Abstract
How to improve the partial or overall performance of rail transit route network, strengthen the connection between different rail network stations, and form corresponding communities to resist the impact of sudden or long-term external factors has earned a lot of attention recently. However, the corresponding research studies are mostly based on the rail network structure, and the analysis and exploration of the community formed by the stations and its robustness are not enough. In this article, the evolution of the China rail transit route network (CRTRN) from 2009 to 2022 is taken as the research object, and its complex network characteristics, BGLL model-based community division, and multi disturbance strategies for network robustness are analyzed in depth to better understand and optimize the rail network structure to further effectively improve the efficiency of the public transport system. It is found that CRTRN is gradually expanding following the southwest direction (with the migration distance of nearly 200 km), the distribution of routes is more balanced, and the number of network communities is steadily decreasing (it dropped from 30 communities in 2009 to 25 in 2019), making various regions become closely connected. However, it can also be found that during the COVID-19 pandemic, the CRTRN is strongly affected, and the network structure becomes relatively loose and chaotic (the number of communities became 30). To protect the railway networks, the CRTRN system should pay more attention to stations with high node degree values; if they get disturbed, more areas will be affected. The corresponding research conclusions can provide some theoretical and practical support for the construction of the rail transit network in China.
1. Introduction
As a mode of transportation with large volume and high efficiency, energy saving, and environmental protection, rail transit has become an extremely important form of transportation in many countries in the world after decades of development. It has brought profound influence on coordinated urban development, pollution reduction, and convenient transportation for residents. Although the development of rail transit in China is relatively short compared with other countries, high-speed rail has developed extremely fast in the past 20 years driven by high-quality industrialization transformation and new urbanization, thus promoting the formation of China’s new era railway network framework. In 2019, China issued the “Outline of Building China into a Transport Power”, which proposed that “123” transport circles should be formed nationwide by 2035, namely, one-hour commute in metropolitan areas, two-hours commute in urban agglomeration, and three-hours commute in major cities across the country. According to the “Outline of the Railway Pioneering Plan for developing China in transportation in the New Era” released in August 2020, China will take the lead in building a modern railway network in the world by 2035. The national railway network will reach 200,000 km, of which 70,000 km is high-speed railway. However, at present, the development of China’s rail transit network is still very unbalanced, and the development speed between regions is not consistent. As the western and central regions of China are characterized by large population distribution and strong traffic demand, the construction of transportation infrastructure can significantly improve the level of regional economic development. However, there are still a large number of regions with lagging rail transit network construction, which makes it difficult to directly connect and transfer between regions.
The outbreak of the epidemic has affected rail transit network lines to some extent. Since December 2019, due to COVID-19, the connectivity and operational capacity of the public transport of China have been strongly affected, making it difficult to travel between cities for some time. At present, China has entered the stage of regular COVID-19 prevention and control, and production and business activities in transportation and other industries are gradually returning to a steady state. With the epidemic situation stabilizing nationwide, rail transit lines in all cities are in normal operation status. However, due to sporadic outbreaks and imported cases, the epidemic prevention and control work will keep continuing, and the urban rail transit system will be directly or indirectly affected by the epidemic risk. Gkiotsalitis and Cats [1] have conducted a detailed review on the public transport in the process of epidemic development. Some scholars then studied the spread of simulated epidemics in public transportation systems and the role of rail transit networks in the spreading process, in which the scale of epidemic spread before and after the implementation of the shutdown program was compared [2]. Therefore, in order to basically meet the needs of inter-regional passengers, some places have adopted measures such as reducing, canceling, changing, or setting up other lines to fully utilize transport resources and reduce the possibility of epidemic transmission in the public transport system. However, there is no specific research on the impact of such a public crisis and management crisis on China’s rapidly developing rail transit network.
2. Literature Review
Based on China’s current rail transit network development and regional economic development needs and background, how to improve the partial or overall performance of the China rail transit route network, strengthen the connection between different regions, and form corresponding communities to resist the impact of sudden or long-term external factors such as COVID-19 are corresponding research problems that have caught our attention.
Research on rail transit network has always been a hot topic in the field of transportation planning, urban economy, and regional economics. Previous studies focused on the competition with other different modes of transportation and the development of regional economic integration [3,4,5,6], the population distribution and passenger flows [7,8,9], real estate [10,11,12], tourism [13,14], energy saving [15,16], and so on. It can be found that most of the previous studies took the construction of the railway network or the opening of high-speed railway as an indicator or influencing factor, and then analyzed other social problems, while there were few studies on the railway network itself. For high-speed rail in the railway network’s research of the corresponding research, and less research on integrated rail transit network, the main research methods have included accessibility evolution research methods [17,18], connectivity evolution [19,20], spatial analysis [21,22,23], spatial econometric analysis [24,25,26], network structure evolution [27,28,29,30,31,32,33], the space syntax [34], the network robustness [35,36], deep learning [37,38], multi-layer network research method [39], etc. Data sources such as railway route maps, railway network timetables, trade flows, and rail transit flows between different stations or cities are studied in depth [40].
Research based on network structure can better describe the association of topological structure, but the consideration of competition and cooperation between geographical locations is insufficient. What is the relationship between different stations? Will it form groups with more closely aligned interests? The original simple topology analysis or traffic network analysis are difficult to further explore these problems. However, the content of network communities has opened up new research directions for this, as the community partition, which is also called “graph clustering” or “community detection” etc., and it can be defined as “locally dense connected subgraphs in a network” [41,42,43,44,45]. Recently, Huang and Chen [46] made an overall comparison of existing works and provided a comprehensive understanding of community detection methods in both single layer and multilayer networks. The changes of regional connectivity and economic connections can be tested with network communities [47], which can be applied to analyze and understand related development plans and policies [48], such as the planning of transportation infrastructure [49,50,51], and some new network spatial structure community detection algorithms were proposed [52]. These studies proved that the research and application of network community division in urban traffic community division are feasible and effective.
Because the characteristics of the railway network construction are long-term and difficult to change, the research on the optimization of the China rail transit route network becomes more realistic, significant, and has long-term social and economic value. Nevertheless, most of the current studies focus on the high-speed rail transit network structure, but these studies ignore the complementary role of other rail transit modes, and the description of the comprehensive rail transit network structure is not inclusive. For example, Feng [53] studied the complexity and structural fragility of China’s high-speed rail network and found that its structural change was not obvious from 2015 to 2020, but its robustness was strengthened from 2020 to 2030. Later, Jiao [54] studied the robustness of China’s high-speed rail network based on the weighted network efficiency metric. Researchers also focus on the impact of rail transit network structure on the surrounding areas. For example, Wang [55] simulated the changes in regional territory, population accessibility, and spatial equity brought by the development of high-speed railway network in the Yangtze River Delta of China, thereby defining the impact of high-speed railway on the development of different cities. Wang [56] explored the influence of high-speed railway construction on accessibility of surrounding areas on cities level. Wang [57] believes that high-speed rail has led to the redistribution and transformation of China’s tourism market, resulting in greater market competition and the reallocation of urban tourism hot spots. Li [24], based on these studies, argues that high-speed rail increases the mobility of production factors and may also lead to the redistribution of industrial enterprises and their pollution emissions among cities. However, there are few studies on the analysis, community division, and robustness of China’s integrated railway network [9,58], and most of the studies are based on algorithm or route optimization [59,60]; therefore, this research has great potential and application scenarios. Researchers such as Lu [50] used the widely used community detection algorithm to study China’s railway network properties and found that the number of communities and average distance between community centers are both decreasing. Zhang [39] abstracted different forms of railway lines into different network layers and used multi-layer transportation network model to study the changes of rail transit operating table in different years, thus showing that there has been some discussion on network communities.
Meanwhile, most of the current studies are based on the network structure at the city or provincial level; limited by data and research accuracy, there are few detailed studies on the station level, which can make the understanding of network structure characteristics more detailed and clearer. For example, Guo [61] studied 20 key cities in the Yangtze River Delta region of China, constructed a combined network of urban high-speed rail network and urban economic network, and proposed the corresponding interactive research framework. Few scholars such as Li [62], based on these 1737 high-speed trains and their stopped stations, transformed the high-speed rail network into a multi-layer network that takes both running time and passenger flow into account, and a corresponding method to comprehensively evaluate the robustness of the high-speed rail network is proposed. Then, Huang [63], based on the timetable and statistical characteristics of China’s railway network and the spatio-temporal pattern of more than 2700 stations, found that the distribution of degree and intensity is scale-free, the average path length decreases, and the network clustering coefficient increases. However, the detailed research based on the station level is the foundational support to improve the regional railway network capacity and optimize the overall network performance in the future, which has extremely important research significance.
Therefore, based on the above research trends and weaknesses, and the data of the China rail transit network at the station level, this paper takes the evolution of the China rail transit route network (CRTRN) from 2009 to 2022 as the research object, and the influences of COVID-19 will further be discussed. The evolution of the network structure, the change of distribution, the division of network community, and the network robustness are deeply studied.
3. Research Methods
3.1. Research Object and Data Collection
This paper takes the evolution of the CRTRN from 2009 to 2022 as the research object. At the end of 2011, China Railway has fully implemented online ticketing, and the China railway system began to enter the era of e-commerce. Customers can log in the corresponding website, check the passenger train schedule, ticket price, the remaining tickets, and other information. The train transit time data in 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2022 comes from 12306 (see Table 1), the official website of China Railway Customer Service Center, which is an important window for railway service customers. The research group used Python crawler to obtain the rail transit time data of 12306 website in different time periods, such as on 30 May 2013, 26 December 2016, 20 July 2019, and 19 April 2022. The rail train time data on 19 July 2009, comes from Jipin schedule /JPSKB.exe, which was launched by Beijing Jipin Time Technology Co., LTD on 25 November 2003; the train transit time data was provided by China Railway Publishing House. It has the advantages of simple operation, fast data update, fast execution, and online upgrade for registered users. The data of train stations were analyzed and cleaned after obtaining the results from 12306 (www.12306.cn, accessed on 1 February 2022) and AMAP API (www.amap.com, accessed on 1 February 2022). Here, in Table 1, No. stand for the name and number of related rail schedules; ‘G’, ‘D’, and ‘C’, followed by a number is the naming way of rail lines in China. Type stands for different types of rails. Station order represents the order of the station in different rail routes. The mileage stands for the mileage of the corresponding stations. Prices 1 and 2 are different ticket prices in Chinese Yuan.

Table 1.
The sample of train transit time data.
3.2. Research Methods and Related Indexes
3.2.1. Network Construction Method
Using graph theory, some characteristics of rail transit network can be expressed clearly and simply [64,65,66]. With this method, the different undirected or directed networks can be used to represent the CRTRN, where V is the set of nodes, and N is the number of nodes when E is the edges connecting different nodes and is denoted by . Moreover, W is the weights of edges; here, it refers to the route numbers between different stations. The number of edges is denoted as M, the adjacency matrix of networks is A, the links between nodes and , which is defined as and where we use to remove any self-connections.
3.2.2. Related Network Structure Indexes
To study the physical appearance of the network, the corresponding structural characteristics of the network are introduced, such as the shortest path and network diameter, degree value and average degree value, betweenness centrality, and average path length.
Then, define Di as the network diameter; here, is the shortest path between node pair i and j.
Freeman [67] suggested the definition of degree centrality. The number of links of a node can reflect the importance of this node in relation to spatial geography, which indicates that a node with more connections with other stations is more important in the rail transit route network. The average degree is the average value of .
The betweenness centrality was proposed by Freeman [67]. It is defined as the total number of shortest paths between two any different stations and passing through station , it reflects the load on station and can alternately be understood as the controllability of the station, as the more important station has more routes passed. Here, is the maximum possible routes passed any station. On this basis, its centrality can be clarified as .
The average shortest path length (), was proposed by Albert and Barabási [68] and defined as the average number of steps along the shortest paths for all possible pairs of stations, where is the shortest path length.
3.2.3. Network Community Division
Modularity is generally used as an index to measure the quality of community division, and the quality of community division can be evaluated by comparing the network after community division with its corresponding null model (random graph model) during calculation. Since the number of communities in the rail network should not be set in advance, here in this article, the BGLL algorithm (also known as Louvain algorithm) is applied to measure the community numbers of rail networks for different years. This algorithm was suggested by Vincent D. Blondel, Jean-Loup Guillaume, Renaud Lambiotte, and Etienne Lefebvre in the article “Fast Unfolding of Community Hierarchies in Large Networks” [69], and it has been referred to and used by many network-related researchers. Compared with other algorithms, the computational complexity of the BGLL algorithm is lower (O(nlogn)), which is very suitable for the calculation of community division in a large-scale transportation network. The time complexity of other algorithms such as Girvan-Newman algorithm [70] is O(n(m + n)), FN algorithm [44] is O(Mn + n2), and Kernighan-Lin algorithm [71] is O(n2), all of which are relatively higher. Moreover, the modularity value of the BGLL algorithm is very high and its value is relatively stable [72], which makes the algorithm have higher credibility and application scenarios. Meanwhile, the BGLL algorithm has been integrated by Gephi and other software, which is easy to be used in the research of massive traffic network characteristics, and this makes the algorithm well used by the corresponding research or application personnel. Furthermore, based on the same algorithm, its standards will be more unified, so that when analyzing and comparing the corresponding networks, more stable and accurate results can be obtained.
Here, is the network adjacency matrix, and and are the node degrees of i and j. is a piecewise function. and are the communities to which nodes i and j belong. If these two nodes belong to the same community, takes the value of 1, otherwise, takes the value of 0.
3.2.4. Standard Deviation Ellipse
Standard deviation ellipse (SDE) is a classical algorithm to measure the distribution and direction, and it is often used to measure the spatial distribution of some research objects such as facilities [73], its application in rail transit network is relatively lacking, and it is mainly used to analyze the distribution state of the research object itself or the evolutionary relationship between different objects [74]. The change trend of the center of gravity can be seen by adding the comparison of different years [75]. Researchers such as Ge [76] further compared spatiotemporal variation and evolution of transport network of China’s megaregions by SDE. Wyatt [77] studied the distribution of employment and housing situation of Personal Rapid Transit in Melbourne based on SDE. In this paper, it is used to measure the distribution characteristics of rail transit network stations in different years, which can clearly see the evolution trend of different years. The measurement of the long and short axis, and the central points of standard deviation ellipse can refer to Lefever [78], Yuill [79], and Schubert and Kirchner [80]. Its long and short axes represent the aggregation or dispersion degree of the object, its center of gravity represents the relative position of the aggregation center of the object, and its change can represent the developing trend and transfer trend of the object in space. Where SDE is the variance of the ellipse in the x and y directions, and are the geographical coordinates of area i, and are the average center coordinates of the ellipse, and n is the total number of areas.
3.2.5. Network Robustness
Based on the ratio of the changing total node degree and the origin total node degree value, the network robustness (NR) of CRTRN 2009 and 2022 will be further analyzed, which reflects the response of a network under different disturbance strategies [81], which can be used to identify the rail stations that are most valuable and most conducive to future development and projects. In this paper, some widely concerned indicators are used to conduct robustness studies to measure the corresponding changes of network structure after the corresponding nodes (top 100 nodes) are disturbed.
According to the corresponding network structure characteristic indexes, different network disturbance strategies are constructed to detect the different change characteristics of rail transit network structure facing different disturbance strategies, which has important theoretical and practical significance in transportation network and operation management. MATLAB will be used to measure the change of network performance by removing the stations in the network through simulation algorithm, and then detect the resilience of the rail transit network. Here, we use the change ratio of node degree value before and after the network is disturbed as the measure index of network robustness. The corresponding selected disturbance strategies in this study are mainly determined according to the maximum node degree (disturbance strategies 1), random node degree (disturbance strategies 2), random connecting edge (disturbance strategies 3), and static (disturbance strategies 4) and dynamic node betweenness centrality value (disturbance strategies 5).
According to the measurement of their initial state network structural characteristics and these corresponding indexes, the corresponding strategies were used to determine the sorting of different stations, which stand for the disturbance order to related stations, then remove the stations from the rail transit network. Once again, the properties of the corresponding network structure and the corresponding index were measured, and the value of NR can be obtained. The centrality of the node betweenness can be subdivided into static and dynamic ones. Dynamic means that the nodes with the largest betweenness centrality value were reordered after each disturbance process, and the nodes with the largest betweenness centrality value were selected to continue the disturbance. Meanwhile, the static disturbance strategy was carried out only according to the order of the initial state of network betweenness centrality value. For the random disturbance strategies, after each disturbance process, a random value was generated until the end of the disturbance. The above process was carried out for 100 times, and the average value of 100 times was taken as the final result of the random disturbance.
4. Research Results
With the sustainable development of CRTRN, the network structure characteristics are analyzed, and then based on the degree value of rail stations, the changes of station betweenness, the changes of detected communities are analyzed, and the network robustness are further analyzed to comprehensively measure the evolution of CRTRN under the natural growth and the influence of the epidemic.
4.1. Evolution of China’s Rail Transit Route Composition Structure
Based on the corresponding data collected by crawlers and data obtained from other platforms, it can be found that the composition structure of China’s rail transit lines has changed greatly from 2009 to 2022. The main train type is D, which stands for CRH China Railway High-speed EMU or bullet trains, with operating at 160 to 250 km/h. G stands for High-Speed Railway, with the current actual maximum speed, which is 350 km/h. T stands for express train, which usually runs at no more than 140 km/h. K refers to the fast train, which runs at no more than 120 km/h. P stands for ordinary passenger express (general express) with a top speed of 120 km/h. Z stands for direct trains, which run at no more than 160 km/h.
It can be found from the route composition structure in different years and the association of different models between stations that K and P types were mainly used in 2009 (accounting for about 86% in total) (Figure 1). Since EMU was in the early stage of development at that time, its coverage rate was low (accounting for about 7%) and it was mostly used between main cities. Between 2013 and 2019, fast trains continued to take a leading position (about 42%, 38%, and 26%, respectively). The share of bullet trains and high-speed railways has skyrocketed to 27 percent, 39 percent, and 62 percent, before peaking at 71 percent in 2022. Meanwhile, the number of slow trains has fallen sharply, from 46 percent in 2009 to 6 percent in 2019. In 2022, there will be a significant increase in the number of bullet trains and high-speed trains, compared with a significant decline in the number of K (34%), while the proportion of slow trains P continues to decline. T and Z showed a trend of fluctuation and decline, reaching the maximum value in 2013 and 2016 respectively, and then continued to decline.
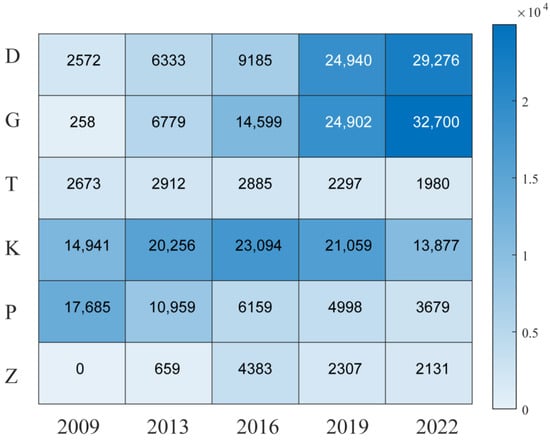
Figure 1.
Rail transit route composition structures in different years.
4.2. Evolution of Network Structural Characteristics of CRTRN
From 2009 to 2022, the number of rail stations fell from 3031 to 2740 in 2016 and then rose to 3065 (Table 2). It can be seen that there are a large number of stations, but the distribution is relatively loose, and some of the stations that are not very critical have been optimized and eliminated with the development of the railway train operation network. However, during the rapid development period from 2016 to 2019, the number of high-speed trains increased rapidly as more high-speed and convenient trains were opened in some areas that had no railway coverage before. It can be seen more clearly from the number of connecting edges and the average degree value of railway lines. From 38,129 edges in 2009 to 80,503 edges in 2019, the average degree value increases from 3.364 to 4.545. It can be clearly seen that the development of railway train operation network is not reduced by the reduction of the number of nodes but is more centralized and optimized. The importance of some sites has been greatly highlighted. From the perspective of network diameter and average path length, the network performance has been greatly improved after 10 years of development. The network diameter has increased from 61 to 40–46, while the average path length has decreased from 10.584 to 8.615. At the same time, it can be seen that although the COVID-19 outbreak has a certain impact on the development of railway lines, the number of train routes in 2022 still increased by about 4%. The spread of COVID-19 has led to the suspension of rail lines in affected areas, which has changed the travel habits of some users. For example, there is now a growing fear among local people of the risks associated with long-distance travel. After the epidemic, due to changes in traffic habits or lines opened, the original rail transit lines will be cancelled due to the reduction of operation costs or the decrease of user numbers; this will force the traffic management department to think more rationally about the connections between different areas, which will lead to corresponding changes in the structure of the rail transit network. From the changing rules of network diameter and average path length, it can be found that China’s railway train operation network has changed from an extensive development mode to a fine and reasonable development mode. Despite the impact of the epidemic, the correlation ability of the core network has not been significantly affected and still remains at a high operation level, and the values of the two indicators have increased compared with 2019.

Table 2.
Structural characteristics of CRTRN.
4.3. The Central Station of CRTRN Has Gradually Become Prominent
It can be seen from Figure 2 that from 2009 to 2019, the number of core stations with high degree values in CRTRN has gradually increased. The number increased from 5 in 2009 to 16 in 2019, and its development trend is gradually spreading from north to south. In 2009, Beijing station had the highest altitude of 79, and in 2019, Beijing station still had the highest altitude of 92. At the same time, Shenyang, Zhengzhou, and Shenyang North all exceeded 80, respectively, 90, 87, and 85. The importance of major stations in provincial capitals and central cities is further demonstrated. The corresponding core sites are mainly distributed in central and southwest China, which are transformed and upgraded from the original secondary centers. Some cities in the middle of the country have greatly strengthened their correlation strength, such as Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou East, Wuhan, Wuchang, Hankou, Jiujiang, and other stations. At the same time, it can be seen that with the emergence of the core site, the secondary stations in the surrounding area will also be affected by the radiation effects, so as to improve accordingly. For example, the establishment of Guangzhou South, Chengdu East, and Hangzhou East railway stations has greatly improved the original weak association strength of many surrounding stations.
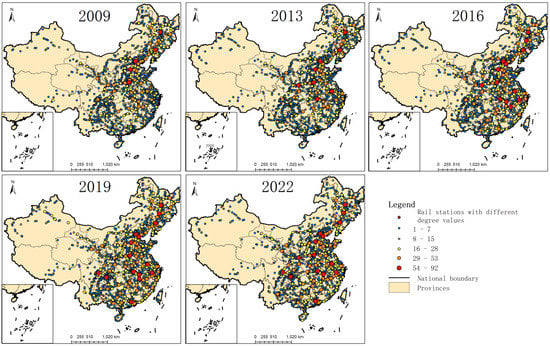
Figure 2.
The distribution of central stations of CRTRN.
The growth of secondary stations tends to be in the eastern seaboard region and the south-central region. With the expansion of the core stations, the situation of distribution around the core station has played an excellent supporting and connecting role, connecting the corresponding core stations. Core stations and secondary stations together constitute the most important stations in the framework of the whole basic railway network in China, and gradually form the corresponding four vertical and four horizontal structures according to the medium- and long-term development plan of the China railway system.
The development and evolution trend are also relatively consistent with the conclusion of the standard deviation ellipse, that is, the development of rail transit network is gradually changing from the trend of narrow short axis in the north to the trend of wide short axis in the south. As can be seen from Figure 3, the center point of the standard deviation ellipse gradually shifts from Heze City, Shandong province (114.93° E, 35.12° N) to Shangqiu city (115.23° E, 34.83° N) (115.11°E, 34.52° N), Zhoukou city (114.51° E, 33.87° N), and Zhumadian city (114.35° E, 33.54° N), Henan province, the migration distance is nearly around 200 km, and the migration velocity has a trend of accelerating to the southwest from 2016 to 2019. It shows that as China’s economic development, according to China’s national level five-year plans, with the railway infrastructure planning and long-term railway network layout and line encryption needs, at the same time due to the economic development of southern growth, corresponding to the demand of railway line and railway line gradually expand to the south.
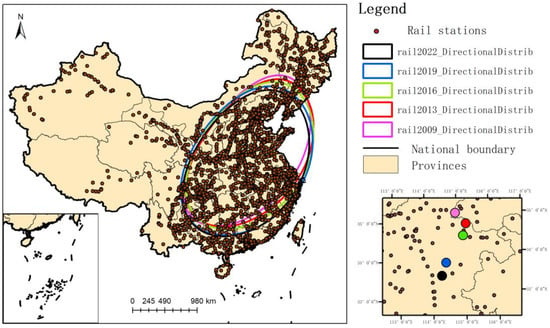
Figure 3.
The standard deviation ellipse analysis for different years.
However, it should also be noted that after the outbreak of the epidemic of COVID-19, China’s railway train operation network was greatly impacted, and the node degree changed greatly. Based on the difference between the degree values in 2022 and 2019, it can be seen from Figure 4 that the stations in CRTRN both exist the situation of increase and decrease in the station association intensity.
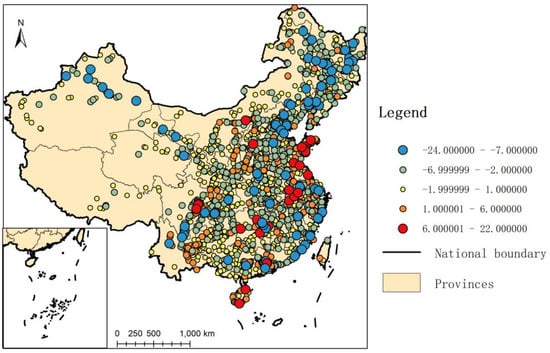
Figure 4.
The change of rail station degree values.
Based on the value of station degree in 2019, 423 sites have increased, accounting for 13.80%. There were 10 stations whose degree value increased by more than 10, mainly distributed in central and eastern, and western regions. The top five stations were Laixi station, Chongqing North station, Wuhu station, Lianyungang station, and Hefei South station. There are 45 stations whose degree value increases by more than 5, and the top five stations are Hohhot station, Linyi station, Pingxiang station, Hengyang station, and Meishan station. The increase of other sites’ association intensity is mainly concentrated on the four vertical and four horizontal backbone networks.
The degree value of 878 sites remained unchanged, accounting for 28.65%, presenting a relatively uniform distribution.
The degree value of 1265 sites were decreased (including those that will be out of service in 2022), accounting for 41.27%, mainly distributed in the non-backbone network and branch lines of network. There were 35 stations with the most severe degree decrease (with a decrease of more than 10), mainly distributed in the northeast, southeast coastal areas, and along the west. The top five stations were Zhuzhou station, Chifeng station, Xiangyang East station, Beijing West station, and Mudanjiang station.
4.4. The Network Betweenness Values Is Gradually Reduced, and the Distribution of Routes Is More Balanced
As can be seen from Figure 5, based on the comparative analysis of the top 25 stations of their betweenness values of CRTRN in different years, the extreme values and mean values of 2009 are larger than those of other years. The betweenness values of the first few stations in 2019 and 2016 fluctuated to some extent, but overall, the betweenness values of the stations in the CRTRN changed over time, and the distribution of the high values became more even. The values showed that the importance of the station is in the overall system. However, with the development of CRTRN, more and more lines are established, so that the betweenness values of some important nodes are constantly decreasing. This is because the increased connection of the network makes the direct connection between different stations, thus reducing the need for transit, so that the betweenness values decreased and the network accessibility is gradually strengthened. This is also the root cause of the decrease in average path length.
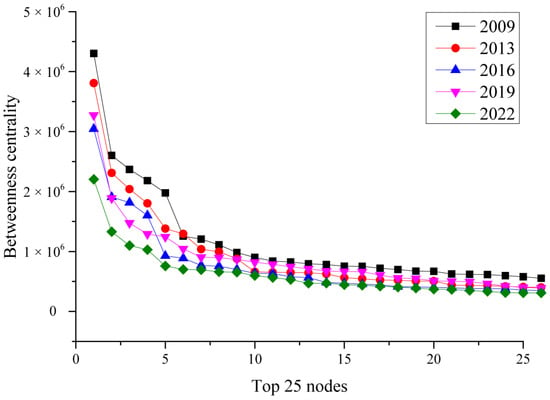
Figure 5.
The betweenness centrality value of top 25 rail stations.
As can be seen from Figure 6, the number of stations with a high betweenness value decreased from 19 in 2009 to 12 in 2019. In 2009, the top 10 stations are Beijing station, Beijing West station, Xi’an station, Shijiazhuang station, Harbin station, Changsha station, Siping station, Lanzhou station, Chengdu station, and Baoji station, respectively. Siping station is extremely important in our country as the traffic hydrophobic button and railway far transport organizing station, its important geographical position, known as the Oriental Madrid, and Siping railway station belonging to Shenyang railway bureau. In 2019, the top 10 stations are Beijing station, Harbin station, Beijing station, Shijiazhuang station, Guangzhou South station, Xi’an station, Zhengzhou East station, Xi’an North station, Tianjin station, and Zhengzhou station. The number changes dramatically, and only six high-value stations remain. In 2022, the number of high stations is even less, and the top eight stations are Beijing station, Beijing West station, Harbin station, Zhengzhou station, Chengdu East station, Xi’an station, Taiyuan South station, and Changsha South station. The values of other stations are relatively small with the reduction of the total number of railway train operation network routes and the optimization of related routes.
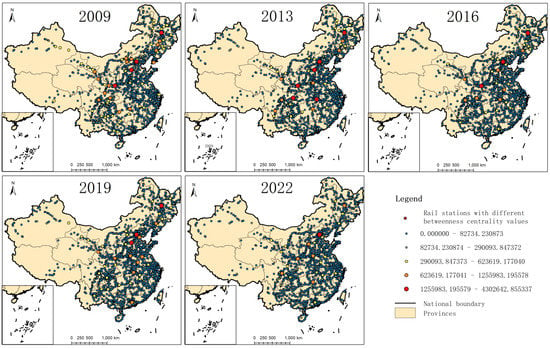
Figure 6.
The distribution of high betweenness centrality value stations.
4.5. The Structure of CRTRN in 2022 Become Relatively Loose and Disorderly
Before the epidemic, the number of communities gradually decreased from 30 in 2009 to 25 in 2019 (see Table 2). The association between sites in different regions was strengthened correspondingly, and their Q values remained around 0.85. In 2009, China’s railway network was based on the rail network of different regions, forming a community division based on inter-regional key lines. It can be seen that in eastern China, western China, and three provinces of eastern China (Liaoning province, Jilin province, and Heilongjiang province), the community division is relatively obvious, forming the corresponding cluster and line shapes. However, in the central and southern regions, the community division of the CRTRN is more complicated, and there are multiple communities in the corresponding urban agglomerations, indicating that the distribution and formulation of railway routes are not well coordinated with the development of urban agglomerations.
Through the development of the past 10 years, more and more railway lines have made the corresponding regions better connected, forming corresponding resultant force between each region, and the division of its community has become more obvious (Figure 7). For example, in 2013, the communities of CRTRN in western regions such as Gansu and Qinghai, Guizhou and Shandong, and Henan provinces began to merge. At the same time, some communities are divided into different communities, such as Anhui and Jiangsu, Hebei and Shanxi railway network communities are divided into different communities. Such changes are combined with regional transportation routes and economic development trends. The development of urban agglomeration promotes the development of regional economy, which correspondingly encourages the development of regional transportation and population flow, and stimulates the growth of railway lines, which in turn improves the network structure of railway lines. In 2016, the community division result followed the emergence of new lines and the disappearance of the old lines, such as Hunan province expanded its network community, and some communities such as Inner Mongolia province is gradually segmented, gradually forming a number of inter-province network communities, which is the greatest evidence to prove that there exist the chances of the regional integration development and their effect. For example, the super-large communities formed in Gansu-Qinghai-Xinjiang-Inner Mongolia, and the groups formed in Guizhou-Yunnan-Guangxi, Liaoning-Jilin are very closely connected. Of course, the Shandong-Henan community had the most drastic changes during this period. Under the influence of the development of Shandong Peninsula urban agglomeration and Central Plains urban agglomeration, the community division was reshuffled, and some stations in the north and south of Shandong were classified into different communities. By 2019, the planning of each urban agglomeration has been issued, the corresponding routes have been greatly developed, the number of communities has reached the minimum value, and the network structure has been optimized to a large extent. It can be found that the division of communities in 2019 is recognizable, and the correlation between different regions is clear. Although some communities are still interlaced with each other, the inheritance of the economic development of urban agglomeration is obvious, and more regions are strongly connected. However, this situation is also affected by the outbreak of COVID-19; it is clear that the structure of CRTRN in 2022 becomes relatively loose and disorderly, such as northeast area, the Shandong peninsula, and Yunnan-Guizhou-Sichuan area, which is because in order control the spread of COVID-19, the local government released some rules, which limits the movement in the regions which epidemic situation is serious. This makes the corresponding risk get controlled, and also reduced the relevant passenger movements. As a result, the network structure is changed accordingly, the result of community division becomes more confusing, the number of communities also increases correspondingly, and the connection between different regions becomes more difficult.
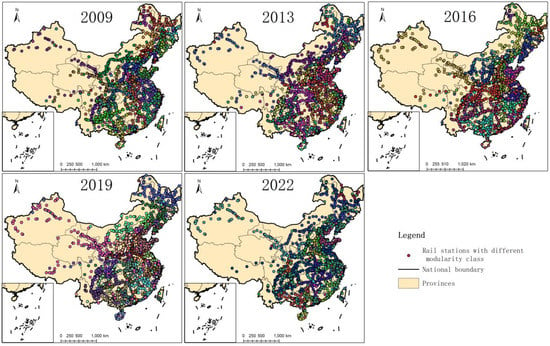
Figure 7.
The evolution of network communities of CRTRN. Different colors stand for different communities.
4.6. The Network Protection Should More Focusing on the Nodes with Higher Degree Values
When the network is disturbed by different disturbance strategies, by definition, the value of NR becomes smaller. However, the rate of change will be different according to different disturbance strategies. When the number of disturbed nodes is smaller, the NR value decreases faster, indicating that this disturbance strategy is more destructive, and the network should pay more attention to the corresponding protection based on this disturbance strategy. From Figure 8, the total degree ratio of CRTRN 2009 and 2022 decreases under different disturbance strategies with the top 100 nodes. It is clear that strategy 1 is extremely destructive compared to other strategies. This indicates that CRTRN system should pay more attention to stations with high node degree values, which can be seen in Figure 2 for the specific distribution of nodes to be protected. Since the corresponding stations with high degree value are often connected with many other stations, the disturbance of these high degree value stations will make the network structure change more drastic, so this strategy is regarded as the strategy with a greater degree of damage. Of course, this does not mean that the influence of other strategies is not obvious, for example, strategies 4 and 5 can also have a strong impact on network performance, but if the protection funds or capacity is insufficient, the implementation of strategy 1 can be given priority, priority should be given to this kind of node. At the same time, by comparing the situation in 2009 and 2022, it is found that compared with the situation in 2009, due to the excessive concentration of lines, the disturbance strategy for node degree value will have a stronger impact in 2022. This shows that with the sustainable development of networks, although network capabilities are becoming more powerful and coordinated, CRTRN in 2022 will become more vulnerable to systemic risks; this can provide some related references for policymakers.
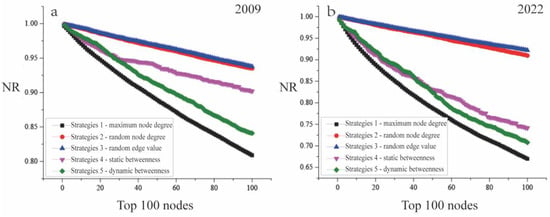
Figure 8.
The network robustness results. Where a and b represent the corresponding network robustness result of 2009 and 2022.
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Based on the above research, it can be found that with its sustainable development, the overall performance of CRTRN tends to be better, the network structure becomes more and more complex, and the efficiency becomes better and better. The composition of CRTRN has changed greatly from 2009 to 2022. The main types of trains have changed from fast trains and slow trains to bullet trains and high-speed trains. At the same time, the network is gradually expanding to the southwest, the accessibility is gradually strengthened, and the distribution of routes is more balanced. However, it can also be found that with the outbreak of the COVID-19, CRTRN has been strongly affected. The betweenness values of stations in CRTRN change over time, and the distribution of high betweenness values becomes more even, so the nodes of high betweenness values are less preserved. From 2009 to 2019, the number of network communities decreased steadily from 30 to 25, with closer connections between regions and more convenient travel for residents. However, the network structure became relatively loose and chaotic in 2022, and the number of communities returned to 30 again. To protect the networks, the CRTRN system should pay more attention to stations with high node degree values.
The key point of railway development is not only the breakthrough of operational mileage, but also the improvement of new technology. The characteristics of railway construction and transportation determine the difficulty of locomotive renewal and track equipment renewal. Therefore, China’s railway development should pay more attention to the existing high-speed railway lines, improve their operation and maintenance level, ensure safety, and improve transport efficiency. At the same time, the government should focus on the development of the next generation of high-speed rail transit, and vigorously promote the interconnection, integrated development, orderly connection, and seamless transfer among national trunk railways, regional railways, local railways, urban express rail, and urban rail transit.
This study is helpful to determine the design and the operation strategy of CRTRN in the future. For the change of the network structure, it can provide some support for the future planning and design of the corresponding lines, so that the line setting will not violate the evolution trend of the overall network structure. In particular, by considering the corresponding characteristics of different stations and the results of community division in different years, it is possible to find out the parts with weak connection in CRTRN, or the areas with not so close relation, so that the corresponding line setting in the next step can be more reasonable and scientific to promote integration and development between different communities. Based on the research of network resilience, we can more clearly understand the weak links of network structure, so that we can have more opportunities to protect the corresponding stations, then corresponding rail transit lines can be better operated and managed.
It should also be noted that in real life, it is not true that the more rail transit network lines are constructed, the more regional connections can be improved. How to improve network capacity economically and quickly with limited cost is not considered in this paper. At the same time, the change of its structure is not only affected by the epidemic, but also by the recent economic development speed of different regions. This paper also does not consider the impact of travel time, which will be the focus of the follow-up study of our research team. Therefore, it is necessary for transportation scholars and decision makers to choose appropriate, scientific, and optimal routes, so that the whole network can achieve a higher degree of correlation, and different regions can use fewer routes to achieve the best connection. This has certain theoretical and practical significance for the operation and management of rail transit network under the influence of the epidemic.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.D. and J.F.; methodology, R.D. and Y.Z. (Yilin Zhang); software, J.F.; validation, Y.D., L.D. and T.Z.; formal analysis, Y.D.; investigation, Y.Z. (Yuqi Zhu); resources, S.S.; data curation, S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, R.D., S.C. and J.F.; writing—review and editing, R.D.; visualization, J.F.; supervision, R.D.; project administration, R.D.; funding acquisition, R.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number: 72001053; and Scientific Research Project of Guizhou University of Finance and Economics (Youth Project): 2021KYQN01.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The related data sets are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank anonymous reviewers’ constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gkiotsalitis, K.; Cats, O. Public transport planning adaption under the COVID-19 pandemic crisis: Literature review of research needs and directions. Transp. Rev. 2020, 41, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-lei, R.; Chao, Y.; Gang, Y.; Xiao-Lei, R.U.; Chao, Y.A.N.G.; Gang, Y.A.N.; Xiao-Lei, M. Control strategy for urban public transit in response to large-scale emergent epidemic. China J. Highw. Transp. 2020, 33, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Kato, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Effects From Expanding High-Speed Railway Network on Regional Accessibility and Economic Productivity in China. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2021, 2676, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Li, S. Spatiotemporal impact of railway network in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau on accessibility and economic linkages during 1984–2030. J. Transp. Geogr. 2022, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Henneberg, J. The influence of the railway network on territorial integration in Europe (1870–1950). J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 62, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, K.; Alvarez-Palau, E.J.; Martí-Henneberg, J. Railway Development and the Economic and Political Integration of the Balkans, c. 1850–2000. Eur. Stud. 2017, 69, 1601–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.; Franch, X.; Martí-Henneberg, J. Evolution of the Territorial Coverage of the Railway Network and its Influence on Population Growth: The Case of England and Wales, 1871–1931. Hist. Methods A J. Quant. Interdiscip. Hist. 2013, 46, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgüngör, S.; Aldemir, C.; Kuştepeli, Y.; Gülcan, Y.; Tecim, V. The Effect of Railway Expansion on Population in Turkey, 1856–2000. J. Interdiscip. Hist. 2011, 42, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Jiao, J.; Wang, L.; Xu, J. Evolving Characteristics of High-Speed Railway Network Structure in Yangtze River Delta, China: The Perspective of Passenger Flows. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2020, 13, 925–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Delmelle, E.; Duncan, M. The impact of a new light rail system on single-family property values in Charlotte, North Carolina. J. Transp. Land Use 2012, 5, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Efthymiou, D.; Antoniou, C. How do transport infrastructure and policies affect house prices and rents? Evidence from Athens, Greece. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pr. 2013, 52, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoran, Y.; Cong, W.; Youyang, Y. The Spatial Structure Evolution of China’s High-Speed Rail Network and Its Impacts on Real Estate Investment. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2021, 15, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Xi, J.-C.; Ge, Q.-S. Spatial Differentiation and Integration Optimization of an Urban Agglomeration Tourism System under the Influence of High-Speed Railway Network Evolution. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2017, 12, 349–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalate, D.; Fageda, X. High speed rail and tourism: Empirical evidence from Spain. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pr. 2016, 85, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acierno, L.; Botte, M. A Passenger-Oriented Optimization Model for Implementing Energy-Saving Strategies in Railway Contexts. Energies 2018, 11, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botte, M.; D’Acierno, L. Dispatching and Rescheduling Tasks and Their Interactions with Travel Demand and the Energy Domain: Models and Algorithms. Urban Rail Transit 2018, 4, 163–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, F.; Mo, H.; Wang, F. Spatiotemporal evolution of China’s railway network in the 20th century: An accessibility approach. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pr. 2009, 43, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liang, Y.; Wu, D. Evaluating the Impact of China’s Rail Network Expansions on Local Accessibility: A Market Potential Approach. Sustainability 2016, 8, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Ma, C. Connectivity and Accessibility of the Railway Network in China: Guidance for Spatial Balanced Development. Sustainability 2019, 11, 7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, J.; Shi, F. Circuity in China’s high-speed-rail network. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 80, 102504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, R.; Li, Y.; He, B.; Fan, Y. The Distribution Pattern of the Railway Network in China at the County Level. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas-Torné, M. Creation of a Geo-Spatial Database to Analyse Railways in Europe (1830–2010). A Historical GIS Approach. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenin, T.; Schwartz, R.; Sapet, L. Mapping the Distortions in Time and Space: The French Railway Network 1830–1930. Hist. Methods A J. Quant. Interdiscip. Hist. 2013, 46, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, H. Spatial spillovers of pollution via high-speed rail network in China. Transp. Policy 2021, 111, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, D.; Li, G. The varying effects of accessing high-speed rail system on China’s county development: A geographically weighted panel regression analysis. Land Use Policy 2021, 100, 104935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardaka, E.; Delgado, M.S.; Florax, R.J. Causal identification of transit-induced gentrification and spatial spillover effects: The case of the Denver light rail. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 71, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cats, O. Topological evolution of a metropolitan rail transport network: The case of Stockholm. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 62, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cai, X. Degree and Weighted Properties of the Directed China Railway Network. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2008, 19, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erath, A.; Löchl, M.; Axhausen, K.W. Graph-Theoretical Analysis of the Swiss Road and Railway Networks Over Time. Networks Spat. Econ. 2008, 9, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Qiu, G. China’s high-speed rail network construction and planning over time: A network analysis. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 70, 40–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, H. The structural and spatial properties of the high-speed railway network in China: A complex network perspective. J. Rail Transp. Plan. Manag. 2018, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cai, K.; Du, W.; Wu, X.; Tong, L.; Zhu, X.; Cao, X. Analysis of the Chinese railway system as a complex network. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2019, 130, 109408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Ujang, N.; Bin Hamid, H.; Manan, M.S.A.; Li, R.; Albadareen, S.S.M.; Nochian, A.; Wu, J. Application of Complex Networks Theory in Urban Traffic Network Researches. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2019, 19, 1281–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Du, N.; Wang, X. Understanding the City-transport System of Urban Agglomeration through Improved Space Syntax Analysis. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2021, 45, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, S.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y. Structural vulnerability and intervention of high speed railway networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 462, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, L. Reliability Optimization of a Railway Network. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, R.; Chen, T.; Nie, H. In-Depth Analysis of Railway and Company Evolution of Yangtze River Delta with Deep Learning. Complexity 2020, 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Luca, G.D.; D’Acierno, L.; Botte, M. Artificial neural networks for forecasting passenger flows on metro lines. Sensors 2019, 19, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cui, H.; Wang, W.; Song, W. Properties of Chinese railway network: Multilayer structures based on timetable data. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, I.A. Railway network timetabling and dynamic traffic management. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Hu, Y. Finding Community Structure and Evaluating Hub Road Section in Urban Traffic Network. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 96, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chin, J.H.; Ratnavelu, K. Detecting Community Structure by Using a Constrained Label Propagation Algorithm. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, L.-Y.; Liu, Z.-P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.-S. Community structure detection based on Potts model and network’s spectral characterization. Eur. Lett. 2012, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Fast algorithm for detecting community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabási, A.-L. Network science. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2013, 371, 20120375. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Chen, D.; Ren, T.; Wang, D. A survey of community detection methods in multilayer networks. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2020, 35, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, T.; Searle, G.; Martinus, K.; Tonts, M. Metropolitan land-use patterns by economic function: A spatial analysis of firm headquarters and branch office locations in Australian cities. Urban Geogr. 2015, 37, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhao, X.; Du, Z. Comparing Community Detection Algorithms in Transport Networks via Points of Interest. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 29729–29738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarswat, A.; Jami, V.; Guddeti, R.M.R. A novel two-step approach for overlapping community detection in social networks. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, X. Exploring the Hierarchical Structure of China’s Railway Network from 2008 to 2017. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, G.; Agarwal, J. Community detection in action: Identification of critical elements in infrastructure networks. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2018, 24, 04017046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, Y. DASSCAN: A Density and Adjacency Expansion-Based Spatial Structural Community Detection Algorithm for Networks. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y. Complexity and vulnerability of high-speed rail network in China. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; pp. 10034–10039. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J. A spatiotemporal analysis of the robustness of high-speed rail network in China. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 89, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, X. High-speed rail network development and winner and loser cities in megaregions: The case study of Yangtze River Delta, China. Cities 2018, 83, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y. Accessibility impact of the present and future high-speed rail network: A case study of Jiangsu Province, China. J. Transp. Geogr. 2016, 54, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Zou, T.; Yan, H. Effects of the high speed rail network on China’s regional tourism development. Tour. Manag. Perspect. 2012, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dobruszkes, F.; Wang, J.; Dijst, M.; Witte, P. Comparing China’s urban systems in high-speed railway and airline networks. J. Transp. Geogr. 2018, 68, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Zhang, T. The generation model of urban rail transit planning line network and its application in route design. Adv. Transp. Stud. 2021, 7, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D. Route Selection of Multimodal Transport Based on China Railway Transportation. J. Adv. Transp. 2021, 2021, 9984659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cao, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Understanding the formation of City-HSR network: A case study of Yangtze River Delta, China. Transp. Policy 2021, 116, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Rong, L. A comprehensive method for the robustness assessment of high-speed rail network with operation data: A case in China. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pr. 2019, 132, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Z. Exploring Railway Network Dynamics in China from 2008 to 2017. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Is the Boston subway a small-world network? Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2002, 314, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crucitti, P.; Latora, V.; Porta, S. Centrality in networks of urban streets. Chaos: Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2006, 16, 015113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.; Barabasi, A.-L.; Watts, D.J. The Structure and Dynamics of Networks, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, L.C. A Set of Measures of Centrality Based on Betweenness. Sociometry 1977, 40, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Barabási, A.-L. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girvan, M.; Newman, M.E.J. Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7821–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernighan, B.W.; Lin, S. An Efficient Heuristic Procedure for Partitioning Graphs. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1970, 49, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Marshall, S.; Cao, M.; Manley, E.; Chen, H. Discovering the evolution of urban structure using smart card data: The case of London. Cities 2021, 112, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hou, H. Analysis on Spatial-Temporal Distribution Evolution Characteristics of Regional Cold Chain Logistics Facilities: A Case Study of BJE[M]//LISS 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Li, H.; Kuang, X.; Strauss, J. Spatial–Temporal Features of Coordination Relationship between Regional Urbanization and Rail Transit—A Case Study of Beijing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Lin, A.; He, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, M. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Urban Land-Use Expansion: A Case Study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Yang, J. Measuring the spatiotemporal variation and evolution of transport network of China’s megaregions. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1497–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, R. GIS-based evaluation of Personal Rapid Transit (PRT) for reducing car dependence within Melbourne, Australia. Appl. GIS 2006, 2, 12.1–12.31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefever, D.W. Measuring Geographic Concentration by Means of the Standard Deviational Ellipse. Am. J. Sociol. 1926, 32, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuill, R.S. The standard deviational ellipse; an updated tool for spatial description. Geogr. Ann. Ser. B Hum. Geogr. 1971, 53, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, P.; Kirchner, M. Ellipse area calculations and their applicability in post urography. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.F.; Antunes, A.P.; Miller, E.J. Interurban road network planning model with accessibility and robustness objectives. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2010, 33, 297–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).