Abstract
(1) Background. Rickettsia japonica (R. japonica) infection induces severe inflammation, and the disappearance of eosinophil in the acute stage is one of the phenomena. (2) Materials and Methods. In the current study, we measured the serum concentrations of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in the acute and recovery stages. (3) Results. In the acute phase, IL-6 and IFN-γ levels were elevated and we speculated that they played a role as a defense mechanism against R. japonica. The high concentration of IFN-γ suppressed the differentiation of eosinophil and induced apoptosis of eosinophil, leading to the disappearance of eosinophil. On day 7, IL-6 and IFN-γ concentrations were decreased, and Th2 cytokines such as IL-5 and IL-9 were slightly increased. On day 14, eosinophil count recovered to the normal level. The transition of serum cytokine concentration in R. japonica infection was presented. (4) Conclusions. IL-6 and IFN-γ seem to be critical cytokines as defense mechanism against R. japonica in the acute phase, and this may deeply connect to the decrease of eosinophil.
1. Introduction
Japanese spotted fever (JSF) caused by Rickettsia japonica (R. japonica) infection was first reported from Tokushima Prefecture in Japan in 1984 [1]. The typical symptom of JSF is characterized by diffuse erythema on the whole body, palmar erythema, headache, high fever, and chills after two to eight days following a tick bite [2,3]. Tetracycline is recommended to treat JSF. One of the severest complications is disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), low consciousness level, low blood pressure, multiple organ failure, and edema, which occurs if the disease progress is sudden or the diagnosis of JSF is delayed, and some fatal cases have been reported [2,3,4]. Therefore, the deterioration of symptoms following a JSF infection needs to be understood. R. japonica infection induces severe inflammation [2,5], and moreover the disappearance of eosinophil in the acute stage of JSF is one of the phenomena. In the current study, we measured the serum concentrations of Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in the acute and recovery stages and discussed the possible immune mechanism in R. japonica infection.
2. Materials and Methods
This study enrolled 7 patients (3 males and 4 females from 70 to 87 years old, living in the endemic area in Mie Prefecture, Japan) after obtaining written informed consent. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Mie University (Tsu, Mie, Japan, permit number 3064). All patients were diagnosed as having JSF by performing PCR for R. japonica-specific DNA from blood and/or skin samples [6], or anti-R. japonica antibody titer of IgM > 80 in the acute stage, or elevation of IgM and/or IgG more than 4 times in the recovery stage compared to acute stage by indirect immunofluorescence assay (IFA). For this assay slides are coated by Vero cells cultured with R. japonica and incubated with the patient’s serum. If antibodies against R. japonica are present, the cells fluoresce.
The serum samples were collected at the first visit (day 1, acute stage) and 14 days after the first visit (recovery stage) and then stored at −80 °C before use. Serum samples were also collected on days 3 and 7 for cases 1–3. We measured cytokine concentrations including Th1 (IFN-γ, IL-12p70, TNF-α, IL-2, IL-8), Th2 (IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-33), and Th17 (IL-6, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-22). All patients received minocycline on day 1 and recovered on day 14 with no symptoms of JSF and no abnormal data. For cases 1, 2, and 3, the above-mentioned cytokines were measured at 4 points: days 1, 3, 7, and 14. The cytokine measurements were performed with 15 µL of serum for each sample using a panel kit (AimPlex Biosciences, Pomona, CA, USA) and flow cytometer analysis with a BD Accuri C6 device (Becton, Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We also presented data of white blood cell (WBC), neutrophil, and eosinophil count, as well as C-reactive protein (CRP). The data were measured at the laboratory in our hospital by using an automated indicator.
Statistical analysis was performed using PRISM software version 6 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA). The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare cytokine concentrations between days 1 and 14. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. WBC and CRP
In all cases, WBC count was elevated in the acute stage and decreased in the recovery phase. The neutrophil count showed similar tendency. Six of the seven patients showed no eosinophil count initially, although one case showed 0.2% in the acute stage, which increased in the recovery stage. CRP was elevated in all cases in the acute stage but decreased to the negative range. All patients responded well without erythema, fever, and fatigue by the treatment of minocycline (Figure 1).
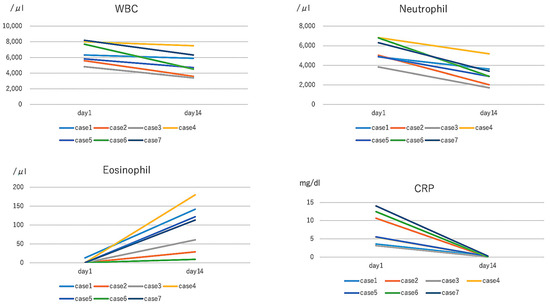
Figure 1.
In the acute phase, white blood cell (WBC) and neutrophil were within the normal range, and C-reactive protein (CRP) were increased, but decreased at day 14 by the treatment of minocycline. The loss of eosinophil was detected in the acute stage but recovered to the normal range in all cases.
3.2. Inflammatory Cytokine
Among the 13 cytokines that we measured, IFN-γ and IL-6 levels were increased in the acute stage and decreased clearly after the treatment except for cases 3 and 5. Regarding the other measured Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines, Th1 cytokines showed a slightly decreased tendency in most of the cases. In contrast, Th2 and Th17 cytokines were unchanged for two data points. In case 3, the counter cytokines against intracellular parasite, IL-6 was undetected at days 1 and 14, but other cytokines were detected (Figure 2). Statistical analysis was performed for the cytokine concentration between days 1 and 14, and significance was detected in IFN-γ and IL-6 levels (p = 0.0111).
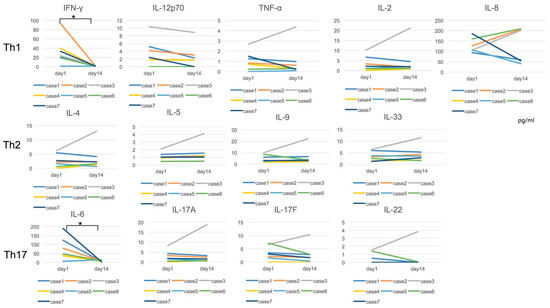
Figure 2.
Cytokine concentration in the acute and recovery stages is shown. The increased IFN-γ and IL-6 levels were clearly decreased in the recovery stage in most of the cases. For Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines, except for IFN-γ and IL-6, cytokine levels were unchanged for 2 data points (days 1 and 14). Case 3 was exceptional and the cytokines, except for IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-12p70, were elevated in the recovery stage. Statistical analysis was performed for the cytokine concentration between days 1 and 14, and significance was detected in IFN-γ and IL-6 levels (* p = 0.0111).
Cytokine concentration was measured at four points in cases 1, 2, and 3. Among 13 cytokines, elevated IFN-γ and IL-6 levels were clearly decreased over time (Figure 3). Th1 cytokines including IL-12p70, TNF-α, IL-2, and IL-8 did not show this decrease. IL-5 and IL-9 are involved in the Th2 cytokine families, and there seems to be no significance in two points of the acute and recovery stages (Figure 2). However, the concentrations of those cytokines increased on day 7 and then decreased in the recovery stage close to the day 1 level. IL-17A/F also showed a slight elevation on days 3 and 7 (Figure 3).
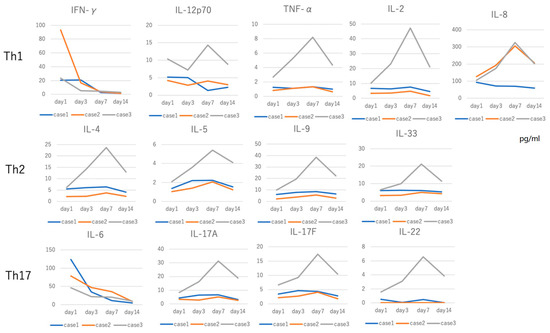
Figure 3.
Cytokine concentrations were measured at 4 points in cases 1, 2, and 3. IFN-γ and IL-6 levels showed a peak on day 1, and reduced in a time-dependent manner. IL-5 and IL-9 are involved in the Th2 cytokine families, and the concentrations of those cytokines increased on day 7 and then decreased in the recovery stage. Th17 families except for IL-6 showed a slight peak on day 7. This tendency was not noticed for 2 data points (days 1 and 14).
4. Discussion
There has been a report of R. japonica infection focused on inflammatory cytokines. In R. japonica infection, IL-6, IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-8, MCP-1a, and MIP-1β levels were elevated according to the previous report [7].
The first line of defense against Rickettsia infection is phagocytosis by macrophage, but Rickettsia is so-called macrophage-tropic bacteria, and interaction occurs during the phagocytosis, releasing IL-6 and IFN-γ from macrophage as an immune protection. Rickettsia existing as an intracellular parasite has the ability to infect the endocapillary cells. Although IL-6 is the key cytokine for the differentiation of Th17 cells, IL-6 was released from the stimulated macrophage-activated Th1 cells during the acute stage of R. japonica infection, and Th1 cells produced IFN-γ. IL-6 together with IFN-γ strongly activate macrophage and evoke differentiation of naïve T cells into mature Th1 cells in order to attack pathogens such as R. japonica from the outside [8,9].
In Rickettsia infection, a high level of CRP was detected, but WBC count showed a slight elevation. A previous report showed that eosinophil counts were diminished similarly to the current cases [10]. Because of the low concentration on day 1 and the increase on day 7 of Th2 cytokine including IL-4, IL-5, and IL-33, we speculated that there may be suppressing factors on eosinophil in R. japonica infection, which is purposeful in the acute stage. Th2 cytokines have lower priority because of no necessity of differentiation to eosinophil in the acute phase. The high concentration of IFN-γ suppresses the differentiation of eosinophil and induces apoptosis of eosinophil [11], leading to the disappearance of eosinophil. Around day 7, the number of R. japonica is decreased, together with the decrease in IL-6 and IFN-γ concentrations, and the number of eosinophil recovers and Th2 and Th17 cytokines are relatively increased. In the current study, case 3 showed a high concentration in most cytokines measured, although the patient did not have a specific past history such as immunodeficiency, severe allergy, or clinical course associated with multiple organ failure and but there might be another accidental event. Otherwise, the innate and acquired immune system may react strongly against danger signals in case 3.
5. Conclusions
We reported the cytokine levels in patients infected by R. japonica before and after the treatment of minocycline. The current information would be beneficial to understanding the immune reaction against R. japonica infection especially for four data points. IL-6 and IFN-γ seem to be critical cytokines as a defense mechanism against R. japonica in the acute phase, and this may be linked to the decrease in eosinophils.
Author Contributions
M.K. planned and investigated the study after obtaining informed consent from patients and wrote this article. Y.M., K.M., and S.I. analyzed the data. K.H. and K.Y. offered advice for the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors did not receive any financial support for the present study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mahara, F. Three Weil-Felix reaction (OX2) positive cases with skin eruptions and high fever. J. Anan. Med. Assoc. 1984, 68, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, M.; Nishii, M.; Gabazza, E.C.; Kurokawa, I.; Akachi, S. Nine cases of Japan spotted fever diagnosed at our hospital in 2008. Int. J. Dermatol. 2010, 49, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahara, F. Japanese spotted fever: Report of 31 cases and review of the literature. Emer. Inf. Dis. 1997, 3, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, K.; Senba, T.; Yamauchi, H.; Nomura, T.; Chikahira, Y. Clinical study of Japanese spotted fever and its aggravating factors. J. Infect. Chemother. 2003, 9, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Fujimoto, T.; Ebisutani, C.; Horiguchi, H.; Ando, S. The first fatal case of Japanese spotted fever confirmed by serological and microbiological tests in Awaji Island, Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 60, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furuya, Y.; Katayama, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Haiho, I. Specific amplification of Rickettsia japonica DNA from clinical specimens by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.; Iwasaki, H.; Ikegaya, S.; Takada, N.; Tamaki, Y.; Tabara, K.; Ueda, T. Significantly higher cytokine and chemokine levels in patients with Japanese spotted fever than in those with Tsutsugamushi disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, M.; Oshita, S.; Yamazoe, N.; Miyazaki, M.; Takemura, Y.C. Important Clinical Features of Japanese Spotted Fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 99, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, A.; Driss, V.; Hornez, N.; Abdallah, M.; Roumier, T.; Abboud, G.; Legrand, F.; Staumont-Salle, D.; Queant, S.; Bertout, J.; et al. Eosinophil–derived IFN-gamma induces airway hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in the absence of lymphocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).