Abstract
The reliability and robustness of global electrical networks are being impacted by the reciprocal effects of climate change and severe weather events. This article assesses research and collaborative trends to further these concerns. This study attempts to identify trends, principal contributors, and emerging fields of research by a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of articles relevant to power system resilience during extreme weather events. A comprehensive search was conducted in the Web of Science and Scopus databases to acquire appropriate papers from 2014 to 2025. The implementation criteria for eligibility requirements comprised peer-reviewed publications, including reviews and conference papers. The Bibliometrix and Biblioshiny tools were used to conduct data analysis, evaluating keyword co-occurrences, citation networks, and cooperation networks. The study selection process and reporting adhered to the PRISMA 2020 framework. A dataset of 1178 documents from 535 sources indicated an annual growth rate of 13.06%. China was the most producing country, while the USA, China, UK, and Iran became the most cited countries. Keyword analysis identified common topics including resilience, power outages, and extreme weather, alongside an increasing focus on AI-driven modeling, distributed energy resources, and optimization algorithms. This systematic review emphasizes the growing research field addressing power system resilience, focusing on improvements in modeling strategies, optimization approaches, and risk management applications. Future research must concentrate on the integration of AI, evaluations of regional vulnerabilities, and the development of predictive frameworks to tackle rising climate concerns.
1. Introduction
Energy networks have become indispensable to today’s society, primarily because of the growth in global energy consumption. Such systems must operate with unprecedented reliability and robustness to meet rising demands. The concept of resilience in power systems has garnered the interest of both researchers in academic inquiries and practitioners, particularly considering the continuous increase in natural disasters, reactions in technical development, and global changes. Resilience in power systems can be interpreted as their capability to predict, resist, adapt to, and even recover from events that are rated as high-impact and low-probability (HILP), which may include natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and other disruptions [1,2,3]. This multifaceted concept encompasses critical dimensions, including the system’s capacity to maintain operational functionality under adverse conditions, speed of recovery following disturbances, and the ability to learn from past experiences to mitigate future risks [4,5]. The resilience of electrical grids extends beyond their physical infrastructure, incorporating cyber and human elements that interact within a complex, interdependent network [6,7]. For instance, the physical-cyber–human framework highlights the importance of understanding the dynamic interplay among these components during emergencies, which significantly influences the overall resilience of urban power systems. This holistic perspective is vital because it recognizes that vulnerabilities may arise not only from physical system failures but also from cyberattacks and human factors, both of which can exacerbate the impacts of disruptive events [7]. Recent studies underscore the need for tailored resilience assessments that effectively reflect the unique characteristics and challenges associated with different electrical grid systems [8,9]. Such resilience indicators must be threat-specific, performance-oriented, and capable of evaluating the consequences of disruptions, while accounting for the inherent uncertainties in grid operations [9]. For example, resilience metrics can be instrumental in measuring a system’s ability to recover from power outages, assessing the effectiveness of resilience-enhancing strategies, and supporting data-driven decisions regarding infrastructure investments [10]. The integration of renewable energy sources into power systems introduces both opportunities and challenges to the grid resilience. Distributed energy resources (DERs) enhance resilience by enabling localized power generation, reducing reliance on centralized infrastructure, and facilitating quicker recovery from outages [11,12]. However, the inherent variability and unpredictability of renewable energy generation poses new challenges, necessitating advanced management strategies to ensure stability and reliability in the face of these fluctuations [13,14]. Advanced technologies, including smart grids and microgrids, are pivotal in strengthening the resilience of power systems. Smart grids facilitate the real-time monitoring and control of electricity distribution, enabling operators to respond promptly to disruptions and optimize resource allocation during critical situations [15]. Microgrids, on the other hand, provide a versatile solution for ensuring power continuity during outages by functioning independently or integrating with the main grid, thereby improving overall system resilience [16,17]. Resilience enhancement strategies can be divided into long and short-term measures. Long-term initiatives may involve upgrading infrastructure, integrating advanced technologies, and implementing regulatory reforms to promote resilience-focused planning [18]. Conversely, short-term strategies typically focus on operational improvements such as deploying automated restoration systems and leveraging advanced data analytics to enhance situational awareness [19]. The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events driven by climate change underscores the urgent need for robust resilience frameworks within power systems [20]. Historical data reveal that power outages caused by natural disasters result in significant economic and social repercussions, compelling stakeholders to prioritize resilience as a core component of their strategic planning and operational efforts [20]. Consequently, power system resilience extends beyond technical considerations, and represents a critical societal issue that requires coordinated action among policymakers, utility operators, and the research community. In the context of power system operations, a blackout signifies a widespread interruption of the electricity supply across multiple service areas. The design, implementation, and management of power grids primarily focuses on two critical aspects: reliability and security. Professionals in the power industry across various countries aim to ensure that the system’s availability surpasses 99%. However, similar to other complex large-scale engineering systems, power grids are not immune to interruption. Many of these disruptions system from the inevitable wear and tear of equipment or damage inflicted by severe weather events, such as winter storms, hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires [21]. In contrast to conventional narrative literature reviews that depend largely on researchers’ expertise and subjective interpretation, bibliometric analysis provides a scalable method for analyzing data across both micro and macro levels [22,23]. This methodology allows for a more systematic and quantitative evaluation of trends, impacts, and contributions within the field. Bibliometrics evaluates scholarly and institutional performance using various indicators, including publication counts, citation frequency, and collaboration patterns [24]. It serves as a robust method for quantitatively assessing scientific literature [25]. Through bibliometric analysis, researchers can derive diverse metrics that reveal the intellectual landscape of a field and assess the influence of scientific contributions. Such studies typically examine research productivity, highly cited works, national publication outputs, commonly used keywords, and publication trends to quantitatively explore a particular area of inquiry [26].
This paper provides a comprehensive review of current issues of power system resilience and operation due to severe weather and develops a bibliometric analysis to carry out a paper to visualize the trends in the existing literature and overview current state-of-the-art topics to help future research. While prior bibliometric reviews have assessed energy resilience broadly, this study uniquely focuses on power system resilience in the context of extreme weather, using PRISMA-guided screening and integrated Biblioshiny visual analytics (thematic maps, trend topics, and keyword evolution). The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 discusses extreme weather conditions and the impact on the resilience and operation of power system. Section 3 and Section 4 discuss the vulnerabilities of power systems and optimization and Section 5 and 6 presents a methodology and bibliometric analysis of power system operation due to severe weather. Section 7 provides concluding remarks.
2. Extreme Weather and Its Impact on Power System Operation
The increasing frequency and severity of extreme weather events driven by climate change have become major issues in global power system operation. These events pose a growing threat to the stability of electricity supply and increase the risk of power outages. The consequences of severe weather on power systems are diverse, impacting not only the reliability of electricity distribution but also the economic and social welfare of communities that rely on consistent power access. One of the greatest hazards of extreme weather is the risk of widespread power outages. This showed that the average annual loss of customer hours over 2447 counties in 2000–2021 peaked at about 520 million hours per customer across the United States, with nearly half of the interruptions attributed to severe weather [27]. Peninsular Malaysia also experienced a flood event in 2021 involving approximately 14,000 people and outages that lasted a couple of weeks. The reliability of the electric grid is essential, because outages during extreme weather can cause serious economic and physical damage to individuals and communities [28]. This highlights the importance of developing strong resilience strategies to reduce the effects of such events. Extreme weather conditions significantly affect the operational dynamics of the power systems. For instance, heavy snow and ice can create complex issues, such as ice-covered line breakage and insulator flashover, which can severely hinder power transmission [29]. Additionally, storms can inflict extensive damage on infrastructure, requiring swift response and recovery efforts from utility companies [30]. The use of advanced predictive models that consider weather-related outages is crucial for strengthening the resilience of power systems [31]. These models enable utilities to foresee outages and to take proactive steps to reduce disruptions. Strategies aimed at enhancing resilience are vital for addressing the weaknesses of power systems during extreme weather events. Resilience can be significantly improved by employing proactive operational strategies that predict sequential changes in system states during such events [32]. For example, the adoption of microgrids, which can function independently from the main grid, provides a practical solution for boosting resilience to the effects of severe weather [33]. Microgrids facilitate localized energy generation and storage, ensuring a continuous power supply, even when the central grid is affected. Additionally, incorporating renewable energy sources such as offshore wind power introduces specific challenges during extreme weather. Offshore wind generation is particularly vulnerable to harsh weather, highlighting the need for well-structured curtailment strategies to maintain grid resilience [34]. Effective management of renewable energy resources in response to changing weather conditions is crucial for ensuring operational stability. However, the economic effects of extreme weather on power systems cannot be ignored. Expenses related to outages, infrastructure repairs, and resilience measures can be significant. Historical data show that although extreme weather events may not happen often, their potential impact on power system can be severe, highlighting the need for effective resilience assessment techniques. These assessments can guide investment decisions and policy frameworks to strengthen the resilience of power systems. Beyond the physical infrastructure, the importance of data and technology in addressing the impacts of extreme weather is becoming increasingly recognized. Machine learning and advanced analytics can enhance outage prediction and response strategies, enabling utilities to better prepare for and reduce the effects of severe weather. For example, social media data can be used to improve the accuracy of outage predictions and provide real-time insights into weather-related disruptions [35]. The dynamic nature of power systems, particularly with the rise in distributed energy resources, demands innovative control strategies to address operational challenges during weather events. Adaptive control methods that consider real-time data and current system conditions can significantly improve the performance and reliability of power systems [36]. This adaptability is essential for maintaining grid stability in unpredictable weather patterns. The growing complexity of power systems highlights the need for a comprehensive resilience framework. As climate change leads to more frequent and severe weather events, the development of resilience-oriented designs and operational strategies is crucial [37]. These frameworks should adopt a holistic approach, integrating technical, economic, and social factors to effectively address the diverse challenges posed by extreme weather. Consequently, the impact of extreme weather on power system operations is significant and complex, requiring a unified effort to bolster resilience through proactive strategies, advanced predictive modeling, and innovative control mechanisms. With the increasing frequency and intensity of weather events, the demand for robust and adaptive power systems has become increasingly urgent. The integration of renewable energy sources, along with advanced technologies and data analytics, provides a promising avenue for enhancing the resilience of power systems and ensuring reliable electricity delivery in the face of climate challenges.
3. Vulnerabilities of the Power System
Extreme weather events have therefore been considered highly impactful vulnerability drivers for power systems globally. Indeed, new evidence of increasing frequency and strength has shown that these are likely to directly impact the reliability and resilience of electricity supply networks. For instance in [38], it has been indicated that sections of distribution and transmission grids are susceptible to faults under unfavorable weather conditions, and as these climatic conditions worsen, the reliability of the electricity supply deteriorates. This argument is also echoed by, who provide the historical background of major outages caused by extreme weather; for example, Hurricane Sandy left more than 8.5 million customers in the dark [39]. These events highlight the need for proactive measures to make the grid resilient to climate-related hazards [40]. The topological modeling approach provides a quantitative measure of the vulnerability of power grids, as performed by the authors [41], who presented ways of measuring the short-term vulnerability of power grid units because of extreme weather conditions. The findings indicate that some nodes and lines in the grid have higher vulnerability, which may be used to develop appropriate strategies for mitigating the effects of such weather conditions. The possibility of cascading failures in a power transmission network, particularly during extreme weather conditions, was considered in a previous study [42], where it was noted that the increased interconnectedness of modern grids could increase the impact of localized failures. This interdependence demands a holistic approach to how extreme weather can cause citywide blackouts, thus placing strong demand on infrastructure planning and investment. In addition, the impact of climate change on electricity demand further complicates vulnerable landscapes with increasing temperature, electricity consumption is expected to rise, especially during peak demand periods driven by air-conditioning needs [43]. This shift in demand, added to possible thermal unit derating because of increased water temperatures and reduced water availability, further adds to the challenge of maintaining proper electricity supply [44]. The interaction between supply constraints and growing demand requires re-examining existing energy systems for their ability to bear the stress exerted by climate variability. These vulnerabilities are three-layered and include direct impacts on infrastructure, risk of cascading failures, and shifting demand for electricity [45]. Therefore, vulnerabilities in power systems to extreme weather have many facets, and the path towards holistic vulnerability should consider state-of-the-art modeling techniques, historical data analyses, and proactive investments in infrastructure strengthening. The study highlights a lack of region-specific research, particularly in tropical and arctic zones, where the impacts of climate change on power systems may differ significantly. There is a need for more granular geographic analysis of resilience strategies tailored to specific climate conditions.
4. Power System Operation Optimization Due to Extreme Weather Conditions
The optimization of power system operations against extreme weather events is among the most critical areas in research and development. Because these events are increased in frequency and strength owing to climate change, the respective power systems should be adapted accordingly to guarantee reliability and resiliency. It deals with some optimization approaches adopted in operations to improve power systems in extreme weather conditions, and draws on recent literature to provide a comprehensive state-of-the-art overview. Several of these extreme weather events that may pose serious challenges to power system reliability include hurricanes, heatwaves, and heavy snowfall. These events can result in increased failure rates of power system components and, therefore, require robust optimization strategies to mitigate their impacts. For example, the authors proposed [46], a resilience enhancement method that incorporated an underground energy storage system to improve the resilience of power systems with high renewable energy penetration. Their approach involves a resilience assessment model that quantifies the impact of extreme weather on system failure, thus informing optimization strategies for operational stability during adverse conditions. The integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into power systems introduces significant opportunities and challenges, particularly in the context of extreme weather conditions. Accurate prediction of electricity demand and renewable energy generation during periods of unusually high temperatures is essential for maintaining the safety and stability of grid operations. This forecasting capability plays a pivotal role in optimizing resource allocation and efficiently managing electricity demand during critical weather events [47]. Similarly, an integrated planning strategy for power networks and electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure has been discussed, underscoring the necessity for coordinated expansion decisions that bolster resilience in various extreme weather scenarios [48]. The frameworks for risk assessment and optimization are imperative for the management of distributed power generation systems under such conditions; a probabilistic risk assessment and risk–cost optimization framework have been meticulously developed to account for the ramifications of these extreme weather conditions on distributed generation systems. Their Monte Carlo simulation methodology facilitates the creation of scenarios that encapsulate both normal and severe weather, thereby enabling operators to make informed decisions pertaining to system resilience [49]. This finding aligns with the conclusions drawn by others who deliberated on the broader impacts of extreme weather and climate change on power system resilience; they highlighted the pressing need for effective mitigation strategies. Furthermore, an investigation into the role of mobile power sources in augmenting grid resilience during adverse weather events was pursued. However, the complexity of these interrelations requires further investigation. A pre-allocation and dispatch strategy for mobile power sources in power-transportation coupled networks has been proposed [50], with emphasis on the importance of considering grid restoration demands and accident risks under extreme conditions. This proactive approach to resource management is critical to maintaining operational continuity during severe weather events. Simulation tools are increasingly utilized to assess the dynamics of power systems under extreme weather conditions. presented a hybrid numerical simulation approach that integrated icing weather events with power system dynamics, allowing for a more comprehensive risk assessment of power systems facing extreme meteorological conditions [51]. Such simulation frameworks are vital for understanding the potential impacts of extreme weather on system performance and developing effective optimization strategies. The coordination of preventive and emergency dispatches in renewable energy-integrated power systems is another area of focus introduced a hierarchical Defender–Attacker–Defender (DAD) dispatching model that accounts for line faults induced by typhoons, illustrating the need for adaptive strategies that can respond to the dynamic challenges posed by extreme weather [52]. This model underscores the importance of resilience-oriented planning for optimizing power system operations under adverse conditions. Topological modeling has emerged as a valuable tool for assessing the functional vulnerability of power grids under extreme weather conditions. Employed mathematical programming models to analyze the impact of wind disasters on transmission lines, providing insights into the structural vulnerabilities of power systems. This approach aligns with the probabilistic resilience analysis conducted by Karangelos, who assessed the resilience of an Icelandic power system during extreme weather events [53]. The impact of extreme weather conditions on wind power generation is also a critical consideration. The authors highlighted the challenges posed by gale weather events, which can lead to turbine shutdowns and significant fluctuations in power generation [54]. This necessitates advanced forecasting and optimization methods to ensure the safe and stable operation of wind power systems. Furthermore, Alhaddad emphasized the role of machine learning in predicting outages caused by extreme weather, thereby providing a foundation for sustainable energy integration into electrical networks [55]. The adaptation of grid recovery strategies to extreme weather conditions is essential for maintaining system reliability. The authors discussed the importance of effective planning and management strategies to mitigate the impact of extreme weather on power systems, emphasizing the need for resilience-oriented approaches [56]. This is echoed by others [57] who analyzed the vulnerability of power grid structures and proposed strategies for enhancing resilience through system analysis. Cascading failures are a significant concern in power systems during weather events. The authors presented [57] a modeling and simulation framework for assessing the reliability and availability of power transmission grids under such conditions, highlighting the importance of understanding cascading failure dynamics for optimizing system operations. This perspective is further supported by the work of authors [57] who proposed a resilience enhancement strategy for distribution grids against extreme weather events, framing the problem as a two-stage stochastic mixed-integer problem. The integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) into power systems presents challenges and opportunities for enhancing resilience. The authors of a previous study [58] proposed prosumer-centric microgrids that incorporate DERs and battery electric vehicles (BEVs) to optimize distribution system resilience during extreme weather. This innovative approach underscores the potential of decentralized energy systems to enhance overall grid resilience. The role of flexible resources in power system management during weather events has gained attention. Some authors [59] emphasized the need for improved forecasting and flexible resource management to prevent power systems from entering dangerous operational states under severe weather conditions. This highlights the importance of adaptive management strategies that can respond to the uncertainties associated with extreme weather conditions. Recent studies have emphasized the role of risk-aversion in power system optimization under uncertainty. For example, a multi-objective approach for resilience under extreme weather using risk models was proposed by [60]. Likewise, the incorporation of energy storage sharing models can significantly improve urban grid resilience during outages, as discussed by [61]. In general, the optimization of power system operations in the context of extreme weather events is a multifaceted challenge that requires a comprehensive understanding of resilience strategies, risk assessment methodologies, and advanced forecasting techniques. The integration of innovative technologies such as machine learning and simulation tools is crucial for enhancing the ability of power systems to withstand and recover from extreme weather conditions. As the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events continue to increase, ongoing research and development in this area is essential to ensure the reliability and resilience of power systems worldwide.
5. Methodology
Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus are the two main repositories of scholarly publications. Although WoS is well-known for its reliability and broad coverage of literature analysis and retrieval, it seems to provide a more extensive selection of journals [62]. To identify the most appropriate database for this study, initial searches were performed using both platforms. Peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers published between 2014 and 2025 in English, focusing on power system resilience and extreme weather were included. Non-English articles, book chapters, editorials, and articles not directly related to power systems or weather events were excluded. This review followed the PRISMA 2020 framework (see Supplementary Materials). During identification, 674 records were retrieved from Web of Science and 597 from Scopus using the query (“power system” AND “resilience” AND [“extreme weather” OR “severe weather”]). After removing 93 duplicates, 1178 articles remained. The screening process involved manual verification of relevance to power system resilience and weather impact, excluding articles not addressing this focus (e.g., purely economic or meteorological studies). Only peer-reviewed journal articles and conference papers in English were included. Articles were assessed based on the relevance of title, abstract, and keywords. The study was not registered on PROSPERO. Data were gathered from both databases in April 2025. To concentrate on recent research, the results were limited to publications from 2014 onward. This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines. The selection process was documented using the Prisma 2020 flow diagram in Figure 1. This review was not registered in any protocol database [63]. The flow diagram delineates the systematic process of identifying and screening studies for comprehensive literature review. The procedure adhered to the PRISMA 2020 guidelines, which constitute a standardized approach for reporting literature reviews and meta-analyses. The diagram elucidates the study selection process, detailing the number of records identified, screened, and included in each stage of the review. This systematic approach ensures a transparent and reproducible method for conducting literature reviews, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of relevant research in the field of study. The final dataset comprised 1178 documents, after excluding certain results. These documents, published between 2014 and 2025, encompass various frameworks and applications related to power system resilience during weather events. Using the Bibliometrix platform [64] and R studio software version 2024.12.1+563 Release, two database information sources (WOS and Scopus) were merged, duplicate references were removed (see Appendix A), and an Excel file was generated to conduct a bibliometric analysis on the Biblioshiny version 4.3.0 platform [65]. The bibliometric visualization map features interconnected nodes, with each node representing a keyword, country, institution, or author [66].
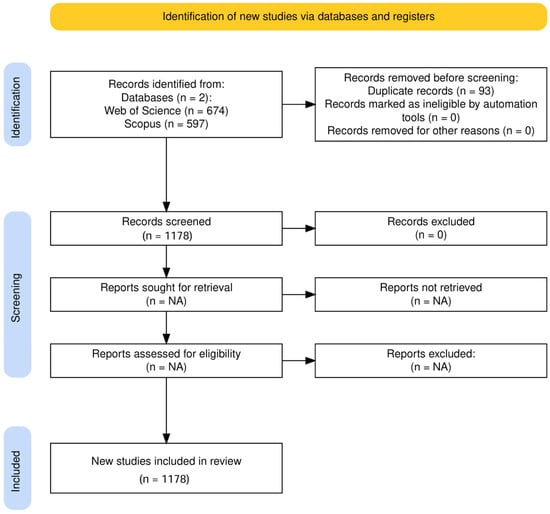
Figure 1.
The PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for bibliometric analysis.
Although approximately 95% of the documents are indexed in the Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus databases [67], this study does not specifically cover WoS literature. Nevertheless, the substantial number of publications examined in this bibliometric analysis ensures a representative sample of major research efforts in power system resilience to weather events. While this study focused on Scopus and Web of Science due to their robust coverage and compatibility with Biblioshiny, the authors acknowledge that some relevant journals in IEEE Xplore or Springer may be excluded. Future research could broaden database inclusion to enhance completeness. The final 1178 documents were vetted through a three-step manual screening process: (1) title relevance, (2) abstract alignment with power system resilience, and (3) exclusion of non-technical or non-peer-reviewed works. No journal prioritization was applied beyond Scopus/WoS indexing filters. Data analysis was conducted using the Bibliometrix package, an R-Tool designed for comprehensive science mapping analysis in scientometrics and Bibliometrics. This tool offers various functions for importing bibliographic data from well-known databases such as Scopus and WoS. Bibliometrix, version 4.3.0 an open-source software, is freely accessible and distributed in terms of MIT license.
6. Bibliometric Analysis
A total of 1178 papers were published on power system resilience to extreme or severe weather from 2014 to 2025. Table 1 shows that the bibliometric study examined 1178 documents from 535 sources, including journals and books, over a ten-year period from 2014 to 2025. Publications have exhibited an annual growth rate of 13.06%. The documents received a mean of 15.71 citations, with a median age of 5.18 years. The analysis revealed 3795 author’s keywords. Regarding authorship, the study identifies 3043 total authors, with 39 single-authored documents. On average, each document had 4.61 co-authors, and 12.22% of the publications involved international collaboration. The documents were categorized into various types, with articles being the most prevalent, followed by proceedings papers and conference papers. Other categories include reviews, book chapters, and editorial materials. This comprehensive analysis provided significant insights into publication patterns, collaborative trends, and document-type distributions over the past decade. Figure 2 illustrates the percentage distribution of the document types published from various sources from 2014 to 2025. Since 2017, the topic of power system resilience has witnessed a notable upward trend in citation frequency. Among various sources, Energies MDPI has emerged as the frontrunner in terms of annual citation counts. Figure 3 shows the number of citations per year for the top four publication sources.

Table 1.
Bibliometrix study main information.
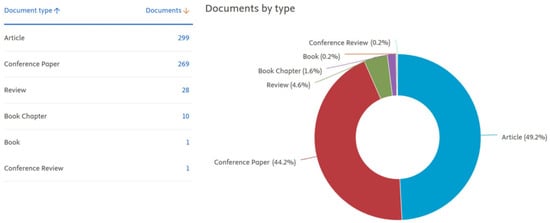
Figure 2.
Type of documents in power system resilience bibliometric analysis from Scopus database.
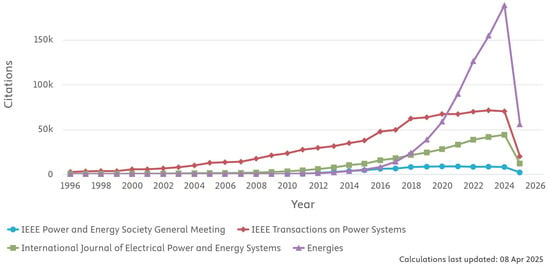
Figure 3.
The number of citations per year in different sources from Scopus database.
Figure 4 presents a cumulative graph of publications in the field of power system resilience. As illustrated in Figure 4, the number of publications has increased since 2017, indicating that this topic is one of the most prominent research areas in power system studies. This trend demonstrates the growing recognition of the importance of power system resilience in the face of increasing challenges and uncertainties. The surge in publications since 2017 suggests that researchers and industry professionals actively pursue innovative solutions to enhance the robustness and adaptability of power systems. As the field continues to evolve, it is anticipated that new methodologies, technologies, and strategies will emerge to address complex issues surrounding power system resilience.
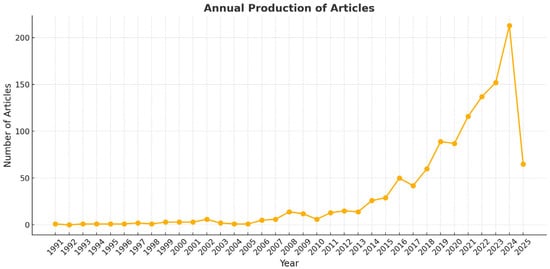
Figure 4.
Annual publication per year in the field of power system resilience.
Figure 5 illustrates the ten most significant sources of publications on power system resilience. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing demonstrated the highest number of publications in this field, whereas IEEE Access ranked second in terms of publication volume in terms of power system resilience. The prominence of these two journals underscores the substantial contribution of IEEE publications to the advancement of research on power system resilience. The remaining sources in the top ten list likely comprise reputable journals and conference proceedings focused on power systems, electrical engineering, and energy infrastructure. The distribution of publications across diverse sources indicates the interdisciplinary nature of research on power system resilience and its increasing significance in the academic community.
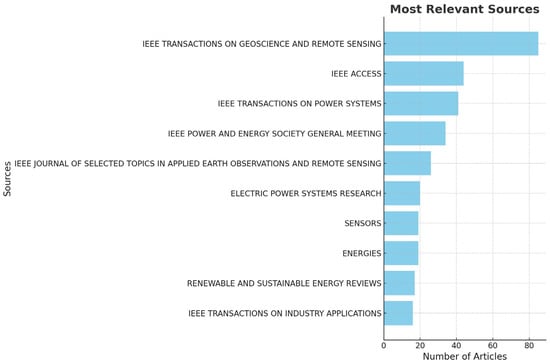
Figure 5.
The top publication sources in the field of power system resilience.
Figure 6 presents the geographical analysis of the corresponding authors’ countries. Within the Biblioshiny framework, the designations MCP and SCP are employed to differentiate between research publications involving international collaborations (multiple country publications) and those conducted within a single nation (single country publications), as determined by the corresponding author’s institutional affiliation. These data offer valuable insights into the landscape of global research collaborations, shedding light on the balance between transnational scientific partnerships and localized research endeavors. The distinction between MCP and SCP facilitates a nuanced understanding of cross-border academic networks and their potential impact on knowledge dissemination across diverse geographical contexts. Figure 7 and Figure 8 illustrate the top 50 network structures for high-frequency author keywords, keyword indices, and word clouds, respectively. The size of the keywords indicates the initial date of the related publications, and the lines represent the co-occurrence links between different keywords. The co-occurrence analysis among the keywords revealed that the most prevalent topics in the literature were power system resilience, power outages, and extreme weather. The analysis of collaboration networks derived from bibliometric data offers significant insight into research partnerships and co-authorship patterns. However, it is important to acknowledge that these networks may not fully encapsulate the intricacies of scientific collaboration. The primary focus on formal co-authorship relationships in these networks potentially overlooks crucial aspects of scientific exchange such as informal collaboration and mentorship. These less tangible forms of interaction, which are not necessarily reflected in publication data, play a substantial role in the advancement of knowledge and scientific processes. The collaboration network used in this study is illustrated in Figure 9. Figure 10 shows the thematic map generated using Biblioshiny, which offers valuable insights into the structural and conceptual organization of research on power grid resilience under extreme weather events. Positioned in the upper-right quadrant, motor themes such as power, system resilience, outages, resilience, and extreme weather events represent well-developed and highly relevant areas, underscoring their central role in the literature. These themes drive the field forward and are the focus of considerable scholarly attention. In contrast, basic and transversal themes, including optimization, uncertainty, smart grids, distribution systems, and grid operation, although highly relevant, exhibit lower internal development. This suggests that while these topics are foundational, they may benefit from deeper theoretical exploration and methodological refinement. Niche themes such as radar, validation, and radiative transfer demonstrate strong internal coherence but lower centrality, indicating their relevance to specialized sub-domains or methodological approaches. Meanwhile, emerging or declining themes such as precipitation, temperature, network, and model exhibit both low centrality and low density. These may reflect nascent research directions or less explored areas that present opportunities for future investigation. The thematic map highlights the maturity of core resilience-related themes while pointing to several underdeveloped but critical areas ripe for further exploration. The keyword co-occurrence network in Figure 11 illustrates the structure of knowledge in the domain of power system resilience under extreme weather conditions. Nodes represent keywords, with node size proportional to centrality, and edges indicating co-occurrence in the same documents. The network is clustered by theme, with distinct groupings observed around meteorological modeling (e.g., storms, satellites, remote sensing) and power system resilience (e.g., resilience, microgrids, optimization). Central keywords such as power system resilience, resilience, and extreme weather events highlight the dominant focus of the field and serve as bridges across thematic areas. This structure underscores the interdisciplinary nature of the research, combining engineering reliability with weather prediction and machine learning techniques. The trend topic analysis in Figure 12 reveals the temporal dynamics of key research themes from 2015 to 2025. Recent years have seen a surge in terms such as power system resilience, resilience, and extreme weather, indicating a growing emphasis on grid robustness under climate stress. Simultaneously, the rise of machine learning and climate change as keywords signals the increasing incorporation of data-driven techniques and sustainability concerns. Earlier focus on weather, remote sensing, and radar highlights the foundational role of meteorological technologies in shaping resilience strategies. This progression underscores a thematic shift from environmental monitoring to systemic adaptation and intelligent resilience planning. In Figure 13, the dendrogram of co-word factorial analysis provides a hierarchical view of how key concepts are structured in the literature. Two dominant clusters emerge: one focusing on distributed energy systems and optimization models (e.g., stochastic models, microgrids, smart grid), and another emphasizing system resilience and climate-related risks (e.g., power system resilience, resilience, outages, extreme weather events). The branching structure reveals both tight thematic connections and broader conceptual groupings, demonstrating the interdisciplinary nature of research at the intersection of power systems and climate resilience.
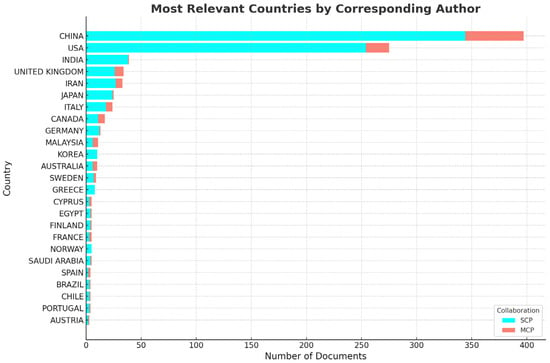
Figure 6.
Total number of publications (MCP and SCP) by top 25 corresponding authors’ countries on power system resilience in severe conditions.
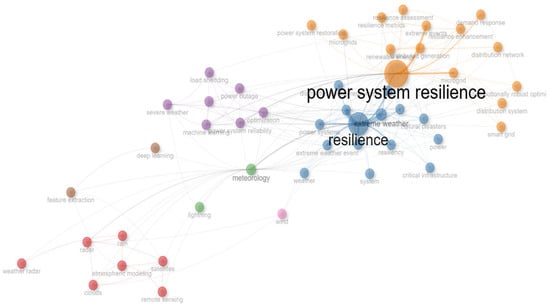
Figure 7.
Network structure of 50 high-frequency authors’ keywords.

Figure 8.
The word cloud of power system resilience in extreme weather.
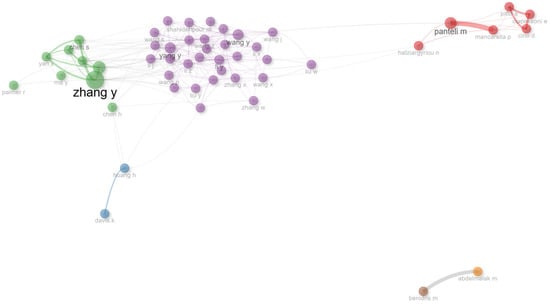
Figure 9.
Collaboration network in the field of power system resilience.
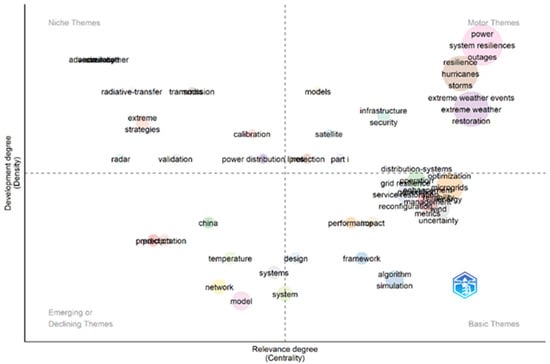
Figure 10.
Thematic map of keyword clusters on power system resilience, showing relevance (centrality) vs. development (density) using Biblioshiny.
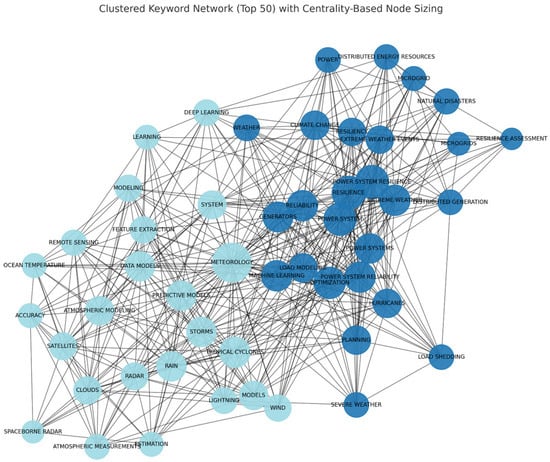
Figure 11.
Top 50 keyword network showing clusters and centrality in power system resilience research.
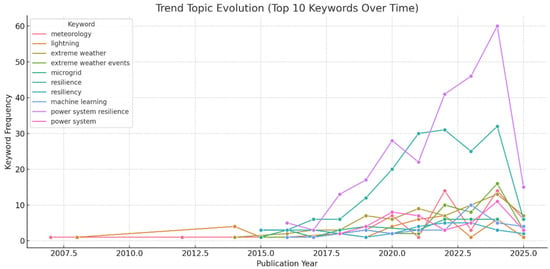
Figure 12.
Trend topics from 2015 to 2025 showing the temporal evolution and frequency of key terms in power system resilience research.
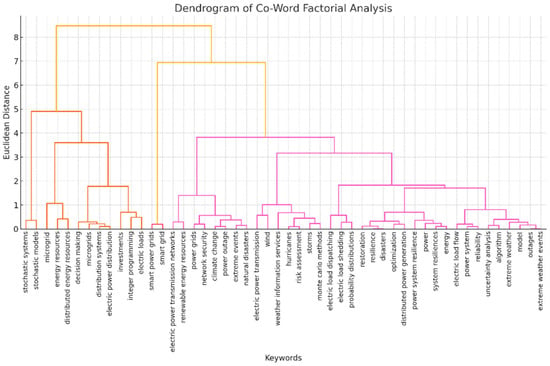
Figure 13.
Dendrogram of co-word analysis showing hierarchical clustering of keywords in power system resilience literature.
7. Practical Implications for Stakeholders
This bibliometric analysis offers actionable insights for stakeholders such as policymakers, power utilities, and researchers. Grid operators can use identified trends (e.g., DERs, microgrids) to align with resilience-enhancing technologies. Policymakers may prioritize region-specific climate adaptation investments, especially in underserved zones like the tropics. R&D agencies may focus on integrating AI and risk-aversion frameworks in power system planning. The evolution of keywords suggests that resilience strategies are increasingly data-driven, enabling predictive modeling to anticipate and mitigate outages.
8. Conclusions
This research offers a comprehensive bibliometric examination of publications on power system resilience in the face of extreme weather, drawing from the WOS and Scopus databases for the period of 2014–2025. A bibliometric study identified extreme weather as the newest focus area in power system resilience research. The dataset, refined by extreme weather, explored trends in the publication year, country, source, keywords, and topics. Over the past decade, annual publications on power system resilience related to extreme weather have shown a steady increase, suggesting the potential for rapid growth in coming years. An analysis of international collaboration helps new researchers to identify potential research partners. The China has emerged as the most prolific country, with over 300 publications on power system resilience under extreme weather conditions from 2014 to 2025. China and USA are also highly collaborative nations in this bibliographic set, and their corresponding authors frequently collaborate with researchers from other countries. An examination of journal evolution in publishing power system resilience research related to extreme weather will help new researchers to identify key publication venues. Research hotspots were identified by identifying keyword occurrences over a 10-year period. The analysis of the authors’ keyword usage shows that the scientific output on power system resilience during extreme weather primarily centers on system resilience. A topical analysis of power system resilience research illuminates the primary focus areas in this field. This study aimed to clarify how research frontiers in power system resilience have evolved over the past ten years. One limitation of this study is its reliance on two bibliographic databases (Scopus and WoS), which may exclude relevant literature from other sources. Additionally, the review was limited to English-language publications. This bibliometric study maps the evolving landscape of power system resilience research under extreme weather. While advances in AI, DERs, and microgrids dominate, gaps remain in geographic coverage and risk-based optimization. Future work should explore network metrics, integrate risk-aversion, and adopt predictive modeling for more adaptive, climate-ready systems.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su17125658/s1, PRISMA Checklist [68].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and visualization, M.A.T.; review and editing, funding acquisition, supervision, J.S.; supervision, N.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the technical and financial assistance of the UM Power Energy Dedicated Advance Center (UMPEDAC) and the Higher Institution Center of Excellence (HICoE) Program Research Grant, UMPEDAC—2020 (MOHE HICOE-UMPEDAC), Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia. Authors would like to thank Collaborative Research in Engineering, Science & Technology Center (CREST) for their continuous support in this research and ASEAN University Network/Southeast Asia Engineering Education Development Network on Research and Education Grant for the University Consortium (UM REd-UC 2501), IF066-2023 Moving towards Carbon Neutrality—Strategy and impact to society and industry (M2CNeu), University of Malaya matching grant MG023-2024 Moving Towards Carbon Neutrality—Analysis On Carbon Emission On Inverter And Non-Inverter Driven Air-Conditioning Unit.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The source code of the R Programming software version 2024.12.1+563 for merging and eliminating duplicate papers is as follows:
> library(readxl)
> WOS <read_excel(“C:/Users/a_tof/Downloads/WOS.xlsx”)
> View(WOS)
> library(readxl)
> SCOP<read_excel(“C:/Users/a_tof/Downloads/SCOP.xlsx”)
> View(SCOP)
> View(WOS)
> library(readxl)
> bibliometrix::biblioshiny()
> COMB<-mergeDbSources(SCOP,WOS,remove.duplicated
= T)
93 duplicated documents have been removed
> View(COMB)
> library(xlsx)
> write.xlsx(COMB, file = “newdata.xlsx”)
References
- Zhang, H.; Li, G.; Bie, Z. Three-module Power System Resilience Assessment Framework under Different Types of Disasters. DEStech Trans. Environ. Energy Earth Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, N.; Abdelmalak, M.; Benidris, M.; Kamruzzaman, M. Power System Resilience: Current Practices, Challenges, and Future Directions. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 18–064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinos, E.I.E.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Trakas, D.N. Microgrids for power system resilience enhancement. iEnergy 2022, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Mancarella, P.; Trakas, D.N. Power Systems Resilience Assessment: Hardening and Smart Operational Enhancement Strategies. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, H.; Vahidinasab, V.; Mehran, K. Power Systems Resilience Metrics: A Comprehensive Review of Challenges and Outlook. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yan, J.; Yan, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, D. Physical-cyber-human framework-based resilience evaluation toward urban power system: Case study from China. Risk Anal. Off. Publ. Soc. Risk Anal. 2022, 43, 800–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghandeh, R.; Meier, A.; Mehrmanesh, L.; Mili, L. On the definition of cyber-physical resilience in power systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufi, H.; Vahidinasab, V. Power system resilience assessment considering critical infrastructure resilience approaches and government pol- icymaker criteria. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2021, 15, 2819–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abantao, G.A.; Ibañez, J.A.; Bundoc, P.E.D.C.; Blas, L.L.F.; Penisa, X.N.; Esparcia, E.A., Jr.; Castro, M.T.; Buendia, R.V.E.; Pilario, K.E.S.; Tio, A.E.D.; et al. Reconceptualizing Reliability Indices as Metrics to Quantify Power Distribution System Resilience. Energies 2024, 17, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Dawson, R.; Wilkinson, S.; Pickering, C.; Mancarella, P. Power System Resilience to Weather: Fragility Modeling, Probabilistic Impact Assessment, and Adaptation Measures. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 3747–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenko, G.; Zaporozhets, A. Enhancing of the power system resilience through the application of micro power systems (microgrid) with renewable distributed generation. Syst. Res. Energy 2023, 2023, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, E.; Samadi, M.; Lotfi, H.; Hajiabadi, M.E. Improving the resilience of the distribution system using the automation of network switches. J. Eng. 2023, 2023, e12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Resilience of renewable power systems under climate risks. Nat. Rev. Electr. Eng. 2024, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragatto, T. Assessment and Possible Solution to Increase Resilience: Flooding Threats in Terni Distribution Grid. Energies 2019, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwifunyi, R.J.; Mnyanghwalo, D.C.; Kawambwa, S.J. Enhancing Service Restoration in Tanzanian Power Grid using Internet of Things Sensors and Renewable Energy Sources. Tanzan. J. Sci. 2023, 49, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Anderson, K.; Miller, B.; Boyer, K.; Warren, A. Microgrid resilience: A holistic approach for assessing threats, identifying vulnerabilities, and designing corresponding mitigation strategies. Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaperumal, G.; Srivastava, A.K. Resilience of the electric distribution systems: Concepts, classification, assessment, challenges, and research needs. IET Smart Grid 2020, 3, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, A.M. Methods for Analysis and Quantification of Power System Resilience. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2023, 38, 4774–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Mancarella, P. The Grid: Stronger, Bigger, Smarter?: Presenting a Conceptual Framework of Power System Resilience. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2015, 13, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteli, M.; Mancarella, P. Influence of extreme weather and climate change on the resilience of power systems: Impacts and possible mitigation strategies. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2015, 127, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Hachmann, C.; Haack, J. Blackouts, Restoration, and Islanding: A System Resilience Perspective. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2020, 18, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Analytic network process: Academic insights and perspectives analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1276–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lim, M.K.; Zhao, L.; Tseng, M.L.; Chien, C.F.; Lev, B. The evolution of Omega-The International Journal of Management Science over the past 40 years: A bibliometric overview. Omega 2019, 93, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghestan, A.G. A Crisis in ‘Open Access’: Should Communication Scholarly Outputs Take 77 Years to Become Open Access? Sage Open 2019, 9, 215–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L. Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid-Thermal Systems: Status, Hotspots, Trends and Outlook. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, S.A.; Poshtan, J.; Ebrahim, N.A.; Jamali, S.M. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Time-Series Classification Using Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 90–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, M.; Obradovic, Z. Enhancing Weather-Related Outage Pre- diction and Precursor Discovery Through Attention-Based Multi-Level Modeling. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 94–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalak, M.; Benidris, M.; Hotchkiss, E.; Cox, J.; Ericson, S. Quantitative Resilience-Based Assessment Framework Using EAGLE-I Power Outage Data. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 7682–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, X.; Sun, J.; Peng, B. Dynamic Simulation of Power Systems Considering Transmission Lines Icing and Insulators Flashover in Extreme Weather. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 39–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrai, D. Predicting Storm Outages Through New Representations of Weather and Vegetation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 29–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baembitov, R.; Brewster, K.A.; Kezunovic, M.; Obradovic, Z. Incorporating Wind Modeling Into Electric Grid Outage Risk Prediction and Mitigation Solution. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 4373–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, F.; Liu, K.; Hou, Y.; Lei, S. Resilience Enhancement with Sequentially Proactive Operation Strategies. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2017, 32, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Zhang, Y. Two-Stage Stochastic Optimal Power Flow for Microgrids with Uncertain Wildfire Effects. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 68–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Ye, R.; Yu, Z. An Ordered Curtailment Strategy for Offshore Wind Power Under Extreme Weather Conditions Considering the Resilience of the Grid. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljurbua, R.; Power, W.; Alharbi, A.; Alshehri, J.; Obradovic, Z. Social Media Sensors for Weather-Caused Outage Prediction Based on Spatio- Temporal Multiplex Network Representation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 125–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinthurat, W.; Surinkaew, T.; Kongsuk, P.; Marungsri, B. An Adaptive Data-Driven-Based Control for Voltage Control Loop of Grid-Forming Converters in Variable Inertia MGs. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 58–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Guo, G.; Su, L.; Qiu, F. Resilience Enhancement of Distribution Grids Against Extreme Weather Events. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2018, 33, 4842–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, A.K.; Dorrell, D.G.; Carpanen, R.P.; Ojo, E.E. A Comparative Assessment of Conventional and Artificial Neural Networks Methods for Electricity Outage Forecasting. Energies 2022, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nateghi, R.; Guikema, S.D.; Wu, Y.; Bruss, C.B. Critical Assessment of the Foundations of Power Transmission and Distribution Reliability Metrics and Standards. Risk Anal. 2015, 36, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Nateghi, R. A Data-Driven Approach to Assessing Supply Inadequacy Risks Due to Climate-Induced Shifts in Electricity Demand. Risk Anal. 2018, 39, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, W. Topological Modeling Research on the Functional Vulnerability of Power Grid under Extreme Weather. Energies 2021, 14, 5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadini, F.; Agliardi, G.L.; Zio, E. A modeling and simulation framework for the reliability/availability assessment of a power transmission grid subject to cascading failures under extreme weather conditions. Appl. Energy 2016, 185, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffhammer, M.; Baylis, P.; Hausman, C.H. Climate change is projected to have severe impacts on the frequency and intensity of peak electricity demand across the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1886–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, F.R.; Craig, M.; Jaramillo, P.; Bergés, M.; Severnini, E.; Loew, A.; Zhai, H.; Cheng, Y.; Nijssen, B.; Voisin, N.; et al. Effects of Climate Change on Capacity Expansion Decisions of an Electricity Generation Fleet in the Southeast U.S. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2522–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, A.T.D.; Nik, V.M.; Chen, D.; Hong, T.; Scartezzini, J.L. Quantifying the impacts of climate change and extreme climate events on energy systems. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Fang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, W.; Wu, D. Underground energy storage system supported resilience enhancement for power system in high penetration of renewable energy. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1138318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, C.; Jia, C. Electric Vehicle and Photovoltaic Power Scenario Generation under Extreme High-Temperature Weather. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Tseng, C.L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wen, F. An Integrated Planning Strategy for a Power Network and the Charging Infrastructure of Electric Vehicles for Power System Resilience Enhancement. Energies 2019, 12, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetta, R.; Li, Y.F.; Zio, E. Risk assessment and risk-cost optimization of distributed power generation systems considering extreme weather conditions. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2014, 136, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Lin, X.; Chen, N.; Du, Z. Mobile power sources pre-allocation and dispatch strategy in power-transportation coupled network under extreme weather. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023, 18, 1129–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Terzija, V.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Q. A Numerical Approach for Hybrid Simulation of Power System Dynamics Considering Extreme Icing Events. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 5038–5046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junjie, R.; Zhi, Z.; Gengyin, L.; Ming, Z. Coordination of preventive and emergency dispatch in renewable energy integrated power systems under extreme weather. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023, 18, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karangelos, E.; Wehenkel, L.; Perkin, S. Probabilistic Resilience Analysis of the Icelandic Power System under Extreme Weather. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Wang, B.; Li, M.; Yu, Y. Impact of Gale Weather Events on Wind Power Generation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2774, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, U.; Basuhail, A.; Eassa, F.E.; Jambi, K.; Khemakhem, M. Towards Sustainable Energy Grids: A Machine Learning-Based En- semble Methods Approach for Outages Estimation in Extreme Weather Events. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qian, F. Method of adapting to grid recovery in extreme weather conditions. J. Eng. 2017, 2017, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Chen, W.; Kong, L.; Tian, X. The Vulnerability of the Power Grid Structure: A System Analysis Based on Complex Network Theory. Sensors 2021, 21, 7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalai, M.; Yuvaraj, T.; Prabaharan, N.; Hariharan, R. Optimizing Distribution System Resilience in Extreme Weather Using Prosumer- Centric Microgrids with Integrated Distributed Energy Resources and Battery Electric Vehicles. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulou, M. Forecasting Transmission and Distribution System Flexibility Needs for Severe Weather Condition Resilience and Outage Management. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xue, Y.; Chang, X.; Su, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, P.; Sun, H. Risk-averse energy management for integrated electricity and heat systems considering building heating vertical imbalance: An asynchronous decentralized approach. Appl. Energy 2025, 383, 125271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.; Song, Y. A Stochastic Bi-Level Optimal Allocation Approach of Intelligent Buildings Considering Energy Storage Sharing Services. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2024, 70, 5142–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, N.A. How to Write a Review Paper. Zenodo. 2013. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/185775 (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Mcguinness, L.A.; Pritchard, C.C. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Le, T.; Choe, J.; Belfiore, A.; Cuccurullo, C. openalexR: An R-Tool for Collecting Bibliometric Data from OpenAlex. R J. 2024, 15, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lim, M.K.; Zhao, L.; Vilela, A.L.M. The evolution of Industrial Management & Data Systems over the past 25 years. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2019, 119, 2–34. [Google Scholar]
- Aghaei, C.A. A Comparison between Two Main Academic Literature Collections: Web of Science and Scopus Databases. Can. Cent. Sci. Educ. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).