Abstract
Aerosol is important to climate and air pollution, and different aerosol types have a non-negligible impact on the environment and climate system. Based on long-term satellite lidar profiles from 2006 to 2020, the four-dimensional (x-y-z-t) spatiotemporal characteristics of different aerosol types, including clean marine (CM), dust (DU), polluted continental/smoke (PC), clean continental (CC), polluted dust (PD), elevated smoke (ES), and dusty marine (DM), over the coastal waters of the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA) were revealed for the first time and compared to the surrounding northern South China Sea (NSCS). (1) The dominant aerosol types in both study areas were found to be CM, ES, and DM, whose proportions summed up to more than 85%. In spring, ES was the dominant aerosol type (>40%); in other seasons, CM dominated (>34%). The proportions of anthropogenic aerosols (PC, PD, and ES) and dust-related aerosols (DU, PD, and DM) were higher in spring and winter than in summer and autumn. (2) Vertically, the number of all aerosol types declined with increasing altitude, with the exception of abnormal increase at the heights of approximately 1.5–2.8 km in spring, which was probably attributed to the effect of local and regional anthropogenic pollutants. Below the height of 2 km, the main aerosol types were CM and DM, whereas ES, PD, and DU aerosols were dominant above 2 km. (3) Horizontally, the dominant aerosol types were spatially uniform in the lower atmosphere (<2 km), while higher altitudes (especially > 4 km) showed significant horizontal heterogeneity in space. The proportion of anthropogenic aerosols over the coastal waters of the GBA was higher than that over the NSCS, due to terrestrial pollution transportation. (4) In terms of the long-term trend, the proportion of CM aerosols was found to be steadily increasing, with the anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols showing a fluctuating and decreasing trend, which resulted from the enforcement of effective air pollution control policies. Overall, the terrestrial aerosol influence tended to decrease in the study areas. The insight into aerosol types and its variation will facilitate the understanding of the aerosol climate effects and pollutant control in the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS.
1. Introduction
Located in the center of Guangdong Province, the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area (GBA, Figure 1a) consists of Guangzhou (GZ), Shenzhen (SZ), Foshan (FS), Dongguan (DG), Huizhou (HZ), Zhongshan (ZS), Zhuhai (ZH), Jiangmen (JM), Zhaoqing (ZQ), the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HK), and the Macau Special Administrative Region (MC) (Figure 1b) [1]. As one of the most economically vibrant regions in China, the GBA is characterized by a rapid increase in population and a fast development of the economy [2]. The “Outline Development Plan for the GBA” issued by the Chinese government in 2019 has pointed out that China should insist on vigorously developing the marine economy and strengthen regional environmental protection and regulatory management. Nowadays, the GBA is one of the four major economically developed bay areas in the world [3,4]. Adjacent to the GBA, the South China Sea (SCS) is a low-latitude marginal sea to the south of Mainland China and in the western part of the Pacific Ocean [5]. With abundant marine resources and massive shipping business, the SCS plays an important role in economic and energy development in China.
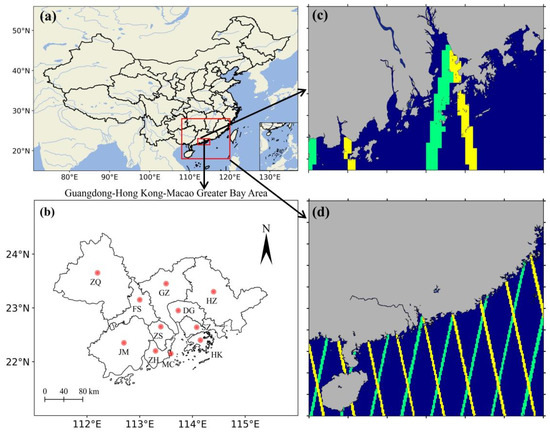
Figure 1.
(a) Map of the study areas of coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS, which are the sea areas in the small red frame (longitude: 112°–115°E; latitude: 21.5°–23°N) and in the large red frame (longitude: 108°–120°E; latitude: 18°–28°N), respectively; (b) cities of the GBA; (c,d) the CALIOP tracks in the two study areas of coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS (yellow and green lines correspond to day and night tracks, respectively).
Since the reform and opening-up policy in 1978, the urbanization and industrialization process of the GBA has been dramatically accelerated [6,7]. In the past 40 years, with the high industrial agglomeration and economic growth in the GBA, the pollutants in the atmosphere and ocean have significantly increased, which has resulted in a negative impact on the ecological environment and human health [8,9,10,11,12]. Recently, the number of vehicles in many cities has increased dramatically, and the transportation sectors have become a source of emissions [13]. Fang et al. [14] showed that at the end of 2016, the number of vehicles in SZ, GZ, DG, and FS reached 318 million, 230 million, 224 million, and 202 million, respectively. Fossil energy dominated the total energy consumption of the GBA, with a proportion of 77% in 2015 [15]. The northern South China Sea (NSCS), which is bounded by the shelves along the southern coasts of China, is also a sensitive ecosystem lying near the region with a high-density population and industry [16]. Influenced by human activities and continental outflow from surrounding regions, not only the coastal GBA, but also the NSCS has experienced serious aerosol pollution [17,18,19]. Hence, understanding maritime aerosol characteristics over the two areas is vital for assessing the status of the marine environment and formulating more targeted air pollution control policies, which can contribute to improving the marine environment.
As important parts of atmospheric environmental components, aerosols play a vital role in global climate change and atmospheric chemistry [20,21,22] and can affect the Earth system through aerosol–radiation and aerosol–cloud interactions [23,24,25,26]. Moreover, the physical and optical properties of aerosols vary with time and space [27]. Aerosols over the oceans, which are produced by marine sources or advected from land sources, are also important for the marine atmosphere, geochemistry, and biogeochemistry [27,28,29,30]. Mallet et al. [31] suggested that maritime aerosols are influenced by continental emissions and contain both natural and anthropogenic aerosols (e.g., dust, soot, carbonaceous material). In recent years, the influence of different aerosol types on the environment and climate has received great attention. Many studies have analyzed the impact of aerosol types over different regions. For example, Jiang et al. [32] suggested that different aerosol types exert inhibitory or invigorating effects on deep convective clouds over South America, Central Africa, and Southeast Asia; Wei et al. [33] identified the impact of black carbon (BC) aerosols on the regulation of dust aerosols and Indian climate during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, explaining the mechanism of BC–climate interactions. Therefore, a better understanding of the spatiotemporal characteristics of different aerosol types can contribute to the further analysis of aerosol impact.
Due to its diverse terrain and large population, China has various aerosol types and has become an ideal place for aerosol studies [34]. Zhang et al. [35] identified four major aerosol types in China using cluster analysis of Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) measurements from 1998 to 2017 and revealed the seasonal variability of the major types. Based on Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) data, Liao et al. [24] studied the seasonal distribution and vertical structure of different aerosol types over the Sichuan Basin, Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and Tibetan Plateau in China. Chen et al. [36] identified the vertical distribution of aerosol types over eight regions in China from 2013 to 2019 using observations from CALIPSO, which improved the understanding of aerosol vertical characteristics after the implementation of the clean air policy. However, the current studies are mainly limited to the spatiotemporal characteristics of aerosol types over land at the regional or city scales, with little attention to those over the ocean. In terms of the maritime aerosol types over the coastal waters of the GBA and NSCS in China, Sun et al. [37] conducted a study on the spatiotemporal variation in the optical depth of different aerosol types utilizing the second Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA-2) over the SCS from 1980 to 2020. Atwood et al. [38] elucidated the springtime aerosol types, sources, and transport patterns in the NSCS between 31 March and 8 May 2010 based on in situ measurements, finding that the vertical inhomogeneity of the aerosol environment in the SCS was significant. Overall, a comprehensive investigation of the long-term spatiotemporal distributions of maritime aerosol types is still lacking.
The study intends to fill these gaps using long-term satellite lidar profiles from 2006 to 2020 over the above regions. The following two aspects are taken as specific objectives: (1) characterizing the four-dimensional (x-y-z-t) spatiotemporal characteristics of aerosol types in the coastal waters of the GBA and comparing them with those in the NSCS, including vertical, horizontal, and temporal (seasonal variation and long-term trend) distributions; (2) revealing the mechanism of the spatiotemporal characteristics of aerosol types from the perspectives of emission source, horizontal diffusion, vertical diffusion, and moisture conditions.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Satellite Data
Being launched on 28 April 2006, the CALIPSO satellite flew with the A-train constellation of satellites, which aimed at improving the understanding of the status of aerosols and clouds in the atmospheric system [39]. The Cloud-Aerosol Lidar with Orthogonal Polarization (CALIOP) is the primary instrument on the CALIPSO satellite. As a two-wavelength polarization lidar, CALIOP contains two bands of 532 nm and 1064 nm, which provide attenuated backscatter data during both daytime (13:30 local Equator-crossing time) and nighttime (01:30 local Equator-crossing time) of the orbit (Figure 1c,d, the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS, respectively) [40]. The CALIOP receiver is polarization-sensitive at 532 nm to identify the non-spherical aerosol particles and cloud ice/water phase [40]. Below 8.2 km, the vertical resolution is 30 m and the horizontal resolution is 333 m [40]. CALIOP takes into account the vertical thickness and location of the layers and the spectral behavior of lidar backscatter [41] so as to distinguish optically thin boundary layer clouds from aerosols and provide long-term cloud and aerosol vertical structure characteristics.
CALIOP provides three basic types of level 2 data products: layer products, profile products, and the vertical feature mask (VFM). Aerosol types are classified in VFM dataset according to altitude, location, surface type, estimated particulate depolarization ratio (δv), and the integrated total attenuated backscatter at 532 nm (γ’) [42]. In version 3 (V3), the aerosols are classified into six types: dust, polluted continental, polluted dust, smoke, clean continental, and clean marine. It is worth noting that “polluted dust” aerosols are mixtures of dust and smoke or urban pollution [42]. “Smoke” and “polluted continental” aerosols are generally related to anthropogenic emissions [24]. In November 2016, version 4.10 (V4) level 2 aerosol data products were released by adopting improved algorithms of aerosol subtype identification and lidar ratio selection. Aerosols in V4 are mainly classified into seven types: marine (hereafter referred to “clean marine” (CM)), dust (DU), polluted continental/smoke (PC), clean continental (CC), polluted dust (PD), elevated smoke (ES), and dusty marine (DM) [43]. The substantial improvements of V4 compared to V3 are as follows: (1) the “DM” aerosol type is introduced to solve the problem of misclassifying the mixtures of dust and marine aerosols near the ocean surface; (2) “smoke” and “polluted continental” are renamed to “elevated smoke” and “polluted continental/smoke”; (3) the lidar ratios of some aerosol types are revised. Among the seven aerosol types in V4, DM aerosols are mixtures of dust and marine aerosols within the marine boundary layer. Because of smoke lofted by convective processes locally or other vertical transport mechanisms, ES refers to smoke layers with tops higher than 2.5 km from the ground (approximately the height of the planetary boundary layer (PBL)) [24,43,44,45]. Within the PBL, it is difficult for CALIOP to distinguish between smoke and polluted continental, so they are collectively referred to as PC to acknowledge their optical similarity [43]. As efficient tools, the VFM products are broadly used for such purposes as evaluating other aerosol products or global aerosol transport models [40,46]. Mielonen et al. [47] validated the accuracy of CALIOP VFM aerosol data, showing that 70% of aerosol types were in agreement with in situ measurements. Uncertainties exist due to the following effects: Limited by the aerosol subtyping algorithm, the misclassification of aerosol type in certain circumstances is a source of systematic uncertainty [43,48]. Moreover, the daytime measurements affected by background solar illumination have a lower signal-to-noise ratio (FNR) than the nighttime ones [43,48]. Although this has no direct effect on the aerosol classification scheme [42], lower FNR in the daytime does result in less sensitive detection for weakly scattering layers that are subsequently classified as aerosols by the cloud–aerosol discrimination algorithm, which is another source of uncertainty [43,48]. Nonetheless, the external uncertainty of daytime signals mainly exists in the upper troposphere, and the updated algorithm in V4 has an enhanced ability to detect more weakly scattering layers than V3 [43,48]. Therefore, both daytime and nighttime data were considered in our study.
Since aerosols mainly exist in the lower troposphere [49,50], we only focused on the aerosol types below the height of 8.2 km to maintain the resolution consistency of the analyzed data in the vertical height. In addition, as the physical interpretation of near-ground aerosols may be compromised by surface contamination errors, resulting in uncertainty [48,51], in this study, the samples below the height of 0.28 km (above ground level) were excluded to reduce these errors in the long-term analysis [36].
In this study, we used CALIOP level 2 VFM products (V4.20) for about 15 years from June 2006 to September 2020 over the ocean during both day and night (Figure 1c,d). “Feature Classification Flags” in the products were adopted to distinguish different types of aerosols. For brevity, we defined PC, PD, and ES types as anthropogenic aerosols; defined DU, PD, and DM types as dust-related aerosols; and defined the aerosol types that cannot be determined as “not-determined”. Furthermore, in order to better analyze the distribution of aerosol types at different altitudes, we divided the altitude into four different altitude bins (i.e., from 0.28 to 2.2 km, from 2.2 to 4.1 km, from 4.1 to 6.1 km, and from 6.1 to 8.17 km).
2.2. Reanalysis and Ensemble Data
European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) fifth-generation atmospheric reanalysis (ERA5) provides hourly estimates for a large number of atmospheric, ocean-wave, and land-surface quantities with high resolution [52]. Atmospheric data including wind and temperature from 2006 to 2020 were derived from ERA5 “hourly data on pressure levels from 1959 to present” products of ECMWF, with regular latitude–longitude grids at 0.25° × 0.25° horizontal and one-hour temporal resolution.
Precipitation data from 2006 to 2020 were obtained from the Multi-source Weighted Ensemble Precipitation (MSWEP). MSWEP is a global precipitation product with 0.1° × 0.1° spatial and 3-h temporal resolution available in real-time. It merges gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data to obtain precipitation estimates at every location [53].
2.3. Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonal Change, and Trend (BEAST) Method
The interpretations of trends and abrupt changes obtained by different statistical algorithms or models for satellite time series data are not the same [54,55]. The satellite time series data may have many matching “best” models [56]. In response to these problems, many scholars have proposed the method of Bayesian statistics. The Bayesian paradigm can combine all candidate models, evaluate the likelihood of each model being the true model, and synthesize many models into an averaged model in a scheme called Bayesian model averaging (BMA) [57]. However, its application in satellite time series analysis is still quite limited. Recently, Zhao et al. [58] introduced a new method named BEAST to analyze time series data through Bayesian modeling. The advantage of BEAST is that it can quantify various sources of uncertainty for satellite time series data, detect abrupt changes of any magnitude, and analyze nonlinear trends [58]. The simple additive model of BEAST is defined as follows:
where t is time, y(t) is a raw time series, are basis functions that are specified by model structure parameters M (numbers and locations of seasonal/trend change points and seasonal harmonic orders), and are coefficients for a given M. The subscript M indicates the dependence of on M. It should be noted that BEAST uses Bayesian model selection to randomly traverse the model space to infer M and then estimate [58]. Therefore, BEAST is essentially a Bayesian general linear regression model, and adopting BEAST can avoid inconsistent results due to the single use of competing models [58]. Meanwhile, Zhao et al. [58] tested it by combining simulation, Landsat, and MODIS data and showed that BEAST can effectively detect abrupt points, seasonality, and trends. For more details and the derivation of BEAST, readers can refer to the work of Zhao et al. [58].
The BEAST algorithm has been proven to be suitable for analyzing time series data such as vegetation dynamics and grassland conversions [59,60] that are susceptible to seasonality or periodic variations, gradual changes, and abrupt changes (e.g., severe disturbances, regime shifts, and altered management practices) [58]. Since the temporal characteristics of maritime aerosols in the study regions are closely related to continental emissions, urbanization, and policy governance, we adopted the BEAST method to study the long-term evolution (2006–2022) of the CALIOP time series of aerosol types from the perspective of abrupt change and trend.
3. Results
3.1. Dominant Aerosol Types
Figure 2 shows the proportions of CM, ES, DM, PD, DU, PC, and CC at altitudes of 0.28–8.17 km over the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS during 2006–2020. It can be observed that the highest proportions of aerosol types over NSCS and coastal waters of the GBA were exhibited by CM, ES, and DM. These three types of aerosols accounted for more than 85% (89.86% for the NSCS and 85.49% for the coastal waters of the GBA). The proportions of PD, DU, and PC aerosols were relatively small (<6%). In general, air pollution in the study areas was mainly attributed to ES and DM, and the coastal waters of the GBA had more serious air pollution than the NSCS.
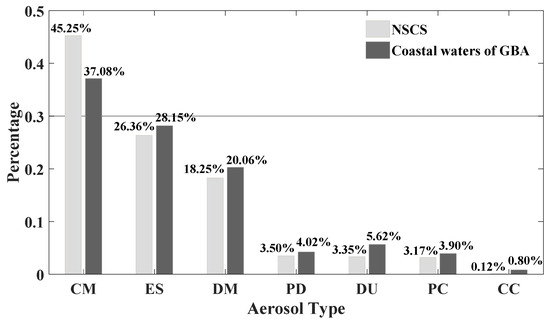
Figure 2.
Percentage of various aerosol types over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA (2006–2020).
As shown in Figure 3, there are noticeable seasonal variations in the percentages of different aerosol types. In spring, the dominant aerosol type was ES (40.99% for the NSCS; 42.72% for the coastal waters of the GBA), followed by CM (17~26%) and DM (~20%); in summer and autumn, the dominant aerosol type was CM (57.84% and 61.32% for the NSCS, respectively; 54.49% and 47.68% for the coastal waters of the GBA, respectively). In winter, CM (48.10% over the NSCS; 34.91% over the coastal waters of the GBA) and ES (25.81% over the NSCS; 29.31% over the coastal waters of the GBA) dominated, followed by DM (17.98% over the NSCS; 22.17% over the coastal waters of the GBA). Among all aerosol types, the proportions of CM and ES aerosols exhibited the most significant seasonal variations.
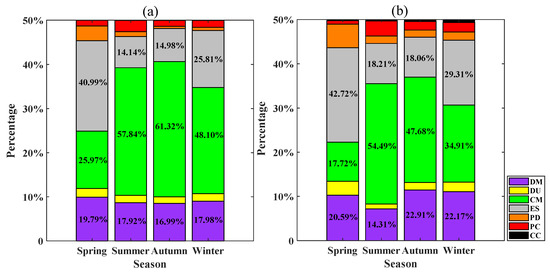
Figure 3.
Percentage of different aerosol types over (a) the NSCS and (b) the coastal waters of the GBA (2006–2020) in different seasons.
From the perspective of seasonal variations in air pollution, the proportions of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols were higher in spring and winter in both study areas than those in summer and autumn, which indicated that the level of air pollution in spring and winter was more serious. The heaviest air pollution found in spring (mostly ES aerosols) might be attributed to serious biomass burning phenomenon (c.f., Section 4.1.1).
3.2. Vertical Distributions
Within the height range of 0.28–8.17 km, Figure 4 shows the vertical variations of the aerosol types in different seasons. Generally, aerosols were mainly distributed below 6 km altitude. In summer, autumn, and winter, the number of all types of aerosols decreased with the increasing altitude, following a roughly exponential declining trend. However, an exception was found in spring, showing that the number of all aerosols began to increase abnormally at the height of 1.5 km and decrease after reaching a peak at about 2.8 km. The phenomenon was similar over the NSCS (Figure 4a) and the coastal waters of the GBA (Figure 4b). Possible mechanisms will be discussed in Section 4.1.1.
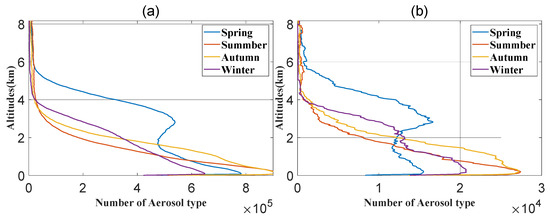
Figure 4.
Seasonal variations of the number of all aerosol types with altitude over (a) the NSCS and (b) the coastal waters of the GBA (2006–2020).
In Figure 5, for each type of aerosol, the characteristics of vertical distribution are displayed. As can be seen from Figure 5(a-1)–(a-4), the major aerosol types below the height of 2 km were CM (green line) and DM (pink line) throughout the year in the study areas; above the height of 2 km, the major types were ES (black line), PD (blue line), and DU aerosols (red line). In general, CM (green line) and ES (black line) aerosols dominated the study areas below and above 2 km, respectively, throughout the year.
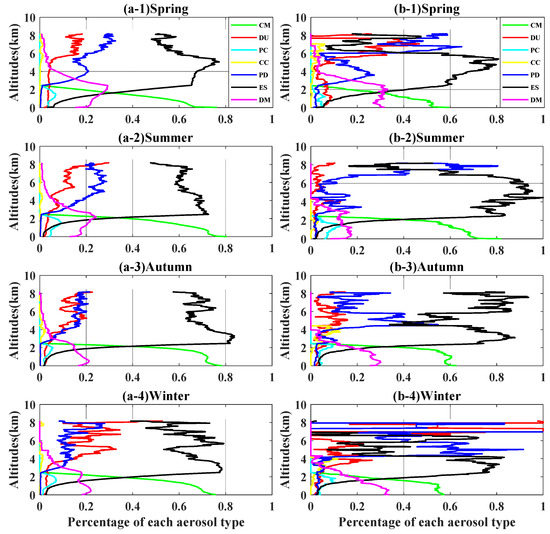
Figure 5.
Vertical distributions of percentages of the 7 aerosol types over the NSCS (a-1–a-4) and the coastal waters of the GBA (b-1–b-4).
Through a comparison between the two columns in Figure 5, it can be found that below 6 km, the vertical distributions of different aerosol types over the coastal waters of the GBA (Figure 5(b-1)–(b-3)) were similar to those of the NSCS (Figure 5(a-1)–(a-3)). However, at the heights of 6–8 km, the aerosol types over the coastal waters of the GBA were more complex than those over the NSCS, which likely reflected the more complicated sources of aerosol over the coastal waters of the GBA.
3.3. Horizontal Distribution in Different Layers
In Figure 6, the color of each pixel in different layers (0.28–2.2 km, 2.2–4.1 km, 4.1–6.1 km, and 6.1–8.17 km) represents the dominant aerosol type with the largest proportion on each grid.
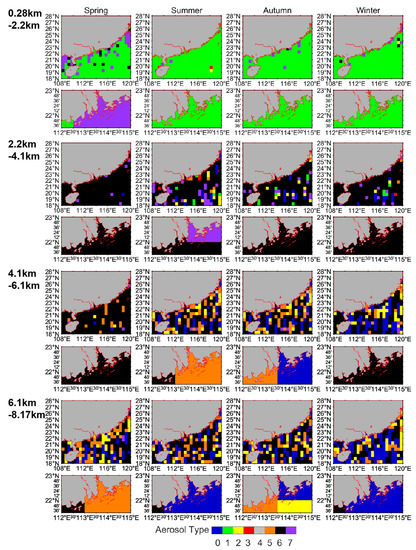
Figure 6.
Dominant aerosol types over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA at different heights (the first row of the same layer is for the NSCS, and the second row is for the coastal waters of the GBA; 0 = Not-Determined; 1 = CM; 2 = DU; 3 = PC; 4 = CC; 5 = PD; 6 = ES; 7 = DM).
Generally speaking, the dominant aerosol types were spatially uniform in the lower atmosphere (<2 km), and significant horizontal heterogeneity can be found at higher altitudes (especially > 4 km). Specifically, for the 0.28–2.2 km layer, CM (green) aerosols dominated the study areas in almost all seasons, with the exception of spring over the coastal waters of the GBA where DM (purple) aerosols dominated. At the heights of 2.2–4.1 km, the two study areas were mainly dominated by ES (black) aerosols. Above 4 km, various types of aerosols coexisted.
3.4. Long-Term Trend
Figure 7 shows the BEAST-derived long-term trend of CM aerosol, anthropogenic aerosols, and dust-related aerosols. It can be found that from 2006 to 2020, the proportion of CM aerosols presented an increasing trend in both study areas. On the contrary, anthropogenic aerosols showed a downward trend in the two study areas, possibly due to the release of the National Action Plan on Air Pollution Control in 2013 [61]; a delayed impact was found for the NSCS as compared to the coastal waters of the GBA (see the black dotted lines in Figure 7b,e). After 2008, dust-related aerosols generally showed a fluctuating downward trend in both areas, possibly due to the implementation of China’s environmental policies [62].
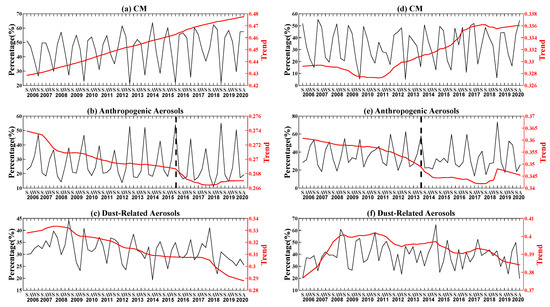
Figure 7.
Seasonal variation in percentage (black lines) and BEAST-derived long-term (2006~2020) trend (red lines) of different aerosol types over the NSCS (a–c) and the coastal waters of the GBA (d–f). The black dotted lines in (b) and (e) denote the abrupt points of the long-term trend.
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanism Analysis
4.1.1. Emission Source
The anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols over the ocean mainly come from the land [63,64]. Aerosols transported to the coastal waters of the GBA come from the adjacent Pearl River Delta region and remote sources (e.g., inner continental China) [65,66]. Anthropogenic aerosols mainly include black carbon (BC), organic carbon, sulfates, and other components [45,67]. Their sources include biomass burning, coal burning, automobile exhaust, and internal combustion engine emissions of ships [68,69,70,71].
Biomass burning, like forest fires and open-field burning (e.g., straw burning), emits particulate matter that is able to travel long distances [72]. During the spring, the general westerly flow pattern above the boundary layer transports the smoke aerosols generated by biomass combustion from Southeast Asia to the NSCS [38,73]. Moreover, the downward transport of smoke to the surface is not significant [73]. This likely contributes to the highest proportion of ES aerosols in spring (Figure 3), especially at the height above 2 km (Figure 5 and Figure 6). In addition, the peak of the number of all aerosol types (Figure 4) in the study areas at the height of about 2.8 km in spring may be caused by the significant increase in the concentration of the ES and the PD aerosols (Figure 3 and Figure 5) due to an increase in local and regional anthropogenic emissions of pollutants [74].
There were many industrial-driven cities, such as JM, where coal burning was the dominant contributor to total emissions in the GBA, resulting in the high proportion of anthropogenic aerosols from 2000 to 2016 [75]. The increase in ambient levels of sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxide (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) caused by transportation sources reflects the increase in anthropogenic aerosols throughout the domain [75,76]. The emissions from heavy loadings of cargo ships and fishing vessels are likely to increase BC, NOx, and sulfur oxide (SOx) in the NSCS [77,78]. These may be the reasons for the relatively high proportion of anthropogenic aerosols before 2013 (Figure 7b,e).
The possible emission sources of dust-related aerosols in the study areas include not only dust from Asian deserts (e.g., Taklimakan and Gobi deserts) through long-distance transportation affected by the East Asian monsoon [79,80,81,82], but also local dust from vehicles, roadways, and construction sites [83,84]. Obviously, from the perspective of vertical distributions, DM aerosols were mainly distributed below 2 km and accounted for a large proportion, while the proportions of DU and PD aerosols were very low (Figure 5), which indicated that the dust particles were mostly mixed with marine aerosols within lower altitudes above ground level in the study areas [85]. DU and PD aerosols mostly concentrated over 2 km and presented seasonal differences in vertical distributions (Figure 5). The possible reason is that under the influence of the East Asian monsoon, dust particles are transported at varying atmospheric levels in different directions [86].
4.1.2. Horizontal Diffusion
Figure 8 shows the variations in wind direction and speed in four seasons. The wind field is one of the main meteorological conditions affecting air quality. When the land wind horizontally transports pollutants, the wind direction always causes the pollutants to be distributed in the downwind direction of the pollution source. Generally, the greater the wind speed is, the easier it is for the pollutants to diffuse and the lower the concentration of pollutants is [87]. The average annual wind speed in the GBA is roughly in the range of 2–3 m/s (Figure 8m). This is conducive to the accumulation of local dust and anthropogenic emissions in the nearshore zone, causing a higher proportion of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols in the coastal waters of the GBA than that over the NSCS from the 15-year observations (Figure 2).
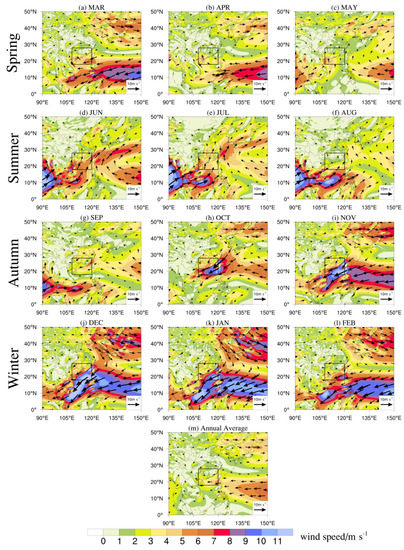
Figure 8.
Distribution of 925 hPa monthly (a–l) and annual (m) average wind fields in the NSCS (region indicated in black box) and neighboring regions from 2006 to 2020.
On the basis of the understanding of emission sources and annual wind speed influence, we further focused on the East Asian monsoon climate which primarily affects the coastal waters of the GBA and NSCS [81,86]. Transport of aerosols driven by monsoon was mainly concentrated in the lower atmosphere [86], and thus the 925 hPa monthly winds of the NSCS and neighboring areas were analyzed. As shown in Figure 8, the strong northeast winter monsoon occurred in October, reached a peak in December, and gradually vanished in April, while southwesterly winds prevailed in the summer monsoon (June to September). In March, dust was partly transported from Central Asia to the NSCS by the northeast monsoon and mixed with anthropogenic aerosols (Figure 8a) [82]. Moreover, in spring, the average wind speed in the study areas was the smallest (Figure 8a–c), which was conducive to the accumulation of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols. Thus, these partly contributed to the highest proportion of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols in spring compared to other seasons (Figure 3). Additionally, due to the easier mixture of dust and marine aerosols in the nearshore zone, DM aerosols dominated below 2.2 km in spring over the coastal waters of the GBA (Figure 6). During the summer monsoon period, under the unfavorable southwesterly wind prevailing environment (Figure 8d–f), aerosol transportation originates from the ocean [86], which prevents land-based anthropogenic emissions and Central Asian dust from dispersing into the study areas. Therefore, the anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols in summer accounted for a relatively low proportion, corresponding to the increased proportion of CM aerosols (Figure 3). However, during the winter monsoon period, the prevailing northeasterly winds not only spread the continental pollutants (e.g., fossil burning, coal combustion, and biomass burning) from eastern, northern, and northeastern China [82,88], but also drove the dust transported from the Asian continent [80,82], leading to the contaminant enrichment over the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS (Figure 8j–l). Thus, the total proportion of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols increased in winter (Figure 3). However, the strong winter cold waves and other weather activities may alleviate regional polluted conditions to a certain extent through the removal of pollutants by strong winds [89], which may be a reason why the air pollution in winter was not the worst.
4.1.3. Vertical Diffusion
Atmospheric vertical condition is related to surface wind speed and temperature difference between the boundary layer and low-troposphere level [90]. We used the 10 m wind speed (Wind_10) and temperature difference between 925 hPa and 850 hPa (ΔT) to quantify the atmospheric vertical diffusion capability. Higher ΔT and surface wind speed indicate stronger vertical convection in the low troposphere, which means stronger vertical diffusion capability and lower concentration of near-surface pollutants [90]. To clearly identify the seasonal condition of vertical diffusion in the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA, we used a density-based clustering method named Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) [91]. For a set of points, the DBSCAN method groups the adjacent points into a cluster and excludes points that lie alone in low-density regions as outliers. DBSCAN has the ability to demarcate a region with high dot density and was helpful in the analysis of the seasonal characteristics of vertical diffusion conditions over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA.
Figure 9 shows the seasonal condition of the monthly average Wind_10 and ΔT from 2006 to 2020 over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA. Since the concentration of pollutants decreases with increasing wind speed and temperature difference, the red dots located in the upper right region of the figure indicate a favorable vertical diffusion condition. There is a similarity in vertical diffusion capability between the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA. In summer and autumn, the values of surface wind speed and temperature difference are approximately 4 m/s and 1 °C, respectively. Compared with the situation in spring and winter, higher Wind_10 and ΔT contribute to more effective vertical transport of local air pollutants and better air quality over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA (Figure 3).
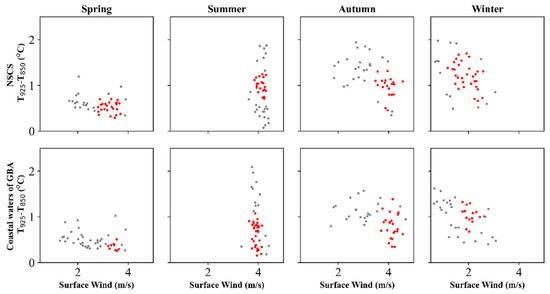
Figure 9.
Seasonal condition of the monthly average 10-m wind speed (Wind_10) and temperature difference between 925 hPa and 850 hPa (ΔT) from 2006 to 2020 over the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA. Red dots indicate the high-density dots according to the DBSCAN method.
Both surface wind speed and temperature difference are influenced by background atmospheric circulation and in turn affect the formation of air pollution [71,92]. In spring and winter, the location of the subtropical high ridge is at 20°N [93], and the NSCS region is controlled by the western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) [94]. The WPSH contributes to light winds and small temperature differences (Figure 9) in spring and winter. The lower atmosphere is stable and the vertical diffusion condition is poor; pollutants do not diffuse easily. Additionally, the land use and land cover near the coastal waters of the GBA have changed rapidly in recent times [95]. The accelerating process of urbanization has altered the land cover type from soil and farmland to asphalt and cement, which makes the land more sensitive to heating and cooling effects and intensifies the urban heat island (UHI) effect, especially in summer [96]. Overall, the vertical diffusion capability in spring and winter is worse than that in summer and autumn.
4.1.4. Moisture Condition
Wet deposition by rainfall is the major sink of aerosols. Influenced by the summer monsoon rainfall over East Asia [97], the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA experience a high amount of rainfall in summer and autumn with a strong wash-out effect (Figure 10), which can explain the lower proportions of ES and DM aerosols in summer and autumn compared to those in spring and winter.
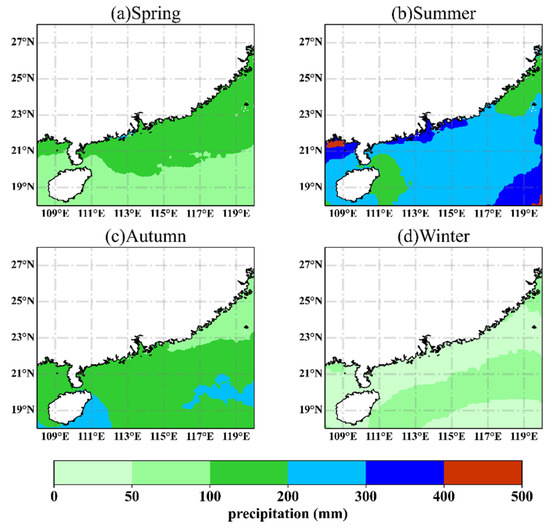
Figure 10.
Spatial distribution of average precipitation in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d) in the NSCS.
The other cause of the high proportion of ES aerosols in spring is the high-humidity conditions in the study areas. In spring, the low-level easterly component with warm and humid air currents contributes to the high relative humidity (RH) in the study areas (Figure 8a–c), and RH is mostly above 80% [98]. When RH is high, the water vapor content increases rapidly, and the hygroscopic growth (an increase in the size of aerosol particles) of hydrophilic aerosols (e.g., sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, and chloride) is enhanced [99], while hydrophobic aerosols (e.g., dust-related aerosols) remain unaffected [100]. Due to the hygroscopic behavior of hydrophilic aerosol particles, the increase in RH corresponds to the increase in backscatter coefficient γ’ [100], which is used to classify aerosol types. When the hygroscopic growth occurs in the component of CM aerosols, such as sulfate, nitrate, ammonium, and chloride, γ’ will increase [100], which may cause CM aerosols to be identified as ES aerosols. It is conjectured that misidentification might occur, and thus CALIOP might overestimate the proportion of ES aerosols in spring to some extent under this condition (Figure 3).
4.2. Policies, Limitations, and Prospect
4.2.1. Pollution Control Policies
The proportions of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols have gradually decreased, and simultaneously the proportion of CM aerosols has increased from 2006 to 2020 in the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA, which indicates that the influence from land-based sources is weakening and air quality in the study areas is improving. Due to a series of low-pollutant policies and the transition from labor-intensive industries to high-tech and knowledge-intensive industries, the concentration of pollutants has been reduced during the period of China’s 11–13th Five-Year Plan (2006–2020) [75,101].
To control dust-related aerosols, GBA cities proposed policies to control construction dust, including strict control of productive dust emissions, application of green production technology, and detailed construction technical standards [102]. It was identified that emission regulations of the power and industry sectors were the major driver of PM2.5 mitigation in China during 2013–2017 [61]. To decrease the concentration of anthropogenic aerosols, the local government proposed a policy of replacing fuel oil with liquefied natural gas (LNG) in 2010 in SZ [75] and constructed two more nuclear power stations to produce electricity in a low-pollution way. Therefore, such an obvious decrease in anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols in the NSCS and the coastal waters of the GBA from 2013 (Figure 7) may be attributed to the enforcement of effective policies and encouragement of clean energy in the past decade.
To further achieve a low-pollutant society, more governmental support is required to overcome the barriers in institutional, technical, and economic areas and accelerate the transformation from a fuel-oil-dependent energy structure to a clean-energy-dominated structure.
4.2.2. Limitations and Prospect
From the CALIPSO scanning trajectory over the coastal waters of the GBA (Figure 1), it can be found that the spatial coverage of the CALIPSO satellite is not high, which may cause uncertainty in data statistics and analysis to certain extent. Moreover, there are missing data in CALIPSO (i.e., February 2016), causing observation interruptions. In addition to CALIPSO, in the future research on the four-dimensional aerosol types, other measurements which are able to provide aerosol type profiles (e.g., airborne high-spectral-resolution lidar measurements from NASA) can be also taken into account to make the analysis more comprehensive [46]. Moreover, the optical properties (e.g., aerosol optical properties) of different aerosol types can be further analyzed in combination with data from MODIS and other satellite-borne sensors.
5. Conclusions
Based on the CALIPSO aerosol profiles from 2006 to 2020, we revealed the four-dimensional (x-y-z-t) spatiotemporal characteristics of maritime aerosol types (clean marine, dust, polluted continental/smoke, clean continental, polluted dust, elevated smoke, and dusty marine) over the coastal waters of the GBA and compared them with those in the NSCS.
The dominant aerosol types were identified to be CM, ES, and DM, all of which accounted for more than 85% in both study areas. Significant seasonal variations of the first two dominant aerosol types (CM and ES) were found. ES aerosols were dominant in spring, while CM aerosols dominated in other seasons. The proportions of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols in spring and winter were higher than those in summer and autumn, which indicated that the level of air pollution in spring and winter was more serious. In addition, the aerosol pollution in the coastal waters of the GBA was more serious than that in the NSCS in all four seasons.
In the vertical direction, except in spring, the number of aerosols showed a decreasing trend with the increase in height in both study areas. The abnormal increase at the height of approximately 1.5 km in spring may be due to the influence of polluted aerosols such as ES and PD. Under the height of 2 km, CM and DM aerosols were most frequently found, while above the height of 2 km, the major types were ES, PD, and DU aerosols. The horizontal distribution of aerosol types was spatially uniform in the lower atmosphere (< 2 km), while considerable heterogeneity of aerosol types was found at higher altitudes (especially >4 km) in the study areas.
In terms of long-term evolution, the proportion of CM aerosols increased year by year, while the proportion of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols decreased with fluctuations, possibly due to the implementation of a series of measures to reduce air pollution implemented by the local government in recent years. Furthermore, the spatiotemporal distribution variations of multiple aerosol types were also affected by emission sources, horizontal diffusion, vertical diffusion, and moisture condition. Overall, the influence of regional human activities and dust sources on the aerosol over the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS has weakened.
The mechanism behind the four-dimensional (x-y-z-t) spatiotemporal characteristics is associated with emission sources, atmospheric horizontal and vertical conditions, and moisture condition. The emission sources of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols over the coastal waters of the GBA and the NSCS are mainly land-based. The westerly winds above the boundary layer transport the smoke generated by biomass combustion from Southeast Asia to the NSCS in spring. From the perspective of the East Asian monsoon, in March, dust was partly transported from Central Asia and mixed with anthropogenic aerosols into study areas due to the northeast monsoon. In addition, the average wind speed is the smallest in spring, which is conducive to the accumulation of pollutants. In summer, the strong southwest monsoon prevented the land-based anthropogenic emissions and Central Asian dust from dispersing into the study areas; in winter, the prevailing northeasterly wind facilitated the influx of land-based pollutants over the sea. Thus, the total proportion of anthropogenic aerosols and dust-related aerosols accounted for a relatively low proportion in summer and a high proportion in winter. Focusing on the vertical condition, we found that the study areas are controlled by the WPSH in spring and winter, which is conducive to a stable vertical condition. As for moisture condition, influenced by the strong southwest monsoon, the coastal waters of the GBA and NSCS experience higher amounts of rainfall, with a strong wash-out effect, in summer and autumn than in spring and winter. Overall, the level of air pollution in the study areas in spring and winter was higher than that in summer and autumn.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.C.; methodology, Q.M., Y.L., T.H. and T.Q.; formal analysis, Q.M., Y.L. and T.Q.; investigation, Q.M., Y.L. and T.Q.; data curation, Q.M., Y.L. and T.Q.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.M., Y.L. and T.Q.; writing review and editing, T.C., T.H., Z.H. and T.D.; visualization, Q.M., Y.L. and T.Q.; supervision, T.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation, China (Nos. 42088101, 42075105); Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Zhuhai) (No. SML2021SP313); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Sun Yat-sen University (No. 22lglj01 and No. 22qntd1913); and China-Korea Joint Ocean Research Center, China (PI-2022-1).
Data Availability Statement
The ECMWF (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 25 July 2022), MSWEP (http://www.gloh2o.org/mswep/, accessed on 25 July 2022), and CALIPSO (https://subset.larc.nasa.gov/calipso/, accessed on 25 July 2022) data used in this study are freely available.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge NASA and ECMWF for their effort in making the data available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lin, B.; Li, Z. Spatial analysis of mainland cities’ carbon emissions of and around Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lin, R.F. Economic Complexity of the City Cluster in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Liu, C.; Galina, P.; Tao, C.; Hou, X.; Bai, F.; Zhao, H. Efficiency Analysis of the Marine Economy in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area Based on a DEA Model. J. Coastal Res. 2020, 106, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.C.M.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Lang, W. Deciphering the spatial structure of China’s megacity region: A new bay area—The Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area in the making. Cities 2020, 105, 102168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, B.; Blackmore, G. South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 1236–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, T.; Wu, X.; Yang, C.; Gao, W.; Li, Q.; Wu, G. Exploring Annual Urban Expansions in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area: Spatiotemporal Features and Driving Factors in 1986–2017. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, T.; Ding, K.; Wu, G. Spatiotemporal evolution of urban agglomerations in four major bay areas of US, China and Japan from 1987 to 2017: Evidence from remote sensing images. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzana, S.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, R.; Kai, Z.; Meng, Y.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Developing interim water quality criteria for emerging chemicals of concern for protecting marine life in the Greater Bay Area of South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Impacts of urbanization on extreme precipitation in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area. Urban Clim. 2021, 38, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, W.; Xiao, K.; Yu, S.; Zheng, C.; Wang, X. Pollution assessment and sources of dissolved heavy metals in coastal water of a highly urbanized coastal area: The role of groundwater discharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B. Urbanization in developing countries: Current trends, future projections, and key challenges for sustainability. Technol. Soc. 2006, 28, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Dou, K.; Fan, G.; Huang, S.; Si, F.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Pei, C.; Tang, F.; Yang, D.; et al. Vertical distributions of tropospheric formaldehyde, nitrogen dioxide, ozone and aerosol in southern China by ground-based MAX-DOAS and LIDAR measurements during PRIDE-GBA 2018 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Guo, Y.; Xu, X. Evaluation of real-time vehicle energy consumption and related emissions in China: A case study of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao greater Bay Area. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Fan, Q.; Liao, Z.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Fan, S. Spatial-temporal characteristics of the air quality in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area of China during 2015–2017. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 210, 14–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Qiu, R. Pathways to a more efficient and cleaner energy system in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area: A system-based simulation during 2015–2035. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Huang, C.; Fang, H.; Cai, W.; Li, D.; Li, X.; Yu, H. The abundance, composition and sources of marine debris in coastal seawaters or beaches around the northern South China Sea (China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.; Luo, L.; Shen, C.; Long, A.; Chen, L.; Long, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric aerosol compositions over the South China Sea: Temporal variability and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, D. Maritime Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties in the South China Sea Under Multi-source Influence. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Leung, L.R. WRF-Chem simulations of aerosols and anthropogenic aerosol radiative forcing in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate Forcing by Anthropogenic Aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. The Effect of Aerosols to Climate Change and Society. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2020, 08, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Mao, Q. Inversion of Aerosol Particle Size Distribution Using an Improved Stochastic Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. Aerosols, clouds and radiation. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1991, 25, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Gui, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Seasonal distribution and vertical structure of different types of aerosols in southwest China observed from CALIOP. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twomey, S. The Influence of Pollution on the Shortwave Albedo of Clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1977, 34, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, T.; Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, K. Quantifying the Long-Term MODIS Cloud Regime Dependent Relationship between Aerosol Optical Depth and Cloud Properties over China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; de Leeuw, G. Marine aerosol production: A review of the current knowledge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 365, 1753–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Bahreini, R.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Hämeri, K.; Pirjola, L.; Kulmala, M.; Jennings, S.G.; Hoffmann, T. Marine aerosol formation from biogenic iodine emissions. Nature 2002, 417, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Slutsker, I.; Giles, D.M.; McClain, C.R.; Eck, T.F.; Sakerin, S.M.; Macke, A.; Croot, P.; Zibordi, G.; et al. Maritime Aerosol Network as a component of Aerosol Robotic Network. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D06204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Huang, T.; Mu, B.; Gao, F.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, R.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal pattern of aerosol types over the Bohai and Yellow Seas observed by CALIOP. Infrared Laser Eng. 2021, 50, 103–109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mallet, M.; Nabat, P.; Johnson, B.; Michou, M.; Haywood, J.M.; Chen, C.; Dubovik, O. Climate models generally underrepresent the warming by Central Africa biomass-burning aerosols over the Southeast Atlantic. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.H.; Su, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Massie, S.; Zhao, B.; Omar, A.; Wang, Z. Contrasting effects on deep convective clouds by different types of aerosols. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3874–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Zhao, X.; Rahimi, S.; Xia, W.; Jiang, Y. Black carbon-climate interactions regulate dust burdens over India revealed during COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, C.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, Q.; Tan, H. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Major Aerosol Types over China Based on MODIS Products between 2008 and 2017. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J. Variability of Major Aerosol Types in China Classified Using AERONET Measurements. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z. Variations and drivers of aerosol vertical characterization after clean air policy in China based on 7-years consecutive observations. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, E.; Fu, C.; Yu, W.; Xie, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lu, C. Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, S.A.; Reid, J.S.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Cliff, S.S.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, N.; Tsay, S.; Chu, Y.; Westphal, D.L. Size resolved measurements of springtime aerosol particles over the northern South China Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowottnick, E.P.; Colarco, P.R.; Welton, E.J.; Da Silva, A. Use of the CALIOP vertical feature mask for evaluating global aerosol models. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3647–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J.A.; Ackerman, S.A.; Charlson, R.J.; Colarco, P.R.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.M.; Kittaka, C.; et al. The CALIPSO Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1211–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R.; et al. The CALIPSO Automated Aerosol Classification and Lidar Ratio Selection Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath-Spangler, E.L.; Denning, A.S. Global seasonal variations of midday planetary boundary layer depth from CALIPSO space-borne LIDAR. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Colarco, P.R.; Harshvardhan, H. The Influence of Elevated Smoke Layers on Stratocumulus Clouds Over the SE Atlantic in the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) Model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Ferrare, R.A.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.H.; Rogers, R.R.; Hostetler, C.A.; Hair, J.W. Aerosol classification from airborne HSRL and comparisons with the CALIPSO vertical feature mask. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Koskinen, J.; de Leeuw, G.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Comparison of CALIOP level 2 aerosol subtypes to aerosol types derived from AERONET inversion data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L18804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Jiang, J.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Su, H.; Fu, R. Seasonal and diurnal variations of aerosol extinction profile and type distribution from CALIPSO 5-year observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4572–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, F.; Dingenen, R.V.; Vignati, E.; Wilson, J.; Putaud, J.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Adams, P. Formation and cycling of aerosols in the global troposphere. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 4215–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Qiu, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y. Negative Aerosol-Cloudre Relationship from Aircraft Observations Over Hebei, China. Earth Space Sci. 2018, 5, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Boiyo, R.; Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Vertical Structures of Dust Aerosols over East Asia Based on CALIPSO Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Pan, M.; Roy, T.; Weedon, G.P.; Pappenberger, F.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Wood, E.F. Daily evaluation of 26 precipitation datasets using Stage-IV gauge-radar data for the CONUS. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Li, J.; Friedlingstein, P.; Koven, C.; Chen, A. Spring temperature change and its implication in the change of vegetation growth in North America from 1982 to 2006. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myneni, R.B.; Keeling, C.D.; Tucker, C.J.; Asrar, G.; Nemani, R.R. Increased plant growth in the northern high latitudes from 1981 to 1991. Nature 1997, 386, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banner, K.M.; Higgs, M.D. Considerations for assessing model averaging of regression coefficients. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Valle, D.; Popescu, S.; Zhang, X.; Mallick, B. Hyperspectral remote sensing of plant biochemistry using Bayesian model averaging with variable and band selection. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 132, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wulder, M.A.; Hu, T.; Bright, R.; Wu, Q.; Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Toman, E.; Mallick, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. Detecting change-point, trend, and seasonality in satellite time series data to track abrupt changes and nonlinear dynamics: A Bayesian ensemble algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardian, J.; Berg, A.; Daneshfar, B. Evaluating the temporal accuracy of grassland to cropland change detection using multitemporal image analysis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, H. Monitoring the Vegetation Dynamics in the Dongting Lake Wetland from 2000 to 2019 Using the BEAST Algorithm Based on Dense Landsat Time Series. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hammer, M.S.; Zheng, B.; Cohen, R.C. Accelerated reduction of air pollutants in China, 2017–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-temporal variation and impact factors analysis of satellite-based aerosol optical depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebert, B.J. An overview of ACE-Asia: Strategies for quantifying the relationships between Asian aerosols and their climatic impacts. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Chou, C.C.K. Satellite-Derived Correlation of SO2, NO2, and Aerosol Optical Depth with Meteorological Conditions over East Asia from 2005 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Han, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, S.; Xie, X. Physical-Optical Properties of Marine Aerosols over the South China Sea: Shipboard Measurements and MERRA-2 Reanalysis. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, B. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of aerosol optical depth and radiative effect in South China and its adjacent area. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhuang, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Wei, W.; Lin, H.; Li, M. Climatic-Environmental Effects of Aerosols and Their Sensitivity to Aerosol Mixing States in East Asia in Winter. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J. Updated emissions from ocean shipping. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aardenne, J.A.; Carmichael, G.R.; Levy, H.; Streets, D.; Hordijk, L. Anthropogenic NOx emissions in Asia in the period 1990–2020. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Chen, S.R.; Xu, Y.S.; Guo, X.C.; Sun, Y.L.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhao, X.D.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, W.X. Mixing state and sources of submicron regional background aerosols in the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the influence of biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13365–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, D.S.; Chiquetto, J.B.; D’Amelio, M.T.S.; Khalid, B.; Herdies, D.L.; Pendharkar, J.; Corrêa, S.M.; Figueroa, S.N.; Frassoni, A.; Capistrano, V.B.; et al. Evaluating Carbon Monoxide and Aerosol Optical Depth Simulations from CAM-Chem Using Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, H.; Zou, B.; Yang, Z.; Ding, Y. Correlation between biomass burning and air pollution in China: Spatial heterogeneity and corresponding factors. Global Planet. Chang. 2022, 213, 103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.; Chang, S.; Lin, N.; Wang, J.; Sheu, G.; Chang, Y.; Lee, C. Aerosol chemical properties and related pollutants measured in Dongsha Island in the northern South China Sea during 7-SEAS/Dongsha Experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heese, B.; Baars, H.; Bohlmann, S.; Althausen, D.; Deng, R. Continuous vertical aerosol profiling with a multi-wavelength Raman polarization lidar over the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6679–6691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, G.; Guan, D. Emissions and low-carbon development in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area cities and their surroundings. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Carmichael, G.; Chen, D.; Tang, Y.; Wang, T. Impacts of different emission sources on air quality during March 2001 in the Pearl River Delta (PRD) region. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5227–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Liu, H.; Ying, Q.; Fu, M.; Meng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Gong, H.; He, K. Impacts of shipping emissions on PM2.5 pollution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15811–15824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, Y.; Tian, C.; Lou, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Matthias, V. Emission factors for gaseous and particulate pollutants from offshore diesel engine vessels in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6319–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Y.; Huang, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T. A 1400-year terrigenous dust record on a coral island in South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Xiang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.P.; Islam, G.M.A.; Chen, M. The present-day atmospheric dust deposition process in the South China Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.K.; Chao, S.Y.; Shaw, P.T.; Gong, G.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tang, T.Y. Monsoon-forced chlorophyll distribution and primary production in the South China Sea: Observations and a numerical study. Deep.-Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1387–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.; Chen, J.; Wong, G.T.F.; Huang, C.; Lien, C. Aerosol input to the South China Sea: Results from the MODerate Resolution Imaging Spectro-radiometer, the Quick Scatterometer, and the Measurements of Pollution in the Troposphere Sensor. Deep.-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 1589–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Huang, J.; Zhao, D.; Yuan, T.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zang, Z.; et al. Fugitive Road Dust PM2.5 Emissions and Their Potential Health Impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8455–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Allaban, M.; Gillies, J.A.; Gertler, A.W.; Clayton, R.; Proffitt, D. Tailpipe, resuspended road dust, and brake-wear emission factors from on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tsay, S.; Lin, N.; Hsu, N.C.; Bell, S.W.; Li, C.; Ji, Q.; Jeong, M.; Hansell, R.A.; Welton, E.J.; et al. First detailed observations of long-range transported dust over the northern South China Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4804–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Ariful Islam, G.M.; Xiang, R.; Yang, X. The Dust Deposition Process and Biogeochemical Impacts in the Northern South China Sea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; An, C.; Lee, K.; Owens, E.; Boufadel, M.; Feng, Q. Dispersion modeling of particulate matter from the in-situ burning of spilled oil in the northwest Arctic area of Canada. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Shen, Y.; Yao, X.; Zheng, M. A clear north-to-south spatial gradience of chloride in marine aerosol in Chinese seas under the influence of East Asian Winter Monsoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Ning, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shang, Z. A quantitative assessment of the air pollution purification effect of a super strong cold-air outbreak in January 2016 in China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2018, 11, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Leng, W.; Jiang, S.; Cao, B. Long-Term Variation in Wintertime Atmospheric Diffusion Conditions Over the Sichuan Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 763504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.; Jalal, S.; Jalal, A.S.; Kumar, M. A Density Based Algorithm for Discovering Density Varied Clusters in Large Spatial Databases. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, H. Haze Days in North China and the associated atmospheric circulations based on daily visibility data from 1960 to 2012. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5895–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaluvadi, R.; Varikoden, H.; Mujumdar, M.; Ingle, S.T. Variability of West Pacific subtropical high and its potential importance to the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 4047–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, X. Comparison on Relationship between Western Pacific Subtropical High and Summer Precipitation over Dongting Lake Basin Based on Different Datasets. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 57, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xia, L. Assessment Impacts of Weather and Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Change on Urban Vegetation Net Primary Productivity (NPP): A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4125–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Shao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Jia, R. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban Rain Islands in China under the Conditions of Urbanization and Climate Change. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Jiang, J.H.; Kishore, P.; Ravindra Babu, S. Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of long-term variations of fog and haze in China in recent 50 years and their relations with atmospheric humidity. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Sun, Y.; Cribb, M. Aerosol hygroscopic growth, contributing factors, and impact on haze events in a severely polluted region in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Cai, Y.; Pan, J.; Yue, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, J. Measurements of atmospheric aerosol hygroscopic growth based on multi-channel Raman-Mie lidar. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Carmichael, G.R.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wei, C.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q. Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and sulfur trends in East Asia since 2000. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6311–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Lu, X.; Yu, M.; Yan, Y.; Wu, M. Low-Carbon Development of the Construction Industry in China’s Pilot Provinces. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 2617–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).