Abstract
Wetlands represent one of the three principal ecosystems and serve a vital function in the protection of water resources and the regulation of climate. However, wetlands are currently experiencing significant challenges, particularly in the agriculturally productive wetlands of the Heilongjiang River Basin, which have been considerably impacted by human activities. This study focuses on three representative wetlands situated within the Heilongjiang River Basin. This study analyses changes in wetland area and landscape patterns from 2002 to 2022, as well as the impact of agriculture and impervious surface expansion on the wetlands. The findings indicate that agricultural expansion is the primary driver of wetland area loss. The wetland area affected by agriculture demonstrates the most significant change, with the largest observed shift reaching 47.2%. The expansion of impervious surfaces was found to have a significant impact on wetland fragmentation, resulting in a notable decrease in wetland connectivity. This was evidenced by a reduction in the average patch size, which decreased by 14.68 ha over the decade from 2007 to 2017, a period during which impervious surfaces expanded. This paper identifies the distinctions in the influence of diverse human activities on wetland landscape patterns in the Heilongjiang Basin and employs natural samples for control, thereby attenuating the impact of the natural environment. This study offers a novel perspective on the processes of wetland change and the maintenance of wetland health, which is crucial for the realisation of clean water and sanitation (Sustainable Development Goal 6.6).
1. Introduction
In recent years, global climate change has attracted considerable attention from the scientific community, becoming a prominent topic of international concern [1]. Wetlands are formed through the interaction between land and water and possess critical ecological functions, being considered one of the world’s three major ecosystems. Wetlands are frequently referred to as the “kidneys of the Earth” due to their vital role in carbon sequestration, biodiversity, and water resource maintenance. Despite occupying only 5–8% of the Earth’s land area, wetlands are estimated to store approximately 20–30% of the planet’s carbon [2]. The anoxic and humid conditions that prevail on the surface of wetland ecosystems provide an ideal environment for the isolation and storage of atmospheric carbon. Wetlands provide an optimal natural environment for the sequestration and long-term storage of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2), facilitated by anaerobic sedimentation, high autochthonous production, and the ability to capture external (marine or river) sediment inputs [3], thereby promoting long-term carbon storage in wetland ecosystems. Wetlands are also a significant biological source of methane, contributing approximately 30% of global methane emissions [4]. They represent the largest and most uncertain natural source of global CH4 emissions [5] and are considered a primary driver of the interannual variability in atmospheric methane growth rates [6]. It is therefore imperative to gain an understanding of the processes of wetland change and the impact of human activities in order to address the issue of global climate change.
The northeast region of China is home to the largest area of inland marshes in the country and is a wetland region of global significance, particularly in regard to boreal wetlands [7]. Among these, the Heilongjiang-Amur River Basin is distinguished as one of the most expansive and intricate aquatic systems in Asia, exhibiting a diverse array of wetland resources and considerable natural variability [8]. In recent years, the acceleration of climate change in mid- and high-latitude regions has disrupted various ecological processes, leading to significant changes in the wetlands of the Heilongjiang River Basin. Furthermore, in addition to the influence of natural factors, the wetlands in this region have been subjected to increasing pressure from human activities, with the impact of such activities becoming more evident over the past century [9]. Over the past three decades, a significant portion of the marshlands within the Zhalong Wetland have been converted into farmland and residential areas [10]. Over the past 50 years, human activities have had a significant impact on the area of marsh wetlands, resulting in an 81% reduction in the Sanjiang Plain and a 70% reduction in the Songnen Plain [11]. A considerable proportion of the wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin have been transformed into agricultural land, resulting in a notable decline in the quality of wetland ecosystems. This degradation has resulted in notable alterations to the structure and functionality of wetland plant communities, thereby impairing the ecological functions of these wetlands [12]. The issue of wetland conservation in the Heilongjiang River Basin requires urgent attention. In recent years, with increased development in the Far East, human activities in the Heilongjiang River Basin have intensified, posing an even greater threat to the region’s wetlands. Therefore, understanding the impact of human activities on the wetlands of the Heilongjiang River Basin is crucial for achieving a balance between regional development and wetland conservation.
A significant number of researchers have conducted studies on the impact of human activities on wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin [12,13]. These studies have distinguished between the extent of human activities and natural influences. From a results-oriented perspective, namely, the analysis of the impact of human activities on wetland landscape patterns, Song et al. (2023) concluded that over the past 100 years, human activities have fragmented the wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin into smaller, more regular patches, with the relative importance of human activity impacts being more significant over a centennial scale [9]. From a process-oriented perspective, Wang et al. (2020) identified human activities as sources of disturbance to wetlands and calculated the ecological risk index for different areas of the Heilongjiang River Basin to directly assess the impact of human activities [14]. Despite efforts to differentiate the impacts of human activities, the majority of studies continue to treat human activities as a singular impact factor, overlooking the specific effects of different types of human activities on wetlands. Given the variability in the impact processes of different human activities on wetlands, it is essential to differentiate between these activities within the context of the Heilongjiang River Basin. Nevertheless, the majority of existing research on the region has not attempted to compare the effects of different human activities. A paucity of studies has compared the impact of diverse human activities on wetland landscapes across different regions of Heilongjiang. Experimental evidence indicates that the loss of wetlands is significantly correlated with the distance to land-use/land-cover changes, with the rate of area degradation being proportional to this distance. However, this pattern does not hold for other artificial landscapes [15], indicating that different types of human activities have varying effects on wetland landscapes, particularly in terms of area impact. Sun et al. (2023) calculated the relationship between wetland degradation and agricultural activities, while Song et al. (2023) also examined the impact of different human activities and the influence of varying administrative regions, policies, international relations, or events on the wetlands of the Heilongjiang River Basin [16]. However, most of the current research is primarily focused on the relationship between wetland area and degradation intensity and human activities, without clear distinctions concerning other landscape patterns that characterise wetland health, such as fragmentation and aggregation. Some studies have detailed the impact of different human activities on wetlands in the Yellow River Basin, but the geographic and human impact characteristics differ significantly from those of the Heilongjiang River Basin, highlighting the need for in-depth studies on the typical wetlands in this region.
It is therefore imperative to gain an insight into the differential impacts of the various types of human activities on the wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin, with a particular focus on areas affected by farmland and urban expansion. This paper presents a study of landscape patterns in three wetlands situated in urban, rural, and natural areas of the Heilongjiang River Basin. This study was conducted between 2002 and 2022 with the objective of investigating the impacts of human activities on wetland landscapes. This study compares and contrasts the impacts of urban and agricultural expansion on wetland landscapes in the Heilongjiang Basin. Furthermore, it delineates the impact of human activities on wetlands in seasonal tundra areas, with a particular emphasis on aggregation and other pertinent factors. Furthermore, the extent of wetlands was selected from different administrative regions in order to facilitate the comparison of disturbances arising from administrative divisions. This paper introduces a novel perspective on the Heilongjiang River Basin, with a view to comparing the differences in landscape patterns of typical wetlands in the region under various human activities. This paper presents a methodology for calculating the temporal changes in landscape patterns under different human impacts and comparing them with natural wetlands. This approach allows for the distinction of the impacts of different human activities on wetlands, thereby providing support for SDG 6.6. This paper selects three typical wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin, situated in proximity to urban, rural, and natural areas, respectively, with the objective of comparing changes in landscape patterns under the influence of different human activities from 2002 to 2022. This paper addresses three key research questions: (1) the changes in area and landscape patterns of these three typical wetlands over the past two decades; (2) the varying impacts of different human activities on these wetland landscape patterns; and (3) the potential reasons for the different impacts of human activities on wetland landscape patterns.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
This study selects three typical wetlands in Heilongjiang Basin as the study area, each located in close proximity to urban, rural, and natural areas, respectively, with the aim of comparing the differential impacts of various human activities. The three wetlands are situated in the Sanjiang Plain, an alluvial plain formed by the Heilongjiang, Wusuli, and Songhua Rivers. The plain is characterised by abundant water resources and extensive wetland coverage. The southwestern portion of the Sanjiang Plain represents the most extensive marshland region. Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of the three wetlands. Wetland A is situated to the southeast of Qiqihar City, at a distance of 20 km from the main urban area, and encompasses an area of 1315.99 km2. The site is surrounded by a number of villages and towns, which have been significantly impacted by the expansion of impermeable surfaces. These surfaces are primarily composed of marsh-type wetlands. The central coordinates are 47.05° N, 124.19° E. Wetland B is located on the southern bank of the lower Heilongjiang River, within the territory of the People’s Republic of China. It covers an area of 1182.67 km2. The site is surrounded by extensive farmland, which is subject to significant agricultural activity, and is primarily composed of marsh-type wetlands. The central coordinates are 47.11° N, 124.26° E. Wetland C is situated primarily on the northern side of the lower Heilongjiang River, within the territory of the Russian Federation, and covers an area of 898.27 km2. The area is predominantly surrounded by grasslands and forests, with minimal human impact, and is characterised by swamp-type wetlands. The central coordinates are 48.45° N, 133.61° E. The disparate national jurisdictions of Wetlands B and C give rise to variations in their respective developmental levels. Despite their proximity, the barrier effect of the Heilongjiang River and the differing administrative regions has resulted in distinct impacts from human activities. The three study areas were selected on the basis of their comparable dimensions. However, due to its more concentrated distribution, Wetland A encompasses a more extensive wetland area within the study region.
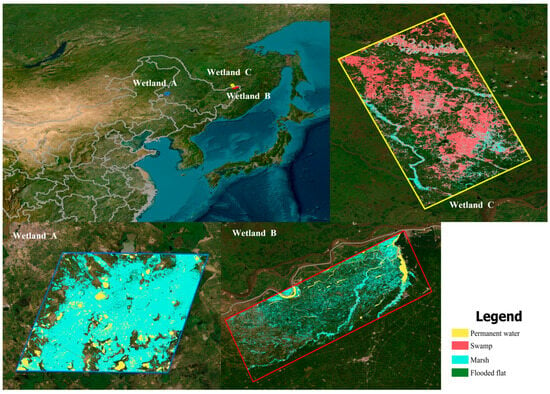
Figure 1.
Distribution of typical wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin. (Data courtesy of Earthstar Geographics).
2.2. Data Pre-Processing
This study employed the GWL_FCS30D dataset developed by Zhang et al. (2024) to ascertain the extent and categories of the aforementioned three wetlands [17]. The dataset employs time-series Landsat images and the Google Earth Engine platform to generate a global wetland map with a resolution of 30 metres. It encompasses the period from 2000 to 2022, with annual updates. The dataset comprises eight distinct wetland subcategories. In 2020, the dataset demonstrated an overall accuracy of 86.95% ± 0.44% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.822, indicating a high degree of accuracy.
In order to facilitate the analysis, data from five specific years (2002, 2007, 2012, 2017, and 2022) were extracted, comprising a total of 15 scenes. The extent of the wetlands within the study areas was delineated by merging multiple wetland map slices using open-source QGIS software 3.28.11. A binary classification was employed to distinguish between wetland and non-wetland areas. A variety of landscape pattern indices were calculated for the 15 scenes using the landscape analysis software Fragstats 4.2. A total of 109 class-level and 116 landscape-level indices were selected, representing patch area, shape, proximity, fragmentation, and diversity characteristics at the landscape level. The similarity search range and the threshold for the associated index calculation were both set to 50 metres. Figure 1 illustrates the specific types of wetlands described above.
2.3. Method
Landscape indices are an effective means of condensing landscape pattern information, thereby serving as simple quantitative indicators that reflect the characteristics of landscape structure and spatial pattern changes. Table 1 delineates the landscape pattern indices utilised in this study, which can be employed to characterise the area, shape, degree of fragmentation, and other indicators of wetlands. Through these indices, the landscape pattern of typical wetlands is calculated in this paper.

Table 1.
Landscape pattern indices used in this study and calculation methods.
The principles and methodologies of landscape patterns have been applied in wetland research since the 1980s [18,19]. From a scientific perspective, landscape patterns encapsulate the spatial distribution of ecosystem services [20], the value of these services [21], and the sustainability [22] of wetland ecosystems. These patterns are used as a means of measuring the health of wetland ecosystems. The analysis of landscape patterns is conducted at three hierarchical levels: the individual patch level, the patch type level, and the landscape mosaic level. Similarly, landscape indices are also categorised at these three levels: individual patch indices, patch type indices, and landscape mosaic indices. This study employs wetlands as the research subject and utilises five landscape indices to evaluate the wetlands, as illustrated in Table 1. There have been studies by other researchers using partial indices [23].
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Changes in the Area of Typical Wetlands
As illustrated in Figure 2a, the average area of Wetland A over the past twenty years has been 983.75 km2, representing 68% of the total area of the Study Region A due to its relatively concentrated distribution. From 2002 to 2007, the area of this wetland exhibited a gradual increase, reaching a peak of approximately 1000 km2 in 2007. However, the area subsequently exhibited a decline, with the total area of Wetland A reaching approximately 960 km2 by 2022. Over this 15-year period, the wetland area contracted by approximately 40 km2, with a shrinkage rate of approximately 2.7 km2 per year. Over the two decades, Wetland A exhibited a relatively uniform decreasing trend, with an overall net reduction of 30 km2, which is likely due to the annual increase in the surrounding impermeable surfaces gradually encroaching upon and reducing the wetland area.
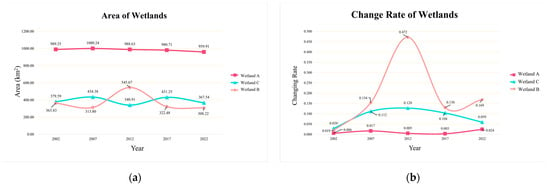
Figure 2.
Map of typical wetland areas and their proportional changes. ((a). Area of three types of wetlands from 2002 to 2022; (b). The change rate of wetlands from 2002 to 2022. The red, orange and blue lines represent Wetland A, Wetland B and Wetland C, respectively).
The mean area of Wetland B over the past twenty years was approximately 370.8 km2, representing an average of 31% of the total area of Study Region B. The study demonstrates that Wetland B exhibited an initial increase, followed by a subsequent decrease, with notable fluctuations. The wetland area reached its maximum extent of approximately 545 km2 around 2012. However, following 2012, the area underwent a rapid decline, reaching 308 km2 by 2022. This represented a reduction of 237 km2 over ten years, with a shrinkage rate of approximately 23.7 km2 per year. The period between 2007 and 2017 saw the most significant fluctuations in wetland area, with absolute changes reaching approximately 400 km2. In conclusion, the area of Wetland B exhibited a slight overall decrease over the twenty-year period, with a net reduction of 46 km2. The absolute and proportional shrinkage of Wetland B was significantly higher than that of Wetland A.
Wetland C remained relatively stable over the long term, with minimal interannual variation. Over the twenty years, the net change in Wetland C was only −12 km2, indicating a stable condition.
Additionally, the study compared the fluctuation characteristics of the areas of the three typical wetlands, as illustrated in Figure 2b. The degree of dispersion of the total area and the average value of the wetlands were calculated on a five-yearly basis from 2002 to 2022. The results demonstrate that the fluctuations in Wetlands B and C both exhibited a trend of initial increase, followed by subsequent decrease. In particular, the period between 2007 and 2017 saw a relatively high rate of change in wetland areas, with considerable variance.
Wetland A exhibited the lowest average fluctuation, with a fluctuation rate of only 1.1%. The period exhibiting the greatest fluctuation for Wetland A was from 2017 to 2022, with a fluctuation rate of 2.4%. Wetland B exhibited the highest average fluctuation, with a fluctuation rate of 18.7%. Additionally, the maximum fluctuation exceeded 47%. In contrast, Wetland C demonstrated comparatively minimal fluctuations, with a fluctuation rate of 8.6%. It is noteworthy that the maximum fluctuation rates for Wetlands B and C both occurred in 2012, while all three typical wetlands exhibited relatively minor changes in 2002.
From a trend perspective, Wetland A, which is subject to the expansion of impermeable surfaces, exhibited an inverse trend to Wetland C, which is not affected by human activities. Conversely, Wetland B, which is subject to the effects of agricultural activities, exhibited a trajectory comparable to that of Wetland C.
3.2. Temporal Changes and Analysis of Landscape Patterns in Typical Wetlands
In landscape pattern analysis, a variety of parameters are employed to quantify the characteristics of landscape structure and the ecological processes that occur within it. These parameters are primarily grouped into five categories: area-edge parameters, shape parameters, core area parameters, contrast parameters, and aggregation parameters. The present study is concerned with the landscape characteristics of wetlands, with a view to selecting parameters that will represent the landscape patterns typical of such wetlands.
Figure 3a illustrates the shape characteristics of the three wetlands, employing the Landscape Shape Index (LSI) as the evaluation criterion. The Landscape Shape Index (LSI) is a measure of the degree of departure from a standard shape (typically circular or square) of an area equal in size to that of the patch in question. In comparison to the other wetlands, Wetland A demonstrated minimal alterations in the Landscape Shape Index, suggesting that the configuration of this wetland remained relatively consistent and aligned with the standard shape over the twenty-year period. Wetland B demonstrated considerable fluctuations in the Landscape Shape Index, with notable absolute values. The index demonstrated a notable decline during the initial ten-year period, indicating a transition from a more complex to a more regular shape, with the lowest point reached in 2012. Subsequently, the index increased, indicating a return towards greater complexity. The Landscape Shape Index of Wetland C exhibited a consistent evolution towards more regular shapes over the twenty-year period. The results of these analyses indicate that different wetlands exhibit distinct patterns of landscape change, which are influenced by a range of factors, including human activities and natural processes. The findings offer insights into the dynamics of wetland landscape structures and their responses to external pressures.
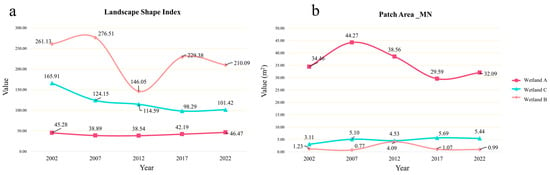
Figure 3.
Plot of changes in indices characterising the size and shape of wetland patches. ((a). Landscape Shape Indices of the three wetlands; (b). Average patch area of the three wetlands. The red, orange and blue lines represent Wetland A, Wetland B and Wetland C, respectively).
The evaluation of patch size within wetland areas, along with an analysis of their edge characteristics, is a fundamental aspect of area-edge information. As illustrated in Figure 3b, the mean patch area was identified as a pivotal parameter for evaluating the internal area of typical wetlands. Wetland A exhibits a more concentrated patch distribution, resulting in significantly larger patch areas in comparison to the other two wetlands. From 2002 to 2022, Wetland A exhibited fluctuations in patch area, initially increasing and then decreasing, reaching a maximum of 44.27 km2 in 2007. The average patch area in Wetland A reached its largest size around 2007, indicating optimal connectivity between patches. Subsequently, the mean patch area exhibited a precipitous decline, decreasing by approximately 15 km2 over a ten-year period. By 2022, it had reverted to levels approximating those observed two decades prior. The average patch area of Wetlands B and C is smaller. The average patch area of Wetland B exhibited minimal variation, reaching a peak in 2012 with fluctuations of approximately 1 km2 in other years. In contrast, the average patch area of Wetland C exhibited a gradual increase over the past two decades, suggesting enhanced connectivity and the consolidation of smaller patches into larger ones.
Figure 4 illustrates the temporal changes in core area, contrast, and aggregation parameters for the three wetlands. Figure 4a illustrates the landscape changes in Wetland A. The Aggregation Index (AI) of Wetland A has experienced minimal change, maintaining a relatively stable state over the long term. Contrast-Weighted Edge Density (CWED), measured in metres per hectare (m/ha), demonstrated a trajectory of initial decline and subsequent growth over the past two decades. This suggests a gradual increase in the edge density of wetland patches per unit area, indicating a potential trend towards fragmentation. The core area of Wetland A initially exhibited an increase, reaching its maximum in 2007, and subsequently demonstrated a decline. It is noteworthy that the trends observed in CWED and core area were diametrically opposed. From 2002 to 2007, the core area exhibited an increase while edge density demonstrated a decrease, indicating aggregation and a healthier wetland condition. Conversely, from 2007 to 2022, the core area exhibited a decrease while CWED demonstrated an increase, indicating an increase in fragmentation and a decline in wetland health. Figure 4b illustrates the landscape pattern of Wetland B, wherein AI and CWED exhibited contrasting trends. From 2002 to 2012, there was a reduction in fragmentation and an increase in aggregation, which was accompanied by an expansion of the core area. However, between 2012 and 2022, there was a notable decline in the core area, accompanied by an increase in fragmentation. This suggests a deterioration in the wetland’s condition. Figure 4c illustrates the landscape pattern of Wetland C, which demonstrates a gradual increase in both aggregation and core area, accompanied by a rapid decrease in fragmentation. This suggests an improvement in the ecological environment.
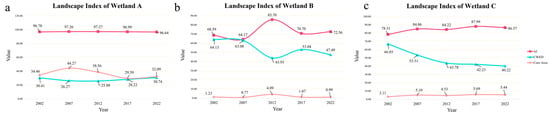
Figure 4.
Wetland core, contrast and aggregation parameters. ((a). The core, contrast and aggregation parameters of Wetland A; (b). The core, contrast and aggregation parameters of Wetland B; (c). he core, contrast and aggregation parameters of Wetland C. The red, blue, and orange lines represent AI, CWED and Core Area, respectively).
3.3. Impacts of Different Human Activities on Wetland Landscape Patterns
Figure 3 and Figure 4 demonstrate that over the twenty-year period, Wetland A exhibited a declining trend in average patch area and an increasing trend in the Landscape Shape Index, indicating that Wetland A is becoming increasingly irregular in shape. Similarly, the average patch area of Wetland B also exhibited a notable decline in comparison to the data from 2002. In contrast, Wetland C exhibited a slight increase in average patch area over the twenty years, and the Landscape Shape Index indicates that its patches are becoming more regular and closer to a standard shape. Both Wetlands A and B, which are subject to human influence, demonstrate a pattern of deterioration, with the area and shape of patches exhibiting difficulty in restoration through natural processes. In a natural state, the area and shape of wetland patches tend to recover at a slow rate.
Given that the area of different wetland regions may impact shape and average patch area, this study normalised the shape and average patch area indices of the wetlands, scaling the indices to a 0–1 range. Figure 5a,b illustrate the temporal evolution of the normalised indices. As illustrated in Figure 5a, the Landscape Shape Index of Wetland C demonstrates a gradual decline, whereas Wetlands A and B exhibit a pattern of initial decrease followed by an increase. The findings indicate that in a natural state, wetland shapes tend to become increasingly standardised. Notwithstanding considerable fluctuations, the shape of Wetland B continues to trend towards a standard form, potentially attributable to the clustered agricultural development, which artificially regularises the shapes of surrounding agricultural fields, thereby influencing wetland shapes. As illustrated in Figure 5b, the average patch area of Wetland C also demonstrates an upward trajectory, which is markedly divergent from the trend observed in wetlands subjected to human influence.
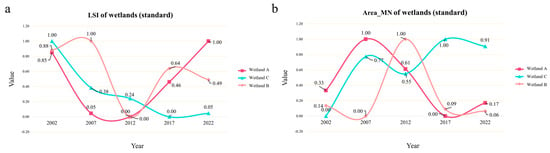
Figure 5.
Map of standardised changes in wetland area and shape. ((a). Standardised wetland landscape shape index; (b). Average area of standardised wetlands. The red, orange and blue lines represent Wetland A, Wetland B and Wetland C, respectively).
In conclusion, human activities result in a reduction in the average patch area of wetlands, as well as an irregularity in the shapes of wetland patches when compared to their natural state.
Moreover, this study examined the influence of human activities on the core area, contrast, and aggregation parameters of wetlands. Figure 6a–c, respectively, illustrate the standardised temporal changes in CWED, CORE_MN, and AI.

Figure 6.
Wetland contrast, core, and aggregation change maps.((a). Standard Contrast-Weighted Edge Density of wetlands; (b). The Standard average core area of wetlands; (c). Standard Aggregation Index of wetlands. The red, orange and blue lines represent Wetland A, Wetland B and Wetland C, respectively).
As illustrated in Figure 6a, the CWED index of Wetland C demonstrates a gradual decline, indicative of diminished edge density and enhanced ecological integrity. In contrast, Wetlands A and B display considerable fluctuations as a result of human activities, which lead to an increase in internal shapes and fragmentation. In natural conditions, the internal edge density of wetlands is observed to decrease, which contributes to the maintenance of healthier ecosystems.
With regard to the core area, as illustrated in Figure 6b, the core area of Wetland C has demonstrated a consistent increase over the past twenty years. In contrast, the core areas of Wetlands A and B have exhibited a decline over time, attributable to human activities. It is notable that the presence of impermeable surfaces has resulted in a sustained reduction in the core area of Wetland A, while the impact of agricultural activities on the core area of Wetland B reached a particularly pronounced level around 2012.
As illustrated in Figure 6c, the AI of natural Wetland C has exhibited an annual increase, indicative of enhanced aggregation and an improved wetland health status. In contrast, Wetlands A and B demonstrate a pattern of initial growth followed by a decline in aggregation, indicating an overall downward trend. This indicates that human activities have resulted in a more dispersed distribution of wetlands.
In conclusion, human activities exert a considerable influence on wetland landscapes, affecting their extent, core zone, and aggregation degree.
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Impact
As illustrated in Figure 2a, the area variations of typical wetlands demonstrate notable discrepancies despite the comparable dimensions of the study regions. Wetland A exhibits a markedly greater area than Wetlands B and C, with comparatively minor fluctuations. In contrast, Wetlands B and C display greater variability in area. This may be attributed to a number of factors. Firstly, Wetlands B and C are situated downstream of the Heilongjiang River, in closer proximity to the ocean, and are subject to greater influence from monsoon and river hydrological fluctuations, resulting in greater area variability. Wetland A, being an inland wetland, is less susceptible to the effects of hydrological and monsoon influences. This finding is consistent with the results of other studies, which have demonstrated that coastal wetlands frequently display considerable fluctuations in area [15]. While precipitation and groundwater can also contribute to changes in inland wetlands, the overall fluctuations are relatively minor [24].
Secondly, the impact of impermeable surfaces on wetland area is comparatively limited. The high cost of adding new impermeable surfaces, coupled with their lengthy lifespan and semi-permanent nature, results in a gradual and sustained influence. In contrast, agricultural lands are subject to greater influence from human activities. The costs of reclaiming farmland and creating polders are lower, and these activities are more susceptible to subjective interference by individuals. In order to offset or mitigate the impacts of climate change on agricultural yields, there is significant potential for fluctuations in agricultural interference with wetlands. In our preceding study, we discovered that comparable alterations were observed in the wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Here, agricultural activities predominantly eroded from the periphery of the wetlands towards the interior, which constituted the primary cause of the reduction in wetland area [25]. Furthermore, the presence of impervious surfaces impeded the connectivity of the wetlands within the wetlands, which corroborates the findings of this study [26]. Furthermore, the most conspicuous alterations in land use and land cover across the remainder of the Heilongjiang River Basin were the precipitous decline in wetland area and the concomitant surge in cropland area. Furthermore, research has indicated that the construction of roads can result in a notable decline in biodiversity within wetland habitats situated more than 1 km from the road [27]. This phenomenon may be attributed to the fragmentation of wetland ecosystems.
Figure 2b illustrates the rate of area change in wetlands that are representative of the typical wetland type. In 2012, significant area changes were observed in Wetlands B and C, which were likely caused by the large-scale rainfall associated with Typhoon No. 15. This led to an abnormal increase in wetland area in the Heilongjiang region. This typhoon was one of the most severe to affect Heilongjiang in recent years. Furthermore, the selection of training samples from areas that had never been wetlands for many years in the GWL_FCS30D dataset may have resulted in an overestimation of wetland areas during the classification process. The classification data source primarily relied on regional spectral characteristics, which may have resulted in the misclassification of flooded farmlands as wetlands, contributing to the anomalous expansion of wetland areas in 2012.
Despite their proximity, the Coriolis effect in the Northern Hemisphere causes river flows to deflect towards the southern bank of Wetlands B and C, rendering the south bank more susceptible to erosion and flooding. It can be reasonably deduced that Wetland B is more susceptible to flooding. Moreover, the southern section of Wetland B is characterised by a paucity of vegetation and comprises predominantly plains and farmland, whereas the northern area is dominated by natural vegetation, rendering it less susceptible to flooding.
It is also noteworthy that the trends in Wetlands B and C are completely opposite, which may be attributed to changes in human activities on the southern side affecting the wetlands. For instance, the extensive reclamation of farmland in the vicinity of Wetland B may result in a reduction in water levels on the southern side, leading to the accumulation of significant volumes of floodwater on the northern bank and an increase in the area of Wetland C. This finding is consistent with existing research indicating that agricultural and human development in the northeastern region exert a considerable influence on the extent of southern river wetlands, resulting in notable discrepancies in area changes despite their proximity [28].
4.2. Quantitative Comparison
In order to evaluate the impact of diverse human activities on wetland ecosystems, this study has selected a set of four landscape parameters for the quantitative comparison of the effects of various activities. Figure 7a illustrates the landscape Aggregation Index for the three wetlands in question. Although Wetlands B and C have similar areas, Wetland C is significantly more aggregated than Wetland B. Furthermore, Wetland A is more aggregated than the other two wetlands, likely due to its location within a wetland protection area where extensive restoration and conservation efforts are made to ensure wetland aggregation. In natural conditions, agricultural activities have been observed to reduce wetland aggregation.
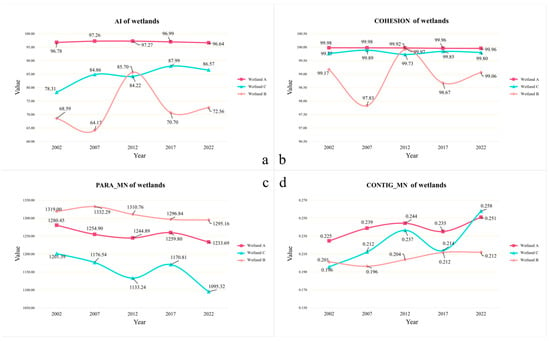
Figure 7.
Comparison of quantitative wetland parameters. ((a). Aggregation Index of wetlands; (b). Cohesion of wetlands; (c). The average of PARA Index of wetlands; (d). The average of Contig Index of wetland. The red, orange and blue lines represent Wetland A, Wetland B and Wetland C, respectively).
Figure 7b presents a similar illustration of the degree of aggregation among the wetlands. Wetland A, situated within the designated conservation area, exhibits a comparable degree of aggregation to that observed in naturally occurring Wetland C. In contrast, Wetland B displays a markedly lower level of aggregation. This suggests that agricultural activities have a significant impact on the degree of wetland aggregation. Figure 7c illustrates the average perimeter–area ratio of the wetlands, representing the average ratio of patch perimeter to area, which is used to evaluate the complexity of landscape shapes. The results demonstrate that agricultural activities exert a considerable influence on wetland morphology, enhancing their complexity to a greater extent than impermeable surfaces. However, both exhibit a discernible increase in comparison to their natural condition.
Figure 7d quantifies patch connectivity by calculating the average adjacency value of patches. This study demonstrates that farmland has a greater impact on wetland connectivity than buildings. Despite the effectiveness of protection areas in maintaining wetland connectivity, the impact of buildings can still cause disruption.
These findings highlight the varying degrees of impact that different human activities have on wetlands, emphasising the need for targeted conservation and management strategies to mitigate negative effects and promote wetland health.
4.3. Prospects and Limitations
It has been demonstrated that there are considerable discrepancies in the consequences of human activities on the configuration of wetlands. Agricultural influences are somewhat arbitrary and irregular, with the primary impact being the erosion of wetlands, which results in a reduction in wetland area. In contrast, the impact of impervious surfaces is more consistent, primarily affecting wetland connectivity. While there is a paucity of studies that can ascertain which activity will have a more pronounced impact on wetlands, neither should be underestimated. It is evident that the protection of wetlands cannot be achieved through the complete cessation of agricultural and impervious surface development. Instead, a policy equilibrium must be established. (1) The construction of artificial wetlands should be considered [29]. The Heilongjiang Basin, which is endowed with abundant water resources, has been identified as a suitable location for the construction of artificial wetlands, which can serve to impede the encroachment of agriculture [30]. (2) It is recommended that suspension bridges be used as much as possible to construct roads within wetlands. Researchers have identified road construction as a significant concern due to the disruption caused by impervious surfaces to wetland continuity from within the ecosystem. Studies have demonstrated that road construction hinders the expansion of wetlands, underscoring the necessity to minimise contact between impervious surfaces and wetlands [31,32,33].
Nevertheless, this study is not without limitations. Primarily, the influence of the natural environment cannot be entirely discounted. Wetland A and Wetland BC are situated at considerable distances from one another and are subject to a certain degree of environmental variation. Despite the normalisation process, natural differences remain. Secondly, the data collection interval is 5 years, which may not be sufficiently frequent to capture extreme events such as floods, which could potentially impact the trend. Thirdly, the influence of human activities is complex and may have direct or indirect effects, making it challenging to discern the precise influence process. Additionally, this study did not consider the coupled effects of human activities and the natural environment. For instance, human activities may exert a greater influence under drought conditions and other circumstances.
The impact of human activities on wetlands is a highly complex process, which not only directly affects the landscape characteristics, such as wetland area and connectivity, but also causes wetland degradation by precipitating hydrological changes and vegetation changes. Hydrological factors, including water quantity and quality, hydrological conditions, and the continuity and stability of water sources, all exert a constraining influence on the formation and development of marshes [34]. A decline in the Heilongjiang River Basin has been observed since the 1950s, resulting in significant alterations to the wetland environment and, to some extent, a reduction in wetland area [35]. Furthermore, human activities have been demonstrated to exert a profound influence on wetland hydrology, which may have a more pronounced impact on water quality [36], water level [37], and wetland perimeter [38], ultimately resulting in alterations to wetland landscapes. In addition, human activities have affected wetland vegetation [39], which in turn has led to changes in the wetland landscape.
5. Conclusions
This study examined the alterations in the landscape patterns of three representative wetlands in Heilongjiang Basin between 2002 and 2022. The findings illustrate the varying impacts of diverse human activities on wetland ecosystems. The impact of urban expansion on wetlands has been relatively limited within this typical range of wetland habitats. However, changes in wetland area have been predominantly influenced by agricultural activities, with agricultural expansion being the primary driver of wetland loss in these regions. Furthermore, the effects of agricultural activities on wetlands are more variable. They can invade from multiple directions simultaneously, which intensifies the irregularity of wetland shape. In contrast, the expansion of impervious surfaces has a less pronounced impact on wetland shape. With regard to the impact on average patch size, the expansion of impervious surfaces was found to exert a greater influence, while agriculture was observed to have a comparatively lesser impact. Dramatic changes in the area of a single patch indicate a large change in the number of patches when the total area has not been significantly affected. This suggests that impervious surfaces can disrupt wetland connectivity and lead to the fragmentation of a larger patch, whereas agricultural activity rarely breaks up contiguous patches. This is analogous to the conclusion reached by AI and CWED, which, in the absence of significant fluctuations in aggregation and area, indicates that damage to wetlands from impervious surfaces tends to manifest as a disruption of connectivity. The impact of agricultural activities on wetlands is more subjective, i.e., there are fewer rules when residents reclaim wetlands for farmland, whereas the erosion of impervious surfaces on wetlands appears to be more planned. For example, CWED fluctuates significantly under the influence of agriculture, while impervious surface expansion shows more regular changes. This paper makes a significant contribution to the existing literature by identifying differences in the impacts of agriculture and construction on wetland landscape patterns in wetlands in the Heilongjiang basin. Furthermore, it minimises the impacts of natural factors on these wetlands by comparing the temporal sequence with that of natural wetlands. Additionally, this paper provides new insights into the long-term influence process of human activities on wetlands in the Heilongjiang River Basin, which offers valuable perspectives for achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6.6.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; methodology, J.L., X.D. (Xinyu Dou) and L.Z.; validation, J.L. and Z.L.; formal analysis, J.L. and D.L.; investigation, Y.L.; resources, Y.L.; data curation, X.D. (Xiaobing Du); writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, L.Z.; visualization, Q.Z.; project administration, L.Z.; funding acquisition, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Research and Development Project of Guangxi [grant number GuikeAB24010046], and the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number U2268217].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, and further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, B.X.; Kjaerulf, F.; Turner, S.; Cohen, L.; Donnelly, P.D.; Muggah, R.; Davis, R.; Realini, A.; Kieselbach, B.; MacGregor, L.S.; et al. Transforming our world: Implementing the 2030 agenda through sustainable development goal indicators. J. Public Health Policy 2016, 37, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altor, A.E.; Mitsch, W.J. Methane flux from created riparian marshes: Relationship to intermittent versus continuous inundation and emergent macrophytes. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 28, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Nielsen, D.A.; Kelleway, J.J.; Atwood, T.B.; Seymour, J.R.; Petrou, K.; Connolly, R.M.; Thomson, A.C.; Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Ralph, P.J. Can we manage coastal ecosystems to sequester more blue carbon? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciais, P.; Sabine, C.; Bala, G.; Bopp, L.; Brovkin, V.; Canadell, J.; Chhabra, A.; DeFries, R.; Galloway, J.; Heimann, M.; et al. Carbon and Other Biogeochemical Cycles. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamaschi, P.; Houweling, S.; Segers, A.; Krol, M.; Frankenberg, C.; Scheepmaker, R.A.; Dlugokencky, E.; Wofsy, S.C.; Kort, E.A.; Sweeney, C.; et al. Atmospheric CH4 in the first decade of the 21st century: Inverse modeling analysis using SCIAMACHY satellite retrievals and NOAA surface measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7350–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, E.G.; Dlugokencky, E.J.; Bousquet, P. Methane on the rise again. Science 2014, 343, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, G.; Mao, M.; Duan, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Qiu, X.; Gong, W.; Liu, T.; et al. Remote sensing and environmental assessment of wetland ecological degradation in the Small Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1125775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Yu, L.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Bao, L. Wetland vegetation cover changes and its response to climate changes across Heilongjiang-Amur River Basin. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1169898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; He, H.S.; Liu, K.; Du, H.; Krohn, J. Impact of historical pattern of human activities and natural environment on wetland in Heilongjiang River Basin. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, X.D.; Zang, S.Y.; Zhang, N.N.; Cui, J. Impact of land use and land cover dynamics on Zhalong wetland reserve ecosystem, Heilongjiang Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Impacts and countermeasures of climate change on wetland ecohydrology taking the Nenjiang River Basin wetland as an example. Ground Water 2014, 36, 197–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Meng, F.; Yu, Z.; Tan, Y. Spatial–temporal characteristics and influencing factors of farmland expansion in different agricultural regions of Heilongjiang Province, China. Land Use Policy 2022, 115, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gong, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, T. Analysis of Disturbance Factors in Zhalong Wetland Landscape Dynamics. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 730, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, C.; Song, K. Regional ecological risk assessment of wetlands in the Sanjiang Plain with respect to human disturbance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Lu, M. Human activities introduced degenerations of Wetlands (1975–2013) across the Sanjiang Plain north of the Wandashan Mountain, China. Land 2021, 10, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Li, X.; He, H.; Sunde, M. Centennial Analysis of Human Activity Intensity and Associated Historical Events in the Heilongjiang River Sino-Russo Watershed. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 34, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, X. Global annual wetland dataset at 30 m with a fine classification system from 2000 to 2022. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L. Spatiotemporal change and landscape pattern variation of eco-environmental quality in Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration from 2001 to 2015. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125534–125548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Progress on the study of process of wetland landscape changes and cumulative environmental effects. Prog. Geogr. 2003, 22, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.S.; Qiao, B.; Chen, G.Q.; Shi, F.F.; Cao, X.Y.; Zhu, C.X. Land use change and evolution of ecosystem service value in Maduo County of source region of the Yellow River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Mo, S.; Wu, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Influence of human activities and climate change on wetland landscape pattern—A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 879, 163112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Yuan, X. Alternative stable state and its evaluation in wetland reconstruction based on landscape design. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B.; Da, L. Analysis on the dynamic changes of landscape patterns of Longfeng wetland nature reserve in 1979–2008. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress 2012, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 24–28 June 2012; Volume 16, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Jensen, K.; McDonald, K.; Hugelius, G.; Gumbricht, T.; Carroll, M.; Prigent, C.; Bartsch, A.; Poulter, B. Development of the global dataset of Wetland Area and Dynamics for Methane Modeling (WAD2M). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2001–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gou, Y.; et al. Dynamic landscapes and the influence of human activities in the Yellow River Delta wetland region. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 899, 166239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Z.M.; Mao, D.H.; Ren, C.Y.; Han, J.X. Remote sensing classification of Wetlands using Object-oriented method and Multi-season HJ-1 Images—A case study in the Sanjiang plain North of the Wandashan Mountain. Wetl. Sci. 2012, 10, 429–438. [Google Scholar]
- T Findlay, C.S.; Bourdages, J. Response time of wetland biodiversity to road construction on adjacent lands. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Pan, H.; Jia, M. Tracking historical wetland changes in the china side of the Amur River Basin based on landsat imagery and training samples migration. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.A.; Liu, X.x.; Du, H.r.; Zhang, M.H. Can artificial ecological islands alter the biodiversity of macroinvertebrate? A case study in Fujin National Wetland Park, the Sanjiang Plain, China. Ecol.Evol. 2021, 11, 14988–15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Li, Y. Study of artificial water replenishment for wetland restoration. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.; Icely, J.; Cristina, S.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Turner, R.E.; Ashan, D.; Cragg, S.; Luo, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Anthropogenic, direct pressures on coastal wetlands. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams-Mounsey, J.; Grayson, R.; Crowle, A.; Holden, J. A review of the effects of vehicular access roads on peatland ecohydrological processes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 214, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekmohammadi, B.; Uvo, C.B.; Moghadam, N.T.; Noori, R.; Abolfathi, S. Environmental risk assessment of wetland ecosystems using Bayesian belief networks. Hydrology 2023, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.J.; Muneepeerakul, R.; Pumo, D.; Azaele, S.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Hydrological drivers of wetland vegetation community distribution within Everglades National Park, Florida. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, Y. A dynamic change map of marshes in the Small Sanjiang Plain, Heilongjiang, China, from 1955 to 2005. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 23, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, M.; Ma, R.; Zhou, H.; Zou, S.; Gan, Y. Nitrate distribution under the influence of seasonal hydrodynamic changes and human activities in Huixian karst wetland, South China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2020, 234, 103700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Răducă, C.; Boengiu, S.; Mititelu-Ionuș, O.; Enache, C. Correlation of the relief conditions, hydrographic network features and human interventions within the Blahniţa river basin (southwestern Romania). Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 16, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.L.; Stefani, M.S.; Smith, W.; Schiavone, D.C.; da Cunha-Santino, M.B.; Bianchini, I., Jr. An applied ecological approach for the assessment of anthropogenic disturbances in urban wetlands and the contributor river. Ecol. Complex. 2020, 43, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Gao, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Cong, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, G. Potential in paleoclimate reconstruction of modern pollen assemblages from natural and human-induced vegetation along the Heilongjiang River basin, NE China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).