Abstract
Climate change not only increases the atmospheric temperature, but also changes the precipitation conditions and patterns, which can lead to an increase in the frequency of occurrence of natural disasters, such as flooding and drought. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has reported fluctuations in the precipitation levels for each country from 1900 to 2005, based on global climate change, suggesting that environmental changes due to climate change manifest very differently based on the region. According to the results of studies that have been carried out recently, changes in the precipitation patterns based on climate change result in changes in the water environment, including alterations to the vegetation, land use, and river flow, while considerably influencing the rate of development of groundwater as well. In this study, the 3Is, which are the important variables of Ideas, Institutions, and Interests that are universal to the international field of political science, were used to comparatively analyze the water environment policies of South Korea and Europe. The first variable, Ideas, examined the influence of awareness on establishing the water environment policy in response to climate change. In particular, differences in the conceptual awareness of the water environment with regard to hyporheic zones were studied. The second variable, Institutions, examined the differences in the water environment policy within the national administration in response to climate change. The South Korean administration’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport and the Ministry of Environment were used in a case study. Finally, the results drawn from the third variable, i.e., Interests, for South Korea appear to differ from those of Europe, in terms of water environment policy. In this study, the water environment policy of South Korea was analyzed and compared to that of Europe in order to identify problems in South Korea’s water environment policy in response to climate change, while seeking a sole solution for a comprehensive water environment policy direction for South Korea.
1. Introduction
A new development objective of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) for the future of Earth was unanimously approved in September 2015 by leaders from 160 countries, including representatives from 193 member countries, at the UN Headquarters in New York City. The SDGs are the new development goals that the international community has been attempting to fulfill jointly since the Millennium Development Goals expired in 2015. To realize sustainable development on Earth, the UN and the international community must accomplish 17 objectives over 15 years, i.e., from 2016 to 2030, of which the following are related to water: Objective 6—the guarantee of water and hygiene; Objective 13—a response to climate change; Objective 14—the conservation of water ecosystems; and Objective 15—the maintenance of wildlife diversity. This accounts for 25% of the total objectives that the international community must accomplish. Hence, it is clear that management of water is a key task for the entire planet in order to prepare for the future.
Climate change not only increases the atmospheric temperature but also changes precipitation conditions and patterns, which can lead to an increase in the frequency of natural disasters, such as flooding and drought [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Centered around the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) [8,9], climate change scenarios related to various greenhouse gases are being reported. The IPCC has reported that, from 1900 to 2005, a huge part of North America—the eastern part of South America, of Northern Europe, and a part of Central Asia—showed significant increases in precipitation levels, while those in regions such as the Mediterranean, Southern Africa, and South Asia actually decreased. This reveals that environmental changes due to global warming are manifesting themselves very differently based on the region. According to recent research results, changes in precipitation patterns based on climate change result in changes in the water environment, including alterations to the vegetation [10], land use, and river flow, while significantly influencing the rate of development of groundwater [11,12,13,14].
Whereas South Korea’s summer precipitation patterns were concentrated in the July monsoon season in the past, since 1980, the August rainfall has increased by 25%, with localized torrential downpours that last for short periods becoming more frequent. As a result, rainfall events of 200 mm or more occurred only once annually, on average, until the end of the 1970s, but increased to a frequency of two per year in the 1980s and thereafter occurred five times in both 1984 and 1998 [5]. The National Institute of Meteorological Research (1912–2008) has analyzed nearly 100 years of data from six domestic weather observation locations. They reported that annual precipitation increased by 19% in the past decade, compared to the first half of the 20th century, with the average annual precipitation from the six observation locations increasing by approximately 220 mm, from 1155 mm in the 1910s to 1375 mm in the 2000s [15,16]. Climate change is predicted to continue in the future [1,17,18]. Furthermore, continuous monitoring of changes in the water environment, based on climate change, is necessary to accomplish 25% of the SDGs that relate to water.
The hyporheic zone, in particular, can be utilized as a sensitive indicator for studying changes in the water environment of river bed ecosystems from climate change [19,20]. The hyporheic zone refers to the area where groundwater and surface water interchange and mix (Figure 1). The unique hydraulic property of this zone is the vitalization of the reduction of pollutants due to indigenous microbes and the provision of ecological functions as a diverse wildlife habitat in the water environment ecosystem. However, in South Korea, a definite concept and an actual managing entity for hyporheic zones are lacking, as is research into hyporheic zones. Hydrological connectivity, in particular, is a highly sensitive factor of climate change. Input from U.S. scientists in multiple fields will be important for policymaking at the federal, state, and local levels and will support water resources management regardless of the level at which those decisions are being made. In addition, they suggested that strengthening the interface between science, policy, and public participation is critical if we are going to achieve effective water resource management. However, this is almost never communicated between scientists and policymakers in Korea. In this study, the cause of the difference in water environment policy between South Korea and Europe was comparatively analyzed, using the 3Is (Ideas, Institutions, and Interests) as variables (3Is).
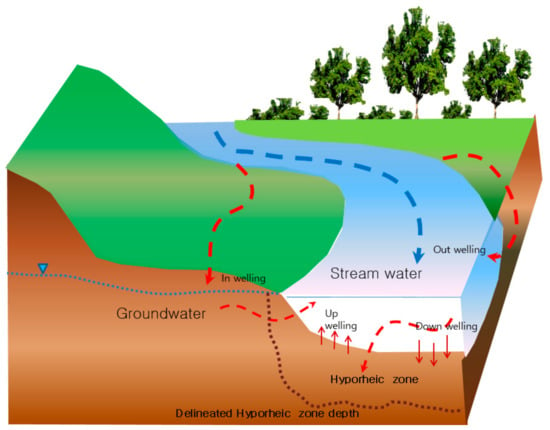
Figure 1.
Schematic view of groundwater and stream water mixing area (hyporheic zone).
2. Methodology
The philosophy of science and comparative political methodology have created opportunities to apply comparative methods to climate change issues. The most important contribution of comparative politics is to offer sharper analytical distinctions that allow us to understand when such differences are genuine. Comparative politics is organized into three groups of political factors: ideas, institutions, and interests.
In this study, these 3Is, which are universal to the international field of political science, were used to analyze South Korea’s water environment policy and compare it with that of Europe [21]. For the first variable, Ideas, we examined the influence of awareness on establishing a water environment policy in response to climate change. The conceptual awareness of the water environment with regard to hyporheic zones by South Korea was studied and compared to that by Europe. For the second variable, Institutions, we examined differences between South Korea and Europe in the water environment policy within the corresponding national administrations in response to climate change. The South Korean administration’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport and the Ministry of Environment were considered in a case study. Finally, the results drawn from the main variables of interest in South Korea appear to be different from those of Europe, in terms of water environment policy.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. South Korea’s Water Environment Research in Response to Climate Change
3.1.1. Ideas
Hyporheic zones are zones in which groundwater and surface water actively lead to a unique hydraulic phenomenon owing to many factors such as geographic and river conditions [22]. They also react sensitively to climate change, acting as an important indicator in water environment studies. In particular, this zone has attracted attention from researchers in many different fields (hydrologists, hydrogeologists, geochemists, ecologists, and microbiologists) owing to its hydraulic uniqueness.
According to Purdon [23], occasionally, the concept of an idea not only reflects knowledge, including concept and science, or development and justification, but also culture, meaning the existing practices are followed. Traditionally, groundwater and surface water have been studied separately in hydrology, which is why a clear concept of hyporheic zones does not exist. However, significant ongoing research has been focusing on the ecological function of hyporheic zones in Europe and other places in recent years. South Korea continues to manage its groundwater and surface water resources separately. When the concept of hyporheic zones is limited to groundwater and stream water, it is managed in accordance with the laws concerning groundwater or stream water by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. However, when hyporheic zones are recognized as a hydroecological indicator, the Ministry of Environment manages them in accordance with the laws regarding water quality and hydroecological conservation. Under the current law system, the ambiguity surrounding the concept of hyporheic zones reveals a lack of management guidelines and laws from the managing departments, putting water environment management in response to climate change in a blind spot.
3.1.2. Institutions
As of 2017, the Government of South Korea consists of 17 ministries. Among them, the water environment is managed by five ministries: the Ministry of Environment (MOE), the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT), the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA), the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE), and the Ministry of the Interior and Safety (MOIS) (Figure 2). In particular, the water quantity, quality, and environment related to natural disasters (e.g., typhoons, floods, heavy rain, storms, tsunamis, heavy snow, drought, and earthquakes) are managed. In South Korea, the Ministry of Environment is a central administrative agency in charge of tasks related to the natural environment, the conservation of the living environment, and the prevention of environmental pollution. The total budget for the Ministry of Environment in 2015 was US 52 billion, of which US 23 billion was allocated for water quality improvement projects and response to the frequent localized torrential downpours due to climate change [24]. The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (hereafter referred to as the Ministry of Land) is a central administrative agency that supervises the affairs related to the establishment and coordination of the comprehensive national land plan, the conservation, utilization, and development of land and water resources, the construction of cities, roads, and housing, and the tasks related to coasts, rivers, reclamation, land transportation, railroads, and aviation. The total budget for the Ministry of Land in 2015 was US 21 billion, of which US 2 billion was allocated for water resource management, such as river management and conservation and management of groundwater [25]. The budget for water environment projects accounted for 1.2% of the total budget of the South Korean government in 2015. The Ministry of Environment’s budget for water-resource-related projects was slightly higher than that of the Ministry of Land for 2015. However, most of the Ministry of Environment’s budget is allocated to the water supply and the sewage system. Focusing on the water-resources-related project budget, the Ministry of Environment is attempting to maximize the organization, budget, and manpower through water environment projects, which is 43% of the total budget, as it competes with the jurisdiction budget. Even though the Ministry of Land allocates approximately 10% of its total budget to water environment projects, it is limited in securing hegemony and maintaining jurisdiction in the water environment business.
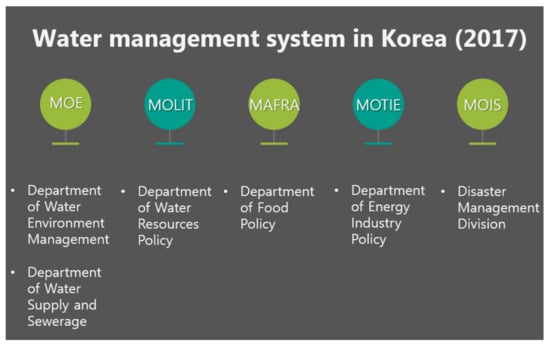
Figure 2.
Water management system in Korea (2017).
Such conflicts among the ministries lead to similar and duplicate projects and policies, which leads to a wastage of budget, thus creating competition for quantitative output that is intended merely for display. In addition, the implementation of various policies by the ministries regarding the same issue reveals the lack of consistency in policy direction and content. For example, concerning water management, quantity projects are managed by the Ministry of Land, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, and the Ministry of Industry and Commerce. Therefore, it is necessary to integrate local water service business with metropolitan water service business, both of which are managed by the Ministry of Environment and Ministry of Land, and it is desirable to simplify water management projects managed by various ministries, such as the Ministry of Environment, the Ministry of Land, and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. While individual projects by these ministries may succeed, the overall management has a high likelihood of failure.
3.1.3. Interests
South Korea lacks the awareness and interest in hyporheic zones, owing to which there are no management initiatives at all. Therefore, it is practically impossible to study this zone in Korea. During the period 2008–2012, the Ministry of Land invested US $20 billion in the Four Major Rivers Project, focusing only on the functional aspects of water resources. The project focused on surface water, while ignoring groundwater and aquatic ecosystems. In addition, the proposal to change the designation of the five major river areas that the Ministry of Land has been promoting since 2013 was directly opposed to the conservation management plan for waterfront areas created by the Ministry of Environment.
The Ministry of Environment ordered the Korea Environment Institute to develop a plan for waterfront areas in 2013, which was completed in March 2014. According to the Ministry of Environment’s “Establishment of Basic Plan for Survey and Evaluation and Conservation Management of Waterside Areas” report, the area within 1 km of the left and right banks of the river was to be designated as “the highest priority conservation management, conservation and restoration management, conservation management after restoration, restoration and buffer management, buffer management, transition area, etc.” However, the Ministry of Land ordered the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology to create a land development plan in July 2013. In December 2014, the Ministry of Land was able to build commercial, sports, accommodation, culture, and leisure facilities. Although the two ministries ordered similar services in 2013, having consulted with municipalities, it can be seen that the two ministries have completely different waterfront area development plans. These results further interfere with the interests of the administrative ministries, hindering the implementation of integrated water environment policies in response to climate change.
3.2. Europe’s Water Environment Research in Response to Climate Change
3.2.1. Accurate Ideas
The concern and focus of the European water environment policy in response to climate change is the establishment of an integrated water environment policy. The roles and functions of the European Water Management Guidelines are organized in the European Water Environment Policy, which was launched in 2000, through 12 water notes. The policy covers the management of rivers and watersheds across Europe, the identification and management of groundwater and surface water exposed to pollution and depletion, the management of groundwater in Europe, which is extensively utilized for drinking water, and the various laws and regulations related to water resources of European Union (EU) member states, as well as the development of measures to combat floods, drought, and ecosystem changes due to climate change. In the past, the EU has also divided groundwater and surface water dichotomically, as South Korea still does. Yet, integrated water environment management was the goal of the new water environment policy in 2000. In particular, the European Commission has implemented an integrated water management policy to improve the quality of underground water, while protecting the quantity of water, in addition to the management of surface water.
3.2.2. De Facto Management System
In Europe, in the mid-1970s, the Drinking Water Abstraction Directive [26] and The First Directive [27] were developed to provide safe water supply, free of groundwater and surface water pollutants. The Water Framework Directive (WFD) was established in 2000 for the integrated management of hyporheic zones, groundwater, surface water, and river ecosystems. Currently, the European Water Management Guidelines are being implemented by EU member states, with a view to link aquatic ecosystems with groundwater surface water quality by 2015.
The European Commission (EC) follows the European Water Management Guidelines in order to improve surface water quality. Based on these guidelines, database creation and watershed condition evaluation have been carried out. The objective of this assessment is to (1) identify areas of significant environmental concern, (2) provide basic data for identifying and assessing environmental threats at global or regional levels, and (3) provide information on sustainable development and sustainability. Finally, it promotes the improvement of the environmental status of water management organizations. The European Water Management Guidelines classify surface waters into rivers, lakes, mixed waters, and coasts. The elements and criteria that should be measured by monitoring water quality are called biomes (phytoplankton, aquatic plants, benthic invertebrates, water ecological continuity, and geological topography) and physicochemical elements (water temperature, oxidation, salinity, nutrition, acidity, pollutants, and priority materials). In addition, in 2007, the European Commission’s Common Implementation Strategy (CIS) of the European Water Management Guidelines was to increase the frequency of monitoring and monitoring points for areas where ecosystems are deeply linked to rivers, lakes, wetlands, and groundwater [28].
However, the UNEP/CBD pointed out that the greatest weakness in the European integrated water management strategy is that the importance of groundwater resources is excluded, with the emphasis being placed only on surface water [29]. In response to this, the European Commission has been working with GENESIS (Groundwater and Dependent Ecosystems: New Scientific and Technological Basis for Assessing Climate Change and Land-use Impacts on Groundwater) [30], a research project for improving the management guidelines for the assessment and protection of groundwater surface mixes, to better manage groundwater resources and protect them against the threat of climate change [30].
3.2.3. Common Interests
The European Water Management Guidelines set targets for the improvement of groundwater and surface water quality by 2015 [30], which required the thresholds for groundwater quality to be set to protect human beings and the aquatic ecosystems associated with groundwater. Under Article 17 of the European Water Management Directive, it has been agreed that groundwater management guidelines should be developed to the damage to groundwater-dependent ecosystems (hyporheic zones). This implies that, in addition to extending the existing water environment policy centered on surface water to also cover groundwater, the concept of the ecosystem of the hyporheic zone has also been included, with consensus on an integrated water environmental policy. In addition, the EC participant countries have also established a common implementation strategy for the integrated management of the hyporheic zones.
4. Conclusions
It was discovered that South Korea’s water environment policy in response to climate change has several problems when compared to the European water environment policy. First, the concept of groundwater and surface water exists only in the domestic water environment, whereas the concept of the extended water environment, namely the hyporheic zone, has not been introduced. Therefore, not only does Korea’s policy not refer to the concept of an integrated water environment, which is the core of the water environment policy in response to climate change, but the conservative attitude toward the existing dichotomous practices regarding water resources is expected to persist. Second, the ambiguity of the concept of water resources mentioned above has deepened the gap among national administrations and hindered the implementation of a common water environment policy in response to climate change. Finally, the project-centered water environment policy of Korea does not include sustainability concepts, such as the ecological maintenance and management of hyporheic zones, as opposed to the European integrated water environment policy, which attaches considerable significance to the functions of the water environment.
At present, the diversification of the management and development of water resources in Korea and the diversification of water quality and quantity management cannot ensure the consistency of an integrated water environment policy. In the future, the water environment policy of the Korean government should be expanded to include the water management system, which can enhance its cultural and recreational functions, as well as the demand for clean water as a key element of a pleasant living environment and industrial activities, while preserving the ecosystem.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NRF 2015R1C1A2A01052726.
Author Contributions
Heejung Kim and Kang-Kun Lee conceived and designed the experiments; Heejung Kim and Kang-Kun Lee analyzed the data; Kang-Kun Lee contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Heejung Kim wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Allen, C.D.; Macalady, A.K.; Chenchouni, H.; Bachelet, D.; McDowell, N.; Vennetier, M.; Kitzberger, T.; Rigling, A.; Breshears, D.D.; Hogg, E.H.; et al. A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 660–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinen, T.; Petschel-Held, G. Integrated assessment of changes in flooding probabilities due to climate change. Clim. Chang. 2007, 81, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirshen, P.; Watson, C.; Douglas, E.; Gontz, A.; Lee, J.; Tian, Y. Coastal flooding in the Northeastern United States due to climate change. Mitig. Adapt. Strat. Glob. Chang. 2008, 13, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, A.; Poortinga, W.; Butler, C.; Pidgeon, N.F. Perceptions of climate change and willingness to save energy related to flood experience. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelkoop, H.; Daamen, K.; Gellens, D.; Grabs, W.; Kwadijk, J.C.; Lang, H.; Wilke, K. Impact of climate change on hydrological regimes and water resources management in the Rhine basin. Clim. Chang. 2001, 49, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Shukla, S. Assessment of drought due to historic climate variability and projected future climate change in the midwestern United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2010, 11, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Houérou, H.N. Climate change, drought and desertification. J. Arid Environ. 1996, 34, 133–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC 4AR (2007) Fourth Assessment Report (4AR) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Reisinger, A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 104. Available online: http://www.ipcc-wg2.gov/publications/AR4/index.html (accessed on 31 January 2018).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC 5AR SPM (2013) Fifth Assessment Report Summary for Policy Makers (5AR SPM) of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC); IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Lafforgue, M. Climate Change Impacts on Forest-Water Interactions and on Forest Management. In Forest and the Water Cycle: Quantity, Quality, Management; Lachassagne, P., Lafforgue, M., Eds.; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2016; pp. 612–649. [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard, S.G.; Rogers, H.H.; Prior, S.A.; Peterson, C.M. Elevated CO2 and plant structure: A review. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1999, 5, 807–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderniaux, P.; Brouyère, S.; Fowler, H.J.; Blenkinsop, S.; Therrien, R.; Orban, P.; Dassargues, A. Large scale surface-subsurface hydrological model to assess climate change impacts on groundwater reserves. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficklin, D.; Luedeling, E.; Zhang, M. Sensitivity of groundwater recharge under irrigated agriculture to changes in climate, CO2 concentrations and canopy structure. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.K.; Ha, K. A Study on the Characteristics of the Sediments of the Rainy Season and the Changes in the Forms of the Ranger. Climate 2002, 12, 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, C.H.; Kang, I. A Study on the Volatility of Korean Precipitation. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 1988, 24, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I.; Huh, C.H.; Min, K. Long-term prediction of precipitation during the summer of the Korean peninsula. J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 28, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Nyirfa, W.N.; Harron, B.H. Assessment of Climate Change on the Agricultural Resources of the Canadian Prairies, Research Report of the Prairie Adaptation Research Collaborative; Prairie Adaptation Research Collaborative: Regina, SK, Canada, 2001; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Showstack, R. IPCC report cautiously warns of potentially dramatic climate change impact. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2001, 82, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.K.; Lee, J.Y. Numerical verification of hyporheic zone depth estimation using streambed temperature. J. Hydrol. 2014, 511, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kaown, D.; Mayer, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Hyun, Y.; Lee, K.K. Identifying the sources of nitrate concentration of groundwater in an agricultural area (Haean basin, Korea) using isotope and microbial community analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 533, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltz, K.N. Man, the State, and War: A Theoretical Analysis; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1959; 263p. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Ahn, J.; Lee, H. Sustainable Hyporheic Zone Management, Korea Environmental Policy Evaluation Institute, 2014, 1–130. Available online: http://repository.kei.re.kr/handle/2017.oak/20201 (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Purdon, M. Advancing Comparative Climate Change Politics: Theory and Method. Glob. Environ. Politics 2015, 15, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment. Available online: http://www.me.go.kr/home/web/main.do (accessed on 3 January 2017).
- Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Available online: http://www.molit.go.kr/portal.do (accessed on 8 January 2017).
- European Commission (EC). Economic Efficiency Calculations in Conjunction with the Drinking Water Directive; Part III: The Parameter for Pesticides and Related Products; Drinking water abstraction; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission (EC). Proposal for a Council Directive Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; COM(98)76; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 1998; p. 94. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission (EC). Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2000, 327, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission (EC). Common Implementation Strategy for the Water Framework Directive, European Communities; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2003; ISBN 92-894-2040-5. Available online: http://europa.eu.int/comm/environment/water/water-framework/implementation.html (accessed on 31 November 2017).
- European Commission (EC). GENESIS (Groundwater and Dependent Ecosystem: New Scientific and Technology Basis for Assessing Climate Change and Land Use Impacts on Groundwater); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).