. Using imaging spectroscopy to study ecosystem processes and properties. Bio. Sci. 2004, 54, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, E.; Chabrillat, S.; Dematte, J.A.M.; Taylor, G.R.; Hill, J.; Whiting, M.L.; Sommer, S. Using imaging spectroscopy for soil properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S38–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocita, M.; Stevens, A.; van Wesemael, B.; Aitkenhead, M.; Bachmann, M.; Barthes, B.; Ben-Dor, E.; Brown, D.J.; Clairotte, M.; Csorba, A.; et al. Spectroscopy: An alternative to wet chemistry for soil monitoring. Adv. Agron. 2015, 132, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Daughtry, C.S.T.; Doraiswamy, P.C.; Hunt, E.R., Jr.; Stern, A.J.; McMurtrey, J.E., III; Prueger, J.H. Remote sensing of crop residue cover and soil tillage intensity. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 91, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delegido, J.; Verrelst, J.; Rivera, J.P.; Ruiz-Verdu, A.; Moreno, J. Brown and green LAI mapping through spectral indices. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2015, 35, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, V.L.; de Bruin, S.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mayr, T.R. The use of remote sensing in soil and terrain mapping—A review. Geoderma 2011, 162, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, S.; Wilczok, C.; Brosinsky, A.; Segl, K. Assessment of sediment connectivity from vegetation cover and topography using remotely sensed data in a dryland catchment in the Spanish Pyrenees. J. Soil. Sediment. 2014, 14, 1982–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.; Bachmann, M.; Müller, A.; Kaufmann, H. A comparison of feature-based MLR and PLS regression techniques for the prediction of three soil constituents in a degraded South African ecosystem. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2012, 2012, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okin, G.; Roberts, D.; Murray, B.; Okin, W. Practical limits on hyperspectral vegetation discrimination in arid and semiarid environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 77, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Staenz, K.; Champagne, C.; Khurshid, K.S. Spatial variability mapping of crop residue using Hyperion (EO-1) hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8107–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K. Hyperspectral satellite data in mapping salt-affected soils using linear spectral unmixing analysis. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2012, 40, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; He, T. Application of Hyperion data to land degradation mapping in the Hengshan region of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 5145–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.A.; Boarsmann, J.W.; Huntingtin, J.F. Comparison of airborne hyperspectral data and EO-1 Hyperion for mineral mapping. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Dennison, P.E.; Gardner, M.E.; Hetzel, Y.; Ustin, S.L.; Lee, C.T. Evaluation of the potential of Hyperion for fire danger assessment by comparison to the airborne visible/infrared imaging spectrometer. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1297–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E.M.; Ungar, S.G.; Mandl, D.J.; Ong, L.; Frye, S.W.; Campbell, P.E.; Landis, D.R.; Young, J.P.; Pollack, N.H. The earth observing one (EO-1) satellite mission: Over a decade in space. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Kaufmann, H.; Segl, K.; Foerster, S.; Rogass, C.; Chabrillat, S.; Kuester, T.; Hollstein, A.; Rossner, G.; Chlebek, C.; et al. The Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program (EnMAP) spaceborne imaging spectroscopy mission for Earth observation. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8830–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J.; Green, R.O. Synergies between VSWIR and TIR data for the urban environment: An evaluation of the potential for the hyperspectral infrared imager (HyspIRI) decadal survey mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Iwasaki, A.; Tsuchida, S.; Tanii, J.; Kashimura, O.; Nakamura, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Tachikawa, T.; Rokugawa, S. Current status of Hyperspectral Imager Suite (HISUI). In Peoceedings of the IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 3510–3513.
- Segl, K.; Guanter, L.; Rogaß, C.; Küster, T.; Roessner, S.; Kaufmann, H.; Sang, B.; Mogulsky, V.; Hofer, S. Eetes- the EnMAP end-to-end simulation tool. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, D.; Rivard, B.; Segl, K.; Grant, B.; Feng, J. Mapping of NiCu–PGE ore hosting ultramafic rocks using airborne and simulated EnMAP hyperspectral imagery, Nunavik, QC, Canada. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Conservation Service. In Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 436; Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 10 August 1999.
- Bachmann, M.; Habermeyer, M.; Holzwarth, S.; Richter, R.; Müller, A. Including quality measures in an automated processing chain for airborne hyperspectral data. In Proceedings of the 5th EARSel Workshop on Imaging Spectroscopy, Bruges, Belgium, 23–25 April 2007.
- Richter, R.; Schlapfer, D. Atmospheric/Topographical Correction for Airborne Imagery: ATCOR-4 User Guide; DLR IB: Wessling, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.; Lehner, M.; Müller, R.; Reinartz, P.; Schroeder, M.; Vollmer, B. A program for direct georeferencing of airborne and spaceborne line scanner images. In Proceedings of the International Archives of Photogrammetry Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Denver, CO, USA, 10–15 November 2002; pp. 148–153.
- Schläpfer, D.; Richter, R.; Feingersh, T. Operational BRDF effects correction for wide-field-of-view optical scanners (BREFCOR). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanter, L.; Segl, K.; Kaufmann, H. Simulation of the optical remote-sensing scenes with application to the EnMAP hyperspectral mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2340–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segl, K.; Guanter, L.; Kaufmann, H.; Schubert, J.; Kaiser, S.; Sang, B.; Hofer, S. Simulation of spatial sensor characteristics in the context of the EnMAP hyper-spectral mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3046–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Marconcini, M.; Felbier, A.; Roth, A.; Heldens, W.; Huber, M; Schwinger, M.; Taubenböck, H.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Urban footprint processor—Fully automated processing chain generating settlement masks from global data of the TanDEM-X mission. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1617–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Gillespie, A.R. Imaging spectroscopy: Interpretation based on spectral mixture analysis. In Remote Geochemical Analysis: Elemental and Mineralogical Composition; Pieters, C.M., Englert, P.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Rogge, D.; Bachmann, M.; Rivard, B.; Feng, J. Spatial sub-sampling using local endmembers for adapting OSP and SSEE for large-scale hyperspectral surveys. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.C. How unique are spectral signatures? Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M. Automated Estimation of Ground Cover Fractions Using MESMA Unmixing. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wuerzburg, Wuerzburg, Germany, December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, M.; Müller, A.; Dech, S. Increasing and evaluating the reliability of multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA). In Proceedings of the 6th EARSeL-SIG-IS, Tel Aviv, Israel, 16–19 March 2009.
- Zabcic, N.; Rivard, B.; Ong, C.; Müller, A. Using airborne hyperspectral data to characterize the surface pH and mineralogy of pyrite mine tailings. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2014, 32, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B.; Scotta, H.D.; Dixon, J.C.; McKimmey, J.M. Applications of fuzzy logic to the prediction of soil erosion in a large watershed. Geoderma 1998, 86, 183–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakimchandra, O. Integrated Fuzzy-GIS Approach for Assessing Regional Soil Erosion Risks. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, December 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Thorp, K.R.; French, A.N.; Rango, A. Effect of image spatial and spectral characteristics on mapping semi-arid rangeland vegetation using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis (MESMA). Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okujeni, A.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Extending the vegetation-impervious-soil model using simulated EnMAP data and machine learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).