Enhancing Wildfire Monitoring with SDGSAT-1: A Performance Analysis
Abstract
Highlights
- Focusing on smoke, fire points and burned area as the research objective, explore the ability of SDGSAT-1 to detect wildfire.
- SDGSAT-1 is highly effective in extracting burned areas, providing clear fire bounda-ries with a higher precision of 95.46%, while the average accuracy of smoke detection is 81.72%.
- The accuracy of SDGSAT-1 in correctly identifying fire points using the fixed threshold method is 91.10%.
- SDGSAT-1 can detect fires as small as 0.0009 km2, which has the capability to identify initial and early small fire.
Abstract
1. Introduction
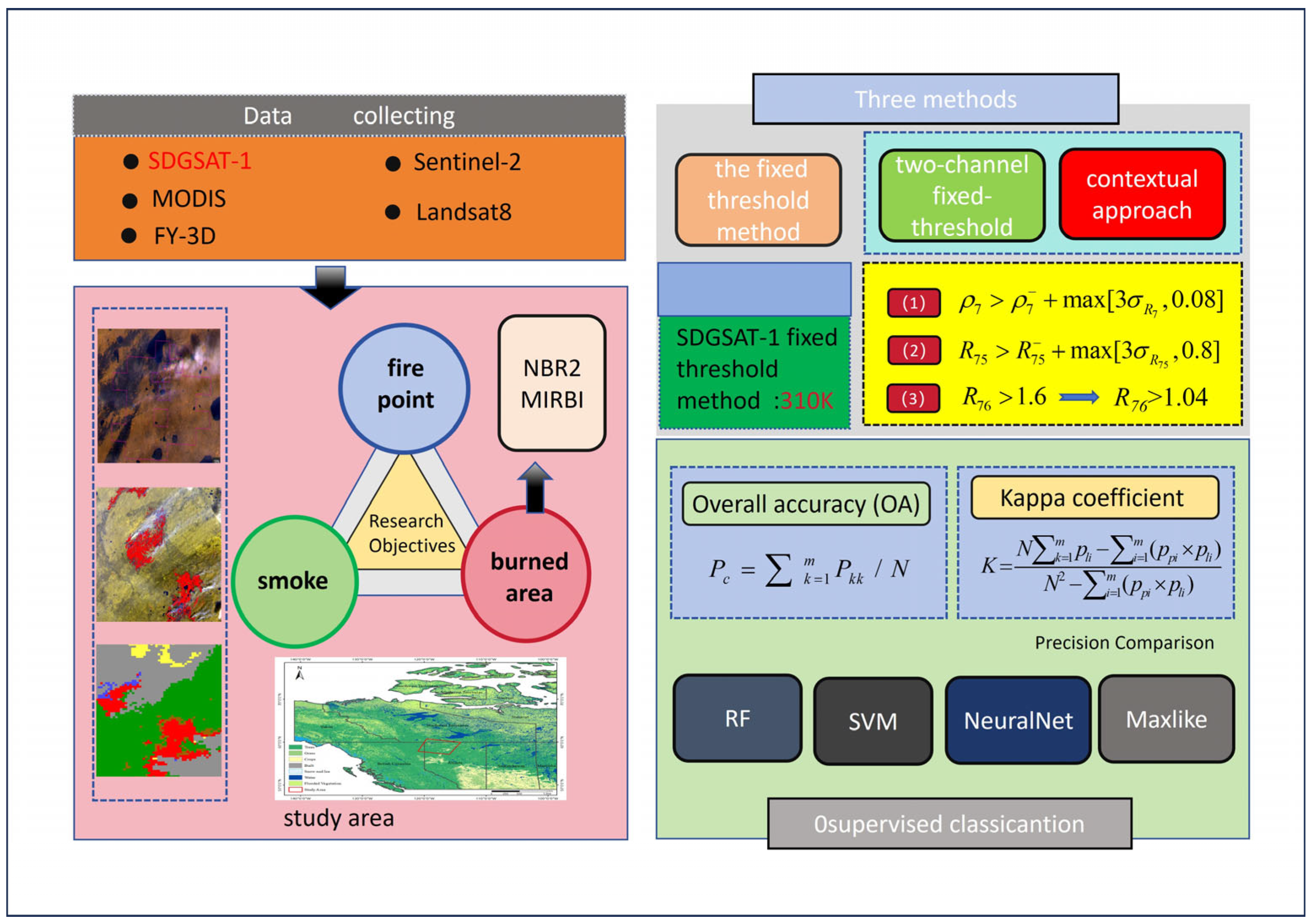
2. Research Method
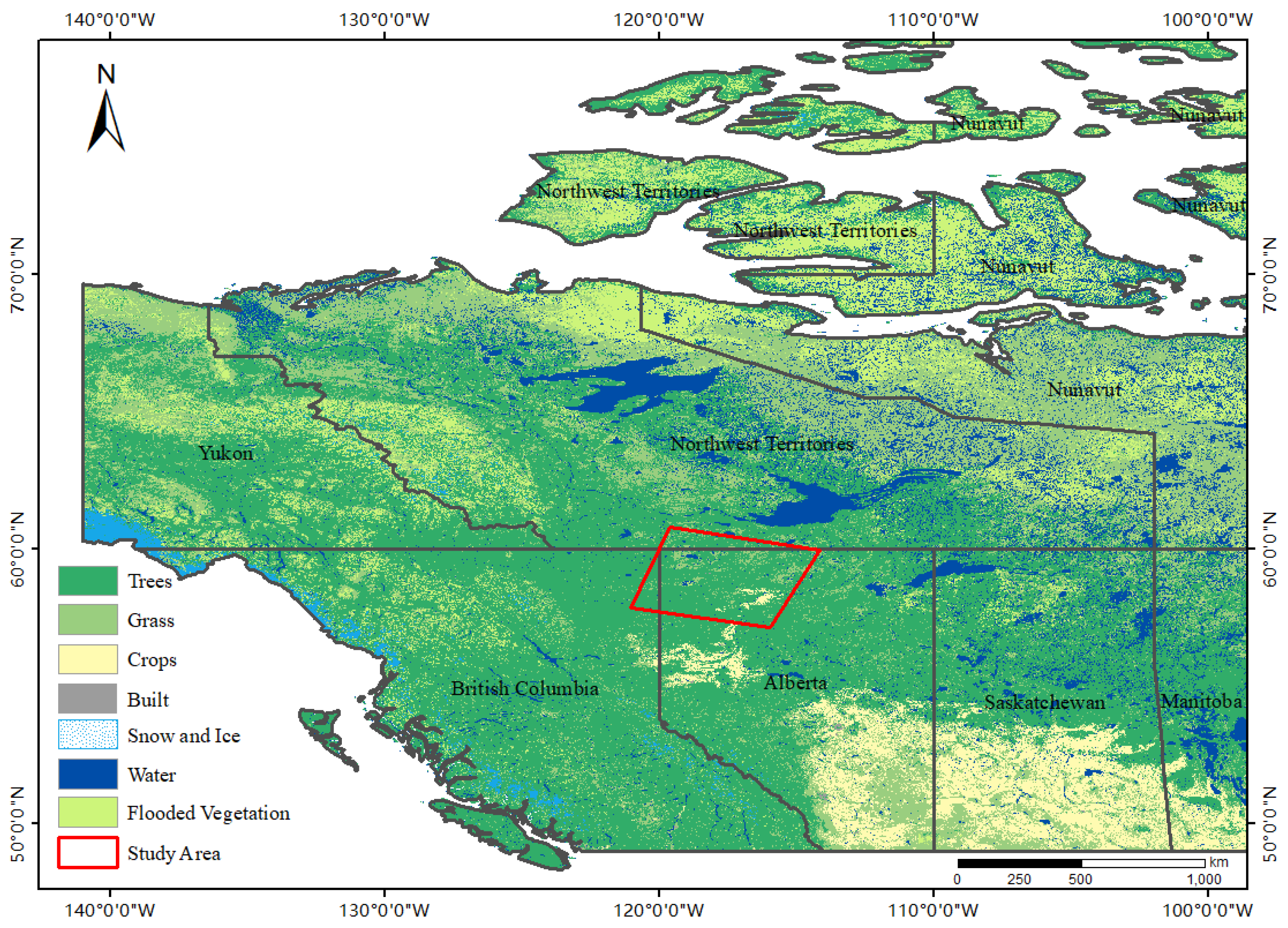
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Extraction of Smoke and Burned Areas
2.2.2. Identification of Fire Point
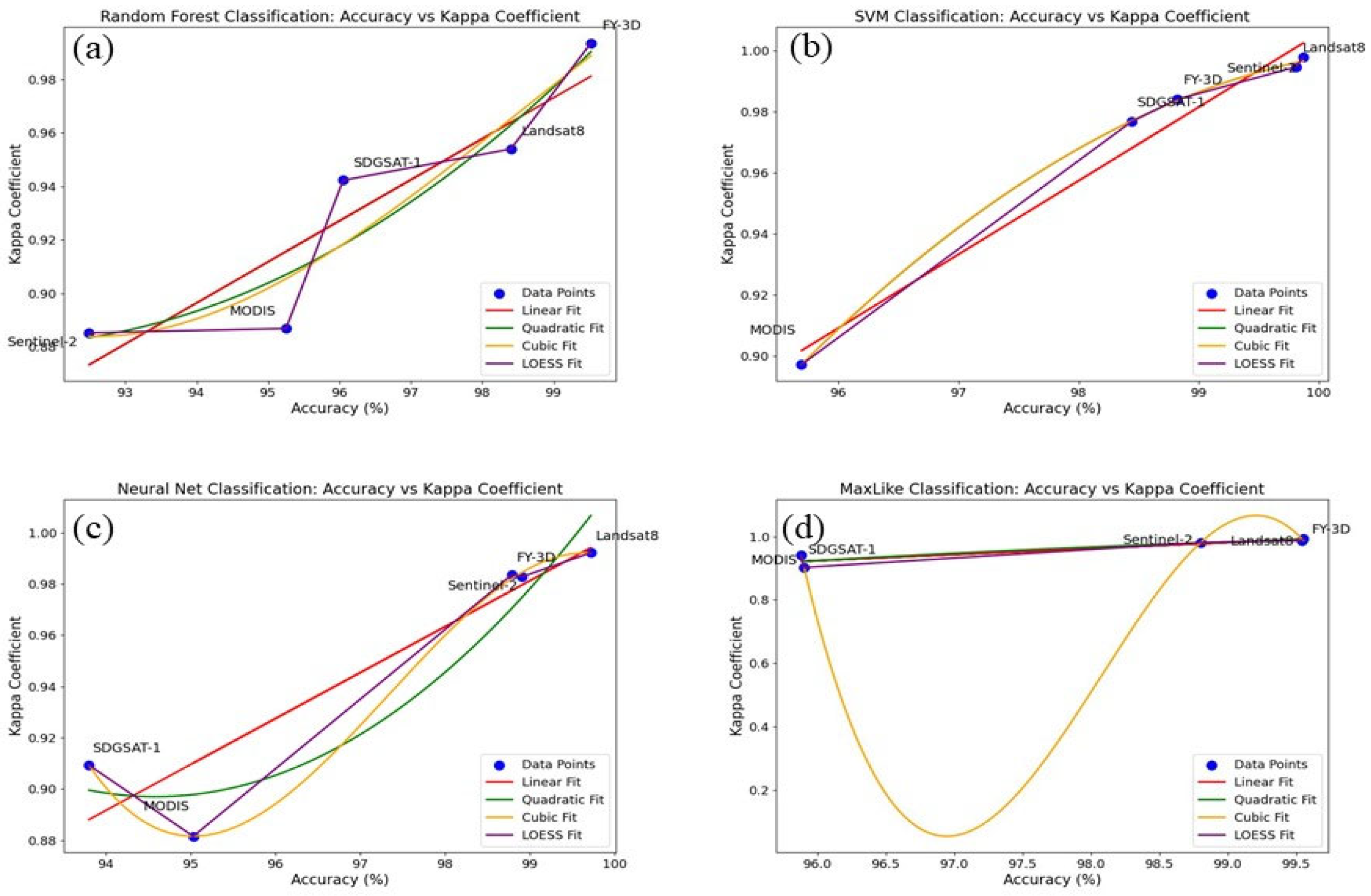
2.2.3. Precision Comparison
3. Results
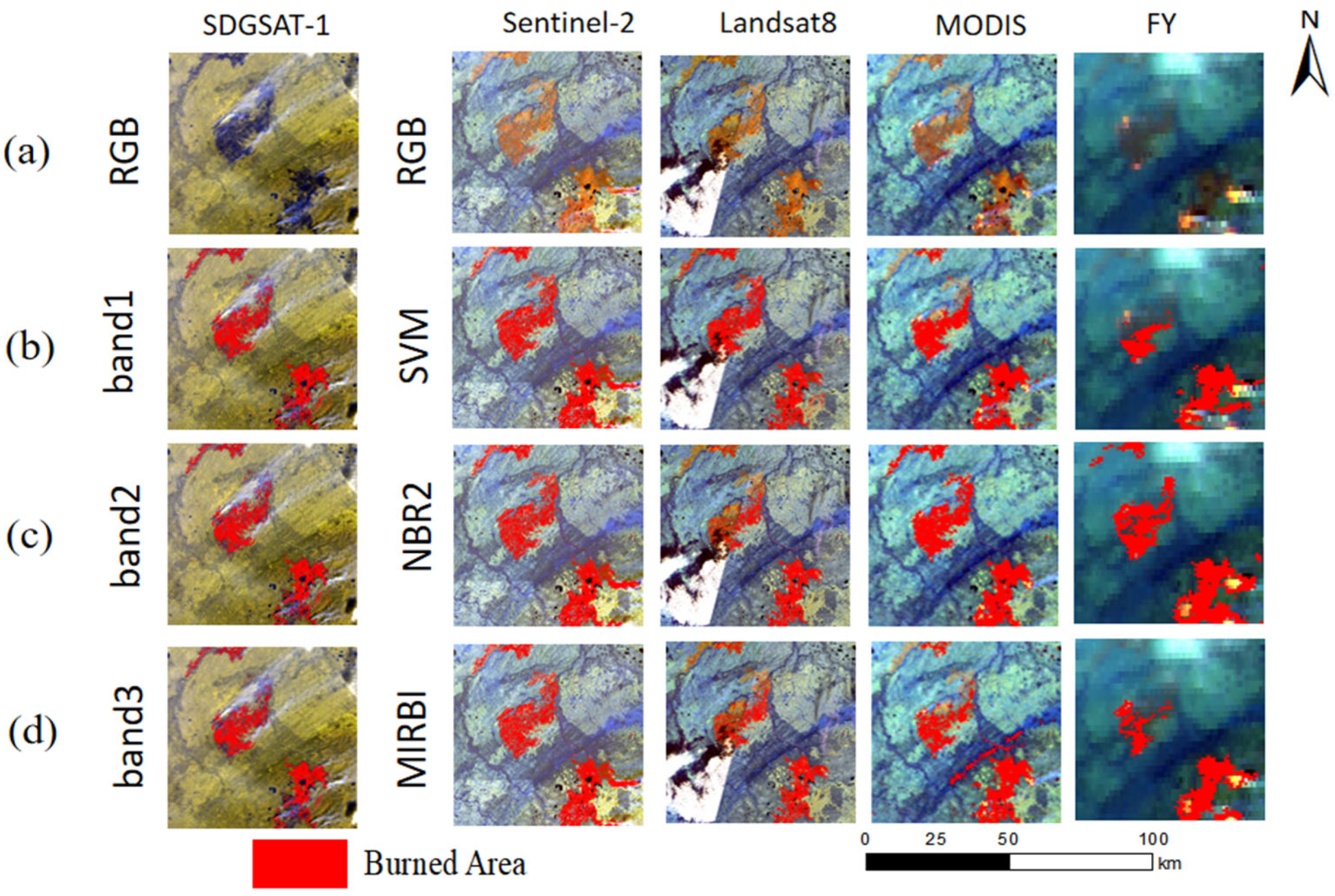
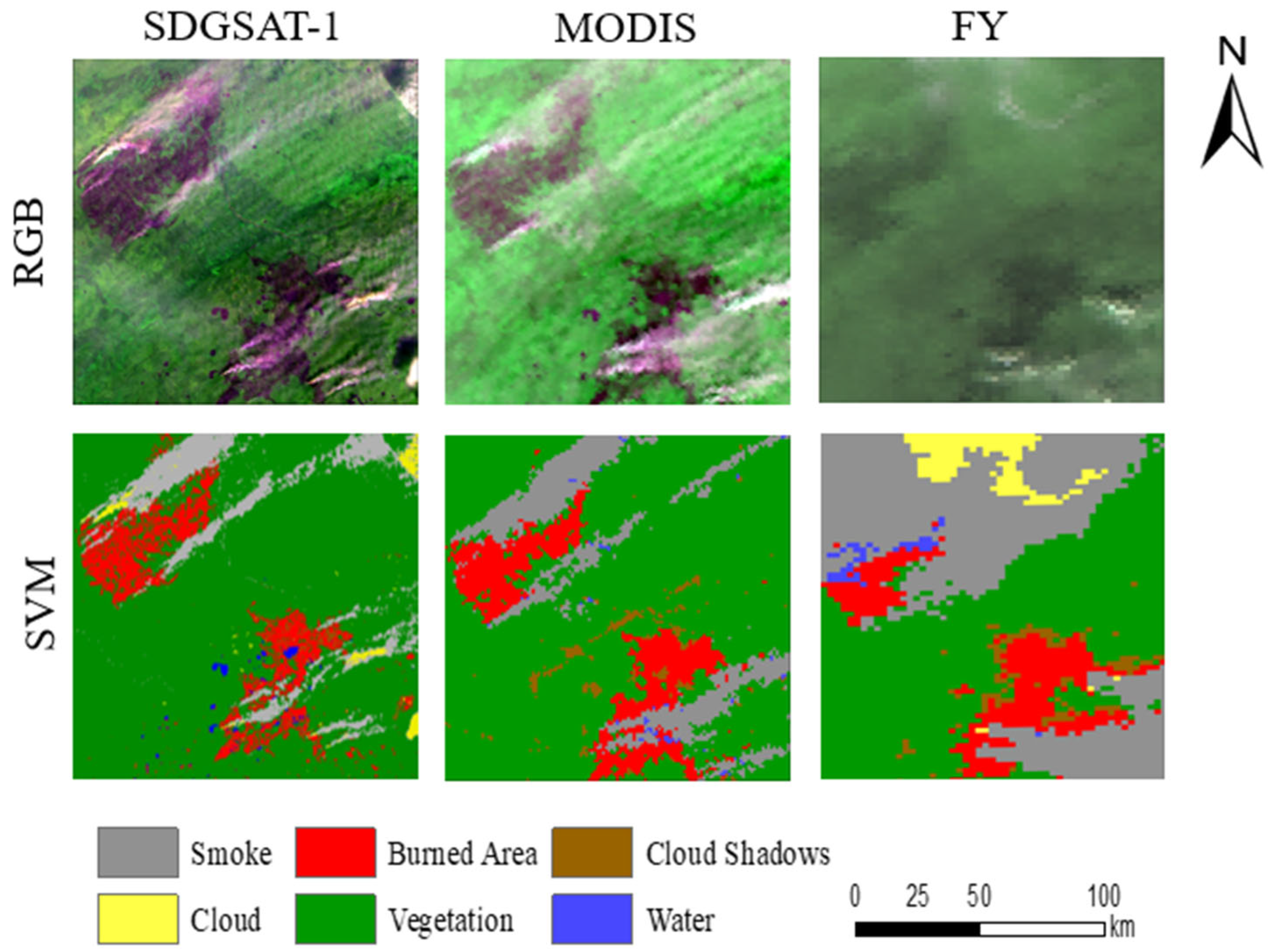
3.1. Effectiveness of Burned Areas
3.2. The Comparison of Smoke Detection
3.3. Performance of Fire Points
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senande-Rivera, M.; Insua-Costa, D.; Miguez-Macho, G. Spatial and temporal expansion of global wildland fire activity in response to climate change. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Huidobro, G.; Lopes, L.F.; Ganteaume, A.; Ascoli, D.; Colaco, C.; Xanthopoulos, G.; Giannaros, T.M.; Gazzard, R.; Boustras, G.; et al. A global outlook on increasing wildfire risk: Current policy situation and future pathways. Trees For. People 2023, 14, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.E.; Deere, N.J.; Imron, M.A.; Nasir, D.; Adul; Asti, H.A.; Soler, J.A.; Boyd, N.C.; Cheyne, S.M.; Collins, S.A.; et al. Impacts of fire and prospects for recovery in a tropical peat forest ecosystem. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2307216121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, I.C.; Lopes, D.; Fernandes, A.P.; Borrego, C.; Viegas, D.X.; Miranda, A.I. Atmospheric dynamics and fire-induced phenomena: Insights from a comprehensive analysis of the Sertã wildfire event. Atmos. Res. 2024, 310, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Yan, H.; Zhang, W.; Dodson, J.; Heijnis, H.; Burrows, M. Rapid warming has resulted in more wildfires in northeastern Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagis, T.; Gitas, I.Z. Assessing the accuracy of MODIS MCD64A1 C6 and FireCCI51 burned area products in Mediterranean ecosystems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagis, T.; Gitas, I.Z. Accuracy estimation of two global burned area products at national scale. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 932, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Su, H.; Sun, M.; Li, M. Reconstructing historical forest fire risk in the non-satellite era using the improved forest fire danger index and long short-term memory deep learning-a case study in Sichuan Province, southwestern China. For. Ecosyst. 2024, 11, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknejad, M.; Bernardino, A. Attention on classification for fire segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Pasadena, CA, USA, 13–16 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 616–621. [Google Scholar]
- Aral, R.A.; Zalluhoglu, C.; Akcapinar Sezer, E. Lightweight and attention-based CNN architecture for wildfire detection using UAV vision data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 5768–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Bergeron, Y.; Valeria, O.; Chavardès, R.D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. Fire detection and fire radiative power in forests and low-biomass lands in Northeast Asia: MODIS versus VIIRS Fire Products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, R.; Akhloufi, M.A. Deep learning approaches for wildland fires using satellite remote sensing data: Detection, mapping, and prediction. Fire 2023, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, E.; Zhang, R.; Zeng, X.; Xin, Y.; Ju, E.; Ling, Z. Spectroscopy of Magnesium Sulfate Double Salts and Their Implications for Mars Exploration. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, M.J.; Roberts, G.J.; Giglio, L.; Roy, D.P.; Freeborn, P.H.; Boschetti, L.; Justice, C.; Ichoku, C.; Schroeder, W.; Davies, D.; et al. Satellite remote sensing of active fires: History and current status, applications and future requirements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; Chu, R.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wu, X.; Xiao, H. Detecting forest fire omission error based on data fusion at subpixel scale. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2024, 128, 103737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.-Y.; Cao, C.-F.; Qu, Y.-X.; Zhang, G.-D.; Zhao, L.; Cao, K.; Song, P.; Tang, L.-C. Smart fire-warning materials and sensors: Design principle, performances, and applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2022, 150, 100690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, M.; Kong, L.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Shu, Q.; Ye, J.; Li, S.; et al. A spatial weight sampling method integrating the spatiotemporal pattern enhances the understanding of the occurrence mechanism of wildfires in the southwestern mountains of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2025, 585, 122619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismanto, H.; Marfai, M.A. Classification tree analysis (Gini-Index) smoke detection using Himawari_8 satellite data over Sumatera-Borneo maritime continent Sout East Asia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 256, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Quayle, B.; Lorenz, E.; Morelli, F. Active fire detection using Landsat-8/OLI data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kganyago, M.; Shikwambana, L. Assessment of the characteristics of recent major wildfires in the USA, Australia and Brazil in 2018–2019 using multi-source satellite products. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakuma, K.; Kuze, H.; Takeuchi, N.; Yahagi, T. Detection of biomass burning smoke in satellite images using texture analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Kliche, D.V.; Chou, J.; Welch, R.M. First estimates of the radiative forcing of aerosols generated from biomass burning using satellite data. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 1996, 101, 21265–21273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, J.; Song, W.; Ma, J.; Telesca, L.; Zhang, Y. Automatic smoke detection in modis satellite data based on k-means clustering and fisher linear discrimination. Photogramm. Eng. Rem. Sens. 2014, 80, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikiou, N.; Rushmeier, H.; Capel, M.I.; Kandakji, T.; Rios, N.; Lahdir, M. Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for Accurate Fire Severity Mapping in Northern Algeria. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Peters, S.; Li, J.; Mueller, N.; Oliver, S. Learning class-specific spectral patterns to improve deep learning-based scene-level fire smoke detection from multi-spectral satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Appl. 2024, 34, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, V.; Lasaponara, R.; Tramutoli, V. Evaluation of a new satellite-based method for forest fire detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1799–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, C.B.; Jones, S.D.; Reinke, K. A seasonal-window ensemble-based thresholding technique used to detect active fires in geostationary remotely sensed data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2020, 59, 4947–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Shao, G. The progress of operational forest fire monitoring with infrared remote sensing. J. For. Res. 2017, 28, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duane, A.; Moghli, A.; Coll, L.; Vega, C. On the evidence of contextually large fires in Europe based on return period functions. Appl. Geogr. 2025, 176, 103539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.; Wooster, M.J. Development of a multi-temporal Kalman filter approach to geostationary active fire detection & fire radiative power (FRP) estimation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 392–412. [Google Scholar]
- Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.; Restás, Á.; Morisette, J.T.; Schroeder, W.; Morton, D.; Justice, C.O. Active fire detection and characterization with the advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer (ASTER). Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3055–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Prins, E.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.; Schmidt, C.; Morisette, J.; Morton, D. Validation of GOES and MODIS active fire detection products using ASTER and ETM+ data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2711–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastarrika, A.; Alvarado, M.; Artano, K.; Martinez, M.P.; Mesanza, A.; Torre, L.; Ramo, R.; Chuvieco, E. BAMS: A tool for supervised burned area mapping using Landsat data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12360–12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroppiana, D.; Azar, R.; Calò, F.; Pepe, A.; Imperatore, P.; Boschetti, M.; Silva, J.M.N.; Brivio, P.A.; Lanari, R. Integration of optical and SAR data for burned area mapping in Mediterranean Regions. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1320–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E.; Roteta, E.; Sali, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Boettcher, M.; Kirches, G.; Storm, T.; Khairoun, A.; Pettinari, M.L.; Franquesa, M.; et al. Building a small fire database for Sub-Saharan Africa from Sentinel-2 high-resolution images. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.C.; Olthoff, A.E.; Hernández-Trejo, H.; Rullán-Silva, C.D. Evaluating the best spectral indices for burned areas in the tropical Pantanos de Centla Biosphere Reserve, Southeastern Mexico. Remote Sens. Appl. 2022, 25, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roteta, E.; Bastarrika, A.; Padilla, M.; Storm, T.; Chuvieco, E. Development of a Sentinel-2 burned area algorithm: Generation of a small fire database for sub-Saharan Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, F.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, D. Big Earth Data: A practice of sustainability science to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Dou, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, B.; Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Liang, D. SDGSAT-1, the world’s first scientific satellite for sustainable development goals. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Zeng, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, C.; Mao, D.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Nighttime light in China’s coastal zone: The type classification approach using SDGSAT-1 Glimmer Imager. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 305, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, F.; Dou, C.; Wu, M.; Niu, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, S. Identification of illumination source types using nighttime light images from SDGSAT-1. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2297013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Jiao, W.; Liu, H.; Long, T.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; He, G.; Portnov, B.A.; Trop, T.; Liu, M.; et al. Modelling the public perception of urban public space lighting based on SDGSAT-1 glimmer imagery: A case study in Beijing, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 88, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, F.; Wang, N.; Yu, B.; Wang, L. SDGSAT-1 nighttime light data improve village-scale built-up delineation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 297, 113764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qiu, S.; Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Qian, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Khoramshahi, E.; Qiu, Y. Vessel detection with SDGSAT-1 nighttime light images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, K.; Borges, J.G. A systematic review of applications of machine learning techniques for wildfire management decision support. Inventions 2022, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Coogan, S.C.; Subramanian, S.G.; Crowley, M.; Taylor, S.; Flannigan, M.D. A review of machine learning applications in wildfire science and management. Environ Rev. 2020, 28, 478–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountrakis, G.; Im, J.; Ogole, C. Support vector machines in remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Mather, P.M. An assessment of the effectiveness of decision tree methods for land cover classification. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Pedrero, A.; Gonzalo-Martin, C.; Lillo-Saavedra, M. A machine learning approach for agricultural parcel delineation through agglomerative segmentation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Schroeder, W.; Justice, C.O. The collection 6 MODIS active fire detection algorithm and fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, D.J.; Callow, J.N.; Duncan, J.M.A.; Setterfield, S.A.; Pauli, N. Regional-scale fire severity mapping of Eucalyptus forests with the Landsat archive. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.; Danaher, T.; Hehir, W.; Collins, L. A remote sensing approach to mapping fire severity in south-eastern Australia using sentinel 2 and random forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Tang, F. Sub-pixel accuracy evaluation of FY-3D MERSI-2 geolocation based on OLI reference imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 7215–7238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, R.; Sobrino, J.A.; Fernández, C.; Fernández-Alonso, J.M.; Vega, J.A. A methodology to estimate forest fires burned areas and burn severity degrees using Sentinel-2 data. Application to the October 2017 fires in the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 95, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantson, S.; Padilla, M.; Corti, D.; Chuvieco, E. Strengths and weaknesses of MODIS hotspots to characterize global fire occurrence. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Hu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, G.; Peng, G.; Xiang, D.; Wang, R.; Meng, R.; Wu, W. A novel strategy to reconstruct NDVI time-series with high temporal resolution from MODIS multi-temporal composite products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, M.O.; Justice, C.; Paynter, I.; Boucher, P.B.; Devadiga, S.; Endsley, A.; Erb, A.; Friedl, M.; Gao, H.; Giglio, L.; et al. Continuity between NASA MODIS Collection 6.1 and VIIRS Collection 2 land products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Huang, H.; Boschetti, L.; Giglio, L.; Yan, L.; Zhang, H.H.; Li, Z. Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 burned area mapping-A combined sensor multi-temporal change detection approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Data | Spatial Resolution | Data Sources | Acquisition Data (UTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SDGSAT-1 | 10 m | International Research Center of Big Data for Sustainable Development Goals http://www.sdgsat.ac.cn | 27 August 2023 |
| Sentinel-2 | 20 m | Copernicus Data Space https://dataspace.copernicus.eu/ | 28 August 2023 |
| Landsat8 | 30 m | U.S. Geological Survey https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ | 21 August 2023 |
| MODIS | 500 m | National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov | 27 August 2023 |
| FY-3D | 1000 m | FENGYUN Satellite Data Center https://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/ | 27 August 2023 |
| Band | Gain | Bias |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0.051560133 | 0 |
| B2 | 0.036241353 | 0 |
| B3 | 0.023316835 | 0 |
| B4 | 0.015849666 | 0 |
| B5 | 0.016096381 | 0 |
| B6 | 0.019719039 | 0 |
| B7 | 0.013811458 | 0 |
| Band | Gain | Bias |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | 0.003947 | 0.167126 |
| B2 | 0.003946 | 0.124522 |
| B3 | 0.005329 | 0.222530 |
| Julian Day | Distance | Julian Day | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9832 | 196 | 1.0165 |
| 15 | 0.9836 | 213 | 1.0149 |
| 32 | 0.9853 | 227 | 1.0128 |
| 46 | 0.9878 | 242 | 1.0092 |
| 60 | 0.9909 | 258 | 1.0057 |
| 74 | 0.9945 | 274 | 1.0011 |
| 91 | 0.9993 | 288 | 0.9972 |
| 106 | 1.0033 | 305 | 0.9925 |
| 121 | 1.0076 | 319 | 0.9892 |
| 135 | 1.0109 | 335 | 0.9860 |
| 152 | 1.0140 | 349 | 0.9843 |
| 166 | 1.0158 | 365 | 0.9833 |
| 182 | 1.0167 | - | - |
| Accuracy | SDGSAT/ Sentinel-2 (%) | SDGSAT/ Landsat8 (%) | SDGSAT/ MODIS (%) | SDGSAT/ FY-3D (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 99.58 | 96.95 | 88.75 | 77.31 |
| NBR2 | 99.39 | 95.18 | 96.76 | 92.23 |
| MIRBI | 98.26 | 94.95 | 89.37 | 78.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiang, B.; Ye, J.; Kong, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, M.; Yang, S.; Wang, W.; Kou, W.; et al. Enhancing Wildfire Monitoring with SDGSAT-1: A Performance Analysis. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193339
Zhu X, Zhang G, Xiang B, Ye J, Kong L, Yang W, Wu M, Yang S, Wang W, Kou W, et al. Enhancing Wildfire Monitoring with SDGSAT-1: A Performance Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193339
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xinkun, Guojiang Zhang, Bo Xiang, Jiangxia Ye, Lei Kong, Wenlong Yang, Mingshan Wu, Song Yang, Wenquan Wang, Weili Kou, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing Wildfire Monitoring with SDGSAT-1: A Performance Analysis" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193339
APA StyleZhu, X., Zhang, G., Xiang, B., Ye, J., Kong, L., Yang, W., Wu, M., Yang, S., Wang, W., Kou, W., Wang, Q., & Huang, Z. (2025). Enhancing Wildfire Monitoring with SDGSAT-1: A Performance Analysis. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3339. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193339









