Abstract
Coastal ecological protection and restoration projects aimed to restore and recover the ecological environment of coastal wetland with high-intensity human reclamation activity, while the integrity of the coastal wetland system with human reclamation activity and the ability of individual land use types to control the overall system were not fully considered. In this study, a six-stage land use conversion network was constructed by using a complex network model to analyze coastal land use dynamic changes in the coastal reclamation area located in eastern China from 1977 to 2016. The results showed that land use types had gradually transformed from being dominated by natural types to artificial types, and the speed of transformation was accelerating. The proportion of un-reclaimed area decreased from 93% in 1977 to 46% in 2007, and finally fell to 8% in 2014 and 2016. Tidal flat and halophytic vegetation were the main output land use types, while cropland, woodland and aquaculture pond were the main input land use types. Cropland had the highest value of betweenness centrality, which played a key role in land use change from 1992 to 2014. The land use system of the coastal reclamation area was the most stable in 2002–2007, followed by 1984–1992, and the most unstable in 2007–2014. The Chinese and local government should carry out some measures to improve the land use in coastal wetland ecosystems, including the allocation and integration of land use for production space, living space, and ecological space, and develop multi-functionality of land use to realize the coastal high-quality development and coastal ecological protection and restoration.
1. Introduction
Land is an essential and increasingly scarce resource, both for the survival and prosperity of humanity, and for the maintenance of all terrestrial ecosystems [1,2]. Land cover addresses the observed layer of soils and biomass that cover the earth’s surface [3], which can be thus directly acquired in the field as well as from remote sensing images [4]. Land use refers to all activities (e.g., grazing) of purposeful development and utilization of land resources and includes the land management practices (e.g., the presence of logging roads) [5], which cannot be always easily observable. Land use and land cover change can markedly impact the climate and the ecosystem at regional and global levels [6]. As urbanization, resources and environmental issues become increasingly prominent, Land Use and Cover Chang (LUCC) was launched in 1994 to address the problem of land use and land cover dynamics. Future Earth was launched in 2014 and continues to focus on the issues of sustainability science worldwide [7]. Therefore, LUCC and its driving force have been hot topics of global change research and sustainability science [8].
Coastal wetlands, which have high ecological value and environmental function and provide various direct and indirect ecosystem services [9], play a key role in human development and face intense ecological stress from human activities. Socio-economic development with increasing of urbanization and industrialization is an important and critical cause of the degradation of coastal wetland ecosystems. In the past decades, coastal wetland reclamation for artificial land use (e.g., agriculture and construction land) has been a common practice around the world [10,11,12,13]. In recent decades, it has become an important way to meet the increasing demand for population growth and socio-economic development in China [14,15]. China reclaimed 2976.1 km2 of coastal wetland, and 910.8 km2 was developed for urbanization in the period of 2002–2018 [15]. High-intensity reclamation activities on coastal wetland ecosystems were studied from the perspective of soil properties [16,17], pollutions [18,19], and land use change [20].
Land use change is the direct result of interactions between humans and nature. Land use patterns can record the evolution of coastal wetlands with the influence of human development as well as the coastal ecological protection and restoration projects. Researchers focused on the characteristics of land use change, specifically from the perspectives of land use types, area of land use type [20], land use intensity [21], and rate of land use change [18], etc. However, little research has focused on the integrity of the coastal wetland system with human reclamation activity, and the ability of individual land use types to control the overall system were not fully considered. All of these traditional indicators can describe the features of land use change, but cannot fully describe the status and role of each land use type in the process of land use change. They also cannot reveal the relationship and influence among land use types in the coastal reclamation activities. Thus, a more scientific and effective method to analyze coastal wetland dynamic changes should be determined. In this aspect, the complex network theory is an appropriate tool that can be employed to analyze such dynamic changes holistically. As an important method of sociological research, the complex network model can better solve these problems. It analyzes the behavior of individuals in the system and the connections between individuals from the perspective of the system as a whole. This method had been widely used in the study of energy trade patterns [21], waste management [22], carbon dioxide emission [23], ecosystem management [24], transportation [25], and urban planning [15], etc. Many scholars have used complex network models to study land use change as well [15,21,26,27], from the perspective of the system as a whole, to identify the key land use types and evaluate the stability of the land use system.
The coastal wetlands of Jiangsu Province are typical silty tidal flats, which are rich in resources, accounting for about 25% of the total coastal wetlands in China. Due to the input of sediment from the Yellow River and the Yangtze River and the special seabed geomorphic environment, the coastal wetlands in Jiangsu are characterized by dynamic growth. The “Outline of Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Development Plan” was released by the Chinese government in 2009, which proclaimed Jiangsu Province’s intention to accomplish a coastal reclamation area of ~1800 km2 from 2010 to 2020, and to build ports, industrial zones and coastal towns [14,15]. The reclaimed areas were mainly concentrated in Yancheng City and Nantong City. Dongtai County is one of the most densely reclamation areas along the coast of Jiangsu. In the planning, the scale of coastal reclamation in Dongtai County went up to 667 km2 [28], which is more than 33% of Jiangsu Province’s reclamation plan. Therefore, Dongtai County had the largest reclamation scale in the coastal development of Jiangsu. High-intensity human reclamation activities are bound to cause drastic land use/cover changes in the coastal wetland ecosystem. Coastal ecological protection and restoration projects have been promoted in China nowadays with the release of a comprehensive 15-year plan (Master plan for major projects of national important ecosystem protection and restoration) since the year of 2020. Therefore, the whole land use change process should be systematically studied to understand the evolution and driving force of coastal wetland ecosystems with the effect of reclamation, which can effectively guide the formulation of ecological protection and restoration measures. With the implementation of coastal ecological protection and restoration project since 2020, a comprehensive and systematic understanding of the evolution process of coastal reclamation is significant to promote the protection and restoration of coastal wetland ecosystems. The objectives of this study were to (i) build complex network models of the dynamic land use conversion of coastal reclamation areas, (ii) depict the dynamic change processes of coastal reclamation areas by calculating indicators of complex networks, and (iii) analyze the driving forces of land use change in coastal reclamation areas.
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located at Dongtai County, Jiangsu Province (32°33′ N–32°57′ N, 120°07′ E–120°53′ E), which is an extremely fragile ecological environment (Figure 1). Dongtai County has a total area of 3175.67 km2, a coastline of 85 km, and a tidal flat area of 156 km2. It faces the Yellow Sea, which is on the edge of the Pacific Ocean to the east. It belongs to the subtropical and warm–temperate transition zone, which is a typical monsoon climate with an annual average temperature of 14.6 °C, annual precipitation of 1051.0 mm, and annual average sunshine duration of 2169.9 h. The terrain in Dongtai County is flat with a ground elevation of 1.4–5.1 m, most of which is 2.6–4.6 m. The coastal tidal flat in Jiangsu is currently expanding seaward, which could provide new land resources for development [18]. The study area covers the main part of the reclamation area in Dongtai County, including all typical land use types along with the entire process of coastal reclamation activity (Figure 2).
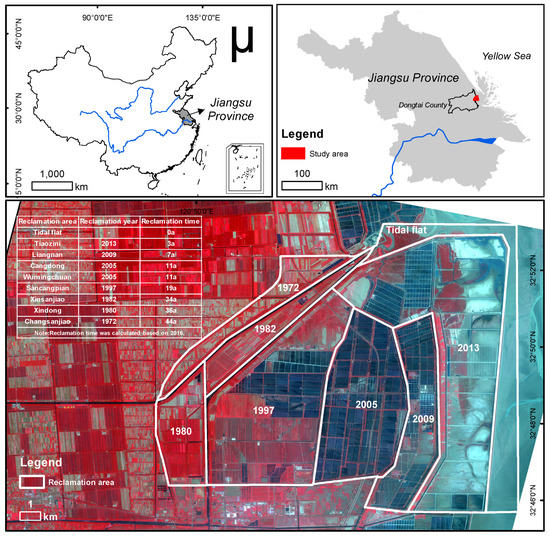
Figure 1.
The location of the study area.

Figure 2.
Typical land use types in Dongtai coastal reclamation areas: (A) tidal flat after tide, (B) newly built dike and bare land, (C) halophytic vegetation, (D) cropland in newly reclaimed area, (E) aquaculture pond, (F) integrated “wind-solar-fishing” power station, (G) cropland in earlier reclaimed area, (H) woodland, and (I) built-up area. All the photos were taken by Caiyao Xu in 2016.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
Seven remote sensing images (e.g., 1977, 1984, 1992, 2002, 2007, 2014 and 2016) of the Dongtai coastal reclamation area were used in this study. Table 1 showed the detailed information of the images. The dates of the images were selected in the growth period of plants. The geometric correction, spatial registration technology and other operations were processed with ENVI 5.3 software. Then, the images were clipped and resampled to the same boundary and the same resolution (30 m) by using ArcGIS 10.5 software. Supervised classification and visual interpretation were combined to interpret the seven remote sensing images, with a classification precision of over 85%. The accuracy of classification was checked through field work. Thus, seven shapefiles of land use maps in Dongtai coastal reclamation area (Figure 3) were obtained to further analyze.

Table 1.
The parameters of remote sensing images.
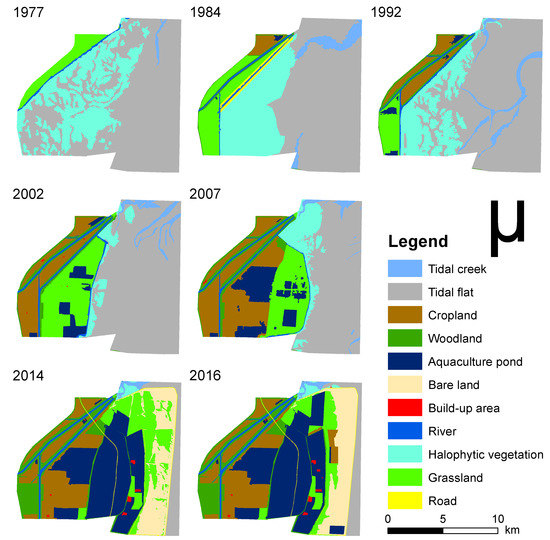
Figure 3.
Land use maps of Dongtai coastal reclamation area from 1977 to 2016.
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Complex Network Model
The man-land system is a complex system consisting of nature, society and economy. Complex networks are the backbone of complex systems, which can quantify system characteristics and analyze the characteristics of the entire network system to determine the interaction of various factors and the state of the influencing factors [29]. Therefore, complex network models help to understand the complex dynamic change of land use systems [30]. Complex networks were constructed based on the land use transfer matrix, to analyze the land use change process, using the igraph package [15] of R software (R core team, version 4.0.5) in this study. Land use types were the nodes of the network, and the conversion between different land use types was the connection of the network edge. The key indices of the network, including the output/input degree of nodes, betweenness centrality of nodes, average shortest path and clustering coefficient, were calculated respectively by the functions of degree, betweenness, mean distance, and transitivity in the igraph package.
2.3.2. Shannon Entropy Method
Entropy can generally be defined as a measure of chaos or the disorder of a system. Claude E. Shannon (1948) introduced this concept to describe the uncertainty of an information source; therefore, it is usually called the Shannon Entropy Index [31]. The entropy concept is a quantitative measure of the disorder of thermodynamic systems, which is employed to identify the most probable spatial structure of a system capable of adapting to numerous uncertain spatial states. In this study, the characteristics of land use conversion were quantitatively analyzed through the Shannon Entropy Index and Equilibrium Degree. The Shannon Entropy Index (H) is a measure of the degree of the order of land use conversion. The value of H reflects the number of land use types and the uniformity of the area distribution of each land use type. The larger the value of H, the more land use types, the smaller the area difference between each land use type, and the more mature the land use system. The calculation formula of H is as follows [32]:
where Pi is the ratio of the area of land use type i to the total area; Ai is the area of land use type i; N is the total number of land use types; A is the total area of the study area.
Constructing the Equilibrium Degree (ED) of a land use system based on the concept of Shannon entropy, ED refers to the ratio of the actual value H to the maximum value Hmax, which is used to describe the difference of area size between land use types and the structural pattern of each land use type. The greater the value of ED, the stronger the homogeneity of the land use system. The calculation formula of ED is as follows [33]:
2.3.3. Stability Analysis of Land Use System
The Shannon Entropy Index could also be applied into the evaluation of the stability of land use systems. For land use systems, the sum of the largest change area in a certain period is equal to the total area of the study area. The proportion of the transformation area of land use type i to the total area of land use type i in a certain period can be regarded as the probability of event occurrence (Qi). Therefore, in the process of land use change within a certain period (T), the formula of land use system Shannon Entropy Index (H’) could be built as follows:
where, the amount of change (area) from a certain type of land to another type of land is called “transfer-out flow” (Fin), and the amount of change (area) from other types of land to that type of land is called “Fout”. The sum of the transfer flow is the “land use transfer flow” of the land use type in a specific period of time (T), which represents the total amount of all participating land use changes in the land use type. A is the total area of the study area.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Land Use Change in Coastal Reclamation Area
Coastal land use types changed obviously with the influence of human activity and reclamation projects (Figure 3). Figure 4 shows the area of each land use type in a study area from 1977 to 2016. The total area of the study area is about 16,031.5 hm2. Tidal flat and halophytic vegetation constituted the key land use types of an unreclaimed area, and other land use types mainly appeared in reclamation areas. The proportion of unreclaimed area decreased from 93% in 1977 to 46% in 2007, and finally fell to 8% in 2014 and 2016, of which the area ratio of halophytic vegetation was only about 0.8%. The land use types after reclamation were mainly aquaculture pond, cropland, woodland, and grassland. The area of aquaculture pond increased gradually from 1977 to 2007, which was from 10.13% to 30.12% and 33.16%, respectively, in 2014 and 2016, and the rate of growth also accelerated. The proportion of cropland also increased to 17.31% and 18.75% in 2014 and 2016, respectively.
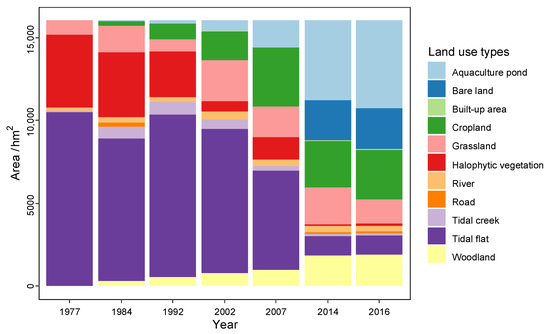
Figure 4.
Area of each land use type in the Dongtai coastal reclamation area from 1977 to 2016.
3.2. Land Use Change Characteristics Based on Complex Network Model
Six complex network models from 1977 to 2016 are shown in Figure 5. In different periods, the land use transitions between different land use types were frequent, and the network was correspondingly complicated, especially in 2007–2014. However, due to the short time span, the land use transition network was relatively simple in the period of 2014–2016. Table 2 shows the output and input degree of nodes in transition networks in each period in the study area. Tidal flat and halophytic vegetation were the main output land use types. The output/input ratio of the tidal flat was 3, 1, 3, 2.5, and 7 in the periods of 1977–1984, 1984–1992, 1992–2002, 2002–2007 and 2007–2014, respectively. The ratio of output/input of the tidal flat gradually increased over time, and reached its maximum during the period of 2007–2014, indicating that the intensity of reclamation activities had been increasing. The output/input ratio of halophytic vegetation was 6, 1.5, 3.5, 1.67, and 9 in 1977–1984, 1984–1992, 1992–2002, 2002–2007 and 2007–2014, respectively. Cropland, woodland and aquaculture ponds were the main input land use types, and their ratio of output/input was mainly between 0 and 1. Overall, tidal flat was an important transfer-out land use type, and its area decreased from 10,485.87 to 1127.62 hm2 during the years of 1977–2016, mainly being transferred to grassland, woodland and aquaculture land.
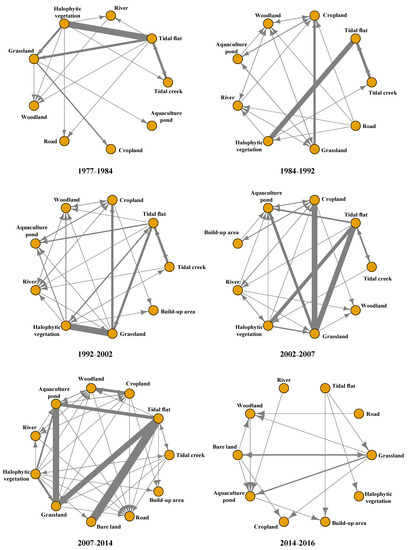
Figure 5.
Complex network models of coastal reclamation areas during different periods. Note: the arrow represents the direction of land use change, and the thickness of the line represents the transition area (relative amount) between two land use types.

Table 2.
Output/input degree of nodes in conversion networks during different periods.
3.3. The Recognition of Key Land Use Types
The values of betweenness centrality of nodes are presented in Figure 6. Cropland had the highest value of betweenness centrality in the transition network in the period of 1992–2014 (Figure 6), which indicated that cropland had the most vital status and role in land use change processes in the Dongtai coastal reclamation land use system. Halophytic vegetation was also found to have a high betweenness centrality, which was second only to that of cropland in the period of 2002–2007. Large areas of halophytic vegetation were converted to woodland, grassland, and bare land from 1990 to 2018. Overall, it could be seen that in the six periods from 1977 to 2016, the key land use types in the study area varied significantly, the track of which was tidal flat (1977–1984, with the value of 7) → river and halophytic vegetation (1984–1992, with the value of 13 and 12 respectively) → cropland (1992–2002, with the value of 9) → cropland (2002–2007, with the value of 20) → cropland (2007–2014, with the value of 6) → aquaculture pond (2014–2016, with the value of 5).
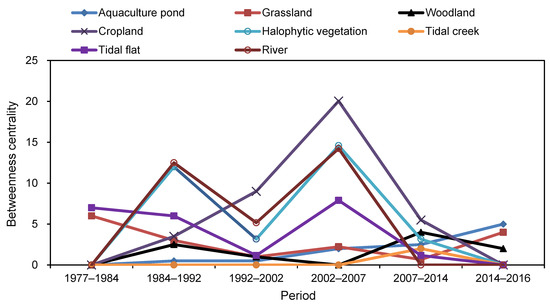
Figure 6.
Betweenness centrality of nodes in conversion networks during different periods.
3.4. Stability Evaluation of Land Use System
The average path length of conversion networks was all less than two in the six periods in the study area, and the specific value was between 1.44 and 1.95 (Figure 7), indicating that the network had poor stability, and land use type conversions were easily conducted [30]. In most cases, two land use types could be connected as long as another land use type was used as a medium. The average path length of the conversion networks showed a fluctuating trend from 1977 to 2016. The order of the average path length of networks in each study period was 2002–2007 > 1984–1992 > 1977–1984 > 2014–2016 > 1992–2002 > 2007–2014. The land use system was the most stable in 2002–2007, with the average path length value of 1.95, followed by 1984–1992 with the average path length value of 1.82; the land use system was the most unstable in 2007–2014, with the average path length value of 1.32. During 2007–2014, two or more reclamation areas were built, and new land use types, such as bare land, also appeared. Therefore, the high intensity of reclamation activity promoted the interaction among land use types, and the new land use types improved the connectivity and accessibility of the network, resulting in the most unstable land system during this period. The clustering coefficient of the networks showed a fluctuating trend that first increased and then decreased (Figure 7). The clustering coefficient was the smallest in 2014–2016, and the largest in 2002–2007.
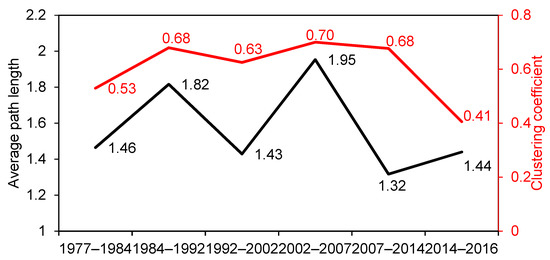
Figure 7.
Average path length and clustering coefficient of conversion networks during different periods. Note: the black polyline indicates the average path length (left Y axis), and the red polyline indicates the aggregation coefficient (right Y axis).
The Shannon entropy method was used to further explore the complexity and balance of land use systems in the study area from 1977 to 2016. At the seven time points from 1977 to 2016 (Figure 8a), the Shannon Entropy Index of the land use system first increased and then turned out to be stable, indicating that the land use system became more and more disorderly during the study period and then reached a new equilibrium. The Shannon Entropy Index was the largest in 2014, and then slightly decreased in 2016. At the same time, the Equilibrium Degree also showed a trend of first increasing and then becoming stable, which showed that the homogeneity of the land use system is increasing. During the process of land use change in the study area (Figure 8b), the disturbance intensity of the land use system by human activities varied greatly in different periods. Among them, the degree of human disturbance to the land use system from 1977 to 1984 was low, so that the intensity of coastal reclamation and development activities in the study area was low. The degree of human disturbance to the land use system from 1984 to 2014 was relatively high. During this period, around 92% of the study area had been encircled, land use types were diversified, and the development intensity was maintained at a high level. The intensity reduced from 2014 to 2016, and the land use system turned into a relatively stable state.
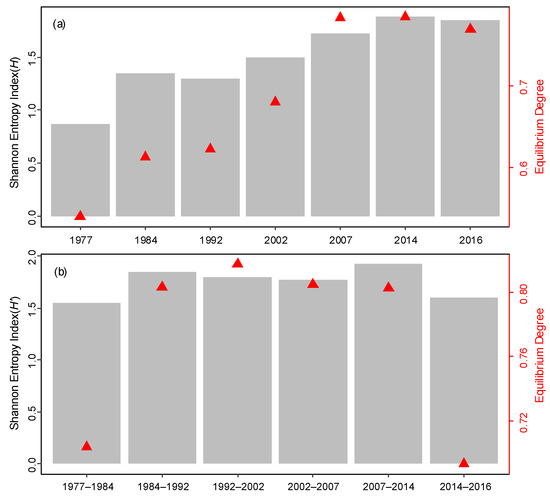
Figure 8.
The Shannon Entropy Index and Equilibrium Degree of the land use system. Note: the gray bar graph represents the Shannon Entropy Index (left Y axis), and the red triangle dot graph represents the Equilibrium Degree (right Y axis).
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Factors of Land Use Change in Coastal Reclamation Area
Dongtai County is the largest county-level city in Jiangsu Province, with the largest area of coastal wetland. It could also be seen from Figure 9 that Dongtai County’s coastal reclamation activity had experienced two high stages since 1970, namely from 1970 to 1985 and 1995 to 2015, with a cumulative reclaimed area of 395.50 km2. The size of the reclaimed area in 1970–1985 accounted for 24.82% of the total reclaimed area, and the speed of coastal reclamation was 6.58 km2/a. During this period, the conflict between man and land gradually appeared. The demand for cropland resources was the main reason for the formation of the first high stage. A new round of coastal reclamation craze set off between 1995 and 2015. During this period, the reclaimed area reached 74.59% of the total reclaimed area, and the speed of coastal reclamation reached 14.84 km2/a. Among them, the speed of confinement in the first five years (1995–2000) of the construction of the “Maritime Eastern Jiangsu” reached 18.56 km2/a, which was the fastest period of Dongtai coastal reclamation activity from 1970 to 2015. In general, the tendency of Dongtai coastal reclamation activity was consistent with the Jiangsu Province, and even China.
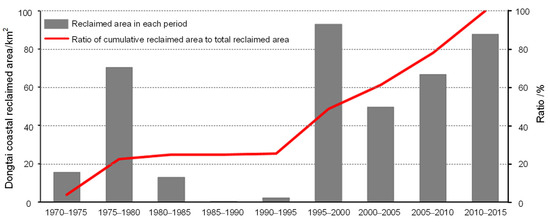
Figure 9.
Dongtai coastal reclamation area from 1970 to 2015 (modified from reference [34]).
In this study, with the dynamic change process in coastal reclamation area, 9 to 11 land use types were regarded as nodes in a conversion network, the conversion relationships between land use types were regarded as edges, and the area of conversion between the land use types was used as the weight of edges. Therefore, the land use change process in each period (1977–1984, 1984–1992, 1992–2002, 2002–2007, 2007–2014, 2014–2016) was regarded as a complex network system composed of nodes and edges. Comprehensively, considering the results of the analysis above and other references, the typical and common land use types were selected to depict the land use change process from sea to land in the coastal reclamation area. The theoretical and actual evolution paths of typical land use conversions in coastal reclamation areas were concluded in Figure 10. Theoretically, a high salinity of soil limits the rapid expansion of agriculture, with the natural succession of vegetation instead. In the initial stage, the reclaimed area was developed as an aquaculture pond, which can produce economic benefits and also to a certain extent promote soil desalination. With the maturation of soil, reclamation areas could be reclaimed for agriculture, then built-up areas can appear and even form settlements. Therefore, the theoretical evolution path is sea →tidal flat → halophytic vegetation → aquaculture pond→ cropland→ built-up area. With the wide application of new salt-tolerant species and the improvement of rapid desalination technology [17], the process and time of the land use evolution path in coastal reclamation areas has fundamentally shortened. Therefore, the actual evolution path is different from the theoretical path. For example, the sea can be directly used for aquaculture, and tidal flat or newly reclaimed areas can be developed for cropland because of salt-tolerant crops.
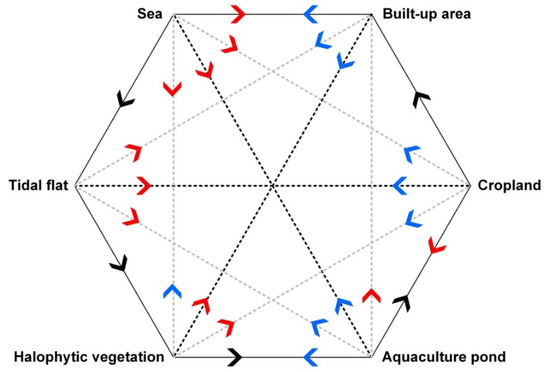
Figure 10.
The evolution path of typical land use changes in coastal reclamation areas (modified from [35]).
The driving factors of land use change can be divided into natural factors (weather, geomorphology, plant succession, etc.) and artificial factors (socio-economic, institutional, policy and technological factors, etc.). In general, with the development of social economy and the growth of populations, the driving force of land use change in coastal reclamation areas has changed accordingly, as shown in Figure 11. China’s coastal reclamation activity has developed rapidly since the 1950s [36]. During this period, there was less pressure from the population and economic development, and coastal area was mainly reclaimed to expand salt fields. Coastal land use change was mostly obviously affected by geology and geomorphology, and ocean dynamics. Then, many big reclamation projects were carried out for agriculture from the mid-1960s to the 1970s, especially in the coastal areas of Zhejiang, Jiangsu and Fujian [14]. In these initial stages, the driving forces of land use change were mainly natural factors, supplemented by human activities. By the 1990s, a new round of coastal reclamation occurred in China with more than 30% of coastal wetlands reclaimed in order to meet the needs of rapid urbanization and industrialization [36]. Because of high salinity land and low levels of desalination technology, most coastal reclamation areas were developed for aquaculture. In 1995, the “Maritime Eastern Jiangsu” cross-century marine economic development project was proposed. Many coastal reclamation projects were carried out to accommodate rapid development of the marine economy. The “Outline of Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Development Plan” proclaimed Jiangsu Province’s intention to accomplish a coastal reclamation area of ~1800 km2 from 2010 to 2020, and to build ports, industrial zones and coastal towns [14,15]. Since the 21st century, the driving force of coastal land use change has primarily been artificial factors.
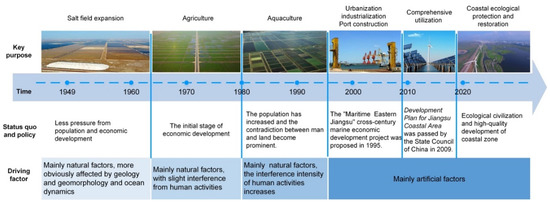
Figure 11.
Driving factors of land use change in the Jiangsu coastal reclamation area.
4.2. Land Use Optimization Measures
Coastal reclamation activities have resulted in serious ecological and environmental problems [9]. As natural land use types and the original forms of coastal wetland ecosystem, tidal flat and halophytic vegetation had important ecosystem functions and ecological value. With the increasing development of coastal zones, natural land use types have been largely reclaimed for the needs of economic growth and human populations, the phenomenon of which has appeared in many coastal zones all around the world [9,12,36,37]. The expansion and key role of cropland has mainly been the outcome of the government policy, the “Outline of Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Development Plan”, which determined the land use pattern of coastal reclaimed areas with 60% of agricultural land, 20% of construction land and 20% of ecological land.
Thus, China released a comprehensive 15-year plan (National Master Plan for Major Ecosystem Protection and Restoration Projects) for ecological protection and restoration with nine major ecological conservation projects, setting a target to improve the country’s environment and achieve the goal of building a Beautiful China by 2035 [21]. Coastal ecological protection and restoration projects are one of the nine special plans, which aim to carry out the ecological protection and restoration of the sea and tidal flats, the shoreline, the estuary bay, typical marine ecosystems (such as mangroves and coral reefs), tropical rainforest protection, and the prevention of invasive species such as Spartina alterniflora. Therefore, the land use change under the coastal ecological protection and restoration project should be further studied in the future and the possible evolution path of land use change is depicted in Figure 10. The main feature is that the artificial land use types would be restored to natural land use types. Natural land use types in coastal zones contained tidal flats, halophytic vegetation and other land use types with high ecological value.
Nowadays, the Chinese government highly values the development of a high-quality marine economy [21]. The core content of land use optimization measures for coastal high-quality development should be the allocation and integration of production space, living space, and ecological space. Firstly, considering the limited land resources, fragile ecological environments and increasingly tense relationship between humans and nature, coastal protection should focus on the transformation from single function to multi-functionality of land use in coastal wetland ecosystems [21]. Secondly, with the strategy of “Land-Sea Coordination”, it should promote the coordinated improvement of social, economic and ecological functions of the land and ocean through scientific, systematic coordination of coastal resources, industries, ecologies and environments [38,39]. Thirdly, with the concept of “a community with a shared future for mankind”, the transformation from fragmented management to coordinated governance should be realized. It is an urgent need to establish a whole-scale, all-element, and systematic land use regulated system for the “mountains–rivers–forests–farmlands–lakes–grasslands” of coastal ecosystem. Finally, with the strategy of “ecology first, green development”, it requires us to optimize the construction logic and practical path of the bottom line of the development, to regulate the time and space order of the development and protection of coastal ecosystem, and to form the security and resilience of coastal ecosystems.
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions of the Study
This study constructed complex network models of the Jiangsu coastal reclamation area and analyzed the integrity of the coastal wetland system with human reclamation activity and the ability of individual land use types to control the overall system. The data used in this study was limited in understanding the latest evolutionary features, which should be further studied in the future. Although the results provide insight into the spatial and temporal changes and the driving forces of land use in coastal reclamation areas, mainly by using a complex network approaches, further research is needed to tackle future challenges from new policy (e.g., high-quality marine economy and coastal ecological protection and restoration project) and to support the understanding of mechanisms that shape the land use patterns of coastal wetland ecosystems. It is necessary for future studies to consider the predictions of changes in man–land interactions under future land use development scenarios and management actions, such as coastal ecological protection and restoration projects, which aim to determine how to affect the supply capacity of coastal wetland ecosystems and to seek a win–win management policy for the government’s ecological planning. What’s more, the land use pattern of coastal wetlands to support the carbon neutrality should also be further studied. Future management policy should ensure the safety of ecological environments and achieve coastal high-quality development under future land use scenarios.
5. Conclusions
This study introduced the complex network method to identify the key land use types, land use processes, and system stability of land use systems from 1977 to 2016 in the Dongtai coastal reclamation area, Eastern China. The following conclusions were made:
(1) The land use types under the influence of coastal reclamation activities had gradually transformed from being dominated by natural types (tidal flat, halophytic vegetation, etc.) to artificial types (cropland, aquaculture pond, construction land, etc.), and the speed of transformation was accelerating. During the period of 1977 to 2016, the proportion of unreclaimed area decreased from 93% in 1977 to 46% in 2007, and finally fell to 8% in 2014 and 2016, of which the area ratio of halophytic vegetation was only about 0.8%.
(2) Tidal flat and halophytic vegetation were the main output land use types, while cropland, woodland and aquaculture ponds were the main input land use types. Cropland had the highest value of betweenness centrality in the transition network in the period of 1992–2014. The key land use types during the six periods from 1977 to 2016 were tidal flat (1977–1984) → river and halophytic vegetation (1984–1992) → cropland (1992–2002) → cropland (2002–2007) → cropland (2007–2014) → aquaculture pond (2014–2016).
(3) The average path length of conversion networks fluctuated between 1.44 and 1.96. Frequent conversions between different land use types led to poor stability of land use systems in coastal reclamation areas. The land use system was the most stable in 2002–2007, followed by 1984–1992; the land use system was the most unstable in 2007–2014.
(4) Artificial factors were the main driving forces in the land use change of coastal reclamation areas. The core content of land use optimization measures for coastal high-quality development could be the allocation and integration of production space, living space, and ecological space, and could develop multi-functionality of land used in coastal wetland ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Data collection and analysis, C.X.; writing—original draft, C.X.; writing—review & editing, C.X., L.P., F.K. and B.L.; research design and methodology, C.X., L.P. and F.K.; constructive suggestions, B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41230751), the Special Project of Cultivating Leading Talents in Philosophy and Social Science of Zhejiang Province (21YJRC12-2YB, 21YJRC2ZD), the Major Research Project of Humanities and Social Sciences in Colleges and Universities of Zhejiang Province (2021QN062), Research Development Fund of Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University (2020FR066).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful and constructive comments that have greatly improved this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995-2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Global land use change, economic globalization, and the looming land scarcity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3465–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verburg, P.H.; van de Steeg, J.; Veldkamp, A.; Willemen, L. From land cover change to land function dynamics: A major challenge to improve land characterization. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Linderman, M. Time series of remote sensing data for land change science. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1926–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verburg, P.H.; Crossman, N.; Ellis, E.C.; Heinimann, A.; Hostert, P.; Mertz, O.; Nagendra, H.; Sikor, T.; Erb, K.-H.; Golubiewski, N.; et al. Land system science and sustainable development of the earth system: A global land project perspective. Anthropocene 2015, 12, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.R. Modernization, Development and Underdevelopment: Reclamation of Korean tidal flats, 1950s–2000s. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2014, 102 Pt B, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sun, W.; Tong, C.; Zeng, C.; Yu, X.; Mou, X. China’s coastal wetlands: Conservation history, implementation efforts, existing issues and strategies for future improvement. Environ. Int. 2015, 79, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.O. The evolution and resolution of conflicts on Saemangeum Reclamation Project. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2007, 50, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, R.; Haberzettl, P.; Walsh, R.P.D. Land reclamation in Singapore, Hong Kong and Macau. GeoJournal 1991, 24, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, R.J. Three stages in the history of land reclamation in the Netherlands. Irrig. Drain. 2007, 56, S113–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.J.; Melville, D.S.; Liu, J.G.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Ren, W.W.; Zhang, Z.W.; Piersma, T.; Li, B. Rethinking China’s new great wall. Science 2014, 346, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuai, X.W.; Huang, X.J.; Wu, C.Y.; Li, J.B.; Lu, Q.L.; Qi, X.X.; Zhang, M.; Zuo, T.H.; Lu, J.Y. Land use and ecosystems services value changes and ecological land management in coastal Jiangsu, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Samaddar, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Jeon, S.; Sa, T. Structural and functional responses of microbial community with respect to salinity levels in a coastal reclamation land. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 137, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Meadows, M.; Sun, L.; Wu, T.; Bu, X.; Xu, Y. Differential effects of various reclamation treatments on soil characteristics: An experimental study of newly reclaimed tidal mudflats on the east China coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wu, W.T.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhou, Y.X. Drivers, trends, and potential impacts of long-term coastal reclamation in China from 1985 to 2010. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Land Use Effects on the Distribution and Speciation of Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Coastal Soils on Chongming Island in the Yangtze River Estuary, China. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H. Characterizing landuse changes in 1990–2010 in the coastal zone of Nantong, Jiangsu province, China. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2013, 71, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, K.; Gao, H.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Soil organic carbon as affected by land use in young and old reclaimed regions of a coastal estuary wetland, China. Soil Use Manag. 2013, 29, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueti, R.; Cinelli, M.; Minervini, L.F. Municipal waste management: A complex network approach with an application to Italy. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Fan, F.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Inter-provincial sectoral embodied CO2 net-transfer analysis in China based on hypothetical extraction method and complex network analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.; Sivakumar, B. Complex networks and integrated centrality measure to assess the importance of streamflow stations in a River basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Derudder, B.; Liu, X. The evolving structure of the Southeast Asian air transport network through the lens of complex networks, 1979–2012. J. Transport. Geogr. 2018, 68, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, L.; Zhang, S.; Feng, C. Assessment on characteristics of LUCC process based on complex network in Modern Yellow River Delta, Shandong Province of China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2015, 9, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y. Temporal and spatial change of land use in a large-scale opencast coal mine area: A complex network approach. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Coastal Areas Development Office. Outline of Jiangsu Coastal Reclamation Development Plan. Available online: http://www.scio.gov.cn/ztk/xwfb/04/4/Document/542277/542277.htm (accessed on 23 July 2021). (In Chinese)
- Boccaletti, S.; Latora, V.; Moreno, Y.; Chavez, M.; Hwang, D. Complex networks: Structure and dynamics. Phys. Rep. 2006, 424, 175–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.E.; Connor, J.D. Land-use change impacts on ecosystem services value: Incorporating the scarcity effects of supply and demand dynamics. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 32, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedajev, A.; Stanujkic, D.; Karabašević, D.; Brauers, W.K.M.; Zavadskas, E.K. Assessment of progress towards “Europe 2020” strategy targets by using the MULTIMOORA method and the Shannon Entropy Index. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziying, Z.; Jiannan, D.; Chunfeng, L. Temporal-spatial changes analysis of land use structure in Changsha City based on information entropy. Ecnomic Geogr. 2012, 32, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z. Research on the Impact of Tidal Flat Reclamation on Ecosystem Services in Dongtai Coastal Area; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jianguo, L. The Impact of Coastal Reclamation on Soil Organic Carbon: A Case Study of Rudong County, Jiangsu Province; Nanjing University: Nanjing, China, 2015. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.-T.; Pan, J.-F.; Pu, X.-M.; Wang, B.; Pan, J.-J. Current status of coastal wetlands in China: Degradation, restoration, and future management. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 164, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Roon, M.R. Wetlands in The Netherlands and New Zealand: Optimising biodiversity and carbon sequestration during urbanisation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 101, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M.; Cai, Y.; Su, S.; Li, B.; Ji, H. Multiscale identification of urban functional polycentricity for planning implications: An integrated approach using geo-big transport data and complex network modeling. Habitat Int. 2020, 97, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Abouel Nasr, E.S.; El-Tamimi, A.M. An indicator system for evaluating the development of land-sea coordination systems: A case study of Lianyungang port. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).