Abstract
Local markets are still an integral part of the food system in developing economies of tropical regions including Samoa. This small South Pacific country is largely dependent on the production of crops in village agriculture, where traditional markets play an important role in sustainability of food supply. Similarly as many small island developing economies, Samoa is currently facing several challenges such as food security and high dependence on food imports. Therefore, we decided to monitor the diversity of plant foods on Samoan local markets and their economic and geographic indicators through interviews with the vendors. Our results suggest that assortment and economical value of plant food products have potential to increase sustainable food security of the local population and support economic growth of the region. For example, underutilized crops available at local markets are prospective species for development of new food products with beneficial nutritional and health properties. Moreover, certain commodities (e.g., papaya, kava and Samoan cocoa) seem to be promising for export. In addition, our findings suggest that development of appropriate processing technologies and the optimization of the logistics of crop products sold at local markets can contribute to an increase in efficiency of the regional agricultural sector.
1. Introduction
A local market might be described as a location frequented by clients and customers who regularly gather and sell products in the region or area in which they are produced. In comparison with large industrialized markets, they have specific production, processing and distribution patterns. For example, local agricultural produce markets are characterized by regional food commodities produced under sustainable agriculture that are distributed over short distances and sold directly by farmers to consumers [1,2]. It is important to mention that despite the continuously increasing role of supermarkets on consumers’ dietary intake and habits in the tropical regions, local markets still play an important role in supplying population dietary needs due to their long tradition, accessibility and the fact that the majority of food products are perishable and must be consumed soon after harvesting [3]. Since the local agricultural produce markets form part of the local food system practices, they significantly contribute to food and health security in both developed and developing countries [4,5]. Typically, they are based on locally available resources having improved economic viability to both farmers and consumers. Their production and distribution practices are more environmentally friendly in comparison to industrialized food systems and they enhance social equity for all members of the particular community [6,7,8]. Additionally, local food systems usually have better availability of fresh items and thus might provide health benefits due to their superior nutritional quality [9,10]. Since the local food systems address the environmental, nutritional, health, economic and social well-being of a specific urban or rural population, studying and gaining a deeper knowledge of local markets have received much interest over the past few years [2].
Market surveys documenting locally sold plant food items are cost-effective techniques providing qualitative and quantitative data concerning the importance, preferences and value that local population imputes to the different edible species [11,12]. Moreover, surveys might give a picture if people have moved away from a culture-based traditional use of the surrounding plants to one grounded on imported goods [13]. An analysis of three main factors might give a good overview of the local market situation and the general habits of local communities: (i) the economic value of given product, (ii) the richness of assortment and (iii) the regional distribution of a particular product [14]. All of these above-mentioned aspects are very important for implementation of socioeconomic improvement strategies aimed at generating economic growth, food security and the conservation of local plant diversity. Besides social and health benefits, economic data (particularly price, supply frequencies and daily sold volumes) of locally sold items might give interesting information about the overall situation of demand and supply and the availability of particular products [15,16]. Moreover, assortment depth and width reflect the richness of diversity in a given location and the proportion of locally-produced/versus imported foods [17,18]. Finally, regional distribution gives an overview of the operation of local market chains, i.e., where agricultural commodities were produced and from what distance they have been transported to their vending location. This information is useful for any understanding of existing market chains as it is necessary to know by whom the particular product is sold to consumers; how possible extra transportation expenditures affects the final price and its environmental-friendliness and what knowledge of the product is shared between vendor and consumer [2]. Data obtained from surveys of local markets, which are still an integral part of the food system in developing economies of tropical regions, are valuable for the identification of new crops/food products [19]. A majority of market surveys performed in tropical countries are therefore chiefly focused on gathering ethnobotanical knowledge [20,21,22]. Despite the existence of sporadic studies describing the economic situation of locally produced plant foods in tropical regions such as Central Africa, South and South-East Asia [12,23,24,25], the research focused on an advanced economic analysis of local food markets is almost exclusively restricted to industrialized countries [4,26].
The Independent State of Samoa (formerly known as Western Samoa) is a small South Pacific island country belonging to the Polynesian region whose economy is historically dependent on the production of cash crops in village agriculture [27]. Here, traditional markets still represent a very important component of the local food chain system. However, the current numbers show that the Samoan market is insufficiently supplied with certain crop products and Samoans are becoming more dependent on imported plant foods [28]. The current critical situation can be illustrated by official numbers showing that the agricultural area of Samoa declined from 58,000 to 22,000 ha under permanent crops and from 18,000 to 8000 ha of arable land in 1988 and 2015, respectively [29]. In addition, it was previously documented that the local population had experienced a shift from a culture based on the traditional use of the surrounding plants to one based on foreign food resources. As a result of this process, many wild and cultural plants have fallen into disuse and have been forgotten, whereas some species have become extinct since they were no longer needed or grown [30]. These changes represent a serious risk to the future sustainable supply of Samoans with affordable healthy foods. Indeed, the inventory of Whistler [13] documented plant foods sold in Samoan market places to be almost entirely composed of commonly known tropical and subtropical crops. This is in contrast with the fact that the Samoan Islands are considered a biodiversity hotspot and genetic centre of Polynesian plant species, harboring approximately 550 vascular plants, of which about 30% are endemic [30]. Correspondingly, the diversity of plant products at Samoan local markets represents a promising source for the identification of new species of underutilized crops [13]. Although the Samoa Bureau of Statistics (SBS) maps on a regular basis general economic data on common/major crops being sold at local markets, detailed analysis of the assortment, economic value and regional distribution of plant food products at local markets in Samoa is still lacking.
In view of the above-mentioned facts, we decided to monitor the diversity of plant foods on Samoan markets and their economic and geographic indicators through interviews with the vendors with the aim to illustrate the economic potential of plant food products at local tropical markets. The specific goals were (i) to document the diversity of commercialized plant species, (ii) to determine the stock volumes and financial values of the main cash crops (iii) and to map the regional distribution of their production.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The data were chiefly collected in the local markets situated along the northern and eastern coasts of Upolu and Savai’i Islands, respectively. In Upolu, where the majority of local markets are concentrated, the interviews with vendors were performed in the capital city Apia at Fugalei, Lemoasina and Taufusi markets, on the main road west from Apia in the town Vaitele (Vaitele market) and the village Afega (Laumua o Tumua market). Fugalei, the biggest farmers market in the country located close to the center of Apia, offers various fresh produce, traditional Samoan foods and handcrafts. Lemoasina is a small market consisting of several simple stands localized just opposite the southeast corner of the Fugalei market. Taufusi is a drive through market with covered stands; located about 200 m south from Fugalei. The relatively modern infrastructure of the public market in Vaitele, opened in 2011, is poorly utilized, probably due to the close vicinity of Apia city. Laumua o Tumua is a new local community market located on the northwestern coast of Upolu, opened in 2014. Regarding Savai´i Island, the data was gathered in Salelologa market, which is a relatively huge marketplace near Salelologa harbor. It is the only official market on the whole island. For larger markets (e.g., in Vaitele and Salelologa), Samoa Land Corporation defines finance policy and guidelines for stock control of commodities sold there. The prices of the products are shown by vendors in Samoan tālā (WST), but a bargain is sometimes possible. The markets have official opening and closing times. Since the individual stands along the roads where farmers sell their agricultural produce are also relatively abundant throughout both of the islands, data was also obtained from several individual vendors selling their products usually in front of local shops in Muiatele village (Upolu), Salelologa city and the villages of Falealupo and Safotu (Savai´i). The stands scattered all around the islands in front of houses along the main roads were not included. These stands usually have on display just one or two products, the most frequent being coconuts.
2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
The survey was conducted in July and August 2014, from August to October 2015 and from May to June 2018 via face-to-face interviews using a structured questionnaire in English, with all vendors willing to participate interviewed. After disclosing fully the intent and scope of the research, the prior informed consent agreement was obtained by the researcher from the vendor. Then, sociodemographic characteristics of the vendors, namely age, gender, place of residence and occupation, were recorded. The assortment of crop species available at each particular stand was identified and local names of crops were verified with data from the literature [13]. Subsequently, the origin of the produce, price, stock and quantities sold were recorded. An average weight of sales unit was determined using a laboratory balance (SSH91, Scaltec Instruments, Gottingen, Germany) and annual volumes for sale and price per kilogram were calculated following methods adapted from similar studies [31,32]. Since the quantitative data on the main cash crops was collected in 2014, the prices of the monitored plant foods recorded in WST were converted to United States dollars (USD) according to the official average 2014 exchange rate (USD 1 = WST 2.33) of The World Bank [33]. For comparison of data collected, all results are expressed in the text as a percentage, whereas stock volume and the financial value of the main cash crops is related to the number of all vendors interviewed (n = 208) and the regional distribution of the vendors, the diversity and market value of the cash crops to the farmers selling their own produce only (n = 148). Crop categories of plant species were classified according to the literature data [13]. Neglected/underutilized crops were categorized based on characteristics proposed by International Plant Genetic Resources Institute [34]. Professor Kokoska verified the authenticity of commonly known agricultural crops and identified neglected crop species, and their voucher specimens are deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Botany and Plant Physiology of the Faculty of Agrobiology, Food and Natural Resources of the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, Czech Republic. The scientific names of all species were also reviewed using The Plant List [35].
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics of Vendors
Information was obtained from a total of 208 vendors, with 63.5% and 36.5% of them selling their products in Upolu and Savai´i Islands, respectively. Out of the total number of vendors questioned, 41.8% were male and 58.2% were female. Their age ranged from 13 to 70 years with an average age of 37 and 42 for men and women, respectively. For 88.5% of respondents market vending was their main occupation, whereas 11.5% had other profitable occupation excluding laboring on their own plantations. Typical examples of other vendors’ occupations were bartender, cook, manual worker, officer and teacher. Most of them (61.5%, n = 128) sell their products on a daily basis, except Sunday. The majority (71.2%) of the vendors were selling their own produce. The data on demographic characteristics of vendors is summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Demographic data on respondents.
3.2. Diversity of Commercialized Plants
During our survey, 53 plant species, their varieties, genetic groups and subgroups belonging to 30 families and 6 categories of agricultural crops were recorded. Musaceae and Solanaceae were the most diverse families (each represented by 9.4% of plant species), followed by Cucurbitaceae (7.5%), Araceae, Brassicaceae, Leguminosae, Rutaceae (5.7% each), Dioscoreaceae, Moraceae, Rubiaceae and Zingiberaceae (3.8% each). The remaining families were only composed of one species. Fruits and nuts (45.3%) were the highest represented agricultural crops, followed by vegetables (24.5%), tuber crops (15.1%), stimulants (7.5%), spices (3.8%), algae and cereals (1.9% each). Correspondingly, the most frequently used plant parts were fruits (including infrutescences) and seeds (66.0%), rhizomes, roots and tubers (22.6%) and leaves (7.5%). Documented species were predominantly perennial herbs and trees (32.1% each), followed by annual herbs (13.2%), biennial herbs and perennial vines (7.5% each). Only one representative was recorded each for algae, annual vines, palms and shrubs. Higher crop diversity was found in Upolu (55.2%) than in Savai´i (44.8%). The vast majority of the species identified during our study in the market were common agricultural crops (90.6%); however, certain plants, namely Adenanthera pavonina, Inocarpus fagifer, Musa troglodytarum and Tacca leontopetaloides were identified as neglected/underutilized crops, having importance only on a local level. The local variety of banana (Musa × paradisiaca; group AAB) called fa´i sāmoa (Samoan banana) can also be included in the same category. Nonseasonal, seasonal and imported (not cultivated in Samoa) crops accounted for 77.4%, 20.8% and 1.9% of the total number of plant species sold in the markets, respectively. The most crops were of moderate availability (58.5%) and cultural salience (69.8%). Largely available (22.6%) and highly culturally important (18.9) plants were dominant over the scarce (18.9%) and low salient (11.3%) species. The detailed data on plant species identified in Samoan markets including their category of use, life form, part used, locality, crop category, family, seasonality, availability, traditional uses and cultural salience and their scientific, English and local names are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Assortment of plant species on Samoan markets.
3.3. Market Value and Regional Distribution of Cash Crops
The analysis of economic data collected on plant commodities at local Samoan markets showed that taro was the crop with highest stock volume (25.8%), closely followed by brown and green coconuts (23.8%), pumpkins, squashes and gourds (18.4%), bananas and plantains (13.6%) and papayas (9.6%) and giant taros (5.1%). The stock volumes of all other crops, namely citruses, cucumbers, kava, Samoan cocoa, taro leaf, tobacco and tomatoes, were less than 5%. Pumpkins, squashes and gourds (23.3%), tobacco (17.2%), brown and green coconuts (13.8%), taros (12.6%) and bananas and plantains (11.9%) were crops with the highest stock value. The stock values of citruses, cucumbers, giant taros, kava, papayas, Samoan cocoa, taro leaves and tomatoes were lower than 5%. Tobacco (24.5%) was the crop with the highest stock value per vendor, followed by pumpkins, squashes and gourds (13.0%), brown and green coconuts (8.8%), taros (8.2%), giant taros (8.1%), kava (7.2%), tomatoes (5.9%), Samoan cocoa (5.8%) and bananas and plantains (5.3%). Stock values per vendor for citruses, cucumbers, papayas and taro leaves were less than 5%. The highest number of vendors was selling bananas and plantains (34.1%), pumpkins, squash and gourds (26.9%), brown and green coconuts (23.6%), taro (23.1%), papaya (17.8%), tomato (11.1%), tobacco (10.6%), cucumber (10.1%), Samoan cocoa (8.2%) and giant taro (7.7%). Citruses, kava and taro leaf were sold by less than 5% of vendors. Table 3 provides detailed data on the main cash crops on Samoan markets including product name and category, the number of vendors selling the product, its average price in USD per kg, stock volume in kg, stock value in USD and stock value per vendor in USD. Percentage parameters characterizing economic value of main cash crops on Samoan markets are shown in Figure 1.

Table 3.
Stock volume and financial value of main cash crops on Samoan markets.
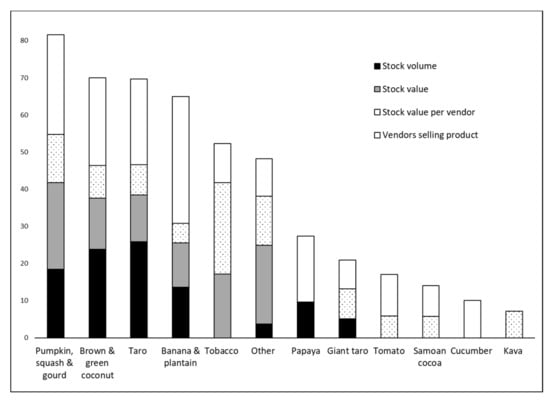
Figure 1.
Parameters characterizing economic value of main cash crops on Samoan markets (in%).
Tuamasaga is the most important district for Samoan market supply because of the large financial value of its production (44.8%), the highest number of vendors (43.2%) and the greatest product diversity (20.6%). It is followed by Gagaemauga district, where 25.3% of the production financial value, 14.9% of vendors and 15.9% of product diversity originate. In Savai´i, Palauli supplies the local market with the highest product diversity (25.0%), whereas Faasaleleaga generates the highest financial value (29.7%). Faasaleleaga and Gagaemauga are the districts accommodating the most vendors in Savai´i (33.3% and 31.4% respectively). Tuamasaga is the most important region in all three parameters in Upolu (56.4% of production financial value, 64.9% of vendors and 31.4% of product diversity). With a majority of production financial value (78.9%), vendors (65.5%) and product diversity (55.6%), Upolu is a significantly more important market than Savai´i. Although exchange between local markets on both islands is generally low, more production (1.6%), vendors (1.4%) and crop products (7.9%) move from Savai´i to Upolu than in the opposite direction (0.3%, 0.7% and 3.2%, respectively). A map illustrating the quantified distribution of financial values of market production, the number of vendors and crop diversity among individual districts is shown in Figure 2.
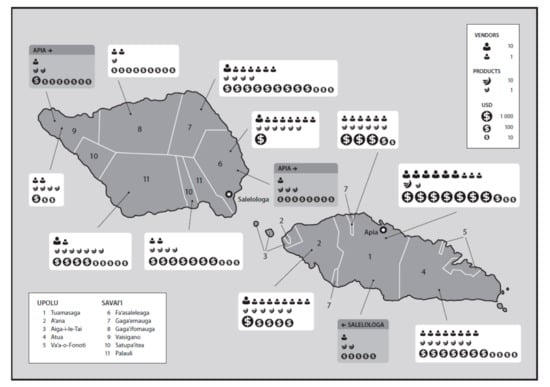
Figure 2.
Regional distribution of vendors, diversity and market value of cash crops at Samoan markets.
4. Discussion
Based on the analysis of data collected during our survey, a typical vendor at the local Samoan market can be described as a female between 31 and 60 years of age living in Upolu. These demographic characteristics correspond well with those observed in previous studies focused on the inventory of various plant commodities sold on local markets in developing regions. For example, Bussmann et al. [36] reported that vendors selling medicinal plants in the markets of La Paz and El Alto in Bolivia were women of an estimated 25–70 years of age. Similarly, women were the main vendors at the wild edible plant markets in Kisangani in the Democratic Republic of Congo [24] and at traditional markets of medicinal plants in Southern Ecuador [37].
As far as diversity of plants commercialized in the local Samoan markets is concerned, the assortment identified during our survey is similar to that described by Whistler [13]. In the period 1995–1996, he recorded 61 various items of fruits, vegetables, starch and miscellaneous crops sold in the market places in Savai´i, Upolu and Tutuila (American Samoa). Although most species are available year round, some products are seasonal and highly perishable (e.g., fruits of Artocarpus.. altilis). Unexpected changes in yield and seasonality of these crops could cause significant economic losses, wasted resources and disrupt local food supplies. This may be mitigated through careful selection of cultivars to extend the season or to help plan for processing them into more stable products [38]. Most of the species identified during our study in the market were common agricultural crops (e.g., Cocos nucifera, Colocasia esculenta, Cucurbita pepo and M. × paradisiaca), however, less known food plants, namely A. pavonina, I. fagifer, M. troglodytarum and T. leontopetaloides, were also present. It has been experimentally proven that plants that are used traditionally as foods but have not been adopted by large-scale agriculture (known also as neglected and underutilized crops) may contain higher amounts of specific health-beneficial constituents (e.g., vitamins, minerals, fiber, secondary metabolites and fatty and amino acids) than conventional agricultural crops. Due to their nutritional and medicinal values, these species could highly contribute to the improvement of both the nutritional and health status of the local populations in rural areas of developing countries and, as a result, increase sustainable food and nutrition security in low-income regions. For example, M. troglodytarum that was found to contain significant levels of β-carotene has been suggested as prospective food for vitamin A deficiency and chronic disease prevention programs in the Pacific [39]. A local variety of banana (M. × paradisiaca; group AAB), called fa´i sāmoa, can be another interesting material for future research based on an analysis of its nutritional properties. Recently, our team proposed seeds of A. pavonina and I. fagifer as promising sources of specific nutrients and compounds, such as fatty acids, minerals, phenolics and vitamins, with potential to reduce the risks of overweightness and obesity-related diseases in Samoa. These underutilized crops have also been proposed for development of novel foods with enhanced health-related properties [40,41]. In contrast to above mentioned species, the nutritional value of T. leontopetaloides, a neglected crop producing starchy tubers used as an additive in traditional Samoan foods [13], is described in general terms only [42]. Since I. fagifer and T. leontopetaloides are naturally occurring in the littoral zone and coastal swamp forests [13], they are better adapted to local environments, including regions with abiotic stress conditions (e.g., high salinity soils), than most conventional crops. Thus, both these underutilized species provide a better chance for organic and low-input agriculture and their growing will have less negative impact on the environment and local ecosystems.
Since agriculture sales belong to the most important sources of household incomes in Samoa [43], the monitoring of common economic indicators such as price, stock volume and the financial value of cash crops can provide useful information on the overall strength of the local agricultural market and general economic health of the country. Since 2008, SBS monitors the prices and volumes of selected agricultural produce at the local markets every month. These products include fruits and nuts (banana, breadfruit and coconut), vegetables (cabbage, cucumber, pumpkin and tomato) and root and tuber crops (tannia, taro and yam) [44]. The results of our survey correspond well with SBS data and with the report of Tamasese [45]. However, they newly indicate that the stimulants (kava, Samoan cocoa and tobacco), along with papaya are also commodities of market interest. Although the contribution margin for agricultural products is small in a typical developing market economy, processes that add value to them can increase their market potential [46]. In Samoa, the food sector actors suggested that local foods could create opportunities for economic growth, particularly through their increased production for export [47]. Samoan cocoa (known as a koko sāmoa), a popular Samoan drink made from roasted cocoa seeds crushed into a paste and sold in the shape of a dried ball or cup [13], can be mentioned as a typical example of a local food product with added value. Similarly, the dried fruits of Carica papaya have been proposed as a lucrative value-added agricultural product in the local Samoan market and for export to New Zealand [46]. Therefore, both these commodities represent a good opportunity for Samoan farmers, market vendors and food producers to earn more income. Concerning tobacco, it is well known that smoking it is an important health risk factor contributing to the dramatic increase in the worldwide diagnosis of cancer, and of cardiovascular and chronic respiratory diseases [48,49]. The incidence of all of these health complaints has increased significantly in Samoa recently [50]. According to our results, the local markets are important sources of tobacco for the Samoan population, which suggests one question the appropriateness and effectiveness of current strategies for the regulation and control of local trade in this commodity. Piper methysticum, a stimulant originating in Polynesia, is an important Samoan domestic and export cash crop, grown by subsistence farmers and larger commercial growers. It is exported to the Pacific Rim markets of Australia, New Zealand and the USA and to neighboring countries such as Fiji. It has been reported that most kava in Samoa is grown on Savai´i [51], which is supported by our survey results showing a relatively high abundance of this commodity in Savai´i market. Especially in this region where society is still following the traditional way of life, local products such as kava help also social sustainability because they favor contacts between producers and consumers, which influences greater information and knowledge of what is consumed and enables developing a feeling of community [52]. The drinking of ceremonial beverage made from the root of the P. methysticum is one of the most important customs of the Samoa Islands, which takes place on most important occasions including the bestowal of a chiefly title, formal occasions and events, significant gatherings and meetings or welcoming and bidding farewell to guests and visitors. Another cultural tradition is the practice of food preparation called umu. This is a local type of above ground earth oven of hot volcanic stones. The Samoan umu starts with a fire to heat rocks, which are then stacked around parcels of food wrapped in banana, breadfruit or taro leaves. Pork, fish, chicken and many traditional plant foods, including taro and breadfruit, are all cooked at the same time without their flavors mingling. Coconut cream is an essential part of many umu recipes [13].
It is well known that the production of crops in the most suitable regions, combined with the ability to transport crop commodities from one region to another, contributes to the comparative advantage of a country. Therefore, a detailed knowledge of the geographical distribution of a particular food commodity in a specific area may harbor promising characteristics for a transition to sustainable food systems in the targeted region [53]. Our results suggest that exchange of crop commodities between local markets in both islands is generally low. This finding can be supported by the observations of Hardin and Ting Kwauk [47] who have previously reported that shipping and transportation have previously been identified as common challenges to the supplying of the Samoan market with affordable foods. Similarly, limited and costly transport options have been identified as serious barriers for access to local markets for subsistence farmers in Fiji, especially for those from remote communities [54]. Although Underhill et al. [55] have previously reported that transport logistics do not have a negative impact on fruit and vegetable markets in Samoa, our results showing the irregular distribution of crop production areas among the islands and their districts suggest that an optimization of the logistics of marketed crop commodities can contribute to an increase in the efficiency of the local agricultural sector. In addition, the improvement of logistics and supply chain management can reduce the negative effect of transportation and storage on nutritional quality and sensory properties of local food products [56]. Providing healthier and better tasting food will subsequently improve the quality of life of Samoans. Moreover, decreased pollution from transportation will minimize negative impacts on the environment, health and well-being of local communities [57]. This will contribute to the environmental, social and health sustainability of the region and its population.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our results suggest that assortment and economical value of plant food products at local markets in developing countries have the potential to increase sustainable food and nutrition security of the local population and support economic growth of these regions. For example, neglected/underutilized crops available at local markets in Samoa such as A. pavonina, I. fagifer, M. troglodytarum and T. leontopetaloides have the potential for development of new food products with beneficial nutritional and health properties and for dietary diversification and provision of micronutrients to local population. Moreover, certain commodities available in local markets in larger quantities (e.g., papaya) or having higher added economic value (e.g., kava and Samoan cocoa) seem to have promising potential for export. In addition, our findings suggest that development of appropriate processing technologies and the optimization of the logistics of crop products sold at markets in developing countries can contribute to an increase in efficiency of the local agricultural sector.
Author Contributions
Economic analysis of collected data and manuscript drafting, V.V.; market inventory and analysis of ethnobotanical data, P.N.; participation in data analysis and manuscript preparation, J.T.; participation in the inventory of local markets, L.H.; verification of the ethnobotanical data and participation in their analysis, J.W.S.; collection of the plant materials and processing the voucher specimens, T.K.; participation in the collection of market data and plant materials. F.L.; conceptualization and coordination of the whole study, botanical identification of crop species, and finalization of the manuscript. L.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Internal Grant Agency of the Faculty of Tropical AgriSciences, grant number IGA 20205001.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Micheal Ua Seaghdha for English linguistic revision of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adams, D.C.; Salois, M.J. Local versus organic: A turn in consumer preferences and willingness-to-pay. Agric. Food Syst. 2010, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, S.; Hand, M.; Da Pra, M.; Pollack, S.; Ralston, K.; Smith, T.; Newman, C. Local Food Systems: Concepts, Impacts, and Issues; Economic Research Report No. 97; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Demmler, K.M.; Klasen, S.; Nzuma, J.M.; Qaim, M. Supermarket purchase contributes to nutrition-related non-communicable diseases in urban Kenya. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guptill, A.; Wilkins, J.L. Buying into the food system: Trends in food retailing in the US and implications for local foods. Agric. Hum. Values 2002, 19, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M. Embeddedness, the new food economy and defensive localism. J. Rural Stud. 2003, 19, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, B.; Purcell, M. Avoiding the local trap: Scale and food systems in planning research. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2006, 26, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, T.; Banks, J.; Bristow, G. Food supply chain approaches: Exploring their role in rural development. Sociol. Rural. 2000, 40, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, N.J.; Anderson, M.D.; Goldberg, J.P.; Houser, R.; Rogers, B.L. Trying and buying locally grown produce at the workplace: Results of a marketing intervention. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 1999, 14, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, E. Food, health, the environment and consumers’ dietary choices. Nutr. Diet. 2005, 62, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, R.A.; Kaiser, L.L. Still a time to act: A review of institutional marketing of regionally-grown food. Agric. Hum. Values 2008, 25, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, A.B. Applied Ethnobotany: People, Wild Plant Use and Conservation; Earthscan: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sundriyal, M.; Sundriyal, R.C. Wild edible plants of the Sikkim Himalaya: Marketing, value addition and implications for management. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whistler, A.W. Plants in Samoan Culture: The Ethnobotany of Samoa; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Basker, E. Handbook on the Economics of Retailing and Distribution; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eastwood, D.B. Using customer surveys to promote farmers’ markets: A case study. J. Food Distrib. Res. 1996, 27, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, R.; Chernev, A. Low prices are just the beginning: Price image in retail management. J. Mark. 2013, 77, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernev, A. Product assortment and consumer choice: An interdisciplinary review. Found. Trends Mark. 2011, 6, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.E.; Chernev, A.; Bockenholt, U.; Bundorf, K.; Draganska, M.; Hamilton, R.; Meyer, R.J.; Wertenbroch, K. Consumer and managerial goals in assortment choice and design. Mark. Lett. 2014, 25, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, G.E. Economic Botany: Principles and Practices; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bye, R.A.; Linares, E. The role of plants found in the Mexican markets and their importance in ethnobotanical studies. J. Ethnobiol. 1983, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, Y.; Ugulu, I.; Durkan, N. Wild edible plants sold in the local markets of Izmir, Turkey. Pak. J. Bot. 2013, 45, 177–184. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.L.T. Insertions and deletions: Evolution in the assemblage of Vietnamese food plants. Ethnobot. Res. Appl. 2006, 4, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suharwardi, M.A.; Hakim, I.A. The Indian rural market: Emerging opportunities and challenges. Indian J. Mark. 2014, 44, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termote, C.; Everaert, G.; Meyi, M.B.; Djailo, B.D.; Van Damme, P. Wild edible plant markets in Kisangani, democratic Republic of Congo. Hum. Ecol. 2012, 40, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-K.; Tao, G.-D.; Liu, H.-M.; Yan, K.-L.; Dao, X.-S. Wild vegetable resources and market survey in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Econ. Bot. 2004, 58, 647–667. [Google Scholar]
- Hardesty, S.D. The growing role of local food markets. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 90, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Statistics Division. Demographic Yearbook; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Crops and Livestock Products. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/TP (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- FAOSTAT. Samoa. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#country/244 (accessed on 29 July 2019).
- Whistler, A.W. The Samoan Rainforest: A Guide to the Vegetation of the Samoan Archipielago; Isle Botanica: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jusu, A.; Sanchez, A.C. Economic importance of the medicinal plant trade in Sierra Leone. Econ. Bot. 2013, 67, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Andel, T.; Myren, B.; van Onselen, S. Ghana’s herbal market. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Bank. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/PA.NUS.FCRF?locations=WS&order=wbapi_data_value_2014+wbapi_data_value&sort=asc (accessed on 29 July 2019).
- Neglected and Underutilized Plant Species. Available online: https://www.bioversityinternational.org/fileadmin/_migrated/uploads/tx_news/Neglected_and_underutilized_plant_species_837.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- The Plant List. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- Bussmann, R.W.; Zambrana, N.Y.P.; Huanca, L.A.M.; Hart, R. Changing markets—Medicinal plants in the markets of La Paz and El Alto, Bolivia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinitana, F.; Rios, M.; Romero-Benavides, J.C.; Rot, M.D.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M. Medicinal plants sold at traditional markets in southern Ecuador. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2016, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Jones, A.M.P.; Murch, S.J.; Ragone, D. Crop productivity, yield and seasonality of breadfruit (Artocarpus spp., Moraceae). Fruits 2014, 69, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englberger, L.; Schierle, J.; Marks, G.C.; Fitzgerald, M.H. Micronesian banana, taro, and other foods: Newly recognized sources of provitamin A and other carotenoids. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huml, L.; Drabek, O.; Pohorela, B.; Kotikova, Z.; Umar, M.; Miksatkova, P.; Kokoska, L. Analysis of nutrients and compounds potentially reducing risks of overweightness and obesity-related diseases in raw and roasted Adenanthera pavonina seeds from Samoa. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huml, L.; Miksatkova, P.; Novy, P.; Drabek, O.; Sabolova, M.; Umar, M.; Tejnecky, V.; Pohorela, B.; Kourimska, L.; Maskova, E.; et al. Fatty acids, minerals, phenolics and vitamins in the seeds of Inocarpus fagifer, a Pacific Island underutilized legume. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2016, 89, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Jukema, J.; Paisooksantivatana, Y. Tacca leontopetaloides (L.) O. Kuntze. In Plants Yielding Non-Seed Carbohydrates; Flach, M., Rumawas, F., Eds.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 156–159. [Google Scholar]
- Brent Vickers, J. More money, more family: The relationship between higher levels of market participation and social capital in the context of adaptive capacity in Samoa. Clim. Dev. 2018, 10, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoa Bureau of Statistics. Local Market Survey, Report May 2019. Available online: https://www.sbs.gov.ws/images/sbs-documents/Economics/Local%20Market%20Survey/E.%20Local%20Market%20Survey%20May%20.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2019).
- Tamasese, E. Samoa Domestic Market Study: Assessing the Effectiveness of Current Domestic Market Data Collection to Determine the Likely Impact of Increased Vegetable Production; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011; Available online: http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/est/AAACP/pacific/04_Samoa_Domestic_Market_Study_Final_Report_October2011.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2019).
- Buenz, E.J.; Fuatai, L. A potential dried fruit market in Independent Samoa. J. Sustain. Agric. 2007, 31, 17–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, J.; Ting Kwauk, C. Producing markets, producing people: Local food, financial prosperity and health in Samoa. Food Cult. Soc. 2015, 18, 519–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, G.P. Cancer. How tobacco smoke changes the (epi)genome. Science 2016, 354, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, D.; Anand, S.; Watkins, D.; Gaziano, T.; Wu, Y.F.; Mbanya, J.C.; Nugent, R. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Related Disorders: Key Messages from Disease Control Priorities, 3rd edition. Lancet 2018, 391, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Country Cooperation Strategy for Samoa, 2013–2017; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Available online: https://iris.wpro.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665.1/7874/CCS_WSM_2013-2017_eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Davis, R.I.; Brown, J.P. Kava (Piper methysticum) in the South Pacific: Its Importance, Methods of Cultivation, Cultivars, Diseases and Pests; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research Technical Reports (Series No. 46): Canberra, ACT, Australia, 1999; Available online: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/113917/files/tr046_pdf_19769.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2020).
- Arenas-Gaitan, J.; Peral-Peral, B.; Reina-Arroyo, J. Local fresh food products and plant-based diets: An analysis of the relation between them. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitan-Cremaschi, D.; Klerkx, L.; Duncan, J.; Trienekens, J.H.; Huenchuleo, C.; Dogliotti, S.; Contesse, M.E.; Rossing, W.A.H. Characterizing diversity of food systems in view of sustainability transitions. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Peterson, L.; Iranacolaivalu, M. Barriers to market for subsistence farmers in Fiji—A gendered perspective. J. Rural Stud. 2018, 60, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, S.J.R.; Zhou, Y.C.; Sherzad, S.; Singh-Peterson, L.; Tagoai, S.M. Horticultural postharvest loss in municipal fruit and vegetable markets in Samoa. Food Secur. 2017, 9, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinska, M.; Tomaszewska, M.; Kolozyn-Krajewska, D. Identifying factors associated with food losses during transportation: Potentials for social purposes. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A. An environmental assessment of food supply chains: A case study on dessert apples. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 560–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).