Abstract
This study examines the role of student co-creation behavior in contributing to student satisfaction, perceived university image, and student positive word of mouth (WOM). Using a sample of 513 students from a Taiwanese university and conducting partial least squares structural equation modeling, the findings indicate that co-creating value is critical to student satisfaction, university image, and positive WOM. The results also show the effect of student satisfaction and university image on student positive WOM. This study confirms the pivotal role of student participation in co-creating value in enhancing satisfaction with the university experience, creating and sustaining a positive image, and building the credibility of the university. This research is particularly important to higher education institutions because it has practical implications for decision-makers, brand managers, and HE marketers who wish to improve understanding of the relationship between the university and students in the process of co-creating value and its outcomes.
1. Introduction
The global and highly competitive environment in which universities operate has led to a requirement for them to develop unique marketing strategies that emphasize the student education experience [1] Various business concepts have been applied in higher education (HE) to enhance competitive advantage and create a superior image that attracts students. Market orientation [2] and relationship marketing theory [3] have been used to treat students as customers, matching their needs, improving offerings, and creating enabling learning platforms to offer a unique experience. However, gaps between marketing theory in the HE literature and practical implementation still exist. Further, there are differences between the services that meet student expectations and the services that universities believe that students should experience [4]. Although both educational institutions and students want to enhance the student experience, there are few avenues for them to work together to do so.
The process of co-creating value is one such avenue, and it improves the ability of universities and students to act as partners [5]. Through this process, student resources are integrated with institutional resources, supporting the tailoring of educational services to meet the specific needs of students and, as a result, assist in developing a unique experience for them during their HE years [6]. Previous studies have investigated student involvement in co-creating value from different perspectives, for instance, enhancing student outcomes [7] and delivering benefits for both universities and students [8]. However, value co-creation is a recent innovation in HE and there is still a lack of comprehensive conceptual models and a large volume of unexplored content [9,10].
Student behavior is inextricably related to value co-creation [11], which offers an opportunity to examine the association between co-creating value, student satisfaction, student perception of university image, and positive word of mouth (WOM). Therefore, this study examines the effect of co-creating value on these factors. First, understanding student satisfaction is of critical importance to universities as they compete in rankings and league tables [12]. Second, creating a favorable institutional image will attract more student applications in the face of competitive market forces [13]. Last, student educational service consumption experiences are an accumulated set of perceptions often gained through multiple sources and WOM [14]. Positive WOM is one of the most influential sources of information transfer by students [15]; it is a useful promotion strategy for HE managers and a highly effective promotional tool in the international education market [16]. Through student positive WOM, the university may gain a sustained competitive advantage [17]. Therefore, this paper investigates whether co-creation can yield positive outcomes for students and institutions based on student perceptions.
It is important to note that while there are empirical studies on co-creating value reported in the HE marketing literature [5,18,19,20], few consider outcomes in the Asian HE context. This study was conducted in the context of HE in Taiwan, which is a country with the third-lowest birth rate in the world. At present, there are approximately 240,000 university students in Taiwan, and this number is expected to decrease to 160,000 students by 2028 [21]. As a result, many universities are faced with closure because of the lack of students [22]. To overcome this crisis, universities are striving to improve their service quality and encourage a higher number of applicants, with various international programs to attract foreign students, especially from South Asian countries [21,23].
Therefore, within this largely unexplored context, this paper aims to advance knowledge in the HE marketing literature, especially in co-creating value, with three main objectives. First, we aim to propose a co-creation model which considers key outcomes, student satisfaction, perceived university image, and positive WOM. Second, the study examines the role of student satisfaction with the university experience and perceived university image in facilitating positive WOM. Last, the study investigates the relationship between university image and student satisfaction.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Co-Creating Value
Co-creating value is a process in which customers play a central role in improving a company’s product or services [24]. Co-creation has been adopted by non-profit organizations, such as universities, which have started to see different stakeholders, including alumni, faculties, and students, interacting to create value [19]. Several scholars have examined the relationship question in the HE context from various perspectives, including the different types and characteristics of educator-student resource interactions; here, student resources include their intelligence, learning ability, study habit and methods, sense of responsibility and personality, and their perspective and opinions [9]. University resources include study courses, modules, syllabi, lectures, homework assignments, examinations, and lab activities [25]. Teaching and learning are a collaborative process [26], but faculty and student partnerships are not easily obtained because the concept is transformative to conventional educator and student relations [27]. However, recent findings highlight the merits of involving students in co-creating value, which benefits both the university and students. Benefits for students include quality interactions, greater satisfaction, and advanced graduate capabilities, and for institutions, student loyalty, university image, and student–university identification [8]. In this study, co-creating value is defined as joint creation and student participation [28]; joint creation highlights the critical importance of students and university staff working together to enhance the student experience in both academic and non-academic matters, and student participation emphasizes student involvement in the process.
2.2. Student Satisfaction
The concept of satisfaction plays a crucial role in HE marketing theory and practice [29]. According to previous research, student satisfaction is a complicated matter [30]. Elliot and Healy [31] noted that student satisfaction reflects a subjective, short-term attitude arising from the evaluation of a student’s educational experience. Students’ university-wide experience is based on core and supplementary factors [4]. The former relates to the student learning experience, which is shaped by capabilities deemed important in enabling students to meet their study obligations. In addition to the core, the supplementary factors include library facilities and educational technology [32], the university’s physical environment [33], and the university-supported student organization [34]. Measuring student satisfaction is important for the institution in evaluating and improving service performance, such as teaching and curriculum design [35]. Empirical research confirms the effect of student satisfaction on student loyalty [36], student WOM [37], and co-creation behavior [17]. In this study, student satisfaction is defined as perceived quality derived from an overall evaluation [29].
2.3. University Image
Brand image is of central importance in marketing. It is the basis of information on the organization and represents the beliefs, associations, attitudes, and impressions held by customers [38]. A university’s image is a crucial factor when students choose to apply for admission [39]. The image can be the immediate mental picture that an individual has about the university [40]. According to Fram [41], a university’s image is often composed of ideas about faculty, the curriculum, teaching quality, and the tuition fee-quality relationship. Arpan et al. [19] indicated that three stable factors affect university image: academic attributes, athletic attributes, and news media coverage. With different brand images, students can recognize the differences between schools and develop their selection intention [17]. In this study, perceived university brand image is measured by student perception of innovation, “goodness” and “seriousness” of university education and business practices, maintenance of ethical standards, social responsibilities, provision of opportunities, and individualized attention [29].
2.4. Student Positive WOM
WOM is the informal transfer of positive or negative feedback regarding usage or characteristics of specific products/services or sellers [42]. WOM plays a crucial role in the formation of customer attitudes [43]. In particular, when consumers make decisions, they usually rely on WOM for information, as it is seen as a trustworthy source, which reduces risk and complexity and increases confidence in the decision [44]. In the HE context, WOM is a form of informal and uncommercialized face-to-face communication about HE [45]. Previous studies have commonly followed two research streams when defining WOM as a construct; the first stream refers to WOM as a bipolar construct, implying that customers make either positive or negative comments to each other [46], and the second refers to positive WOM which is viewed as a desirable marketing outcome [47]. Our approach uses positive WOM and is consistent with the second stream, in which students make positive comments to one another about their university. Positive WOM was found to be enhanced by perceived service quality and innovation experience [15], and it influences student re-enrolment intention [37].
3. Development of Hypotheses
In this study, a research model was developed to explain the proposed relationship between study constructs diagrammatically. As demonstrated in Figure 1, the model suggests that student satisfaction, university image, and student positive WOM are influenced by co-creating value. Student satisfaction with the university is also determined by the perceived university image. In addition, student positive WOM is expected to be influenced by student satisfaction and perceived university image. The following sections present the study constructs and the development of research hypotheses.
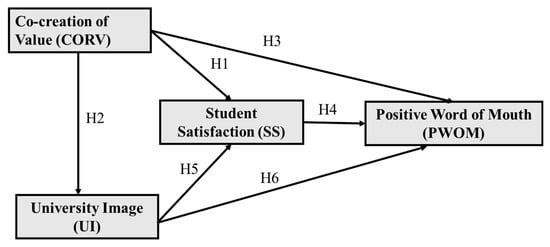
Figure 1.
Conceptual model.
3.1. Effect and Outcomes of Co-Creating Value
Education is not a one-sided service; students need to participate actively to achieve the desired outcomes [26]. Co-creating value is a crucial component of the student experience. It is about giving room for interaction in a setting where the students themselves feel they can contribute and co-create to the learning experience [20]. Through co-creation, students with different knowledge and resources can interact with university faculty and staff to achieve more integrated and superior outcomes than would be possible if only one group tried to satisfy the needs of the other alone [7]. Nystrand and Gamoran’s [48] indicated that co-creation or student “substantive engagement” has a strong and positive impact on their achievement and is therefore fundamental to student satisfaction. Maxwell-Stuart et al. [28] also indicated that students participating in the co-creation process in both academic and non-academic matters pertaining to student life see the entire student experience in a way that positively relates to student satisfaction. The link between student co-creation behavior and satisfaction has been confirmed in empirical research [49,50]. Therefore:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Co-creating value positively affects student satisfaction.
Co-creating value and university image are fundamental aspects of marketing theory and its application [18]. Value creation requires a continuous interaction between companies and their consumers, where both parties combine and integrate resources to help drive the company forward and establish its reputation and image in the market [51]. This interaction significantly enhances customer perceptions of the brand image [52]. In the HE context, previous studies have found that university image can be enhanced through the active interaction and collaboration between students and the university [53]. Student participation in value co-creation indicates their brand commitment and sense of belonging to the university community [54]. Hence, co-creating value significantly affects university image [40,55]. Therefore:
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
Co-creating value has a positive effect on university image.
The service-dominant logic of marketing [56] considers the customer perspective within value creation and recognizes the resources that customers bring with them. Ballantyne and Varey [57] highlighted the role of customer co-creation in helping firms understand how to satisfy customers, promoting long-term relationships and loyalty. Previous studies indicate that customer cooperation with companies in value co-creation is more effective in initiating positive WOM [58]. In HE, when students join in co-creating value, institutions and students have improved interactions, creating an educational experience that genuinely satisfies the students’ need in two ways: learning services (e.g., study programs, syllabi, examinations) and student services (e.g., administrator services, students support services, university facility services, and library facilities) [20]. Elsharnouby [10] found that student participation in value co-creation has an indirect effect on student positive WOM intention through greater satisfaction; further, Mahmoud and Grigoriou [59] found direct and positive impacts of co-creation on WOM. Therefore:
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Co-creating value has a positive effect on student positive WOM.
3.2. Effect of Student Satisfaction and Positive WOM
There are numerous theoretical explanations in marketing for a positive relationship between customer satisfaction and positive WOM [15,59]. The likelihood of customers engaging in positive WOM communication is strongly related to their level of satisfaction [42]. In HE, previous researchers have proposed a direct effect of student satisfaction in predicting positive WOM based on different university service perspectives, such as university website design quality [60], university brand strength [15], and comparing student WOM behavior in public and private universities [59]. In short, student satisfaction with their university influences positive WOM communication. Thus:
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
Student satisfaction positively affects positive WOM.
3.3. Effect of University Image on Student Satisfaction and Positive WOM
The influence of firm image on satisfaction has been empirically validated [3,17,61]. Andreassen and Lindestad [62] noted that corporate image has a strong effect on customer satisfaction, especially if the customer has little knowledge of the service. Similarly, in the HE context, university image is an important topic for students [63]. Student satisfaction with the institution results from the evaluation of the teaching service and study support offered by the university [61]. Based on student data from eight countries in the Middle East, Azoury et al. [64] found that university image statistically and significantly impacts student satisfaction. Similarly, Chandra et al. [65] reported that university image has a positive effect on university student satisfaction. Therefore:
Hypothesis 5 (H5).
University image has a positive effect on student satisfaction.
Brand image is reflected in the brand associations held in the customer’s mind. Brand associations can be a critical determinant in customers’ responses and how they feel and think about the brand, which is largely based on the strength, uniqueness, and favorability of the brand association [66]. Previous research in marketing has established a link between university image and student WOM. While some researchers have argued that WOM is a predictor of university image [67,68]; we argue that WOM behaviors are favorable associations held by students toward their university, consistent with Ajzen and Fishbein [69], because WOM could also be considered to be a behavioral outcome of university brand image associations registered in a student’s mind; this view is consistent with previous studies on other service perspectives [70,71]. Consequently, we propose:
Hypothesis 6 (H6).
University image is positively related to positive WOM.
4. Research Methodology
4.1. Measurement and Data Collection
4.1.1. Measures
The measurement instrument was based on a comprehensive review of the literature on service marketing and HE. The terminology was adjusted to make it more relevant to a sample of university students, thus enhancing content validity. The scales used in the study were adapted from various literature sources; that is, student value co-creation (CORV) was measured with six items that were taken from previous studies focusing on different dimensions of student participation in value co-creation with the university [28,72]. Student satisfaction (SS) was measured using seven items from a previous study [29]; Perceived university brand image (UNI) was measured with eight items adopted from the study of Sultan and Wong [29]. Positive WOM (PWOM) was measured using the three-item scale of Casidy and Wymer [15]. Respondents were asked to rate their perception of each measure using a 5-point Likert scale, from 1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree.
4.1.2. Pilot Test
A pilot test was conducted to ensure the readability, validity, and relevance of the study measures. A questionnaire was developed which covered different facets of the university experience and emphasized student co-creation, student satisfaction, perceived university image, and positive WOM. The questions were translated and back-translated by Mandarin Chinese and English language experts. Then, the questionnaire was reviewed by two university faculty members (one foreign and one Taiwanese) for readability, validity, clarity, and relevance. Additionally, group discussions were conducted with students resulted in some modifications to the wording; the group included eight international students (two Indonesian, two Vietnamese, two Indian, and two Mexican) for the English version and seven Taiwanese students for the Chinese version. These participants were full-time students on at least their second study semester, to ensure relevant experiences of university services.
4.1.3. Participants and Data Collection
The demand for study abroad is growing among the middle classes in Asia. Until the mid-1990s, the majority of students opted for English speaking-countries as educational destinations, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia. However, by the beginning of the 2000s, this trend was changing, and Asian countries have become the destinations of choice for many foreign students [23]. With the trend of internationalization seen in other Asian countries, HE in Taiwan has increased the number and quality of its international programs [73]. Therefore, the population in this study comprised both international and domestic students in Taiwanese universities. Thus, the study is not limited to national strategies but also opens avenues for evaluating and implementing university internationalization strategies.
An online survey questionnaire link was delivered to a Taiwanese university Facebook group over two weeks (16 December 2020, to 7 January 2021). Online surveys have advantages, including low processing fees and an intention to participate; however, this method often achieves a low response rate [74]. Therefore, to encourage students to participate in the survey, six prizes were given to randomly selected students, including a restaurant coupon worth USD 46 and cash gifts (two USD 7 and three USD 4); 550 responses were collected. Participants enrolled in exchange programs along with incomplete cases were deleted. The final dataset comprised 513 responses, with 83.2% domestic students and 16.8% international students; 59.6% were male and 66.5% were pursuing an undergraduate degree.
Common method bias potentially affects the validity of results. To minimize such bias, several steps were taken. First, students were informed that their answers would remain anonymous. Second, statistical tests were conducted using Harman’s single factor test and a common latent factor test. According to Podsakoff et al. [75], if the explained variance is below the threshold of 50%, common method bias may not be significant. The result of Harman’s single factor test was 42.29%, below the threshold. In addition, all the variance inflation factor (VIF) coefficients at factor-level were less than 3.3, which demonstrates that common method bias is not a significant issue [76].
4.2. Data Analysis and Results
Partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) was implemented to test the research model, and the data were analysed using Smart PLS software version 3.0. PLS-SEM supports researchers examining causal relation models and complex models with many constructs [77]. Consistent PLS bootstrapping was employed and 5000 subsamples were tested, as recommended by Hair et al. [78]. The purpose of the bootstrapping test was to determine the significance level of loadings and weights, as well as path coefficients.
4.2.1. Measurement Model
To evaluate the measurement model, convergent and discriminant validity were tested. First, Cronbach’s Alpha, composite reliability (CR), item loading, and average variance extracted (AVE) were accessed to demonstrate convergent validity. Hair et al. [77] suggested that Cronbach’s Alpha, CR, and item loading values are required to be above a threshold of 0.7, and the AVE value should be higher than a threshold of 0.5 for all constructs in the model. Second, discriminant validity was tested using Fornell and Larcker’s [79] criterion and the heterotrait–monotrait (HTMT) ratio recommended by Henseler et al. [80]. Fornell and Larcker’s criterion suggests that the square root of AVE of any latent variable should be higher than its correlation with any other construct. Meanwhile, Fram et al. [41] stated that if the HTMT ratio is lower than 0.9, discriminant validity is achieved.
In this research, all the item loadings are higher than 0.7, except for co-creating value CORV5, student satisfaction SS2, university image UNI6, and UNI8 with loading values of 0.644, 0.578, 0.694, and 0.699, respectively. However, Hair et al. [78] suggested that items with loading values ranging from 0.4 to 0.7 should be considered for removal only if the deletion of this item results in an increase in AVE or CR above the required threshold. In this study, all the Cronbach’s Alpha and CR values are higher than 0.8 and the AVE of all the latent variables is higher than the threshold of 0.5 (Table 1). Therefore, these four items were retained in the model and the convergent validity of the measurement model is demonstrated.

Table 1.
Construct reliability and validity.
The result of the discriminant validity test indicates that all the latent constructs have a square root of EVA higher than its correlation with other constructs (Table 2). In addition, HTMT ratios also show values ranging from 0.350 to 0.789 (Table 3), below the threshold of 0.9. Thus, the discriminant validity of the measurement model is established.

Table 2.
Discriminant validity—Fornell and Larcker’s criterion.

Table 3.
Discriminant validity—Heterotrait–Monotrait Ratio (HTMT).
4.2.2. Structural Model
After the measurement model was approved, the quality of the structural model was evaluated by the procedure recommended by Hair et al. [77], with three assessment criteria: VIF, R2 value, and Q2 value. Analysis showed that each variable in the model has a VIF coefficient that is lower than the required cut-off value of 5.0, demonstrating that the model has no issues of multicollinearity (Table 4). Then, the R2 value of endogenous latent variables was examined and the result showed that the R2 values of SS, UNI, and PWOM are 0.565, 0.108, and 0.513, respectively. Thus, the model explains 56.5% of student satisfaction, 10.8% of university image, and 51.3% of positive WOM. Further, a blindfolding procedure was implemented to examine Q2 values. The rule of thumb is that Q2 values above 0.02, 0.15, and 0.35 demonstrate the small, medium, and large predictive relevance of the PLS-path model. Analysis revealed that SS and PWOM have Q2 values above 0.35 (0.381 and 0.393, respectively) while the Q2 value of UNI is 0.062 (higher than 0.02).

Table 4.
Collinearity statistics.
4.2.3. Hypothesis Testing
The study conducted a bootstrapping test with 5000 subsamples to examine the significance level of path coefficients, as presented in Figure 2.
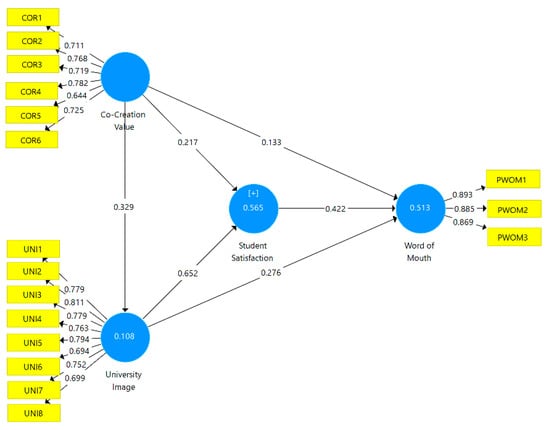
Figure 2.
The structural model.
The results in Table 5 show that the six hypotheses are supported. The co-creation value has a positive and significant impact on student satisfaction (β = 0.217, p < 0.01), university image (β = 0.329, p < 0.01), and positive WOM (β = 0.133, p < 0.01). Therefore, hypotheses H1, H2, and H3 are supported. In addition, university image was found to be significantly related to both student satisfaction (β = 0.652, p < 0.01) and positive WOM (β = 0.276, p < 0.01). Hence, hypotheses H5 and H6 are also supported. Lastly, student satisfaction also significantly affects positive WOM (β = 0.422, p < 0.01), supporting H4.

Table 5.
Results of structural model analysis.
5. Discussion and Implications
Recent research has paid attention to the definition and concepts encompassed by co-creation, as well as its implications [8]. In this study, we introduced and developed this principle in relation to the HE sector. From the student perspective, we investigated the relationship between co-creating value, student satisfaction, student-perceived university image, and positive WOM. A review of existing co-creation literature showed that previous studies have examined the relationship between co-creating value and student satisfaction [10,28,50] but few studies have analyzed the direct effect on student positive WOM in co-creating value or the relationship between student satisfaction and perceived university image on student positive WOM. Based on the model in Figure 1, which is the result of an interactive process with the university, our research recognizes the relevance of co-creation as a mean of achieving not only student satisfaction but also a set of outcomes (perceived university image and positive WOM) that are in the interests of the university.
Given the intensive competitive pressure in the HE sector, co-creating value offers universities an opportunity to enhance the appeal of educational service offerings. All the study hypotheses are confirmed. The findings show that co-creation direct affects student satisfaction. Students are more satisfied when participating in a joint learning experience and working with the university to enhance service offerings that are adapted to their needs. These results are in the line with extant research [10,49,50]. More importantly, as noted by previous studies [36], co-creating value facilities a meaningful and interactive dialogue between organizations and customers. In the HE setting, this dialogue allows for early problem identification and joint problem-solving, which ultimately lead to superior student satisfaction.
Consistent with prior studies, the findings confirm that student participation in value co-creation further leads to benefits for the university, such as an enhanced university image [40,54,55] and favorable comments from students as they release more positive WOM to others, both inside and outside the institution. The university may gain a sustainable competitive advantage when it continuously seeks to enhance its brand image and reputation with good reviews from both domestic and international students [17].
Student satisfaction and perceived university image are also critical predictors of positive WOM in developing countries with challenges of low birth rates, such as Taiwan. This finding confirms the conclusions of previous studies in other contexts [59,64,65,71]. Forming policies and strategies that enhance these aspects is an essential marketing strategy for HE in a competitive environment. In addition, student satisfaction is also enhanced by the perceived university image, which also supports the findings of other studies [3,17,61]. These studies show that, for existing students, the real experience from various university image attributes positively affects their level of satisfaction. The positive effect of student satisfaction may predict future behavior, such as favorable WOM intention [10].
The findings of this study have critical practical implications for HE institutions (HEIs) and open a way forward in strategic marketing for universities to achieve competitive advantage and sustainability. Now and into the future, students will be able to choose their university based on the value proposition that the university offers. Education has never been a stand-alone product; it has always been a co-created interaction between students and HEIs [7,20]. Therefore, HEIs need to have a deep understanding of the shared responsibility among participants and of the importance of student responsibility in shaping value experiences.
With the competition in the HE sector and the need for universities to differentiate themselves, co-creation appears to be a useful tool to achieve this differentiation. This study provides HE managers with the knowledge and approach to the resources and marketing needed to execute co-creation strategies with their students. HE practitioners should ensure that students are actively involved in the decision-making process that affects the student experience, including how universities improve both academic and non-academic services (e.g., administrative, career consulting, pastoral, and commercial services). Practitioners should also create opportunities for students to work with university staff to find solutions to problems that students may face in their HE years. By doing so, a university will not only increase student satisfaction but will also enhance the university image and increase the chances of students generating positive WOM. Enhancing student satisfaction and perceived university image also leads to positive WOM. Therefore, a university can not only increase student positive WOM through co-creating value but can also enhance the WOM marketing channel by raising student satisfaction levels and improving the perceived university image. Positive WOM is one of the most powerful marketing tools in the global market and has a significant influence on re-enrolment intentions [37].
Given the current situation in Asian HE, especially in Taiwan with its challenging birth rate, this study has significant practical implications for HE managers devising strategies to attract both domestic and international students. Taiwan is one of several growing international education hubs in Asia [23]. When students choose to study overseas, in education hubs like China, India, South Korea, and Japan, their evaluation of university image and student feedback based on study experiences is expected to be driven by variables similar to those used in this study. Therefore, to attract students, a university must invest in value co-creation to improve student satisfaction, develop and maintain a positive and distinctive image to achieve a competitive advantage, and ultimately generate positive WOM.
6. Conclusions and Limitations
This study attempted to examine the vital role of co-creating value in generating student satisfaction, university image, and student positive WOM. The study also investigated the effect of student satisfaction and university image on positive WOM, as well as the relationship between university image and student satisfaction. Having collected data from both domestic and international students from a Taiwanese university, we conducted quantitative research. The most critical finding is confirmation of the positive effects of co-creating value on student satisfaction, university image, and positive WOM. Both student satisfaction and university image are also predictors of student positive WOM. Additionally, student-perceived university image was found to lead to higher levels of satisfaction.
Student value co-creation behavior is becoming a critical factor in shaping student experience and enhancing satisfaction, building a successful university image, and creating student positive WOM. This research makes a significant contribution to HE marketing knowledge by demonstrating empirically that co-creation generates positive outcomes for both students and HEIs, enhancing student satisfaction, building a superior university image, and boosting favorable student comments regarding the university. This paper also offers a contribution to decision-makers, marketing managers, and brand image managers who wish to understand student involvement in the process of co-creating services and its outcomes.
Despite the study’s significant contributions, the study is not without limitations. First, the samples collected from a single HEI in Taiwan face generalization issues; hence, future studies need to be more widely based, with data collected in other universities or countries. In addition, further study should consider gender aspects by comparing the results between males and females, as well as between international and domestic students, and investigating whether there are any differences. Second, this study used a cross-sectional approach to examine co-creation behavior and its outcomes. However, given the transitory and changing nature of the co-creation experience and its related outcomes, future research should include a longitudinal study to eliminate the effect of measurement at a specific time. Third, a previous study [19] indicated that the effective co-creation of value depends not only on the relationship between a company and its customers but also on cooperation with other stakeholders. However, this paper only focused on the co-creation of value within a university. Therefore, future studies could consider forms of co-creation that involve external stakeholders, such as connections with other universities and partnerships. Finally, the study only considers the relative effect of positive WOM as a result of consumers’ emotional assessment. However, studies have suggested that a person who participates in negative WOM is twice as likely to influence the receiver’s opinion of the firm [46]. Thus, examining this linkage presents another avenue for future research.
Author Contributions
Methodology, L.T.K.N. and H.P.L.; Writing—review & editing, L.T.K.N. and T.M.Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simões, C.; Soares, A.M. Applying to higher education: Information sources and choice factors. Stud. High. Educ. 2010, 35, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagle, L.; Brennan, R. Are students customers? TQM and marketing perspectives. Qual. Assur. Educ. 2007, 15, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.; Cervera, A.; Iniesta, M. Ángeles Key Elements in Building Relationships in the Higher Education Services Context. J. Promot. Manag. 2015, 21, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, I.C.L.; Forbes, J. Education as Service: The Understanding of University Experience through the Service Logic. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2009, 19, 38–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollinger, M.; Lodge, J. Student-staff co-creation in higher education: An evidence-informed model to support future design and implementation. J. High. Educ. Policy Manag. 2020, 42, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovill, C.; Cook-Sather, A.; Felten, P. Students as co-creators of teaching approaches, course design, and curricula: Implications for academic developers. Int. J. Acad. Dev. 2011, 16, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasnakoğlu, B.T.; Mercan, H. Co-creating positive outcomes in higher education: Are students ready for co-creation? J. Mark. High. Educ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollinger, M.; Lodge, J.; Coates, H. Co-creation in higher education: Towards a conceptual model. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2018, 28, 210–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Méndez, M.; Gummesson, E. Value co-creation and university teaching quality: Consequences for the European Higher Education Area (EHEA). J. Serv. Manag. 2012, 23, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharnouby, T.H. Student co-creation behavior in higher education: The role of satisfaction with the university experience. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2015, 25, 238–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celuch, K.; Bačić, D.; Chen, M.W.; Maier-Lytle, J.; Smothers, J. The Potential of Student Co-Creation in Extracurricular Experiences. Mark. Educ. Rev. 2017, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.; Balakrishnan, M.S. Assessing student satisfaction in transnational higher education. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2013, 27, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.; Huisman, J. Factors affecting university image formation among prospective higher education students: The case of international branch campuses. Stud. High. Educ. 2014, 40, 1256–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.D.; Robinson, L.J.; Dobele, A.R. Understanding high school students use of choice factors and word-of-mouth information sources in university selection. Stud. High. Educ. 2019, 45, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casidy, R.; Wymer, W. The impact of brand strength on satisfaction, loyalty and WOM: An empirical examination in the higher education sector. J. Brand Manag. 2015, 22, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarol, T.; Soutar, G.N. “Push-pull” factors influencing international student destination choice. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2002, 16, 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, S.R.; Ho, J.S.Y.; Al Mahmud, A. Revisiting the ‘university image model’for higher education institutions’ sustainability. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2020, 30, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Foroudi, P.; Nazarian, A.; Ziyadin, S.; Kitchen, P.; Hafeez, K.; Priporas, C.; Pantano, E. Co-creating brand image and reputation through stakeholder’s social network. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 114, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpan, L.M.; Raney, A.A.; Zivnuska, S. A cognitive approach to understanding university image. Corp. Commun. Int. J. 2003, 8, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smørvik, K.K.; Vespestad, M.K. Bridging marketing and higher education: Resource integration, co-creation and student learning. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2020, 30, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethany Green. Taiwan’s Universities Are Fighting for Their Lives as Birth Rates Plummet. 2020. Available online: https://ketagalanmedia.com/2020/01/30/taiwans-universities-are-fighting-for-their-lives-as-birth-rates-plummet/ (accessed on 30 January 2020).
- Tzu-ti, H. Private Colleges Face Closures amid Low Birth Rates in Taiwan. 2020. Available online: https://www.taiwannews.com.tw/en/news/4033015 (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Lin, A.F.Y. Internationalization initiatives of Taiwan’s higher education: A stepping stone to regional talent circulation or reproduction of unbalanced mobility scheme? High. Educ. Eval. Dev. 2020, 14, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönroos, C.; Gummerus, J. The service revolution and its marketing implications: Service logic vs service-dominant logic. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2014, 24, 206–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, S.; Ćalić, J. Audiovisual Media Open Educational Resources. In Proceedings of the ECLAP 2012 Conference on Information Technologies for Performing Arts, Media Access and Entertainment, Florence, Italy, 7–9 May 2012; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cook-Sather, A.; Luz, A. Greater engagement in and responsibility for learning: What happens when students cross the threshold of student–faculty partnership. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2015, 34, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipponen, L.; Kumpulainen, K. Acting as accountable authors: Creating interactional spaces for agency work in teacher education. Teach. Teach. Educ. 2011, 27, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell-Stuart, R.; Taheri, B.; Paterson, A.S.; O’Gorman, K.; Jackson, W. Working together to increase student sat-isfaction: Exploring the effects of mode of study and fee status. Stud. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, P.; Wong, H.Y. How service quality affects university brand performance, university brand image and be-havioural intention: The mediating effects of satisfaction and trust and moderating roles of gender and study mode. J. Brand Manag. 2019, 26, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.T.E. Instruments for obtaining student feedback: A review of the literature. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2005, 30, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, K.; Healy, M. Key factors influencing student satisfaction related to recruitment and retention. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2001, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavondo, F.T.; Tsarenko, Y.; Gabbott, M. International and Local Student Satisfaction: Resources and Capabilities Perspective. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2004, 14, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parahoo, S.K.; Harvey, H.L.; Tamim, R.M. Factors influencing student satisfaction in universities in the Gulf region: Does gender of students matter? J. Mark. High. Educ. 2013, 23, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehpour, M.; Chau, K.Y.; Zheng, J.; Hanjani, A.N.; Hoang, M. The mediating role of international student satisfaction in the influence of higher education service quality on institutional reputation in Taiwan. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2020, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, C.S.; Murdoch, N.; Mertova, P. Benchmarking the student experience: The offshore campus experience. TQM J. 2011, 23, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, A.J.; Pervaiz, S. The relation between “student loyalty” and “student satisfaction” (a case of col-lege/intermediate students at Forman Christian College). Eur. Sci. J. 2017, 13, 100–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.A.; Woyo, E.; Akahome, J.E.; Sohail, M.D. The influence of course experience, satisfaction, and loyalty on students’ word-of-mouth and re-enrolment intentions. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2020, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B.B.; Levy, S.J. The Product and the Brand. Brands Consum. Symb. Res. Brands Consum. Symb. Res. 2012, 33, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloutsou, C.; Lewis, J.W.; Paton, R.A. University selection: Information requirements and importance. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2004, 18, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroudi, P.; Yu, Q.; Gupta, S.; Foroudi, M.M. Enhancing university brand image and reputation through customer value co-creation behaviour. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 138, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fram, E. Maintaining and enhancing a college or a university. In Twenty-Second Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research; 16–19 May ERIC Reports; ERIC: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 220, p. 044. [Google Scholar]
- De Matos, A.C.; Rossi, C.A.V. Word-of-mouth communications in marketing: A meta-analytic review of the ante-cedents and moderators. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2008, 36, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.C.; Lueg, J.E. Modeling word-of-mouth usage. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J. Word of mouth and impersonal communication: A review and directions for future research. J. Consum. Psychol. 2014, 24, 586–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold, K.; Tarkiainen, A.; Sundqvist, S. How the source of word-of-mouth influences information processing in the formation of brand attitudes. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2016, 26, 64–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, A.; Lilly, B.; Babakus, E. The effects of social- and self-motives on the intentions to share positive and negative word of mouth. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2013, 41, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.H.; Cao, Y. Examining WeChat users’ motivations, trust, attitudes, and positive word-of-mouth: Evidence from China. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 41, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrand, M.; Gamoran, A. Instructional discourse, student engagement, and literature achievement. Res. Teach. Engl. 1991, 25, 261–290. [Google Scholar]
- Giner, G.R.; Rillo, A.P. Structural equation modeling of co-creation and its influence on the student’s satisfaction and loyalty towards university. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2016, 291, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutarso, Y.; Halim, R.E.; Balqiah, T.E.; Tjiptoherijanto, P. The role of co-creation activities, trust and gender on higher education marketing performance. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2017, 20, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeau, Y.; Bennion, A. Forms of embeddedness and discourses of engagement: A case study of universities in their local environment. Stud. High. Educ. 2014, 39, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.; Guzmán, F. Co-creation of brand identities: Consumer and industry influence and motivations. J. Consum. Mark. 2016, 33, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, M.J.; Schultz, M. Toward a theory of brand co-creation with implications for brand governance. J. Brand Manag. 2010, 17, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, R.; van Beers, C.; Doorn, N. Value capture and value creation: The role of information technology in business models for frugal innovations in Africa. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 131, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaz, M.; Ikram, A.; Basma, A.; Tariq, Z.; Jafri, S.K.A.; Khurram, W. Role of Social Media Marketing Activities in Creating University Brand Image and Reputation: The Mediating Role of Customer Value Co-creation Behavior. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies (ICICT), Karachi, Pakistan, 16 November 2019; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Vargo, S.L.; Lusch, R.F. Service-dominant logic: Continuing the evolution. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2008, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, D.; Varey, R.J. Creating value-in-use through marketing interaction: The exchange logic of relating, communicating and knowing. Mark. Theory 2006, 6, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.F.Y.; To, W.M. The effects of customer involvement on perceived service performance and word-of-mouth: The mediating role of service co-creation. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2020, 33, 1014–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.B.; Grigoriou, N. When empathy hurts: Modelling university students’ word of mouth behaviour in public vs. private universities in Syria. High. Educ. Q. 2017, 71, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Im, H. Role of web site design quality in satisfaction and word of mouth generation. J. Serv. Manag. 2012, 23, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerli-Palacio, A.; Meneses, G.D.; Pérez, P.J.P. The configuration of the university image and its relationship with the satisfaction of students. J. Educ. Adm. 2002, 40, 486–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, T.W.; Lindestad, B. The Effect of Corporate Image in the Formation of Customer Loyalty. J. Serv. Res. 1998, 1, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.M.; Mazzarol, T.W. The importance of institutional image to student satisfaction and loyalty within higher education. High. Educ. 2009, 58, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoury, N.; Daou, L.; El Khoury, C. University image and its relationship to student satisfaction- case of the Middle Eastern private business schools. Int. Strat. Manag. Rev. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, T.; Hafni, L.; Chandra, S.; Purwati, A.A.; Chandra, J. The influence of service quality, university image on student satisfaction and student loyalty. Benchmarking Int. J. 2019, 26, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.L.; James, J.D.; Kim, Y.K. A Reconceptualization of Brand Image. Int. J. Bus. Adm. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.; Raposo, M. The influence of university image on student behaviour. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2010, 24, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clow, K.E.; Kurtz, D.L.; Ozment, J.; Ong, B.S. The antecedents of consumer expectations of services: An empirical study across four industries. J. Serv. Mark. 1997, 11, 230–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajzen, I.; Fishbein, M. The Influence of Attitudes on Behavior. In The Handbook of Attitudes; Albarracín, D., Johnson, B.T., Zanna, M.P., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 173–221. [Google Scholar]
- Papadimitriou, D.; Apostolopoulou, A.; Kaplanidou, K. Destination Personality, Affective Image, and Be-havioral Intentions in Domestic Urban Tourism. J. Travel Res. 2013, 54, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, B.; Woratschek, H. Consumer–brand identification revisited: An integrative framework of brand identification, customer satisfaction, and price image and their role for brand loyalty and word of mouth. J. Brand Manag. 2017, 24, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nysveen, H.; Pedersen, P.E. Influences of Cocreation on Brand Experience. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2014, 56, 807–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.Y.W.; Hou, A.Y.-C. A farewell to internationalisation? Striking a balance between global ambition and local needs in higher education in Taiwan. High. Educ. 2019, 80, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutskens, E.; De Ruyter, J.; Wetzels, M.; Oosterveld, P. Response Rate and Response Quality of Internet-Based Surveys: An Experimental Study. Mark. Lett. 2004, 15, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P.M.; MacKenzie, S.B.; Lee, J.Y.; Podsakoff, N.P. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kock, N. Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. Int. J. e-Collab. (IJEC) 2015, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to use and how to report the results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Hopkins, L.; Kuppelwieser, V.G. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2014, 26, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).