Abstract
Ecotourism is recognized as a fundamental aspect of sustainable tourism development. This study aimed to identify the factors influencing ecotourism in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam, specifically focusing on streams and waterfalls, using an ecotourism potential model. This model utilizes quantitative approaches, incorporating questionnaires and spatial information, including remote sensing data. The model is employed to determine the factors affecting ecotourism potential in the 31 locations of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province. The model considers ecotourism potential as the dependent variable, while the independent variables are greenness using the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), connectivity, accessibility, and infrastructure, e.g., restaurants and hotels. The results revealed that greenness has the most significant positive impact on ecotourism potential around streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, followed by accessibility, restaurants, and hotels, while connectivity has a negative impact on ecotourism potential in these areas. This analysis underscores the importance of prioritizing the conservation of natural environments and ecosystems surrounding streams and waterfalls. Furthermore, this study utilizes geospatial methodologies to identify and enhance our understanding of the key factors influencing ecotourism.
1. Introduction
Ecotourism is a specialized form of nature-based tourism and represents a growing trend in sustainable tourism development globally. The term “ecotourism” was introduced in 1983 by Hector Ceballos-Lascurain, and a modified version of his definition was officially adopted by the IUCN in 1996: “Ecotourism is environmentally responsible travel and visitation to relatively undisturbed natural areas, in order to enjoy, study and appreciate nature, that promotes conservation, has low negative visitor impact, and provides for beneficially active socio-economic involvement of local populations” [1]. A World Tourism Organization report mentioned that ecotourism is the key to sustainable tourism development [2]. In the Vietnam Tourism Development Strategy for the period up to 2020 with a vision to 2030, ecotourism is also identified as one of the four main tourism product lines with high competitiveness compared to other countries in the region and around the world. Ecotourism has been defined in various ways, each highlighting distinct aspects such as nature-based experiences, conservation, sustainability, and community benefits. It emphasizes educational activities, fostering a deeper appreciation for the natural world. This tourism connects travelers with untouched environments and promotes awareness of environmental conservation [1,3,4,5,6]. It focuses on safeguarding endangered species and fragile ecosystems while also providing economic incentives for local communities to engage in conservation efforts [1,3,4,7]. According to the UNWTO’s definition, ecotourism refers to forms of tourism that have the following characteristics: (1) all nature-based forms of tourism in which the main motivation of the tourists is the appreciation of nature, and the traditional cultures prevailing in natural areas; (2) it contains educational and interpretation features; (3) it is typically organized by specialized tour operators for small groups; (4) it minimizes negative impacts upon the natural and socio-cultural environment; (5) and it supports the maintenance of natural areas used for ecotourism by generating economic benefits for host communities and conservation authorities [1]. According to the International Ecotourism Society (TIES), ecotourism can be defined as responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education, with the education component meant to be inclusive of both staff and guests [8]. Ecotourism emphasizes not only environmentally sustainable travel and human development but also socially responsible tourism, promoting the active and beneficial socioeconomic participation of local communities [9,10,11]. It emphasizes responsible travel to natural areas, ensuring environmental conservation and improving the well-being of local populations [12].
Generally, ecotourism is a focused subset of nature-based tourism, emphasizing conservation, sustainability, and socially responsible tourism. The concept of ecotourism must be viewed as dynamic and adaptable, as it can occur in a variety of settings, including coastal regions, forested landscapes, national parks and protected areas, wildlife reserves, and private land [13]. Unlike traditional tourism, ecotourism seeks to balance tourism development with environmental protection and community well-being. Thus, one of the primary obstacles to the development of ecotourism is maintaining this equilibrium. While other forms of tourism may focus on urban attractions or luxury services, ecotourism operates in fragile ecosystems that require careful management to avoid over-exploitation and degradation. Ecotourism has been recognized by conservationists as a valuable strategy for preserving local communities and natural resources. By promoting conservation, it reduces negative impacts on both natural and socio-cultural environments by aiding in the conservation of natural areas used for ecotourism [13]. This nature-based tourism aims for sustainability by balancing environmental, economic, and cultural factors. It promotes long-term sustainability, ensuring tourism activities preserve the integrity of ecosystems and local communities [3,13,14,15].
Tourism events occur in remote regions, where access to infrastructure and services are limited, posing further challenges to sustainable development. However, it is essential to assess the potential of ecotourism, because this can provide opportunities for sustainable development. Tourism potential can be defined as a set of resources, products, and services that can be included in existing tourism markets in a certain area [16]. Tourism potential depends on both endowed resources and established resources [17]. Buckley (2012) defined ecotourism potential as the capacity of a destination to attract visitors interested in experiencing natural environments and cultural heritage while contributing to conservation and local community development [18]. Ecotourism potential encompasses the ability of natural areas to provide tourism experiences that are environmentally sustainable, economically viable, and socially equitable, ultimately contributing to the conservation of ecosystems [19]. To assess nature-based tourism, these criteria may include attractiveness, accessibility, climate, sustainability, infrastructure, and socioeconomic development [20]. Ecotourism potential can be assessed by evaluating the natural resources, biodiversity, and cultural attributes of a location, alongside the infrastructure and community engagement that support sustainable tourism practices [21]. To determine the nature-based tourism potentials of three lakes in Artvin Province, twenty-six criteria belonging to seven dimensions have been used, the latter comprising tourism resources, accessibility, touristic infrastructure, demand, promotion and marketing, conservation status, and socioeconomic development [22]. Potential ecotourism sites were identified in the Menz Gera Midir district in Ethiopia based on three critical criteria—landscape, topography, and accessibility [23].
Geographical information system (GIS) technology can be used to identify ecotourism sites by enabling researchers and planners to analyze spatial data effectively [1,7]. The integration of spatial data and environmental indicators allows for a comprehensive analysis of natural and infrastructural factors, making it a versatile tool. GISs have been widely used in ecotourism research to map natural resources and identify potential tourism sites [24,25]. Moreover, a suitability model was designed using GIS technology to assess the suitability of an area for tourism considering suitability factors such as land cover types, wild animal zones, unique features, topography, and distances to roads [26]. While GISs serve as a valuable tool, this study focuses on streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, a region characterized by unique natural and cultural resources that have not been thoroughly explored in the context of ecotourism. Most of the streams and waterfalls in this area are situated far from the city, making them challenging to access for both tourists and researchers. This study integrates spatial data and conducts spatial analyses to understand relationships between factors and ecotourism potential. This study identifies the factors affecting the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls using GIS and remote sensing data. In addition, this study selected factors such as greenness, accessibility, infrastructure, and connectivity to assess the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls.
This study was conducted in January 2023 for the development of ecotourism associated with streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province. To maximize the ecotourism potential of a destination, understanding the relationships between factors and ecotourism potential is the first step. Ecotourism is also one of the most vulnerable types of tourism, which makes it crucial to properly identify the factors that contribute to its potential development. Therefore, the primary research question driving this study is: “What factors influence the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province?” By identifying these factors, this study aims to provide insights that will help governments and businesses develop effective strategies to harness the ecotourism potential of a destination.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
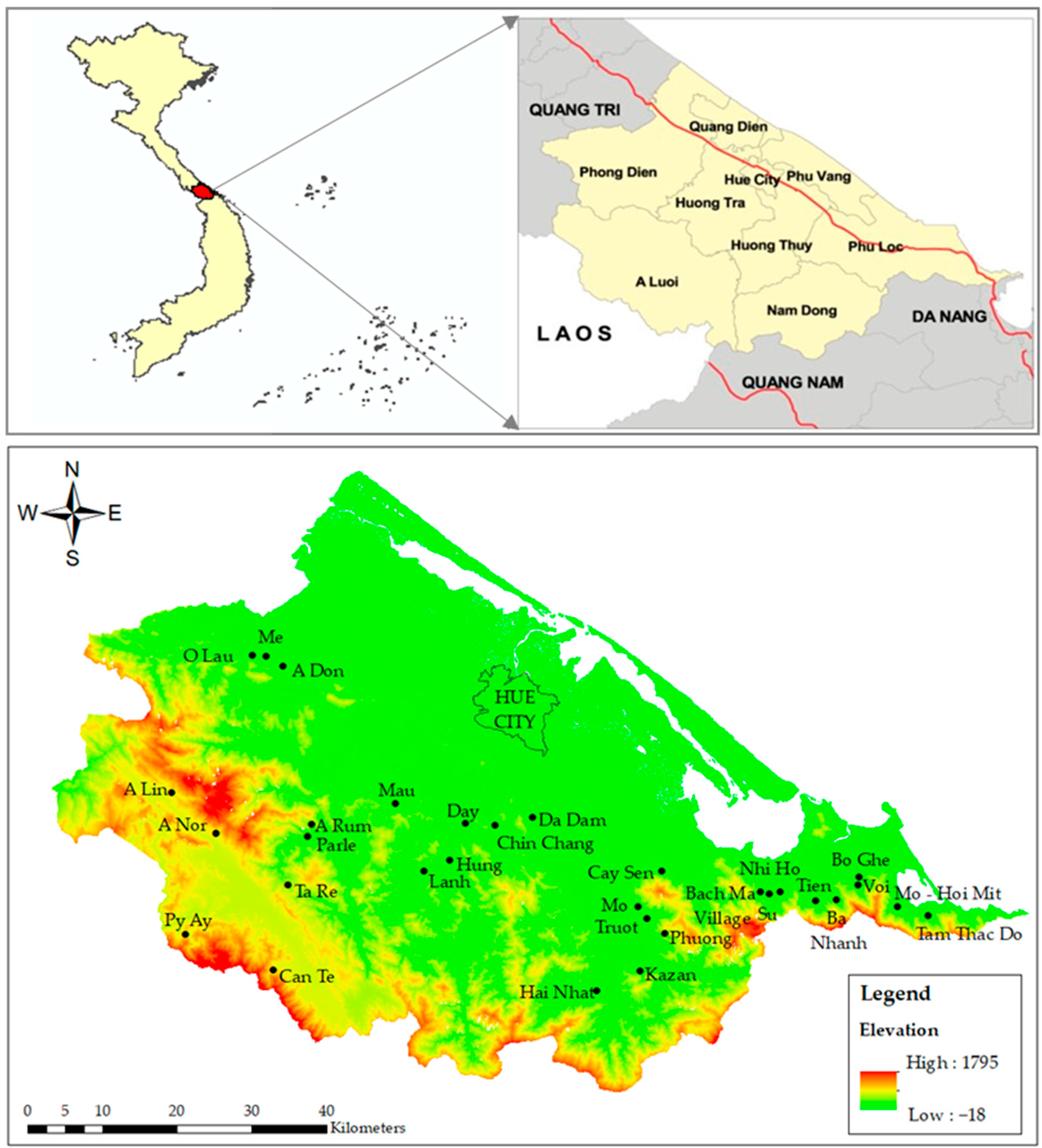
Thua Thien Hue, situated in central Vietnam, boasts a coastline of 128 km, 22,000 hectares of lagoons, and more than 200,000 hectares of forest. Thua Thien Hue province has strengths not only in heritage tourism, spiritual cultural tourism, and sea tourism but also in ecotourism associated with streams and waterfalls. Throughout the districts and towns of Thua Thien Hue, from lowlands to highlands, it is evident that there exists substantial potential for ecotourism based on streams and waterfalls. A stream is a flowing body of water that moves continuously, while a waterfall is a location of a river or stream where water flows over a steep drop. The location of Thua Thien Hue province and a terrain map is shown in Figure 1. Thua Thien Hue features a distinct hierarchical geographic structure. The region’s terrain includes mountainous areas extending from the Vietnam–Laos border to Da Nang city, covering approximately one-quarter of the total area. Midland regions make up about half of the area, with an average elevation of less than 500 m. Additionally, the local delta is characterized by sand dunes and a lagoon, encompassing around 1400 square kilometers.
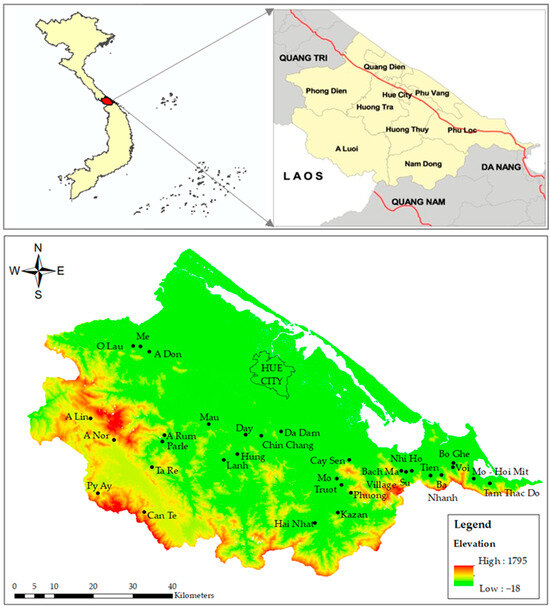
Figure 1.
Map of Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam (top). Location of streams and waterfalls and terrain map of Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam (bottom). Source: DEM from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) version 3.0.
Thua Thien Hue is one of the national tourism destinations that has many tourist attractions for both domestic and international tourists. Thua Thien Hue also has plenty of streams and waterfalls forming a dense network, primarily originating from the mountainous and hilly terrain in the eastern part of the Truong Son mountain range. Due to the territorial structure, the streams and waterfalls are located 20–90 km away from the city center. In particular, most of the waterfalls have a wild and attractive beauty, such as Mo waterfall, Voi stream, Tien stream, Bo Ghe waterfall, and Nhi Ho waterfall. Among them, four streams and waterfalls have been recognized as tourist destinations. Each waterfall has a quality rarely found in other areas. Because most streams and waterfalls are remote and quite far from residential areas, the area around the waterfalls is still natural. This supports ecotourism because most of the ecotourism objectives concern the authenticity and uniqueness of the tourist attraction [27]. However, the development of ecotourism in streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province has encountered some difficulties, such as most of the locations being located in remote areas. It is not easy to get there, and there are not many support services like accommodation, shopping, etc. Given the area’s own strengths and unique characteristics, developing ecotourism around streams and waterfalls is one of the directions that Thua Thien Hue province has been focusing on and will continue to exploit. The district’s People’s Committee also has programs and solutions to attract and call on investors to develop ecotourism in streams and waterfalls.
It is acknowledged that there is significant potential for ecotourism based on streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. According to statistics from Thua Thien Hue Department of Tourism, the entire province currently has 31 streams and waterfalls that have been assessed as having the potential for tourism development based on their favorable terrain, topography, hydrology, diverse ecosystems, and wild natural beauty. Therefore, 31 waterfalls identified with ecotourism potential were included in this study (Figure 2). Figure 2 shows that most streams and waterfalls are located far from the main center (Hue city) in remote and mountainous areas and quite far from residential areas in the forest.

Figure 2.
Field photos of famous waterfalls and streams in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. (a) Tien stream, (b) Mo waterfall, (c) Nhi Ho waterfall, (d) Tam Thac Do waterfall.
2.2. Methods
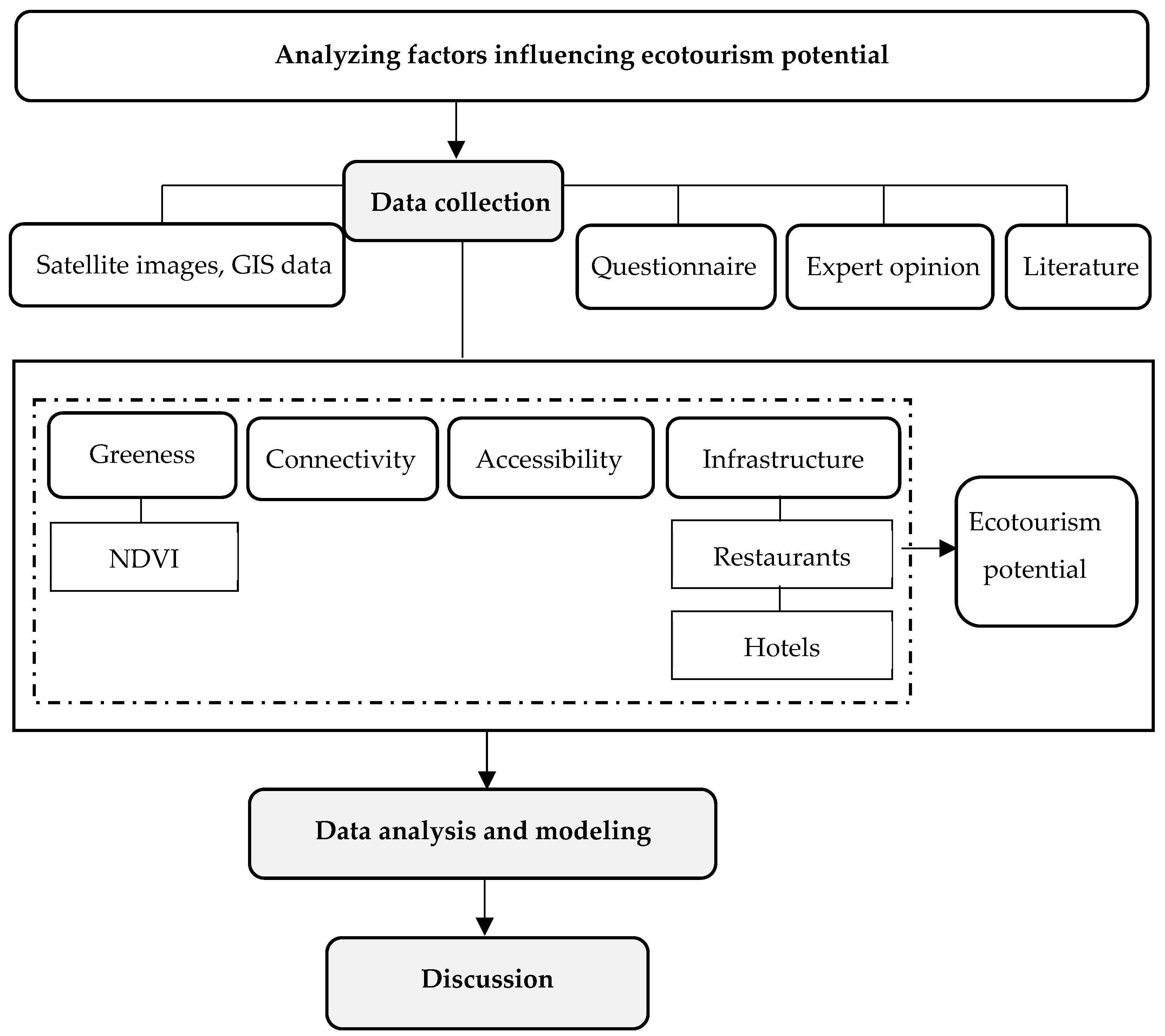
Figure 3 shows the research process. Ecotourism potential data were collected by quantitative methods from interviews. Then, we identified the features of each criterion using GIS technology and remote sensing. Elements within a region can be recorded as points, polygons, or as lines. Distance components related to criteria are addressed by placing buffers of a certain distance around features. The final stage determined the factors affecting ecotourism potential in the region using regression analysis. Ordinary least squares (OLS) is widely used in the literature related to tourism potential [28,29]. A linear relationship between the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province and independent variables was assumed. Multiple regression was employed to estimate the relationship between these attributes. In this study, major components affecting ecotourism potential are proposed, including ecotourism potential as a dependent variable, which is affected by independent variables such as greenness, connectivity, accessibility, and infrastructure (restaurants and hotels) (Table 1). Following this, the baseline model was used to identify the factors influencing ecotourism potential associated with streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province.
Here, Pi is the ecotourism potential of location i, Gi is the greenness that is determined by the NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) surrounding location i, Ci represents the connectivity indicator of location i, Ai represents the accessibility indicator of location i, Ri represents the existence of restaurants at sample i; Hi represents the existence of hotels at location i, and β represents the corresponding parameters of each variable.
Pi = β0 + β1Gi + β2Ci + β3Ai + β4Ri + β5Hi
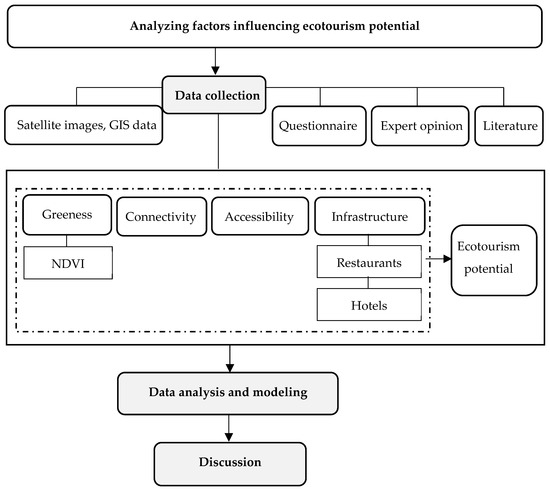
Figure 3.
Research flowchart and process.

Table 1.
Definitions of dependent and independent variables.
2.3. Dataset
- Ecotourism potential (P)
Ecotourism potential data were collected from interviews with 310 tourists in January 2023 about ecotourism development potential in the study area. Questions were designed to assess the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. There were two sections in the questionnaire. Section A contained 21 questions aimed at assessing the ecotourism potential of the streams and waterfalls of Thua Thien Hue province: 7 questions about the attractiveness of greenness, 3 questions regarding connectivity, 3 questions on accessibility, 3 questions addressing safety, and 5 questions focused on the supporting services available around the stream and water areas. A five-point Likert scale, a widely used technique for grading respondents’ ideas, was used in the construction of the questionnaire, where 1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, and 5 = strongly agree. Section B comprised 5 questions designed to elicit the socio-economic background of the visitors. The ecotourism potential of a stream or waterfall was calculated based on the average scores provided by tourists in the questionnaire for all factors, which included greenness, connectivity, accessibility, safety, and supporting services.
- Greenness (G)
To identify the factors influencing ecotourism potential, firstly GIS data required for this research were acquired from various sources. Administrative boundary maps, road networks, and satellite imagery were used for connectivity and identification of infrastructure such as restaurants and hotels.
The greenness of a landscape or a habitat is one of the most important criteria for ecotourism [21,22,23,30]. The NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) can represent greenness to become an invaluable tool in assessing ecotourism potential. The NDVI is valuable for evaluating the vegetative density around waterfalls, such as forests, grasslands, or agricultural areas, which are important for ecotourism and conservation efforts [31]. NDVI values around a stream or waterfall can enrich the primary attraction, providing an extra dimension of ecotourism [32]. Tourists participating in ecotourism not only appreciate the beauty of the streams and waterfalls but also enjoy the surrounding scenery, so the surrounding landscape is significant for ecotourism at the streams and waterfalls. Therefore, the NDVI was included in the regression model as an independent variable. By utilizing remote sensing data, we were able to capture critical information about the region’s vegetation cover, often represented through the NDVI, which is a vital indicator of ecological health. The NDVI indices of 31 waterfalls were derived from the analysis of remote sensing imagery based on this individual measurement as: NDVI = (NIR − R)/(NIR + R), where NIR is near-infrared band and R is red band. NDVI values range between minus one (−1) to plus one (+1): no green leaves give a value close to zero, and close to +1 indicates the highest possible density of green leaves. However, researchers can expand this value scale (if required) to be more visualized in a map. In this study, we adjusted the NDVI value scale to 0–1 as a quantitative variable in the regression model.
- Connectivity (C)
The connectivity of a destination reflects how well connected it is to the transport network [33,34]. Some authors emphasize that effective connectivity enhances the accessibility of rural tourism areas, which is critical for sustainable development and can foster economic growth, social engagement, and environmental preservation in these regions [19]. Connectivity in this study was the buffer distance from the streams and waterfalls to the main road within a range of three kilometers. The buffer can be created by the satellite images and by using the distance operation function of GIS software ArcMap 10.8. Connectivity was included in this study as a dummy variable.
- Accessibility (A)
Accessibility, defined as the potential for opportunities for interaction, is an important external factor influencing ecotourism potential, as it indicates the transport facilities that support tourists [35,36]. Accessibility relates to the ease of physically reaching destinations, as well as the ease with which the destination itself can be enjoyed as a tourism product [37]. The diverse transportation options and their easy accessibility play a significant role in drawing visitors to tourist destinations [16,20,22,23]. Some streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province are inaccessible due to poor transport routes. Poor accessibility significantly hinders the development of nature-based tourism. A region reachable via a sandy track received a low rating due to its restricted accessibility, requiring a four-wheel-drive vehicle [38]. This indicator was assigned values ranging from 0 to 5: very poor, poor, moderate, good, and very good accessibility. Accessibility and connectivity measure different dimensions of a location, reflecting how well it is located or connected to the transport network, respectively. Therefore, it is significant to include both of these in the measure of location attractiveness. The study conducted in-depth interviews with 12 individuals who represent local government agencies and possess knowledge of ecotourism development associated with streams and waterfalls to evaluate accessibility to these natural features.
- Infrastructure: Restaurants (R) and Hotels (H)
Infrastructure plays a big role in the development of a tourism destination [32]. Whilst nature-based tourism relies on natural attractions, the availability of amenities can elevate the visitor experience [20,21,22]. Moreover, the absence of facilities at tourist destinations may discourage people from visiting or revisiting a location [39]. To maintain or enhance the natural attractiveness of nature-based tourism, infrastructure is required, regardless of the type of tourism or the activity itself [38]. This study also focused on the existence of restaurants and hotels within a 1 km buffer as independent variables in the regression model. Restaurant and hotel variables representing infrastructure are included in this study as two separate dummy variables because they play distinct roles in the ecotourism experience. Restaurants are often associated with offering local cuisine and cultural experiences, contributing to the authenticity of a destination. Restaurants provide spaces where ecotourists can socialize, share stories, and build a sense of community. Thus, dining at restaurants is a social activity that brings ecotourists together. Hotels provide accommodation and comfort for tourists. Contrary to dining needs, which are essential in any tourist activity, including ecotourism, accommodation needs are only necessary for overnight stays at the destination. Therefore, it is beneficial to separate these variables to gain a better understanding of their individual contributions to ecotourism potential.
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
- Ecotourism potential
Table 2 presents scoring results for ecotourism potential derived from the survey results of tourists. The scores are based on factors such as the attractiveness of streams and waterfalls, tourism facilities, and accessibility.

Table 2.
Categorization of ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province.
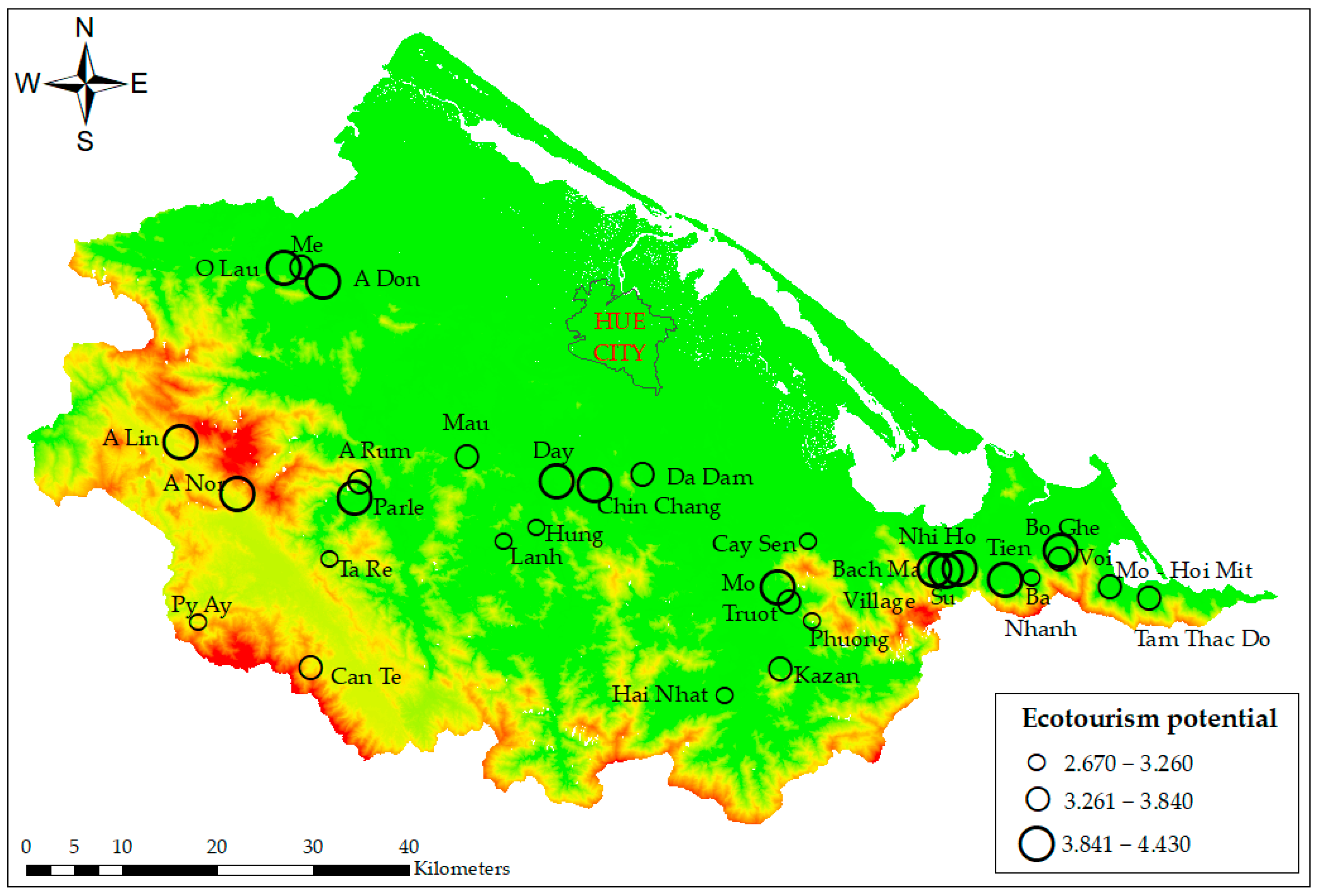
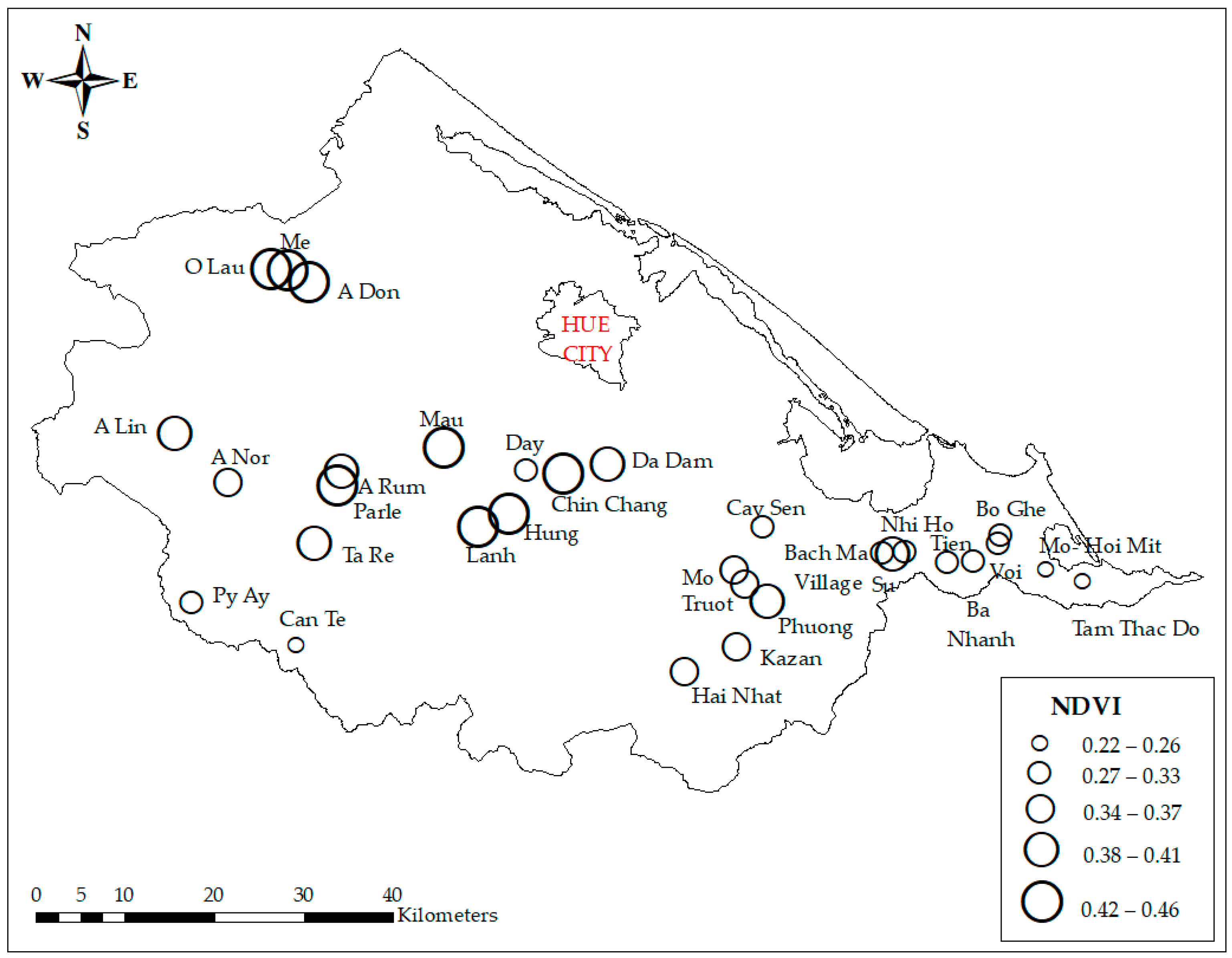
Ecotourism potential in streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, which scored from 2.67 to 4.43, was categorized into three classes (low, moderate, and high). The results showed that the high-ecotourism-potential class comprised Mo waterfall, Bach Ma village (Truot waterfall), Chin Chang waterfall, O Lau stream, Nhi Ho waterfall, Su stream, A Nor waterfall, Parle stream, Day stream, Bo Ghe waterfall, A Lin stream, A Don waterfall, and Tien stream. The moderate class comprised Can Te stream, Mo – Hoi Mit stream, Mau stream, Da Dam waterfall, Voi stream, A Rum stream, Tam Thac Do waterfall, Kazan waterfall, Me stream, and Truot waterfall. The low-ecotourism-potential class comprised Hung stream, Lanh stream, Ta Re waterfall, Hai Nhat waterfall, Py Ay stream, Ba Nhanh stream, Phuong waterfall, and Cay Sen waterfall (Figure 4).
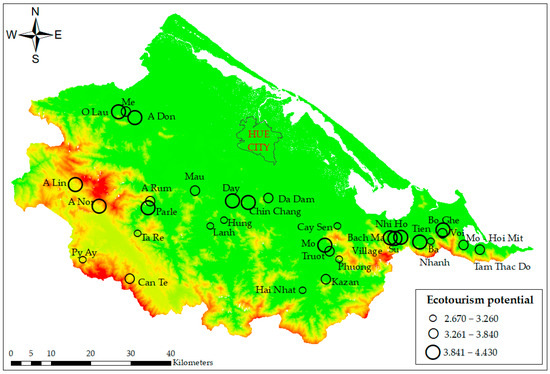
Figure 4.
Ecotourism potential of waterfalls and streams in Thua Thien Hue province.
- Descriptive statistics
With a minimum value of 2.670 and a maximum of 4.430, ecotourism potential suggests a range of potential levels across the dataset, indicating varying degrees of attractiveness for ecotourism activities (Table 3). The results show that the average ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province is quite high, with a mean value above the average (3.40) based on the five-point Likert scale. Table 3 shows the streams and waterfalls studied in this research: 45.2% are located near the main road (within 3 km), which indicates limited connectivity of the streams and waterfalls with the transportation system. Although most of the streams and waterfalls are located far from the main roads, 25.7% of the streams and waterfalls are considered difficult to access according to expert assessments. Additionally, 67.7% of these sites have restaurants within a 1 km radius, while 71% have nearby hotels. This means that 30% of the potential tourism streams and waterfalls studied lack any nearby infrastructure services.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics.
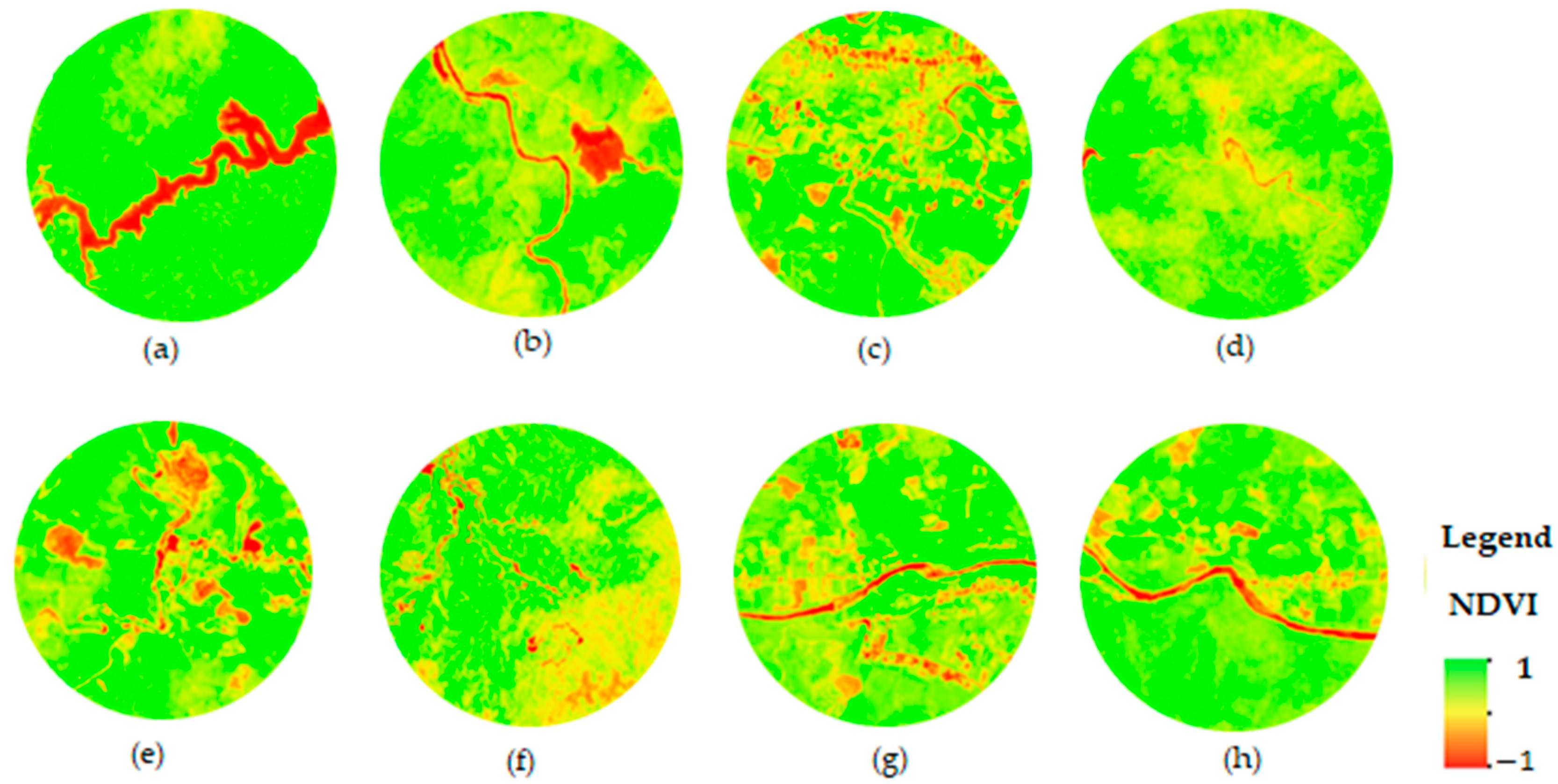
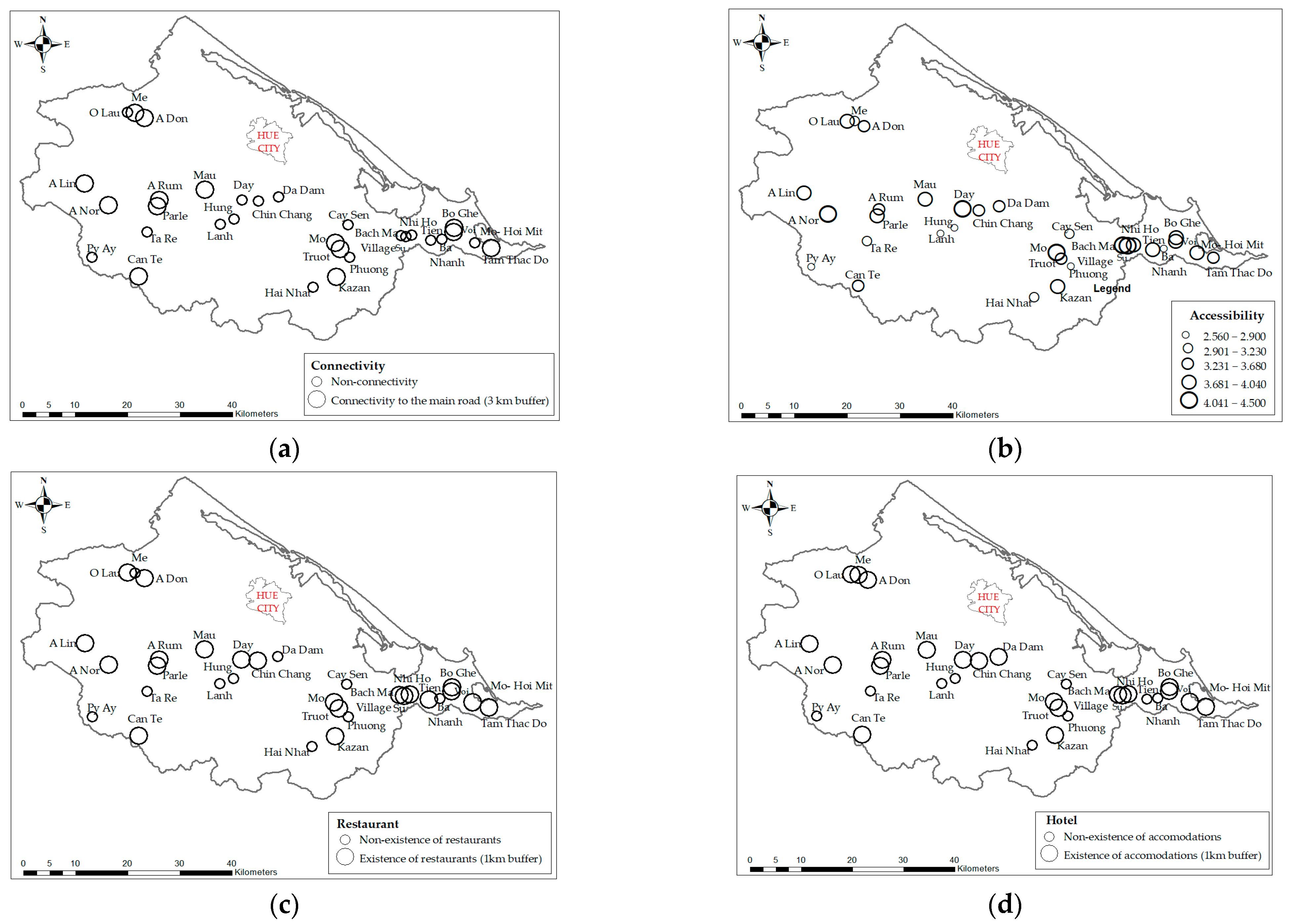
NDVI images, which represent vegetation patterns, have resulted from remote sensing imagery analysis (Figure 5). There are five classes of NDVI values: class 1 (non-vegetation area: −1 to −0.03), class 2 (very little dense vegetation: −0.03 to 0.15), class 3 (little dense vegetation: 0.15 to 0.25), class 4 (moderately dense vegetation: 0.26 to 0.35), and class 5 (highly dense vegetation: 0.35 to 1) [40]. From Table 3, the range of NDVI values, from a minimum of 0.22 to a maximum of 0.46, signifies the variation in vegetation density across these sites from little dense vegetation to highly dense vegetation. Figure 6 shows the average NDVI level around waterfalls and streams in Thua Thien Hue province. The mean NDVI value indicates an important measure of vegetation density and health, reflecting the greenness and vitality of plant life around streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province. Figure 7 illustrates the connectivity, accessibility, restaurants, and accommodation around waterfalls and streams of Thua Thien Hue province. Notably, the distribution patterns of restaurants and hotels are quite similar, indicating that both types of establishments are positioned to serve visitors seeking to explore these natural attractions. This correlation suggests a well-planned approach to ecotourism development, where amenities are positioned to enhance the overall experience for tourists. Proximity and accessibility to scenic spots can significantly contribute to visitor satisfaction and promote longer stays in the region. Furthermore, this clustering of facilities could also support local businesses and services, encouraging economic growth in the area.
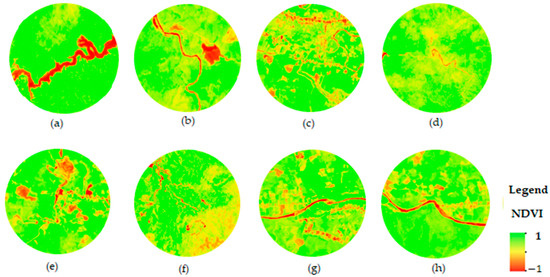
Figure 5.
NDVI images for eight waterfall and stream areas within a 1 km buffer in Thua Thien Hue province: (a) Lanh stream; (b) Chin Chang waterfall; (c) A Don waterfall; (d) Hung stream; (e) Mau stream; (f) Ta Re waterfall; (g) Me stream; (h) O Lau stream.
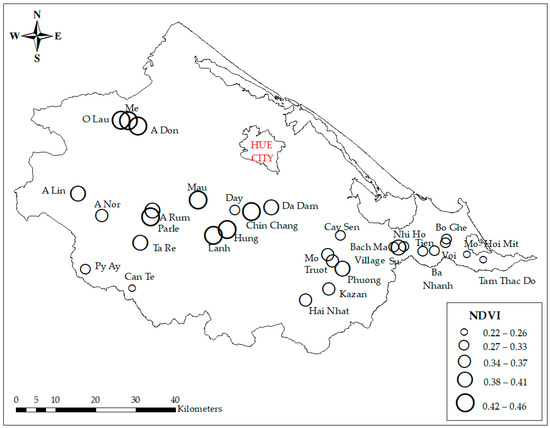
Figure 6.
Average NDVI levels around waterfalls and streams in Thua Thien Hue province.
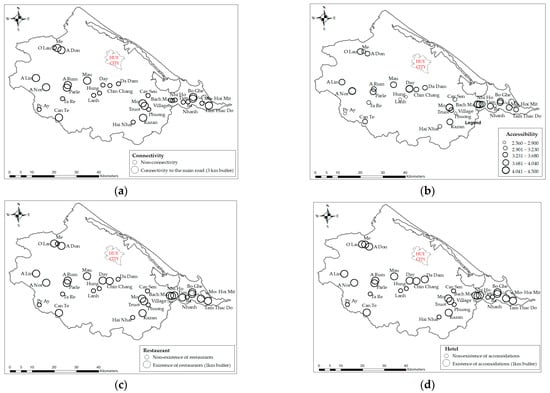
Figure 7.
(a) Connectivity, (b) accessibility, (c) restaurants, and (d) hotels around waterfalls and streams of Thua Thien Hue province.
3.2. Ecotourism Potential Model
The regression result showed high suitability of the regression model (R2 = 0.883; adjusted R2 = 0.86). The R2 of 0.883 means that the independent variables, NDVI, connectivity, accessibility, restaurants, and hotels have 88.3% influence on the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province and 11.7% by other factors that are not considered in this research. Most variables had a positive impact on ecotourism potential, except connectivity (β2 = −0.229). The impact of greenness (β1 = 1.605) on ecotourism potential was the highest, followed by accessibility (β3 = 0.483), restaurants (β4 = 0.379), and hotels (β5 = 0.337) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Regression model of ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam.
The estimation model is:
Pi = 0.952 + 1.605Gi − 0.229Ci + 0.483Ai + 0.379Ri + 0.337Hi
In the above formula, the components are:
Pi: Ecotourism potential (dependent variable).
Gi: Greenness surrounding streams/waterfalls.
Ci: Connectivity of streams/waterfalls to road networks.
Ai: Accessibility to streams/waterfalls.
Ri: Restaurants surrounding streams/waterfalls.
Hi: Accommodation or hotels surrounding streams/waterfalls.
Notably, the most important factor in the ecotourism development potential of waterfalls is the greenness. The positive impact of the greenness on ecotourism potential suggests a strong relationship with vegetation density (as indicated by the NDVI). This means that more greenness indicates a higher potential for tourism development. The results show accessibility of waterfalls plays an important role in ecotourism potential. Improving accessibility at streams and waterfalls should be a focus in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. This study identified that the infrastructure facilities at potential natural tourism areas are minimal; however, they play a crucial role in ecotourism potential. The results show that both hotels and restaurants are necessary factors for the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, with restaurants having a higher impact on ecotourism potential than hotels. While the main focus of nature-based tourism is on natural regions, some services must be offered in order to maintain the quality of the environment. Service infrastructure such as restaurants is essential for tourism development potential. Restaurants play a crucial role in offering authentic and unique local cuisine and cultural experiences. The results also show that connectivity has a negative effect on ecotourism potential in streams and waterfalls (β2 = −0.229), which means a destination’s unique nature can outweigh the distance factor. If a place offers exceptional experiences that are not easily found, tourists may be willing to travel longer distances to visit. This indicates significant ecotourism development potential for waterfall and stream locations situated far from the city center, as long as they are attractive enough and have good accessibility and infrastructure services.
4. Discussion
4.1. Aspects of Ecotourism
The findings underscore important factors influencing ecotourism potential within the context of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. Positive influences such as greenness, accessibility, restaurants, and hotels demonstrate remarkable contributions to this ecotourism potential. Notably, greenness emerges as a pivotal factor, showcasing a strong association between vegetation density and tourism development. This correlation accentuates the importance of preserving natural habitats to sustain their allure for tourists while ensuring their long-term viability. Previous studies have emphasized that pristine environments, including rich biodiversity and scenic landscapes, are critical in driving ecotourism demand [11,21]. Aligning with several well-established theories on ecotourism and sustainability, the study advocates for sustainable ecotourism practices focused on conserving these environments. The results also reinforce the idea that accessibility and supporting infrastructure, such as restaurants and hotels, are essential for balancing tourist demand with sustainability [20,21,22,23].
The strong influence of greenness on ecotourism potential also underscores the importance of preserving and maintaining natural habitats [41]. The results of the study were consistent with previous research on ecotourism potential, which emphasizes that prioritizing ecosystem protection is essential in planning ecotourism [42]. Sustainable ecotourism practices should aim to protect and conserve these environments to sustain their attractiveness for tourists while ensuring their long-term viability. Ecotourism activities need to be combined with environmental education for both tourists and residents, contributing to the protection of natural resources [6]. In particular, enhancing accessibility at these natural sites emerges as a key recommendation. Given the region’s minimal infrastructure facilities, there is a vital need to strengthen these aspects of ecotourism potential [20,21,22]. While the study underscores the necessity of both hotels and restaurants, it emphasizes the substantial role restaurants play in ecotourism potential. Restaurants serve as gateways to authentic local experiences, enhancing overall tourism. Surprisingly, the study found a negative impact of connectivity on ecotourism potential. This finding suggests that the unique allure of a destination can outweigh the deterrent of distance. This revelation holds significant implications, signaling promising tourism potential for locations distant from urban centers providing good attractiveness, accessibility, and infrastructure. The study underscores the importance of steering future research efforts toward a holistic approach that harmonizes the allure of natural landscapes with the enhancement of accessibility, infrastructure, and gastronomic offerings. This balanced strategy aims to unlock the potential of ecotourism by not only leveraging the inherent appeal of pristine environments but also by fortifying the supporting elements crucial for visitor engagement.
4.2. Modeling with Key Factors
The proposed model integrating remote sensing and GIS techniques offers valuable insights into evaluating the ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam. Applications of GISs in tourism and recreation planning illustrate that GISs are an effective tool to aid in tourism planning and decision-making [43,44]. By incorporating variables like the NDVI, connectivity, accessibility, and infrastructural elements, this model serves as a fundamental tool for understanding and predicting tourism development in natural landscapes. The NDVI, reflecting vegetation density, emerges as the most influential factor in ecotourism potential. Its highly positive impact suggests a strong correlation between lush greenery and tourism prospects. This highlights the significance of remote sensing in capturing environmental attributes crucial to visitor attraction. The model integrated within GISs provides a comprehensive understanding of the spatial dynamics shaping ecotourism potential. The role of variables such as connectivity and accessibility in influencing visitor patterns is illustrated, emphasizing the importance of geographic context in tourism attractiveness. The findings underscore the crucial role of accessibility, infrastructure, and service facilities in ecotourism potential [45,46]. The model highlights the need for a balanced approach where natural allure is complemented by essential amenities, ensuring sustainable tourism and enhancing visitor experiences [47].
The model serves as a foundation for future research, enabling a deeper understanding of ecotourism potential and guiding strategic interventions for encouraging responsible tourism practices. As noted in the literature, GISs have been widely used in ecotourism research to map natural resources and identify potential tourism sites [24,25]. In our research, continual advancements in remote sensing technologies and GIS capabilities offer prospects for adapting this model. Incorporating real-time data and community perspectives can enhance the accuracy and relevance of the model. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of GIS and remote sensing technologies in assessing ecotourism potential. This inclusive approach not only enhances the accuracy and relevance of the model but also plays a pivotal role in fostering sustainable tourism planning and strengthening conservation efforts, particularly valuable for developing countries or regions with extensive natural landscapes, where on-ground surveys may be challenging [1,7]. The integration of remote sensing, spatial data, and environmental indicators allows for a comprehensive analysis of natural and infrastructural factors, making it a practical tool for future research.
5. Conclusions
There has been investment in both infrastructure and tourism services around streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province in recent years, but the area’s ecotourism potential has not previously been evaluated. This study has developed a methodology to identify the factors influencing ecotourism potential of streams and waterfalls by utilizing GIS and remote sensing data. The results indicate that factors influencing the ecotourism potential at streams and waterfalls, ranked by impact level, are the NDVI, accessibility, restaurants, and hotels, which together account for 88.3% of the influence on ecotourism potential in Thua Thien Hue province. Greenness significantly influences the ecotourism potential of the area. It attracts ecotourists by providing stunning natural landscapes, rich biodiversity, and a strong commitment to sustainability and conservation. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of GIS and remote sensing technologies in assessing factors that impact ecotourism potential. The integration of spatial data and environmental indicators allows for a comprehensive analysis of natural and infrastructural factors, making it a versatile tool for future research. The application of GIS and remote sensing technologies in other geographic regions could further validate these findings and contribute to a more global understanding of factors influencing ecotourism potential. This study suggests that decision-makers should prioritize enhancing the key factors that influence ecotourism at streams and waterfalls, in the following order: greenness, accessibility, restaurants, and hotels. It highlights the importance of conserving natural resources in these areas, focusing on greenness and biodiversity by implementing ecosystem conservation programs through reforestation projects and habitat restoration efforts. This is essential for encouraging the creation of ecotours to increase stakeholders’ understanding of environmental preservation. Future research can build on this methodology by exploring additional factors such as climate data or local community involvement, both of which are increasingly recognized as key components in sustainable ecotourism development.
Additionally, the study reveals that ecotourism sites located away from major roads possess greater tourism potential. The research illustrates the spatial distribution of streams and waterfalls in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam, with most of these natural features being situated in remote areas, far from the city center. To maximize the region’s tourism potential, improving the transportation system will benefit the socioeconomic development of the local community. The creation of public transport options and eco-friendly services, such as electric shuttles or bicycles, will further improve the accessibility of these sites. It is essential to support the local community in developing businesses in the restaurant and hotel sector, especially encouraging sustainable infrastructure such as eco-friendly restaurants, accommodation, and visitor centers that minimize environmental impact and enhance the ecotourism potential of a destination. By addressing these factors, governments can strike a balance between ecotourism development and safeguarding the destination’s natural resources. Prioritizing sustainable practices will enable authorities to promote ecotourism while protecting the natural landscapes and ecological integrity of the destination for future generations. Future research could explore the ecotourism suitability index and the mapping of ecotourism potential zones.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.T.H.; methodology, H.-J.C. and T.T.T.H.; formal analysis, H.-J.C. and T.T.T.H.; investigation, T.T.T.H.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T.T.H.; writing—review and editing, H.-J.C.; supervision, H.-J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to participants interviewed in this study. We thank Google Earth Engine and Google Earth Pro for providing data archiving and processing services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ceballos-Lascurain, H. Tourism, Ecotourism and Protected Areas; IUCN, The World Conservation Union: Gland, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- UNWTO. Ecotourism: Definition and Principles; United Nations World Tourism Organization: Madrid, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fennel, D.A. Ecotourism; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Blamey, R.K. Principles of ecotourism. In The Encyclopedia of Ecotourism; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, D.B. The Encyclopedia of Ecotourism; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Orams, M.B. Towards a more desirable form of ecotourism. Tour. Manag. 1995, 16, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyonyi, J.W.; Imwati, A.; Boitt, M. GIS in analysis of potential sites for ecotourism–a case study of Kwale County. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2016, 10, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wight, P.A. Ecotourism: Ethics and Guidelines for Responsible Travel; The Ecotourism Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Surendran, A.; Sekar, C. A comparative analysis on the socio-economic welfare of dependents of the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ART) in India. Margin J. Appl. Econ. Res. 2011, 5, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheyvens, R. Ecotourism and the empowerment of local communities. Tour. Manag. 1999, 20, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Wall, G. Ecotourism: Towards congruence between theory and practice. Tour. Manag. 1999, 20, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TIES. Ecotourism: An Overview; The International Ecotourism Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Honey, M. Ecotourism and Sustainable Development: Who Owns Paradise? Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg, K.; McKercher, B. Ecotourism: A critical overview. Pac. Tour. 1997, 1, 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, G. Is Ecotourism Sustainable? Environ. Manag. 1997, 21, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, S.; Kaymaz, Ç.K. Nature Tourism Potential of Çağlayandibi Waterfall Natural Park and Örümcek Forests Natural Conservation Area. In Theory and Practice in Social Sciencin; ST. KLIMENT OHRIDSKI UNIVERSITY PRESS: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2019; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, L.; Kim, C.W. Destination competitiveness: A model and indicators. Curr. Issues Tour 2003, 6, 369–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R. Ecotourism and Conservation. In Ecotourism: Principles and Practice, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.; Frolova, E. Connectivity and accessibility: Their importance for tourism development in rural areas. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2018, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-F. Understanding the factors determining the attractiveness of camping tourism: A hierarchical approach. Tour. Plan. Dev. 2020, 17, 556–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honey, M. Ecotourism and Certification: Setting Standards in Practice; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zorlu, K.; Dede, V. Evaluation of nature-based tourism potential in protected and sensitive areas by CRITIC and PROMETHEE-GALA methods. Int. J. Geoheritage Parks 2023, 11, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, B.; Gebre, S.L.; Gemeda, D.O.; Getahun, K. Using geospatial techniques in the selection of potential ecotourism sites in Menz-geramidir district, Ethiopia. Ghana J. Geogr. 2019, 11, 201–227. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, S.W.; Butler, R.W. Sustainable tourism: A global perspective. In Global Tourism: A New Perspective; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.; Jansen-Verbeke, M.; Arnaud, C. The use of GIS in tourism research: A review of applications. Tour. Manag. 2009, 30, 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Nino, K.; Mamo, Y.; Mengesha, G.; Kibret, K.S. GIS based ecotourism potential assessment in Munessa Shashemene Concession Forest and its surrounding area, Ethiopia. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 82, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidrawati, H.; Normayasari, N.; Sahari, S.; Fyka, S.A.; Yusria, W.O. A Study of the Potential of Ecotourism Development in Konawe Islands Regency, Southeast Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. Habitat 2022, 31, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, H. Gravity model approach: An appication on tourism potential for Turkey. In Interdisciplinary Researches in Economics and Administration Sciences: Concepts, Researches and Applications; Livre De Lyon: Villeurbanne, France, 2022; pp. 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Vidanage, S.P.; Kotagama, H.B. Potential and factors affecting ecotourism in Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the International Forestry and Environment Symposium, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka, 15–16 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Asadpourian, Z.; Rahimian, M.; Gholamrezai, S. SWOT-AHP-TOWS analysis for sustainable ecotourism development in the best area in Lorestan Province. Soc. Indic. Res. 2020, 151, 289–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, U.K.; Smrita, K.; Paul, S.K.; Sudhakar, S. Remote Sensing and GIS Based Ecotourism Planning: A Case Study for Western Midnapore; ESRI Publications: West Bengal, India, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Susanti, R.; Ramadhani, Y.H.; Harimurti, M. Evaluating Nature Tourism Destination Potentiality in Samosir Regency using Remote Sensing and GIS. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 280, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willigers, J.; Van Wee, B. High-speed rail and office location choices. A stated choice experiment for the Netherlands. J. Transp. Geogr. 2011, 19, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Jin, F.; Liu, W. Roles of accessibility, connectivity and spatial interdependence in realizing the economic impact of high-speed rail: Evidence from China. Transp. Policy 2020, 91, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, W.G. How accessibility shapes land use. J. Am. Inst. Plan. 1959, 25, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Chung, Y.; Nishii, K.; Jung, B.D. The effect of accessibility improvement on tourist excursion behaviors. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2011, 15, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.N.; Craig-Smith, S.J.; Collier, A. Principles of Tourism; LongmanCheshire: Melbourne, Australia, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Priskin, J. Assessment of natural resources for nature-based tourism: The case of the Central Coast Region of Western Australia. Tour. Manag. 2001, 22, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, D. Tourist Development; Longman Scientific & Technical: Harlow, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hartoyo, A.P.P.; Pamoengkas, P.; Mudzaky, R.H.; Khairunnisa, S.; Ramadhi, A.; Munawir, A.; Komarudin, A.; Hidayati, S.; Sunkar, A. Estimation of vegetation cover changes using normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in Mount Halimun Salak National Park, Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1109, 012068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Zong, Q.; Jin, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, P. Spatial patterns and driving forces of urban vegetation greenness in China: A case study comprising 289 cities. Geogr. Sustain. 2024, 5, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. Application of GIS in Ecotourism Development: A Case Study in Sundarbans, Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Mid-Sweden University, Ostersund, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Giles, W. GIS Applications in Tourism Planning. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Congress, Comm. II, Istanbul, Turkey, 12–23 July 2004; pp. 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Pareta, K. Remote Sensing and GIS Application for Potentiality of Ecotourism: A case study for Majuli island, Assam, India. Madhya Bharti J. Phys. Nat. Sci. 2010, 56, 38–51. [Google Scholar]
- Menbere, I.P.; Admassu, F. Challenges and opportunities for ecotourism development: A case study in Dilla university botanical and ecotourism garden, South Ethiopia. Glob. J. Ecol. 2020, 5, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Zhao, D. Evaluating the accessibility of public service facilities to tourists and residents in island destinations: Evidence from the Changhai County. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1090341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktymbayeva, A.; Nuruly, Y.; Artemyev, A.; Kaliyeva, A.; Sapiyeva, A.; Assipova, Z. Balancing nature and visitors for sustainable development: Assessing the tourism carrying capacities of Katon-Karagay National Park, Kazakhstan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).