Abstract
Marine sediments may easily accumulate contaminants, posing a high risk to human health and biota. Beneficial use applications exist for natural sediments and sediments contaminated with organic and inorganic pollutants. In this research, the term marine sediments (MSs) was used to refer to all marine sediments, which could be clean, natural marine sediments, as well as contaminated marine sediments and dredged materials, as the main focus of this research. Sediment remediation often involves costly and time-consuming processes. Assessment frameworks are essential for selecting suitable remediation alternatives for MSs. This research aims to provide regulatory frameworks for the sustainable beneficial use of all marine sediments. No studies have been reported on this issue in Colombia until now. The current states of marine sediments on the Colombian Caribbean Coast were mainly investigated. Concentrations of specific harmful heavy metals (HHMs) in Colombia’s sediments were higher than the environmental standards of various nations. Ex situ remediation technologies were evaluated through cost–benefit analysis and environmental feasibility to be adopted in Colombia. The results identified solidification/stabilization (S/S) as promising technologies. Sustainable remediation of MSs may offer ample opportunities for environmental enhancement and economic benefits. Continuous research and adopting appropriate environmental regulations, such as the London Protocol 1996, would contribute to effectively managing all marine sediments in Colombia. More innovative and cost-effective remediation technologies with beneficial uses would still be needed. Decision makers may use the proposed frameworks to select optimal remediation alternatives and implement sustainable MSs management by achieving their beneficial uses.
1. Introduction
Marine sediments represent valuable natural resources for humans in the context of sustainable development. Unfortunately, anthropogenic actions and land-based activities may have changed their natural state because of (environmental) dredging activities except for monitored natural recovery (MNR) or in situ capping [1]. The adverse effects of organic pollutants or harmful chemicals have attracted urgent global attention. Harmful chemicals may be adsorbed into sediments, becoming the main sink of various pollution sources in aquatic ecosystems (Figure 1) [2]. Therefore, sustainable management of all marine sediments is inevitably required to solve these problems.
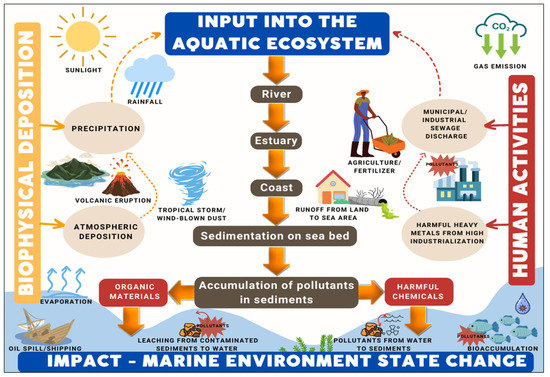
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the main contamination sources of marine sediment.
Marine sediments (MSs), which are clean and natural or contaminated, including dredged materials, have been defined as valuable natural resources rather than waste by the London Protocol of 1996 (LP) [3]. Unfortunately, dredged materials are commonly disposed of by ocean dumping. Instead, sustainable beneficial uses of MSs should be prioritized before disposal.
In this research, beneficial use is defined as the use of contaminated or natural sediments in applications that are beneficial and in harmony with human and natural development [4].
To increase the beneficial uses of MSs, it is essential not only to develop various remediation technologies that may successfully remove contaminants but also to establish assessment management frameworks. Frameworks have historically been developed to assist decision makers in selecting appropriate remediation projects [5].
Ex situ remediation technologies were mainly studied because of their applicability to treat MSs that have been removed from their original aquatic environment and constituted DMs [6]. Followed by the application of remediation technologies, MSs could be successfully transformed into marketable products such as construction materials, agricultural products, coastal protection, and various engineering applications. As a result, sustainability could be achieved in the context of the three pillars of sustainable development: economic value, environmental enhancement, and social improvement [4].
This research, therefore, will work in compliance with the sustainable development goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) [7], which are a universal call for action to develop integrated approaches to a green economy and sustainable development. These approaches will improve the environment’s health and bring social and economic benefits. New approaches [8,9] were conducted to achieve sustainable advanced technologies through alternative sources of clean energy and the production of natural gas hydrates from marine sediments—natural resources, not wastes.
This research aims to (1) evaluate and identify promising ex situ remediation technologies of MSs to be adopted in Colombia and (2) provide regulatory frameworks to optimize beneficial uses of MSs. The developed frameworks may be used in selecting optimal remediation alternatives and be effective from the point of view of new global issues, such as the sustainable management of MSs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Areas
The Caribbean Coast of Colombia extends from the Gulf of Venezuela (east) to the Gulf of Uraba (west), with an extensive 1760 km coastline [10]. This coastal area is an underindustrialized port region representing a strategic economic position for the country. The Cartagena Bay (CB), located on the north coast of Colombia (10°21′54″ N and 75°31′48″ W), is one of Colombia’s most important industrial coastal zones on the Caribbean Coast. One of the best coral reefs on the continental shelf of Colombia is found in this area [11].
Unfortunately, CB is highly vulnerable to anthropogenic sources of pollution, including runoff from wastewater treatment plants, harmful chemicals discharged directly into the bay, and large amounts of sediments and contaminants from the Dique Channel, a 114-kilometer-long artificial construction connected with the Magdalena River basin (principal panel in Figure 2). In northwestern South America, the Magdalena River delivers the highest amount of freshwater discharge (205 km3 y−¹) and sediment load (144 × 106 t y−1) to the Caribbean Sea. It is also considered one of the rivers with the highest sediment and freshwater discharge (144 × 106 t yr−1 and 7200 m3 s−1, respectively) in the world and the most important river of Colombia [12]. The study areas were finally determined, as shown in Figure 2.
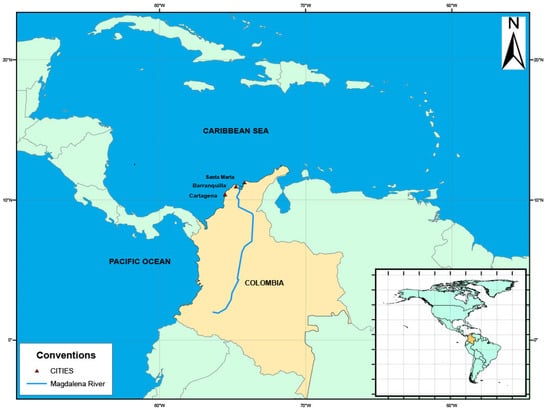
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the study areas, including the three main cities of the Caribbean Coast of Colombia. Principal panel: location of Cartagena Bay (CB), Santa Marta (SM), Barranquilla, Atlántico (AT), and the flow of the Magdalena River. Secondary panel: location of Colombia.
2.2. Methodologies
The qualities of marine sediments in the Caribbean Coast of Colombia were evaluated. Data were taken and analyzed from the most recent studies regarding the marine sediment of the Colombian Caribbean, including Santa Marta (SM), Cartagena Bay (CB), Atlántico (AT), and the General Caribbean Region of Colombia (GCC).
Sediment quality guidelines (SQGs) of selected developed countries from Asia, Europe, and North America were collected to assess contamination levels because there is still a need for current legislation for MSs in Colombia. Ex situ remediation technologies were researched to identify the best-suited technologies through comprehensive evaluation criteria, considering each technology’s economic, environmental, time, and efficiency aspects. Evaluation values were assigned to each technology, where the higher the value obtained, the higher the reliability of the remediation technology. Through this research, regulatory frameworks were developed for the sustainable management of MSs in Colombia to facilitate economic benefits.
3. Results
3.1. Marine Sediment Qualities of the Colombian Caribbean
International SQGs with Upper Action Levels (AL1), which are the limit levels used to avoid chronic effects concerning decisions about disposal at sea, and Lower Action Levels (AL2), which identify action levels below which there is “negligible environmental concern” concerning the disposal decisions [3], were compared to evaluate acceptable values of contaminants in marine sediments of the Colombian Caribbean (Table 1).

Table 1.
Evaluation of the Colombian Caribbean sediment qualities based on international sediment quality guidelines (SQGs).
Exceeded concentration limits of SQGs may represent adverse effects on aquatic organisms and increase the risk of humans being exposed to harmful chemicals.
Little data on the Colombian Caribbean marine sediment qualities were available during the literature review. Based on the results, no significant concentrations of contaminants were found. However, concentrations of mercury (Hg) were higher than the AL1 (>1.5 mg/kg), mainly in areas with a strong influence of anthropogenic contaminants such as CB and SM. In contrast, inorganic and organic pollutants were relatively low in regions with low industrialization.
The historical Hg concentrations in Cartagena Bay’s marine sediments have been attributed to the pollution caused by a chlor-alkali plant operating from 1967 to 1978 [13]. Moreover, large amounts of harmful heavy metals (HHMs) have been discharged by metallurgical industries in the city’s industrial zone called Mamonal, and incidental spills resulting from maritime activities. Other activities include chemical plants, petrochemical factories, petroleum refineries, cement factories, aquaculture, pharmaceutical complexes, the production of plastics, food processing industries, and more than 57 industrial docking areas [13].
After determining the levels of contaminants in marine sediments, remediation technologies should be applied to remove pollutants and obtain beneficial uses of MSs. Remediation technologies and pretreatment techniques are also applied to natural sediments to meet material standards and obtain valuable commercial end products. Beneficial uses may involve pre and post-treatment techniques such as dewatering or particle separation. Multiple assessment methods such as environmental impact assessment, regulatory frameworks, life cycle assessment (LCA), and cost–benefit analysis should also be considered to evaluate the feasibility of various remediation technologies [17].
3.2. Ex Situ Remediation Technologies
Subsequent to environmental dredging, ex situ remediation technologies could be the most suitable option for MSs because of their more effective and easy control of environmental parameters in various sediment conditions than in situ technologies. Moreover, in situ technologies may not be an adequate alternative for highly contaminated sediments [18]. All remediation technologies’ objectives would be to transform contaminants into less hazardous forms according to environmental standards. Significant facts such as the advantages, disadvantages, applicability, and cost of each ex situ technology were verified in this research.
3.2.1. Physical Technologies
Particle Separation
Particle separation sorts particles based on size. These processes may be used as pretreatments and applied to remove fine, more contaminated particles from sediments [1]. Highly contaminated fractions such as clay or silt may require further treatment or restricted disposal. Physical technologies could concentrate contaminants in smaller volumes. Thus, their application before chemical, thermal, or more advanced technologies might be recommended [19]. Reducing the volume of materials to be treated could efficiently reduce costs and treatment time. The volume of fine particle residuals may be minimized by mechanical dewatering techniques followed by separation.
Thermal Technologies
Vitrification involves using electrodes in the sediments to carry a current and then melting them down thermally to solidify as they cool. Toxic gases could be produced during vitrification [1]. Additionally, vitrification may be unsuitable for sediments with high levels of electrically conducting metals since, under transient heating conditions, the conductivity of those metals decreases with increasing temperature. Thus, achieving the required degree of electric conductivity during high temperatures may be more challenging and require relatively expensive treatment costs. Demerits of thermal technologies may be the extensive special facilities required to support high temperatures, high moisture contents (more than 20%) limiting applicability, and high costs that must be considered before their applicability in Colombia.
3.2.2. Chemical Technologies
Sediment Washing
Sediment washing involves the addition of a solution to transfer contaminants from sediments to the extracting solution [20]. Washing treated sediment before disposal may also be required to eliminate hazardous residuals [19]. Numerous additives, such as surfactants, chelating agents, and particularly biosurfactants, may enhance treatability. Chemical technologies could be suitable for treating large particles (sand and gravel.) However, some disadvantages include the limitation of extracting only weakly bonded HHMs and difficulties in decontaminating fine grain-sized sediments (less than 0.075 mm).
Electrochemical Technologies
Electrokinetics uses a low direct current (DC) to electrodes placed on the contaminated sediments. These technologies involve electrokinetic flows that cause the migration of charged particles and water toward the electrodes, as positive ions are attracted to the negatively charged cathode, and negative ions are attracted to the positively charged anode [1,21]. Electrokinetics may be appropriate for fine-grained sediments because fine particles readily adsorb metals with a strong electric field and high electric conductivity.
Volatilization occurs when a compound evaporates in the vapor phase to the atmosphere from another environmental compartment [20]. Vapor density and solubility are directly related to the volatilization rate in chemicals. Since volatile HHMs have a high vapor pressure and low water solubility, electrochemical and thermal technologies can effectively remove volatile HHMs, which are only tiny amounts in HHMs. Some disadvantages should be considered before its adaptation in Colombia, such as its elevated treatment cost and the presence of high water contents that could also increase costs.
3.2.3. Physicochemical Technologies
Solidification reduces the mobility of the HHMs by adding an agent such as lime, fly ash, or Portland cement [20]. Stabilization, on the other hand, aims to reduce contaminant leachability by adding chemical binders. Solidification/stabilization (S/S) are considered one of the most effective remediation technologies for inorganic pollutants because of the lack of destructive technologies to treat sediments polluted by HHMs. Compared with other technologies, S/S have a relatively low cost, universal applicability, and good workability [22]. S/S could successfully treat arsenic (As), Pb, Cr, and Hg. The no necessity for disposal facilities and the final commercial products obtained after remediation are significant advantages to implementing S/S technologies in Colombia.
According to the US EPA [23], the recommended management strategies for MSs include monitored natural recovery, in situ capping, and environmental dredging, followed by ex situ S/S technologies. Table 2 summarizes previous studies investigating the applicability of S/S, including large-scale projects in which beneficial products were obtained. In particular, a Portland cement-based method has been widely used to recycle dredged materials into commercialized construction materials such as road fills, aggregates, or bricks [24].

Table 2.
The feasibility of solidification/stabilization technologies applied to remediate marine sediments (MSs) from which beneficial products were obtained.
3.2.4. Biological Technologies
Phytoremediation involves using plants and microorganisms to oxidize and reduce HHMs by biochemical reactions [20]. This technology could be applied for sand and gravel-sized sediments with low levels of HHMs contaminants. However, the time-consuming and low-efficacy removal of highly contaminated sediments should be considered before adopting this technology in Colombia.
4. Discussion
One of the main goals of this research was to develop regulatory frameworks to achieve beneficial uses of MSs. An evaluation of ex situ remediation technologies was conducted to identify sustainable technologies to be adopted in Colombia.
Cost-effectiveness, treatability per unit time, and removal efficiency (Figure 3) were considered optimal conditions for adequately treating MSs. However, the cost of each technology could vary depending on the remediation duration, environmental conditions, sediment volume, and the target pollutants to be removed. Treatment time and removal efficiency may also vary depending on physicochemical parameters and sediment characterization such as dissolved oxygen, total organic carbon content, Eh, pH, etc. Therefore, the selection of remedial technologies may ultimately vary, becoming a case-by-case process instead of a generalized one. In Figure 3, the optimal conditions in determining remediation technologies are achieved as a result of a surface matrix combining the axes x, y and z.
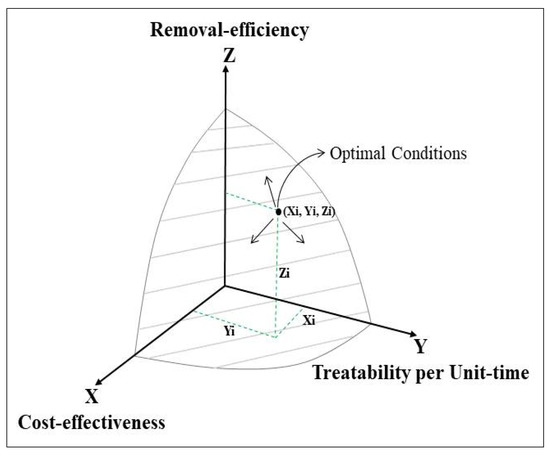
Figure 3.
Conceptual model of optimal conditions for suitable treatment of marine sediments (MSs).
Much research on sustainable remediation of MSs has been conducted in developed countries. Unfortunately, experiences of sediment remediation, particularly with treatment processes, are very limited in developing countries. In addition, challenges, such as economic issues, are often country specific. For instance, developing countries may have different approaches and face an even more significant challenge of limited funds for high-cost treatments than developed countries.
As a novelty of this research, the developed conceptual model of optimal conditions (Figure 3) could be applied to different scenarios and various contaminated sites depending on each nation’s specific needs or priorities.
Generally, pretreatment requirements, residual materials generated, public acceptability, and commercial products obtained might also be significant during the technology selection criteria [23,28]. Therefore, such essential aspects were considered in Table 3 for evaluating various ex situ remediation technologies where 3, 2, 1, and 0 points were assigned in priority, respectively, for each criteria item assessed.

Table 3.
Index criteria for evaluating ex situ remediation technologies of Table 4.
Various ex situ remediation technologies with values assigned depending upon their level of reliability, where 15 points represent high reliability and 0 points the lowest reliability, were evaluated in Table 4. The higher the value assigned, the higher the benefit and reliability in economic, environmental, and efficiency aspects of the remediation technology.
 where, Si represents the cumulative sum of evaluated values assigned according to the index criteria for evaluating ex situ remediation technologies (Table 3).
where, Si represents the cumulative sum of evaluated values assigned according to the index criteria for evaluating ex situ remediation technologies (Table 3).


Table 4.
Comprehensive evaluation of various ex situ remediation technologies through cost–benefit analysis, treatment time, removal efficacy, and environmental aspects.
On the basis of the review results, physical remediation technologies could be mainly applied as pretreatment techniques with high removal efficiency. However, additional treatments should be considered for highly contaminated fractions. Chemical technologies may be very effective for sand and gravel-sized sediments, but still challenging to decontaminate fine-grain-sized particles. Electrochemical and thermal technologies have high efficiency in removing volatile HHMs, but their expensive financial implications and extensive special facilities required should be assessed before their adoption in Colombia. Bioremediation technologies could be eco-friendly and cost-effective alternatives but relatively time consuming. Interestingly, S/S were identified as promising technologies and a strategic medium to obtain beneficial uses of MSs with considerable economic incomes to be adopted in Colombia.
Many researchers have investigated various technologies to remediate MSs [19,20,32,33]. For instance, Gang et al. [34] have shown that high water contents with exceeded concentrations of HHMs, and a large fraction of fine particles in dredged materials could be successfully improved by mixing with S/S agents. Other authors [5,21,35,36,37,38] have proposed assessment strategies and environmental tools for managing MSs. Pasciucco [17] and Barjoveanu [39] implemented a life cycle assessment (LCA) of the environmental impacts during the application of S/S to remediate MSs. Thew authors of [40] proposed a risk-based decision-making framework for the selection of sediment dredging options.
Unfortunately, many developing countries, such as Colombia, have not proposed regulatory frameworks for beneficial uses of MSs until now. To date, no work has been published in Colombia on the role of remediation technologies in achieving beneficial uses of MSs. To fill those gaps, regulatory frameworks to achieve sustainable beneficial uses of all marine sediments were established (Figure 4). Essential aspects to consider during the selection of remediation alternatives were identified.
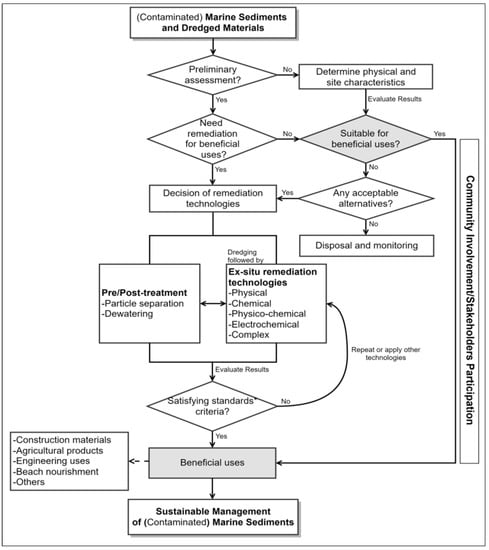
Figure 4.
Preliminary frameworks for sustainable beneficial uses of marine sediments (MSs) in Colombia. * Environmental standards and material standards are met.
The frameworks were designed to be applied in different scenarios for various countries serving as an integrated environmental tool to improve current environmental legislation and reduce decision-making uncertainty. Remarkably, the developed frameworks may also help environmental authorities, researchers, and stakeholders comply with sustainable management practices during dredging activities and promote the beneficial uses of MSs.
Beneficial uses of MSs are not usually considered during remediation processes. However, it would reduce the disposal of dredged volume, improve the high demand for construction materials through manufactured end products, and implement new circular economy strategies. The new circular economies will work in compliance with the related SDGs No. 12 and No. 14 established by UNEP [7]. Thus, beneficial uses of MSs should be considered a priority in a sustainability vision.
In general, more than one remediation technology should be considered since a single method may be insufficient for efficient remediation because of the complex heterogeneous characteristics of sediments. Pre or post-treatment technologies might be required according to the target pollutants [23]. For instance, particle separation technologies are essential to reduce the volume of MSs to be treated for beneficial uses or disposed of in disposal facilities. In contrast, the dewatering process will reduce the remaining fine particles.
Other migration techniques include methods commonly used in mining, the mineral processing industry, and wastewater treatment applications. These techniques may be applied to prepare MSs for subsequent treatment processes and separate them into specific fractions to reduce the volume of materials to be treated [41]. Consequently, the treatment costs will also be reduced. The costs of pretreatment techniques are moderate compared with other remediation technologies.
In this case study, relatively high concentrations of Hg in Colombia’s sediment samples were found to exceed the AL1 of international SQGs (Table 1). As stated by Tosic et al. [13], historically high concentrations of Hg in the Colombian Caribbean marine sediments are mainly generated by growing industrialization and increment of maritime activities. It implies a possible risk to the aquatic ecosystem, including the coastal community. Thus, new strategies for sustainable remediation of MSs are needed to control and reduce the large amounts of HHMs discharged from various anthropogenic contaminants in the Colombian Caribbean, especially in the CB and SM region.
The sustainable remediation of MSs could generate various opportunities for environmental improvement and valuable monetary benefits. Decision-making tools such as impact assessment and LCA, along with regulatory frameworks, may more effectively achieve the beneficial uses of MSs and assist environmental authorities in selecting integrated remediation alternatives.
The results of this research may improve the sustainable management of MSs and dredging activities in Colombia, where the lack of environmental regulations inhibits appropriate environmental management leading to detrimental consequences for the marine environment.
This research has some limitations, such as the lack of sediment quality data from various contaminated sites. Also, technologies to remediate MSs have not been well established in Colombia yet or are constrained to small-scale applications. Additionally, there is high uncertainty regarding treatment costs. Nevertheless, this research could be the foundation and the starting point to encourage policy makers and related authorities, including the scientific community, to work towards integrated management of MSs and promote their beneficial uses in the context of developing sustainable solutions.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The advantages and disadvantages of remediation technologies should be compared and carefully considered before decision making. The favorable effect of combining two or more technologies to remediate MSs may enhance the results;
- (2)
- S/S combined with complex technologies were found to be efficient and cost-effective technologies to be adopted in Colombia. Remarkably, S/S may offer valuable end products obtained from treated sediments that may achieve environmental benefits and promote new circular economy strategies;
- (3)
- Policy makers may use the developed frameworks in this research as an integrated environmental tool to improve the selection of remediation alternatives. Significantly, the sustainable management of MSs will be achieved by optimizing their beneficial uses;
- (4)
- Beneficial uses of MSs directly or after treatment should be considered a priority and be promoted as much as possible, avoiding their common perception as waste. This new approach can generate positive environmental impacts and waste minimization;
- (5)
- New, simple, eco-friendly, and cost-effective technologies, along with integrated innovative management practices, are urgently required for the sustainable management of MSs.
More detailed research would be continuously required in Colombia to formulate national environmental standards for MSs based on adapting appropriate conventions such as the LP and referencing experiences of other developed countries.
The findings of this research may provide insights into the sustainable management of MSs in Colombia and other developing countries. Furthermore, this research may serve as a reference to understand the importance of MSs as valuable natural resources in a vision of sustainable development, comply more closely with ratified environmental conventions, and work in line with the related SDGs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.T.G.C. and K.K.; methodology, W.T.G.C. and K.K.; validation, W.T.G.C. and K.K.; formal analysis, K.K.; investigation, W.T.G.C.; resources, W.T.G.C. and K.K.; data curation, W.T.G.C. and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, W.T.G.C.; writing—review and editing, WW.T.G.C. and K.K.; supervision, K.K.; project administration, W.T.G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Korean Institute of Ocean Science and Technology under grant numbers (PO01418 and PEA0012), Republic of Korea.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data and models developed that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mulligan, C.N.; Fukue, M.; Sato, Y. Sediments Contamination and Sustainable Remediation; IWA Pub: London, UK; CRC Press: Raton, FL, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4200-6153-6. [Google Scholar]
- Edokpayi, J.; Odiyo, J.; Popoola, O.; Msagati, T. Assessment of Trace Metals Contamination of Surface Water and Sediment: A Case Study of Mvudi River, South Africa. Sustainability 2016, 8, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO London Convention and Protocol: Guidance for the Development of Action Lists and Action Levels for Dredged Material. Available online: https://www.gc.noaa.gov/documents/gcil_imo_dmaction.pdf (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Sustainable Management of the Beneficial Use of Sediments. Available online: http://www.dredging.org/media/ceda/org/documents/resources/cedaonline/2019-05-BUS-ip.pdf (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Zheng, Z.-J.; Lin, M.-Y.; Chiueh, P.-T.; Lo, S.-L. Framework for Determining Optimal Strategy for Sustainable Remediation of Contaminated Sediment: A Case Study in Northern Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Guerra, M.; Alvarez-Guerra, E.; Alonso-Santurde, R.; Andrés, A.; Coz, A.; Soto, J.; Gómez-Arozamena, J.; Viguri, J.R. Sustainable Management Options and Beneficial Uses for Contaminated Sediments and Dredged Material. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2008, 17, 16. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.unenvironment.org/explore-topics/oceans-seas/what-we-do/working-regional-seas/coastal-zone-management (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Luo, T.; Han, T.; Madhusudhan, B.N.; Zhao, X.; Zou, D.; Song, Y. Strength and Deformation Behaviors of Methane Hydrate-Bearing Marine Sediments in the South China Sea during Depressurization. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 14569–14579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Cai, J.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Qi, R.; Meng, F.; Xie, Y.; Sha, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, C. Phase Equilibria of Natural Gas Hydrates in Bulk Brine and Marine Sediments from the South China Sea. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 4064–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Maestre, R.; Johnson-Restrepo, B.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Heavy Metals in Sediments and Fish in the Caribbean Coast of Colombia: Assessing the Environmental Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2018, 12, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Olivero-Verbel, J.; Corada-Fernández, C.; Lara-Martín, P.A.; Juan-García, A. Emerging Contaminants and Priority Substances in Marine Sediments from Cartagena Bay and the Grand Marsh of Santa Marta (Ramsar Site), Colombia. Env. Monit Assess 2021, 193, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restrepo, J.C.; Schrottke, K.; Traini, C.; Ortíz, J.C.; Orejarena, A.; Otero, L.; Higgins, A.; Marriaga, L. Sediment Transport and Geomorphological Change in a High-Discharge Tropical Delta (Magdalena River, Colombia): Insights from a Period of Intense Change and Human Intervention (1990–2010). J. Coast. Res. 2016, 319, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosic, M.; Restrepo, J.D.; Lonin, S.; Izquierdo, A.; Martins, F. Water and Sediment Quality in Cartagena Bay, Colombia: Seasonal Variability and Potential Impacts of Pollution. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 216, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte-Restrepo, E.; Noguera-Oviedo, K.; Butryn, D.; Wallace, J.S.; Aga, D.S.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.E. Spatial Distribution of Pesticides, Organochlorine Compounds, PBDEs, and Metals in Surface Marine Sediments from Cartagena Bay, Colombia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 14632–14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckel, A.; Osorio-Martinez, J.; Pinto, D.; Bodah, B.W.; Adelodun, B.; Silva, L.F.O. Hazardous Elements Present in Coal Nanoparticles in a Caribbean Port Region in Colombia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torregroza-Espinosa, A.C.; Martínez-Mera, E.; Castañeda-Valbuena, D.; González-Márquez, L.C.; Torres-Bejarano, F. Contamination Level and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals in Water and Sediments of El Guájaro Reservoir, Colombia. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Labianca, C.; Chen, L.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M.; Guo, B.; Sun, J.; Ding, S.; Wang, L. Sustainable Ex-Situ Remediation of Contaminated Sediment: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Song, Y.; Yuan, P.; Cui, X.; Qiu, G. The Remediation of Heavy Metals Contaminated Sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Hogland, W. An Overview and Assessment of the Existing Technological Options for Management and Resource Recovery from Beach Wrack and Dredged Sediments: An Environmental and Economic Perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, C.N.; Yong, R.N.; Gibbs, B.F. An Evaluation of Technologies for the Heavy Metal Remediation of Dredged Sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2001, 85, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciucco, F.; Pecorini, I.; Di Gregorio, S.; Pilato, F.; Iannelli, R. Recovery Strategies of Contaminated Marine Sediments: A Life Cycle Assessment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cho, D.-W.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Cao, X.; Hou, D.; Shen, Z.; Alessi, D.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Poon, C.S. Green Remediation of As and Pb Contaminated Soil Using Cement-Free Clay-Based Stabilization/Solidification. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Contaminated Sediment Remediation Guidance for Hazardous Waste Sites; Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN EPA-540-R-05-012. Available online: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/11/175398.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2022).
- Yu, C.; Cui, C.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, J. A Novel Approach to Utilizing Dredged Materials at the Laboratory Scale. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cai, G.; Cheeseman, C.; Li, J.; Poon, C.S. Sewage Sludge Ash-Incorporated Stabilisation/Solidification for Recycling and Remediation of Marine Sediments. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gisi, S.; Todaro, F.; Mesto, E.; Schingaro, E.; Notarnicola, M. Recycling Contaminated Marine Sediments as Filling Materials by Pilot Scale Stabilization/Solidification with Lime, Organoclay and Activated Carbon. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvidat, J.; Benzaazoua, M.; Chatain, V.; Bouamrane, A.; Bouzahzah, H. Feasibility of the Reuse of Total and Processed Contaminated Marine Sediments as Fine Aggregates in Cemented Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortone, G.; Palumbo, L. (Eds.) Sediment and Dredged Material Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 978-0-08-046668-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of the Environment Waste and Recycling Measures. Available online: https://www.rncc.co.jp/tech/tc_1/7 (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Estes, T.J.; McGrath, C.J. Economical Treatment of Dredged Material to Facilitate Beneficial Use; ISBN ERDC/EL TR-14-11. The US Army Engineer Research and Development Center (ERDC): Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Ministry for the Environment and Forestry of Rhineland-Palatine. Treatment and Confined Disposal of Dredged Material; Ministry for the Environment and Forestry of Rhineland-Palatine: Mainz, Germany, 2002; p. 39.
- Peng, W.; Li, X.; Xiao, S.; Fan, W. Review of Remediation Technologies for Sediments Contaminated by Heavy Metals. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1701–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, F.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M. Contaminated Marine Sediments: Waste or Resource? An Overview of Treatment Technologies. Procedia Environ. Sci. Eng. Manag. 2016, 3, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Gang, Y.; Won, E.-J.; Ra, K.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, K. Environmental Assessment of Contaminated Marine Sediments Treated with Solidification Agents: Directions for Improving Environmental Assessment Guidelines. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, K.M.; Kim, K. Preliminary Framework for Sustainable Beneficial Use of Dredged Materials in Yangon River, Myanmar. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2020, 42, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manap, N.; Voulvoulis, N. Environmental Management for Dredging Sediments—The Requirement of Developing Nations. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemière, B.; Laperche, V.; Wijdeveld, A.; Wensveen, M.; Lord, R.; Hamilton, A.; Haouche, L.; Henry, M.; Harrington, J.; Batel, B.; et al. On-Site Analyses as a Decision Support Tool for Dredging and Sustainable Sediment Management. Land 2022, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourabadehei, M.; Mulligan, C.N. Selection of an Appropriate Management Strategy for Contaminated Sediment: A Case Study at a Shallow Contaminated Harbour in Quebec, Canada. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjoveanu, G.; De Gisi, S.; Casale, R.; Todaro, F.; Notarnicola, M.; Teodosiu, C. A Life Cycle Assessment Study on the Stabilization/Solidification Treatment Processes for Contaminated Marine Sediments. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manap, N.; Voulvoulis, N. Risk-Based Decision-Making Framework for the Selection of Sediment Dredging Option. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 496, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. ARCS Remediation Guidance Document. ISBN EPA 905-B94-003. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/ (accessed on 11 October 2022).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).