Variations in Water and Deposited Sediment Qualities in the Tidal River Basins of Bangladesh and Their Implications for TRM Success
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
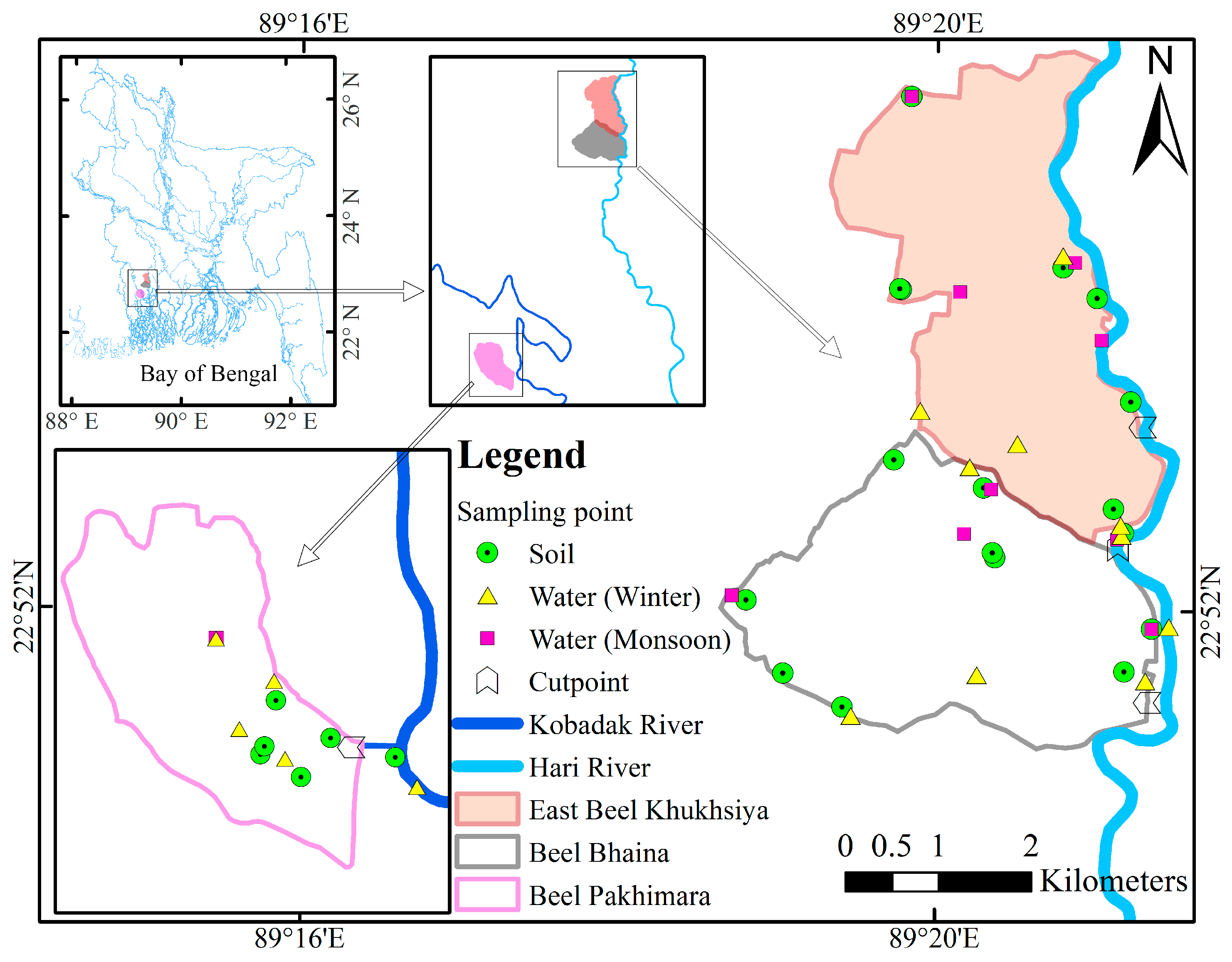
2.1. Selection of the Tidal River Basins
2.1.1. Beel Bhaina
2.1.2. East Beel Khuksia
2.1.3. Beel Pakhimara
2.2. Analysis of Water Quality
2.3. Assessment of Suitability of Water for Irrigation Purpose
2.3.1. SAR
2.3.2. Na%
2.3.3. PS
2.3.4. PI
2.3.5. KI
2.3.6. MR
2.3.7. Ca:Mg
2.4. Analysis of Deposited Sediment Quality
2.5. Collection of Agricultural and Socioeconomic Data
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality in the Tidal Basins
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. EC
3.1.3. TDS and TSS
3.1.4. Cations
3.1.5. Anions
3.2. Agricultural Suitability Indices
3.2.1. SAR
3.2.2. Na%
3.2.3. PS
3.2.4. PI
3.2.5. KI
3.2.6. MR
3.2.7. Ca:Mg
3.3. Quality of the Deposited Sediment in the Tidal Basins
3.3.1. pH
3.3.2. EC
3.3.3. Calcium
3.3.4. Magnesium
3.3.5. Iron
3.3.6. Phosphorus
3.3.7. Sulphur
3.3.8. Chloride
3.4. Deposited Sediment Composition in the Tidal Basins
3.4.1. Soil Texture
3.4.2. OM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Islam, M.F.; Schot, P.P.; Dekker, S.C.; Griffioen, J.; Middelkoop, H. Physical controls and a priori estimation of raising land surface elevation across the southwestern Bangladesh delta using tidal river management. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 903–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Minnen, J.N. Sediment Transport in the Tidal Basins, South West Delta Bangladesh, A Historical and Physical Perspective. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, M.A. Geologic framework and environmental status of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 826–836. [Google Scholar]
- Die, L.D. Tidal River Management: Temporary Depoldering to Mitigate Drainage Congestion in the Southwest Delta of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gain, A.K.; Benson, D.; Rahman, R.; Datta, D.K.; Rouillard, J.J. Tidal river management in the south west Ganges-Brahmaputra delta in Bangladesh: Moving towards a transdisciplinary approach? Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 75, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Dustegir, M.; Karim, R.; Haque, A.; Nicholls, R.J.; Darby, S.E.; Nakagawa, H.; Hossain, M.; Dunn, F.E.; Akter, M. Recent sediment flux to the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna River basin. In Irrigation in Southern and Eastern Asia, AQUASTAT Survey—2011; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mehzabin, S.; Mondal, M.S. Assessing impact of climate variability in southwest coastal Bangladesh using livelihood vulnerability index. Climate 2021, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Hasan, K.; Kabir, K.H. Determinants of households’ livelihood vulnerability due to climate induced disaster in southwest coastal region of Bangladesh. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2022, 15, 100243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, M.G.; Saha, D.; Kabir, T.; Naher, T.; Maliha, S.; Mondal, M.S. Achieving food security in storm-surge prone coastal polders of south-west Bangladesh. South. Asia Water Stud. (SAWAS) J. 2015, 5, 26–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mutahara, M. Turning the Tide? The Role of Participation and Learning in Strengthening Tidal River Management in the Bangladesh Delta. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brammer, H. Bangladesh’s dynamic coastal regions and sea-level rise. Clim. Risk Manag. 2014, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Alam, R.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Khan, M.N.A.A.; Jahan, I.N. Methodology of crest level design of coastal polders in Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Water & Flood Management (ICWFM-2013), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 9–11 March 2013; Institute of Water and Flood Management, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, R.; Ahmed, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, G. Coastal vulnerability assessment of Meghna estuary of Bangladesh using integrated geospatial techniques. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchabhadel, R.; Nakagawa, H.; Kawaike, K. Tidal River Management (TRM) and Tidal Basin Management (TBM): A case study on Bangladesh. E3S Web Conf. 2016, 7, 12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, S.; Mondal, M.S. Risk-based determination of polder height against storm surge hazard in the south-west coastal area of Bangladesh. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 8, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, M.S.I.I. Socio-Technical Assessment of Sediment Management Options in Tidal Basin in Southwestern Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rouf, M.A. Evaluating Flood Control and Drainage Management Systems from a Productive Efficiency Perspective: A Case Study of the Southwest Coastal Zone of Bangladesh. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Kibria, Z. Unraveling KJDRP: ADB Financed Project of Mass Destruction in South West Coastal Region of Bangladesh; Uttaran: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A.; Dawes, L.; Donehue, P.; Rahman, M.R. Cross-temporal analysis of disaster vulnerability of the southwest coastal communities in Bangladesh. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2021, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.H.; Hossain, M.J.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Billah, M. Salinity intrusion in southwest coastal Bangladesh: An insight from land use change. In Water, Flood Management and Water Security under a Changing Climate; Haque, A., Chowdhury, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Mondal, M.S.; Islam, M.T.; Saha, D.; Hossain, M.S.S.; Das, P.K.; Rahman, R. Agricultural adaptation practices to climate change impacts in coastal Bangladesh. In Confronting Climate Change in Bangladesh: Policy Strategies for Adaptation and Resilience; Huq, S., Chow, J., Fenton, A., Stott, C., Taub, J., Wright, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 28, pp. 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Moslehuddin, A.Z.M.; Abedin, M.A.; Hossain, M.A.R.; Habiba, U. Soil health and food security: Perspective from southwestern coastal region of Bangladesh. In Food Security and Risk Reduction in Bangladesh. Disaster Risk Reduction; Habiba, U., Hassan, A., Abedin, M., Shaw, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2015; pp. 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basar, A. Water security in coastal region of Bangladesh. Bangladesh e-J. Sociol. 2012, 9, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, Z.; Hussain, S.G.; Ahmed, M. Salinity Problems and Crop Intensification in the Coastal Regions of Bangladesh; Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council (BARC): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1990; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- BWDB. EIA Report on Coastal Embankment Improvement Program, Phase 1 (CEIP-I); Ministry of Water Resources, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2013.
- Uttaran. People’s Plan of Action for Management of Rivers in South-West Coastal Region of Bangladesh; Uttaran: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Masud, M.M.A.; Moni, N.N.; Azadi, H.; Van Passel, S. Sustainability impacts of tidal river management: Towards a conceptual framework. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Maren, D.S.; Beemster, J.G.W.; Wang, Z.B.; Khan, Z.H.; Schrijvershof, R.A.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Tidal amplification and river capture in response to land reclamation in the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. Catena 2023, 220, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhuis, P.H. Environmental History of the Rhine-Meuse Delta: An Ecological Story on Evolving Human-Environmental Relations Coping with Climate Change and Sea-Level Rise; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Essink, G.H.P.; van Baaren, E.S.; de Louw, P.G.B. Effects of climate change on coastal groundwater systems: A modeling study in the Netherlands. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 2009WR008719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Mondal, M.K.; Shew, A.; Jagadish, S.V.K.; Khan, Z.H.; Sutradhar, A.; Bhandari, H.; Humphreys, E.; Bhattacharya, J.; Parvin, R.; et al. Community water management to intensify agricultural productivity in the polders of the coastal zone of Bangladesh. Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 18, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEGIS. Coastal Land Use Zoning in the Southwest: Impact of Sea Level Rise on Land Use Suitability and Adaptation Options; CEGIS: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, S.; Shams, J.; van Laerhoven, F.; Driessen, P. The impact of decision-making on conflict: Rethinking the roles of technocrats and residents during tidal river management in coastal Bangladesh. Land Use Policy 2022, 117, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowreen, S.; Jalal, M.R.; Khan, M.S.A. Historical analysis of rationalizing south west coastal polders of Bangladesh. Water Policy 2014, 16, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, M.A. Water logging in south-western coastal region of Bangladesh: Local adaptation and policy options. Sci. Postprint 2014, 1, e00038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadim, F.K.; Kar, K.K.; Halder, P.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Morshed, A.K.M.M. Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM) impacts in south west coastal zone of Bangladesh and fact-finding on Tidal River Management (TRM). J. Water Resour. Prot. 2013, 5, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kibria, Z. Tidal River Management (TRM): Climate Change Adaptation and Community Based River Basin Management in Southwest Coastal Region of Bangladesh; Uttaran: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Seijger, C.; Datta, D.K.; Douven, W.; van Halsema, G.; Khan, M.F. Rethinking sediments, tidal rivers and delta livelihoods: Tidal river management as a strategic innovation in Bangladesh. Water Policy 2019, 21, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, L.W.; Goodbred, S.L.; Mondal, D.R.; Wilson, C.A.; Ahmed, K.R.; Roy, K.; Steckler, M.S.; Small, C.; Gilligan, J.M.; Ackerly, B.A. Reply to “Tidal River Management in Bangladesh”. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 492–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Staveren, M.F.; Warner, J.F.; Khan, M.S.A. Bringing in the tides. From closing down to opening up delta polders via tidal river management in the southwest delta of Bangladesh. Water Policy 2016, 19, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shampa, M.I.M.P. Tidal River Management (TRM) for selected coastal area of Bangladesh to mitigate drainage congestion. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jakarya, M.; Sikder, M.T.; Yousuf, A.I. Review of an integrated strategy of climate change adaptation using tidal river management. J. Health Environ. Res. 2016, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paul, A.; Nath, B.; Abbas, M.R. Tidal River Management (TRM) and its implication in disaster management: A geospatial study on Hari-Teka River basin, Jessore, Bangladesh. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2013, 4, 125–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, S.; Osawa, K.; Akamatsu, Y. Sediment and nutrients transport in watershed and their impact on coastal environment. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2009, 85, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, H.M.; Hasan, M.R.; Ahmed, B.; Miah, M.S.U. Investigation of soil and water salinity, its effect on crop production and adaptation strategy. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2013, 5, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Hassan, K.M.; Alam, M.; Akid, A.S.M.; Riyad, A.S.M. Effects of salinity on land fertility in coastal areas of Bangladesh. Int. J. Renew. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 2, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, S.A. Salinity problems and crop production in coastal regions of Bangladesh. Pak. J. Bot. 2006, 38, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Mutahara, M.; Warner, J.F.; Wals, A.E.J.; Khan, M.S.A.; Wester, P. Social learning for adaptive delta management: Tidal river management in the Bangladesh delta. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2018, 34, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.M.; Islam, T.; Rouf, T. Limitations of institutional management and socio-economic barriers of tidal river management, a semi-natural process to save Bhabodaho from water-logging problem. In Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Kyoto, Japan, 2–5 September 2013; pp. 2173–2183. [Google Scholar]
- Parvin, G.A.; Ali, M.H.; Fujita, K.; Abedin, M.A.; Habiba, U.; Shaw, R. Land use change in southwestern coastal Bangladesh: Consequence to food and water supply. In Land Use Management in Disaster Risk Reduction. Disaster Risk Reduction; Banba, M., Shaw, R., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; pp. 381–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.F.; Middelkoop, H.; Schot, P.P.; Dekker, S.C.; Griffioen, J. Enhancing effectiveness of tidal river management in southwest Bangladesh polders by improving sedimentation and shortening inundation time. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, R.M. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Soil Collected from Some Selected Agro-Ecological Zones of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh Agricultural University, Mymensingh, Bangladesh, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mahtab, M.H.; Zahid, A. Coastal surface water suitability analysis for irrigation in Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaha, M.K.; Kibria, K.Q.; Datta, D.K. Assessing the water, sediment and soil quality of Mayur River, Khulna, Bangladesh. In Peri-Urban Water Security in South Asia: Adapting to Climate Change and Urbanization; SaciWATERs: Hyderabad, India, 2013; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Karim, M.R.; Akter, F.; Islam, M.S.; Ahmed, K.; Rahman, M.; Datta, D.K.; Khan, M.S.A. Hydrochemistry, water quality and land use signatures in an ephemeral tidal river: Implications in water management in the southwestern coastal region of Bangladesh. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Islam, A.; Majumder, A. Seawater intrusion into groundwater and its impact on irrigation and agriculture: Evidence from the coastal region of West Bengal, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, B.; Islam, A.; Shit, P.K.; Quesada-Román, A.; Gazi, H.A.R. Surface water and groundwater suitability for irrigation based on hydrochemical analysis in the lower Mayurakshi River Basin, India. Geosciences 2022, 12, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, O.K.; Adedokun, O.A.; Yusuf, R.K.; Adeleye, E.A. Seasonal changes in physico-chemical parameters and nutrient load of river sediments in Ibadan City, Nigeria. Glob. NEST J. 2008, 10, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, R.; Mondal, R. Local stakeholder analysis of Tidal River Management (TRM) at Beel Kapalia and the implication of TRM as a disaster management approach. Hydrology 2017, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Saha, D.; Hossain, M.S.S.H.; Mondal, M.S.; Rahman, R. Agricultural adaptation practices in coastal Bangladesh: Response to climate change impacts. J. Mod. Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, I.H. Remote Sensing Based Estimates of Reference Evapotranspiration for the Southwest Region of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz, N. Assessment of the Variability in Nutrient Content of Water and Deposited Sediment in Selected Tidal Basins of Bangladesh. Master’s Thesis, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hossen, M.A. The Gorai River restoration and the Ganges-Kobodak projects. In Water Policy and Governance in South Asia: Empowering Rural Communities; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 54–80. [Google Scholar]
- Jaji, M.O.; Bamgbose, O.; Odukoya, O.O.; Arowolo, T.A. Water quality assessment of Ogun River, south west Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; Clesceri, L.S., Greenboug, L.S., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environmental Federation: Chicago, IL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils. Handbook No 60; United States Department of Agriculture, Soil and Water Conservation Research Branch Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaray, S.K.; Nayak, B.B.; Bhatta, D. Environmental studies on river water quality with reference to suitability for agricultural purposes: Mahanadi River estuarine system, India—A case study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 155, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture; Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao, M.; Reddy, M.R.B. Groundwater quality assessment in Srikalahasthi Mandal, Chittoor District, Andhra Pradesh, South India. IOSR J. Eng. (IOSRJEN) 2018, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.K.; Tewari, G.; Kumar, S. Evaluation of groundwater quality for suitability of irrigation purposes: A case study in the Udham Singh Nagar, Uttarakhand. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 6924026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilagavathi, R.; Chidambaram, S.; Prasanna, M.V.; Thivya, C.; Singaraja, C. A study on groundwater geochemistry and water quality in layered aquifers system of Pondicherry region, southeast India. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.P. Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci. 1963, 95, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, K.V. Irrigation with Saline Water, Monogram No. 2 (New Series); Indian Agricultural Research Institute: New Delhi, India, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 29, Revision 1; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- BARC. Fertilizer Recommendation Guide-2005; Soils Publication No. 45; Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2005.
- Gee, G.W.; Bauder, J.W. Particle-size analysis. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 1—Physical and Mineralogical Methods; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA; Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.J.; Smethurst, P.J.; Herbert, A.M. Relationships between three measures of organic matter or carbon in soils of eucalypt plantations in Tasmania. Aust. J. Soil. Res. 1996, 34, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BADC. Water Quality for Irrigation: Emphasis on Arsenic Contamination in Agriculture; Bangladesh Agricultural Development Corporation: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2007.
- MoEFCC. Environment Conservation Rules, 2023; Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023.
- EPA. Guidelines for Water Reuse; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Holmes, S. Field guide. In South African Water Quality Guidelines; Holmes, S., Ed.; Department of Foreign Affairs and Forestry, Republic of South Africa: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Todd, D.K. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- SRDI. Land and Soil Utilization Guide, Mollahatthana, Bagerhat; Soil Resource Development Institute, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tutu, A.-U.-A. River management in Bangladesh: A people’s initiative to solve waterlogging. In Participatory Learning and Action 51: Civil Society and Poverty Reduction; International Institute for Environment and Development (IIED): London, UK, 2005; pp. 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- IWM. Monitoring of Sedimentation, Salinity, Tide and Flood in Kobadak River System and TRM Basin; Institute of Water Modelling, Bangladesh Water Development Board: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Determination Method |
|---|---|
| pH | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| EC | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| TDS | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| TSS | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| Na+, K+ | Flame photometric method [66] |
| Ca2+, Mg2+ | Titrimetric method [66] |
| HCO3− | Titration method [66] |
| Cl− | Titration by silver nitrate [66] |
| NO3−, NO2−, PO43−, SO42−, total Fe | Turbidimetric method (Thermo Spectronic, UV-visible spectrophotometer) [66] |
| Parameter | Determination Method |
|---|---|
| Soil texture | Hydrometer [77] |
| Organic matter | Loss by ignition [78] |
| pH | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| Salinity | HANNA Instrument, pH 211 [66] |
| Ca2+, Mg2+ | Titrimetric method [66] |
| Total Fe, total P, S | Turbidimetric method (Thermo Spectronic, UV-visible spectrophotometer) [66] |
| Cl− | Titration by silver nitrate [66] |
| Season | Source | pH | EC µS/cm | TDS mg/L | TSS mg/L | Total Fe mg/L | Na+ mg/L | K+ mg/L | Ca2+ mg/L | Mg2+ mg/L | PO43− mg/L | NO3− mg/L | NO2− mg/L | SO42− mg/L | HCO3− mg/L | Cl− mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Hari River | 6.8 | 19,210 | 9600 | 2099 | 0.005 | 5014 | 114 | 168 | 442 | 0.7 | 2.8 | 0.004 | 2519 | 159 | 3722 |
| Basin | 7.2 | 18,245 | 9130 | 1378 | 0.005 | 4328 | 112 | 128 | 433 | 0.8 | 6.0 | 0.004 | 1942 | 180 | 4271 | |
| GW | 7.7 | 3010 | 1486 | 310 | 0.005 | 609 | 9 | 111 | 58 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 0.004 | 287 | 375 | 540 | |
| Monsoon | Basin | 7.1 | 1613 | 815 | 59 | 0.005 | 357 | 2 | 42 | 29 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 0.006 | 142 | 220 | 390 |
| GW | 7.6 | 1852 | 925 | 195 | 0.005 | 399 | 2 | 61 | 32 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.005 | 86 | 498 | 390 | |
| Permissible Limit * | 6.5–8.5 | 2250 | 1000 | 50 | 2 | 920 | 2 | 400 | 61 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 960 | 610 | 600 |
| Season | Source | pH | EC µS/cm | TDS mg/L | TSS mg/L | Total Fe mg/L | Na+ mg/L | K+ mg/L | Ca2+ mg/L | Mg2+ mg/L | PO43− mg/L | NO3− mg/L | NO2− mg/L | SO42− mg/L | HCO3− mg/L | Cl− mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Hari River | 7.3 | 18,900 | 9450 | 8679 | 0.005 | 4709 | 108 | 168 | 369 | 0.4 | 5.9 | 0.004 | 3010 | 171 | 4360 |
| Basin | 7.7 | 9800 | 4900 | 923 | 0.005 | 3453 | 57 | 136 | 168 | 0.4 | 4.2 | 0.004 | 1979 | 159 | 2411 | |
| GW | 7.3 | 1385 | 690 | 221 | 0.005 | 237 | 2 | 55 | 35 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.004 | 113 | 519 | 239 | |
| Monsoon | Hari River | 6.9 | 844 | 422 | 349 | 0.005 | 145 | 4 | 36 | 23 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.003 | 122 | 214 | 177 |
| Basin | 7.0 | 2135 | 1075 | 721 | 0.005 | 421 | 13 | 41 | 34 | 0.9 | 8.0 | 0.004 | 217 | 189 | 471 | |
| GW | 7.7 | 666 | 334 | 59 | 0.005 | 106 | 2 | 56 | 22 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.004 | 506 | 302 | 157 |
| Season | Source | pH | EC µS/cm | TDS mg/L | TSS mg/L | Total Fe mg/L | Na+ mg/L | K+ mg/L | Ca2+ mg/L | Mg2+ mg/L | PO43− mg/L | NO3− mg/L | NO2− mg/L | SO42− mg/L | HCO3− mg/L | Cl− mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Kobadak River | 7.1 | 977 | 489 | 358 | 0.005 | 258 | 9 | 32 | 24 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.004 | 142 | 153 | 142 |
| Basin | 7.4 | 1149 | 575 | 379 | 0.005 | 106 | 10 | 67 | 31 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.005 | 149 | 336 | 263 | |
| Monsoon | Kobadak River | 6.9 | 806 | 406 | 1395 | 0.005 | 71 | 5 | 52 | 21 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 0.004 | 34 | 378 | 145 |
| Basin | 7.0 | 711 | 356 | 367 | 0.005 | 65 | 5 | 47 | 16 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 0.005 | 91 | 223 | 115 |
| Season | Source | SAR | Na% | PS meq/L | PI | KI | MR | Ca:Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Hari River | 46.05 | 83.13 | 131.39 | 83.56 | 4.86 | 81.22 | 0.23 |
| Basin | 41.41 | 81.77 | 140.89 | 82.28 | 4.57 | 84.51 | 0.18 | |
| GW | 13.42 | 71.51 | 18.26 | 78.14 | 3.57 | 45.23 | 1.22 | |
| Monsoon | Beel | 10.35 | 77.56 | 12.49 | 86.99 | 3.45 | 53.28 | 0.88 |
| GW | 10.30 | 75.20 | 11.91 | 87.52 | 3.06 | 47.12 | 1.17 |
| Season | Source | SAR | Na% | PS meq/L | PI | KI | MR | Ca:Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Hari River | 46.47 | 84.24 | 3.93 | 84.75 | 5.27 | 78.32 | 0.28 |
| Basin | 44.80 | 87.45 | 2.87 | 88.63 | 6.99 | 61.95 | 0.68 | |
| GW | 6.12 | 64.12 | 5.74 | 82.14 | 1.82 | 50.69 | 0.99 | |
| Monsoon | Hari River | 4.63 | 63.38 | 3.95 | 81.70 | 1.70 | 51.28 | 0.95 |
| Basin | 11.77 | 79.46 | 5.97 | 86.84 | 3.81 | 58.47 | 0.72 | |
| GW | 3.03 | 50.35 | 1.24 | 74.64 | 1.01 | 37.98 | 1.76 |
| Season | Source | SAR | Na% | PS meq/L | PI | KI | MR | Ca:Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Kobadak River | 8.36 | 76.06 | 5.48 | 86.36 | 3.11 | 55.48 | 0.80 |
| Basin | 2.91 | 47.35 | 8.99 | 66.32 | 0.96 | 43.58 | 1.39 | |
| Monsoon | Kobadak River | 2.09 | 42.60 | 4.46 | 75.38 | 0.71 | 39.50 | 1.53 |
| Beel | 2.12 | 42.88 | 4.20 | 72.50 | 0.81 | 34.28 | 2.48 |
| Parameters | Beel Bhaina | East Beel Khuksia | Beel Pakhimara | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Monsoon | Dry | Monsoon | Dry | Monsoon | |
| pH | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 7.6 ± 0.3 | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 7.9 ± 0.1 |
| EC (dS/m) | 9.2 ± 5.5 | 5.3 ± 4.3 | 6.2 ± 4.1 | 4.5 ± 1.7 | 11.0 ± 2.0 | 8.3 ± 2.1 |
| Ca2+ (meq/100 g soil) | 20.5 ± 3.9 | 23.0 ± 5.4 | 21.7 ± 3.6 | 24.0 ± 2.9 | 21.3 ± 2.7 | 23.5 ± 3.0 |
| Mg2+ (meq/100 g soil) | 8.2 ± 2.2 | 8.0 ± 2.6 | 6.0 ± 1.5 | 5.8 ± 2.9 | 6.7 ± 1.2 | 7.7 ± 2.6 |
| Total Fe (ppm) | 94.7 ± 91 | 7.0 ± 6.9 | 122.5 ± 106 | 22 ± 39 | 185.7 ± 96 | 13.4 ± 2.4 |
| Total P (ppm) | 39.6 ± 20 | 33.0 ± 11 | 44.0 ± 21 | 57.1 ± 38 | 37.0 ± 7.9 | 37.6 ± 5.1 |
| S (ppm) | 380 ± 355 | 79 ± 143 | 582 ± 199 | 113 ± 94 | 754 ± 81 | 258 ± 107 |
| Cl− (ppm) | 1440 ± 1131 | 1300 ± 440 | 1214 ± 988 | 1131 ± 369 | 2015 ± 439 | 1452 ± 403 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafiz, N.; Biswas, S.; Mondal, M.S.; Islam, M.A.; Khan, M.S.A. Variations in Water and Deposited Sediment Qualities in the Tidal River Basins of Bangladesh and Their Implications for TRM Success. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13855. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813855
Hafiz N, Biswas S, Mondal MS, Islam MA, Khan MSA. Variations in Water and Deposited Sediment Qualities in the Tidal River Basins of Bangladesh and Their Implications for TRM Success. Sustainability. 2023; 15(18):13855. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813855
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafiz, Nureza, Subir Biswas, M. Shahjahan Mondal, Md. Atikul Islam, and M. Shah Alam Khan. 2023. "Variations in Water and Deposited Sediment Qualities in the Tidal River Basins of Bangladesh and Their Implications for TRM Success" Sustainability 15, no. 18: 13855. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813855
APA StyleHafiz, N., Biswas, S., Mondal, M. S., Islam, M. A., & Khan, M. S. A. (2023). Variations in Water and Deposited Sediment Qualities in the Tidal River Basins of Bangladesh and Their Implications for TRM Success. Sustainability, 15(18), 13855. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813855







