Abstract
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation is a well-known curative treatment for patients with chronic granulomatous disease. We present our experiment regarding ten patients with chronic granulomatous disease who underwent a reduced intensity conditioning regimen consisting of melfalan, fludarabine, and antithymocyte globulin. Donor lymphocyte infusion was used in three representative patients who developed mixed donor chimerism. After at least 2 years of median follow-up, 8 of the 10 patients are alive and well.
1. Introduction
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is the only curative treatment for patients with Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) which is a primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by an inherited defect in one of five subunits of the neutrophilic NADPH oxidase that leads to life threatening bacterial and fungal infections. In addition to the proneness for infection, hyperinflammation and noninfectious inflammatory complications such as colitis are important parts of the symptomatology in CGD [1,2]. Myeloablative conditioning regimens have been historically employed in CGD, but due to myeloablative several disadvantages including greater susceptibility to tissue injury, longer duration of neutropenia, and fears of secondary tumors, nowadays, reduced-intensity conditioning (RIC) regimens are being used progressively more in different centers [3,4,5,6]. RIC regimens have been used to diminish transplant-related mortality, but carry the risk of mixed donor-recipient chimerism that may progress to graft loss [7]. The likelihood of graft rejection in the mentioned approach could be reduced by infusions of donor lymphocytes after transplantation [8,9,10].
We describe here the experience of our center with a reduced toxicity regimen for patients with CGD and donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) in those who appeared to have mixed chimerism.
2. Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis of ten patients who underwent allogeneic HSCT for CGD at Shariati hospital, Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Research Center (HORCSCT), Tehran, Iran. The characteristics of the patients are listed in Table 1. The diagnosis of CGD in our patients was confirmed by nitroblue tetrazolium test (NBT) [11]. Unfortunately, molecular diagnosis and genetic testing was not available for any of the patients. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching of the donors and recipients was confirmed by molecular typing of the HLA class I and HLA class II loci and all the donors were fully matched. All the patients were using sulphamethoxazole-trimethoprim and itraconazole as bacterial and fungal infection prophylaxis at the time of stem-cell transplantation. Four of the patients were receiving interferon gamma therapy at the time of HSCT; five of the patients were on antituberculosis prophylaxis by isoniazid due to history of disseminated BCGosis or pulmonary tuberculosis.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the patients and donors.
All patients had undergone a conditioning regimen consisting of melphalan at a dose of 70 mg per square meter of body-surface area (days 7 and 6 before transplantation), fludarabine at a dose of 30 mg per square meter of body-surface area (days 5 to 1 before transplantation), and antithymocyte globulin at a dose of 2.5 mg per kilogram (days 5 to 2 before transplantation). Administration of cyclosporine was started on day 4 before transplantation.
3. Results
From May 2012 to October 2016, ten patients with CGD were submitted to HSCT in our center. Median age at transplant was 9 years (range 1–15).
The least follow-up time was 2 years. The median duration of neutropenia (defined as an absolute neutrophil count of <500 per cubic millimeter) was 11 days (range, 8 to 11), and the median duration of thrombocytopenia (defined as a platelet count of <20,000 per cubic millimeter) was 13 days (range: 11 to 15). Characteristics of HSCT course in the patients are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Characteristics of HSCT course in the patients.
Acute graft versus host disease (GVHD) grade II-III was encountered in 4 patients (1 = only skin and 1 = skin, gut and liver, 1 = only gut and 1 = only liver). One patient developed limited chronic pulmonary GVHD.
Three month after HSCT, low donor chimerism (less than 40%) was encountered in 4 patients, among which DLI was employed for 3 patients. In the first patient, after one episode of DLI, chimerism was reached from 40% to 95%. In two other patients, even after three episodes of DLI, donor chimerism was sustained at a level of about 30% with which patients remained symptom free until the present time (Figure 1). In one of the patients with mixed chimerism due to unavailability of the donor’s vein access, DLI could not happen; however, with only tapering the dose of cyclosporine, donor chimerism reached 95% within 2 months.
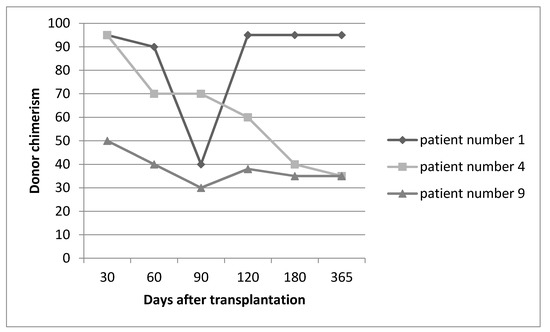
Figure 1.
Sequence of donor chimerism in three representative patients who underwent DLI.
As a final point, eight of ten patients are alive and symptom free at the present time.
4. Discussion
Allogeneic HSCT with reduced toxicity regimen is a good alternative in the treatment of patients with CGD. However, it carries an increased risk of incomplete donor hematopoietic cells engraftment or graft rejection. Studies have shown that even partial engraftment of donor stem cells is able to restore normal immune function in patients with CGD [12]. Donor lymphocytes infusion could be an aid for overcoming incomplete engraftment in these patients. Horwitz et al. using a nonmyeloablative T cell depleted HSCT in patients with CGD, confirmed the existing data showing that infusion of donor lymphocytes in graded increments could facilitate engraftment of donor stem cells [5,10]. In our experiment, DLI helped one of the patients to reach full donor chimerism and helped the other two to stay symptom free.
Considering the transplant related mortality, our only patient whose donor was unrelated, died due to sepsis, and one of our patients developed deterioration of mental status and progressive encephalopathy after receiving fludarabine, which is a rare but known adverse effect of the mentioned drug [13,14]. She unfortunately died due to complications of CNS toxicity while developing full donor chimerism. Other series have reported death due to progressive fungal infection and severe GvHD in their patients with CGD after HSCT [3].
From the GvHD point of view, none of our patients encountered severe GvHD. In a survey of the European experience, using a myeloablative busulphan-based regimen, severe GVHD developed in 4 out of 27 patients [13]. Interestingly, those patients who had mixed donor chimerism did not develop GvHD. It is reported that mixed hematopoietic chimerism is able to suppress GvHD occurrence with poorly understood mechanisms [15,16,17,18].
In conclusion, we suggest that the HSCT with a reduced intensity conditioning regimen from an HLA-identical sibling could benefit patients with CGD, and DLI could be useful for those who are leaning towards graft failure.
Author Contributions
T.R. and A.K. managed the patients and performed the study, analysed data and co-wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare having no conflict of interest.
References
- Smith, R.J.; Shearer, A.E.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Van Camp, G. GeneReviews® [Internet]; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Åhlin, A.; Fasth, A. Chronic granulomatous disease–conventional treatment vs. hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: An update. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seger, R.A.; Gungor, T.; Belohradsky, B.H.; Blanche, S.; Bordigoni, P.; Di Bartolomeo, P.; Flood, T.; Landais, P.; Müller, S.; Ozsahin, H.; et al. Treatment of chronic granulomatous disease with myeloablative conditioning and an unmodified hemopoietic allograft: A survey of the European experience, 1985–2000. Blood 2002, 100, 4344–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gungor, T.; Halter, J.; Klink, A. Successful low toxicity hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for high-risk adult chronic granulomatous disease patients. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, M.E.; Barrett, A.J.; Brown, M.R. Treatment of chronic granulomatous disease with nonmyeloablative conditioning and a T-cell-depleted hematopoietic allograft. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, B.; Mahadeo, K.; Kapoor, N.; Abdel-Azim, H. Low-dose total-body irradiation and alemtuzumab-based reduced-intensity conditioning regimen results in durable engraftment and correction of clinical disease among children with chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatric Transplant. 2015, 19, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshrine, B.; Morsheimer, M.; Heimall, J.; Bunin, N. Reduced-intensity conditioning for hematopoietic cell transplantation of chronic granulomatous disease. Pediatric Blood Cancer 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aker, M.; Kapelushnik, J.; Pugatsch, T. Donor lymphocyte infusions to displace residual host hematopoietic cells after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for beta-thalassemia major. J. Pediatric Hematol. Oncol. 1998, 20, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, A.J.; Mavroudis, D.; Tisdale, J. T cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation and delayed T cell add-back to control acute GVHD and conserve a graft-versus-leukemia effect. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998, 21, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akioka, S.; Itoh, H.; Ueda, I. Donor lymphocyte infusion at unstable mixed chimerism in an allogeneic BMT recipient for chronic granulomatous disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998, 22, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Baehner, R.L.; Nathan, D.G. Quantitative nitroblue tetrazolium test in chronic granulomatous disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1968, 278, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamani, N.; August, C.S.; Douglas, S.D.; Burkey, E.; Etzioni, A.; Lischner, H.W. Bone marrow transplantation in chronic granulomatous disease. J. Pediatric 1984, 105, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.G.; Leyland-Jones, B.R.; Caryk, S.M.; Hoth, D.F. Central nervous system toxicity of fludarabine phosphate. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1986, 70, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beitinjaneh, A.; McKinney, A.M.; Cao, Q.; Weisdorf, D.J. Toxic leukoencephalopathy following fludarabine-associated hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011, 17, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ildstad, S.T.; Wren, S.M.; Bluestone, J.A.; Barbieri, S.A.; Stephany, D.; Sachs, D.H. Effect of selective T cell depletion of host and/or donor bone marrow on lymphopoietic repopulation, tolerance, and graft-vs-host disease in mixed allogeneic chimeras. J. Immunol. 1986, 136, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sykes, M.; Sheard, M.A.; Sachs, D.H. Graft-versus-host-related immunosuppression is induced in mixed chimeras by alloresponses against either host or donor lymphohematopoietic cells. J. Exp. Med. 1988, 168, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, M.; Eisenthal, A.; Sachs, D.H. Mechanism of protection from graftvs- host disease in murine mixed allogeneic chimeras. I. Development of a null cell population suppressive of cell-mediated lympholysis responses and derived from the syngeneic bone marrow component. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.S.; Petersen, F.B.; Storb, R. Mixed hematologic chimerism after allogeneic marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia is associated with a higher risk of graft rejection and a lessened incidence of acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1986, 67, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).