Abstract
Innovation serves as the cornerstone for high-quality development in high-tech enterprises, with intelligent development emerging as a central aspect of innovation efforts. However, how intelligent development promotes the innovative development of high-tech enterprises is still a topic of continuous debate and exploration. By integrating enterprise innovation theory and knowledge-based theory, this paper constructs a theoretical framework to examine the influence of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation. Through an analysis of 694 listed high-tech enterprises on China’s manufacturing A-share market from 2013 to 2021, we empirically investigated the effects of mediating mechanisms and moderating effects of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation. The results show that intelligent development significantly boosts high-tech enterprise innovation. Knowledge breadth plays a mediating role in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation, indicating that intelligent development promotes high-tech enterprise innovation by enhancing knowledge breadth. Additionally, knowledge absorptive capacity can strengthen the impact of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation, that is, the stronger the knowledge absorptive capacity, the greater the impact of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation. The conclusion of this paper provides a theoretical basis and practical guidance for high-tech enterprises regarding how to better use intelligent technology for innovation. Relevant enterprises can strengthen their knowledge management and mobility strategies and fully utilize the potential of intelligent technology to achieve more innovative and competitive development.
1. Introduction
As technology continues to advance and global industries undergo transformation, innovation has emerged as the driving force behind enterprises achieving a competitive edge and fueling economic growth. Innovation theory points out that innovation is the recombination of production factors and this combination is a process of creative destruction [1], which not only promotes the progress of technology and the development of productivity [2] but also forces enterprises to constantly adapt their strategies to new market demands and competitive situations. The Chinese government has emphasized the implementation of an innovation-driven development strategy, elevating the strategic importance of innovation to the national level. This underscores the critical role of innovation in a nation’s path to prosperity. As an important force promoting the transformation and upgrading of enterprises, high-tech enterprises have high innovation ability and innovation levels, which is an important pillar of the development of the national economy and also the main performance indicator of national innovation and development. However, with the continuous development of digital technology, high-tech enterprises are facing increasing competitive pressure and market changes. Relying only on traditional innovative means can no longer meet the rapid development needs of enterprises. Therefore, it is particularly important to explore the driving forces of high-tech enterprise innovation under the background of new technology.
Intelligent technology, a technology that simulates intelligent human behavior [3], has surpassed human thinking in enterprise applications and is reshaping the innovation path across various industries, including high-tech enterprises. The application of intelligent technology not only helps high-tech enterprises to obtain more in-depth market insight, accurately grasp the needs and changes of the market, and innovate enterprise products and services but can also change an enterprise’s innovation mode, reduce the cost of innovation, shorten the innovation cycle, and achieve the leapfrog development of innovation level. In this process, how can intelligent development drive high-tech enterprise innovation? What are the specific mechanisms and paths? What are the boundary conditions? This has become the main concern of all circles.
Scholars have conducted numerous explorations on the relationship between intelligent development and enterprise innovation. Most authors believe that intelligent development can drive enterprise innovation. For example, Mariani et al. (2023) conducted a systematic overview of the innovation research chain of artificial intelligence and explained in detail the driving factors and outcomes of enterprises adopting artificial intelligence for innovation [4]. Haefner et al. (2021) analyzed how artificial intelligence reshapes enterprises and affects innovation management, arguing that artificial intelligence might force management to rethink the entire innovation process [5]. Brem et al. (2023) discussed different ways in which artificial intelligence changes innovation and noted that artificial intelligence acts as a creator and promoter of innovation [6]. However, due to the high complexity and broad application scope of intelligent development, existing studies mainly focused on its macro-level effects, while there is still a lack of in-depth exploration of its specific micro-level mechanisms, such as how the internal innovation processes within enterprises become more efficient as a result of intelligent development.
Intelligent development exerts a profound influence on enterprise innovation by optimizing the structure of human capital [7], promoting organizational learning [8], improving resource utilization efficiency [9], and reducing innovation costs [10]. The impact of intelligent development on enterprise innovation varies due to factors such as industry characteristics [11], enterprise size [12], and market competition [13]. In general, studies provide important theoretical support and practical experience regarding the relationship between intelligent development and enterprise innovation, whether from the perspective of theoretical analysis or through empirical research. As the driving force of enterprise innovation and development, innovation is a process in which enterprises constantly absorb, share, and utilize knowledge. In this process, enterprises need to constantly integrate heterogeneous knowledge in different fields. In a complex dynamic environment, through the collision, integration, and deep interaction of knowledge, enterprises form new market insights, thus stimulating their innovation ability. Intelligent technology can help enterprises search and analyze knowledge in different fields and make use of strong innovative thinking ability to think about the connection between knowledge at a high speed, accurately identify potential innovation paths, and help enterprises obtain more innovation opportunities [14]. A pivotal concern in the innovation process is how enterprises can internalize the heterogeneous knowledge discovered during intelligent development, enhance their knowledge breadth for re-creation, and form core competitive advantages. Knowledge breadth refers to the range or number of technological niches within which an enterprise operates [15], which represents the richness of enterprise knowledge. The greater the knowledge breadth, the greater the difference between the types of knowledge possessed by enterprises, the wider the knowledge that enterprises can organize and use, and the greater the impact on the innovation efficiency and innovation speed of enterprises. Therefore, it is worth considering whether knowledge breadth plays a mediating role in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation. Therefore, utilizing enterprise innovation theory and knowledge-based theory, we empirically tested the impact of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation using 694 listed high-tech enterprises on China’s manufacturing A-share market between 2013 and 2021. The aim was to reveal the mechanism by which high-tech enterprises accelerate innovation through intelligent development.
This paper makes several contributions to the literature. Firstly, it comprehensively examines the impact of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation based on enterprise innovation theory. It expands the research on the application of intelligent technologies and enterprise innovation, providing theoretical support for leveraging intelligent applications to drive enterprise innovation. We find that intelligent development significantly enhances high-tech enterprise innovation. This finding aligns with studies by Liu et al. (2020) and Han et al. (2022) [16,17], which also demonstrate that intelligent applications significantly promote enterprise innovation. Additionally, Jiao’s (2023) research indicates that the application of intelligent technologies in enterprise innovation significantly enhances corporate competitiveness [18], providing further theoretical evidence for the role of intelligent application in enterprise innovation. By revealing the role of intelligent development in high-tech enterprise innovation, this paper enriches the understanding of the innovation process in enterprises and provides specific theoretical guidance on how to better realize the application of intelligent technology against the background of the rapid development of intelligent technology.
Secondly, from the perspective of knowledge-based theory, this paper explores the mediating role of knowledge breadth in the relationship between intelligent development and enterprise innovation. This enriches and deepens the research on how intelligent development and knowledge breadth affect enterprise innovation. The theory indicates that the knowledge held by the enterprise plays an important role in the occurrence and realization of innovation [19]. The empirical results indicate that knowledge breadth plays a bridging role between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation, indicating its significant mediating role in the process of enterprise innovation. This paper also confirms the viewpoints of Xu et al. (2015) and Yang et al. (2017) [20,21], who noted that knowledge breadth is a vital factor influencing enterprise innovation capability. This paper broadens the understanding of the role of knowledge breadth in enterprise innovation in the context of intelligent development, indicating that when enterprises effectively use intelligent technologies to enhance their knowledge breadth, their innovation capability is significantly strengthened. These findings offer new perspectives for understanding the role of intelligent development in enterprise innovation.
Finally, this paper introduces knowledge absorptive capacity as a moderating variable, clarifying the boundary conditions under which intelligent development influences high-tech enterprise innovation, thereby expanding the boundaries of existing research on intelligent development. Knowledge absorptive capacity is the ability to acquire, absorb, and utilize external knowledge, and has been widely recognized as an important factor in the innovation process [22]. The results show that knowledge absorptive capacity significantly moderates the relationship between knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation. When a high-tech enterprise’s knowledge absorptive capacity is strong, the positive impact of knowledge breadth on innovation is more pronounced. This finding is consistent with studies by Xie et al. (2018) and Duan et al. (2020) [23,24], which confirmed the important position of knowledge absorptive capacity in the process of enterprise innovation. This paper further improves the theoretical extension of the process in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation.
2. Theoretical Basis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Intelligent Development and High-Tech Enterprise Innovation
Innovation is a complex process that encompasses various business activities such as production, technology, and management. In each stage of innovation, high-tech enterprises need to invest a lot of capital and human resources. Moreover, each stage carries a high risk of failure, which seriously restricts innovation development and competitiveness. According to enterprise innovation theory, resource integration is the essence of enterprise innovation. Enterprises not only need to accumulate internal resources but also require input from external knowledge and technologies [25]. Intelligent development is manifested in the process of enterprises using intelligent technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data to transform various business operational activities, which has become an important engine to promote the innovation and development of high-tech enterprises.
On the one hand, the robust data-driven capabilities of intelligent technologies can be used as leverage to accelerate R&D and innovation in high-tech enterprises. Intelligent technology has powerful computing capabilities and machine learning algorithms, which can help enterprises quickly analyze and process vast datasets [26], deeply explore the value behind the data, accurately understand the market demand and user behavior, effectively lower innovation risk, and provide data-driven decision support for enterprise innovation [27]. By integrating data and algorithms at the core of the innovation process, intelligent technology quickly facilitates rapid prototyping, iteration, and optimization based on the instructions of the R&D personnel [28]. This reduces the large amount of time and resources required in the traditional R&D process, thereby shortening the product development cycle, lowering the cost of enterprise R&D, and accelerating the innovation process [29].
Furthermore, as an interdisciplinary technology, intelligent technology has penetrated various industries and fields. Through integration with various emerging technologies, it promotes cooperation and innovation across different fields. Intelligent development is an interdisciplinary field, involving multidisciplinary knowledge and expertise such as computer science, data science, and engineering. Thus, enterprises frequently collaborate with experts and institutions from other industries and fields when applying intelligent technologies [30]. Such cross-border cooperation can bring a cross-integration of knowledge and professional skills in different fields, which helps enterprises to stimulate innovative thinking so as to obtain new innovative ideas and technologies and promote the generation of innovation [31]. Additionally, the development of intelligent technologies has led to the emergence of open innovation platforms [32]. These platforms provide enterprises with more opportunities to participate in ecosystem collaborations. Open innovation platforms integrate external resources through intelligent technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data, providing rich materials for enterprise innovation. At the same time, enterprises can communicate and interact with multiple parties on the platform, and through cooperating sharing and data make up for the knowledge defects of enterprises and broaden the depth of innovation of enterprises, thus accelerating the innovation process of enterprises and improving the quality and sustainability of innovation [33]. High-tech enterprises in particular benefit immensely from these advancements. Their reliance on cutting-edge technology and constant need for innovation make the use of intelligent technologies and open innovation platforms crucial. By adopting these technologies, high-tech enterprises can maintain a competitive edge, rapidly adapt to market changes, and drive sustained growth through continuous innovation.
Based on the above analysis, the following research hypothesis is proposed:
H1:
Intelligent development positively impacts high-tech enterprise innovation.
2.2. The Mediating Role of Knowledge Breadth
According to knowledge-based theory, an enterprise is a collection of various knowledge elements, and its ability to apply and combine knowledge elements is crucial for its technological innovation activities [34]. Within this theoretical framework, intelligent technologies facilitate the extraction and integration of knowledge elements from vast and diverse information sources, thereby expanding the enterprise’s knowledge breadth. Knowledge breadth refers to the range or number of different technological niches in which an enterprise operates [15]. Existing research confirms that knowledge breadth can increase enterprise innovation [35]. Therefore, this paper posits that knowledge breadth is one possible pathway by which intelligent development influences enterprise innovation.
On the one hand, intelligent development helps to enhance an enterprise’s knowledge breadth. Firstly, intelligent technologies permeate the entire innovation process of enterprises [36], which changes the process of traditional knowledge transmission, brings revolutionary changes to the generation, acquisition, analysis and application of knowledge, and can significantly improve the efficiency of enterprise knowledge utilization. These technologies cross the boundaries of traditional industries and help enterprises quickly screen valuable knowledge elements from large volumes of information through natural language processing, machine learning, and other means, prompting enterprises to gain innovative knowledge across industries and fields, thus forming a broader knowledge network and enriching the enterprise’s knowledge base [10]. At the same time, intelligent technology can automatically classify and organize the knowledge base formed by enterprises, which not only improves the utilization rate of knowledge but also reduces information redundancy and loss in the process of knowledge transfer [37]. Secondly, intelligent technology can help enterprises build a comprehensive knowledge network and promote internal and external knowledge exchange and cooperation. Through knowledge graphs, natural language processing, and other technologies, enterprises integrate knowledge from different sources [38]. Through intelligent collaboration platforms and tools, knowledge exchange inside and outside enterprises becomes more efficient [39]. This efficient flow of knowledge contributes to the accumulation and sharing of knowledge [40], preventing the formation of information silos and creating a comprehensive knowledge network. At the same time, employees are able to find new ideas and methods related to themselves in the knowledge network and convert tacit knowledge into explicit knowledge so as to further expand the knowledge breadth of enterprise.
On the other hand, knowledge breadth benefits enterprise innovation. Firstly, knowledge breadth helps enterprises better identify and utilize innovation opportunities, which increases innovation efficiency. As knowledge breadth increases, it provides enterprises with diverse perspectives and ways of thinking, fostering the collision and fusion of innovative ideas. The convergence of knowledge from different industries often spurs new technologies and products [41], and this kind of cross-disciplinary innovation is particularly important in enterprises. Secondly, knowledge breadth facilitates collaborative innovation both internally and externally. Through knowledge sharing and cooperation, different departments within an enterprise can fully leverage their respective knowledge advantages for the joint development of innovative projects. Simultaneously, knowledge exchange and collaboration with external research institutions and partners allow the integration of external information and knowledge with the enterprise’s existing knowledge stock [42], thereby promoting enterprise innovation. Finally, knowledge breadth enhances an enterprise’s ability to tackle complex innovation challenges. A broad knowledge base enables enterprises to better respond to market changes and competitive pressures during technological transformations, effectively adjust their research and development strategy, and swiftly develop new products that meet market demand, thus maintaining a competitive advantage [21,43].
In summary, this paper believes that intelligent development helps enterprises acquire multi-domain knowledge, facilitates knowledge exchange, and improves knowledge management efficiency and continuous learning, thereby increasing knowledge breadth. Enterprise knowledge breadth reflects the scope of knowledge coverage in different technical fields. The broader the knowledge breadth, the more knowledge enterprises can comprehensively utilize, which in turn helps the enterprise better identify and leverage innovation opportunities, enhance its ability to address complex innovation challenges, and thereby drive its innovation activities. Evidently, knowledge breadth plays a crucial mediating role in the process of the impact of intelligent development on enterprise innovation. High-tech enterprises in particular benefit immensely from these advancements, as their reliance on cutting-edge technology and constant innovation necessitates a broad and dynamic knowledge base. Furthermore, the stock of knowledge is a fundamental prerequisite for innovation in high-tech enterprises.
Based on the above analysis, the following research hypothesis is proposed:
H2:
Knowledge breadth mediates the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation.
2.3. The Moderating Role of Knowledge Absorptive Capacity
According to resource-based theory, an enterprise’s sustainable competitive advantage stems from its unique and valuable internal resources, which are characterized by their rarity, inimitability, and non-substitutability [44]. Among these resources, knowledge assets and capabilities are considered key elements that facilitate innovation and secure a competitive edge. In particular, knowledge breadth, a crucial dimension of knowledge assets, is regarded as a critical driver of enterprise innovation, especially for high-tech enterprises, where innovation is paramount. However, the impact of knowledge breadth on innovation is critically influenced by the enterprise’s knowledge absorptive capacity. Knowledge absorptive capacity refers to the ability to recognize, acquire, transform, and utilize external knowledge [22]. This capability not only affects the role of knowledge breadth in enterprise innovation but also determines whether an enterprise can fully leverage its extensive knowledge resources to foster innovation.
On the one hand, knowledge absorptive capacity enhances the efficiency of utilizing knowledge breadth in the context of intelligent development. When an enterprise has a high knowledge absorptive capacity, intelligent technologies can more effectively identify and integrate knowledge from various fields, thereby amplifying the contribution of knowledge breadth to innovation. Through efficient knowledge absorption, enterprises can rapidly acquire external knowledge and internalize it as part of their core competencies, further driving the development of innovative activities [23,45]. On the other hand, knowledge absorptive capacity can mitigate the information overload and complexity associated with intelligent development. In the absence of sufficient absorptive capacity, enterprises may be slow to respond to the rapidly changing market and technological environment, which makes enterprises unable to effectively use information and knowledge, leading to wasted resources and a decline in innovation efficiency [46]. With the development of intelligent technology, the information that enterprises can obtain is also increasing dramatically. Enterprises with strong knowledge absorptive ability can better screen and apply a large amount of information brought by intelligent technology [47] and integrate this new knowledge into their operation and development. Through the effective use of external knowledge resources, they can further optimize the contribution of knowledge breadth to enterprise innovation. Moreover, knowledge absorptive capacity promotes the sharing and reutilization of internal knowledge. By building and managing internal knowledge networks, enterprises can better activate and utilize tacit knowledge and experience among their personnel [48], further enhancing innovation. This is particularly critical for high-tech enterprises, which often rely on specialized knowledge and continuous innovation to maintain a competitive edge.
Therefore, this paper posits that knowledge absorptive capacity plays a significant moderating role in the relationship between knowledge breadth and enterprise innovation. High knowledge absorptive capacity not only amplifies the positive impact of knowledge breadth on enterprise innovation but also facilitates the effective management and utilization of diverse knowledge resources, thereby enhancing the overall innovation performance of the enterprise. For high-tech enterprises, this capability is especially vital, as it supports their need for rapid innovation and adaptation in a highly competitive and technologically advanced environment.
Based on the above analysis, the following research hypothesis is proposed:
H3:
Knowledge absorptive capacity positively moderates the relationship between knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation.
The conceptual model of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
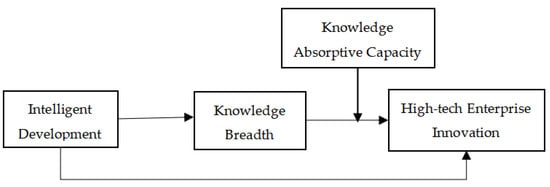
Figure 1.
Conceptual model of the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation.
3. Research Design
3.1. Data Collection
In this paper, according to the high-tech industry classification of the National Bureau of Statistics in China from 2017, listed A-share enterprises in six categories of manufacturing industries were selected to represent high-tech enterprises: pharmaceutical manufacturing; aerospace, spacecraft, and equipment manufacturing; electronic and communication equipment manufacturing; computer and office equipment manufacturing; medical instrument and equipment manufacturing; and chemical manufacturing. Then, the data of the listed enterprises from 2013 to 2021 were selected as the research sample. In order to ensure the reliability of the study, the following screening was carried out in the process of sample selection: (1) ST and *ST enterprises were excluded; (2) enterprises with serious missing key data were eliminated; and (3) to mitigate the impact of extreme outliers, all continuous variables underwent 1% winsorization at both ends. Ultimately, 4496 observations from 694 enterprises were obtained. Data on artificial intelligence applications were gathered through keyword text analysis of the enterprises’ annual reports collected from the CNINFO website (http://www.cninfo.com.cn/ accessed on 25 October 2023). Patent data were sourced from the CNRDS database, while other data were obtained from the CSMAR database.
3.2. Variable Measurement
3.2.1. Explanatory Variable: Intelligent Development (Intel)
Following the method of Wu et al. (2021) [49], the frequency of keywords related to intelligent development in the annual reports of listed enterprises was used to construct a measure of intelligent development. The specific steps were as follows. First, a data pool was created. Annual reports from 2013 to 2021 for all A-share high-tech manufacturing listed enterprises on the CNINFO website were collected and converted into txt format to form the data pool. Next, keywords were identified. Drawing on the research of Meng et al. (2022) [28], keywords for enterprise intelligent development were determined. Then, keyword frequency was calculated. Python was used to search, match, and count the frequency of keywords. Finally, the indicator was formed. The keyword frequencies were summed, and the logarithm of the sum plus one was taken to obtain the final proxy indicator.
3.2.2. Explained Variable: High-Tech Enterprise Innovation (Invo)
Patents are an important indicator of enterprise innovation outcomes [50]. Following existing research, the number of invention patent applications was used to measure enterprise technology innovation behavior. Considering the time lag between patent application and acceptance, patents lagging one period were used for measurement. Additionally, since some enterprises had zero patents, the logarithm of one plus the number of patents was taken to obtain the final proxy indicator.
3.2.3. Mediator Variable: Knowledge Breadth (Width)
Referring to the method of Li et al. (2021) [51], the main IPC classification numbers of patent applications by listed enterprise were obtained. Based on the IPC secondary classification of International Patent Classification, knowledge breadth was measured by the following equation:
In Equation (1), pik is the ratio of the number of patents of enterprise i under the secondary classification k to the total number, n is the number of patent applications of enterprise i, Widthit is knowledge breadth, and a higher value indicates a higher degree of knowledge diversification of the enterprise, that is, greater knowledge breadth.
3.2.4. Moderating Variable: Knowledge Absorptive Capacity (Kac)
Following a study by Huang et al. (2015) [52], the logarithm of the total number of technical personnel in the enterprise was used to measure knowledge absorptive capacity.
3.2.5. Control Variables
The following control variables were selected: enterprise size (Size), measured by the natural logarithm of the enterprise’s total assets at the end of the period; enterprise age (Age), calculated based on the difference between the fiscal year and establishment year; ownership nature (Soe) as a dummy variable, with state-owned enterprises coded as 1 and otherwise as 0; debt ratio (Lev), expressed as the ratio of total liabilities to total assets; capital intensity (Capital), calculated as the ratio of total assets to operating revenue; enterprise growth (Growth), measured by the ratio of operating revenue growth to initial operating revenue; and equity concentration (Top1), referring to the proportion of shares held by the largest shareholder. Additionally, the model further controlled for year and industry (Ind). Descriptive statistics for the variables are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
3.3. Model Setup
To examine the direct impact of intelligent development on enterprise innovation, the following regression model was constructed:
In the above equation, i and t represent the enterprise and the year, respectively; Invoit is high-tech enterprise innovation; Intelit is intelligent development; Controlit is the set of a series of control variables; λ is the industry fixed effect; γ is the time fixed effect; and ε is the random disturbance term.
To verify the mediating role of knowledge breadth in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation, we adopted the method of Wen et al. (2014) [53] and constructed the following mediation effect models:
In the above equations, Widthit is knowledge breadth. Equation (3) tests the impact of intelligent development on knowledge breadth, while Equation (4) simultaneously regresses intelligent development, knowledge breadth, and high-tech enterprise innovation. If β1, δ1, and δ2 are all significant, it indicates that the mediation effect is significant.
To verify the moderating role of knowledge absorptive capacity, an interaction term between knowledge absorptive capacity and knowledge breadth was incorporated into the model, leading to the following model:
In the above equation, Kacit represents knowledge absorptive capacity. If χ2 is significant, it indicates that the moderating effect is significant.
4. Empirical Results
4.1. Correlation Analysis
Table 2 presents the results of correlation analyses of the variables. According to Table 2, intelligent development is significantly positively correlated with high-tech enterprise innovation (r = 0.256, p < 0.01). Knowledge breadth is also significantly positively correlated with high-tech enterprise innovation (r = 0.328, p < 0.01), and knowledge absorptive capacity shows a significant positive correlation with high-tech enterprise innovation (r = 0.644, p < 0.01). These findings provide preliminary support for the research hypotheses. Additionally, the results of variance inflation factor (VIF) analysis indicate that all VIF values are well below the empirical threshold of 10, suggesting that there is no severe multicollinearity among the variables, thus allowing regression analysis to proceed.

Table 2.
Correlation analysis.
4.2. Direct Effect Test
According to column 1 of Table 3, when no control variables are added, but year and industry fixed effects are controlled, the regression coefficient between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation is 0.128, significant at the 1% level. Column 2 shows that when various control variables are included, along with year and industry fixed effects, the coefficient between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation is 0.0809, also significant at the 1% level. This indicates that intelligent development has a significant impact on high-tech enterprise innovation, thus verifying H1.

Table 3.
Regression analysis results.
4.3. Mediation Effect Test
Column 3 of Table 3 shows that without any control variables, but with year and industry fixed effects controlled, the regression coefficient between intelligent development and knowledge breadth is 0.0274, significant at the 1% level. Column 4 shows that when various control variables are included along with year and industry fixed effects, the coefficient between intelligent development and knowledge breadth is 0.0188, significant at the 1% level. These results indicate that intelligent development helps to enhance enterprise knowledge breadth. As in column 5, when knowledge breadth is included, the coefficients for intelligent development and knowledge breadth are 0.0766 and 0.359, respectively, both significant at the 1% level. This demonstrates that knowledge breadth partially mediates the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation. Combined with the results of column 2, it can be seen that the direct effect of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation is in the same direction as the indirect effect through knowledge breadth. According to the definition of complementary partial mediation and competitive partial mediation used by Zhao et al. (2010) [54], it can be concluded that knowledge breadth plays a complementary partial mediating role in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation, indicating that intelligent development can help to improve the innovation ability of high-tech enterprises, which is achieved not only through a direct effect but also indirectly through expanding knowledge breadth. Therefore, H2 is verified.
4.4. Moderation Effect Test
Column 7 of Table 3 shows that when various control variables, year, and industry fixed effects and the interaction term between knowledge absorptive capacity and knowledge breadth (Width*Kac) are included, the interaction term has a significant positive impact on enterprise innovation. The regression coefficient between the interaction term and enterprise innovation is 0.229, significant at the 1% level. This suggests that knowledge absorptive capacity strengthens the relationship between knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation, meaning stronger knowledge absorptive capacity is more conducive to knowledge breadth promoting high-tech enterprise innovation. Thus, knowledge absorptive capacity plays a moderating role in the process of knowledge breadth promoting high-tech enterprise innovation. Based on the work of Sharma (2003) [55], an additional check was performed to determine whether knowledge absorptive capability acts as a pure or quasi-moderator. Column 6 shows that knowledge absorptive capability has a significant positive effect on high-tech enterprise innovation. Furthermore, column 7 reveals that both knowledge absorptive capability and its interaction term have a significant positive effect on high-tech enterprise innovation. These results indicate that knowledge absorptive capability serves as a quasi-moderator in the relationship between knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation. Therefore, H3 is validated.
To represent the moderating effect of knowledge absorptive capacity intuitively, we drew on the research of Aiken et al. (1991) [56] and plotted the corresponding moderation effect diagram based on the regression results, as shown in Figure 2. According to Figure 2, knowledge breadth has a significant positive impact on high-tech enterprise innovation. However, the strength of this relationship varies with the level of knowledge absorptive capacity. When knowledge absorptive capacity is low, the impact of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation is relatively mild. In contrast, when knowledge absorptive capacity is high, the positive relationship between knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation is significantly enhanced. This means that when a high-tech enterprise has higher knowledge absorptive capacity, the effect of knowledge breadth on promoting innovation is more pronounced, further verifying H3.
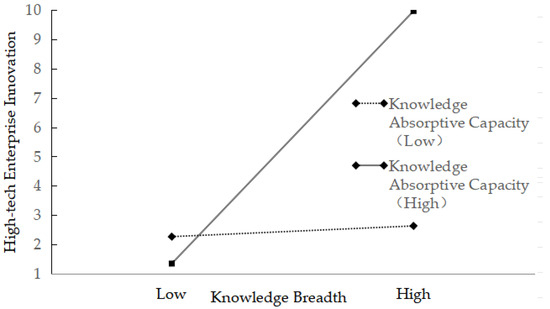
Figure 2.
The moderating effect of knowledge absorptive capacity on knowledge breadth and high-tech enterprise innovation.
4.5. Robustness Tests
4.5.1. Endogeneity Test
There may be reverse causality between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation such that high-tech enterprises with strong innovation capabilities are more likely to pursue intelligent development. To address endogeneity, we used the instrumental variable method. Lewbel (1997) [57] proposed a method to construct instrumental variables based on mean differences. In this paper, we used the cube of the difference between the intelligent development of the enterprise and the industry average as the instrumental variable (Lewbel IV) and employed the two-stage least squares (2SLS) method for empirical testing. The regression results are shown in columns 1 and 2 of Table 4. Column 1 shows the first-stage regression coefficient of the instrumental variable on intelligent development, which is 0.312 and significant at the 1% level. The first-stage F-statistic is greater than 10, indicating no weak instrumental variable problem. Column 2 shows the second-stage results, where the regression coefficient of the effect of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation is 0.147, significant at the 1% level, consistent with the results of H1.
4.5.2. Other Robustness Tests
Firstly, we replaced the explanatory variable. A dummy variable for intelligent development (set to 1 if intelligent development was above the median, otherwise 0) was used instead of the continuous variable. The results are shown in column 3 of Table 4. The regression coefficient of the effect of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation is 0.109, significant at the 1% level, supporting H1.
Secondly, we replaced the explained variable. Given that different types of patents reflect different degrees of innovation, we used the application volume of utility model patents and invention patents to recalculate high-tech enterprise innovation. The regression results are shown in column 4 of Table 4. The regression coefficient of the effect of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation is 0.096, significant at the 1% level, supporting H1.
Thirdly, we used an alternative measurement model. Since enterprise patent applications had a left-censored characteristic at zero, we used the tobit model for regression. The results are shown in column 5 of Table 4. The coefficient of intelligent development remains significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that H1 is robust.

Table 4.
Endogeneity and robustness test results.
Table 4.
Endogeneity and robustness test results.
| Variable | Instrumental Variable | Replacing Explanatory Variable | Replacing Explained Variable | Alternative Measurement Model | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Stage | Second-Stage | ||||
| Intel | Invo | Invo | Invo | Invo | |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
| Lewbel IV | 0.312 *** (102.64) | ||||
| Intel | 0.147 *** (7.42) | 0.109 *** (3.73) | 0.096 *** (5.51) | 0.178 *** (10.33) | |
| Size | 0.637 *** (7.30) | 0.813 *** (45.59) | 0.678 *** (25.56) | 0.667 *** (26.22) | 0.825 *** (44.61) |
| Age | −0.002 (−1.37) | −0.0009 (−0.03) | 0.007 (1.27) | 0.005 (0.90) | −0.0003 (−0.12) |
| Soe | 0.008 (0.43) | 0.221 *** (5.49) | 0.184 *** (2.89) | 0.107 * (1.76) | 0.219 *** (5.25) |
| Lev | 0.118 ** (−2.25) | −0.224 ** (−2.10) | −0.102 (−0.83) | −0.115 (−0.99) | −0.239 ** (−2.15) |
| Capital | 0.004 (0.58) | −0.122 *** (−8.69) | −0.092 *** (−5.65) | −0.107 *** (−6.95) | −0.127 *** (−8.66) |
| Growth | 0.003 (0.13) | 0.220 *** (4.13) | 0.062 (1.55) | 0.075 ** (1.98) | 0.233 *** (4.20) |
| Top1 | 0.001 *** (2.64) | −0.007 *** (−5.85) | −0.004 *** (−2.05) | −0.003 ** (−2.02) | −0.007 *** (−5.88) |
| year | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control |
| Ind | Control | Control | Control | Control | Control |
| _cons | −0.047 (−0.25) | −14.888 *** (−39.32) | −12.005 *** (−20.87) | −11.532 *** (−20.93) | −15.197 *** (−38.59) |
| R2 | 0.813 | 0.500 | 0.154 | 0.229 | 0.191 |
Note: This table presents an endogeneity test using two-stage least squares (2SLS) and a robustness test between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation. *, **, *** indicate significance at 10%, 5%, and 1% confidence level, respectively.
5. Conclusions and Implications
In today’s global economic environment, change and uncertainty have become the norm. The competitive pressure faced by enterprises is increasing; therefore, enterprises must constantly innovate and optimize their own development mode. Intelligent development has become the core driving force promoting the innovation of enterprises, and not only accelerates enterprise innovation but also enhances the competitiveness and market position of enterprises in the global market. Based on enterprise innovation theory and knowledge-based theory, this paper empirically analyzes the impact of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation in 694 high-tech manufacturing enterprises listed on China’s A-shares from 2013 to 2021. It explores the mediating role of knowledge breadth and the moderating role of knowledge absorptive capacity. The paper yields the following conclusions: intelligent development significantly promotes high-tech enterprise innovation; knowledge breadth serves as a significant mediator in the relationship between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation; and knowledge absorptive capacity strengthens the impact of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation, meaning the stronger the knowledge absorptive capacity, the greater the impact of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation.
5.1. Theoretical Contributions
Firstly, based on enterprise innovation theory, this paper finds that intelligent development significantly promotes high-tech enterprise innovation. The existing literature indicates that intelligent technology can enhance innovation by improving an enterprise’s technological capabilities and operational efficiency [16,17]. This paper further validates this theory, demonstrating that intelligent development is a key factor for high-tech enterprise innovation. Intelligent technology not only aids in improving technological capabilities and operational efficiency but also provides more accurate market insights and decision support through data analysis and prediction. By advancing intelligent development, enterprises can better integrate and utilize diverse knowledge resources, thereby enhancing their innovative capability and driving the development of new products and services. This finding deepens the understanding of the relationship between intelligent development and enterprise innovation, providing new ideas and methods for enterprises to achieve continuous innovation in a competitive market environment.
Secondly, based on knowledge-based theory, this paper shows that knowledge breadth significantly mediates the impact of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation and plays a complementary partial mediating role. This means that the influence of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation is multifaceted, which not only can directly promote innovation activities but also further promote innovation by enhancing the knowledge breadth of enterprises. Knowledge breadth represents the range of diverse knowledge and skills an enterprise possesses [15]. Intelligent technology, through extensive data collection and analysis, enables enterprises to acquire and integrate knowledge and information from various fields, thereby expanding their knowledge breadth. This finding confirms that knowledge breadth, a crucial means for enterprises to acquire and integrate diverse knowledge and resources, plays a vital role in enhancing their innovation capability [58]. By expanding their knowledge breadth, enterprises can better identify innovation opportunities and apply technologies across different fields and thus improve their market competitiveness. This offers a new perspective on how enterprises can optimize their knowledge management strategies through intelligent means.
Finally, this paper confirms that knowledge absorptive capability acts as a quasi-moderator of the effect of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation. This indicates that knowledge absorptive capability not only directly influences high-tech enterprise innovation but also further enhances the effect of knowledge breadth on high-tech enterprise innovation through its moderating role. Knowledge absorptive capacity refers to the ability to recognize, assimilate, transform, and apply external knowledge. Specifically, the stronger the knowledge absorptive capacity, the more significant the positive effect of knowledge breadth on enterprise innovation. This result supports the views of Xie et al. (2018) and Duan et al. (2020) [23,24] on the crucial role of knowledge absorptive capacity in enterprise innovation. Knowledge breadth represents the diversity of enterprise knowledge, and enterprises with higher knowledge absorptive capacity are better at identifying and filtering information and using it to further enhance the positive impact of knowledge breadth on innovation. This conclusion reveals the importance of knowledge absorptive capacity in enterprise knowledge management and innovation activities.
5.2. Management Implications
Firstly, high-tech enterprises should actively promote the investment and application of intelligent development. On the one hand, high-tech enterprises should increase their investment in intelligent technology and adopt advanced tools to enhance their technological capabilities and operational efficiency. By applying intelligent technology, enterprises can better integrate internal resources, improve production efficiency, and elevate management levels, thereby providing a solid foundation for innovation activities. Furthermore, high-tech enterprises should actively build intelligent management platforms. Intelligent platforms realize the intercommunication and integration of internal and external data by breaking up information silos. On an intelligent management platform, enterprises can use deep learning and other technical means to analyze the potential demand pattern of customers and quickly and effectively capture future market trends and customer needs so as to help them adjust innovation strategies and develop products and services that meet market demand in a timely fashion. Additionally, enterprises should focus on cultivating and recruiting intelligent technology talent. With the development of the intelligent era, the demand structure of technical talents has changed, and these talents not only need to master advanced technical and management knowledge but also need to have the ability to solve practical problems. Therefore, enterprises can build training bases with universities to jointly cultivate intelligent skills while strengthening the continuous training and learning of enterprise employees to master the latest technical and management knowledge.
Secondly, knowledge breadth should be expanded to foster innovation outcomes. High-tech enterprises should acquire diverse knowledge resources through various channels, including internal R&D and innovation and external collaboration and exchange, as well as set up R&D centers and innovation labs to foster ideas and technological progress independently. Externally, enterprises may strive for opportunities for collaboration with institutions and research centers in joint research projects to tap into cutting-edge scientific discoveries and technical knowledge to provide support for enterprise innovation. Secondly, enterprises need to establish a robust knowledge management system to manage and utilize knowledge resources effectively. Through the introduction of knowledge management platform, enterprises can establish a complete knowledge base and knowledge sharing platform, which can help them quickly and conveniently access required information and knowledge, promote knowledge transfer and sharing, and improve the utilization efficiency of knowledge resources so as to promote the improvement in their overall innovation ability. Lastly, enterprises should encourage internal and external knowledge exchange and cooperation to enhance the integration and utilization of knowledge resources. By forming cross-department project teams, enterprises could foster knowledge exchange and collaboration among internal employees through performance appraisal, bonuses, and promotion. Simultaneously, collaborations with upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain could establish mechanisms for knowledge sharing and technical cooperation, jointly driving technological innovation and product development.
Finally, knowledge absorptive capacity should be enhanced. In this paper, we found that knowledge absorptive capacity moderates the relationship between knowledge breadth and enterprise innovation: the stronger the absorptive capacity, the more significant the positive effect of knowledge breadth on innovation. Therefore, enterprises should prioritize enhancing their knowledge absorptive capacity. On the one hand, enterprises should establish scientific knowledge absorption mechanisms, encompassing stages such as knowledge selection, internalization, and transformation. During the knowledge selection stage, enterprises should choose knowledge that is beneficial to their development based on their needs and strategic goals. In the internalization stage, enterprises should facilitate understanding and mastery of new knowledge by employees through training, exchanges, and seminars. In the transformation stage, new knowledge should be applied in practical work, in order to realize its value through innovation activities. On the other hand, enterprises should foster a culture and policies that promote knowledge absorption awareness among employees. Employees need to understand the value of knowledge absorption and engage in activities to enhance their skills and expertise levels effectively. Enterprises can set up knowledge absorption rewards to create a good atmosphere to stimulate employees ‘enthusiasm for knowledge absorption. Additionally, enterprises should organize training programs focusing on knowledge search and application technology to improve employees’ ability to absorb knowledge and incorporate tasks into their daily work. This will help employees develop ways to collect information and use it effectively, thereby improving their knowledge absorptive capacity.
5.3. Research Limitations and Expectations
In this paper we conducted theoretical and empirical analyses of the roles of intelligent development, knowledge breadth, and knowledge absorptive capacity in high-tech enterprise innovation. However, due to the complexity of the research questions, there are some limitations. Firstly, intelligent development is a multi-indicator system encompassing various aspects such as automation level, informatization degree, and intelligent manufacturing capability. In this paper, we used text analysis based on keyword frequency related to intelligent development, which limited the comprehensiveness and systematicity of the research, and did not fully capture the multidimensional nature of intelligent development. Future research could introduce more diverse indicators, such as the prevalence of intelligent production equipment and the degree of application of intelligent management systems, to establish a more systematic method to measure intelligent development levels and more comprehensively evaluate their impact on high-tech enterprise innovation. Secondly, the mediating mechanism considered in this paper was limited to knowledge breadth, providing a relatively singular perspective. The impact of intelligent development on high-tech enterprise innovation might occur through various pathways, such as knowledge integration capability, enhanced technological capability, or efficient innovation resource allocation. Future research could further expand the scope of mediating mechanisms by combining relevant theories to fully understand how intelligent development promotes high-tech enterprise innovation through the influence of mediating mechanisms. Finally, this paper explores the moderating role of knowledge absorptive capacity, but does not fully consider other potential moderating factors. In the process of intelligent development affecting high-tech enterprise innovation, external factors such as policy support and market competition intensity and internal factors such as enterprise culture might play important moderating roles between intelligent development and high-tech enterprise innovation. Future research can explore the changes of other moderating factors on high-tech enterprise innovation under different conditions so as to help high-tech enterprises better use intelligent development to promote innovation in different situations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B. and J.Z.; data curation, J.Z.; formal analysis, D.B. and J.Z.; funding acquisition, J.Z.; methodology, J.Z.; software, J.Z.; supervision, D.B.; writing—original draft, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Youth Foundation for Humanities and Social Sciences of the Ministry of Education of China under grant 22YJC630201 and the General Project for Humanities and Social Sciences Research in Universities in Henan Province of China under grant 2025-ZDJH-058 and 2024 Graduate Education Reform and Quality Improvement Project (Excellent Teaching Case Project) in Henan Province of China under grant 139.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this paper are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge WeTab Al Pro, a ChatGPT web plugin, for assisting with language corrections during the editing of this manuscript, resulting in improved readability and language quality.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Schumpeter, J.A. Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy; Harper and Brothers: New York, NY, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Schilling, M.A. Strategic Management of Technological Innovation; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bahoo, S.; Cucculelli, M.; Qamar, D. Artificial intelligence and corporate innovation: A review and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2023, 188, 122264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Machado, I.; Magrelli, V.; Dwivedi, Y.K. Artificial intelligence in innovation research: A systematic review, conceptual framework, and future research directions. Technovation 2023, 122, 102623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haefner, N.; Wincent, J.; Parida, V.; Gassmann, O. Artificial intelligence and innovation management: A review, framework, and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2021, 162, 120392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, A.; Giones, F.; Werle, M. The AI digital revolution in innovation: A conceptual framework of artificial intelligence technologies for the management of innovation. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hou, Y.-L. How does industrial intelligence reshape the employment structure of Chinese labor force. China Ind. Econ. 2019, 5, 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Xiu, P.; Yang, J. How does intelligent manufacturing affects enterprise innovation? The mediating role of organisational learning. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2022, 16, 630–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. The effect of manufacturing intelligence on green innovation performance in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2022, 178, 121569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verganti, R.; Vendraminelli, L.; Iansiti, M. Innovation and design in the age of artificial intelligence. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2020, 37, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ying, L.; Gao, M. The influence of intelligent manufacturing on financial performance and innovation performance: The case of China. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 14, 812–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. A comparative study of the effects of different factors on firm technological innovation performance in different high-tech industries. Chin. Manag. Stud. 2019, 13, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, A.W.; Shuhaiber, A.; Mashal, I.; Al-Okaily, M. Antecedents of Industry 4.0 capabilities and technological innovation: A dynamic capabilities perspective. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2024, 36, 566–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuah, C.T. Guest editorial: Advances in intelligent techniques for knowledge management and decision making. Cybern. Syst. 2017, 48, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- George, G.; Kotha, R.; Zheng, Y. Entry into insular domains: A longitudinal study of knowledge structuration and innovation in biotechnology firms. J. Manag. Stud. 2008, 45, 1448–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, H.; Forrest, J.Y.-L.; Yang, B. Influence of artificial intelligence on technological innovation: Evidence from the panel data of China’s manufacturing sectors. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2020, 158, 120142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jiang, C.; Liu, R. Does intelligent transformation trigger technology innovation in China’s NEV enterprises? Energy 2023, 270, 126823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H. Digital platform-based ecosystem view: A new perspective on management theory in the era of digital economy. China Ind. Econ. 2023, 7, 122–141. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, R.M. Toward a knowledge-based theory of the firm. Strateg. Manag. J. 1996, 17, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S. Balancing the two knowledge dimensions in innovation efforts: An empirical examination among pharmaceutical firms. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2015, 32, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Jin, L.; Sheng, S. The effect of knowledge breadth and depth on new product performance. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2017, 59, 517–536. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, W.M.; Levinthal, D.A. Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Admin. Sci. Q. 1990, 35, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zou, H.; Qi, G. Knowledge absorptive capacity and innovation performance in high-tech companies: A multi-mediating analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2018, 88, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, W. The multiple mediation effect of absorptive capacity on the organizational slack and innovation performance of high-tech manufacturing firms: Evidence from Chinese firms. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.M. The Innovator’s Dilemma: When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail; Harvard Business Review Press: Brighton, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mariani, M.M.; Perez-Vega, R.; Wirtz, J. AI in marketing, consumer research and psychology: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Psychol. Mark. 2022, 39, 755–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Nambisan, S. Innovation analytics and digital innovation experimentation: The rise of research-driven online review platforms. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2021, 172, 121009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, G. Research on the influence mechanism of “intelligence +” on the innovation performance of manufacturing enterprises. Sci. Res. Manag. 2022, 43, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Rana, N.P.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Baabdullah, A.M. Understanding AI adoption in manufacturing and production firms using an integrated TAM-TOE model. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2021, 170, 120880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-F.; Cao, A.-J.; Guo, J.-B.; Guo, D.-M. A study of the impact of artificial intelligence on employment based on patents data: Evidence from zhongguancun enterprises. China Ind. Econ. 2023, 5, 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Pinero, M.; Paez-Aviles, C.; Juanola-Feliu, E.; Samitier, J. Cross-fertilization of knowledge and technologies in collaborative research projects. J. Knowl. Manag. 2021, 25, 34–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulimowski, A.M.J.; Koehler, T. A future-oriented approach to the selection of artificial intelligence technologies for knowledge platforms. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 74, 905–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, X. Digitalization capabilities, open innovation, and firm performance: The moderating effect of appropriability regimes. Sci. Sci. Manag. S. T. 2023, 44, 132–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kogut, B.; Zander, U. Knowledge of the firm, combinative capabilities, and the replication of technology. Organ. Sci. 1992, 3, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, F. How does digital M&A affect radical innovation: The analysis based on knowledge breadth and innovation efficiency. Collect. Essays Financ. Econ. 2023, 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn, I.M.; Henderson, R.; Stern, S. The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Innovation; National Bureau of Economic Research: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 24449. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, E.; Garner, B.J.; Staab, S. The role of artificial intelligence in knowledge management. Knowl-Based. Syst. 2000, 13, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olan, F.; Arakpogun, E.O.; Suklan, J.; Nakpodia, F.; Damij, N.; Jayawickrama, U. Artificial intelligence and knowledge sharing: Contributing factors to organizational performance. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, M.H.; Askay, D.; Eshraghi, A.; Smith, P. Artificial intelligence and knowledge management: A partnership between human and AI. Bus. Horiz. 2023, 66, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traskman, T.I.; Skoog, M. Performing openness: How the interplay between knowledge sharing and digital infrastructure creates multiple accountabilities. J. Strategy Manag. 2022, 15, 194–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Z.; Li, C.B. How knowledge affects radical innovation: Knowledge base, market knowledge acquisition, and internal knowledge sharing. Strateg. Manag. J. 2012, 33, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.; Hewitt-Dundas, N. Knowledge stocks, knowledge flows and innovation: Evidence from matched patents and innovation panel data. Res. Policy 2015, 44, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, S.A.; Medase, K. The diversity of knowledge sources and its impact on firm-level innovation: Evidence from Germany. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2019, 22, 681–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Rodriguez, A.L.; Roldan, J.L.; Ariza-Montes, A.; Leal-Millan, A. From potential absorptive capacity to innovation outcomes in project teams: The conditional mediating role of the realized absorptive capacity in a relational learning context. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 2014, 32, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-H. Social capital, absorptive capability, and firm innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2013, 80, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Foul, M.; Ruiz-Alba, J.L.; Lopez-Tenorio, P.J. The impact of artificial intelligence capabilities on servitization: The moderating role of absorptive capacity—A dynamic capabilities perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 157, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, R.; Archibald, D. Harnessing your staff’s informal network. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2010, 88, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Hu, H.; Lin, H.; Ren, X. Enterprise digital transformation and capital market performance: Empirical evidence from stock liquidity. J. Manag. World 2021, 37, 130–144+10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zheng, M. Is it substantive innovation or strategic innovation? Impact of macroeconomic policies on micro-enterprises’ innovation. Econ. Res. J. 2016, 51, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D. Research on patent quality’s impact mechanism on the competitiveness of enterprises for export: The exploration from the perspective of knowledge width. World Econ. Stud. 2021, 32–46+134. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.-F.; Lin, K.-H.; Wu, L.-Y.; Yu, P.-H. Absorptive capacity and autonomous R&D climate roles in firm innovation. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Z.; Ye, B. Analyses of mediating effects: The development of methods and models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2014, 22, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.G., Jr.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering baron and kenny: Myths and truths about mediation analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N. The role of pure and quasi-moderators in services: An empirical investigation of ongoing customer–service-provider relationships. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2003, 10, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, L.S.; West, S.G.; Reno, R.R. Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Lewbel, A. Constructing instruments for regressions with measurement error when no additional data are available, with an application to patents and R&D. Econometrica 1997, 65, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar]
- del-Corte-Lora, V.; Molina-Morales, F.X.; Vallet-Bellmunt, T.M. Mediating effect of creativity between breadth of knowledge and innovation. Technol. Anal. Strateg. 2016, 28, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).