Abstract
Ceftriaxone sodium is a cephalosporin with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and belongs to the third generation of cephalosporins. Regarding the quality control of medicines, a validated microbiological assay for the determination of ceftriaxone sodium in powder for injectable solution has not been reported yet. This paper reports the development and validation of a simple, accurate and reproducible agar diffusion method to quantify ceftriaxone sodium in powder for injectable solution. The assay is based on the inhibitory effect of ceftriaxone sodium on the strain of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 9371 IAL 1027 used as test microorganism. The results were treated statistically by analysis of variance and were found to be linear (r = 0.999) in the selected range of 15.0–60.0 μg/mL, precise with a relative standard deviation (RSD) of repeatability intraday = 1.40%, accurate (100.46%) and robust with a RSD lower than 1.28%. The results demonstrated the validity of the proposed bioassay, which allows reliable ceftriaxone sodium quantitation in pharmaceutical samples and therefore can be used as a useful alternative methodology for the routine quality control of this medicine.
1. Introduction
The key intermediate for semisynthetic production of a large number of cephalosporins is 7-aminocephalosporanic acid, which is formed by hydrolysis of cephalosporin C produced by fermentation. Cephalosporins can be divided into first, second, third and fourth generation agents, based roughly on the time of their discovery and their antimicrobial properties [1,2,3,4,5].
Among the cephalosporins, ceftriaxone sodium has excelled in the healthcare market, especially in the hospital [6]. Ceftriaxone sodium is a semisynthetic cephalosporin of the third generation with high antibacterial activity, which is widely used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible, usually Gram-positive organism, meningitis caused by aerobic Gram-negative bacteria and other medical conditions [6,7,8,9,10]. The chemical structure of ceftriaxone sodium is represented in Figure 1.
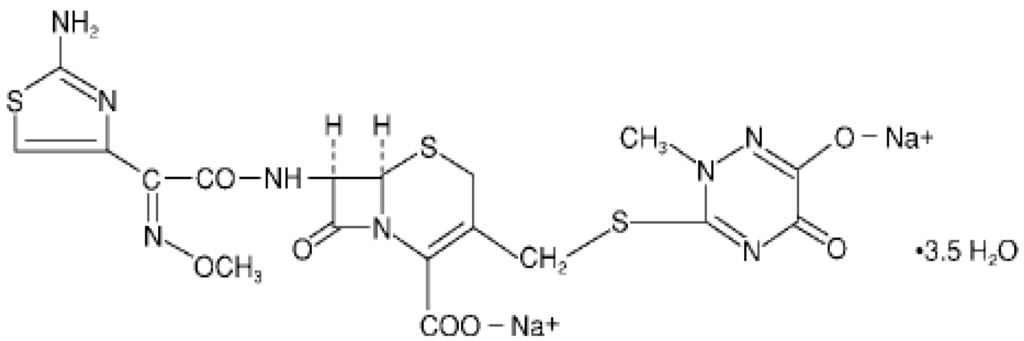
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of ceftriaxone sodium (CAS 74578-69-1).
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of ceftriaxone sodium (CAS 74578-69-1).
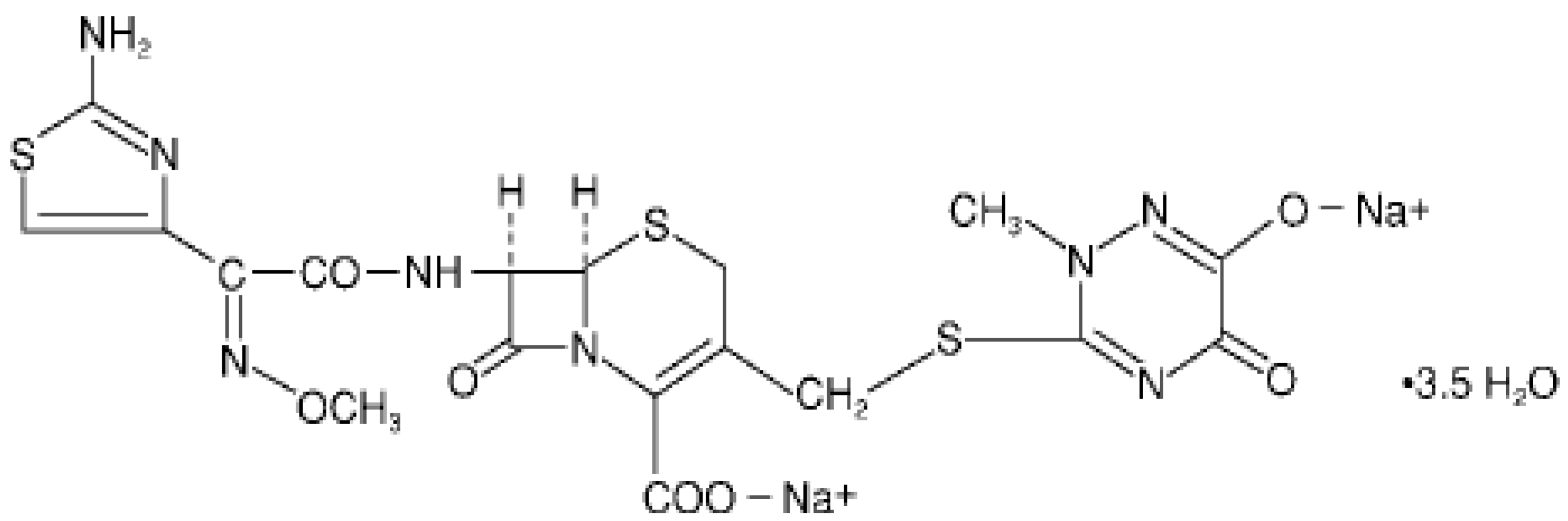
Ceftriaxone sodium is chemically known as, (Z)-7-[2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetylamido]-3-[(2,5-dihydro-6-hydroxy-2-methyl-5-oxo-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)thiamethyl]-3-cephem-4-carboxylic acid, disodium salt [11,12].
Ceftriaxone sodium is administered parenterally and it penetrates into the body fluids and tissues in a satisfactory manner. Two factors contribute to the prolonged duration of action of ceftriaxone: a high fraction protein binding in the plasma and a slow urinary excretion. Ceftriaxone is excreted both in the bile and in the urine [13,14].
In the references several methods of analysis for ceftriaxone sodium were found. These methods are high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [15,16,17,18] fluorimetry [19,20], titration [21], spectrophotometric [21,22,23,24,25] and micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography [26,27,28].
However, only a few methods of analysis for ceftriaxone sodium are standardized in official compendia; the literature still needs new analytical procedures aimed at speed, selectivity, low cost and simplicity of application in work routines in the quality control of pharmaceutical industries.
Hence, an attempt has been made to develop a simple, accurate and reproducible method for the determination of ceftriaxone sodium in pharmaceutical dosage forms along with method validation.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
The ceftriaxone sodium reference substance (assigned purity 99.8%) was supplied by Sigma-Aldrich. The lyophilized powder for injectable solutions containing 1g of ceftriaxone sodium was kindly donated by União Química Company (Pouso Alegre, MG, Brazil). All reagents used were of analytical grade. Purified water was used in all experiments.
2.2. Ceftriaxone Sodium Reference Solutions
An accurately weighed amount of powder equivalent to 12.5 mg of ceftriaxone sodium reference standard was transferred to 25 mL volumetric flasks and added to a phosphate buffer with pH 6.0 to obtain the final concentration of 500 μg/mL. Aliquots of 300, 600 and 1200 µL of this solution were transferred to a 10 mL volumetric flask supplemented with a phosphate buffer at pH 6.0 to obtain solutions with the concentrations of 15.0, 30.0 and 60.0 μg/mL (S1, S2 and S3), respectively that were used in the bioassay.
2.3. Preparation of the Sample Solutions
The content of the three vials containing an average weight of 1.1 g lyophilized powder ceftriaxone sodium was added to a closed container. A quantity of powder, equivalent to 12.5 mg of ceftriaxone sodium, was transferred to a 25 mL volumetric flask supplemented with a phosphate buffer with pH 6.0. Aliquots of this solution were transferred into flasks of 10 mL in pH 6.0 phosphate buffer solution to give concentrations of 15.0, 30.0 and 60.0 μg/mL (T1, T2 and T3), respectively, which were tested against S1, S2 and S3.
2.4. Microorganism and Inoculum Standardization
Bacillus subtilis ATCC 9371 IAL 1027 used in micro test showed to be more suitable due to their susceptibility to ceftriaxone sodium and the ability to form well-defined growth inhibition zones allowing accurate measurements and reduced pathogenicity compared with other microorganisms. The cultures of B. subtilis ATCC 9371 IAL 1027 were grown and maintained in culture medium Casoy (Difco, Brazil).
The organism was standardized according to the procedure described in Brazil and the United States Pharmacopoeia [29,30]. Before use, the microorganism was cultured in Casoy broth in an Erlenmeyer flask which was incubated for 24 h at 35 ± 2 °C. Using a spectrophotometer with the wavelength set at 580 nm and an absorption cell 10 mm, the broth containing the microorganism was diluted to give a suspension containing 25 ± 2% turbidity (transmittance) using a sterile broth as a blank. From this standardized suspension, an aliquot of 1.0 mL was used in through-Grove Randal n°2.
2.5. Agar Diffusion Bioassay
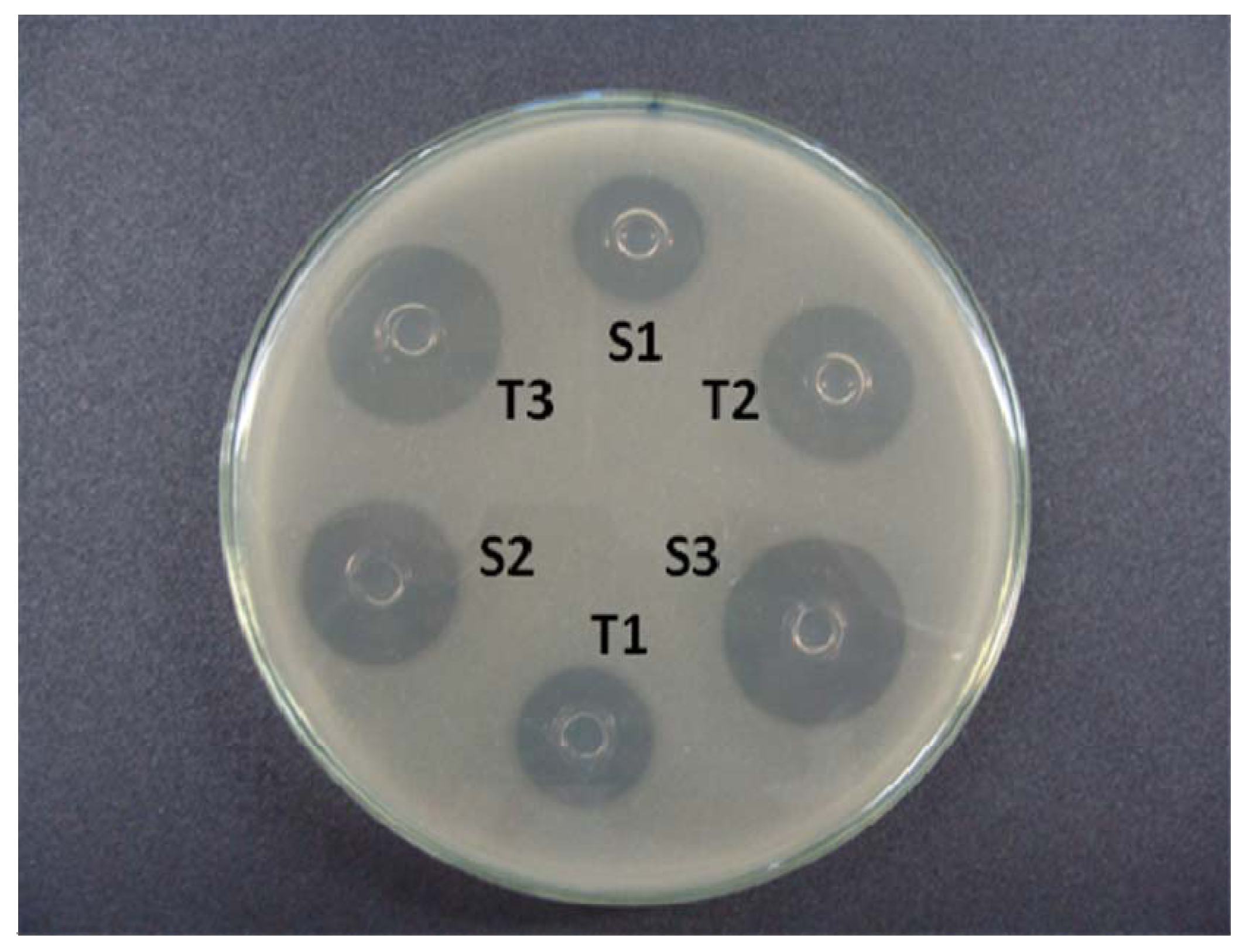
The base layer of the agar medium was composed per 20 mL culture Grove Randall-1 (Difco) which was poured into a Petri dish of 100 mm × 20 mm [29,30]. After solidification of this layer, portions of 5 mL of 2-Grove Randall inoculated medium were added to 1% on the base layer. In each plate, a “template” stainless steel was distributed evenly over the surface of the inoculated medium. Alternate three holes were filled with 200 μL of the reference solutions (S1, S2 and S3), and the other three holes were filled with the sample concentration solutions (T1, T2 and T3, Figure 2). Six plates were used for each assay. The plates were incubated at 35 °C aerobically for 18 h. The diameter of the growth inhibition zone (mm) was carefully measured with a digital caliper.
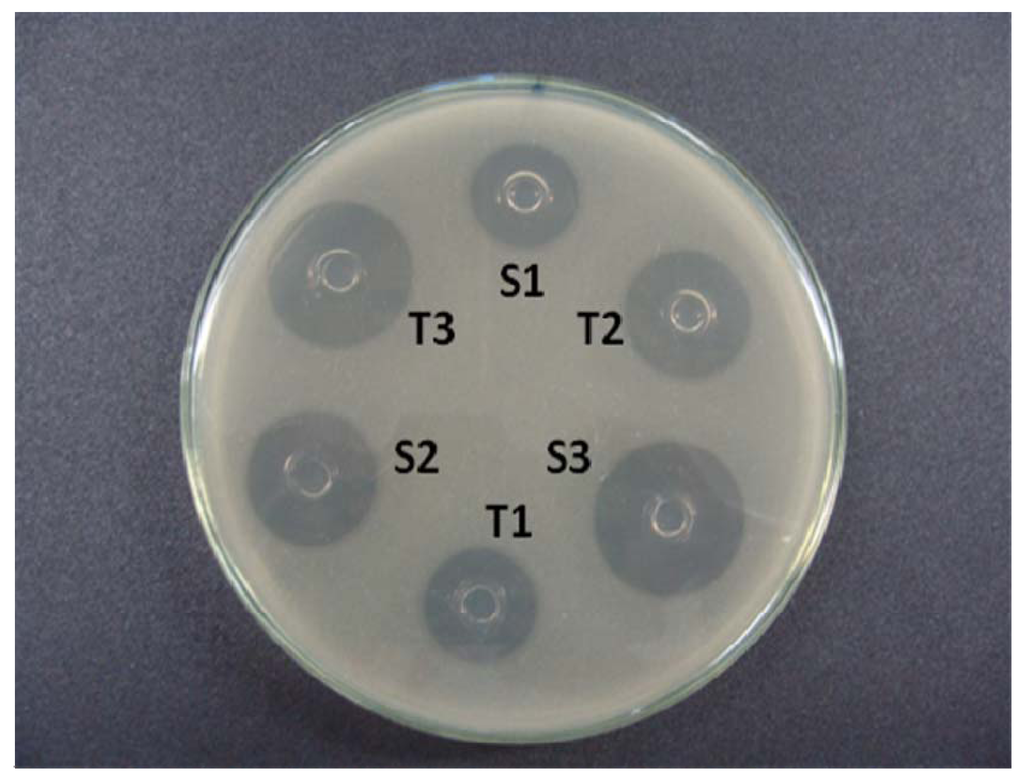
Figure 2.
Agar diffusion assay using a strain of B. subitilis ATCC 9371 IAL 1027 as the test microorganism. Ceftriaxone sodium reference substance is at concentrations of 15 (S1), 30 (S2), and 60 (S3) μg/mL and the ceftriaxone sodium sample at concentrations of 15 (T1), 30 (T2), and 60 (T3) μg/mL.
Figure 2.
Agar diffusion assay using a strain of B. subitilis ATCC 9371 IAL 1027 as the test microorganism. Ceftriaxone sodium reference substance is at concentrations of 15 (S1), 30 (S2), and 60 (S3) μg/mL and the ceftriaxone sodium sample at concentrations of 15 (T1), 30 (T2), and 60 (T3) μg/mL.
2.6. Calculation of Activity and Method Validation
To calculate the activity of ceftriaxone sodium, the Hewitt equation was used [31]. The assays were calculated statistically by the linear parallel model and regression analysis and verified using analysis of variance (ANOVA). The method was validated by determination of the following operational characteristics: linearity, precision, accuracy, and robustness [30,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40].
2.6.1. Linearity
In order to assess the validity of the assay, three doses of the reference substance were used. The linearity was evaluated by linear regression analysis, which was calculated by the least-squares method.
2.6.2. Precision
The precision of the method was determined by repeatability and intermediate precision and was expressed as the relative standard deviation (RSD). The repeatability was examined by assaying six samples of ceftriaxone sodium on the same day (intraday) and under the same experimental conditions against the ceftriaxone sodium reference standard. The intermediate precision of the method was evaluated through the performance of the analysis on three days (interday) in the same laboratory.
2.6.3. Accuracy
To determine the accuracy of the proposed method, the test was performed over three concentration levels, 80%, 100% and 120%, covering the specified range. Accurate aliquots of the reference standard solution (500 μg/mL) were transferred into 10 mL volumetric flasks together with aliquots of the sample solutions (500 μg/mL) and diluted with phosphate buffer solution pH 6.0 to give the final concentrations of 24.0, 30.0, and 36.0 μg/mL, (T1, T2 and T3), respectively, which were tested against S1, S2 and S3.
2.6.4. Robustness
The robustness of this method was determined by analyzing the same samples under a variety of conditions. The factors considered were incubation time, incubation temperature and inoculum concentration. Analysis was performed under normal conditions and in parallel altered by assessing interference of changes in the final result.
3. Results and Discussion
The method was developed and validated by linearity, accuracy, precision, repeatability and robustness. For drug analysis in quality control, the simplest and fastest procedures can be applied.
The development and validation of the analytical methods for the potency determination has received considerable attention in recent years, mainly from regulatory agencies, because of their importance in pharmaceutical analysis [34,35,36,37,38,39,40].
The potency of an antibiotic may be demonstrated under suitable conditions by comparing the growth inhibition of sensitive microorganisms induced by known concentrations of the antibiotic to be examined and a reference standard [31,32].
In this experimental work of 3 × 3 design (Figure 2), three dose levels for each standard and sample, were used following the procedures described in the Brazilian Pharmacopoeia [29]. The calculation procedures normally assume a direct relationship between the observed zone diameter and the logarithm of the applied dose. The results of growth inhibition zone diameter of the ceftriaxone sodium reference substance are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Diameters of inhibition zones obtained in the microbiological assay for evaluation the linearity of ceftriaxone sodium in pharmaceutical products-agar diffusion method.
| Diameter of inhibition zones (mm) a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | A1 | A2 | A3 | |
| (15 µg/mL) | (30 µg/mL) | (60 µg/mL) | (15 µg/mL) | (30 µg/mL) | (60 µg/mL) | |
| Day 1 | 16.41 | 18.45 | 20.80 | 16.31 | 18.45 | 20.70 |
| Day 2 | 16.19 | 18.45 | 20.85 | 16.23 | 18.35 | 20.85 |
| Day 3 | 16.20 | 18.30 | 20.75 | 16.01 | 18.45 | 20.90 |
| Diameter medium | 16.27 | 18.40 | 20.80 | 16.18 | 18.42 | 20.82 |
| RSD% b | 0.76 | 0.47 | 0.24 | 0.96 | 0.31 | 0.50 |
a Mean of 3 assays with 6 plates en each; b RSD% = percentage coefficient of variation.
The representative linear equation for ceftriaxone sodium was y = 3.2966Ln(x) + 7.26 (n = 3, r = 0.9993), where x is the log dose and y is the zone diameter. The experimental values obtained for the determination of ceftriaxone sodium in samples are presented in Table 1. These conditions must be verified by validity tests for a given probability, usually P = 0.05. The assays were validated by means of ANOVA, as described in the official codes. There were no deviations from parallelism and linearity with the obtained results (P < 0.05).
The method precision was determined by repeatability (intraday) obtaining a RSD of 1.15% and the intermediate precision was determined by analyzing the same sample on three days (between-day) with obtained RSD values of 1.40%.
The accuracy of the method was confirmed by determining the average recoveries from the samples through the method of standard addition. The mean percentage recoveries of the product were in accordance with the fixed limits of 98.0 up to 102.0, indicating the suitability of the developed method in quantifying the concentration of ceftriaxone in pharmaceutical injectable forms.
The accuracy of the method was evaluated at 80%, 100% and 120% of the nominal analytical concentration in the specified range of 15.0–60.0 μg/mL. The mean accuracy was 100.46% and RSD was 0.20% (Table 2).

Table 2.
Values obtained in the recovery test agar diffusion method for determination of ceftriaxone sodium.
| Ceftriaxone sodium SQR added (µg/mL) | Ceftriaxone sodium SQR found a (µg/mL) | Recovery (%) | Recovery average (%) | RSD b(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 4.0 | 4.00 | 100.00 | 100.46 | |
| R2 | 10.0 | 10.05 | 100.50 | 0.20 | |
| R3 | 16.0 | 16.14 | 100.88 |
a Mean of 3 assays with 6 plates en each; b RSD% = percentage coefficient of variation.
The robustness of the method was evaluated by making some modifications to the method, the results showed no significant difference demonstrating the robustness of the method, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Parameters assessing the robustness of the method microbiologically.
| Variable | Range investigated | Ceftriaxone sodium a (g/vial) | Ceftriaxone sodium a (%) | RSD b(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incubation time (time) | 18 | 0.974 | 97.40 | 1.01 |
| 24 | 0.992 | 99.23 | ||
| Incubation temperature (°C) | 35 | 0.967 | 96.72 | 1.28 |
| 30 | 0.962 | 96.29 | ||
| Inoculum concentration (%) | 1.0 | 0.980 | 98.03 | 1.12 |
| 1.2 | 0.996 | 99.68 |
a Mean of 3 assays with 6 plates en each; b RSD% = percentage coefficient of variation.
The quantification of antibiotic components by physicochemical methods, such as HPLC and UV spectrophotometry, although precise, cannot provide a true indication of biological activity. Therefore, bioassays continue to play an essential role in manufacturing and quality control of antibiotic medicines, and still demand considerable skill and expertise to assure success [41].
The results obtained in this study were very satisfactory, and the performed validation proved that the microbiological assay is a good alternative methodology for pharmaceutical analysis of ceftriaxone sodium lyophilized powder for injectable preparations. It is a useful analytical tool as a supplement or substitution for the physicochemical method.
4. Conclusions
The method using a microbiological agar assay for the determination of ceftriaxone sodium demonstrated good linearity, precision and accuracy at concentrations ranging from 15.0 to 60.0 μg/mL, therefore, being an acceptable alternative method for the routine quality control of ceftriaxone sodium in pharmaceutical forms. The method uses simple reagents with minimum sample preparation procedures and no toxically residues, encouraging its application in routine analysis.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to FAPESP (São Paulo, Brazil), CNPq (Brasília, Brazil), and PADC/FCF/UNESP (Araraquara, Brazil) for research fellowships.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- El-Shaboury, S.R.; Saleh, G.A.; Mohamed, F.A.; Rageh, A.H. Analysis of cephalosporin antibiotics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, S.S.; Christian, J.S. The cephalosporins antibiotics. Prim. Care Update OB/GYNS 1997, 4, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, C.; Narayana, B. A simple method for the spectrophometric determination of cephalosporins in pharmaceuticals using variamine blue. Eclet. Quim. 2008, 33, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, J.G.; Limbird, L.E.; Gilman, A.G. Goodman e Gilman: As bases farmacológicas da terapêutica, 10th ed; McGraw-Hill: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2003; p. 1647. [Google Scholar]
- Akl, M.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Ahmed, R. Validation of an HPLC-UV method for the determination of ceftriaxone sodiumresidues on stainless steel surface of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipments. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, G.A.; El-Shaboury, S.R.; Mohamed, F.A.; Rageh, A.H. Kinetic spectrophotometric determination of certain cephalosporins using oxidized quercetin reagent. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2009, 73, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.G. Spectrophotometric determination of ampicillin, dicluxacillin, flucoxacillin and amoxicillin antibiotic drugs: Ion-pair formation with molybdenum and thiocyanate. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde, Relação Nacional de Medicamentos Essenciais—Rename; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brizil, 2007.
- Chutipongtanate, S.; Thongboonkerd, V. Ceftriaxone crystallization and its potential role in kidney stone formation. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.S.; Ragab, G.H. Spectrophotometric determination of certain cephalosporins in pure form and in pharmaceutical formulations. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2004, 60, 2831–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale–The Complete Drug Reference; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2002; p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, M.J. TheMerck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals, 14th ed; Merck: Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 322–323. [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath, B.; Mruthyunjayaswamy, B.H.M. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ceftriaxone sodium and its application to drug quality control. Anal. Lett. 2009, 42, 2180–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzung, B.G. Farmacologia: Básica & Clínica; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2006; pp. 623–624. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Momani, I.F. Spectrophotometric determination of selected cephalosporins in drug formulations using flow injection analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 25, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, L.; Ke, Y.; Khang, F.; Liang, X. Determination of ceftriaxone sodium by HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phattanawasin, P.; Sotanaphun, U.; Sriphong, L.; Kanchanaphibool, I. Stability-indication TLC-image analysis method for quantification of ceftriaxone sodium in pharmaceutical dosage forms. J. Planar Chromatogr. 2011, 24, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Kumar, J.; Reddy, D.; Negi, P.S.; Chaudhary, M.; Srivastava, S.M.; Singh, R.M. Development and validation of high performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of ceftriaxone and vancomycin in pharmaceutical formulations and biological samples. Sci. Asia 2010, 36, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, H.; Blanchin, M.D.; Lerner, D.; Mandrou, B. Determination of cephalosporins utilising thin-layer chromatography with fluorescamine detection. Analyst 1985, 110, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksic, M.; Savic, V.; Popovic, G.; Buric, N.; Kapetanovic, V. Acidity constants of cefetamet, cefotaxime and ceftriaxone; the effect of the substituent at C3 position. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.L.; Falcó, C.P.; Cabeza, S.A. Comparison of several methods used for the determination of cephalosporins. Analysis of cephalexin in pharmaceutical samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 29, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H.; Saleh, G.A. Selective spectrophotometric determination of phenolic β-lactam antibiotics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Zhou, M.; Li, L.; Chen, H. Determination of Ceftriaxone Sodium in Pharmaceutical Formulations by Flow Injection Analysis with Acid Potassium Permanganate Chemiluminescence Detection. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luypaert, J.; Massart, D.L.; Heyden, Y.V. Near-infrared spectroscopy applications in pharmaceutical analysis. Talanta 2006, 72, 865–883. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, M.A.; Abdelmageed, O.H.; Attia, T.Z. Kinetic spectrofluorimetric determination of certain cephalosporins in human plasma. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.R.; Lin, S.J.; Chou, Y.W.; Wu, H.L.; Chen, S.H. Simultaneous determination of cefepime and L-arginine by micellar electrokinetic chromatography and applications to commercial injections. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, A.; Andrási, M.; Kardos, S. Application of capillary zone electrophoresis to the analysis and to a stability study of cephalosporins. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 775, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacchitano, C.J.; Mopper, B.; Specchio, J.J. Identification and separation of five cephalosporins by micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1994, 657, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Pharmacopeial Convention, Brazilian Pharmacopoeia, 5th ed; Anvisa: Brasília, Brazil, 2010.
- The United States Pharmacopeia, The National Formulary (NF24). By Authority of the United States Pharmacopeial Convention; United States Pharmacopeial Convention: Rockville, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 1697–1698.
- Hewitt, W. Microbiological Assay for Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Rational Approach; Interpharm/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 97–115. [Google Scholar]
- International Conference on Harmonization (ICH), Q2(R1): Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology; ICH: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005.
- Gomes, G.C.; Salgado, H.R.N. Microbiological assay for determination of lomefloxacin in coated tablets. J. AOAC Int. 2006, 89, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Salgado, H.R.N.; Lopes, C.C.G.O.; Lucchesi, M.B.B. Microbiological assay for gatifloxacin in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.R.; Salgado, H.R.N. Microbiological assay for ceftazidime injection. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar]
- Tozo, G.C.G.; Salgado, H.R.N. Microbiological assay for cefoxitin sodium in dosage form. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 452–455. [Google Scholar]
- Marona, H.R.N.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Desarrollo de análisis microbiológico para la determinación de esparfloxacino en polvo y en comprimidos de 200 mg. Inf. Tecnol. 1998, 9, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, C.C.G.O.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of a stability-indicative Agar diffusion assay to determine the potency of linezolid in tablets in the presence of photodegradation products. Talanta 2010, 82, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazedey, E.C.L.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of a microbiological agar assay for determination of orbifloxacin in pharmaceutical preparations. Pharmaceutics 2011, 3, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resolução no 899 de 29 de maio de 2003. Guia para validação de métodos analíticos e bioanalíticos (in Portuguese), Diário Oficial da República Federativa do Brasil, DF, 2 Jun. 2003.
- Baird, R.M.; Hodges, N.A.; Denyer, S.P. Handbook of Microbiological Quality Control: Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
