Abstract
At present, some related studies on semantic segmentation are becoming complicated, adding a lot of feature layers and various jump splicing to improve the level of refined segmentation, which often requires a large number of parameters to ensure a better segmentation effect. When faced with lightweight tasks, such as sea and land segmentation, the modeling capabilities of these models far exceed the complexity of the task, and reducing the size of the model can easily weaken the original effect of the model. In response to this problem, this paper proposes a U-net optimization structure combining Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) and FReLU, namely ACU-Net. ACU-Net replaces the two-layer continuous convolution in the feature extraction part of U-Net with a lightweight ASPP module, retains the symmetric U-shaped structure of the original U-Net structure, and splices the output of the ASPP module with the upsampling part. Use FReLU to improve the modeling ability between pixels, and at the same time cooperate with the attention mechanism to improve the perception ability and receptive field of the network, reduce the training difficulty of the model, and fully tap the hidden information of the samples to capture more effective features. The experimental results show that the ACU-Net in this paper surpasses the reduced U-Net and its optimized improved network U-Net++ in terms of segmentation accuracy and IoU with a smaller volume.
1. Introduction
Remote sensing images are images that use remote sensing satellites to record and analyze the Earth’s surface through optical sensors, remote sensing platforms, data compression equipment, data transmission equipment, and ground receiving stations. It is an important data source for information such as cloud cover and ocean exploration [1].
Before the convolutional neural network was developed, it was mainly based on image features (grayscale features, color features, information entropy features, texture features, etc.), to extract key information in remote sensing images, and depended on feature fusion, latitude, and longitude prior information [2], etc., to strengthen the classification and segmentation effect. The sea and land segmentation algorithm of SAR images based on the statistical characteristics of Otsu [3] and sea areas proposed by Chen Xiang et al. combines the coarse threshold with the precise threshold [4], and achieves the effect of fast processing speed and high segmentation accuracy at the same time; Li Jing et al. used information entropy to analyze the sea and land The information possessed by remote sensing images further refines the segmentation results [5]; Pang Ying et al. improved a superpixel-based SAR image sea and land segmentation algorithm by using the SLIC algorithm [6], extracted the fused grayscale and texture features, and used a vector machine (SVM) to judge the pixel category and optimize the segmentation effect. With the rise of visible light remote sensing images and the continuous improvement of their resolutions, the surface texture differences between similar objects in the images are magnified, which poses a challenge to the feature extraction-based sea and land segmentation methods.
After recent years of development, deep learning networks have become an integral part of computer vision. It relies on broad applicability and accuracy to perform better than previous methods in most image processing tasks. With the excellent results of the convolutional neural network [7] (CNN) and deep convolutional neural network [8] (DCNN) in tasks such as image classification and target recognition, deep learning has embarked on the stage of the world’s computer vision tasks and has given birth to the fully convolutional neural network (FCN) [9], which is more suitable for semantic segmentation. In the absence of a link layer, the FCN first extracts the features of the image through continuous convolution, finally restores the size of the feature map, and obtains the output result after activation normalization. This enables the entire network to complete the classification prediction for each pixel on the premise of preserving the image information, and there is no fixed requirement for the size of the image.
Most of the commonly used semantic segmentation algorithms are improved based on the fully convolutional neural network framework, such as U-Net [10] and Seg-Net [11]. These networks are gradually used in remote sensing image segmentation tasks. Schuegraf et al. linked two U-Net networks in parallel to extract deep-level features in remote sensing images, and at the same time effectively acquired the spectral features of the images [12]. Minglong Li from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a global–local attention network GLANet [13] and proposed a double-associative distillation framework DRD. The advantage of GLANet is that it simultaneously reduces the classification errors of large-area classification and local edge classification in the task of semantic segmentation of ground objects. Zhang Gang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed an optimization algorithm for neural networks [14], that is, before and after matching it with the current superpixel segmentation that performs better. Peng Hu of Harbin Institute of Technology proposed an improved method of deep feature extraction for DeepLab v3+ deep and shallow layer fusion [15], which added a batch normalization layer to optimize the performance of DeepLab v3+ and reduce the training difficulty of the model. Wang Lanyu of Harbin Institute of Technology proposed to use Xception_71 as a feature extraction network to optimize DeepLab v3+ [16]. Wang Junqiang, an engineer of Unit 78123, proposed a new remote sensing image segmentation method by combining improved PSPNet and CRF [17]. This method introduces two loss functions and designs a two-step training method for this, which achieves excellent end-to-end network training and improves the size of the global receptive field of the model. Based on HRNet [18], Wang Shuqi of the Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications redesigned the dual attention module for the four semantic segmentation problems of small objects in remote sensing satellite images, dense arrangement, same-spectrum different objects, and same-spectrum different objects [19]. Aiming at common problems such as edge information loss, an edge refinement module is designed. Most of the methods above have complex structures and are not efficient in the face of lightweight tasks, and may also bring side effects that are difficult to train and difficult to converge.
This paper proposes a U-net optimization structure combining Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) and FReLU [20]: ACU-Net, which uses Atrous convolution to improve the receptive field and detail capture ability, reduce the number of parameters, and use FReLU. The activation function and attention network are used to capture the complex image layout details so that the model has better performance, the loss function is improved, and the attention module is added to reduce the training difficulty of the model and improve the information modeling ability of the model.
2. Materials
The dataset used for training comes from the “MASATI_shipDetection” high-resolution optical remote sensing ship dataset [21]. This dataset provides remote sensing ocean scenes in the visible light band. The average size of the images is 512 × 512 and the format is PNG, which is taken from the satellite image mode of Bing-Map. To verify the generalization ability of the model, this paper selects the “NWPU-RESISC45” remote sensing dataset for random testing [22]. This dataset provides many kinds of remote sensing images, and we select the coastal dataset among them. The average size of these images is 256 × 256, while the format is PNG, and it is taken from the satellite image mode of Google Earth.
The coast is often foggy, and the remote sensing images obtained are also susceptible to it. Therefore, fog processing is performed on both the training set and the validation set to simulate the influence of sea fog and heavy fog and clouds on the recognition effect. This paper uses a simple central fog group processing method, which calculates the pixel value after adding fog according to the distance of each pixel from the center point of the image. Its calculation formula is as follows:
where and is the position of the pixel in the image, and is the center of the image, is the pixel value of the image at that location, is the output pixel value. Among them, is the brightness parameter, which is set to 0.8, and is the density parameter, which is set to 0.055.
The fogging preview is shown in Figure 1a,b. Picture a is the original picture, and picture b is the picture after fogging.

Figure 1.
Image fog enhancement processing. (a) The original picture; (b) the picture after fogging.
In this paper, a total of 1000 images in the MASATI_shipDetection dataset are manually annotated. After fogging, there are 2000 images in total, of which 1600 are used for training and 400 are used for verification. We use the original image and the fogged image for training at the same time, which is also a training data enhancement process, which can reduce the overfitting phenomenon in training, improve the generalization ability and robustness of the model, and make the model in less time. It is easier to converge under the data. An additional 100 images from the NWPU-RESISC45 dataset are extracted for labeling to test the adaptation performance of the model.
3. Methods
After FCN, many classic network models emerged in the direction of convolutional neural network semantic segmentation, which greatly improved the training accuracy and application scope of basic FCN models, such as U-Net. Between feature extraction and image restoration, U-Net uses skip connections to stitch together deep and shallow feature maps and the network is symmetrical in a U-shape. This jump splicing provides local information from shallow layers for upsampling and fully integrates the depth information, which is the key to improving pixel connection and reducing information loss.
According to our experiments, reducing or increasing the number of U-Net downsampling and channels may reduce the segmentation accuracy, and we need to adjust the number of downsampling for the task itself. In simpler tasks such as sea and land segmentation, the performance of U-Net after reducing the number of downsampling is not ideal. This paper proposes ACU-Net (Atrous Convolution U-Net) using an Atrous spatial convolution pyramid to improve the model’s performance in small volumes. The basic structure and details of the model are shown in Figure 2.
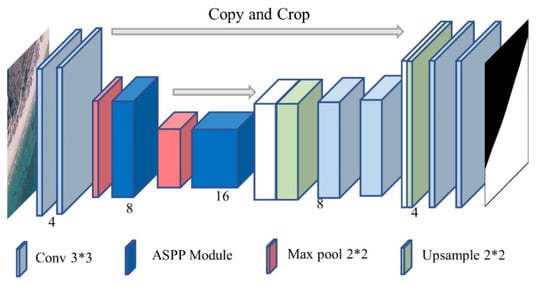
Figure 2.
ACU-Net structure diagram.
Two layers of convolution with a kernel of 3 × 3 are used to capture the basic features of the input image, then ACU-Net uses the optimized ASPP module to replace the two ordinary convolutions in the original U-Net network downsampling and uses the 2 × 2 maximum pooling layer with stride 2 to connect the front and rear layers, expanding the receptive field of each downsampling, making the deepest semantic information at the bottom of the U-shape is more sufficient to contain more image information, to provide feature input with more semantic information during the upsampling process. In the process of upsampling, the structure of ACU-Net and U-Net is the same. Each downsampling step consists of the 2 × 2 convolution (up-convolution) that halves the number of feature channels and the repeated application of two 3 × 3 convolutions. Additionally, the visual activation function FReLU is used to completely replace ReLU, so every layer is followed by a FReLU, which effectively improves the ability of pixel-to-pixel modeling.
3.1. ASPP Module
Atrous convolution has the advantages of expanding the receptive field and capturing global semantic information, but the biggest problem in the actual use of Atrous convolution is that there is no connection between the convolution results obtained with the same dilation rate. If only one dilation rate of convolution is repeatedly superimposed, a lot of local pixel information will be lost. So if it is not optimized, training time and difficulty will increase. From DeepLab-v2 to DeepLab-v3+, Chen et al. deeply studied the effects of dilated convolutions with different dilation rates in parallel and series, where the parallel spatial convolution outputs are combined to form a dilated spatial convolution pyramid [23,24].
ASPP performs Atrous convolution with different dilation rates on the same feature map while capturing global relations and pixel detail features at different distances. Then these convolution results are spliced together, and a two-dimensional convolution with a convolution kernel size of 1 × 1 is used to restore the input feature map size. The structure diagram of basic ASPP is shown in Figure 3.
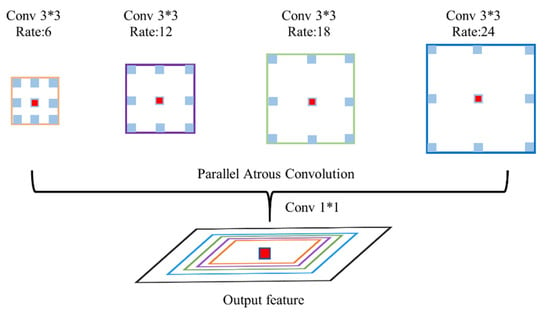
Figure 3.
Basic ASPP structure diagram.
According to the conditions of ASPP in the DeepLab-v3+ model proposed by Chen et al., and in order to balance the volume and performance of U-Net with ASPP added, the improved ASSP module used in this paper contains a total of three layers: the first layer is an ordinary convolution layer with a convolution kernel of 3 × 3 and an expansion rate of 1; the second layer Keeping the size of the convolution kernel unchanged, the expansion rate is changed to 6; the expansion rate of the third layer is changed to 12. Its structure diagram is shown in Figure 4.
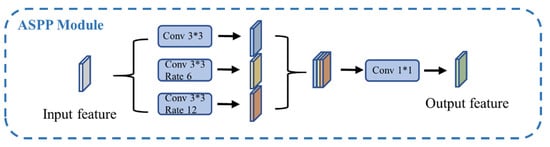
Figure 4.
Improved ASPP module of this paper.
3.2. Attention Module
The attention network module is widely used in convolutional neural networks because of its plug-and-play characteristics, and because it can effectively improve accuracy. After Hu proposed SE-Net [25], the originator of the attention mechanism, various attentions such as channel space serial attention module CBAM [26], parallel attention module BAM [27], and non-local attention module [28].Non_local based on the self-attention module has been born. In recent years, there have been more lightweight and better-coordinated attention modules CA-Net [29], ECA-Net [30], and self-attention-based dual-attention DANet [31]. According to the experimental results, the lightweight SE-Net has a good effect on the task of sea and land segmentation and does not bring more parameter burden.
The purpose of SE-Net is to optimize the coding quality in channel links, improve the information synthesis ability of the entire network by compressing and dilating channel information, enhance the intrinsic connection between feature layer channels, and reduce unnecessary coding information and links. It enables the network to use more information on the channel during training and use, and adjust the information adaptively. Its structure diagram is shown in Figure 5. Through the global average pooling layer, the attention module converts the feature input of H × W × C into the feature of 1 × 1 × C and then uses the fully connected layer to perform squeeze-and-excitation on the feature. It should be noted here that the first fully connected layer (squeeze) is followed by ReLU instead of FReLU, and the second fully connected layer (excitation) is followed by Sigmoid. Then, the output after the fully connected layer is multiplied by the original feature to obtain the final result of the attention network.
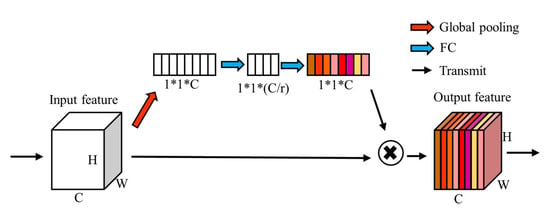
Figure 5.
SE-Net structure diagram.
At the bottom of the U-shaped structure, that is, between the last downsampling and the first upsampling, an attention module is added to improve the model’s ability to perceive context and receptive field, and at the same time reduce the training difficulty of the model and further improve the efficiency of the model. The schematic diagram after adding the attention module to ACU-Net is shown in Figure 6.
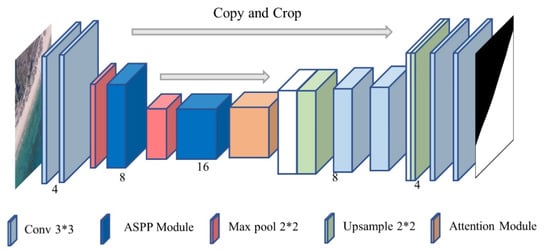
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram after adding attention module.
3.3. FReLU Activation Function
The ReLU function has a small amount of calculation and a fast convergence speed, but there are also problems of loss of information and difficulty in data updating during training backpropagation. The FReLU function is optimized for the problem of neuron disappearance in which all negative inputs are zero. The formula is:
where is a 2D convolution function whose parameters can be updated with training.
FReLU has greatly improved in classification, target localization, and semantic segmentation tasks. The important reason is that multiple trainable parameters are introduced to improve the adaptability of the network. Among them, 2D convolution is used to capture complex 2D spatial information, the sensitivity to hidden information is improved through parameter training and iteration, and pixel-level network modeling is realized in a way that the number of parameters can be ignored. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 7, and the size of the convolution kernel is 3 × 3.
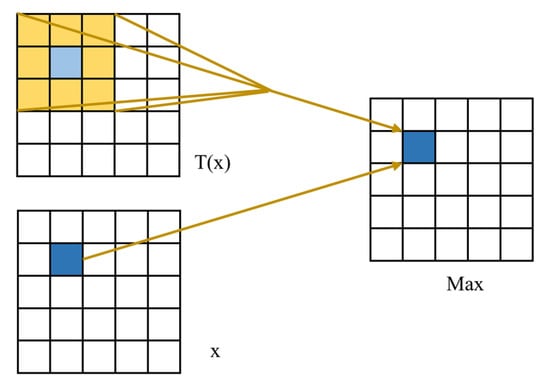
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of FReLU activation function.
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Settings
This article uses a Linux-based server for training. The specific configuration is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Development environment.
Based on the trade-off between the performance and size of the model, the input image size of the model in this experiment is a color image of 128 × 128 × 3, and the output is predicted to be a 128 × 128 × 2 dual-channel layer for classification.
We perform zero-padding operations on the image edges in the convolution, the initializer of the convolutional layer adopts the He normal distribution and uses the Adam optimizer for training. During training, the optimal model is continuously saved according to the accuracy rate, and the learning rate is multiplied by 0.1 without decreasing the verification loss 28 consecutive times.
4.2. Evaluation Index
The prediction diagram of semantic segmentation is shown in Figure 8.
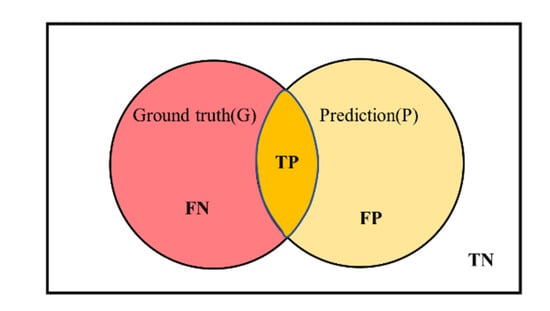
Figure 8.
Schematic diagram of prediction in semantic segmentation problem.
For the sea–land segmentation task, this paper adopts IoU as the evaluation index. Its calculation formula is:
where .
In general, IoU can be used directly for two-partition networks. Multi-partition networks also need to sum and average to obtain mean intersection over union (MIoU). Its calculation formula is as follows:
In the process of neural network training, the difference between the predicted results and the real values can be obtained by comparing them. The difference is used to calculate the loss. Then, according to the change of the loss value, the weight is modified through the backpropagation of the network, to achieve the purpose of constantly reducing the loss value. The cross-entropy loss function (CE) can be used for classification problems as follows:
where is the true value of sample i, is the predicted value of sample i.
However, CELoss has the same weight for different difficult categories in the calculation of loss, leading to the training being easily influenced by the easily trainable categories and reducing the accuracy of the difficult categories. Given these problems and the particularity of semantic segmentation, many loss functions suitable for segmentation tasks are derived, such as Dice loss, Focal loss, and Tversky loss. Dice loss increases the weight of prediction targets, so that categories with smaller regions can also have good training results, and can effectively reduce the impact of unbalanced samples. The Dice loss formula is as follows:
Aiming at the problem of predicting edge blur when simply using the cross-entropy loss function, this paper adopts a method combining cross-entropy and Dice loss to make the prediction output more accurate and the fuzzy area smaller. Its formula is:
where the parameter is set to 0.8.
4.3. Segmentation Results
To reflect the improvement brought by FReLU and the excellent performance of ACU-Net under small volumes. Under the same conditions as above, this paper uses the typical semantic segmentation network U-Net, its improved network U-Net++ [33], Deeplab-V3+, and the ACU-Net network in this paper. U-Net++ uses both deep and shallow features based on U-Net and achieves high-performance improvement at a small parameter cost.
We conduct a comparative analysis of various usage scenarios when using the model. First of all, this paper reduces the standard U-Net model, and the specific experimental results are shown in Table 2. The parentheses after the model structure in the table are specific requirements in the format of (a, b), where “a” represents a total number of downsampling times excluding the input part of the network, and “b” represents the highest number of channels. According to the structure of U-Net, the number of channels doubles with each downsampling and shrinks by half with each upsampling. For example, (4, 1024) means four times downsampling and five times channel number change including image input, and the rule of channel number change is (64, 128, 256, 512, 1024). Different combinations can result in differences in model size and performance.

Table 2.
Comparison of training results (volume reduction).
As mentioned earlier, the number of downsampling and the number of channels of U-Net need to be specially adjusted for the task. From the data in Table 2, it can be found that the accuracy of U-Net (4, 512) and U-Net (4, 256) is higher than the others. Among them, U-Net (4, 256) achieves higher accuracy with a smaller volume. From this, we can speculate that the U-Net under this parameter setting is the optimal solution of the U-Net model for the sea route segmentation task. We can also notice that because U-Net (4, 1024) has too many parameters, it becomes more difficult to train and has obvious overfitting for binary classification tasks such as land and sea segmentation.
Different combinations of expansion rates are also tried in this paper. The data are presented in Table 3. Since we hope to obtain higher accuracy in a smaller volume, the data of U-Net (3, 32) is used as a comparison baseline, and this model is only about 0.5M. Maybe a model of tens or hundreds of megabytes has better accuracy, but it is not the focus of this paper. On this basis, it can be found from the data that different combinations of expansion rates have little influence on experimental results, and IoU indicators are basically the same. This paper recommends the combination of (1, 6, 12), which can obtain broader picture information and have better effects under a smaller model.

Table 3.
Comparison of training results (different combinations of expansion rates).
The activation functions in ACU-Net were turned into FReLU and related experiments were conducted. However, since FReLU will bring a certain amount of parameters, although the amount of parameters is very small, it cannot be ignored for a 0.5 M model, so after replacing FReLU, this paper further reduces the number of downsampling times of ACU-Net.
At the same time, to more effectively prove that FReLU can bring good improvement and more effectively prove that ACU-Net has higher accuracy than U-Net, this section also fully replaces the ReLU activation function in U-Net with FReLU. The results are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Comparison of training results (change the activation function).
It can be found that the training accuracy of U-Net has been greatly improved after using the FReLU activation function, which can prove that FReLU can indeed bring huge gains in the segmentation task. The ACU-Net proposed in this paper has a further training accuracy after using FReLU, which is close to 97%. Moreover, when ensuring the same number of downsampling, the volume of the method in this paper will become larger than the basic U-Net model due to the introduction of ASPP. The addition of FReLU has exacerbated this state. So we reduce the number of downsampling and keep only two downsamplings, the results are like (ACU-Net (2, 16) (FReLU) Rates (1, 4, 8)) and (ACU-Net (2, 16) (FReLU) Rates (1, 6, 12)), the volume is smaller and the accuracy is more advantageous. This is also the key to the smaller size and higher accuracy of the method in this paper.
Based on the above experiments, this paper continues to add the SE-Net attention module, and obtains the final network structure, as shown in Figure 6. In this section of experiments, we also test DeepLab-v3+ and add it to the comparison. After adding the attention module, the accuracy of ACU-Net in this paper is increased by 0.127% again, and the IoU index is increased by 0.003. The results can be found in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comparison of training results (joined the attention network).
The ACU-Net proposed in this paper uses the FReLU activation function. To reflect that the structure of ACU-Net itself is better than that of U-Net, this paper also replaces the activation function of U-Net with FReLU, as shown in the data in groups d and f in the table. It can be found that FReLU can indeed improve the sea and land segmentation task, but the training accuracy of ACU-Net is still 0.485% higher, and the IoU index is 0.9% higher. At the same time, the ACU-Net with the addition of the attention module can further improve the accuracy, which is 0.127% higher than that without the addition of the module, and the IoU index is 0.3% higher.
Compare 0.514 M U-Net, 0.710 M U-Net with FReLU activation function, 0.645 M U-Net++, and 0.477 M ACU-Net with SE-Net attention module. The specific picture test results are shown in Figure 9.
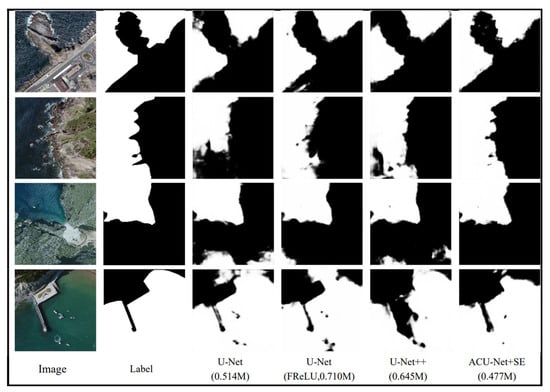
Figure 9.
Model effect comparison.
In the actual segmentation results, it can be found that the ACU-Net in this paper has a better effect on the recognition of port shadows, mountain shadows, waves, and reefs in the picture, and the segmentation results are closer to the real label value. Since the training samples in this paper do not label the ships in the ocean, these models cannot effectively identify info on ships, but ACU-Net does not suffer too much interference in the face of this new object. Taking the second picture and the last picture as an example, ACU-Net cooperates with the SE-Net attention module to more accurately segment messy reefs, protruding trestle bridges, and gradient beaches, and the black shadow has the least influence on the segmentation result.
4.4. Different Datasets
If a model can perform well on datasets with different conditions, it means that the model can face more complex tasks. The experiments in this paper show that ACU-Net achieves higher accuracy with fewer parameters on the same dataset. On this basis, this paper uses a new, non-training dataset to test the recognition efficiency of the model, namely the NWPU-RESISC45 dataset. The evaluation metric is IoU as well.
There are two ways to obtain the IoU indicators involved in the comparison: 1. calculate the IoU for each image in the validation set and take the average; 2. select the same 100 images in another spare dataset (not involved in training and validation) for average IoU calculation to test the generalization ability of the model.
In Table 6, the U-Net and U-Net++ of the data in group b and group c have four downsampling times, and the highest number of channels is 512. The d and e groups of data are the results of U-Net and U-Net++ reduction, which are reduced to only three downsamplings, and the maximum number of channels is 32. Comparing these four sets of data, it can be found that in the face of lightweight tasks, the large model adds a large number of parameters but does not bring significant improvement, making it bloated and redundant, so a reasonable reduction in size can improve efficiency.

Table 6.
Comparison of training results (adaptability test).
Additionally, it can also be found that the method in this paper shows improvements when applied to new samples, with no sign of the sample set’s overfitting, showing its adaptability. Due to the higher resolution of the selected new sample image, the details of the white waves and the black reefs in the image are more obvious. Meanwhile, the colors of the images obtained by different satellites are also different, so the final recognition accuracy will have a certain change. However, compared with other models, it has also improved by 1% to 2%.
5. Discussion
Expansion Rate
This paper discusses the expansion rate combination in the improved ASPP module, and studies (1, 6, 12) and (1, 4, 8) two combinations, respectively. This section uses the new dataset to conduct experiments on models with different inflation rates, and the obtained data are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Comparison of training results (different expansion rates).
Although the model with the (1, 4, 8) expansion rate combination has lower validation accuracy on the original dataset than the (1, 6, 12) combination, its accuracy on the new dataset is higher. Since sea and land segmentation belongs to the segmentation of large objects, there are fewer categories, and the segmentation area is also larger, so the hole convolution in ASPP can more effectively obtain the information in the image, which greatly improves the accuracy of the model. However, the expansion rate cannot be as large as possible. A large expansion rate can cause the model to miss the details of some small objects such as reefs and ocean waves, making it difficult for the model to model these details. The experiments in this paper reflect this. The model with the combination of (1, 4, 8) expansion rates is better for the segmentation of waves and reefs in the new sample, and the overall IoU index is better than the combination of (1, 6, 12) expansion rates. improved by 0.013. Therefore, for settings of samples and models with different characteristics, the combination of expansion rates should be flexibly adjusted to maximize efficiency.
In future work, we will continue to increase the variety of datasets to test the generalization ability of the model structure and explore the effect of the continuous use of the ASPP module in the model. Since the experimental dataset in this paper is relatively simple, the efficiency of ACU-Net needs to be further experimentally verified after increasing the complexity of the dataset and the size of the model. We need to try to propose a more effective hole convolution module or attention module to optimize the segmentation effect for possible problems.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose ACU-Net which still has an efficient segmentation effect under a small volume. Thanks to FReLU and the attention network, the segmentation effect of this structure is further improved, improving the model’s ability to perceive context and the receptive field. Experiments show that the network achieves or even exceeds the effect of U-Net, U-Net++, and U-Net with a changed activation function under a smaller volume, and can use fewer parameters to mine the hidden information of the sample, with better segmentation performance and energy efficiency ratio. With a size of 0.444 M, the ACU-Net in this paper is 2.9% higher than the U-Net structure with a size of 0.514 M in the IoU index, and 1.744% higher in the accuracy index, and is also higher than the U-Net++ structure of 0.645 M by 2.3% and 1.102%, respectively. At the same time, it is 0.9% and 0.485% higher than the 0.710 M U-Net structure that replaces FReLU. After adding the SE-Net attention module, the ACU-Net in this paper improves the IoU index and accuracy by 0.3% and 0.127%. These experimental results all demonstrate the effectiveness of the ACU-Net structure as well as its information capture ability and strong adaptability in the task of sea–land segmentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L., Z.H. and Y.W.; methodology, J.L.; software, Z.H.; validation, J.L., Z.H. and Q.L.; formal analysis, Z.H.; investigation, J.L. and Z.H.; resources, J.L. and Q.L.; data curation, Z.H.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.H.; writing—review and editing, J.L. and Y.W.; visualization, J.L. and Z.H.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, J.L. and Y.W.; funding acquisition, Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported in part by the Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Province of China (2020CXGC010705, 2021ZLGX05).
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, M.; Zhu, D. Review on Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Fully Convolutional Network. Comput. Syst. Appl. 2021, 3, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. A Sea-land Segmentation Method of SAR Image Based on Prior Information and U-Net. Radio Eng. 2021, 5, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobuyuki, O. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, J.; Yi, K. Sea-Land Segmentation Algorithm of SAR Image Based on Otsu Method and Statistical Characteristic of Sea Area. J. Data Acquis. Processing 2014, 29, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Research on Sea-Land and Sea-Cloud Segmentation for High Resolution Ocean Remote Sensing Image. Master’s Thesis, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, C. Modified Sea-land Segmentation Method based on the Super-pixel for SAR Images. Foreign Electron. Meas. Technol. 2019, 38, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification. In Proceedings of the EMNLP, Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kalchbrenner, N.; Grefenstette, E.; Blunsom, P. A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.2188. [Google Scholar]
- Evan, S.; Jonathan, L.; Trevor, D. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, B.; Alex, K.; Roberto, C. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuegraf, P.; Bittner, K. Automatic Building Footprint Extraction from Multi-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Using a Hybrid FCN. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2017, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Research on Semantic Segmentation Technology of Aerial Images Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Research on Key Technologies of Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation Based on Deep Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H. Research on Semantic Segmentation and Improvement of Aerial Remote Sensing Image Based on Fully Convolutional Neural Network. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Research on Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images of the Ground Objects Based on Deeplab V3+ Network. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, F.; Teng, M.; Zhang, C. Remote Sensing Image Segmentation Method Using Improved PSPNet with ConvCRF. Geomat. World 2021, 28, 58–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5686–5696. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research on Key Technologies of Satellite Image Semantic Refined Segmentation Based on Deep Learning. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. Funnel Activation for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, A.-J.; Pertusa, A.; Gil, P. Automatic Ship Classification from Optical Aerial Images with Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification: Benchmark and State of the Art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Wu, E. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 2011–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhou, D.; Feng, J. Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet plus plus: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis/8th International Workshop on Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).