Abstract
The emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) decreased under China’s air quality control policies. However, concern remains regarding the response of ozone (O3) in the metropolitan areas. The characteristics and trends of ambient O3 and NOx in Shenzhen were investigated during the 2011–2017 period. Both the human population and vegetation are exposed to higher O3 at suburban and rural sites than at the urban site. The O3 weekend effect is significant (p = 0.062) at the urban site, with O3 levels 1.19 ppb higher on Sunday than on weekdays. Solar radiation, precipitation, and relative humidity are the most relevant meteorological factors that affect O3 daily variations. Wind speed is the least relevant factor, but wind direction is related to the presence of high O3 air concentrations. Both 1-h and 8-h O3 exhibit an increase, opposite to the trend of NOx. A slight decline in O3 occurs in autumn at less urbanized sites. The increase in O3 is more prevalent and rapid in the winter at more urbanized sites. This can be due to the transport of increased O3 from northern China, as well as a lowered O3 titration effect with NOx reduction. O3 increases fastest at the urban site, with an estimated rate of 4.3% (95% confidence intervals (CIs): 0.96, 8.25) per year (p < 0.05) for 8-h O3 and 2.5% (95% CIs: −0.46, 6.12) per year (p > 0.1) for 1-h O3, posing greater human health risks to areas with high population density.
1. Introduction
China’s rapid economic growth and urbanization greatly increased energy consumption and air pollutant emissions since economic reforms in 1978 [1]. Environmental monitoring campaigns carried out in urban centers highlighted O3 values that are of concern for human health [2,3]. Elevated surface ozone (O3) is a growing environmental concern in China [1,2,3,4,5]. Serious O3 episodes are frequent in China’s most economically vibrant and densely populated regions, such as the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH) area and the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) and Pearl River Delta (PRD) regions [5]. Studies showed substantial detrimental effects of elevated ground-level O3, including declining forest ecosystem services, crop yield loss, and associated premature deaths [4,6,7].
Tropospheric O3 is formed by a series of complex nonlinear photochemical reactions between O3 precursors, namely methane, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and nitrogen oxides (NOx = NO + NO2) [8]. Because NOx is mainly anthropogenic, control of O3 is usually through NOx regulation [9]. In China’s 12th five-year plan (2011–2015), the goal was set to reduce national NOx emissions by 10% relative to the 2010 level [10]. Both satellite retrievals and emission inventories show success in reducing NOx emissions nationwide [11,12,13,14,15]. Compared with other large NOx emission regions such as BTH and YRD, the decline in NOx emissions in the PRD region started earlier in 2005 [11,14].
Shenzhen is a major megacity in the PRD region and a twin megalopolis to Hong Kong. Shenzhen was established as China’s first Special Economic Zone in 1980 and developed from a small village into a large metropolitan area with a population over 10 million in three decades. Accompanied by rapid economic growth, the air quality in Shenzhen deteriorated [16]. Epidemiologic studies showed significant associations between O3 levels and increased mortality and respiratory diseases in Shenzhen [17,18]. To tackle air pollution issues, the governments of Guangdong Province and Hong Kong worked closely to reduce emissions of SO2, NOx, and VOCs throughout the region [19]. In addition to national and regional environmental control efforts, Shenzhen also implements energy reforms for public transportation and private motor vehicles. It is the world’s first city that electrified 100% of public buses and will electrify all taxis by the end of 2020 [20]. The decline in NOx emissions is fastest in Shenzhen compared with other megacities like Shanghai, Beijing, and Guangzhou [11].
NOx regulation showed effectiveness in reducing peak O3 levels over the long term and elevated mean O3 levels at the same time [21,22,23,24]. However, due to the nonlinear relationship between NOx and O3, NOx control might worsen the O3 problems in urban areas in the short term [19,25]. This is mainly caused by the lessened titration effect of NO in urban areas, where the O3 photochemical chemistry is mainly VOC-sensitive [21,22,23,24]. Simulation results showed that peak O3 levels could be effectively reduced in the PRD region when cutting down NOx and VOC emissions [15,19,25]. Recent observations showed that annual mean O3 levels were increasing at both urban and suburban sites in the PRD region [24]. However, the changes in peak O3, which is closely related to human health, are rarely shown by observation data.
Apart from emissions of O3 precursors, meteorological factors are also important in affecting O3 levels both directly and indirectly. Meteorological factors can directly impact the formation of O3 because the reactions are sensitive to the changes in sunlight and temperature [5,26,27]. Meteorological factors such as wind speed, surface pressure, and precipitation also impact the accumulation, dilution, and deposition of O3 [5,27,28,29]. The prevailing wind direction that changes with the season is closely related to air pollutant transport from near and distant areas [5,27,28]. Actually, the relationship between air pollutants and meteorological factors varies greatly by geographical location and season [5]. The investigation of the relationship between O3 and meteorological parameters in Shenzhen will help understand the pollution situation in the PRD region, as well the large cities that are close to Shenzhen, namely Hong Kong and Macau.
The characteristics of O3 at urban, suburban, and rural sites depend on the O3 photochemical sensitivity of the region. One previous study reported higher 1-h and 8-h O3 in central areas of Shenzhen, which is uncommon for most large cities [17]. Higher urban O3 is a possible pattern for some cities, e.g., Atlanta and Houston, where large sources of VOCs originate from biological and anthropogenic emissions [30,31]. For most populous areas in the PRD region, the photochemical regime was indicated as VOC-sensitive, with a mixed or transitional regime in Shenzhen [32]. Studying the spatial O3 pattern between urban and rural areas will help determine the controlling precursors related to the O3 production rate, which is critical for O3 control and management.
The comprehensive monitoring of O3 and NOx by the Shenzhen Meteorological Bureau was carried out at four air monitoring sites, starting in 2010. This is three years earlier than the introduction of CAAQS GB 3095–2012 in Shenzhen in 2013, allowing us to analyze the spatial and interannual variations of air pollutants. In this study, we investigate the characteristics and trends of O3 at urban, suburban, and rural sites of Shenzhen based on seven years of observations of O3 and NOx from 2011 to 2017. Our objectives were to (1) assess and compare O3 risks to human and plants at urban, suburban, and rural sites; (2) investigate weekly and monthly O3 and NOx variations and their influences; and (3) evaluate O3 and NOx trends during the 2011–2017 period.
2. Data and Methods
2.1 Sites
Shenzhen is the second largest populated city in the PRD region and located to the north of Hong Kong. Figure 1 illustrates the location of Shenzhen and four O3 monitoring stations, Zhuzilin (ZZL), Shiyan (SY), Longgang (LG), and Xichong (XC). The urban site ZZL (22°32′28.94″N, 114°0′17.15″E, 63 m elevation) is in the Futian District and had a population density of 19091/km2 in 2016 [33]. It is within the original boundary of the Special Economic Zone (former SEZ), which is one of Shenzhen’s earliest developed regions, with well-established high-density commercial and residential areas. Two suburban sites, SY (22°39′13″N, 113°53′37″E, 51 m) and LG (22°43′27″N, 114°14′32″E, 90 m) were in the Bao’an and Longgang districts with moderate population densities of 7607/km2 and 5522/km2, respectively. Rural coastal site XC (22°28′52.95″N, 114°31′35.16″E, 19 m) is on the Dapeng Peninsula, far from the downtown area. It had a population density of 477/km2 and is greatly impacted by the land−sea breeze circulation. In addition to O3, NOx concentrations are monitored at ZZL and XC. Hourly O3 and NOx data were analyzed for the 2011 to 2017 period. Meteorological data at SY (solar radiation, wind speed, air temperature, and precipitation, relative humidity, and surface air pressure) from 2014 to 2017 were provided by the Shenzhen Meteorological Bureau.
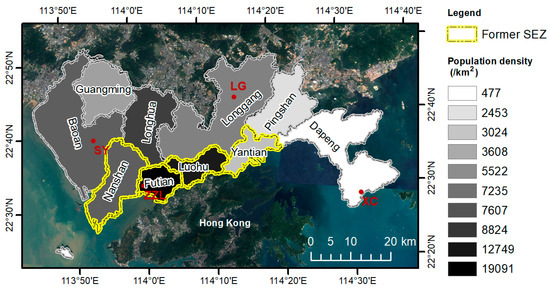
Figure 1.
Location of ozone (O3) monitoring sites at the urban site Zhuzilin (ZZL), suburban sites Shiyan (SY) and Longgang (LG), and the rural coastal site Xichong (XC) in Shenzhen. ZZL and XC also monitor nitrogen oxides (NOx) concentrations. SY also monitors meteorological parameters.
2.2 Measurement of Air Pollutants
Commercial trace gas instruments (i-Series, Thermo Environmental Instruments Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) were used to continuously measure concentrations of O3 (Model 49i) and NO/NO2/NOx (Model 42i). The O3 analyzer uses ultraviolet (UV) photometry to detect the absorption of UV radiation from O3 molecules at a wavelength of 254 nm via the Beer−Lambert law. The working principle of the NOx analyzer is that NO and O3 react to produce characteristic luminescence, and its intensity is linearly proportional to the NO concentration (www.thermoscientific.com). Both instruments output ppb by default.
To ensure instrumental accuracy, quality assurance/quality control procedures were applied in strict accordance with the national standard. Automatic zero/span checks of gas analyzers were performed once per day. Manual checks were done bi-weekly, and multipoint calibrations were done after equipment maintenance or at least every six months. The coefficient of determination (R2) of the linear equation derived by multipoint calibration had to exceed 0.999 for the calibration to be accepted. Calibrations of Model 49i were performed using a portable O3 transfer standard (Sabio Environmental Model 2030) over the entire study period. The Model 42i was calibrated using a dynamic gas calibrator (Model 146) and a zero air supplier (Model 111). More detailed descriptions of the installation and maintenance procedures are given in the Chinese atmospheric composition monitoring service specification [34].
The validity data rates for O3 and NOx at each monitoring site in each year from 2011 to 2017 are listed in Table 1. Except for a large amount of data missing from the LG monitoring station in 2011, the data coverage of all other monitoring stations generally exceeded 70% per year. LG’s data missing in 2011 was due to data monitoring delays by external factors at the initial operational stage. Data release did not begin until the end of July.

Table 1.
Validity data rates for ozone (O3) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) at each monitoring site in each year from 2011 to 2017 (%). ZZL—Zhuzilin; SY—Shiyan; LG—Longgang; XC—Xichong.
2.3 Methods
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, histogram, and quantile-quantile (Q-Q) charts were used to verify the normality of air pollutant recording. The results show that both O3 and NOx data were not normally distributed. Therefore, most of our analyses were based on nonparametric methods. Data for each station were summarized as annual, seasonal, monthly, daily, and 8-h mean concentrations. The O3 index AOT40, which is commonly used to assess forest and ecosystem health protection, was calculated as the sum of daylight (8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m.) O3 over the threshold of 40 ppb. Due to the long growing season in southern China (280–320 days), AOT40 was calculated from April to September, which is the season of main vegetation activity [35]. Because AOT40 is a sum and therefore, sensitive to missing data, values for sites with at least 75% of data available were used to ensure the completeness of the measurement series, and the index was corrected with the following equation (1):
where AOT40measured was calculated from the available hourly O3 data, and Ntotal/Navail is the ratio of the total number of hours (the number of days × 12) divided by total possible hours.
The meteorological parameters were analyzed on a daily basis. Total solar radiation was calculated as the sum of direct and scattered radiation between 7:00 a.m. and 6:00 p.m., the normal daytime hours of local time. Hourly rainfall data were calculated as daily total precipitation. Because daily values contained numerous zeroes, precipitation data were summed on a monthly basis to show the monthly variations in precipitation. All the sum data were also corrected using Equation (1).
To minimize the O3 variations caused by different amount of O3 precursor emissions, the relationship between air pollutants and meteorological factors was also analyzed in each season using Spearman’s rank correlation [36]. March, April, and May are considered spring. June, July, and August are considered summer, while September, October, and November are considered autumn. December, January, and February are considered winter. Statistical comparison was performed using the nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum test, which is robust for non-normality and the presence of serial correlation [37].
Conditional probability functions (CPF) were also used to plot the percentile wind pollution rose figure [38]. This method is very useful for showing which wind directions are dominated by high concentrations, and gives the probability. In this study, we used percentile values greater than the 90th percentile to represent all the high values. The CPF is calculated as follows:
where is the number of samples in the wind θ with mixing ratios greater than some “high” concentration, and is the total number of samples in the same wind sector. This analysis was performed using the R package “openair” [38].
The Theil-Sen (T-S) estimator [39] was used to determine the magnitude and direction of the trend for a given period (i.e., annual and seasonal). This method was chosen because it does not require assumptions about the functional form or statistical distribution of the data and is resistant to outliers. This analysis was also performed using the R package “openair” [38]. Slope estimates as a percentage of change per year were chosen for comparing sites with different levels of air pollutant. The trend T is calculated as follows:
where Cend and Cstart are the mean concentrations for the end and start dates, respectively. Nyears is the number of years. R software was used to perform all statistical analyses and plot the figures [40,41].
3. Results
3.1 Comparison of O3 and NOx at Urban, Suburban and Rural Sites
Table 2 summarizes a statistical comparison of O3 and NOx at urban, suburban, and rural sites from 2011 to 2017. Annual mean O3, maximum daily 8-h O3, maximum 1-h O3, and AOT40 were generally lower at the urban site and higher at the rural site. The suburban sites had intermediate values. Annual mean O3, maximum daily 8-h O3, maximum daily 1-h O3, and cumulative AOT40 at the rural coastal site were 88%, 54%, 32%, and 67% higher, respectively, than those at the urban site. There is no significant difference in the annual mean O3 between the urban site ZZL and the suburban site SY (p > 0.05). The annual mean NOx levels were significantly higher at the urban site than at the rural coastal site (p < 0.05). The median level differences reached as high as 22 ppb (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Statistical comparison of NOx and O3 at urban, suburban, and rural sites from 2011 to 2017.
The AOT40 value from April to September is commonly used by the European Union to guide O3 control for forest protection [6]. Since there is currently no vegetation standard in China, this method is often used to assess the risk of O3 pollution to plants [5,7]. Our results show AOT40 was highest at the rural site with a median value of 19.4 ppm∙h and lowest at the urban site with a median value of 11.6 ppm∙h (Table 2). The AOT40 values in Shenzhen are about 1−3 times higher than the critical values for forest protection (5 ppm∙h) based on an estimated production loss of 5% [6].
The latest Chinese O3 standard (GB 3095-2012) defines two classes for human health protection from O3 pollution. Class 1 is more stringent and is mainly aimed at remote areas, with critical values of 100 μg/m3 (~47 ppb, 8-h O3) and 160 μg/m3 (~75 ppb, 1-h O3). Class 2 is mainly targeted at urban/industrial and surrounding rural areas, with critical values of 160 μg/m3 (~75 ppb, 8-h O3) and 200 μg/m3 (~93 ppb, 1-h O3). The thresholds of Class 1 are comparable with the World Health Organization (WHO) O3 guidelines, so it can better guide human health protection [42]. Shenzhen, Hong Kong, and other cities in the PRD region apply to Class 2 standards, but the exceedance rate of Class 1 was also calculated for a more comprehensive evaluation of O3 impacts in this area.
Table 3 shows the average percentage of days that exceeded the national ambient O3 standards. The results show a relatively small exceedance rate (7–16%) of the national Class 2 standards of 1-h and 8-h O3. The exceedance rate of 8-h O3 was highest at the rural site and lowest at the urban site. By contrast, there was a much larger exceedance rate (16–59%) of the national Class 1 standards of 1-h and 8-h O3. The national Class 1 8-h threshold has the same limit as the WHO O3 guideline, and indicated that about 28% (103 days) of the year had alarm levels that could have adverse impacts on human health at ZZL. The average numbers of over-limit days in a year were 124 days (34%) at SY, 139 days (38%) at LG, and 215 days (59%) at XC (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Average exceedance rate over national ambient O3 standards (GB 3095-2012) at urban, suburban, and rural sites for the 2011 to 2017 period.
3.2 Weekly and Diurnal Variations of O3 and NOx
No statistical difference in air concentrations O3 was found between weekdays and weekends at any site, except for the NOx concentration, which was 2.39 ppb lower on the weekend than on weekdays at the ZZL urban site (p < 0.1) (Figure 2a,b). By graphical comparison, the weekday–Saturday O3 difference was found to be much smaller than the weekday–Sunday difference. Comparing weekday and Sunday O3 levels, O3 was 1.19 ppb higher on Sunday than on weekdays at the urban site (p = 0.062) (Figure 2c). The NOx concentration on weekdays was 3.87 ppb higher than on Sunday (p < 0.01) (Figure 2d). At the rural site of XC, NOx concentration on Sunday showed an opposite pattern, i.e., 1.41 ppb higher than on weekdays (p = 0.43) (Figure 2d).
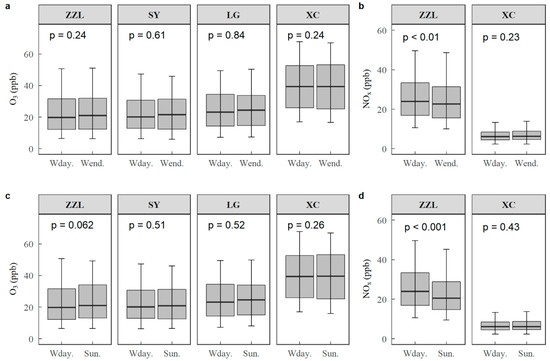
Figure 2.
Boxplot of O3 and NOx air concentrations at all representative sites from 2011 to 2017. (a) Weekday and weekend O3 comparison; (b) weekday and weekend NOx comparison; (c) weekday and Sunday O3 comparison; and (d) weekday and Sunday NOx comparison. The horizontal solid lines indicate the median and range, where the top and bottom of the box indicate the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively. The top and bottom whiskers indicate the 95th and 5th percentiles, respectively. The p-values in figures refer to significance level by Wilcoxon rank−sum test. ZZL is an urban site, LG and SY are suburban sites, and XC is a rural site.
As illustrated in Figure 3, NOx at the urban site ZZL shows typical diurnal variations that are affected by the daily routine of human activities. NOx levels increase from about 20 ppb at 5:00 a.m. to the initial daily peak of 35 ppb at 8:00 a.m. This period is coincident with the time of the morning rush hour. The synchronous decrease of O3 from 19 ppb to 14 ppb is mainly caused by the titration effect of NO, which is a dominant reaction when sunlight is limited for O3 production. Then, O3 increases rapidly and reaches its daily maximum values of 40 ppb at 3:00 p.m. with an average rate of 3.7 ppb/h. This process is very likely to be caused by local photochemical production. The second daily NOx peak at the urban site is around 9:00 p.m., later than the evening rush hour (5:30–7:30 p.m.). This second peak is possibly caused by continuous emissions of NOx from the movement of heavy diesel-powered trucks, which are only allowed to enter the city after 8:00 p.m. on weekdays if they do not have local license plates.
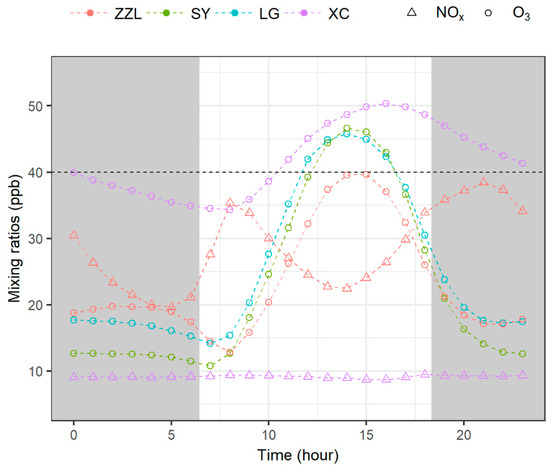
Figure 3.
Diurnal variations of hourly mean O3 and NOx concentrations at ZZL, SY, LG, and XC from 2011 to 2017. NOx data are only valid at ZZL and XC. The gray horizontal dashed line is the reference of 40 ppb, and the gray area represents nighttime based on local sunrise and sunset averaged throughout the whole year.
The two suburban sites exhibit a more pronounced diurnal O3 pattern with larger diurnal range and higher daily O3 peaks than the urban site. O3 at SY decreases slightly in the early morning and reaches its minimum at 7:00 a.m. O3 increases rapidly before reaching its maximum of about 46.7 ppb at 2:00 p.m. The average increasing rate is 5.1 ppb/h, which is the highest compared with the other three sites. Similarly, O3 at LG also decreases slightly in the early morning before reaching its maximum of 45.7 ppb at 2:00 p.m. The average increasing rate is about 4.4 ppb/h at LG, which is also higher than that at the urban site. The diurnal O3 pattern is slightly different at XC. XC has much higher nighttime O3 levels and a much lower diurnal range of about 16 ppb. The increase in O3 during the daytime occurs at a slower rate of about 2 ppb/h. The NOx levels at XC are much lower than those at ZZL. The few diurnal variations in NOx suggest this site is less impacted by direct human influence.
3.3 Monthly Variations and the Impacts of Meteorological factors
The monthly variations of daily maximum 8-h average O3 and 24-h mean NOx are shown in Figure 4. Due to the similarity of monthly variations of air pollutants between sites, O3 and NOx are only shown at one site. The variations in O3 are shown at SY to match with meteorological variations at this site. As can be seen from the figure, the monthly O3 variations show maximum values in the autumn (October) and minimum values in the summer (June) (see Figure 4a). Because XC has very low NOx levels, monthly NOx variations are shown at ZZL. The result shows maximum values in the winter (January) and minimum in the summer (June) (see Figure 4b).
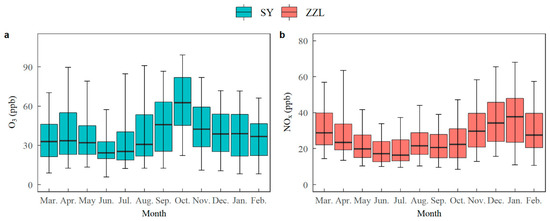
Figure 4.
Boxplot of (a) daily maximum 8-h average O3, and (b) daily 24-h mean NOx at the site SY for the 2011 to 2017 period. The horizontal solid lines indicate the median and range, where the top and bottom of the box indicate the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively. The top and bottom whiskers indicate the 95th and 5th percentiles, respectively.
Monthly variations in meteorological conditions are shown in Figure 5a–f. Wind speed is highest in June and lowest in September (see Figure 5a). Solar radiation is generally higher in the summer months when the sun is directly overhead in the northern hemisphere (see Figure 5b). Similar to solar radiation, the temperature is also higher in the summer and lower in the winter. The temperature is generally warm in Shenzhen, with median values of daily maximum temperature >20 °C throughout the year (see Figure 5c). The monthly variations in surface pressure show an opposite pattern to the temperature (see Figure 5d). Monthly total precipitation is higher from May to August, which is the main rainy season in Shenzhen (see Figure 5e). The monthly variations in relative humidity are small, with the lowest value in December (see Figure 5f).
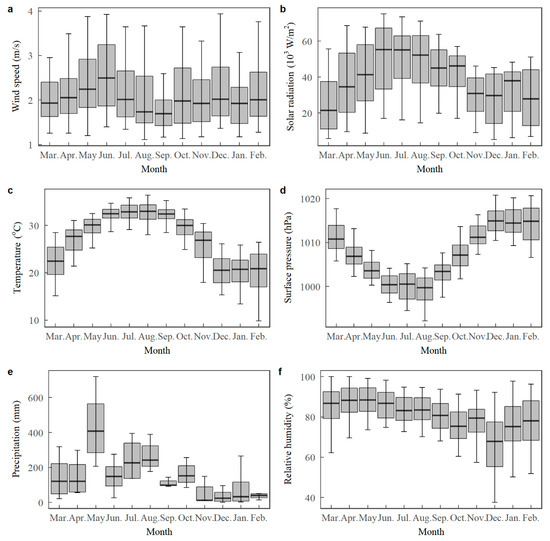
Figure 5.
Boxplot of (a) daily total solar radiation (103 W/m2), (b) daily mean wind speed (m/s), (c) daily maximum temperature (°C), (d) daily average surface pressure (hPa), (e) monthly total precipitation (mm), and (f) daily average relative humidity (%) at the site SY in each month from 2014 to 2017. The horizontal solid lines indicate the median and range, where the top and bottom of the box indicate the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively. The top and bottom whiskers indicate the 95th and 5th percentiles, respectively.
The relationships between daily maximum 8-h O3 and meteorological parameters are shown in Table 4. O3 is significantly positively correlated with both solar radiation and temperature. The correlation between O3 and solar radiation is strongest in the winter and moderate in the summer. The correlation between O3 and temperature is strong in the summer and winter. Wind speed is the least relevant factor, and O3 and wind speed are negatively correlated only in the winter (p < 0.001). O3 is negatively related to precipitation and relative humidity in all seasons. The relationship between O3 and surface pressure is inconsistent in different seasons with a negative relationship in the summer but a positive one in other seasons.

Table 4.
Analysis of the relationships between daily maximum 8-h O3 and meteorological parameters based on Spearman’s rank correlation. SR is the daily total solar radiation (W/m2), WS is the average daily wind speed (m/s), T is the daily maximum air temperature (°C), Prep is the daily total precipitation (mm), RH is the average daily relative humidity (%), and SP is the daily average surface pressure (hPa).
The relationship between high O3 air concentrations and wind speed/direction are shown in Figure 6. As can be seen from the figure, the high concentrations of O3 (greater than the 90th percentile for all observations) are controlled by a westerly wind direction with wind speeds of about 2–4 m/s for all seasons. The pattern is most distinct in the summer, with a single source of pollution from the northwest. In the autumn and winter seasons, there is obviously another pollution source from the northeast wind direction. The pattern is distinctive during the wintertime, where the probability of high O3 levels controlled by the northeast wind direction can reach as high as 0.7 with a wind speed of 6–9 m/s. The conditional probability of high O3 levels experienced for the southerly-like wind directions is very low in all seasons.
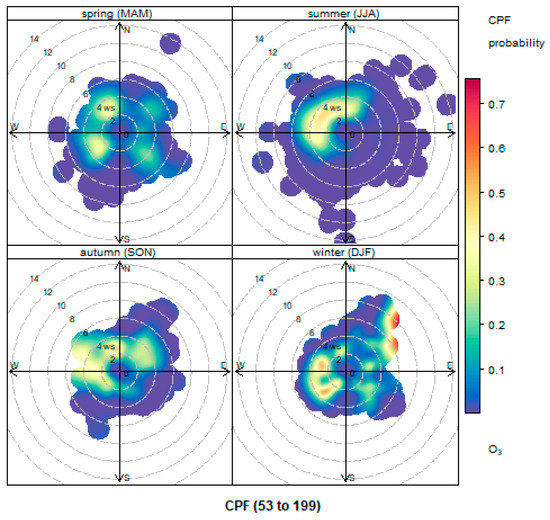
Figure 6.
Polar plot of O3 air concentrations at site SY in each season based on the conditional probability function (CPF) function for the higher percentiles (from 90th = 53 ppb to 100th = 199 ppb).
3.4 Trends of O3 and NOx from 2011 to 2017
The percentage of changes per year and the 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the daily maximum 8-h O3 and daily 24-h mean NOx from 2011 to 2017 are shown in Figure 7. The 8-h O3 shows an increase at all sites (see Figure 7a). The overall O3 growth rate follows the order of the urbanization rate across all sites (ZZL > SY > LG > XC). The increasing trends at ZZL and SY are significant with an estimated rate of 4.3% (95% CIs: 0.96, 8.25) per year (p < 0.05) and 3.61% (95% CIs: 0.36, 7.6) per year (p < 0.05), respectively. NOx decreased significantly at both sites (see Figure 7b). The decreasing rate is faster at ZZL, with an estimated rate of −5.85% (95% CIs: −7.99, −2.72) per year (p < 0.001), compared with −4.14% (95% CIs: −6.96, −0.26) per year at XC (p < 0.05).
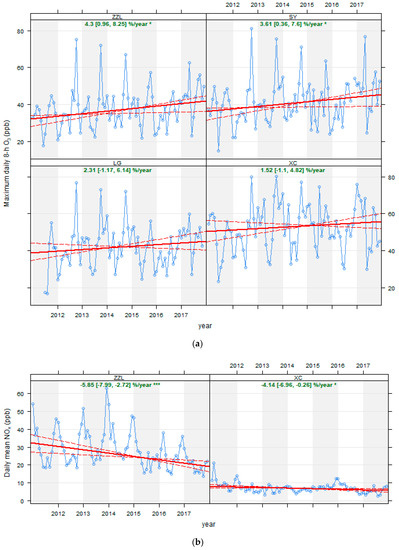
Figure 7.
The trend of (a) daily maximum 8-hour average O3, and (b) daily 24-h mean NOx from 2011 to 2017. The solid red line shows the trend estimate, and dashed red lines show the 95% confidence intervals for the trend based on resampling methods. The overall trend is shown at the top as the percentage of changes per year and the 95% confidence intervals of the slope. * and *** represent to the significance levels of p < 0.05 and p < 0.001, respectively.
The Theil-Sen trends of the maximum daily 8-h O3 and daily 24-h mean NOx for all representative sites during a specific period from 2011 to 2017 are shown in Table 5. The decline of NOx is fastest in the winter, with an average decline rate of −7.87% (p < 0.001) at the urban site and −9.45% (p < 0.1) at the rural site. The increase in O3 is fastest in the winter at more urbanized sites, with an average growth rate of 6.02% (p < 0.1) at the urban site and 8.89% (p < 0.1) at the suburban site. A negative trend (p > 0.1) is mainly found at less urbanized sites (LG and XC) in the autumn.

Table 5.
Theil-Sen trend of daily maximum 8-h average O3 and 24-h mean NOx values for all representative sites from 2011 to 2017 (%).
The Theil-Sen trends of the daily maximum 1-h O3 from 2011 to 2017 are shown in Table 6. The overall trends of daily maximum 1-h O3 are positive at all sites (p > 0.1). The overall O3 growth rate follows the order of the urbanization rate at the urban and suburban sites (ZZL > SY > LG). The slight decline in O3 occurs mainly at less urbanized sites in autumn, i.e., SY, LG, and XC. Only the urban site ZZL increases in all seasons. O3 increases faster on the weekend than on weekdays at all sites. In particular, the increasing trend of ZZL during the weekend is significant, with an estimated rate of 3.13% (95% CIs: −0.35, 6.87) per year (p < 0.1).

Table 6.
Theil-Sen trends of the daily maximum 1-h O3 for all representative sites from 2011 to 2017 (%).
4. Discussion
The common autumn (October) O3 maxima and summer (June) O3 minima at all representative sites are consistent with seasonal characteristics of O3 air concentrations in subtropical Asia, including western India [43], central and southwestern Taiwan [44,45], the PRD region [17,46], Hong Kong [28], and the South China Sea area [47]. All those areas are geographically close to each other and have similar atmospheric background conditions. Solar radiation, precipitation, and relative humidity are the most significant impact meteorological factors that affect O3 daily variations. The formation of O3 is favored by sunlight and high temperature [5,26,27,48]. The strong positive correlation in the winter between O3 and both of these meteorological factors is likely due to the cold season, which makes them limiting factors for O3 production. Surface pressure showed the opposite relationship in the summer and other seasons. O3 production favors high-pressure systems with the subsidence of air [28,47]. This explains the observed positive relationship between O3 and surface pressure in all other seasons except summer. This negative relationship in the summer was probably controlled by a synoptic-scale feature with the co-product of the negative correlation between temperature and pressure [48]. The negative correlation between O3 and relative humidity and precipitation explains the summer O3 trough. With an increase in relative humidity, the cloud abundance usually increases at the same time, and the photochemical processes of O3 production will decrease [27]. Rainy weather is also not conducive for O3 production, and heavy rain will remove O3 from the air [46].
In contrast, wind speed is the least relevant factor and is only negatively related to O3 levels in the winter. Higher wind speed will increase the turbulence of the air and cause dispersion of O3 [28]. The negative relationship between O3 and wind speed in winter might be influenced by the wind direction in winter which is an important factor that affects O3 transport [5]. Wind direction is found more important for influencing air pollutant levels. Shenzhen has at least two different sources of air pollution. One is a more regional emission source from the west and is active throughout the year. Emissions from the shipping business on the Pearl River Estuary and industrial activities in Guangzhou and Foshan to the west of Shenzhen might contribute to the continuous regional sources [49]. The high concentrations associated with the northeasterly wind in the winter confirms that the impact of air pollutant transport from northern China [5]. Interestingly, there are no substantial air pollutants associated with the southerly winds in all seasons, which means that contribution of air pollutants from big cities to the south of Shenzhen (i.e., Hong Kong) are less important in impacting air pollutants in Shenzhen.
The difference in NOx air concentrations is significant between weekdays and the weekend at the urban site. This is probably caused by a weekly routine of human activities. Traffic volume is increased in the city center during workdays. Similar to a previous study result for the PRD region, we also found no statistically significant difference between weekdays and the weekend at all sites in Shenzhen [46]. However, the O3 weekend effect was significant (p = 0.062) at the urban site, with O3 levels being 1.19 ppb higher on Sunday than on weekdays. O3 is elevated mainly by less on-road vehicular emissions on the weekend with NOx reduction and a lowered O3 titration effect [24,46,50]. In our study, we found the difference in O3 and NOx air concentrations between weekday and Saturday were less than those between Saturday and Sunday. A carryover of heavy Friday evening emissions is likely explained the diminished weekday and Saturday O3 difference [50]. Overtime work on Saturday might also be an important factor. Individual mobility studies show that a Saturday morning peak of passengers is significant, indicating a large proportion of citizens working on that day [51]. Moreover, heavy-duty trucks that contribute to strong emissions of NOx are more active on Saturday because of fewer traffic restrictions [52].
Different from a previous study that showed that central areas of Shenzhen had higher 1-h and 8-h O3 [17], we showed results similar to most large cities whereby the urban site has lower O3 compared with other sites [18,23,26]. The reliability of the previous study is questionable because only one-year observations were used and no statistical comparison was performed. Shenzhen had a lower maximum 1-h, 8-h, and cumulative O3, as well as exceedances of O3, compared with suburban and rural sites. The annual mean levels that are lower (p > 0.05) at SY than at ZZL may be caused by the low nighttime O3 at SY, possibly related to continuous emissions of NOx from industrial activities [53,54,55]. The characteristics of the O3 relationship between urban, suburban, and rural sites can be explained by O3 photochemical sensitivity as indicated by the O3 diurnal pattern. The sharp decline in O3 at the urban site in the early morning is mainly caused by the strong titration effect resulting from high levels of NO from traffic emissions when sunlight is limited for O3 production [53]. The slower O3 increasing rate at the urban site than at the suburban sites suggests O3 production might be limited by VOC availability [21,27].
The faster daytime O3 increasing rates at the suburban sites suggest a more suitable photochemical environment. The highest O3 daily peak and fastest O3 production rate at SY were possibly due to the abundance of both precursors. We previously reported high levels of NO2 in the surrounding area of SY, which were even higher than NO2 levels at the urban center [55]. Additionally, larger sources of VOCs are from vegetation emissions [21,23,30]. Moreover, industrial and construction activities are also active in suburban areas; both are major sources of anthropogenic VOC emissions [54]. According to research on O3 at a coastal site in South China, the highest O3 levels at the rural coastal site are probably due to weaker NO titration and a high O3 production rate because of stronger oxidative capacity in the air [56]. VOC data need to be measured as well to understand the O3 dynamics.
The overall NOx levels decreased significantly from 2011 to 2017. Winter has the highest NOx levels and the fastest decline rate. NOx is high in winter because of more emissions and longer NOx lifetime during the cold season [26]. In northern China, emissions from coal for heating are substantial; however, as a southern city, Shenzhen does not have central heating in the winter. As can be seen from the pollution rose map, the air pollutant levels in Shenzhen during the wintertime are greatly impacted by prevailing northeast winds which bring polluted air masses from northern China [5,28,47]. The fastest decline in winter at both sites is possibly attributed to the effectiveness of NOx control in northern China [15].
Different from previous simulation results, both daily maximum 1-h and 8-h O3 showed overall increases from 2011 to 2017 at all sites [15,25]. There is a clear linkage between the degree of urbanization and the direction of the O3 trends. The increases in O3 are profound in the winter at more urbanized sites. This rise can be attributed to increases in O3 from the transport of continental air masses by northeasterly wind and a lowered O3 titration effect by NO due to the NOx reduction [23,57]. A small decline in O3 occurred mainly at less urbanized sites in the autumn, the highest O3 season [22]. This implies that the photochemical sensitivity might shift from being VOC-sensitive to NOx-sensitive in the autumn when photochemical reactions are the most active [19,57]. The increasing changes in 1-h O3 at all sites indicate that the O3 sensitivity in the afternoon might not be limited by NOx availability in Shenzhen [57].
Great challenges remain in controlling O3 in Shenzhen. Generally speaking, the O3 chemistry is mainly VOC-sensitive. As NOx decreases, O3 levels increase at all sites, with a faster increasing rate at more urbanized areas, posing greater human health risks in areas with high population density. Our results showed a slight decline of O3 in autumn, which means that controlling NOx emissions in this period would be the most effective way of lowering the O3 levels in the less urbanized areas. For the more urbanized sites, emphasis should be placed on VOC reduction. The national VOC reduction strategy is specified in the 13th five-year plan (2015–2020). The goal was set to reduce major industrial VOC emissions by 10% compared with the 2015 level [58]. In Southern China, VOC emissions are dominated by biogenic sources [32]. More work is needed for spatial variability and the O3 formation potential of VOCs for more efficient O3 control management.
5. Conclusions
In this study, four stations, including one urban, one rural, and two suburban sites in Shenzhen, were investigated for characteristics and trends of O3 air pollution from 2011 to 2017. O3 matched seasonal O3 characteristics of subtropical Asia, i.e., a maximum in the autumn (October) and a minimum in the summer (June). Solar radiation, precipitation, and relative humidity are the most important meteorological factors that affect O3 daily variations.
Wind speed is the least relevant factor, but wind direction is important in impacting the presence of high O3 air concentrations. Shenzhen has at least two different sources of air pollution. One is a more regional emission source from the west and is active throughout the year. Another source is active mainly in the winter, where the high concentrations are associated with the northeasterly wind indicating the impact of air pollutant transport from northern China. The impact of the southerly wind is minimal compared with other wind directions.
O3 pollution is serious in Shenzhen, with about 28–53% of days per year exceeding the WHO ambient O3 guideline, and about 1-3 times above the limits for vegetation protection. Both the human population and vegetation are exposed to high O3, and more exceedances occur at the suburban and rural sites than at the urban site.
The O3 weekend effect is significant (p = 0.062) at the urban site with O3 levels of 1.19 ppb higher on Sunday than on weekdays. A carryover of heavy Friday evening emissions and overtime work on Saturday might be the primary reason for a diminishing weekday and Saturday O3 difference.
Both 1-h and 8-h O3 are increasing at all sites, opposite to the trend of NOx levels. The rapid decline in NOx in the winter might be related to the transport of cleaner air masses from northern China. The increase in O3 is fastest in the winter at more urbanized sites. This can be attributed to the transport of elevated O3 from northern China and a reduced O3 titration effect with NOx reduction. A slight decline in O3 occurs at less urbanized sites in autumn. This might be caused by photochemical sensitivity shifting from being VOC-sensitive to NOx-sensitive during this period.
Our results show faster O3 increases in more urbanized areas, which brings greater human health risks to areas with high population density. Great challenges remain in controlling O3 in Shenzhen with the reduction of NOx. VOC reduction should be emphasized in more urbanized areas, while NOx reduction in the autumn would be the most effective way of controlling O3 levels. The characteristics and trends of VOCs need to be studied as well to understand O3 dynamics for more efficient O3 control.
Author Contributions
Data curation, L.Z. and C.Z.; formal analysis, D.H.; funding acquisition, Q.L. and B.H.; methodology, D.H. and X.W.; project administration, Q.L.; software, G.L.; supervision, Q.L.; visualization, L.S.; writing—original draft, D.H.; writing—review and editing, Q.L. and X.W.
Funding
This study was supported by the Innovation of Science and Technology Commission of Shenzhen Municipality via Grants JCYJ20170413164957461, in part by the Science Technology and Innovation Committee of Shenzhen Municipality under Grant GGFW2017073114031767, in part by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) via Grant 41701167 and U1435215, and in part by Excellent Youth Innovation Fund from Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology via Grant Y5G007.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannistraro, G.; Cannistraro, M.; Cannistraro, A.; Galvagno, A. Analysis of the Air Pollution in the Urban Center of Four Sicilian Cities. Int. J. Heat Technol. 2016, 34, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannistraro, M.; Ponterio, L.; Cao, J. Experimental study of air pollution in the urban centre of the city of Messina. MMC 2018, 79, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, K.; Nam, K.M.; Selin, N.E.; Lamsal, L.N.; Reilly, J.M.; Paltsev, S. Health damages from air pollution in China. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2012, 22, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, E. Impact of ozone on Mediterranean forests: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, E.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X. Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillman, S. The relation between ozone, NOx and hydrocarbons in urban and polluted rural environments. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 1821–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G.E.; et al. Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. The 12th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-12/05/content_5143290.htm (accessed on 9 November 2018). (In Chinese)
- Gu, D.; Wang, Y.; Smeltzer, C.; Liu, Z. Reduction in NOx emission trends over China: Regional and seasonal variations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 12912–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Satellite NO2 retrievals suggest China has exceeded its NOx reduction goals from the twelfth Five-Year Plan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Yan, L.; Zheng, Y.; He, K. Recent reduction in NOx emissions over China: Synthesis of satellite observations and emission inventories. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Henze, D.K.; Capps, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Keller, M. Monthly top-down NOx emissions for China (2005–2012): A hybrid inversion method and trend analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4600–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Zhao, B.; Jang, C.; Hao, J. Effectiveness of national air pollution control policies on the air quality in metropolitan areas of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Heilig, G.K.; Chen, J.; Heino, M. Interactions between economic growth and environmental quality in Shenzhen, China’s first special economic zone. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Krafft, T. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Ozone and Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disease Mortalities Due to Ozone in Shenzhen. Sustainability 2017, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, J.; Ma, H.; Zheng, J.; Lin, D.; et al. The association between air pollution and outpatient and inpatient visits in Shenzhen, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Lyu, X.P.; Deng, X.J.; Guo, H.; Deng, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.Q. Assessment of regional air quality resulting from emission control in the Pearl River Delta region, southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Goldmann, M.; Lagercrantz, J. Sustainable Mobility the Chinese Way—Opportunities for European Cooperation and Inspiration; Exakta Print: Malmö, Sweden, 2018; pp. 1–107. ISBN 978-91-87379-45-1. [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti, E.; de Marco, A.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Manning, W.J. Ozone levels in European and USA cities are increasing more than at rural sites, while peak values are decreasing. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.; Reff, A.; Wells, B.; Xing, J.; Frank, N. Ozone trends across the United States over a period of decreasing NOx and VOC emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, P.; Serra, R.; Rossello, P. Spatiotemporal trends in ground-level ozone concentrations and metrics in France over the time period 1999–2012. Environ. Res. 2016, 149, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, K.; Lv, W.; Li, J.; Zhong, L.; Ou, Y.; Chen, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fast increasing of surface ozone concentrations in Pearl River Delta characterized by a regional air quality monitoring network during 2006–2011. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Fung, J.C.H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, S. Importance of NOx control for peak ozone reduction in the Pearl River Delta region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9428–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhu, K.; Wang, T.; Chen, P.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Shu, L. Temporal characterization and regional contribution to O3 and NOx at an urban and a suburban site in Nanjing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; He, M.; Xu, N.; Zhang, J.; Qian, F.; Feng, J.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides at urban, suburban and rural sites in Ningbo, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.Y.; Cheung, T.F.; Lam, K.S. A study of surface ozone and the relation to complex wind flow in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3203–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.-M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chameides, W.L.; Lindsay, R.W.; Richardson, J.; Kiang, C.S. The role of biogenic hydrocarbons in urban photochemical smog: Atlanta as a case study. Science 1988, 241, 1473–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinman, L.I.; Daum, P.H.; Imre, D.; Lee, Y.N.; Nunnermacker, L.J.; Springston, S.R.; Weinstein-Lloyd, J.; Rudolph, J. Ozone production rate and hydrocarbon reactivity in 5 urban areas: A cause of high ozone concentration in Houston. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Holloway, T. Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7229–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenzhen Statistics Bureau, NBS Survey Office in Shenzhen. Shenzhen Statistical Yearbook—2017. Available online: http://www.sztj.gov.cn/xxgk/zfxxgkml/tjsj/tjnj/ (accessed on 1 November 2018). (In Chinese)
- China Meteorological Administration. China Atmospheric Composition Monitoring Service Specification; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 1–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Linderholm, H.; Chen, D.; Walther, A. Trends of the thermal growing season in China, 1951–2007. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The proof and measurement of association between two things. Am. J. Psychol. 1904, 15, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods. Biom. Bull. 1945, 1, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R package for air quality data analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for statistical computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Oxide and Sulfur Dioxide—Global Update. 2005. Available online: http://www.who.int/phe/health_topics/outdoorair/outdoorair_aqg/en/ (accessed on 9 November 2018).
- Lal, S.; Naja, M.; Subbaraya, B.H. Seasonal variations in surface ozone and its precursors over an urban site in India. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2713–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Wang, Z.; Chou, C.C.K.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, S.C. A numerical study of an autumn high ozone episode over southwestern Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3684–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, D.H.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, C.H.; Chan, C.C. A study of ground-level ozone pollution, ozone precursors and subtropical meteorological conditions in central Taiwan. J. Environ. Monit. 2008, 10, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhong, L.; Wang, T.; Louie, P.K.K.; Li, Z. Ground-level ozone in the Pearl River Delta region: Analysis of data from a recently established regional air quality monitoring network. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, H.; Blake, D.R.; Kwok, Y.H.; Simpson, I.J.; Li, Y.S. Measurements of trace gases in the inflow of South China Sea background air and outflow of regional pollution at Tai O, southern China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2005, 52, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ji, X.; Deng, X. Surface ozone and meteorological condition in a single year at an urban site in central–eastern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 151, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yue, J.; Cao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, R. Seasonal variations and chemical characteristics of sub-micrometer particles (PM1) in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 118, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.L.; Tanenbaum, S.J. Differences between weekday and weekend air pollutant levels in southern California. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2003, 53, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hou, A.; Biderman, A.; Ratti, C.; Chen, J. Understanding individual and collective mobility patterns from smart card records: A case study in Shenzhen. In Proceedings of the 12th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, St Louis, MO, USA, 4–7 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Fung, J.C.H.; Xue, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, J.; Lau, A.K.H. Ozone changes in response to the heavy-duty diesel truck control in the Pearl River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Lei, W.F.; Tie, X.X.; Hess, P. Industrial emissions cause extreme urban ozone diurnal variability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6346–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, J.; Ma, B. Industrial zone development policy related to real estate and transport outcomes in Shenzhen, China. Land Use Policy 2015, 47, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, L. Tougher Targets for China’s Clean Air Cities? Implications from Air Quality Assessment in Shenzhen. Preprints 2018, 2018100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lyu, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zou, S.; Ling, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, F.; Zeren, Y.; Pan, W.; et al. Ozone pollution around a coastal region of South China Sea: Interaction between marine and continental air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4277–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zeng, L.; Hu, M.; Cohan, D.; Russell, A. Decoupled direct sensitivity analysis of regional ozone pollution over the Pearl River Delta during the PRIDE-PRD2004 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4941–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. The 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-03/17/content_5054992.htm (accessed on 9 November 2018). (In Chinese)
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).