Experimental Determination of the Ionospheric Effects and Cycle Slip Phenomena for Galileo and GPS in the Arctic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
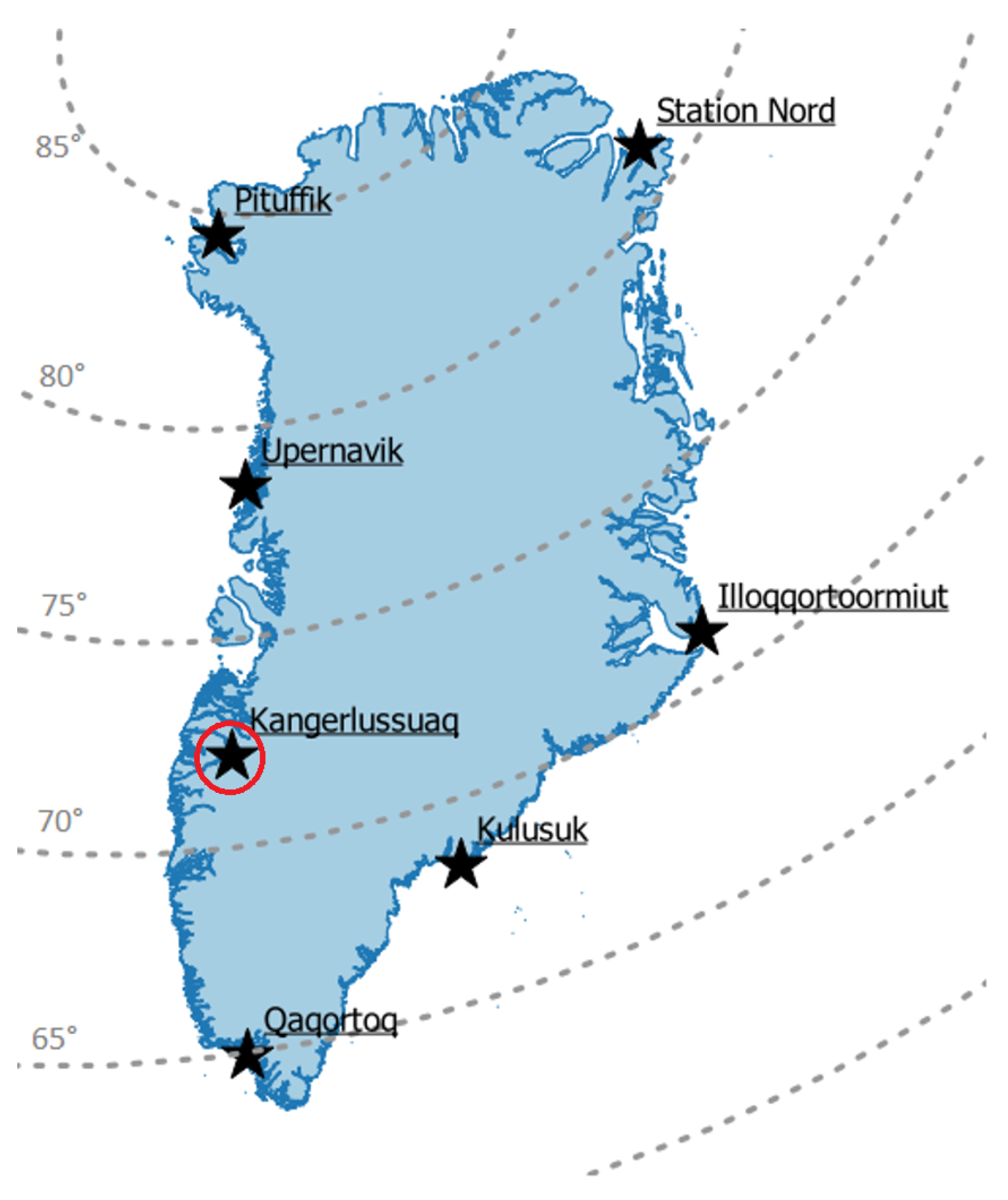
2.1. GNSS Stations and Data Used
2.2. Estimation of Phase Scintillation
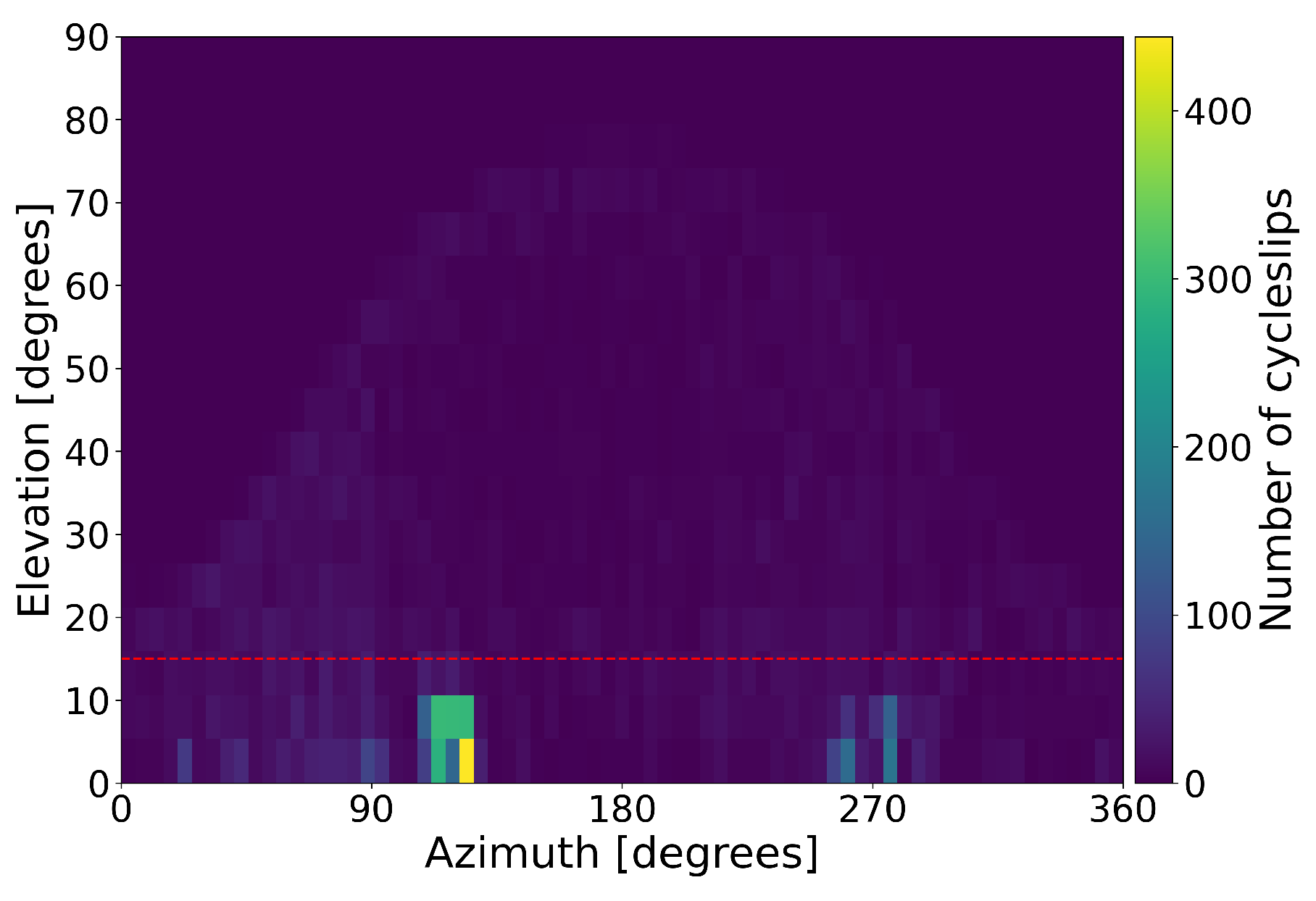
2.3. Identification of Cycle Slips and Data Outages
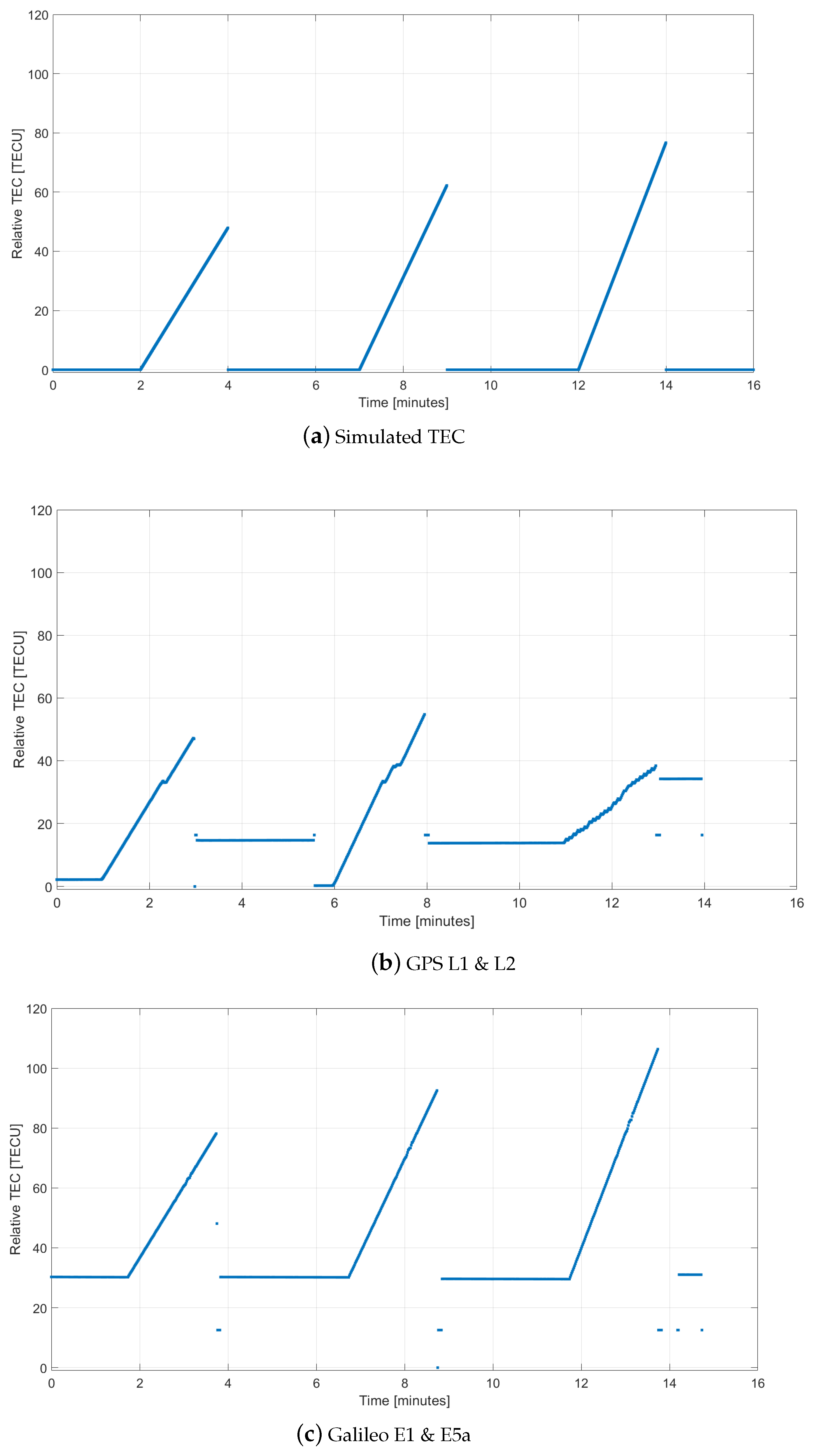
2.4. Scintillation Simulation
3. Results
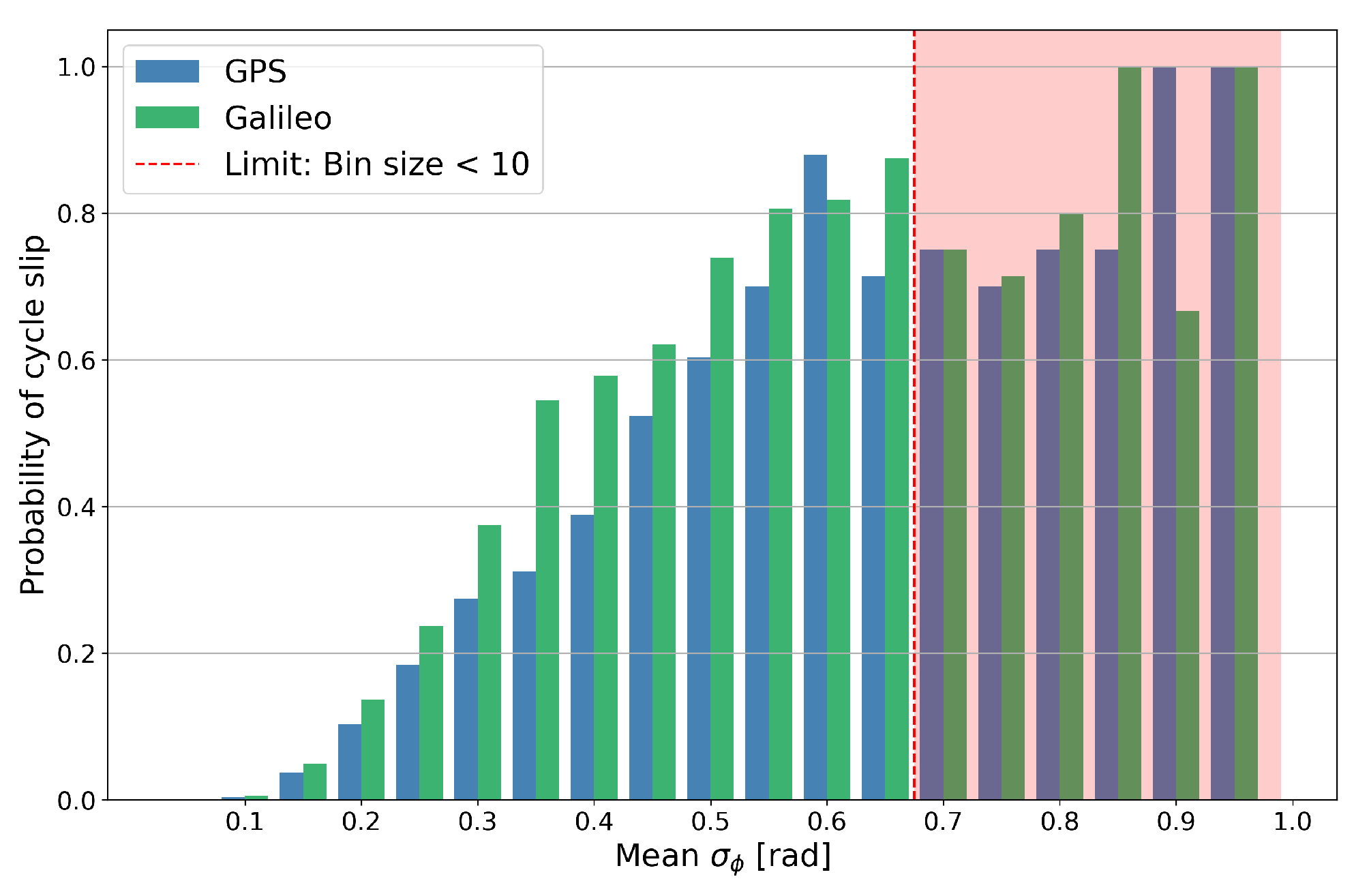
3.1. Probability of Cycle Slips as a Function of σϕ
3.2. Cycle Slips and Outages in Numbers
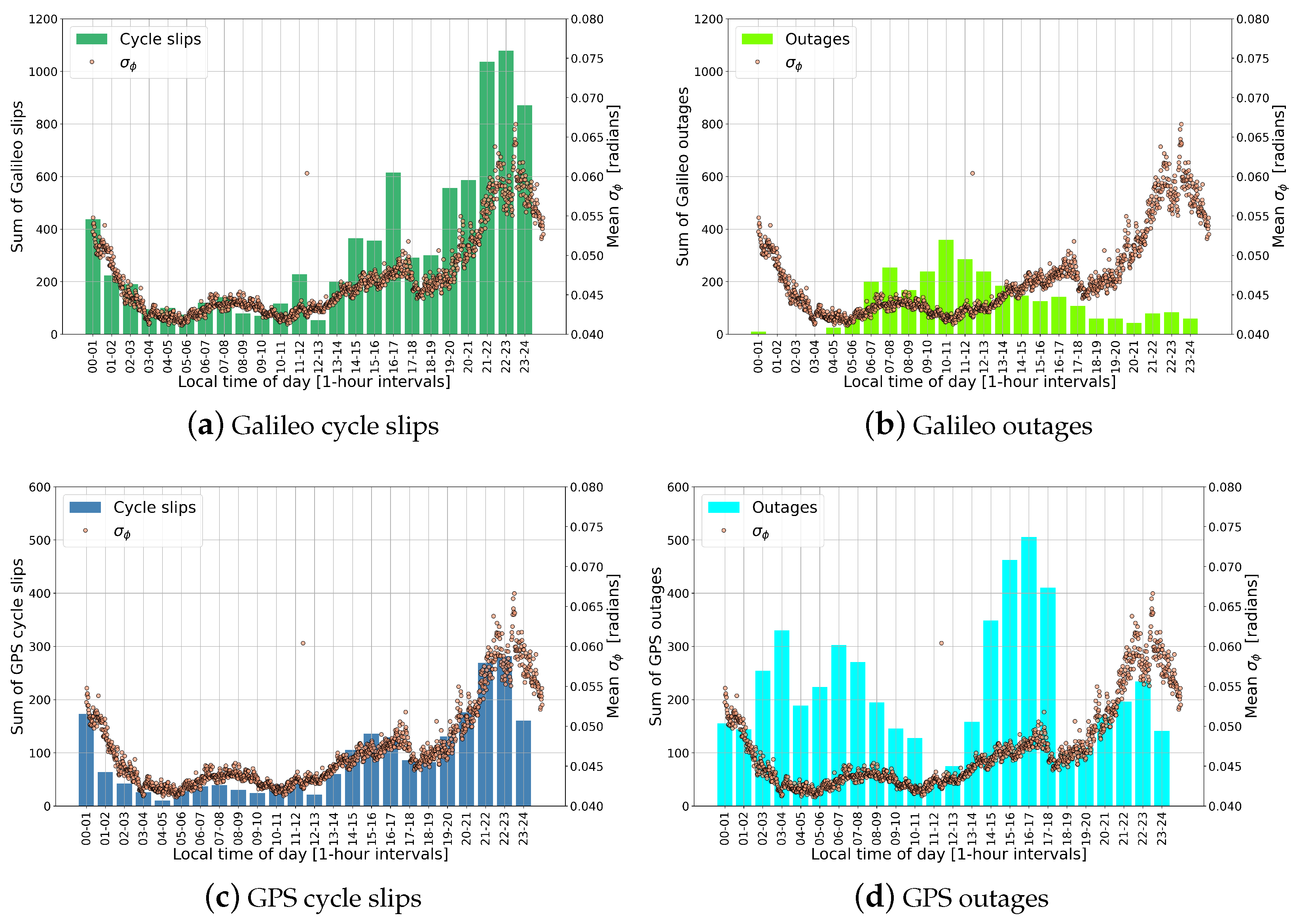
3.3. Daily Variations in Cycle Slips and Outages
3.4. Simulation of Scintillation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GISTM | GNSS Ionospheric Scintillation and TEC Monitor |
| GLONASS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GNET | Greenland GPS Network |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IOD | Ionospheric Delay |
| ISMR | Ionospheric Scintillation Monitoring Record |
| RF | Radio Frequency |
| RINEX | Receiver Independent Exchange format |
| SWADO | Space Weather Forecasting for Arctic Defence Operations |
| TEC | Total Electron Content |
| TECU | TEC Units |
| TEQC | Translating, Editing and Quality Checking |
| UCD | User Command Define |
| UTC | Universal Time Coordinated |
References
- Titheridge, J.E. The diffraction of satellite signals by isolated ionospheric irregularities. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1971, 33, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintner, P.M.; Ledvina, B.M.; de Paula, E.R. GPS and ionospheric scintillations. Space Weather 2007, 5, S09003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Morton, Y.; Taylor, S.; Pelgrum, W. Characterization of high-latitude ionospheric scintillation of GPS signals. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarons, J. Global positioning system phase fluctuations at auroral latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17219–17231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Jayachandran, P.T.; Mushini, S.C.; Chadwick, R. Climatology of GPS phase scintillation and HF radar backscatter for the high-latitude ionosphere under solar minimum conditions. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 29, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, T.E.; Psiaki, M.L.; Kintner, P.M. GPS Carrier Tracking Loop Performance in the presence of Ionospheric Scintillation. In Proceeding of the 18th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, ION GNSS 2005, Long Beach, CA, USA, 13–16 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hinks, J.C.; Humphreys, T.E.; O’Hanlon, B.; Psiaki, M.L.; Kintner, P.M. Evaluating GPS receiver robustness to ionospheric scintillation. In Proceeding of the 21st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Ion GNSS 2008, Savannah, GA, USA, 16–19 September 2018; Volume 3, pp. 1390–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, S.; Morton, Y.; Marcus, R.; Bourne, H.; Pelgrum, W.; Van Dierendonck, A.J. Ionosphere Scintillation Receivers Performance Based on High Latitude Experiments. In Proceeding of the ION 2013 Pacific PNT Meeting, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–25 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, X.; Mannucci, A.J.; Lindqwister, U.J.; Ho, C.M. Monitoring of global ionospheric irregularities using the worldwide GPS network. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veettil, S.V.; Aquino, M.; Spogli, L. A statistical approach to estimate Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) receiver signal tracking performance in the presence of ionospheric scintillation. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2018, 8, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estey, L.; Wier, S. Teqc Tutorial: Basic of Teqc Use and Teqc Products; UNAVCO: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Prikryl, P.; Jayachandran, P.T.; Mushini, S.C.; Pokhotelov, D.; MacDougall, J.W.; Donovan, E.; Spanswick, E.; St.-Maurice, J.-P. GPS, TEC, scintillation and cycle slips observed at high latitudes during solar minimum. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prikryl, P.; Jayachandran, P.T.; Mushini, S.C.; Richardson, I.G. High-latitude GPS phase scintillation and cycle slips during high-speed solar wind streams and interplanetary coronal mass ejections: A superposed epoch analysis. Earth Planets Space 2014, 66, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggs, R.W.; Mitchell, C.N. GPS scintillation over the European Arctic during the November 2004 storms. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta-Barua, S.; Doherty, P.H.; Delay, S.H.; Dehel, T.; Klobuchar, J.A. Ionospheric Scintillation Effects on Single and Dual frequency GPS Positioning. In Proceedings of the 16th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation ION GPS/GNSS 2003, Portland, OR, USA, 9–12 September 2003; pp. 336–346. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, R.; Linty, N.; Cristodaro, C.; Dovis, F.; Alfonsi, L. On the Use and Performance of new Galileo Signals for Ionospheric Scintillation Monitoring. In Proceeding of the Institute of Navigation Technical International Meeting (ITM 2017), Monterey, CA, USA, 30 January–2 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Carrano, C.S.; Groves, K.M.; McNeil, W.J.; Doherty, P.H. Scintillation Characteristics Across the GPS Frequency Band. In Proceedings of the 25th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS 2012), Nashville, TN, USA, 17–21 September 2012; pp. 1972–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Delay, S.H.; Carrano, C.; Groves, K. A Statistical Analysis of GPS L1, L2 and L5 Tracking Performance During Ionospheric Scintillation. In Proceeding of the 2015 ION Pacific PNT Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 20–23 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hlubek, N.; Berdermann, J.; Wilken, V.; Gewies, S.; Jakowski, N.; Wassaie, M.; Damtie, B. Scintillation of the GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo signals at equatorial latitude. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2014, 4, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Bhardwaj, S.C.; Vidyarthi, A.; Jassal, B.S. Ionospheric Scintillation analysis using ROT and ROTI for Slip Cycle Detection. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 21–22 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vankadara, R.K.; Jamjareegulgarn, P.; Seemala, G.K.; Siddiqui, M.I.H.; Panda, S.K. Trailing Equatorial Plasma Bubble Occurrences at a Low-Latitude Location through Multi-GNSS Slant TEC Depletions during the Strong Geomagnetic Storms in the Ascending Phase of the 25th Solar Cycle. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septentrio. PolaRx5S Reference Guide; Septentrio: Leuven, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Morton, Y. Time lags in Ionospheric Scintillation Response to Geomagnetic Storms; Alaska Observations. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2020), Online, 21–25 September 2020; pp. 3494–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, B.; Radicella, S.M. Problems in data treatment for ionospheric scintillation measurements. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septentrio. PolaRx5S User Manual; Version 2.3; Septentrio: Leuven, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Estey, L.H.; Meertens, C.M. TEQC: The Multi-Purpose Toolkit for GPS/GLONASS Data. GPS Solut. 1999, 3, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirent.com. Spirents Official Website. Available online: https://www.spirent.com/products/gnss-simulator-gss7000 (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Mohd Ali, A. GNSS in Aviation: Ionospheric Threats at Low Latitudes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bath, Bath, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Beeck, S.S.; Jensen, A.B.O. ROTI maps of Greenland using kriging. J. Geod. Sci. 2021, 11, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitsch, B.; Morton, Y.J. Triple-Frequency GNSS Cycle Slip Detection Performance in Presence of Diffractive Ionosphere Scintillation. In Proceedings of the ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, ON, USA, 20–23 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Skone, S.; Knudsen, K.; de Jong, M. Limitations in GPS Receiver Tracking Performance Under Ionospheric Scintillation conditions. Phys. Chem. Earth (A) 2001, 26, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Chung, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.; Kwak, Y. Characteristics of Ionospheric Irregularities Using GNSS Scintillation Indices Measured at Jang Bogo Station, Antarctica (74.62°S, 164.22°E). Space Weather 2020, 18, e2020SW002536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.; Hansen, A.; Walter, T.; Enge, P. High-Latitude Measurements of Ionospheric Scintillation Using the NSTB. Navig. J. Inst. Navig. 2000, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraimovich, E.L.; Lesyuta, O.S.; Ushakov, I.I.; Voeykov, S.V. Geomagnetic storms and the occurrence of phase slips in the reception of GPS signals. Ann. Geophys. 2002, 45, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshov, A.A.; Miloch, W.J.; Jin, Y.; Zakharov, V.I. Relationship between TEC jumps and auroral substorms in the high-latitude ionosphere. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GPS.gov. Official U.S. Government Information about the Global Positioning System (GPS) and Related Topics. Available online: https://www.gps.gov/systems/gps/modernization/civilsignals/ (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Esper, M.; Chao, E.L.; Wolf, C.F. Federal Radio Navigation Plan; United States Department of Defense, Department of Transportation, Department of Homeland Security: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande, K.B.; Bust, G.S.; Clauer, C.R.; Rino, C.L.; Carrano, C.S. Satellite-beacon Ionospheric-scintillation Global Model of the upper Atmosphere (SIGMA) I: High-latitude sensitivity study of the model parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 4026–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.B.; Bust, G.S.; Clauer, C.R.; Scales, W.A.; Frissell, N.A.; Ruohoniemi, J.M.; Spogli, L.; Mitchell, C.; Weatherwax, A.T. Satellite-beacon Ionospheric-scintillation Global Model of the upper Atmosphere (SIGMA) II: Inverse modeling with high-latitude observations to deduce irregularity physics. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 121, 9188–9203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.B.; Zettergren, M.D. Satellite-Beacon Ionospheric-Scintillation Global Model of the upper Atmosphere (SIGMA) III: Scintillation simulation using a physics-based plasma model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 4564–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernov, N.N.; Driuk, A.V. Coherence properties of high-frequency wave field propagating through inhomogeneous ionosphere with anisotropic random irregularities of electron density: 1. Theoretical background. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 205, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Investigating the inconsistency of ionospheric ROTI indices derived from GPS modernized L2C and legacy L2 P(Y) signals at low-latitude regions. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCaffrey, A.M.; Jayachandran, P.T.; Langley, R.B.; Sleewaegen, J.-M. On the accuracy of the GPS L2 observable for ionospheric monitoring. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GPS | GPS Corrected | Galileo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cycle slips | 2862 | 2197 | 8183 |
| Intervals with cycle slips | 1200 | 921 | 1149 |
| Number of outages | 6895 | 5292 | 2929 |
| Sum of cycle slips and outages | 9757 | 7489 | 11,112 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beeck, S.S.; Mitchell, C.N.; Jensen, A.B.O.; Stenseng, L.; Pinto Jayawardena, T.; Olesen, D.H. Experimental Determination of the Ionospheric Effects and Cycle Slip Phenomena for Galileo and GPS in the Arctic. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245685
Beeck SS, Mitchell CN, Jensen ABO, Stenseng L, Pinto Jayawardena T, Olesen DH. Experimental Determination of the Ionospheric Effects and Cycle Slip Phenomena for Galileo and GPS in the Arctic. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(24):5685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245685
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeeck, S.S., C.N. Mitchell, A.B.O. Jensen, L. Stenseng, T. Pinto Jayawardena, and D.H. Olesen. 2023. "Experimental Determination of the Ionospheric Effects and Cycle Slip Phenomena for Galileo and GPS in the Arctic" Remote Sensing 15, no. 24: 5685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245685
APA StyleBeeck, S. S., Mitchell, C. N., Jensen, A. B. O., Stenseng, L., Pinto Jayawardena, T., & Olesen, D. H. (2023). Experimental Determination of the Ionospheric Effects and Cycle Slip Phenomena for Galileo and GPS in the Arctic. Remote Sensing, 15(24), 5685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15245685






