Abstract
Community gardening has become a growing movement in cities all over the world, where these diverse collectively managed spaces provide various economic, ecological, and social benefits for urban residents. Particularly in developed countries such as Germany, social benefits are the motivation to participate in community gardens more so than the harvests. Although research on community gardens has grown, including the question of their benefits to a sustainable development, there is little literature studying the social importance and social sustainability of community gardens. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to examine social interaction, participation, and perceived success as a concept to assess social sustainability. The paper further aims to examine the conditions influencing social sustainability within community gardens. With the help of an online survey, we collect data from 123 community gardens throughout Germany, with which we assess diverse degrees of social sustainability. Causalities of gardens’ social sustainability are analyzed with a multiple linear regression model. Results indicate that there is no significant relationship between size of community and social sustainability, rather aspects of trust and management have a strong effect on social sustainability. Findings like these lead to a better understanding of social interaction in urban communities that contribute to more social sustainability.
1. Introduction
In the last three decades, the importance of urban agriculture has increased to become a growing international movement [1,2,3]. Driving forces of this movement are global developments, their local consequences and the urgency to shift towards sustainable development. Very generally and most frequently, sustainable development is defined as a “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” [4]. The necessity to move towards sustainable development is underlined by the global Agenda 2030 and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), adopted by the United Nations in 2015. These 17 SDGs are integrated and consistent with the three dimensions of sustainable development: the environment, focusing on the conservation of natural resources [5]; the economy, focusing on prosperity for all human beings [6]; and society, focusing on people’s basic needs [5,7]. Although more complex concepts of sustainability are developed and discussed, sustainability is predominantly seen in regard to these three dimensions. However, there are no widely acknowledged definitions for these dimensions.
Although the SDGs do not explicitly address urban agriculture, various topics are connected to it, such as end poverty and hunger (SDGs 1 and 2), ensure healthy lives (SDG 3), reduce inequalities (SDG 10), make cities resilient and sustainable (SDG 11), ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns (SDG 12), take action to combat climate change (SDG 13), and protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems (SDGs 15) [8,9,10]. Consequently, urban agriculture with its diverse aims, actors, structures and organizations, contributes in various ways to sustainable development and its three dimensions [11,12].
However, urban agriculture’s contribution to the dimensions of sustainability depends on the type of urban agriculture observed [13]. While we find professional and sometimes very technical urban agriculture activities focusing on food production and food provision for the urban population, we further find small social-orientated gardening activities as an expression of self-determination, self-experience, social interaction or social change.
In our research, we are particularly focusing on community gardens as a socially-oriented subset of urban agriculture and its contribution to the social dimension of sustainability. Within community gardens, as in urban agriculture in general, we still find a high diversity of actors, motivations, structures, sizes, locations, as well as services offered to the wider community. Community gardens mostly emerge as bottom-up initiatives and are collectively organized and self-managed networks [14,15,16,17]. Commons are defined as complex institutions in which land and other resources are used collectively by self-governance and rules that are self-restrictive and self-sanctioning [18]. Thus, community gardens also belong to the commons movement [17,19].
Commons such as community gardens are furthermore a way to organize material resources, immaterial resources, and social relations [20,21]. Hence, they provide not only locally-produced food for urban residents [22,23], but also benefits such as education, community development, new experiences inherent to democratic forms of governance, ecosystem services, green infrastructure, or space for recreation, just to name a few [15,16,17,22,24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. All those benefits play a role in the increasing popularity of community gardens and their potential for sustainable development. Although community gardens fulfill various functions in all three dimensions of sustainability [11,30], the benefits of this type of urban agriculture are more social [13,31].
Reflecting this richness and multi-dimensionality of social sustainability, a clear and widely acknowledged definition is missing [32,33,34]. On this account, some authors provide key components, themes or indicators to describe the nature of social sustainability [34]. The United Nations Commission on Sustainable Development (UNCSD) for instance draws on the themes equity, health, education, security, housing, and population [35]. Additional themes outlined by Rasouli and Kumarasuriyar [34] are, e.g., diversity, sense of place, or social capital. Furthermore, Dempsey, Bramley and Brown [32] described social sustainability within the urban context by reference to two main concepts: social equity and sustainability of community. Some but not all of these topics overlap with the urban agriculture and community garden literature.
Issues in urban agriculture, and in particular community gardens, linked to the social dimension of sustainability are health [3,8,16,23,30,31,36,37,38], well-being [16,22,29,30,31], education and knowledge [3,8,12,20,27,30,31], environmental justice [3,31,38], food security [3,8,12,23,39,40], community cohesion [3,23,27,36,37], and social capital [29,31,41]. The potential of food security is therefore not only relevant for developing countries but also for developed countries [12,39,42], however, the motivations for farming in the city are more diverse [39,43]. While food production can be a motivation of gardeners to participate, Pourias, Aubry and Duchemin [23], Spilková [16] and Nettle [29] mentioned social interaction (e.g., collective activities, socializing, and belonging to community) as a main motivation to participate in community gardens in Europe and Australia. We understand this motivation as an expression of the citizens’ social needs and use social interaction—often referred to as social capital—as a key criterion to assess social sustainability in community gardens.
We assume that the more central the social interactions are, the more community gardens contribute to various social needs and have thus a widespread impact on social sustainability. In doing so, they also provide space for learning, education, trial and error, not only regarding food production but also regarding the production of social networks, social skills, and different ways of how we can live together. Even if community gardens (and other urban agriculture activities) are not able to replace the industrial food system or education system, they provide a “flavor” of various alternatives [29,44]. Community gardens can therefore also be seen as a social economy, where production is not taking place for profit, but collectively and to satisfy human urban needs [45,46]. Social economies like community gardens are a “new model for restoring community and democratic participation” [47]. Martin, Clift and Christie [31] described this set of features as social sustainability services. Over and above this, social interaction is described by many authors as an indicator that contributes to social sustainability [11,31,32,34,48,49].
Although there are many studies dealing with the social benefits of community gardens, there is only a limited number of studies deeply analyzing gardens’ social function and assessing their social sustainability, especially on a larger scale [29,30]. Moreover, there is a recognized general lack of academic research and concomitant statistics at national and international levels [15,50] that explore the social functions empirically.
We intend to fill this gap by providing a concept that assesses social sustainability and elaborating on the social processes within community gardens. Further, we want to consider the chances to partake in social activities taking place in community gardens, and draw conclusions on community gardens’ performance. Therefore, social interaction, participation, and perceived success are criteria we use to define and measure diverse degrees of social sustainability. Additionally, we are interested in finding out what characteristics of community gardens such as size, social heterogeneity, or trust, facilitate social interaction.
To do this, we conduct a quantitative survey that asks respondents to rank their gardens in terms of the criteria that we are determining to be measures of social sustainability. With the help of an online questionnaire, we collect data from 123 community gardens throughout Germany. We therefore contribute to scholarly empirically driven research in developed countries, especially in Europe, and non-English speaking countries where studies on community gardens are still rare [16].
In the following, we present how we developed and designed criteria and variables to assess social sustainability, the data collection, and data analysis. Results of the study disclose various degrees of social sustainability in the community gardens examined, and demonstrate that aspects of trust within the community have a strong effect on gardens’ social sustainability. Finally, we discuss the findings and challenges of the study and give future research directions.
2. Method
The research design consists of three steps: (1) development of criteria and variables that measure and influence social sustainability; (2) survey design; and (3) data analysis.
2.1. Criteria and Variable Development
To develop criteria and variables that measure and influence social sustainability of community gardens, our study was based on a literature review on community gardens, sustainable development, social sustainability, commons, and success [15,17,23,36,40,43,48,51,52,53,54,55,56]. Drawing on the systematic set-up of the database SESMAD [57], we likewise classified variables as dependent variable (to measure social sustainability) or independent variable (variables that have an impact on social sustainability). The variables development was mainly based on commons theory, and were adapted to community gardens characteristic. We first needed to start with some rather general statements to grasp the diversity and the complexity of the gardens.
The criteria and variables developed to measure social sustainability are presented in Section 2.1.1. Section 2.1.2 outlines the independent variables, which have an impact on garden’s contribution to social sustainability.
2.1.1. Social Sustainability Criteria
Since community gardens are socially-orientated initiatives, we refer to social and collective processes taking place within community gardens to assess their social sustainability. We developed the criterion social interaction to examine what is used and done collectively in community gardens, the criterion participation to examine the possibility to partake within these social interactions, and the criterion perceived success to further assess the performance of these social processes. All three criteria are based on several variables presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Criteria and variables to measure social sustainability.
We chose social interaction as a main criterion to assess social sustainability of community gardens. To define the criterion social interaction, we referred to the collective characteristic, which is essential for community gardens [29,41,43] and sets them apart from other urban agriculture and urban gardening activities. The collective characteristic included the collective use of diverse resources, social activities within the community, and the importance of social exchange [15,16,29,40,41,43].
Based on the literature review, we identified 23 resources that can be used collectively [3,15,16,19,20,29,41]. These resources include material resources such as a tool shed, water connection, compost, soil or the harvest. It further includes immaterial resources such as diverse work activities. Collective use can take place to varying degrees. For instance, some community gardens offer individual plots, some offer collectively used plots (collectively divided by a division of resources or collectively shared), and some offer a combination of individual and collectively used plots [15,29,41,43]. Therefore, we developed different styles of use ranging from 1 individual use to 5 shared use. Regardless of the plot design, there is always a minimum of shared areas like social spaces to be found [41]. The 5 styles of use are applied to all 23 resources (see Supplementary Materials, Table S1 for all 23 resources and the five styles of use). As an example, watering plants can be done individually on the private plot, or collectively through dividing or sharing. In this example, collective dividing means that watering is done through a collective allocation of the working task. If watering the plants is done through sharing, that means gardeners also do the watering together at specific garden meetings. We assume that the more resources are used collectively, the more social interaction is required to manage this collective use. We further assume that sharing requires even more social interaction since the absence of clearly allocated resources and allocated working tasks needs an ongoing exchange within the garden group. Indeed, the resource use in community gardens differs widely, and we assume that, to perform well, it needs to be adjusted to the particular members and their needs. However, our current study has not been able to identify a relationship between resource use and performance.
Next to work, an additional immaterial resource is social time. Social time can be spent together through diverse social activities such as barbeques or garden parties. Since social activities can only be done together and not individually, we opt for the variable frequency of social activities, coded from 1 (less than once a month) to 5 (four times a month and more).
The third variable that characterizes social interaction is the perceived importance of social exchange within the community garden project. This variable can reach values from 1 (very unimportant) to 5 (very important). By calculating the average of all three variables the degree of social interaction is defined. Since the value of each variable covers a range of values from 1 to 5, social interaction can reach values from 1 to 5 as well. We are aware of using the arithmetic mean for an ordinal scale. We assume that our items are quasi-metric and opt for the arithmetic mean instead of the median, to consider values deviating from others [58,59].
The next criterion we developed to measure social sustainability is participation. Participation seems relevant, since it is a broadly acknowledged mechanism to promote sustainable development, and therefore also to be found in scientific literature to define the concept of social sustainability [32,33,48,56]. Bendt, Barthel and Colding [15] pointed out the possibility of immediate participation in “public-access community gardens” (PAC-gardens), which they define as gardens that are open for all citizens at all times, are collectively managed by various groups, and have absent to low formal obstacles (e.g., contract regulation, license or queue system), and thus a high degree of openness to participation. Following Bendt, Barthel and Colding [15] we referred to access right, management right, and the amount of precondition to participate as variables defining participation.
Access right signifies the right to enter the resource and enjoy non-subtractive benefits [51,55], such as enjoying the garden without taking fruits. Individuals who have access rights may or may not have rights permitting participation in particular activities and collective-choice action [32,55]. Although community gardens are often called public gardens regarding access, ownership, and the degree of democratic control [3], some gardens are fenced and have access restrictions, for instance limited access hours, and only members or plot holders may have keys [16,29,60]. We therefore examine access rights in community gardens coded from 1 to 5 and distinguish if the right is held by a third party (1); by the leader group (2); by the core group (3); by all gardeners (4); or all citizens (5). The latter matches to the above-mentioned PAC-gardens. The leader group may consist of the board members of an association or the garden founders. The core group is defined as the group that regularly partakes within the garden project, including the leader group. By “all gardeners” we mean the total gardeners group consisting of the leader group, the core group, and gardeners that do not participate regularly. In public access community gardens, we further find residents who are using the garden for e.g., recreational purposes but do not participate in gardening activities. We understand this group as external users and categorize them as “all citizens”.
With the variable management right, we examined what kind of user group is holding the management right and therefore holds power in decision-making processes [14,15,55]. We use the same values as for the variable access right, ranging from 1 (third party) to 5 (all citizens).
The variable precondition to participate leads to prevailing obstacles to participate in community gardens. We identified 4 preconditions: membership of the formal association, available garden plots, regular participation, and others. Depending on how many preconditions exist the variable ranges from 1 (four preconditions exist) to 5 (no preconditions exist).
Again, we used the average of all three variables to calculate the degree of the criterion participation. Same as the criterion social interaction, the criterion participation can reach values ranging from 1 to 5. Higher values indicate that residents can participate or benefit from the garden, easily. However, there may be many reasons why gardens are more or less open to the broader community, e.g., gardens do not allow public access or have to be fenced due to their specific location. Since the degree of participation does not enable us to predict a garden’s success, a third criterion is required.
With the third criterion, we wanted to investigate on the successful performance of community gardens as an essential criterion to determine social sustainability. Success can be defined in many ways, however, studies investigating success within social initiatives, such as community gardens, are still at an initial stage and the social dynamic processes are difficult to identify and assess [53,56]. According to de Haan, Meier and Haartsen [53], the aspect of an active citizen and the production of a sense of community is more important than reaching the original goals of the initiative [53]. Oppositely, if citizens are not participating in social interaction and do not feel responsible for the initiative, it can be defined as failed.
Regarding community gardens, we opted for the following variables to assess their success: rules compliance, fairness, participants’ perspective on success, and complaints. These variables are measured based on gardener’s perception.
The importance of rules compliance by garden members for effective and sustainable resource systems is well explored within commons theory [52,61,62,63,64,65]. We defined this variable to range from very low (1) to very high (5).
Fairness is an additional variable used as a success factor within commons theory that has an impact on rules compliance [62,64,65,66]. In regard to the social sustainability literature, fairness is a further part of the concept of equity [35,56]. We measured the perceived fairness within the community group by values ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high).
The third variable examined how gardeners perceive success, first related to their personal success and, second, related to their judgement on the success of the garden project as a whole. Thus, we could incorporate diverse understandings of success from the participants’ perspective. It is measured by values ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high). The average of both sub variables corresponds to the value for the variable participants’ perspective on success.
The last variable that we used as a converse to success [53] is complaints. The variable is built on the average of the sub-variables frequency of complaints regarding community interaction, frequency of complaints regarding the collective use of resources, and conflicts within the community on a scale from 1 (very often/very high) to 5 (very rarely/very low).
Similarly, as for the criterion social interaction and participation, the average of all four variables are used to calculate the degree of the criterion perceived success, ranging from 1 to 5.
By calculating the average of all three criteria we thus determine the degree of social sustainability, ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high).
The variable and criteria combinations were adjusted and reviewed with the help of factor analysis (principal-axis factoring and varimax rotation, SPSS 24).
2.1.2. Variables Affecting Social Sustainability
In the next step, we wanted to examine determinants of diverse degrees of social sustainability. Drawing on variables appearing in the Social-Ecological System Framework [52,64], we opted for 7 variables as most important for community gardens and social sustainability (Table 2). The number of variables was adjusted to the sample size.

Table 2.
Variables affecting social sustainability (independent variables).
While in commons theory relationships between dependent and independent variables are likely to be nonlinear [64], we assumed linearity between the variables. We tested the linear relationship of variables by scatterplots and residuals as an assumption of multiple linear regression analysis (see Section 2.3).
We opted for the variable size of the community and heterogeneity of the community since both encourage the garden initiatives and their successful performance over time [54,66,67].
Concerning the variable size of the community, we assume a negative relationship to social sustainability, since within bigger initiatives more skills and investments are required, and the risk of failure increases [53]. We measure the size of the community by referring to the size of the core group, defined as the group that regularly participate in the garden project.
In regard to communities’ heterogeneity and its effect on social sustainability, the literature seems more complex. In community gardens literature, scholars often pointed out that the cultural heterogeneity is valuable for the society, e.g., due to express and experience culture collectively, or due to generating knowledge [20,68,69]. Eizenberg [20] for instance described community gardens as spaces that emphasize diversity. In addition to that, Jabareen [70] mentioned diversity as a process that ensures social sustainability. On the contrary, in commons theory, very homogenous and very heterogeneous communities are both assumed to have negative effect on social interaction (non-linearity) [64]. However, the relationship of heterogeneity and successful performance is also often discussed in the commons literature [67,71]. In our research, we considered various forms of social diversity and refer to differences in age, education, income, and culture each measured from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high). The heterogeneity of the community is measured by the average of all these values. Therefore, a “very high” value of heterogeneity means a “very high” diversity according to all of these social differences. We understood diversity of garden communities as an important characteristic and assumed that communities are in general heterogeneous, at least to some degree. Thus, we argued that rather too heterogeneous communities, make cooperation and social interaction more difficult. Therefore, we assume a negative effect of the variable heterogeneity of the community and our concept of social sustainability. However, this negative relation should rather be understood as the difficulty of social interaction and cooperation according to too many diverse interest groups (see Section 4).
Besides the size of the community and its heterogeneity, trust contributes to the emergence and maintenance of social interaction [54,64,72]. However, trust can also emerge through social interaction [73] and thus can be understood as an outcome, too. Nevertheless, we understood trust in the first place, as input to gardens social sustainability, necessary to establish cooperation in the management of urban resources [72] (see Section 4). Trust is measured as general perceived trust within the garden community ranging from 1 (very low) to 5 (very high).
Concerning the variable size of the garden area, we assumed a positive effect on social sustainability. Commons theory refers to medium sizes to be most conducive, while large sizes (e.g., because of high costs to sustain them), as well as too small sizes (e.g., because of little valuable products) face negative effects on sustaining them [52,74,75]. Since community gardening takes place in smaller urban areas [1] and gardens are in general limited in size regarding the urban conditions, we assumed that negative effects due to too large sizes will not affect community gardens.
An additional variable which we wanted to assess in its effect on social sustainability is the management group, as this group actually manages, organizes and coordinates the gardening processes. We referred to the already mentioned characteristic value ranging from management is performed by a third party (and therefore not by the gardeners themselves) (1), to management is performed by all citizens (5).
With the final two variables, we wanted to examine the impact of existing rules and the degree to which they are monitored and sanctioned. Inspired by Ostrom [76] and Schlager and Ostrom [55], we identified the following group of rules important for community gardens: rules to restrict community size, rules to restrict access to the garden area, rules that govern roles or position within the community, rules that govern harvest rights, rules that govern gardening and food production, and rules that govern the sharing of information. Depending on how many of these rules exist and whether they are defined roughly or in detail in the respective community gardens, they can reach values of rule set and design ranging from 0 (no rules exist) to 12 (detailed rules for all of these groups exist) (see Supplementary Materials, Table S2). Related to theory we expect a positive relationship between well-defined rules and social sustainability. The variable monitoring and sanctioning is measured by the already mentioned characteristic value ranging from “a third party” to “all citizens” in combination with sanctioning is taking place or not. For this, gardens can reach values ranging from 0 (no monitoring and no sanctioning is taking place) to 8 (monitoring is taking place by the broader community and sanctions were imposed in the case of rules non-compliance) (see Supplementary Materials, Table S3).
2.2. Survey and Data Collection
Community gardens have been selected drawing on the most comprehensive available listing of anstiftung und ertomis that currently contains 643 community gardens in Germany [77]. The database offers information on garden location, year of foundation, homepage, contact email, size of the area, and additional information about the garden project. We searched for further information such as size of the city where the project is located or timeliness, to check if the community is still active.
We excluded gardening activities that were still in the planning stage or that appeared to be single public plots with no characteristics of community gardens. Since we also focus on urbanized areas, we excluded gardens in cities with less than 20,000 inhabitants. We further selected productive urban gardens where vegetables and fruits are grown. Overall, we identified 433 gardens suitable for our investigation.
Based on the criteria, we designed a questionnaire consisting 57 questions assigned to seven groups of questions: the garden area, the garden community, funding (not part of this paper), collective action, management and participation, rules, success and failure. We used a questionnaire with predominantly closed questions with a minor number of semi-open questions; the latter were included to discover additional criteria. The online questionnaire was directed to leaders or at least members of the core group of a garden, from whom we expected to have well-founded knowledge to answer specific questions. The respondents were asked to rank their gardens in terms of the presented criteria and variables. Prior examination ensured that questions were easily understood and that the wording did not suggest any particular answer.
The research was conducted from 15 December 2016 to 31 March 2017. We opted for collecting data outside the garden season to allow gardeners to find the required time to answer the questionnaire. Of 433 questionnaires sent out, 123 completely-filled questionnaires were returned (response rate of 28%).
2.3. Data Analysis
The completed questionnaires were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics 24 (IBM, New York, USA). The multiple linear regression analysis with a threshold of p = 0.05 was used to determine the effect of seven independent variables: size of the community, heterogeneity of the community, perceived trust within the community, size of the area, management group, rule set and design, and monitoring and sanctioning on the dependent, likewise empirically composed variable social sustainability. We examined the residuals and tested independent variables of multicollinearity, and found results to be acceptable.
3. Results
The following section presents the results of our study: firstly, the assessment of social sustainability in community gardens, and, secondly, the determinants influencing social sustainability.
3.1. Social Sustainability in Community Gardens
We developed the criteria social interaction, participation, and perceived success to assess social sustainability. The criteria are, in turn, each based on a set of measurable variables. The criterion social interaction is based on the variables collective use, frequency of collective action, and perceived importance of social exchange. The criterion participation is based on the variables access right, management right, and amount of precondition to participate. The criterion perceived success draws on variables that depict the rules compliance, fairness, participants’ perspective on success, and complaints.
The first step was the analysis of the above mentioned ten variables concerning the 123 community gardens examined (Figure 1) (see Supplementary Materials, Table S4 for all data presented in this section).
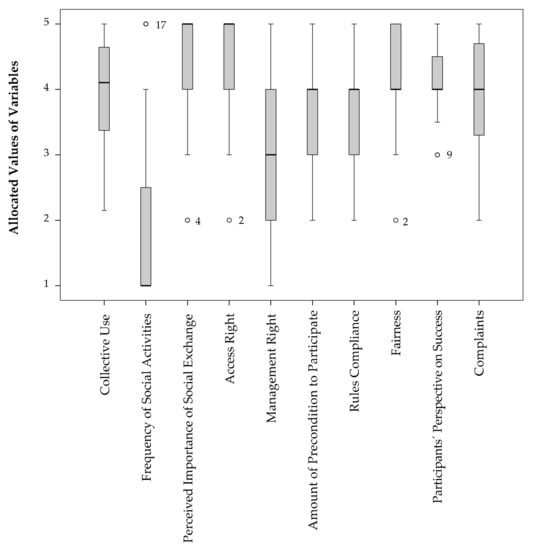
Figure 1.
Boxplot of variables to determine the criteria social interaction, participation, and perceived success. Note: n = 123, except for perceived importance of social exchange, access right, and complaints n = 122; fairness n = 121; management right n = 117; and rules compliance n = 112. The dots in the boxplot represent outliers.
The boxplots indicate various ranges within each variable, however overall gardens mostly reach values higher than 3.
The variable collective use demonstrates a range from 2.15 to 5 of the 123 community gardens examined. This result points to a wide range of collective use of resources within community gardens. While there is no community garden using all resources individually (Value 1), we find gardens where all resources are used through sharing without a clear allocation (Value 5). The position of the box between Value 3 and Value 5 indicates that collective use of resources is in general of a high degree.
Frequency of social activities is a variable for which community gardens mostly reach values below 3. The median for the frequency of social activities is right-skewed and reached a value of 1. That means that the variable is not normally distributed and social activities are taking place less than once a month in most of the examined community gardens. Looking at the data in detail, 59.3% of the 123 examined community gardens reach values of 1. Community gardens that reach values of 5 (i.e., social activities are taking place four times a month and more), are shown as outliers in the boxplot. In total, we have 17 outliers (13.8% of the community gardens) for this variable.
Compared to the variable frequency of social activities, the median for the variable management right is 3, while all other variables reach values of 4, and the variable importance of social exchange and access right even a value of 5.
By looking at the data in detail, taking as an example the variable perceived importance of social exchange, 30.1% of the examined gardeners mentioned importance of social exchange within the garden as “important” (Value 4) and 60.2% as “very important” (Value 5). In total, 5.7% mentioned the importance of social exchange as “neither unimportant nor important” (Value 3), while 3.2% mentioned social exchange as “unimportant” (Value 2). The latter are illustrated as outliers in the box plot in Figure 1. We further have one missing value for this variable (one gardener answered “I do not know”; n = 122).
Taking another example, in 54.5% of the examined community gardens all citizens have access rights to the garden area (Value 5), in 41.5% of the gardens all gardeners have access rights (value 4), while in 1.6% of the examined gardens only the core group (Value 3), and in 1.6% of the examined community gardens only the leader group has access right to the garden area (Value 2; illustrated as outliers). Again, we have one missing value for this variable (n = 122).
Participants’ perspective on success is yet a further example where most of the gardens reach values of 4 and higher. By looking at the data in detail, we see that in 75.5% of the examined gardens participants perspective on success is “high” (Value > 3.5) to “very high” (Value 5), and in 24.5% “neither high nor low” (Value 3–3.5). The latter are again illustrated as outliers. However, none of the outliers shown in Figure 1 are excluded from further calculations.
Based on the results of the variables, the criteria social interaction, participation, and perceived success are calculated. As can be seen in Figure 2, for perceived success, community gardens reach higher values, compared to the criteria social interactions and participation. The median for the criterion perceived success is 4.1 (Arithmetic mean = 4.0). The median for the criteria social interaction and participation are 3.4 (Arithmetic mean = 3.5) and 3.7 (Arithmetic mean = 3.7), respectively.
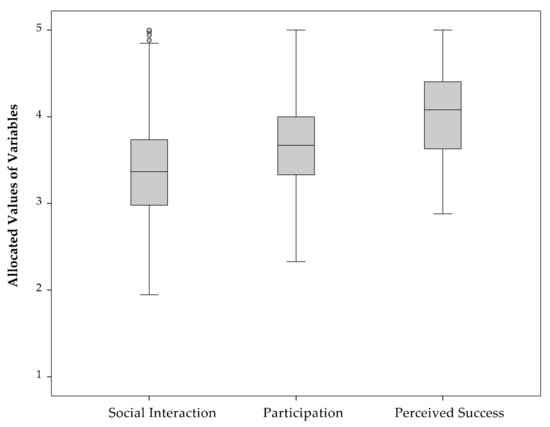
Figure 2.
Boxplot of criteria determining social sustainability. Note: The dots in the boxplot represent outliers.
The arithmetic mean of the three criteria is used to calculate the degrees of social sustainability of individual garden projects. The results indicate diverse degrees of social sustainability and suggest a normal distribution (Figure 3), confirmed by the skewness (0.267) and kurtosis (−0.146). The values of social sustainability range from 2.80 to 4.94, with an arithmetic mean of 3.74. While we have only two gardens (1.6%) reaching a value of social sustainability lower than 3.0, 35 community gardens (28.4%) reach values from 3.0 to 3.5, and 55 (44.7%) from 3.5 to 4.0. Of the examined community gardens, 26 (21.2%) reach values ranging from 4.0 to 4.5, while five gardens (4.1%) reach a degree of social sustainability higher than 4.5.
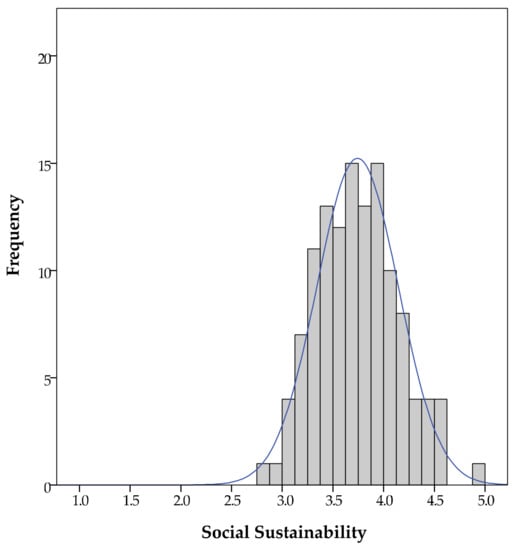
Figure 3.
Normal distribution of social sustainability.
3.2. Determinants of Social Sustainability
This section demonstrates the causality of social sustainability as our dependent variable to the defined independent variables: community size, heterogeneity of the community, perceived trust within the community, size of the area, management group, rule set and design, and monitoring and sanctioning. Table 3 presents the results of the seven independent variables and the 123 community gardens examined. Table 4 presents the results of the multiple linear regression analysis (see Supplementary Materials, Table S5 for all data presented in this section).

Table 3.
Variables affecting social sustainability.

Table 4.
Results of multiple linear regression of social sustainability and independent variables.
As can be seen in Table 3, the size of the community ranges from 2 to 82 participants and confirms the diversity of group sizes within community gardens found in literature. The arithmetic mean of the community core size is 13.19. The mode indicates that 10 is the core group size that appears most often in the 123 community gardens examined. Regarding the heterogeneity of the community, values range from 1.5 to 5, with an arithmetic mean of 3.41. In addition to the mode of 3, this result indicates that the heterogeneity in community gardens is mostly “neither low nor high”. The results for perceived trust within the community range from 2 to 5, the median and mode of 4 indicate a “high” perception of trust.
Looking at the sizes of the area, the smallest is 25 square meters, while the largest is 12,000 square meters. The arithmetic mean of the area size is 2323 square meters. These results again confirm the diversity of community gardens.
Regarding the variable management group, values range from 1 to 4. The median and mode of 3 indicate that mostly the core group is actually managing the garden. We further find a spread of values for the variable rule set and design, covering a range from 0 (no rules exist) to 12 (detailed rules for the six identified groups exist). The result of the arithmetic mean of 3.6 (median and mode of 4) indicates that, within community gardens, detailed rules are not of high importance.
In addition, the results for monitoring and sanctioning range from 0 (no monitoring and no sanctioning is taking place) to 8 (monitoring is taking place by the broader community and sanctions were imposed in the case of rules non-compliance). However, the mode of 3 indicates that, in the community gardens examined, monitoring is mostly taking place by all gardeners, while no sanctions were imposed if gardeners do not follow the rules (see Supplementary Materials, Table S3).
We carried out a multiple linear regression to analyze the relation of the independent variables and the dependent variable social sustainability. Table 4 shows an r2 of 0.396 and an adjusted r2 of 0.358. The p-value < 0.001 indicates the statistical significance of the regression. The regression coefficients indicate a positive statistical significant influence of the variables perceived trust within the community and management group on the dependent variable social sustainability. The results further indicate a negative statistical significant influence of the variable heterogeneity of the community on the dependent variable social sustainability. Our empirical data show that the variables size of the community, size of the area, and rule set and design have a negative effect on social sustainability, however, these results are not statistically significant. The variable monitoring and sanctioning point to a positive impact on social sustainability, even though not statistically significant.
Looking at the Beta values, perceived trust within the community has the highest effect on social sustainability. The second highest effect comes from the management group, followed by the heterogeneity of the community, size of the community, the rule set and design, and the size of the area. The variable monitoring and sanctioning has the weakest effect on social sustainability.
4. Discussion on Social Sustainability of Community Gardens
Community gardens are socially-oriented and collectively managed urban agriculture activities that provide economical, ecological, and, in particular, social benefits. Referring to the increasing number of studies discussing the social benefits of community gardens, this paper provides a new methodological approach to evaluate the social sustainability of community gardens according to their social interaction, often referred to as social capital. We thus aim to empirically analyze the social functions and make social sustainability operational. Hence, we refer to social interaction as an important criterion contributing to social sustainability [11,32,48,49], a main motivation, and essential characteristic of community gardens, particularly in developed countries. We further consider the possibility for urban residents to participate in community gardens and the success of these social arrangements. Therefore, the criteria social interaction, participation, and perceived success are developed and defined by respective variables. Calculating social sustainability by using the arithmetic mean of criteria and variables instead of the median appears helpful to achieve more differentiated results. The range of gardens’ social sustainability varying from 2.80 to 4.94 seems sufficient to illustrate various degrees of social sustainability and express the importance of community-serving functions of the gardens (Figure 3). While we find similarities within the community gardens, the results further indicate differences by comparing the single variables, as well by looking at one single variable. Consequently, the results confirm the diversity of community gardens as well.
Through the various degrees of social sustainability, we are able to examine causalities to further garden characteristics. We opted for seven independent variables mainly based on commons theory, of which we wanted to measure their effect on social sustainability. The results of the multiple linear regression analysis indicate that social sustainability is positively influenced by perceived trust within the community. Therefore, our results confirm the positive effect of trust on social interaction described in literature and commons theory. It seems obvious that higher perception of trust leads to higher interaction, more collective action, as well as to less conflicts and higher rules compliance, and thus higher social sustainability. While we understand trust as an independent variable that affects the outcome social sustainability, trust can also emerge through social interaction and thus can be understood as an outcome, too—a circular process naturally occurring in dynamic systems such as community gardens. In a long-term perspective, social interactions may lead to higher levels of trust. Trust can, therefore, be more important as a product of social sustainability than as a contributor. However, this requires repeated interaction among the same members of the communities, i.e., communities that are stable over longer periods with less fluctuation. As we have to take a partly static view—at least for the moment of analysis—we considered trust relations as an input to the system. We further opted to consider trust as an independent variable since it enables the establishment of the new urban communities.
Besides trust, our results demonstrate that the management group has a positive statistical significant impact on social sustainability. There seems to be a higher potential of social sustainability if not a small party (a third party or the leader group) is managing the garden, but rather a broader community group is in charge of the initiative.
Another variable that shows a statistically significant impact on social sustainability is the heterogeneity of the community. Our results of the linear regression analysis indicate a negative relation of too heterogeneous communities and social sustainability, and therefore confirms our assumption at the high and of the scale. However, we have to state out, that our concept of social sustainability bases on social interaction, and cooperation. These negative relations should rather be understood as the difficulty of social interaction and cooperation according to too many diverse interest groups, than a value of social sustainability. Too heterogeneous hereby means a high diversity in many aspects: age, education, income, and culture. Further, research could investigate on these diverse aspects (e.g., education, culture, age, and income) and its contribution to social sustainability separately. Additionally, according to the literature, the impact of heterogeneity on collective action is likely to be non-linear, however, the scatterplots did not indicate a curvilinear relationship. A reason might be that for its justification we would need larger datasets. However, Mansuri and Rao [71] and Ostrom [54,67] pointed to the complexity of social heterogeneity and the fact that the variable is also affected by other variables.
Our results on size of the community show a negative but not statistically significant effect on social sustainability, which confirms results in other studies, showing that too large communities may negatively affect social interaction among community members, since too many diverse interests need to be considered and more complex negotiation processes would be necessary [52,53]. However, Ostrom [67] also pointed to several studies that do not confirm the effect on community size on successful management of shared resources. Nevertheless, according to our results, sizes of 10–15 gardeners participating regularly seems to be a moderate group size. In addition, group size may depend on the size of the garden area. However, our results indicate only a weak correlation of sizes of the community and size of the garden area (r = 0.216; p = 0.016; Pearson’s correlation coefficient) [58].
An interesting point for the scholarly debate in commons theory is that the variable rule set and design shows a negative effect on social sustainability of gardens. Although we could not show this with statistical significance, the indication of such a relation deserves a closer look. We expected a positive connection of social sustainability by the presence of well-developed, detailed rules [55,76]. The apparent discrepancy to theoretically based assumptions might be due to the very open and dynamic structure of community gardens, confirmed by a detailed look at the data. Of all of the examined rules, access rules and community size rules are those for which most of the gardens do not even have rules (71.5% of the gardens do not have access rules and 78.0% do not have community size rules). This fact suggests the openness of community gardens and their welcoming culture, even though they have to face conflicts due to a high number of users. Most rules, as well as most detailed rules, are developed regarding gardening and food production, however withdrawal rules (e.g., who can harvest and how much) are less developed. Since community gardens do mainly serve social functions and as this main purpose is obvious to the gardeners joining, not all rules have to be spelled out in a detailed manner, or if so, this might even affect the social sustainability negatively.
Our results further indicate no relationship of the size of the area on social sustainability. On the one hand, we expected a positive causality due to more physical space for social interaction and more possibilities to test new forms of interaction. On the other hand, this result confirms the importance of the openness and welcoming culture, even if just little space is available. This is proven by an additional analysis of correlations between the size of the area and access rights (r = −0.055; p = 0.544; Spearman’s correlation coefficient), and the size of the area and community rules (r = 0.037; p = 0.684; Spearman’s correlation coefficient) that indicates no correlation. Based on our empirical data, this result proves that even small community gardens are open to the public and do not implement rules to restrict the community size.
The weakest effect on social sustainability shows the variable monitoring and sanctioning, likewise not statistically significant. According to the result that rule design is not of high importance, it is not surprising that monitoring rules compliance and performing sanctioning has such a weak effect. A detailed look at the data disclose that monitoring is mainly taking place by “all gardeners”. In addition, only in 37.4% of the gardens de-facto sanctioning is taking place, while in 52.0% no sanctioning is taking place in the case of non-compliance to rules (10.6% of the gardeners did not know if sanctioning is taking place).
Finally, even though not all results are statistically significant we are able to explain 35.8% (adjusted r2) of the variance in the dependent variable by the determinants we developed in the presented methodological approach. Since we examine social processes which depend on many diverse factors, the r2 of 0.358 can be considered as good. An even higher r2 might be achieved if additional factors were to be considered, however, an even larger sample size would be necessary.
Although our study measures social sustainability by focusing on social interaction, we see a connection to additional subjects of social sustainability. Social interaction in community gardens leads to social cohesion and social ties, which can contribute to citizens’ well-being and health, since they can bring positive health effects and community involvement. Therefore, our model can also be included in further research studies to measure social sustainability, or more particular additional aspects of social sustainability.
A weakness of our empirical data collection is that only one member of the leader or the core group was involved in the study. Regarding the variables, e.g., social importance of the community garden, participants’ perspective on success or complaints, we thus only received the perception of one community member. In addition, leaders or core group members are most aware of collective aspects of the gardens or are most interested in them and thus provide positive biased answers. Further research could lead to adapt our model assumptions and may find further determinants of social sustainability in community gardens. Additional social benefits, e.g., health, environmental justice, or food security, can be relevant to assess social sustainability in developed as well as developing countries. Analyses with our data were not carried out on the broader social functions of community gardens as a form of urban agriculture that answers a few key challenges of current urban settings. They provide a way to integrate immigrants better into existing communities, on account of cultural exchange possibilities and just working next to each other without further specifically designed integration attempts. Furthermore, being active in “successful” self-organization in a public space could confront the widely recognized democratic fatigue and discontent with political power holders expressed in the recent election results all over Europe. In addition to that, it is of great interest to analyze community gardens impact on social change and social transformation leading to sustainable lifestyles in the long-term perspective.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/10/4/1085/s1, Table S1: Data and analysis of the variable collective use, Table S2: Data and analysis of the variable rule set and design, Table S3: Data and analysis of the variable monitoring and sanctioning, Table S4: Data and analysis of the variables and criteria that determine social sustainability, Table S5: Data and analysis of the variable participants’ perspective on success, Table S6: Data and analysis of the variable complaints, Table S7: Data of variables affecting social sustainability, Table S8: Data and analysis of the variable heterogeneity of the community.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all participants involved in the study for taking the time to respond the questionnaire and helped to improve it. We further gratefully acknowledge support from Ulrich Frey for contributing to questionnaire design and Cona Ehresmann and Jan Felix Kersten for their assistance with statistic. We further acknowledge the financial support within the funding programme Open Access Publishing by the German Research Foundation (DFG).
Author Contributions
Nicole Rogge elaborated and conducted the empirical work, analyzed the data, and wrote the paper. Insa Theesfeld contributed to study design, criteria development and theoretical-conceptual foundations. Carola Strassner contributed to language editing and gave insights on self-organization of local groups in resource use and management. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the results, read and approved the final version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Smit, J.; Nasr, J.; Ratta, A.; Urban Agriculture: Food, Jobs, and Sustainable Cities. Chapter 1: Cities That Feed Themselves. Available online: http://jacsmit.com/book.html (accesed on 14 August 2017).
- Smit, J.; Nasr, J.; Ratta, A. Urban Agriculture: Food, Jobs, and Sustainable Cities. Chapter 2: Urban Agriculture Yesterday and Today. Available online: http://jacsmit.com/book.html (accesed on 14 August 2017).
- Ferris, J.; Norman, C.; Sempik, J. People, Land and Sustainability: Community Gardens and the Social Dimension of Sustainable Development. Soc. Policy Adm. 2001, 35, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED). Our Common Future; WCED: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- United Nation Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). Agenda 21; UNCED: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Vallance, S.; Perkins, H.C.; Dixon, J.E. What is social sustainability? A clarification of concepts. Geoforum 2011, 42, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Game, I.; Primus, R. Brief for GSDR, 2015. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/index.php?page=view&type=111&nr=5764&menu=35 (accesed on 20 March 2018).
- Landert, J.; Schader, C.; Moschitz, H.; Stolze, M. A holistic sustainability assessment method for urban food system governance. Sustainability 2017, 9, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, M.; Manu, R. Growing Greener Cities: Urban Agriculture and the Impact on SDG 11. Available online: http://sdg.iisd.org/commentary/generation-2030/growing-greener-cities-urban-agriculture-and-the-impact-on-sdg-11/ (accesed on 20 March 2018).
- Pearson, L.J.; Pearson, L.; Pearson, C.J. Sustainable urban agriculture: Stocktake and opportunities. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2010, 8, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, K.; Conard, M.; Culligan, P.; Plunz, R.; Sutto, M.-P.; Whittinghill, L. Sustainable food systems for future cities: The potential of urban agriculture. Econ. Soc. Rev. 2014, 45, 189–206. [Google Scholar]
- Krikser, T.; Piorr, A.; Berges, R.; Opitz, I. Urban agriculture oriented towards self-supply, social and commercial purpose: A typology. Land 2016, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colding, J.; Barthel, S.; Bendt, P.; Snep, R.; van der Knaap, W.; Ernstson, H. Urban green commons: Insights on urban common property systems. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendt, P.; Barthel, S.; Colding, J. Civic greening and environmental learning in public-access community gardens in Berlin. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2013, 109, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilková, J. Producing space, cultivating community: The story of prague’s new community gardens. Agric. Hum. Values 2017, 34, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.R. Collective action and the urban commons. Notre Dame Law Rev. 2011, 87, 57–133. [Google Scholar]
- De Moor, T. The Dilemma of the Commoners: Understanding the Use of Common-Pool Resources in Long-Term Perspective; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, C. Mapping the New Commons. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Biennial Conference of the International Association for the Study of the Commons, Cheltenham, UK, 14–18 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eizenberg, E. Actually existing commons: Three moments of space of community gardens in New York city. Antipode 2012, 44, 764–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, M. Reflections on alternatives, commons and communities or building a new world from the bottom up. Commoner 2003, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- McIvor, D.W.; Hale, J. Urban agriculture and the prospects for deep demoracy. Agric. Hum. Values 2015, 32, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourias, J.; Aubry, C.; Duchemin, E. Is food a motivation for urban gardeners? Multifunctionality and the relative importance of the food function in urban collective gardens of Paris and Montreal. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, S.; Folke, C.; Colding, J. Social–ecological memory in urban gardens: Retaining the capacity for management of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2010, 20, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, N. Why farm the city? Theorizing urban agriculture through a lens of metabolic rift. Camb. J. Reg. Econ. Soc. 2010, 3, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, N.; Mahmoudi, D.; Simpson, M.; Santos, J.P. Socio-spatial differentiation in the sustainable city: A mixed-methods assessment of residential gardens in Metropolitan Portland, Oregon, USA. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldivar-Tanaka, L.; Krasny, M.E. Culturing community development, neighborhood open space, and civic agriculture: The case of latino community gardens in New York city. Agric. Hum. Values 2004, 21, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejre, H.; Simon-Rojo, M. Introduction. In Urban Agriculture Europe; Lohrberg, F., Lička, L., Scazzosi, L., Timpe, A., Eds.; Jovis Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nettle, C. Community Gardening as a Social Action; Ashgate: Farnham, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, S.T. Multifunctional urban agriculture for sustainable land use planning in the United States. Sustainability 2010, 2, 2499–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Clift, R.; Christie, I. Urban cultivation and its contributions to sustainability: Nibbles of food but oodles of social capital. Sustainability 2016, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, N.; Bramley, G.; Brown, S.P.A.C. The social dimension of sustainable development: Defining urban social sustainability. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 19, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, S. Social Sustainability: Towords Some Definitions; Hawke Research Institute, University of South Australia: Adelaide, SA, USA, 2004; Volume 27, pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rasouli, A.H.; Kumarasuriyar, D.A. The social dimention of sustainability: Towards some definitions and analysis. J. Soc. Sci. Policy Implic. 2016, 4, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Comission on Sustainable Development (UNCSD). Indicators of Sustainable Development: Framework and Methodologies; UNCSD: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, D. A survey of community gardens in upstate New York: Implications for health promotion and community development. Health Place 2000, 6, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angotti, T. Urban agriculture: Long-term strategy or impossible dream?: Lessons from prospect farm in Brooklyn, New York. Public Health 2015, 129, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolch, J.R.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J.P. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogus, S.; Dimitri, C. Agriculture in urban and peri-urban areas in the United States: Highlights from the census of agriculture. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2014, 30, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Berges, R.; Piorr, A.; Krikser, T. Contributing to food security in urban areas: Differences between urban agriculture and peri-urban agriculture in the global north. Agric. Hum. Values 2016, 33, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, L.; Lawson, L.J. Results of a us and canada community garden survey: Shared challenges in garden management amid diverse geographical and organizational contexts. Agric. Hum. Values 2015, 32, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, S. The purpose of urban food production in developed countries. In Sustainable Food Planning; Viljoen, A., Wiskerke, J.S.C., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Gelderland, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rosol, M. Public participation in post-fordist urban green space governance: The case of community gardens in Berlin. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2010, 34, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.O. Explanation and emancipation in marxism and feminism. Sociol. Theory 1993, 11, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson Graham, J.K. A Postcapitalist Politics; University of Minnesota Press: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, E.O. Compass points. Towards a socialist alternative. New Left Rev. 2006, 41, 93–124. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.; Cameron, A.; Hudson, R. The alterity of the social economy. In Alternative Economic Spaces; Leyshon, A., Lee, R., Williams, C., Eds.; SAGE Publications: London, UK, 2003; pp. 27–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, C.; Lee, S. Neighborhood built environments affecting social capital and social sustainability in Seoul, Korea. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, I.; Specht, K.; Berges, R.; Siebert, R.; Piorr, A. Toward sustainability: Novelties, areas of learning and innovation in urban agriculture. Sustainability 2016, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, D.; Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. Past results and future directions in urban community gardens research. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Ostrom, E. A framework for analysing the microbiological commons. Int. Soc. Sci. J. 2006, 58, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. A general framework for analyzing sustainability of social-ecological systems. Science 2009, 325, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, E.; Meier, S.; Haartsen, T. Defining ‘success’ of local citizens’ initiatives in maintaining public services in rural areas: A professional’s perspective. Eur. Soc. Rural Sociol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. How types of goods and property rights jointly affect collective action. J. Theor. Politics 2003, 15, 239–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlager, E.; Ostrom, E. Property-rights regimes and natural recources: A conceputual analysis. Land Econ. 1992, 68, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizenberg, E.; Jabareen, Y. Social sustainability: A new conceptual framework. Sustainability 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SESMAD. Social-Ecological Systems Meta-Analysis Database: Background and Research Methods. Available online: http://sesmad.dartmouth.edu/ (accesed on 28 November 2017).
- Bryman, A. Social Research Methods, 5 ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cleff, T. Deskriptive Statistik und Explorative Datenanalyse—Eine ComputergestüTzte EinfüHrung Mit Excel, Spss und Stata (Descriptive Statistics and Exploratory Data Analysis—A Computer-Assisted Introduction with Excel, Spss and Stata), 3rd ed.; Gabler Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzkopf, K. Urban community gardens as contested space. Geogr. Rev. 1995, 85, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Baerlein, T.; Kasymov, U.; Zikos, D. Self-governance and sustainable common pool resource management in Kyrgyzstan. Sustainability 2015, 7, 496–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.; Villamayor-Tomas, S.; Epstein, G.; Evans, L.; Ban, N.C.; Fleischman, F.; Nenadovic, M.; Garcia-Lopez, G. Synthesizing theories of natural resource management and governance. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 39, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, U.J.; Rusch, H. Modeling ecological success of common pool resource systems using large datasets. World Dev. 2014, 59, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenny, A.; Fuentes, F.H.; Mosler, H.-J. Psychological factors determining individual compliance with rules for common pool resource management: The case of a cuban community sharing a solar energy system. Hum. Ecol. 2007, 35, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Crafting Institutions for Self-Governing Irrigation Systems; Institute for Contemporary Studies: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, E. Common-pool resources and institutions: Toward revised theory. In Handbook of Agricultural Economics; Gardner, B.L., Rausser, G.C., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1315–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Colding, J.; Barthel, S. The potential of ‘urban green commons’ in the resilience building of cities. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 86, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational (UNESCO). Links between Biological and Cultural Diversity—Concepts, Methods and Experiences. Report of the International Workshop; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jabareen, Y.R. Sustainable urban forms—Their typologies, models, and concepts. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2006, 25, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuri, G.; Rao, V. Community-based and -driven development: A critical review. World Bank Res. Obs. 2004, 19, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, E. Analyzing collective action. Agric. Econ. 2010, 41, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.R. The city as an ecological space: Social capital and urban land use. Fordham Law Sch. Occas. Pap. 2006, 82, 527–582. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, C.; Ostrom, E. A framework for analyzing the knowledge commons. In Understanding Knowledge as a Commons—From Theory to Practice; Hess, C., Ostrom, E., Eds.; The MIT Press: London, UK, 2005; pp. 41–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, E.; Burger, J.; Field, C.; Norgaard, R.B.; Policansky, D. Revisiting the commons: Local lessons, global challenges. Science 1999, 284, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, E. The challenge of crafting rules to change open access resources into managed resources. In Proceedings of the International Economic Association Roundtable on the Sustainability of Economic Growth, Beijing, China, 13–14 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stiftungsgemeinschaft Anstiftung & Ertomis. Die Urbanen Gemeinschaftsgärten im Überblick (Overview of Urban Community Gardens). Available online: http://www.anstiftung-ertomis.de/urbane-gaerten/gaerten-im-ueberblick (accesed on 12 January 2018).
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).