Abstract
A multi-disciplinary investigation of loess sections in the southeast and northwest of the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) and a sediment core drilled in Zhejiang Province of southeast China was conducted. Discrepancies among grain size distribution, rock magnetic properties, geochemical characteristics and chroma features, and up-section weakening relation between various proxies in the Sanmenxia loess section were found. The results were compared with those of the Baicaoyuan loess section in the northwest of the CLP and the sediment records across the plateau and elsewhere. It was suggested that human impacts began to increase soil erosion on the CLP since the middle Holocene. In addition to the increased soil erosion being decoupled from drying climate after 4 ka, renewed intensification of soil erosion was suggested to occur within the interval of 1.5–2.5 ka as a result of enhanced human activities. The two detected increases in human-induced soil erosion on the CLP are consistent with the human-driven land use changes or human–land interactions at national or regional scales, including the anthropogenic influences on the changes in the sediment load of the Yellow River. In contrast, no human impacts overwhelming hydroclimate control of soil erosion was revealed in the Beihuqiao cores, Zhejiang. The population growth during the past 2400 years showed a relative decreasing trend on CLP and a relative increasing trend in Zhejiang. It is indicated that anthropogenic factors have played a key role in modulating the Earth’s surface environment. In particular, ecologically fragile areas, such as the CLP, would be much more susceptible to human disturbance and climate change. The current serious land degradation on the CLP mainly results from the negative feedback between human–land interactions. Regional heterogeneity should be taken into account for sustainable development.
1. Introduction
Accelerated soil erosion has been pervasively changing landscapes across the world and is recognized to have substantial implications for land use sustainability. There are differences in the sensitivity to erosion among soil types and climates [1,2]. However, only recently have the studies on soil erosion at a historical scale been made and the human imprint on soil erosion been investigated [1]. The timings of the first increase in human-induced soil erosion were revealed at global and regional scales. A significant portion of the Earth’s surface was indicated to shift to human-driven soil erosion following deforestation since 4 ka (thousand years ago) [3]. In southeastern Europe, impact of human activity on soil erosion was observed at 3.2 ka [4]. In China, general acceleration in sediment accumulation and human-induced soil erosion was suggested to occur at 5 ka [5]. Consistently, human activities through land-use modifications completely altered the natural vegetation trend at 5–6 ka, as revealed by a marine pollen record from the northern South China Sea [6]. By contrast, increased soil erosion in southwestern China occurred at 1.8 ka, as weathering proxies of a core in the northern South China Sea indicated. The spatial heterogeneity remains to be further studied. It is demonstrated that soil erosion is strongly linked to land use and agricultural sustainability [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. More research work on the spatial and temporal variations in soil erosion is needed in order to better understand the interactions and feedback effects.
The Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) is known as the cradle of Chinese civilization. The loess used to serve as fertile soils upon which the great Chinese civilization was founded. However, it has become the most severe soil erosion region in the world. Soil erosion not only determined the evolution process of the Yellow River and the security of the lower reaches but also restricted the socio-economic sustainable development. Human-induced soil erosion on the CLP occurred around 2.5 or 3.1 ka, as reported [7,8,9,10]. The human impacts on accelerating sediment yields of the Yellow River over the past 2–2.5 ka [11,12,13,14] and the land use cycles on the CLP [22] were suggested. In this paper, Holocene loess records from the northwest and southeast of the CLP were studied. A sediment record in Zhejiang, southeast China was also selected for comparison. It aimed to gain a better insight into the human–land relationship within the climatic change context and the regional disparities in sustainability between the CLP and southeastern China.
2. Materials and Methods
The Baicaoyuan section is located in Huining County, Gansu Province, northwest CLP (Figure 1), with a mean annual precipitation of 320 mm. The information of the section and the revealed Holocene climatic evolution was reported [26]. The Sanmen Gorge area is the transition between the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River (Figure 1). The mean annual precipitation in Sanmenxia city is approximately 550 mm. The Sanmenxia eolian section (34°47′ N, 111°16′ E, 524 m asl) is in the inlet of the Sanmen Gorge. It is totally more than 100 m thick [27]. The 4.5–22.6 m depth interval is a L1-S1 couplet, which is commonly observed within the Sanmen Gorge [28,29,30]. The topmost 4.5 m are Holocene paleosols, which are a distinguished light brown-red color and underlain by calcareous nodules. The Holocene paleosols can be further divided into three parts according to the color changes observed in the field: the lower weak paleosols (3.2–4.5 m), the middle developed paleosols (2.5–3.2 m), and the upper loess (0–2.5 m). Samples were collected at 2 cm interval for 0–3.2 m and at 5 cm for the rest.
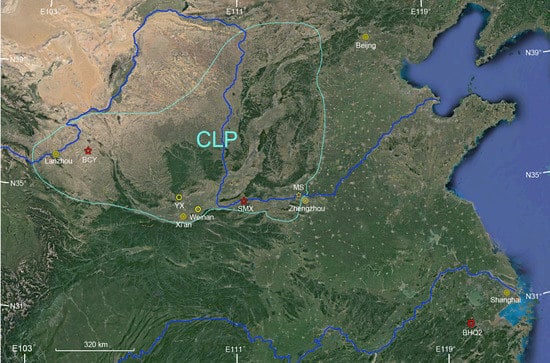
Figure 1.
Map showing the Chinese Loess Plateau (CLP) and the location of studied sites, SMX: the Sanmenxia loess section; BCY: the Baicaoyuan loess section; MS: the Mangshan loess section; BHQ2: Beihuqiao core 2.
Two cores (BHQ and BHQ2) were drilled at Beihuqiao village (30°22′443″ N, 119°56′237″ E) in the southeast of Hangjiahu Plain. Lacustrine and alluvial deposits are widespread, and the average annual precipitation is 1000–1400 mm in the plain. A total of 792 limnological sediment samples were collected from the 19.8 m long BHQ2 core with 2.5 cm intervals. Dating results of the sediments from both cores were attained, and the Early-middle Holocene climate was constructed based on the BHQ core [31].
Magnetic parameters of Baicaoyuan loess were measured in the Key Laboratory of Western China’s Environmental Systems (Ministry of Education), Lanzhou University, using the same method used for those of Sanmenxia loess. Samples from Sanmenxia and BHQ2 were air-dried, ground, placed in diamagnetic plastic boxes, and sealed with adhesive tape. The magnetic susceptibility (χ), the frequency-dependent susceptibility (χfd), the anhysteretic remanent magnetisation (ARM), the ARM susceptibility (χARM), and the saturation isothermal remanent magnetisation (SIRM) were measured or acquired, as describe by Han et al. [32]. Grain size distribution was measured using a Mastersizer 2000 laser particle-size analyser. Pre-treatment of samples followed the method commonly adapted by others [33]. Major geochemical elements were measured using a Thermo Scientific ARL PERFORM’X X-ray fluorescence (XRF) sequential spectrometer [32]. Colour properties were measured with a Konica Minolta CR-400 Colour Reader. Most magnetic parameters were measured at the State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Mountain Ecology, Fujian Normal University. Major geochemical elements were measured in the Instrumental Analysis Centre, Xinyang Normal University. The other measurements were performed in the Geography Process Laboratory, Zhejiang Normal University.
3. Results
3.1. Early Holocene Pedostratigraphic Correlations between Loess Sections
The results of the whole Sanmenxia section reveal a positive relation between χ and pedogenetic intensity and show minimum values of χ and χfd at around 4.5–5.5 m [27], which is consistent with the filed observation and suggests that the topmost 4.5 m are Holocene soils. The lower limit of the Holocene soils is also indicated by the correlation with the 14C dated adjacent Zhangbian loess section, which is less than 20 km away. The Zhangbian loess record since the last deglaciation was responsive to past global change [34]. Four ages, approximately 8.00 ka, 8.39 ka, 11.87 ka, and 19.49 k, were attained at 0 m, 65 m, 1.25 m, 2.65 m, and 5.55 m, respectively (Figure 2). The Younger Drays (YD) and the 8 ka cold event (also known as 8.2 ka event [26,35]) were observed in the magnetic susceptibility and grain size curves. The depth intervals at around 5.5 m and 3.2 m in the Sanmenxia section can be respectively correlated to the Younger Drays, and the 8 ka cold event. χfd% of Sanmenxia loess is not as sensitive as grain size to the 8 ka event. However, χfd% fluctuations at 5.5–7.3 m are similar to the GISP2 Greenland ice core record between 14.8 ka and the YD [36]. Note that the maximum of the grain size occurred later than the minimum of the magnetic parameter during the identified YD. This is consistent with the results at Zhangbian.
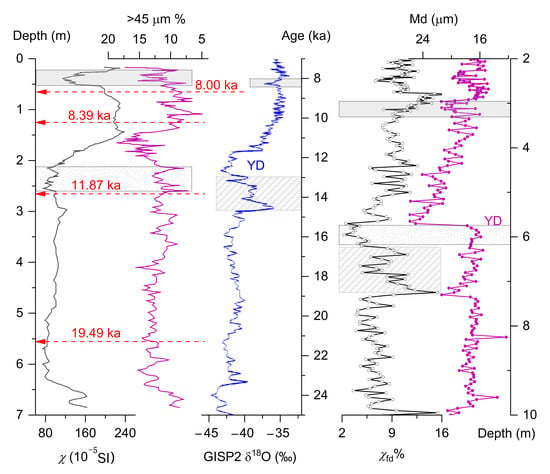
Figure 2.
Covaries of media grain size (Md, black curve with hollow white dots) and frequency-dependent susceptibility (χfd%, carmine curve with filled dots) of early Holocene loess at Sanmenxia and their correlation with records from the adjacent Zhangbian loess section (black curve for χ, carmine curve for >45 μm; [34]) and the GISP2 Greenland ice core (blue curve; [36]); based on the correlation (indicated by the rectangles), the Younger Dryas (YD) is designated to the depth intervals at around 5.5 m, and 8 ka event at around 3.2 m (grey shadowed).
3.2. Results of Sanmenxia Loess
Redness (a*) denotes the red–green chromaticity, which is controlled mainly by the types and concentrations of iron oxides. It is sensitive to pedogenetic intensity [32]. Low values of (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 indicate intense weathering and pedogenesis [37]. χARM preferentially responds to stable single-domain ferrimagnetic grains. Magnetic parameters reveal the concentration, composition, and grain size of magnetic minerals [38,39]. χARM/χ (or ARM/SIRM) is indicative of the relative concentration of fine ferrimagnetic grains and is used as a moisture proxy. The <2 μm fraction is strongly influenced by the pedogenetic process [40]. Coarse grain fraction content is indicative of winter monsoon intensity on the CLP. The >63 μm fraction content and median grain size (Md) are widely used as wind strength indicators [41]. The >63 μm fraction is always derived from a nearby, rather sandy source region, and is sensitive to dust storm events or cold events.
The redness shows an upward decreasing trend at 0–2.5 m, indicating a decrease in pedogenetic intensity. However, the geochemistry parameter (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 suggests that the topmost 0.5 m has undergone more intensive chemical weathering than the 0.5–1.62 m depth interval (Figure 3). χARM/χ shows the more noticeable up-section changing trend at 0–3 m than the other parameters, with maximum values at 2.5–3 m and minimum values at 4.3–5.7 m and 0.1–1 m.
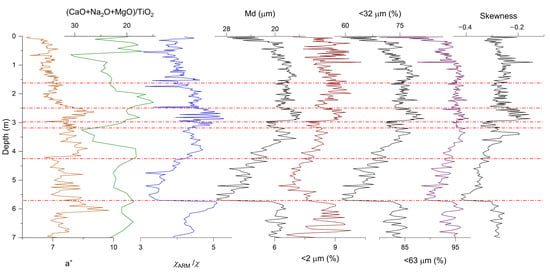
Figure 3.
Redness (a*, yellow curve), geochemical(green curve for (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2), magnetic (blue curve for χARM/χ), and granulometric parameters (left black curve for Md, red curve for <2 μm, middle black curve for <32 μm, purple curve for <63 μm, and right black curve for skewness) versus depth at Sanmenxia.
Consistent with field observations, all proxies suggest that the paleosols in the 1.62–3 m depth interval developed in a more humid climate compared to the neighboring layers (Figure 3). At around 2.98–3.2 m, 2.5 m, and 1.62 m, significant changes in the parameters are observed and can be correlated to the 8 ka event (Figure 1; with cold-dry conditions interpreted as occurring at 7.8 ka and 8.2 ka at Baicaoyuan [26]), 5.9 ka event [42], and 4.2 ka event [4,43]. These events were also recorded by other studied loess sections in the southeast of CPL [9,44,45,46]. Variations of the chromatic, geochemical and rock magnetic parameters are consistent with the identified events, as illustrated in the Section 4. However, discrepancies between various proxies can be observed.
Loess grain size distribution can help to identify the transportation dynamics and origins. The grain size parameters consistently show an up-section fining trend at 5.7–3 m and a coarsening trend at 3–0 m (Figure 3). It is worth noting that both >63 μm and <2 μm fractions show high contents at 0–1 m. Skewness decreases with increasing grain size. The loess formed during the YD is characterized by a high concentration around a coarse modal grain size (about 40 μm) (Figure 4). In contrast, the sample from the top of the section show less concentration around the modal grain size (>30 μm), though it is also coarse and negatively skewed. Compared to the magnetic parameters, the grain size parameters have a relatively low amplitude at 0.5–3 m with less noticeable peaks at around 1.5 m.

Figure 4.
Grain size distribution of typical samples from Sanmenxia.
3.3. Results of BHQ2
The depth–age models of both cores drilled at Beihuqiao village are show in Figure 5, which show good agreement. It discloses that no significant change in the sediment accumulation rates occurred after 8 ka. Instead, a slight decrease in the sediment accumulation rates can be observed at 5–6 ka. The results are consistent with other sediment records in the study area [24,25].
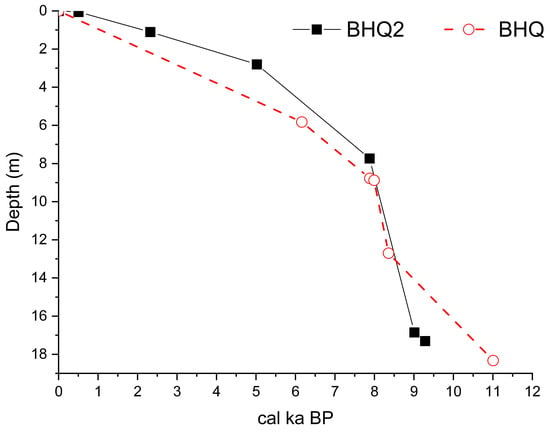
Figure 5.
Age–depth models for BHQ and BHQ2.
The BHQ2 sediments are dominated by silt and clayey silt, except for a silt sand layer from 17 to 12 m (Figure 6). The core can be divided into five zones. The bottom part (below 17 m) mainly consists of dark gray clayey silt with relatively fine grain size and high χ and χfd. The depth interval of 17–9 m is composed of yellow-gray and gray silt, which can be further subdivided into two layers: the lower layer dominated by gray-yellow silt (17–12 m) and the upper layer that is composed of gray silt and is relatively fine (12–9 m).
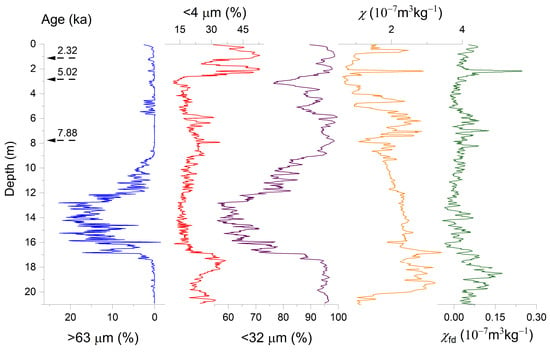
Figure 6.
Grain size and magnetic proxies and dating results of BHQ2 (blue curve for >63 μm fraction, red curve for <4 μm fraction, purple curve for <32 μm fraction, yellow curve for χ, and green curve for χfd).
Moreover, the upper layer shows an upward increasing trend in the <32 μm fraction and χfd and a decreasing trend in χ. The depth interval of 9–5.8 m is a dark gray and gray clayey layer with fine grain size and high χ and χfd compared to the underlying zone. The depth interval of 5.8–2.5 m shows an increase in grain size and a decrease in χ and χfd. The topmost 2.5 m demonstrates a very high <4 μm fraction and a slightly high χfd compared to the underlying zone.
4. Discussion
4.1. Decoupling from Climatic Evolution since 4 ka
The relative concentration of SP (<30 nm), SSD (30~100 nm), PSD (with grain size ranging between SSD and MD), and MD (with the coarsest grain size) ferrimagnetics (magnetite or maghemite) can disclose the origins of the magnetic imprints in loess and the provenience of loess [38,39]. χfd is sensitive only to the ferrimagnetic particles around SP and the SSD boundary, which are of postdepositional pedogenetic origin and are used as a more reliable pedogenetic or paleoclimatic proxy than χ [47]. Likewise, χARM or ratio parameter of χARM/χ is used as an indicator of pedogenetic intensity [48,49,50].
A good relationship between χ and χfd or χARM is found in the Sanmenxia loess, as generally observed on the Chinese Loess Plateau, suggesting that χ is dominated by ultrafine magnetic grains of pedogenetic origin resulting from an intensified summer monsoon [48,49,50]. The poor relationship between χ and χfd or χARM in loess deposits can be attributed to changes in source area. In arid central Asia, χfd or χARM decreases and shows a weak linear relation with χ, and χ is positively correlated with grain size if the eolian contribution from the proximate source increases [49,50]. In southern CLP, the decrease in χ and χfd is attributed to soil erosion associated with the natural process or human disturbances [9,51]. In the Sanmenxia section under study, the stepwise decrease in χ and χfd and the weakening relation between χ versus χfd at the glacial–interglacial timescale is interpreted as being caused by soil erosion and proximate source changes for loess accumulation [27]. High SIRM in relation to χ is found in the paleosols directly overlying fluvial deposits in another loess section at Sanmenxia [52], implying that the relation between SIRM and χ or SIRM/χ is indicative of chemical weathering associated with hydrological changes.
The plots of magnetic parameters versus Md (Figure 7) and the plots of magnetic parameters (Figure 8) differentiate the depth interval at 0–2.48 m from that at 2.48–7 m in the Sanmenxia section. Furthermore, the linear relationship between SIRM and χ shows stepwise weakening at 3.25–7 m, 1–3.25 m, and 0–1 m. In contrast, the Holocene loess from Baicaoyuan, which is in the northwestern margin of the CLP and in a more arid climate, exhibits a good linear relation between the magnetic parameters (Figure 9). These observations suggest that climate alone was not adequate as the driving force of sediment dynamics and soil erosion.
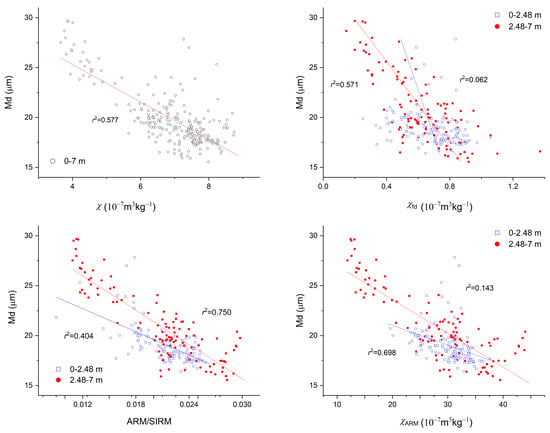
Figure 7.
Plots of magnetic parameters versus median grain size (Md) for Sanmenxia loess.
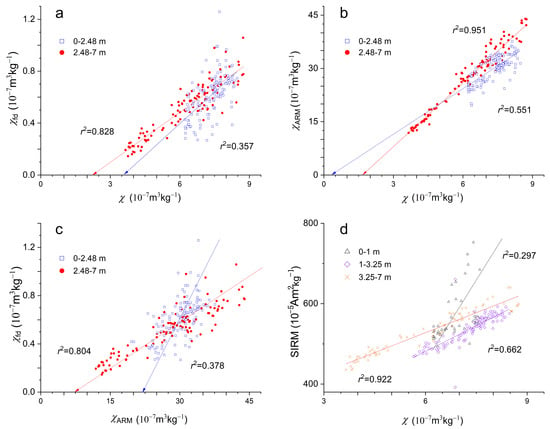
Figure 8.
Plots of magnetic parameters for Sanmenxia loess. (a) plots of χfd and χ, (b): plots of χARM and χ, (c) plots of χfd and χARM, (d) plots of SIRM and χ.
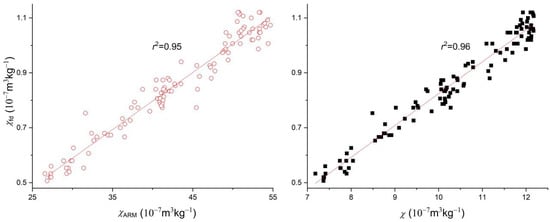
Figure 9.
Plots of magnetic parameters for Baicaoyuan loess.
Previous studies demonstrated a similar monsoon-dominated variation pattern of the Holocene climate [53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] and a similar magnetic enhancement model for typical loess across the CLP [48,50,54]. Based on the aforementioned fluctuations in and weakening relation between the proxies, an age frame for the Sanmenxia section is attained by interpolation with the ages of 12.9 ka, 11.7 ka, 8.2 ka, 7.8 ka, 5.9 ka, and 4.2 ka being assigned to the depth at 5.7 m, 4.25 m, 3.2 m, 2.98 m, 2.5 m, and 1.62 m, respectively (Figure 10). The Holocene paleoclimatic evolution constructed with this age frame is in concert with other results from the southeastern CLP [9,44,59,61]. The inferred paleoclimatic events are observed worldwide [45] and consistent with local records [46]. The 8 ka event is recorded by the Zhangbian section (Figure 2; [34]). The 5.9 ka event can be correlated to the ending of the Holocene optimal at 6 ka as revealed by five loess sections, including the Lingbao and Dingcun sections [58]. The 4.2 ka event can be correlated with the transition between loess subunits at Weinan and Yaoxian [9,44,62].
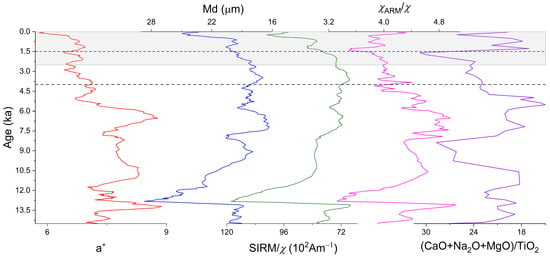
Figure 10.
Variations of paleoclimatic proxies at Sanmenxia (red curve for a*, blue curve for Md, modena curve for S300, carmine curve for χARM/χ, green curve for SIRM/χ, and purple curve for (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2). Ages are interpolated between paleoclimatic tie points at 12.9 ka (5.7 m), 11.7 ka (4.25 m), 8.2 ka (3.2 m), 7.8 ka (2.98 m), 5.9 ka (2.5 m), and 4.2 ka (1.62 m). The corresponding depths are indicated by red chain lines in Figure 3. The shadow indicates 0–2.5 ka, corresponding to the weakest relation between SIRM versus χ shown in Figure 8d. Except for the (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 curve, all curves are five-point smoothed.
The reconstructed Holocene paleoclimate at Sanmenxia is consistent with the general pattern on the CLP [59] with the optimal in the middle Holocene. During 12.9–11.7 ka BP, the climate was cold and dry, dominated by the Younger Dryas. Between 11.7 and 10 ka, the climate turned warm and wet, and 10–5.9 ka BP was the Holocene Optimum Period, during which a relatively dry-cold event at around 8 ka could be observed. At around 5.9 ka, the climate rapidly deteriorated. Afterwards, the climate slowly became dry and cold. At around 4.2 ka, the climate further deteriorated. The magnitude of paleoclimatic change is small at 4–1.5 ka but large since 1.5 ka.
A recent study on Holocene loess at Yulin, a transitional zone between the CLP and Mu Us Desert, reveals asynchronous variations of East Asian summer monsoon, vegetation, and soil formation, which are ascribed to the differences in respective controlling factors [63]. It is exhibited that soil-formation-related proxies, such as magnetic susceptibility and grain size, could be inconsistent with monsoon strength. However, our results suggest that the same magnetic parameters could show different correlations at different localities (Figure 7 and Figure 9). The result of the Sanmenxia loess shows obvious discrepancies between different paleoclimatic proxies, in particular, between magnetic proxies and grain size proxies. From 7.8–4 ka (2.98–1.5 m) to 4–1.5 ka (1.5–1 m), <2 μm%, χARM/χ and (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 illustrated more significance changes than Md and <63 μm (Figure 3 and Figure 10). Since 1.5 ka (1 m), the grain size coarsened, and the hard magnetic mineral content might increase (as revealed by SIRM/χ in Figure 10). Such observation is generally interpreted as resulting from the drying climate. However, (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 showed intensified chemical weathering since 1.5 ka (Figure 3 and Figure 10). Therefore SIRM/χ as well as the geochemistry parameter probably indicate accelerated soil erosion [19,52].
It is suggested that the paleoclimatic evolution in east China since 4 ka was characterized by 13 low-amplitude warm/cold fluctuations [64] or a gradual cooling trend [45,62]. A recent study in south CLP suggests that the rainfall decreased after 5 ka [53] (Figure 11). Newly synthesized results suggest that sediment accumulation rates covaried with monsoon intensity during 40–6 ka, increasing/decreasing with intensifying/weakening monsoons but increased rapidly and decoupled from weakened hydroclimates after 5 ka [5] (Figure 11). Consistently, the weakening relation between various parameters after 4.2 ka (above 2.48 m) and the discrepancy between various proxies at Sanmenxia could be interpreted as being caused by other factors that overwhelmed climatic control.
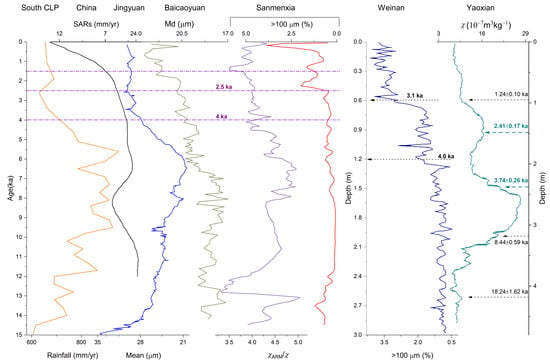
Figure 11.
Comparisons of variations of multiple proxies from Holocene records. South CLP 10Be-based rainfall reconstruction (earthy yellow curve) is modified after [53]; synthesized trend of sediment accumulation rates (SARs) from 191 sediment archives in China (black curve) after [5]; mean grain size of Jingyuan loess ( blue curve) after [57]; median grain size (Md) of Baicaoyuan loess (celadon curve) after [26]; χARM/χ (purple curve) and >100 μm (red curve) of Sanmenxia; >100 μm fraction of Weinan loess (dark blue curve) after [9]; and χ of Yaoxian loess (cyan curve) after [44].
4.2. Human Impacts Overwhelming Climate Control of Soil Erosion on the CLP
The study on the Holocene loess at Guanzhong, south CLP shows that three end members of the loess deposits can be identified [55]. The fine grain end member is interpreted as being associated with weathering and pedogenesis dominated by the East Asia summer monsoons. The coarse grain end member is suggested to originate from near-source sediments from the Yellow River floodplains transported by strong winds. The third end member is thought to be the major component of the loess deposits linked to the northwest monsoon. The study on Mangshan loess suggests that the clayey loess component representing the fine dust supplied over the entire CLP by long-term suspension processes during major dust outbreaks and as part of a background supply system [65]. The Sanmenxia loess in southeast CLP partly sources from the middle reaches of the Yellow River [66]. Therefore, the changes in the magnetic parameters of loess from southwest CLP can be partly attributed to the overall weathering and erosion variation across the CLP [67,68].
The adjacent Wangguan loess section is notable for its high sedimentation rate in the last loess–paleosol couplet [29]. The accelerated loess accumulation is attributed to the more fluvial sediments serving as a proximate dust source produced by the intensified incision of the Yellow River. However, the Holocene loess at Wangguan is very thin. Similarly, the Holocene loess at Mangshan is thin and shows no increase in accumulation rate in the middle-late Holocene, though it is also characterized by the major contribution of the floodplains to loess accumulation [69]. In the Sanmenxia section, the <63 μm fraction show little change at 3.5–1 m (9.2–2.5 ka), suggesting that the changes in proximate source areas is limited. Besides, the persistent changing trend in various proxies at Sanmenxia indicates that the magnetic behavior and grain size characteristics are not likely caused by occasional overland flows. Thus, significant changes that occurred at 4–5 ka can be interpreted as responding to soil erosion in wide areas rather than local source change. In the cool-dry periods, soils erosion was generally very low because there was low precipitation. In warm-wet periods the land surface might be protected by a well-developed vegetation cover (forest or steppe), which is not favorable to soil erosion. In general, soil erosion during the transition from cool-dry to warm-wet stages was more intensive than that during the warm-wet to cool-dry transition [11]. The synthesized study suggests that 5–6 ka, when the warm-wet Holocene optimal was turning into the cool-dry late Holocene, was a transitional period with anthropogenic impacts intensifying in China at a continent scale [5]. Enhanced human activities through land-use modifications altered vegetated landscapes and resulted in accelerated soil erosion after 5 ka in China [5,6]. Land cover change was pervasive at 5–6 ka across the CLP, as sediment records across the CLP suggest [62]. The 4–6 ka interval shows a noticeable decrease in χARM/χ and redness and a increase in grain size in the Sanmenxia loess. However, it is hard to partition the natural and anthropogenic contributions. Within chronological uncertainty, 4–6 ka could be regarded as a transitional period before the onset of accelerated soil erosion at Sanmenxia (Figure 10 and Figure 11). The intensified human impact at 4 ka was coeval with the onset of the Bronze Age and the first prehistoric dynasty in China [21,45].
Moreover, the soil erosion at Sanmenxia could be correlated to that in Baicaoyuan, Weinan [9], or Yaoxian [44] (Figure 11). The mean grain size of Jingyuan loess, which is suggested to be sensitive to the Asian summer monsoon intensity, has had low amplitude since 4 ka [57]. Note that Md of Baicaoyuan, which was interpreted to be indicative of monsoon intensity, is more similar to χARM/χ than to Md of the Sanmenxia loess (Figure 3 and Figure 11).
An increase in coarse grain size fraction in loess is generally interpreted as resulting from the drying climate [41]. However, loess grain size can also be affected by erosion. Previous studies in south CLP suggest that >100 μm fraction indicates human-induced erosion [9]. As revealed by SIRM versus χ relation, SIRM/χ, and >100 µm fraction (Figure 8d, Figure 10 and Figure 11), soil erosion intensified after 2.5 ka at Sanmenxia. Since 1.5 ka, soil erosion further increased. The rapid changes in (CaO + Na2O + MgO)/TiO2 at around 1.5 ka are consistent with the intensified soil erosion and weathering intensity at 1.8 ka in southwest China [19]. The low χARM/χ possibly responds to the weakening hydroclimate. The coarse grain size fraction (>100 μm%) and weak relation between SIRM and χ indicate aggravated soil erosion, while the geochemical parameters suggest intensified chemical weathering due to soil erosion. A recent study demonstrated that the effect of intensified human activity outpaced natural climatic variability on earth surface processes as the major control of dust storm activity since 2 ka [10], which is consistent with the late Holocene renewed acceleration in erosion on the CLP. Besides, the studies on the Duowa loess section [7,8], Dadiwan marsh section [56], sediment discharge of the Yellow River [11], the sediment yield of the Yellow River (Figure 12) [12,13,14], and increased fire activity [20] and poor grain production in China [18] also indicate temporal coherence with our results.
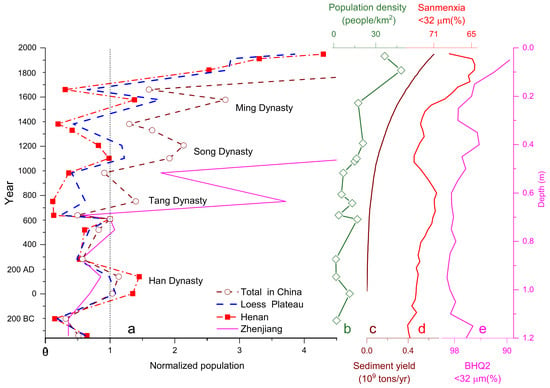
Figure 12.
a: Population fluctuations of Zhejiang, Henan, Loess Plateau (Henan, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Gansu and Ningxia), and China since 340 BC (normalized by the population in 606 AD) [70]; b: population density in hilly or gully areas on the CLP, modified after [71]; c: anthropogenic increment of sediment yield of the Yellow River since 2 ka, after [12]; d: <32 um fraction of Sanmenxia loess since 2.36 ka; e: <32 um fraction of BHQ2 (0–1.2 m).
Instead of land use cycles or a single significant increase in soil erosion in the middle Holocene (5–6 ka) or in the late Holocene (within the 1.5–3.1 ka span) highlighted in previous studies, two increases in soil erosion were indicated in the Sanmenxia loess, with 4–6 ka being the transitional period before the first increase. Such a temporal pattern is similar to that of the intensification of pastoralism revealed by lake sediments in the northeastern margin of the CLP [15].
4.3. Contrasting Sustainability between Zhejiang and CLP
In Zhejiang, the prehistoric culture was suggested to be dominated by climate with the turning point of the response of prehistoric culture to climate change happening at 4 ka [24,25,72,73]. BHQ showed a significant increase in the pollen of cultivated Oryza during the environmental evolution from lake to marsh at 5.68–4.17 ka, implying that the cool and dry climate might result in the declining level of groundwater and be conducive to human activity and cultural prosperity in the area [31]. The high content of <4 μm fraction at 0–2.5 m of BHQ2 might result from the weakened hydrodynamics after 4 ka. The study area was less susceptible to human disturbance. There was no acceleration in sediment accumulation or soil erosion rates in the drying climate since the middle Holocene, as the BHQ cores and other local records indicate [24,25,72].
With the higher population density than on the CLP since the Early Tang Dynasty (1.4 ka) [70], the present-day Zhejiang Province might see much less human-induced soil erosion. As Figure 12 demonstrates, the population in Henan or on the CLP fluctuated and did not increase significantly until after the Qing Dynasty (1616 AD), while the population in Zhejiang increased dramatically after Tang Dynasty (618 AD). The population growth on the CLP is approximately correspondent with the anthropogenic increment of sediment yield of the Yellow River [12,13,70,71] and the coarsening trend of Sanmenxia loess (Figure 12).
The comparable increasing <32 μm fraction of Sanmenxia and BHQ2 indicate similar drying trends in Zhejiang and the CLP. The contrast in human-induced soil erosion and population growth could be partly attributed to the difference between the loess on the CLP and the zonal soils in Zhejiang. Similar negative feedback between civilization and the environmental impact to those reported elsewhere [4,16] could be traced. The origin of Chinese agriculture is believed to be associated with loess [74]. Natural vegetation helps to enhance the porosity and, thus, the permeability and water-storage capacity of loess. However, human destruction of natural vegetation would result in the initiation of serious soil erosion. On the CLP, grazing was still the major type of land use as late as 2.4 ka [2]. Cultivation and settlement occurred since the Qin dynasty (221 BC). However, much farmland was abandoned from the Western Han Dynasty to the Sui Dynasty (9–618 AD). Farming became pervasive again since the Tang dynasty (618 AD). The resultant accelerated soil erosion, possibly canceling out technology development and affecting land productivity and crop yield.
The CLP was no more the most prosperous area in China, and the population proportion of CLP decreased, while the southeast of China developed rapidly since 1 ka. Given the enormous disparities across China, understanding the combined effects of geographical setting, soil formation, hydroclimate, and human activity at the regional level is of significance to sustainable development.
5. Conclusions
The multidisciplinary study of the Holocene loess on the CLP and the temporal coherence with other records suggest that the effect of intensified human activity outpaced climatic variability on earth surface processes, beginning in the middle Holocene. The first phase of significant human-driven soil erosion probably began at around 4 ka. A renewed acceleration in soil erosion was indicated to occur during the 2.5–1.5 ka span. By contrast, Zhejiang, in the southeast of China, shows much lower susceptibility to soil erosion. The reverse correlation between enhancing soil erosion and relative population growth represents a negative feedback between civilization and the environmental impact on the CLP, where agriculture development resulted in decreased land productivity and undermined regional sustainability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); methodology, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); software, G.Z. (Guocheng Zhang) and W.W.; validation, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); formal analysis, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); investigation, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); resources, Q.C., J.G. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); data curation, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guoyong Zhao); writing—original draft preparation, Q.C.; writing—review and editing, Q.C. and G.Z. (Guocheng Zhang); supervision, J.G. and Q.C.; project administration, Q.C. and J.G.; funding acquisition, Q.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41402155 and 42130507).
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this work can be obtained in Figshare (https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.19520140.v1, accessed on 6 April 2022) or are available from the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ye Wei and Zhu Lidong for the fieldwork at Beihuqiao village and the interpretation of the core records and Liu Xiuming and LÜ Bin for their help in magnetic measurements and related resources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vanwalleghem, T.; Gómez, J.; Infante-Amate, J.; de Molina, M.G.; Vanderlinden, K.; Guzmán, G.; Laguna, A.M.; Giraldez, J. Impact of historical land use and soil management change on soil erosion and agricultural sustainability during the Anthropocene. Anthropocene 2017, 17, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei-E, R.; Xianmo, Z. Anthropogenic influences on changes in the sediment load of the Yellow River, China, during the Holocene. Holocene 1994, 4, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, J.-P.; Koirala, S.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Francus, P.; Niemann, C.; Ahrens, B.; Brovkin, V.; Baud, A.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Normandeau, A.; et al. Human and climate global-scale imprint on sediment transfer during the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22972–22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothacker, L.; Dosseto, A.; Francke, A.; Chivas, A.R.; Vigier, N.; Kotarba-Morley, A.; Menozzi, D. Impact of climate change and human activity on soil landscapes over the past 12,300 years. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Sun, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Nie, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Human Impacts Overwhelmed Hydroclimate Control of Soil Erosion in China 5,000 Years Ago. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Weng, C.; Steinke, S.; Mohtadi, M. Anthropogenic modification of vegetated landscapes in southern China from 6000 years ago. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.; Wintle, A.G.; Maher, B.; Hu, M. Holocene sediment-accumulation rates in the western Loess Plateau, China, and a 2500-year record of agricultural activity, revealed by OSL dating. Holocene 2001, 11, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, B.A.; MengYu, H.; Roberts, H.; Wintle, A.G. Holocene loess accumulation and soil development at the western edge of the Chinese Loess Plateau: Implications for magnetic proxies of palaeorainfall. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2003, 22, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Jia, Y.; Pang, J.; Zha, X.; Su, H. Holocene colluviation and its implications for tracing human-induced soil erosion and redeposition on the piedmont loess lands of the Qinling Mountains, northern China. Geoderma 2006, 136, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Gowan, E.J.; Qiang, M.; Dong, G.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Asian dust-storm activity dominated by Chinese dynasty changes since 2000 BP. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, K. Soil erosion response to climatic change and human activity during the Quaternary on the Loess Plateau, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2006, 6, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Dian, Z.; You, L. Changes in sediment yield of the Yellow River basin of China during the Holocene. Geomorphology 2002, 46, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, L. Sedimentation in the lower reaches and sediment yield in the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River in the past 2600 years. Quat. Sci. 2009, 29, 116–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F. Intensification and Driving Forces of Pastoralism in Northern China 5.7 ka Ago. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL092288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.M. The impact of environmental change and human land use on alluvial valleys in the Loess Plateau of China during the Middle Holocene. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dodson, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X. Increases of population and expansion of rice agriculture in Asia, and anthropogenic methane emissions since 5000BP. Quat. Int. 2009, 202, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Fang, X.; Yin, J. Impact of climate change on fluctuations of grain harvests in China from the Western Han Dynasty to the Five Dynasties (206 BC–960 AD). Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Toucanne, S.; Clift, P.D.; Zhao, D.; Bayon, G.; Yu, Z.; Cai, G.; Yin, X.; Révillon, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Human impact overwhelms long-term climate control of weathering and erosion in southwest China. Geology 2015, 43, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, F.; Lin, Z.; Song, X. Holocene fire history in China: Responses to climate change and human activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 753, 142019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Li, R.; Lu, M.; Zhang, D.; James, N. Evolution of human–environmental interactions in China from the Late Paleolithic to the Bronze Age. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2019, 44, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Ren, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, L.; Xu, Q.; Birks, H.J.B. Cycles of grazing and agricultural activity during the historical period and its relationship with climatic and societal changes in northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3315–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. A Test of Climate, Sun, and Culture Relationships from an 1810-Year Chinese Cave Record. Science 2008, 322, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Innes, J.B.; Zong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Environmental history, palaeoecology and human activity at the early Neolithic forager/cultivator site at Kuahuqiao, Hangzhou, eastern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 2277–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y. Characteristics of Climate around 4.0 ka BP and its impacts on the collapse of Liangzhu Civilization in the Taihu Lake Region. Master Dissertation, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Lü, B.; Niu, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, P. Paleoclimatic evolution of Holocene loess and discussion of the sensitivity of magnetic susceptibility and median diameter. Quat. Int. 2012, 296, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Jia, J.; Ye, W.; Lü, B.; Meadows, M.; Guan, J. 0.2 Ma or 1.2 Ma? Timing of the Linking of the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yellow River Inferred from Loess-Palaeosol Sequences. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B. Paleomagnetic dating of the topmost terrace in Kouma, Henan and its indication to the Yellow River’s running through Sanmen Gorges. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Pan, B.; Gao, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Su, H. Instability characteristics of the East Asian Monsoon recorded by high-resolution loess sections from the last interglacial (MIS5). Sci. China Ser. D: Earth Sci. 2007, 50, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Pan, B.; Bridgland, D.; Vandenberghe, J.; Guo, L.; Fan, Y.; Westaway, R. The linking of the upper-middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River as a result of fluvial entrenchment. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 166, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Li, F.; Wang, T.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Early middle Holocene climate oscillations recorded in the Beihuqiao Core, Yuhang, Zhejiang Province, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2017, 59, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Lü, B.; Chen, Q. Magnetic characteristics of Guangshan loess from northern piedmont of Dabie Mountains, east-central China. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 222, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; An, Z. Pretreated methods on loess-palaeosol samples granulometry. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, F.; Wu, X. Paleomonsoon Events from the Last Glacial Maximum to Early Holocene in Sanmenxia Area. Acta Geoscientia Sinica 1999, 20, 433–438. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Alley, R.B.; Mayewski, P.A.; Sowers, T.; Stuiver, M.; Taylor, K.; Clark, P.U. Holocene climatic instability: A prominent, widespread event 8200 yr ago. Geology 1997, 25, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayewski, P.A.; Bender, M. The GISP2 ice core record-Paleoclimate highlights. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ding, F.; Ding, Z. Pleistocene chemical weathering history of Asian arid and semi-arid regions recorded in loess deposits of China and Tajikistan. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Heller, F. Environmental Magnetism—Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; pp. 1–299. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.; Oldfield, F. Environmental Magnetism; Allen and Unwin: London, UK, 1986; pp. 1–227. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Q.; Oldfield, F.; Bloemendal, J.; Guo, Z. Particle size separation and evidence for pedogenesis in samples from the Chinese Loess Plateau spanning the past 22 m.y. Geology 2008, 36, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Derbyshire, E.; Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, T. Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2005, 237, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, G.; Showers, W.; Cheseby, M.; Lotti, R.; Almasi, P.; Demenocal, P.; Priore, P.; Cullen, H.; Hajdas, I.; Bonani, G. A Pervasive Millennial-Scale Cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and Glacial Climates. Science 1997, 278, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, E.; Overpeck, J.; Briffa, K. Palaeoclimate. In Climate change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 435–497. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, F.; Li, S.-H.; Wintle, A.G.; Fan, Y.-X.; Xia, D.-S. A record of Holocene climate change in the Guanzhong Basin, China, based on optical dating of a loess-palaeosol sequence. Holocene 2007, 17, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. The Holocene Climate Change; China meteorological press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 1–283. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-B.; Han, S. An Imaging Algorithm for Space-borne SAR Based on Range Walk Correction. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2008, 30, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rolph, T.; Bloemendal, J.; Shaw, J.; Liu, T. Quantitative estimates of palaeoprecipitation at Xifeng, in the Loess Plateau of China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 1995, 113, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Deng, C.; Torrent, J.; Zhu, R. Review of recent developments in mineral magnetism of the Chinese loess. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 26, 368–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Heller, F.; Hirt, A.; Lü, B.; Guo, X.; Mao, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.; Feng, H.; et al. Susceptibility variations of multiple origins of loess from the Ily Basin (NW China). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Mao, X. Loess-palaeosol sequences in diverse environments: Aeolian accumulation identification and magnetic susceptibility models. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 584, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Pang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Holocene dust accumulation and the formation of polycyclic cinnamon soils (luvisols) in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2003, 28, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Qiang, X.; Ao, H. Rock Magnetism Study on Loess-Paleosol Sequence at Huixinggou Section of Sanmenxia Basin. Adv. Earth Sci. 2017, 32, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.W.; Zhou, W.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; White, L.; Xian, F.; Kong, X.; An, Z. A 550,000-year record of East Asian monsoon rainfall from 10 Be in loess. Science 2018, 360, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Løvlie, R.; Sun, Z.; Pei, J. Environmental magnetism and paleoclimatic interpretation of the Sanmenxia loess-paleosol sequence in the southeastern extremity of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, J.; Zha, X. Characteristics of Holocene Loess-Palaeosol Particle Size Composition and Paleoclimatic Significance in East Guanzhong, Shaanxi Province. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 12. [Google Scholar]
- An, C.; Feng, Z.; Tang, L. Evidence of a humid mid-Holocene in the western part of Chinese Loess Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Clemens, S.C. Impacts of post-depositional processes on rapid monsoon signals recorded by the last glacial loess deposits of northern China. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 289, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Wen, A.B.; Liu, X.Z.; Chu, G.W.; Li, K. Relationship between Soil organic carbon and bulk density in the stocky desertification process of Karst ecosystem in Guizhou. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2011, 19, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Huang, X. Warming-induced northwestward migration of the East Asian monsoon rain belt from the Last Glacial Maximum to the mid-Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13178–13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Lu, R.; Ding, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z. Holocene Environmental Changes Inferred from an Aeolian-Palaeosol-Lacustrine Profile in the Mu Us Desert, Northern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 799935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q. The Climatic Evolution During the Holocene in the Baoji Region. Master Dissertation, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Chen, F.; An, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, C.; Chen, F.; An, C. Holocene vegetation and climate changes from fossil pollen records in arid and semi-arid China. Dev. Quat. Sci. 2007, 9, 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Lu, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. Asynchronous variations of East Asian summer monsoon, vegetation and soil formation at Yulin (North China) in the Holocene. J. Quat. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q. Climate Change in China in the Past; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011; pp. 1–705. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Prins, M.A.; Zheng, H.; Beets, K.; Troelstra, S.; Bacon, P.; Kamerling, I.; Wester, W.; Konert, M.; Huang, X.; Ke, W.; et al. Dust supply from river floodplains: The case of the lower Huang He (Yellow River) recorded in a loess-palaeosol sequence from the Mangshan Plateau. J. Quat. Sci. 2008, 24, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Stevens, T.; Rittner, M.; Stockli, D.; Garzanti, E.; Limonta, M.; Bird, A.; Andò, S.; Vermeesch, P.; Saylor, J.; et al. Correction: Corrigendum: Loess Plateau storage of Northeastern Tibetan Plateau-derived Yellow River sediment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, R. Environmental magnetism of Chinese loess-paleosol sequences. Quat. Sci. 2007, 27, 193–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Shaw, J.; Liu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, R. Mineral magnetic variation of the Jingbian loess/paleosol sequence in the northern Loess Plateau of China: Implications for Quaternary development of Asian aridification and cooling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 241, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Pang, J.; Su, H.; Li, S.; Ge, B. Holocene environmental change inferred from the loess–palaeosol sequences adjacent to the floodplain of the Yellow River, China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 2633–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Teng, Z. An Investigation on Historical Provincial Population in China; Shandong people’s publishing house: Shandong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P. Population geography in the middle Yellow River in history. In Collections of Researches on Environmental Changes of the Yellow River Basin and Laws of Water and Sediment Transportation; Wang, S., Ed.; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993; Volume 5, pp. 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Hou, S.; Shi, C.; Mo, D.; Liu, B.; Zhou, L. Palaeoecological records of environmental change and cultural development from the Liangzhu and Qujialing archaeological sites in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Quat. Int. 2010, 227, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, C.; Li, F.; Ma, C.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Shui, T.; Wang, X.; Shao, S.; et al. Response of Prehistoric Culture to Climatic Environmental Changes since Holocene in Zhejiang, East China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping-Ti, H. The Loess and the Origin of Chinese Agriculture. Am. Hist. Rev. 1969, 75, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).