Abstract
Genetic variability and diversity of genotypes are very important for all living organisms. Knowledge of the genetic diversity is a potential tool for pre-breeding parental selection. The present experiment was conducted at two locations (Isfahan, Khuzestan) under field conditions during the 2017–2018 growing season, with fifteen short day onion genotypes which were evaluated by multivariate methods. Nine quantitative traits were studied. MANOVA showed that the locations, varieties and location × variety interaction were significantly different for all nine traits. Significant positive correlation observed for two locations for yield and single weight (0.85 in Khuzestan and 0.61 in Isfahan), yield and bulb height (0.52 in Khuzestan and 0.55 in Isfahan), bulb height and index shape (0.68 in Khuzestan and 0.70 in Isfahan) and bulb diameter and single weight (0.81 in Khuzestan and 0.66 in Isfahan). Further, yield was significantly correlated with dry matter: positively in Isfahan (0.62), and negatively in Khuzestan (–0.54). In Khuzestan, the first two canonical variants explained 79.19% of the total variation between the varieties; however, the greatest variation was found for the Saba and Behbahan improved population. The first two canonical variables explained 86.76% of the total variation between the varieties in Isfahan. Saba and Behbahan improved population varieties were the smallest, while Paliz and Early Super Select were the largest. The Saba and Behbahan improved population, as the most diverse genotypes, were recommended for further inclusion in future crop improvement programs.
1. Introduction
Onion (Allium cepa L.) is the most economically important Allium crop, which is a commercially important vegetable crop across in the world [1]. According to FAO statistics, in the crop year 2020–2021, around 100 million tons of onions were produced around the world. India has been the first producer with a production of 26.7 million tons, followed by China with 24 million tons, the United States with 3.8 million tons, Egypt with 3.1 million tons and Turkey with 2.28 million tons are in the second to fifth rank in the world. Iran, with the production of more than 2 million tons of onions, has been the 7th largest producer of onions, which exports more than 100,000 tons of onions annually and is among the 15 exporting countries of this product (FAO.org). Thus, onion is as one of the most important vegetables in Iran, with a cultivated area about 67,000 ha and productivity about 49 t ha−1 during 2019–2020. The highest productive yield of onions in Iran was reported in Isfahan with about 66 t ha−1 [2]. Due to high genetic diversity of onions shown in the eastern Mediterranean countries, regions such as Pakistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan and northern Iran are thought to be the origin of diversity of this crop [3].
Onion is a highly cross-pollinated crop, annual for bulb production and biennial for seed production. Bulb initiation in onion depends on day-length (11–16 h) and temperature (10–30 °C). According to day-length response to bulb initiation, onions are classified as short-day, intermediate-day, and long-day. Short-day onions initiate bulbs when day-length exceeds 11–12 h, intermediate-day types when day-length exceeds 12–14 h, and long-day types require more than 14 h [3]. Genetic divergence analysis estimates the extent of diversity present among the genotypes and these could help the plant breeder in selecting the diverse parents for purposeful hybridization [4]. During a previous study, the genetic diversity of thirty-eight onion accessions over two years under filed conditions was investigated by multivariate analysis [5]. Studies have classified all accessions into six different clusters. Multivariate analysis tools, such as canonical variables analysis, canonical correlation analysis and Mahalanobis D², are powerful and reliable tools with which to study the genetic divergence in the genotypes; these could help the plant breeder in selecting diverse parents for pre-breeding selection and hybridization [6,7,8,9,10,11]. The aim of this study was to investigate the genetic variability and diversity of twelve commercial short onion hybrids on the basis of nine quantitative traits by multivariate statistical methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The current study included 12 commercial short day onion hybrids such as Sahar, Super Perfect, Paliz, Saba, Vania, Early Super Select, Savannah Sweet, Golden eye, Duster, Hybrid 6326, Imperatriz and Behbahan improved population along with Primavera, Cirrus and Texas Early Grano as check hybrids (Table 1). The characteristics of the hybrids were mentioned in their entirety in Abbasi et al. [12].

Table 1.
The name and characteristics of onion genotypes were used in study.
2.2. Field Evaluation
Fifteen onion genotypes (Table 1) were grown as seedlings in two environments at the Isfahan Agricultural and Natural Resources Research and Training Center (Kabutarabad Agricultural Research Location, 25 km east of Isfahan, 51°51′ E and 30°31′ N, 1545 m altitude) and Khuzestan Agricultural and Natural Resources Research and Training Center (Behbahan Agricultural Research Location, 30°36′ N and 51°51′ E, 320 m altitude) in field conditions during the October 2017 to May 2018 growing season for Khuzestan and the December 2017 to July 2018 growing season for Isfahan. The results of the soil and water tests are given in Table 2 and Table 3, respectively.

Table 2.
Soil test results for Isfahan and Khuzestan location.

Table 3.
Water test results for Isfahan and Khuzestan location.
For each experiment, a complete block design with three replications was used. Each plot contained four 4 m long rows with spaces of 0.3 m between rows and 0.1 m inside the row, where each plot with the area of 4 × 1.2 m2 contained 160 plants. Standard cultural practices were followed for seedling bed preparation, transferring, irrigation and the control of weed and pests [12]. In Khuzestan, the seedling nursery was prepared during October–December 2017 and transplanted from the nursery to the main plot after two-to-three leaf stages in late December 2017. In the Isfahan experiment, due to the winter cold and the risk of spring, the seedling nursery was prepared during December 2017 to Mar 2018 and transferred to the main plot in early March 2018. The bulbs were harvested on 14 May 2018 and 17 July 2018 in Khuzestan (with total crop duration of about 210 days) and Isfahan (with total crop duration of about 180 days), respectively. Post-harvest traits of onion samples were performed during May–July 2018 in Khuzestan and July–September 2018 in Isfahan.
2.3. Observed Traits
2.3.1. Bulb Yield per Plot
Bulb yield for each genotype was calculated per plot. Based on the plot bulb yield, bulb yield per hectare was calculated and expressed in tons per hectare [13].
2.3.2. Single Bulb Weight
For single weight (g), five randomly selected plants from each treatment and replication were weighed to determine the average weight of the bulbs [13].
2.3.3. Dry Matter Content
To calculate the dry matter content of each genotype, five bulbs were randomly selected from each plot, cleaned and weighted. After drying complete samples in the oven (70 °C) and fixing the weights (about 72 h), samples were weighed again and the dry matter was calculated [14].
2.3.4. Soluble Solid Content
To measure the total soluble solid, five bulb samples were randomly selected and, after cutting from the second and third layers, the extract was placed on the glass refractometer (ATAGO Brix 0–32%) and the device number was recorded [15].
2.3.5. Storage Waste Content
To measure the storage properties of onion samples, 10 kg of healthy bulbs per hybrid were stored in lattice boxes and maintained under normal conditions for three months. Before storage, boxes containing bulbs were weighed. After three months, the first bulb sprouting was counted. In this way, the amount of bulb weight loss of each treatment was accurately determined. During storage, the temperature changes in Khuzestan ranged from 32 to 39.5 °C, relative humidity ranged from 27 to 58% and the condition in Isfahan was 15–20 °C for temperature and 60–70% for relative humidity. Waste (W) was calculated at the end of the third month using the formula given below [16]:
where: P0—initial bulbs weight, P1—bulbs weight after 90 days.
2.3.6. Bulb Height, Bulb Diameter, Neck Diameter
For obtaining bulb height, diameter and neck diameter, five bulb samples were randomly selected and were measured using a digital caliper [12].
2.3.7. Index Shape
This trait was calculated as the ratio of bulb height to bulb diameter [17].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The normality of the distributions of the studied traits (yield, single weight, dry matter, soluble, storage waste, bulb height, bulb diameter, neck diameter and index shape) was tested using Shapiro–Wilk’s normality test [18]. Multivariate normality and homogeneity of variance–covariance matrices were tested by Box’s M test [19]. A two-way (location, variety) multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) was performed [20]. Further, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was carried out to determine the effects of location and variety as well as location × variety interaction [21] on variability of yield, single weight, dry matter, soluble, storage waste, bulb height, bulb diameter, neck diameter and index shape. The relationships between the observed traits were estimated on the basis of the varieties’ means using Pearson’s correlation coefficients [22] independently for locations. The results were also analyzed using multivariate methods. A canonical variate analysis was applied in order to present a multi-trait assessment of the similarity of the tested varieties in a lower number of dimensions with the least possible loss of information [23]. This made it possible to illustrate, in graphic form, any variation in the varieties in terms of all the observed traits. The Mahalanobis distance was suggested as a measure of “polytrait” varieties’ similarity [24], the significance of which was verified by means of critical value Dα called “the least significant distance” [25]. Mahalanobis distances were calculated for the varieties independently for locations. All analyses were conducted using the GenStat v. 18 statistics software [26].
3. Results
3.1. MANOVA and ANOVA Results
In the current study, all quantitative traits had a normal distribution as well as multivariate normality (Table 4).

Table 4.
Shapiro–Wilk W statistic value for testing of normal distribution of particular traits and multivariate normality.
The results of MANOVA showed that the locations (Wilks’ λ = 0.004916; F = 809.61; p < 0.001), varieties (Wilks’ λ = 0.000056; F = 5.98; p < 0.001) and location × variety interaction (Wilks’ λ = 0.000637; F = 3.72; p < 0.001) were significantly different when investigated for all nine quantitative traits jointly. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated that the main effects of location and variety were significant for all the traits of study. Location × variety interactions were significant for all the traits except storage waste and index shape (Table 5).

Table 5.
Mean squares from two-way analysis of variance of nine traits of the onion.
3.2. Correlation Analysis
The results of the correlation analysis are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2. Yield was significantly positively correlated with single weight in both locations (0.85 in Khuzestan and 0.61 in Isfahan) and with bulb height (0.52 in Khuzestan and 0.55 in Isfahan). Bulb height was positively correlated with index shape in both locations (0.68 in Khuzestan and 0.70 in Isfahan). Bulb diameter was positively correlated with single weight in both locations (0.81 in Khuzestan and 0.66 in Isfahan); however, soluble was negatively correlated with bulb height in both locations (–0.79 in Khuzestan and –0.53 in Isfahan). Yield was significantly correlated with dry matter—positively in Isfahan (0.62), and negatively in Khuzestan (–0.54) (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Additionally, only in Khuzestan did we observe correlations between: yield and bulb diameter (0.94), single weight and dry matter (–0.79), single weight and soluble (–0.64), single weight and bulb height (0.79), dry matter and soluble (0.94), dry matter and bulb height (–0.81), dry matter and bulb diameter (–0.59) and soluble and index shape (–0.53), as well as storage waste and index shape (–0.72) (Figure 1). Additionally, only in Isfahan was bulb diameter negatively correlated with index shape (–0.54) (Figure 2).

Figure 1.
Heatmaps for linear Pearson’s correlation coefficients between the observed traits on the basis of mean values for varieties in Khuzestan; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 (r0.05 = 0.51, r0.01 = 0.64, r0.001 = 0.76).
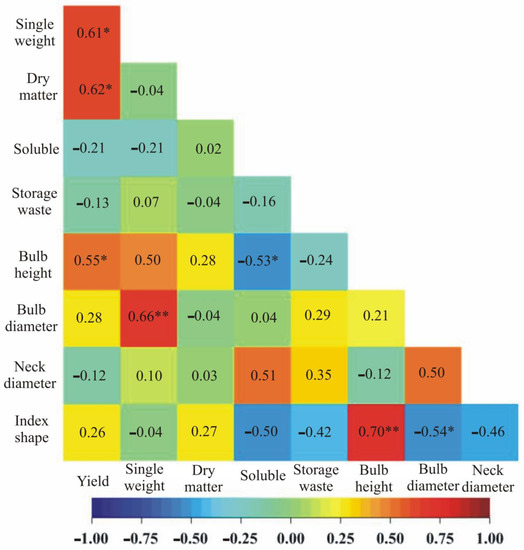
Figure 2.
Heatmaps for linear Pearson’s correlation coefficients between the observed traits on the basis of mean values for varieties in Isfahan; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01 (r0.05 = 0.51, r0.01 = 0.64).
3.3. The Canonical Variate Analysis (CVA) and Mahalanobis Distances D2
The analysis of canonical variables is a statistical tool which makes it possible to solve the problem of multivariate relationships [6,27,28]. The results of the CVA for the varieties are shown in Table 6 and Figure 3 and Figure 4.

Table 6.
Correlation coefficients between the first two (V1 and V2) canonical variables and observed traits in two locations.
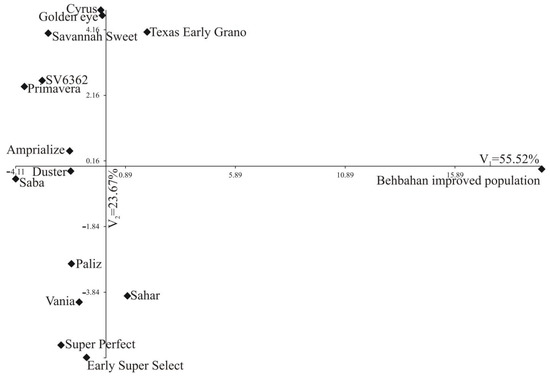
Figure 3.
Distribution of 15 varieties of onion in the space of the first 2 canonical variables in Khuzestan. In the diagrams, the coordinates of a given variety are the values of the first (V1) and second (V2) canonical variable, respectively.
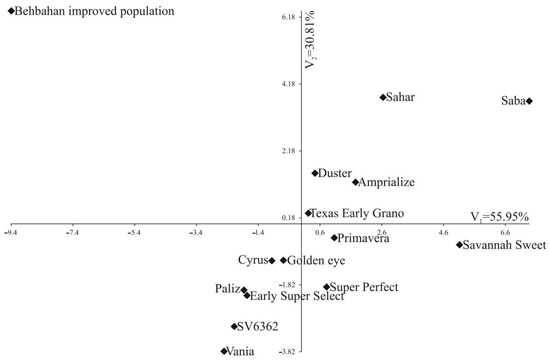
Figure 4.
Distribution of 15 varieties of onion in the space of the first 2 canonical variables in Isfahan. In the diagrams, the coordinates of a given variety are the values of the first (V1) and second (V2) canonical variable, respectively.
3.3.1. Khuzestan
The first and second canonical variables explained 55.52% and 23.67% of the total variation between the varieties (Table 6, Figure 3) in Khuzestan, respectively. Figure 3 shows the distribution of the varieties in the system of the first two canonical variables in Khuzestan. In the diagrams, the coordinates of a given variety are the values of the first and second canonical variable, respectively. A significant linear relationship with the first canonical variable was found for dry matter and soluble (positive dependencies) as well as single weight, bulb height and index shape (negative dependencies) (Table 6). The second canonical variable was significantly positively correlated with yield, single weight, storage waste and bulb diameter, while negatively with index shape (−0.68) (Table 6). In this location, the greatest variation in terms of all the nine traits jointly measured with Mahalanobis distances was found for the Saba and Behbahan improved population (distance between them amounted to 24.409). The greatest similarity was found between Paliz and Vania (3.549) (Table 7).

Table 7.
Mahalanobis distances between varieties studied in Khuzestan (above diagonal) and Isfahan (below diagonal).
3.3.2. Isfahan
The first and second canonical variables explained 55.95% and 30.81%, respectively, of the total variation between the varieties (Table 6, Figure 4) in Isfahan. Figure 4 shows the distribution of the varieties in the system of the first two canonical variables in Isfahan. A significant positive linear relationship with the first canonical variable was found for yield, dry matter, bub height and index shape, while negative with soluble and neck diameter (Table 6). The second canonical variable was significantly positively correlated with dry matter and negatively with storage waste. In this location, the greatest variation in terms of all nine traits jointly measured with Mahalanobis distances was found for the Saba and Behbahan improved population (17.070). The greatest similarity was found between Paliz and Early Super Select (1.084) (Table 7).
4. Discussion
Genetic variations were observed in the present study for bulb yield and its associated traits due to genetic divergence among the varieties, locations and interactions. The previous study results on onion showed genetic divergence among the genotypes [29,30]. A significant yield difference was observed among the genotypes in Isfahan and Khuzestan, with the most sensitive genotypes being severely affected by climatic conditions during the bulb development stage. Bulb yield reduction might be due to reduction in leaf photosynthesis and the translocation process toward developing bulbs. In agreement with the results of this study, Lee et al. [4] reported that the difference in maturity and environmental conditions can affect the bulb yield, rather than the variety. Lee et al. [4] evaluated the performance of 55 intermediate-day onion cultivars and clustered the genotypes based on fresh bulb weight, bulb initiation, bulb maturity and marketable bulb yield. Their results classified 55 cultivars into five clusters, with close distances in clusters among late-maturing cultivars. The findings were further supported by the study of Tesfaendrias et al. [31]: in a long-term trial of 12 years using cultivars harvested between September 6 and 15, there was no significant difference in market bulb yield of five cultivars during the 1997 to 2000 growing seasons, but temperature and rainfall in the different years significantly affected bulb yield.
The correlation analysis showed a significantly higher positive correlation between single weight and yield in both locations, indicating that genotypes with high single weight, have more bulb yield in different conditions. The present study results are consistent with those of a previous study, where 55 intermediate-day onion cultivars were clustered in five groups and fresh bulb weight and marketable bulb yield of clusters 3, 4 and 5 were not significantly different from one another [4]. In the study of Singh et al. [32], on the basis of single linkage cluster on 34 onion genotypes, means cluster-I was most important for average bulb weight, minimum bolters, high marketable bulb percentage and total bulb yield, whereas cluster-II was important for maximum number of leaves/plant and minimum neck thickness. Nakamura [33] and McCollum [34,35,36], as well as Dowker and Fennell [37], estimating the heritability of bulb size and shape in different populations of onion, realized that diameters and weights showed low heritability, while height and shape indices (calculated as the ratio of height over diameter) demonstrated high heritability. Thus, it is possible to increase yield by focusing on the selection of two traits, height and shape index. The positive correlation between yield and dry matter in Isfahan and negative association between yield and dry matter in Khuzestan indicates that a high-yielding genotype can have high or low dry matter, although many studies have indicated a negative relationship between yield and dry matter [1]. Thus, the present finding in Isfahan is not supported by previous study results.
In this study, the greatest Mahalanobis distances were shown between the Saba and Behbahan improved population (22.076) and the Savannah Sweet and Behbahan improved population (12.259) in Khuzestan and Isfahan, respectively. These results should be considered interesting. Further, unique progenies can be obtained from crossing between high yielding onion genotypes and high-quality genotypes to ingress the genes in the progenies without affecting the inherent yield potential. The current study results were in agreement with the results of Bal et al. [29] who, using Mahalanobis D2, grouped twenty-three onion genotypes in eight groups and reported super genotypes as parents for future hybridization programs.
The results of the analyses described here indicate the power of multivariate analysis as an exploratory technique. For discrimination, the Mahalanobis distance is a particularly powerful concept (due to invariant under any scaling of the original variables); it indicated the presence of a great amount of diversity in the onion genotypes under study. Furthermore, the other studies on the onion from Prashanthi et al. [38], Rashid et al. [39] and Mohanty [40] reported the importance of D2 analysis in the destination among genotypes. Canonical variate analysis allowed for the distinction between our plant materials and the biggest difference in terms of all the investigated traits. Since ~85% of the total generalized variation is displayed by the first two canonical variables in two locations, a satisfactory level of discrimination is achieved without the need to consider the influence of the third or fourth canonical variable axes.
5. Conclusions
- During this study, significant correlations were observed for the traits under study. The use of canonical variable analysis grouped genotypes into two clusters. Genotypes Paliz and Vania showed the lowest variability in Khuzestan, whereas Paliz and Early Super were reported in Isfahan;
- Multivariate methods were an effective tool for assessing the similarity/difference of the studied genotypes in terms of the nine quantitative traits taken together. The multivariate approach is very important when correlation of observed traits is observed;
- The tested genotypes were very diverse. The Saba and Behbahan improved population, as the most diverse genotypes, are recommended for further inclusion in future crop improvement programs, independent of location.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.A.; methodology, Z.A., A.D. and J.B.; software, J.B.; validation, Z.A. and A.D.; formal analysis, J.B.; investigation, Z.A., A.D. and J.B.; resources, Z.A.; data curation, Z.A. and A.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.A., A.D. and J.B.; writing—review and editing, Z.A., A.D. and J.B.; visualization, J.B.; supervision, Z.A.; project administration, J.B.; funding acquisition, J.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Havey, M.J. Onion breeding. Plant Breed. Rev. 2018, 42, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, K.; Ebadzade, H.; Hatami, F.; Mohamadnia Afruzi, S.; Esfandiari, E.; Taghani, R.A. Agricultural Statistics of Crops; Information and Communication Technology Center, Ministry of Jihad Agriculture: Tehran, Iran, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 1–89. [Google Scholar]
- Brewster, J.L. Onions and Other Vegetable Alliums, 2nd ed.; CAB International: London, UK, 2008; 432p. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Moon, J.S.; Kim, J.; Park, G.O.; Kwon, J.H.; Ha, I.J.; Kwon, Y.S.; Chang, Y.H. Evaluation of onion cultivars as affected by bulb maturity and bulb characteristics of intermediate-day yellow onions in South Korea. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R.; Lal, S.; Ahmed, N.; Srivastava, K.K.; Kumar, D.; Jan, N.; Amin, A.; Malik, A.R. Determination of genetic diversity in onion (Allium cepa L.) using the multivariate analysis under long day conditions. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 7, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocianowski, J.; Majchrzak, L. Analysis of effects of cover crop and tillage method combinations on the phenotypic traits of spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using multivariate methods. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 15267–15276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Pastor, J.L.; Barre, P.; Keep, T.; Ledauphin, T.; Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.; Roschanski, A.M.; Willner, E.; Dehmer, K.J.; Hegarty, M.; Muylle, H.; et al. Canonical correlations reveal adaptive loci and phenotypic responses to climate in perennial ryegrass. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21(3), 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Dong, F.; Zhang, S. Adaptive spatio-temporal feature extraction and analysis for horizontal gas-water two-phase flow state prediction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 268, 118434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwarc, J.; Niemann, J.; Bocianowski, J.; Jakubus, M.; Mrówczyński, M. Connection between Nutrient Content and Resistance to Selected Pests Analyzed in Brassicaceae Hybrids. Agriculture 2021, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, T.; Skrzypek, E.; Bocianowski, J.; Sutkowska, A. Impact of Selected PSII Parameters on Barley DH Lines Biomass and Yield Elements. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrońska-Pilarek, D.; Maciejewska-Rutkowska, I.; Bocianowski, J.; Korzeniewicz, R.; Lechowicz, K.; Hauke-Kowalska, M. Does the Reaction of Inflorescences and Flowers of the Invasive Prunus serotina Ehrh. to Various Herbicides Give Hope for Elimination of This Species from Polish Forests? Forests 2022, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, Z.; Darabi, A.; Shahmansouri, E. Evaluation of short day onion (Allium cepa L.) genotypes for quantity and quality traits. J. Hortic. Postharvest Res. 2022, 5, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafie, M.R.; Khoshgoftarmanesh, A.H.; Shariatmadari, H.; Darabi, A.; Dalir, N. Influence of foliar-applied zinc in the form of mineral and complexed with amino acids on yield and nutritional quality of onion under field conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 216, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahane, R.; Vaillle-Guerin, E.; Boukema, I.; Tzanoudakis, D.; Bellamy, C.; Chamaux, C.; Kik, C. Changes in non- structural carbohydrate composition duringbulbing in sweet and high-solid onions in field experiments. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 45, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, L.K.; Hoyle, B.J. Use of the refractometer for selection of onion bulbs high in dry matter for breeding. Proc. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1945, 46, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Aske, V.; Jain, P.; Lal, N.; Shiurkar, G. Effect of Micronutrients on Yield, Quality, and Storability of Onion cv. Bhima Super. Trends Biosci. 2017, 10, 1354–1358. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Narayan-Lal/publication/314283800_Effect_of_Micronutrients_on_Yield_Quality_and_Storability_of_Onion_cv_Bhima_Super/links/58bf94caa6fdccff7b1fa27f/Effect-of-Micronutrients-on-Yield-Quality-and-Storability-of-Onion-cv-Bhima-Super.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Association of Official Agricultural Chemists; Horwitz, W. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA; AOAC Int.: Arlington, TX, USA, 1990; Volume 222, 58p. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P. A General Distribution Theory for a Class of Likelihood Criteria. Biometrika 1949, 36, 317–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, R.T. A primer on multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) for behavioral scientists. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2014, 19, 1–10. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=52eff0488d0b93ea4a259815148faeb3e9646600 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Cochran, W.G.; Cox, G.M. Experimental Designs, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Available online: https://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/bitstream/handle/1840.4/2425/ISMS__4.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Pearson, K. Notes on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. Available online: https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/pdf/10.1098/rspl.1895.0041 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Rencher, A.C. Interpretation of canonical discriminant functions, canonical variates, and principal components. Am. Stat. 1992, 46, 217–225. Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00031305.1992.10475889 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Seidler-Łożykowska, K.; Bocianowski, J. Evaluation of variability of morphological traits of selected caraway (Carum carvi L.) genotypes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 35, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. On the generalized distance in statistics. Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. India 1936, 12, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- VSN International. GenStat for Windows, 18th ed.; VSN International: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lahuta, L.B.; Ciak, M.; Rybiński, W.; Bocianowski, J.; Börner, A. Diversity of the composition and content of soluble carbohydrates in seeds of the genus Vicia (Leguminosae). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2018, 65, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrońska-Pilarek, D.; Szkudlarz, P.; Bocianowski, J. Systematic importance of morphological features of pollen grains of species from Erica (Ericaceae) genus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bal, S.; Maity, T.K.; Maji, A. Genetic divergence studies for yield and quality traits in onion (Allium cepa L.). Internat. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedam, P.A.; Thangasamy, A.; Shirsat, D.V.; Ghosh, S.; Bhagat, K.P.; Sogam, O.A.; Gupta, A.J.; Mahajan, V.; Soumia, P.S.; Salunkhe, V.N.; et al. Screening of onion (Allium cepa L.) genotypes for drought tolerance using physiological and yield based indices through multivariate analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 600371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaendrias, M.T.; McDonald, M.R.; Warland, J. Consistency of long-term marketable yield of carrot and onion cultivars in muck (organic) soil in relation to seasonal weather. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 90, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R.; Ahamed, N.; Srivastava, K.K.; Kumar, D.; Yousuf, S. Assessment of genetic divergence in long day onion (Allium cepa L.) through principal component and single linkage cluster analysis. J. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 15, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, N. Studies on the breeding of Allium cepa L., I. Estimating heritability. Jpn. J. Breed. 1959, 8, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, G.D. Heritability and genetic correlation of some onion bulb traits: Estimates from S1 offspring-on-parent regression. J. Heredity 1966, 57, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, G. Heritability and genetic correlations of soluble solids, bulb size and shape in white sweet Spanish onion. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 1968, 10, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, G. Heritability of onion bulb shape size: Estimates from half-sib families. J. Hered. 1971, 62, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowker, B.; Fennell, J. Heritability of bulb shape in some north European onion varieties. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1974, 77, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prashanthi, M.; Lakshminarayana, D.; Mallesh, S.; Nikhil, B.S.K.; Sathish, G. Genetic diversity in onion (Allium cepa L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2021, 10, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.H.; Islam, A.K.M.A.; Mian, M.A.K.; Hossain, T.; Kabir, M.E. Multivariate Analysis in Onion (Allium cepa L.). Bangladesh J. Agric. Res. 2012, 37, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, B.K. Genetic variability, inter-relationship and path analysis in onion. J. Trop. Agric. 2006, 39, 17–20. Available online: http://www.jtropag.kau.in/index.php/ojs2/article/view/5/5 (accessed on 1 January 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).