Abstract
Nowadays, both BDS-3 and Galileo can provide global positioning and navigation services. This contribution carried out a comprehensive analysis and validation of positioning performance in terms of positioning accuracy (RMS) and convergence time, which are derived from BDS-3 and Galileo precise point positioning (PPP) solutions at a global scale. Meanwhile, the comparison with GPS was demonstrated. The performance and geographical distribution of RMS and convergence time for each satellite system were analyzed. GPS outperforms the other two systems on a global scale. Galileo and BDS-3, on the other hand, only perform moderately well in certain latitude zones. The combination of dual systems related to each single system is analyzed. For the dual-system combinations, the combination of systems presents a definite advantage over Galileo and BDS-3, and this advantage is more pronounced for the kinematic PPP. For GPS, the combination with Galileo and BDS-3 has little improvement in positioning performance. For the dual-system combination based on Galileo and BDS-3, the RMS and convergence time can be improved by 50% compared with the single system. The influence of single-system kinematic PPP selection for precise products from different MGEX analysis centers on positioning performance was studied. Among the five precise products, grg products have the best positioning performance for GPS, while cod products have the best positioning performance for Galileo and BDS-3. The difference in RMS and convergence time between 2 cm and 15 min can be caused by different precise product selections.
1. Introduction
In the past two decades, precise point positioning (PPP) has gradually been developed for GPS [1,2]. Through the PPP algorithm, only one receiver can achieve the absolute positioning of the target point. Compared to other positioning methods, PPP has massive application scenarios, including seismogeodetic, engineering survey, offshore exploration, geometric orbit estimation for satellites, emerging applications, etc. [3,4,5,6,7,8]. The main disadvantage of using PPP algorithms is the interminable convergence durations required to attain improved positioning accuracy. With the development of satellite constellations and tracking infrastructure, PPP using multi-system observations has become increasingly popular. To profit from multi-system and multi-frequency observations, the user must be provided with all calibration parameters that are system-dependent [9,10]. As a result, the research community and enterprise are working on developing GNSS processing algorithms, methodologies, and associated models. The International GNSS Service (IGS) launched a MGEX to track, collect, and evaluate all GNSS signals available [11]. MGEX analysis centers (ACs) already provide precise satellite products, including satellite orbits and clock corrections, for all GNSS constellations [12]. The difference between multi-system PPP and single-system PPP is that the clock deviation between different systems and the corresponding inter-system bias (ISB) and hardware delay need to be estimated. In order to obtain high-accuracy positioning results, precision ephemeris and orbit selection are important. Previous research has explored and compared the performance of PPP with products from various analysis centers (ACs) [13,14,15,16,17,18]. With comprehensive reference to these studies, the precision ephemeris of GFZ is chosen to conduct a series of multi-system PPP experiments in this paper. Initially, the system combination PPP was mainly based on GPS and GLONASS [19,20,21,22]. Researchers have been studying the performance of the combined GPS and GLONASS PPP, which shows improved accuracy and shorter convergence time when compared to GPS-only PPP. With the rapid development of muti-frequency BDS and Galileo in recent years, GPS combined with BDS [23,24,25,26,27] and GPS combined with Galileo [28,29,30,31] have received more and more attention. Especially since the opening of BDS-3 in 2020, the sufficient number of satellites on BDS-3 can further improve the geometric distribution of the satellite constellation and increase the number of observations. Redundant observations can be better realized to improve the positioning accuracy and shorten the convergence time of PPP positioning. Furthermore, the latest research has examined the performance of the combined four constellations (GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou) PPP. Single-system PPP will be gradually replaced by multi-system PPP [32,33,34,35,36,37].
These studies compare the positioning accuracy and convergence time of different system combinations with those of single systems, such as GPS, but most of them select a small number of stations and do not present the corresponding distribution pattern on a global scale. Therefore, in this paper, GPS, BDS-3, and Galileo are selected to study the gain of the system combination with respect to the single system. In order to provide a comprehensive assessment for the different system PPP solutions on a global scale, 143 MGEX tracking stations, which can receive signals from these three systems, have been selected worldwide. The positioning accuracy and convergence time distribution of the three single systems are analyzed. Then, the gain of the three dual-system combinations, including the GPS with BDS-3 combination (GC), GPS with Galileo combination (GE), and BDS-3 with Galileo combination (CE), with respect to the corresponding single-system combinations is evaluated. The influence of single-system kinematic PPP selection of precise products from different analysis centers on positioning performance is studied. In the last conclusion section, the results in this paper are summarized.
2. Methods
2.1. Ionosphere-Free PPP Observation Model
Ionosphere-free (IF) observations can be used to remove first-order ionospheric delays from pseudo-range and carrier-phase measurements. For a receiver r that has observed a satellite s (such as GPS, BDS-3, or Galileo) at a specific epoch, the linearization of the ionosphere-free code and carrier-phase observation equations are perhaps defined as
where
- and represent the observed minus calculated values of ionosphere-free code and carrier-phase observables, respectively;
- the superscript corresponds to G, C, or E, which indicate the satellite systems GPS, BDS-3, or Galileo;
- stands for the geometric distance between the receiver and the satellite; is the speed of light; and denote the receiver clock offset and satellite clock offset, respectively;
- is the tropospheric delay;
- and are the uncalibrated code hardware delays (UCDs) by the receiver and satellite, respectively;
- and represent the total of code and carrier-phase observation measurement noise and multi-path errors, respectively;
- is the carrier-phase ambiguity, which consists of the ionosphere-free combined receiver and satellite UCDs ( and ), the receiver and satellite uncalibrated phase hardware delays (UPDs) ( and ), the ionosphere-free wavelength (), and the ionosphere-free combined integer-phase ambiguity ().
The error components not mentioned above are supposed to be properly adjusted using their respective models, such as PCO and PCV, phase wind-up, solid earth tides, polar tides, ocean loading, and earth rotation parameters (ERPs). The tropospheric delay can be divided into the hydrostatic component and the wet component. The zenith hydrostatic delay (ZHD) is adjusted with the Saastamoinen model. The zenith wet delay (ZWD) has to be approximated as an uncertainty. The slant hydrostatic delays (SHDs) and slant wet delays (SWDs) can be corrected using the mapping function, which simulates the connection between the SHD and SWD to the corresponding zenith delays.
For a single-system PPP, the clock parameter is often regarded as an epoch-wise parameter. A GNSS clock and an inter-system time difference parameter (referred to as ISB) are estimated for the multi-system combined PPP. There are various methods for modeling the ISB parameter. Epoch-wise ISB should be calculated for robust data analysis.
The difference between the common pseudo-range and phase hardware delays is assimilated into the ambiguity parameter in the multi-system combined PPP model, while the common pseudo-range hardware delay is assimilated into the clock parameter. The Ionosphere-free PPP model with multi-constellation can be described as the following by taking the aforementioned concepts into consideration:
with
2.2. Data Sets and Processing Strategies
To evaluate the impact of different constellation combinations on PPP performance, datasets from 143 MGEX stations were selected (shown in Figure 1) and used from 1 to 30 September 2022 (DOY 244 to 273). Signals from GPS, BDS-3, and Galileo can all be received by all stations. All data are downloaded through the GAMP-GOOD software, which is open-sourced at GitHub [38]. All PPP analysis was carried out using the open-source GAMP software [39], which is publicly available via the GPS Toolbox webpage. Static PPP and kinematic PPP modes are respectively used to evaluate the positioning performance of the double-frequency PPP model of six schemes, namely, GPS-only (G), BDS-3-only (C), Galileo-only (E), GC, GE, and CE combinations. Table 1 shows the PPP processing strategies in detail.
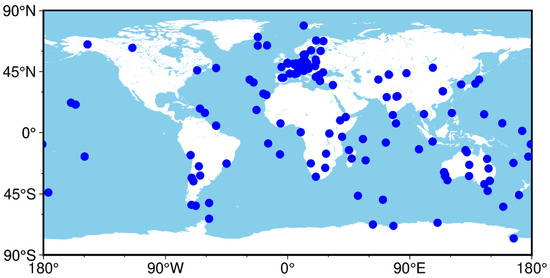
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of the selected 143 worldwide MGEX tracking stations.

Table 1.
Processing strategy for system combination PPP.
2.3. Availability Analysis of GNSS Constellations
Figure 2 depicts the global distribution of the average number of visible satellites for single systems and combinations of different orbital types of BDS-3, with an elevation cut-off of 7°, over a day (1 September 2022). As shown in Figure 2, the globally average number of GPS reaches more than 10, and specifically in low- and high-latitude regions, it rises to more than 12. However, there are fewer than 10 for Galileo. For BDS-3, it is combined with MEO, IGSO, and GEO satellites. It is apparent that in the combination of BDS-3, MEO, and IGSO, there are more than 12 visible satellites in the area between longitude 45–180E and latitude 20S–20N. Compared with BDS-3 MEO, it is clear that in high-latitude regions, the number of visible satellites for BDS-3 MEO+IGSO satellites increases greatly. Thus, it has more visible satellites in the Asia-Pacific region than GPS and Galileo. In contrast, the number of BDS-3 satellites in the western hemisphere at low and middle latitudes is under 8. The DPOP values are shown in Figure 3. It is clear that the value for each system corresponds to the distribution of their number of visible satellites.
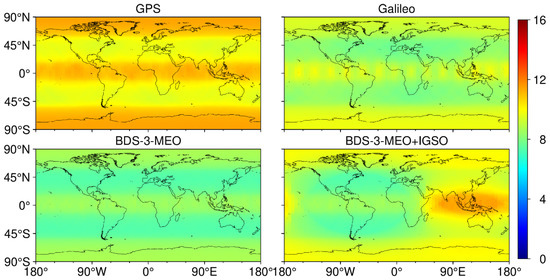
Figure 2.
Average visible satellite numbers of GPS, Galileo, BDS-3 MEO, and BDS-3 MEO+IGSO over a day (1 September 2022) with an elevation cut-off of 7°.
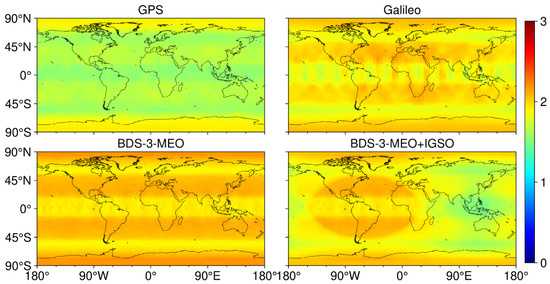
Figure 3.
Average PDOP value of GPS, Galileo, BDS-3 MEO, and BDS-3 MEO+IGSO over a day (1 September 2022) with an elevation cut-off of 7°.
The distribution of the number of visible satellites and the value of PDOP for the single systems and combinations of different orbital types of BDS-3 over a day (1 September 2022), with an elevation cut-off of 7°, is shown in Figure 4. It is clear that the range for GPS is from 9 to 12, which is the largest number among all single schemes, while it is only from 7 to 9 for Galileo, which has the least visible satellites in all the single systems. There are a range of 7–11 globally visible satellites for the BDS-3 MEO+IGSO, which is the widest distribution. The extensive distribution of BDS-3 MEO+IGSO indicates that there are fewer satellites for some stations, which may reduce the positioning accuracy of those stations. Although the visible satellite number can meet the basic requirement, it is worth noting that there are not many discernible satellites in a single system. For PDOP, BDS-3 MEO has the smallest number of visible satellites, so its PDOP is also the largest of the four systems. However, GPS has the smallest PDOP of the three systems because of its centralized distribution of the number of visible satellites. BDS-3 MEO+IGSO has the largest PDOP value among the four systems because of its wide distribution of the number of visible satellites.
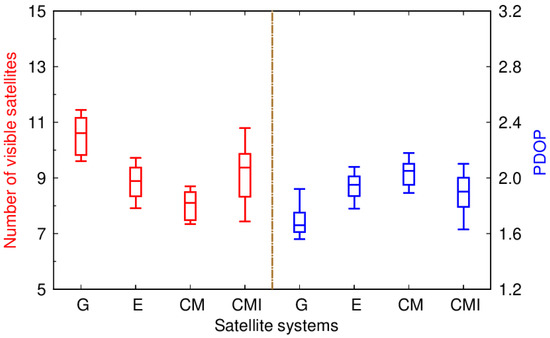
Figure 4.
Distribution of the number of visible satellites and PDOP values for different systems (G is short for GPS, E is short for Galileo, CM is short for BDS-3 MEO, and CMI is short for BDS-3 MEO+IGSO) over a day (1 September 2022) with an elevation cut-off of 7°.
3. Results
3.1. Positioning Performance of the Single Systems
In order to analyze the positioning accuracy and convergence time performance of a single system, we obtain the corresponding quantile by using data from each tracking station for each system for a month in static or kinematic mode to plot the boxplot. Figure 5 illustrates the monthly convergence time and RMS of static PPP based on the three single-system schemes, and the month median RMS and convergence time are also indicated. Here, we define “convergence” as obtaining a 3D-positioning error less than the predefined threshold at the current epoch and the following 20 epochs, which has been adopted from Li and Zhang [40]. Only when the positioning errors of all 20 epochs are within the threshold do we consider that the position has converged at the current epoch. Here, the threshold is 1 dm, which has been suggested by Lou et al. [41]. For positioning accuracy (RMS), it is calculated through the same convergence period; here, we have chosen 2 h after the start of PPP filtering for each test. In order to facilitate the analysis, the east and north component vectors are synthesized as the horizontal component, and the up component is taken as the vertical component. For the convergence time in the horizontal component, GPS-only has the least convergence time of static PPP solutions, about 10.9 min. The performance of the remaining two single systems is not as good as GPS-only. Specifically, Galileo-only performs better than BDS-3-only, with values of about 16.5 min, and it is 20.4 min for BDS-3-only. Similar to the horizontal component, GPS-only has the shortest convergence time in the vertical component, which is 11.0 min for static PPP. With convergence times of about 16.5 min, BDS-3-only outperforms Galileo-only, which has values of roughly 17.0 min for static PPP. As shown in the figure, the RMS of both PPP solutions in the horizontal component is vastly better than in the vertical component. The median RMS values for GPS-only are 0.39 and 1.00 cm; they are 0.57 and 1.03 cm for Galileo-only. We can see that the RMS of GPS-only and Galileo-only in the static PPP solution are comparable. However, the median RMS of PPP solutions for BDS-3-only is larger than that of the other two single-system schemes, where the values are 0.86 and 1.55 cm in the horizontal and vertical components, respectively.
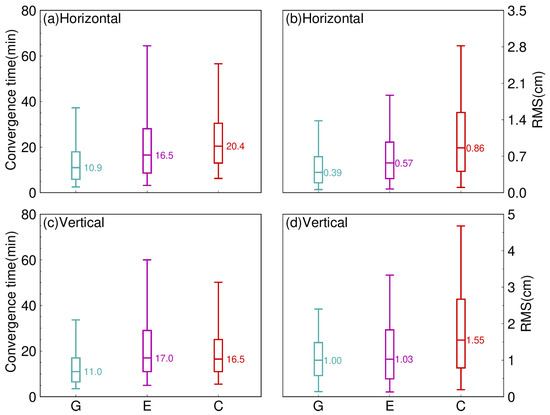
Figure 5.
Distribution of the convergence time and RMS of static PPP solutions in three single systems (G is short for GPS, E is short for Galileo, and C is short for BDS-3) in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component of convergence time, (b) Horizontal component of RMS, (c) Vertical component of convergence time, (d) Vertical component of RMS.
For different solutions, as is generally known, the accuracy of kinematic PPP is obviously lower than that of static PPP due to the weaker model. Meanwhile, the performance of different single systems is compared. Similar to Figure 5, Figure 6 shows the distribution of the convergence time and RMS of the kinematic PPP. Each panel in Figure 6 depicts the static and kinematic PPP convergence times using three single systems in the horizontal and vertical components, respectively. In contrast to the RMS performance, the convergence time of both PPP solutions, except Galileo, in the vertical component is shorter than in the horizontal component. For the horizontal component, GPS-only has the least convergence time of the kinematic PPP solutions, about 21.9 min. Galileo-only performs better than BDS-3-only, with values of about 27.5 min, whereas it is 32.0 min for BDS-3-only. Similar to the horizontal component, GPS-only has the shortest convergence time, which is 17.0 min. With convergence times of about 31.0 min, BDS-3-only outperforms Galileo-only, which has values of roughly 35.5 min. The median RMS for GPS-only is 2.30 and 3.83 cm, and the median RMS of the PPP solutions for Galileo-only and BDS-3-only is twice as large as GPS-only, with a value of 4.75 and 7.07 cm for Galileo and 4.73 and 7.62 cm for BDS-3 in the horizontal and vertical components, respectively. In general, GPS-only has the best positioning accuracy of all the single-system kinematic PPP solutions. Meanwhile, convergence time is used to assess positioning performance.
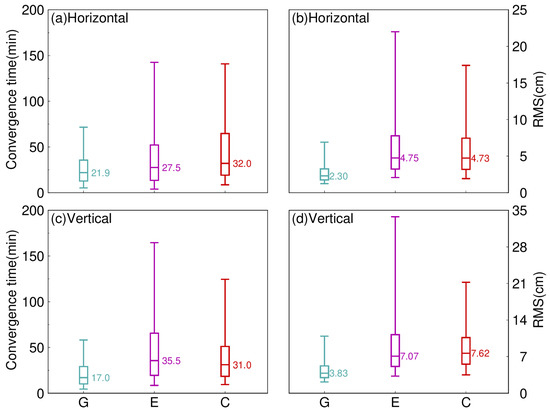
Figure 6.
Distribution of the convergence time and RMS of kinematic PPP solutions in three single systems (G is short for GPS, E is short for Galileo, and C is short for BDS-3) in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component of convergence time, (b) Horizontal component of RMS, (c) Vertical component of convergence time, (d) Vertical component of RMS.
Overall, the higher convergence performance of GPS-only is particularly apparent in kinematic PPP. Thus, GPS-only PPP solutions have the best positioning performance in both positioning accuracy and convergence time among all the single-system PPP solutions.
3.2. Geographical Distribution of the Single Systems
In order to study the geographical distribution pattern of the single system, we use the RMS and convergence time of each tracking station for one month and take its median to represent the convergence time and RMS of the station and present it in the global map. We display the convergence time statistics of static PPP across three single systems over one month (September 2022) for the horizontal and vertical components at the selected 143 stations using a color bar (but different scales) along a global map in Figure 7. To make the analysis more intuitive, the mean convergence time of the different latitude zones for static PPP is listed in Table 2, where H and V represent the horizontal and vertical components, respectively, and N and S represent the northern and southern hemispheres, respectively. Accordingly, the range from 60° to 90° is defined as the high-latitude zone (denoted by High_N in the northern hemisphere and High_S in the southern hemisphere), the range from 30° to 60° as the middle-latitude zone (Med_N and Med_S), and the range from 0° to 30° as the low-latitude zone (Low_N and Low_S). Further, the tracking station numbers in the different latitude zones are listed. For static PPP in the horizontal component, we can see that the convergence time of GPS-only tracking stations in the high latitudes is well below 10.00 min, which is shorter than that in the low and middle latitudes. In addition, the convergence time in other zones is less than 15.00 min, except for the low latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Galileo-only tracking stations have a convergence time of less 20.00 min in the middle latitudes of the southern hemisphere and in the high latitudes all around the world. For BDS-3-only, stations in the middle latitudes have a convergence time of more than 23.00 min, while the time for stations in the high latitudes is shorter than 17.00 min. The three single systems all follow the law that in the northern hemisphere, the higher the latitude, the shorter the convergence time, whereas in the southern hemisphere, the convergence time is shortest in the low latitudes and slightly worse in the middle and high latitudes. In terms of the vertical component, the three single-system tracking stations have a similar distribution, that is, the convergence time from high latitude to low latitude changes in turn long.
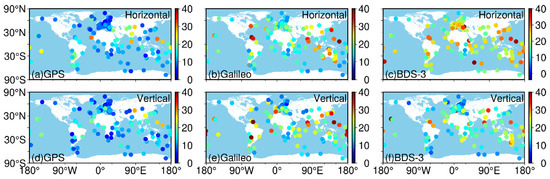
Figure 7.
Geographical distribution of the median convergence times of static PPP for the selected 143 worldwide MGEX tracking stations over a month (September 2022) using three single systems.

Table 2.
The number of stations and the mean convergence times (unit: min) of the different latitudes for static PPP.
Figure 8 shows the convergence time statistics of kinematic PPP, the same as in Figure 7. Further, Table 3 depicts the mean RMS of the different latitude zones for kinematic PPP. For kinematic PPP in the horizontal component, it is evident that the distributions of the convergence times of Galileo-only tracking stations show striking similarity to the static PPP. GPS-only tracking stations have a convergence time of above 24.00 min in the middle latitudes, but it is below 22.00 min in the high latitudes. BDS-3-only tracking stations have a convergence time of about 30.00 min, which is shorter than the stations in the low and middle latitudes. GPS-only and Galileo-only tracking stations have a vertical component distribution that is equivalent to the static PPP. The convergence time for BDS-only tracking stations is shorter in the low and high latitude zones than in the middle latitude zone. In general, the higher the latitude, the shorter the convergence time for most tracking stations.
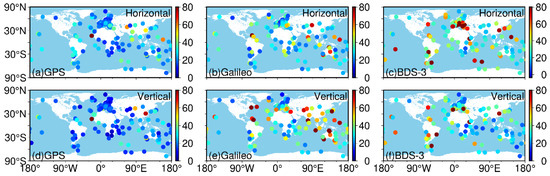
Figure 8.
Geographical distribution of the median convergence times of kinematic PPP for the selected 143 worldwide MGEX tracking stations over a month (September 2022) using three single systems.

Table 3.
The mean convergence times (unit: min) of the different latitudes for kinematic PPP.
The geographical distribution of the RMS is depicted (Figure 9 for static PPP, Figure 10 for kinematic PPP), and the mean RMS of the various latitudes is listed (Table 4 for static PPP, Table 5 for kinematic PPP). For the horizontal component, we can see that the RMS value of GPS-only tracking stations reaches more than 0.48 cm in the low latitudes and performs relatively better in the middle and high latitudes of the northern hemisphere, where the RMS statistics are well below 0.38 cm. Galileo-only tracking stations have an RMS of above 0.60 cm in the middle and high latitudes, but better performance in the low latitudes, with a value of below 0.60 cm. For BDS-3-only, most stations have an RMS of more than 0.95 cm in the middle and high latitudes of the southern hemisphere and the low and high latitudes of the northern hemisphere, while the stations in the middle latitude of the northern hemisphere and low latitudes of the southern hemisphere performed relatively better, with a value below 0.95 cm. For the vertical component, all three systems performed significantly better at high latitudes than at low latitudes.
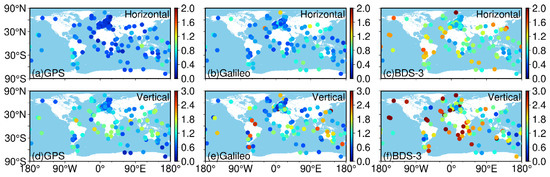
Figure 9.
Geographical distribution of the median RMS of static PPP for the selected 143 worldwide MGEX tracking stations over a month period (September 2022) using three single systems.
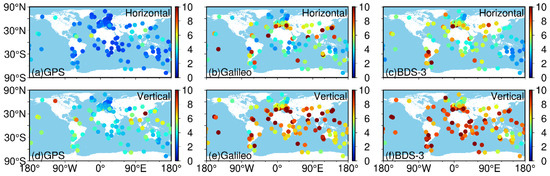
Figure 10.
Geographical distribution of the median RMS of kinematic PPP for the selected 143 worldwide MGEX tracking stations over a month period (September 2022) using three single systems.

Table 4.
The mean RMS (unit: cm) of the different latitudes for static PPP.

Table 5.
The mean RMS (unit: cm) of the different latitudes for kinematic PPP.
For the kinematic PPP solutions in the horizontal component, the geographical distribution of the median RMS for GPS-only are similar to those of the static PPP solutions. Galileo-only performs better in the high latitudes, with a value of about 4.00 cm. Meanwhile, it is clear that for stations located in the high latitudes all around the world and the low latitudes of the southern hemisphere, the RMS of BDS-3-only is well below 5.00 cm, and it is larger than 5.00 cm in the other areas. For the vertical component, it is apparent that, compared with the low latitudes, the respective RMS of both GPS-only and BDS-3-only in the high latitudes is relatively lower. On the whole, the RMS statistics of almost all the PPP solutions perform better in the high latitudes than in the low latitudes. Although the number of stations located in different latitude zones is not the same, this is a general conclusion. This can be explained by the similar distribution of the average number of visible satellites for the three single-system constellations.
3.3. Positioning Performance of the Dual Systems
The three dual-system schemes are compared to their corresponding single-system schemes in the same way that the single-system schemes are. Figure 11 illustrates the monthly convergence time and RMS of single-system and dual-system combination static PPP solutions, and the month median convergence time and RMS are also indicated. First, convergence time is used to assess positioning performance. For the horizontal component, the GE combination has the least convergence time of all the dual-system PPP solutions, about 8.1 min. The performance of the GC combination is not as good as the GE combination. Specifically, the median convergence time of the GC combination is 9.4 min. The performance of the CE combination is not as good as the GE and GC combinations. Specifically, the median convergence time of the CE combination is 11.8 min. All three dual-system combinations have a shorter convergence time than all three single systems in the horizontal component. Similar to the horizontal component, the GE combination has the shortest convergence time in the vertical component, which is 9.0 min. The convergence time for this GC combination is about 9.5 min. The convergence time of the CE combination is 12.0 min. Both the GC and GE combination outperform GPS-only. As shown in the figure, the RMS of PPP solutions in the vertical component is vastly better than in the horizontal component. The performance of dual-system combinations is compared. The median RMS for the GC combination is 0.48 and 1.23 cm in the horizontal and vertical components, respectively; it is 0.41 and 0.99 cm for the GE combination, respectively, and it is 0.51 and 1.21 cm for the EC combination, respectively. We can see that the RMS statistics of GPS-only perform better than all three dual-system schemes.
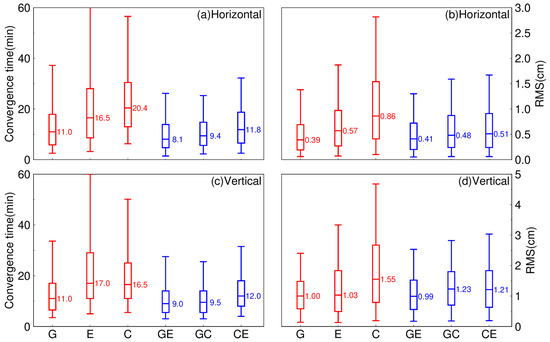
Figure 11.
Distribution of the convergence time and RMS of static PPP solutions for the single systems (G is short for GPS, E is short for Galileo, and C is short for BDS-3) and dual-system combinations (GE is short for GPS combined with Galileo, GC is short for GPS combined with BDS-3, and CE is short for BDS-3 combined with Galileo) in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component of convergence time, (b) Horizontal component of RMS, (c) Vertical component of convergence time, (d) Vertical component of RMS.
The situation with kinematic PPP is shown in Figure 12. The advantages of system combination are more obvious in kinematic PPP. The convergence time of all dual-system combination PPP solutions in the vertical component is shorter than in the horizontal component. For the horizontal component, the GE combination has the least convergence time of all dual-system PPP solutions, about 12.1 min. The median convergence time of the GC combination is 13.2 min. The performance of the CE combination is not as good as the GE and GC combinations. Specifically, the median convergence time of the EC combination is 16.2 min. All three dual systems have a shorter convergence time than GPS-only in the horizontal component. Both the GE and GC combinations have the same median convergence time in the vertical component, which is 11.5 min. The convergence time of the EC combination is 15.5 min. All three dual-system combinations outperform GPS-only. It is clear that the RMS of PPP solutions in the vertical component is vastly better than in the horizontal component. Both the GE and GC combinations are obviously superior to GPS-only in the horizontal component. The median RMS of the two combinations is 2.19 and 1.97 cm, respectively. The median RMS of the CE combination is 2.61 cm. The CE combination performed better than BDS-3-only and Galileo-only, but not as well as GPS-only. For the vertical component, only the GE combination performed better than GPS-only. It is 3.58, 4.03, and 4.75 cm for the GE, GC, and CE combinations, respectively. The GC and CE combinations performed better than BDS-3-only and Galileo-only. As is well known, the accuracy of kinematic PPP is clearly lower than that of static PPP for various solutions due to the weaker model. Therefore, the RMS statistics of kinematic PPP are four times as large as static PPP. However, the system combination significantly reduces the error of kinematic PPP.
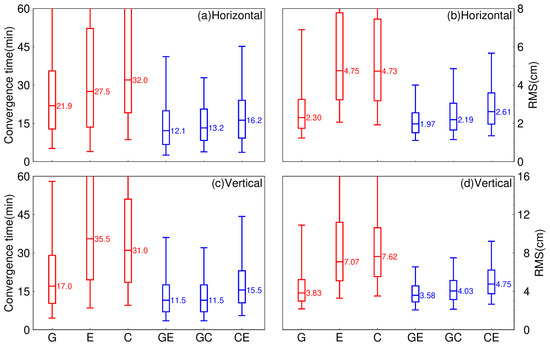
Figure 12.
Distribution of the convergence time and RMS of kinematic PPP solutions for the single systems (G is short for GPS, E is short for Galileo, and C is short for BDS-3) and dual- system combinations (GE is short for GPS combined with Galileo, GC is short for GPS combined with BDS-3, and CE is short for BDS-3 combined with Galileo) in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component of convergence time, (b) Horizontal component of RMS, (c) Vertical component of convergence time, (d) Vertical component of RMS.
For convergence time, all three dual-system combinations have a shorter convergence time than the GPS-only PPP solutions. For RMS, it is clear that with Galileo combined, GPS performs better than without. On the other hand, with BDS-3 combined, GPS does not perform as well as without.
3.4. Positioning Performance of the Single System with Different Types of Precise Products
We chose five precise products from different analysis centers to compare the positioning performance of single systems with different types of precise products. GPS and Galileo use precise products from five analysis centers, while BDS-3 uses precise products from four analysis centers. Specific information about the precise products is given in Table 6.

Table 6.
Details of the precise products used in this section.
In order to better analyze the impact of using different analysis center products on positioning accuracy, the following figures (Figure 13 and Figure 14 for GPS, Figure 15 and Figure 16 for Galileo, and Figure 17 and Figure 18 for BDS-3) show the distribution of convergence times and RMS at 143 tracking stations using different analysis center products for three single-system PPP solutions over a month. For the convergence time of GPS kinematic PPP solutions, the performance in the horizontal components is consistent with RMS. In the vertical direction, the cod, gfz, grg, and iac products have similar convergence time distributions, and the median convergence time is 17.00 min. The convergence time of the whu product is 17.50 min. For RMS, the grg products performed best, with a median RMS of 1.85 and 3.11 cm in both the horizontal and vertical components, respectively. The cod, iac, and whu products are 1.89 and 3.18 cm, 1.93 and 3.19 cm, and 1.94 and 3.21 cm, respectively. The gfz product performed the worst, with RMS values of 2.30 and 3.83 cm, respectively.
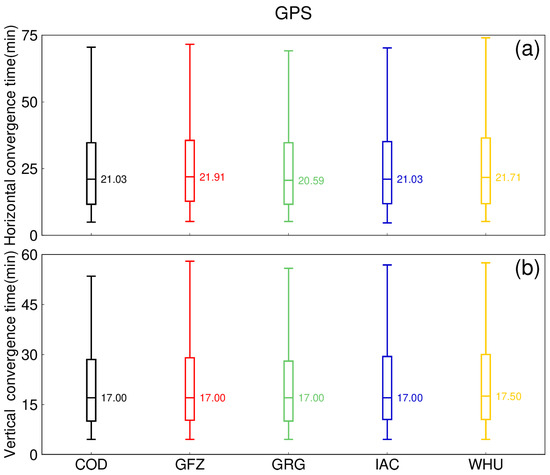
Figure 13.
Distribution of the convergence time of the GPS kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
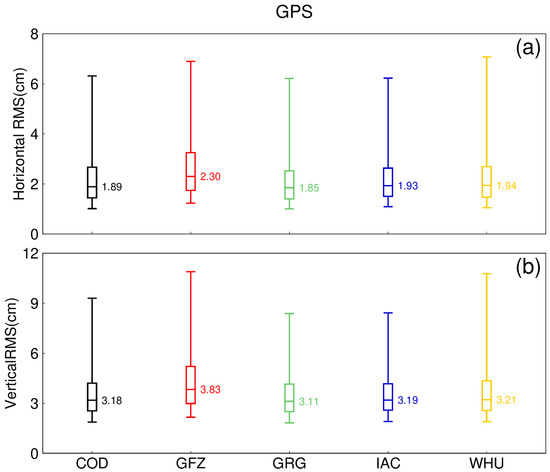
Figure 14.
Distribution of the RMS of the GPS kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
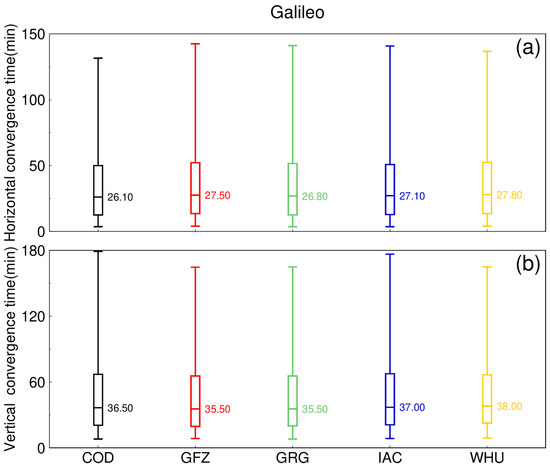
Figure 15.
Distribution of the convergence time of the Galileo kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
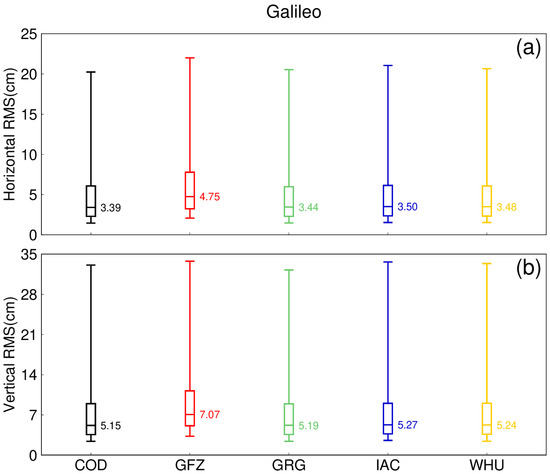
Figure 16.
Distribution of the RMS ((a,b) for the horizontal and vertical component, respectively) of the Galileo kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
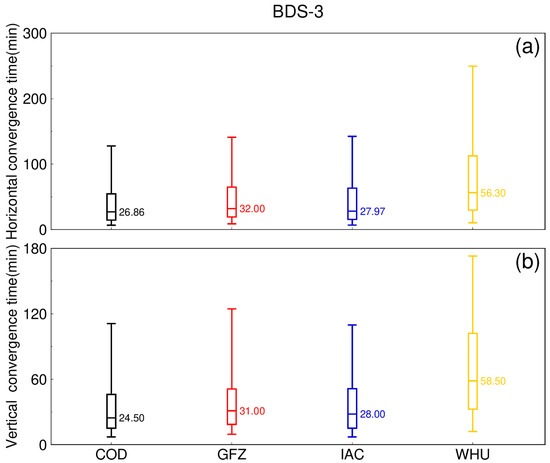
Figure 17.
Distribution of the convergence time of the BDS-3 kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
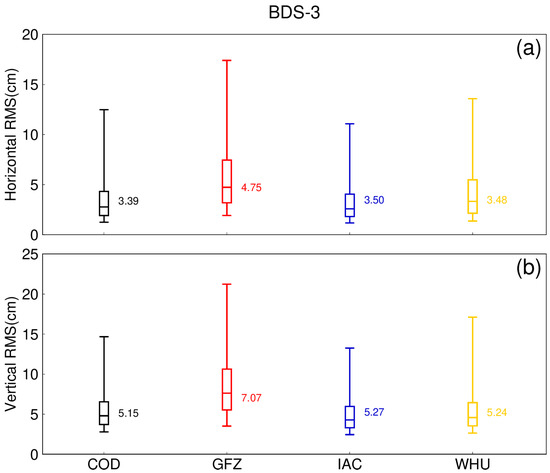
Figure 18.
Distribution of the RMS of the BDS-3 kinematic PPP solutions with five types of precise products for the 143 MGEX tracking stations in September 2022. (a) Horizontal component, (b) Vertical component.
4. Discussion
The positioning performance of three single systems (GPS-only, BDS-3-only, and Galileo-only) and three dual systems (GC, GE, and CE) in static and kinematic PPP solutions has been thoroughly investigated and assessed based on one-month observations (September 2022) of 143 MGEX stations that are capable of tracking GPS, BDS-3, and Galileo signals. The positioning accuracy and convergence time of single-system kinematic PPP with different precise products are also studied.
For the single systems, in terms of RMS and convergence time distributions, the static PPP of GPS-only has slightly better RMS than Galileo-only in both the horizontal and vertical components, while it is much better than BDS-3-only; for the kinematic PPP, the RMS of GPS-only is significantly smaller than the other two systems. The convergence time shows different patterns in the two components. For all the PPP solutions, whether in the horizontal component or the vertical component, there is no doubt that the convergence time performance of GPS-only ranks first. Galileo-only outperforms BDS-3-only in the horizontal, while BDS-3-only outperforms Galileo-only in the vertical. Meanwhile, the relationship among RMS, convergence time, and latitude is being investigated. The GPS-only solution shows a trend of progressively worse performance from high to low latitudes. Galileo-only has the same pattern as GPS-only. For BDS-3-only, it performs significantly better in the low and high latitude zones than in the middle latitude zone.
For the dual-system combinations, the RMS and convergence times of the three system combinations have nearly the same distribution pattern, with the GE combination having the highest positioning accuracy and the shortest convergence time, followed by the GC combination, and finally the CE combination. For GPS-based dual-system combinations, using Galileo and BDS-3 combined has not improved the positioning accuracy of GPS, nor has it shortened the convergence time. For the dual-system combination based on Galileo, combined with GPS and BDS-3, the RMS value will be reduced by more than 0.10 cm for static PPP and more than 2.00 cm for kinematic PPP, and the convergence time will be reduced by more than 4.0 min and more than 10.0 min, respectively. For the dual-system combination based on BDS-3 combined with GPS and Galileo, the RMS value will be reduced by more than 0.30 cm for static PPP and more than 2.00 cm for kinematic PPP, and the convergence time will be reduced by more than 4.5 and 15.0 min, respectively.
For single-system kinematic PPP solutions with different types of precise products, the positioning performance of different products under different systems is also different. For GPS, the median RMS difference between the best performing product and the worst performing product can reach more than 0.50 cm. However, the difference in convergence time is smaller, less than two minutes. For Galileo, the difference in RMS between products can reach a maximum of about 2.00 cm. The maximum difference in convergence time is only 2.5 min. Finally, for BDS-3, the maximum difference of the RMS can reach 1.90 cm, and the maximum difference of the convergence time can reach 30.0 min.
5. Conclusions
Overall, GPS has the best global performance of the three single systems, while Galileo and BDS-3 have better performance only at high latitudes. In general, the three single systems’ RMS and convergence times are better in high latitude zones than in low latitude zones.
For the dual-system combinations, the combination of systems presents a definite advantage over Galileo and BDS-3, and this advantage is more pronounced for kinematic PPP. For the dual-system combination based on Galileo, combined with GPS and BDS-3, the RMS and convergence time can be improved by 50% compared with the single system. For the dual-system combination based on BDS-3 combined with GPS and Galileo, the RMS can be improved by 50% and the convergence time can be improved by 60% compared with the single system. For GPS, the combination with Galileo and BDS-3 has little improvement in positioning performance.
The precise products used in PPP have a great impact on positioning performance. Among the five precise products studied in this paper, the grg products have the best positioning performance for GPS, and the cod products have the best positioning performance for Galileo and BDS-3. The difference in RMS and convergence times between 2 cm and 15 min can be caused by different precise product selections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.H.; methodology, Z.H.; software, F.Z. and Z.H.; validation, F.Z.; formal analysis, Z.H.; investigation, F.Z. and Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, F.Z. and Z.H.; writing—review and editing, F.Z. and Z.H.; visualization, Z.H.; supervision, F.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Laoshan Laboratory (LSKJ202205104, LSKJ202205104_01) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M673669).
Data Availability Statement
The GNSS raw observation data was available at ftps://gdc.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/pub/gnss/data/daily/ (accessed on 6 May 2022). The precise orbit and clock data was available at ftps://gdc.cddis.eosdis.nasa.gov/pub/gnss/products/mgex/ (accessed on 6 May 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zumberge, J.F.; Heflin, M.B.; Jefferson, D.C.; Watkins, M.M.; Webb, F.H. Precise Point Positioning for the Efficient and Robust Analysis of GPS Data from Large Networks. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1997, 102, 5005–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Héroux, P. Precise Point Positioning Using IGS Orbit and Clock Products. GPS Solut. 2001, 5, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Bock, Y.; Melgar, D.; Crowell, B.W.; Haase, J.S. A New Seismogeodetic Approach Applied to GPS and Accelerometer Observations of the 2012 Brawley Seismic Swarm: Implications for Earthquake Early Warning. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2013, 14, 2124–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Qu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shi, C.; Liu, J. Initial Results of Precise Orbit and Clock Determination for COMPASS Navigation Satellite System. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Huang, W. Sea Ice Remote Sensing Using GNSS-R: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Ding, X. Application of carrier phase smoothing pseudorange in city location. J. Nav. Posit. 2021, 9, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Xi, C.; Yang, L.; Gao, S. Accuracy analysis of BDS in railway engineering survey. J. Nav. Posit. 2022, 10, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, Q.; Dardanelli, G. A Review on Multi-GNSS for Earth Observation and Emerging Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J.; Street, B. A Guide to Using International Gnss Service (Igs) Products; Geodetic Survey Division, Natural Resources Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Tegedor, J.; Ovstedal, O.; Vigen, E. Precise Orbit Determination and Point Positioning Using GPS, Glonass, Galileo and BeiDou. J. Geod. Sci. 2014, 4, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)—Achievements, Prospects and Challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s New Solar Radiation Pressure Model for GNSS Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Gao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, C. Evaluation and Analysis of Real-Time Precise Orbits and Clocks Products from Different IGS Analysis Centers. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Loyer, S.; Perosanz, F.; Prange, L.; Dach, R.; Uhlemann, M.; Gendt, G.; Montenbruck, O. Galileo Orbit and Clock Quality of the IGS Multi-GNSS Experiment. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. The Contribution of Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) to Precise Point Positioning. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2714–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Gao, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, R. Evaluation of Carrier-Phase Precise Time and Frequency Transfer Using Different Analysis Centre Products for GNSSs. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2019, 30, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y.; Li, W. Assessment of the Positioning Performance and Tropospheric Delay Retrieval with Precise Point Positioning Using Products from Different Analysis Centers. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xiao, G.; Chang, G.; Xu, T.; Yang, L. Assessment of GPS/Galileo/BDS Precise Point Positioning with Ambiguity Resolution Using Products from Different Analysis Centers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y. Precise Point Positioning Using Combined GPS and GLONASS Observations. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2007, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Gao, Y. Modeling and Assessment of Combined GPS/GLONASS Precise Point Positioning. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yi, W.; Song, W.; Lou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, R. GLONASS Pseudorange Inter-Channel Biases and Their Effects on Combined GPS/GLONASS Precise Point Positioning. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, B. GPS/GLONASS System Bias Estimation and Application in GPS/GLONASS Combined Positioning. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2013 Proceedings; Sun, J., Jiao, W., Wu, H., Shi, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 244, pp. 323–333. ISBN 978-3-642-37403-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Teunissen, P.; Zhang, B.; Verhagen, S. Precise Point Positioning Using GPS and Compass Observations. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2013 Proceedings; Sun, J., Jiao, W., Wu, H., Shi, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 244, pp. 367–378. ISBN 978-3-642-37403-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Qu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Li, X. Precise Point Positioning with the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. Sensors 2014, 14, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Li, M.; Guo, J.; Su, X.; Liu, J. Precise Point Positioning Using Combined Beidou and GPS Observations. In China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2013 Proceedings; Sun, J., Jiao, W., Wu, H., Shi, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 245, pp. 241–252. ISBN 978-3-642-37406-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Ruan, R.; Liu, X. Evaluation of PPP-RTK Based on BDS-3/BDS-2/GPS Observations: A Case Study in Europe. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Su, K. PPP Models and Performances from Single- to Quad-Frequency BDS Observations. Satell Navig 2020, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Teunissen, P.J.G. Characterization of Between-Receiver GPS-Galileo Inter-System Biases and Their Effect on Mixed Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbou, M.A.; El-Rabbany, A. Performance Analysis of GPS/GALILEO PPP Model for Static and Kinematic Applications. Geomatica 2015, 69, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A. Precise Orbit Determination of GIOVE-B Based on the CONGO Network. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J.; Wielgosz, P. Assessment of GPS + Galileo and Multi-Frequency Galileo Single-Epoch Precise Positioning with Network Corrections. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pan, L. Precise Point Positioning with Almost Fully Deployed BDS-3, BDS-2, GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and QZSS Using Precise Products from Different Analysis Centers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, J.; Yu, K.; Qian, N.; Zuo, X.; Chang, J. Performance Assessment of Positioning Based on Multi-Frequency Multi-GNSS Observations: Signal Quality, PPP and Baseline Solution. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 5845–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Z.; Yue, D. Evaluating the Latest Performance of Precise Point Positioning in Multi-GNSS/RNSS: GPS, GLONASS, BDS, Galileo and QZSS. J. Navig. 2021, 74, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N.; Tan, B.; Chen, Y. Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning (MGPPP) Using Raw Observations. J. Geod. 2017, 91, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H. An Analysis of Satellite Visibility and Single Point Positioning with GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou-2/3. Appl. Geomat. 2021, 13, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Jin, S.; Jiao, G. Assessment of Multi-Frequency Global Navigation Satellite System Precise Point Positioning Models Using GPS, BeiDou, GLONASS, Galileo and QZSS. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 064008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—Zhouforme0318/GAMPII-GOOD. Available online: https://github.com/zhouforme0318/GAMPII-GOOD (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. GAMP: An Open-Source Software of Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning Using Undifferenced and Uncombined Observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X. Integrating GPS and GLONASS to Accelerate Convergence and Initialization Times of Precise Point Positioning. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gu, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Feng, Y. Multi-GNSS Precise Point Positioning with Raw Single-Frequency and Dual-Frequency Measurement Models. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).