Local Colonic Administration of a Serine Protease Inhibitor Improves Post-Inflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
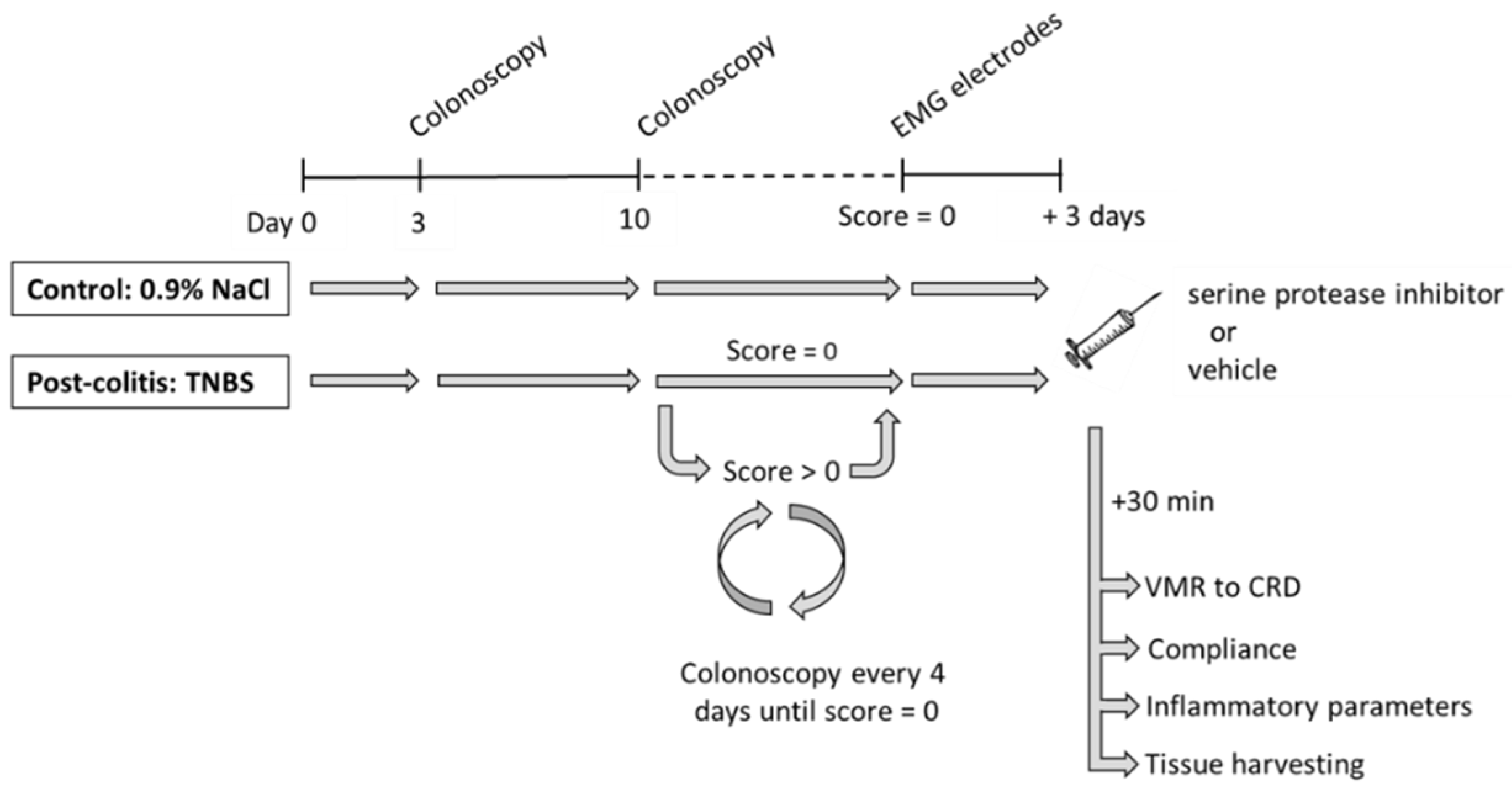
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Materials and Reagents
2.4. Induction of Colitis
2.5. Intracolonic Drug Administration
2.6. Colonic Mechanosensitivity
2.7. Colonic Compliance
2.8. Inflammatory Parameters
2.8.1. Colonoscopy
2.8.2. Macroscopic Score
2.8.3. Microscopic Score
2.8.4. Myeloperoxidase Activity
2.9. Proteolytic Activities on Fecal and Colonic Samples
2.10. Pharmacokinetic Experiments
2.11. Data Presentation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
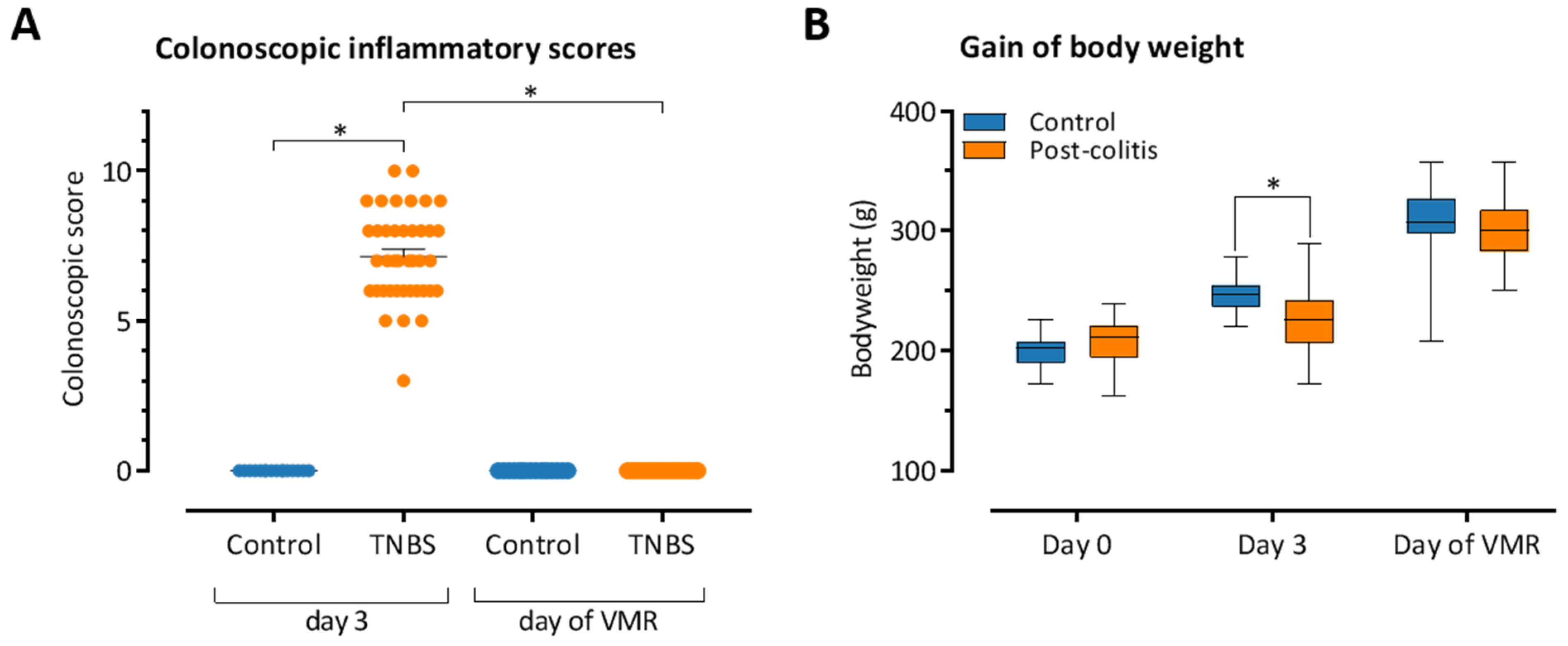
3.1. TNBS-Induced Colitis Resolves Spontaneously after 10–14 Days
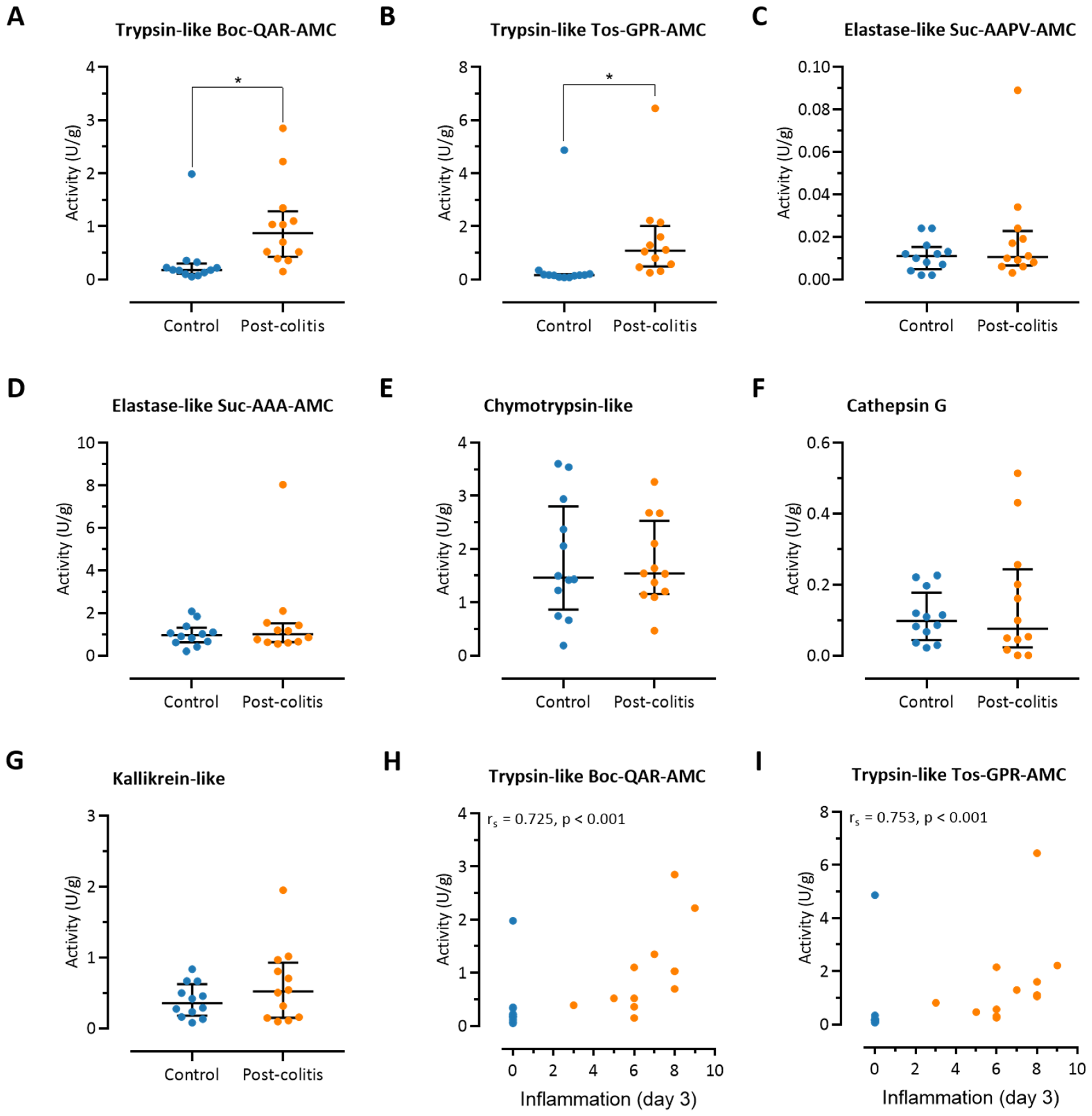
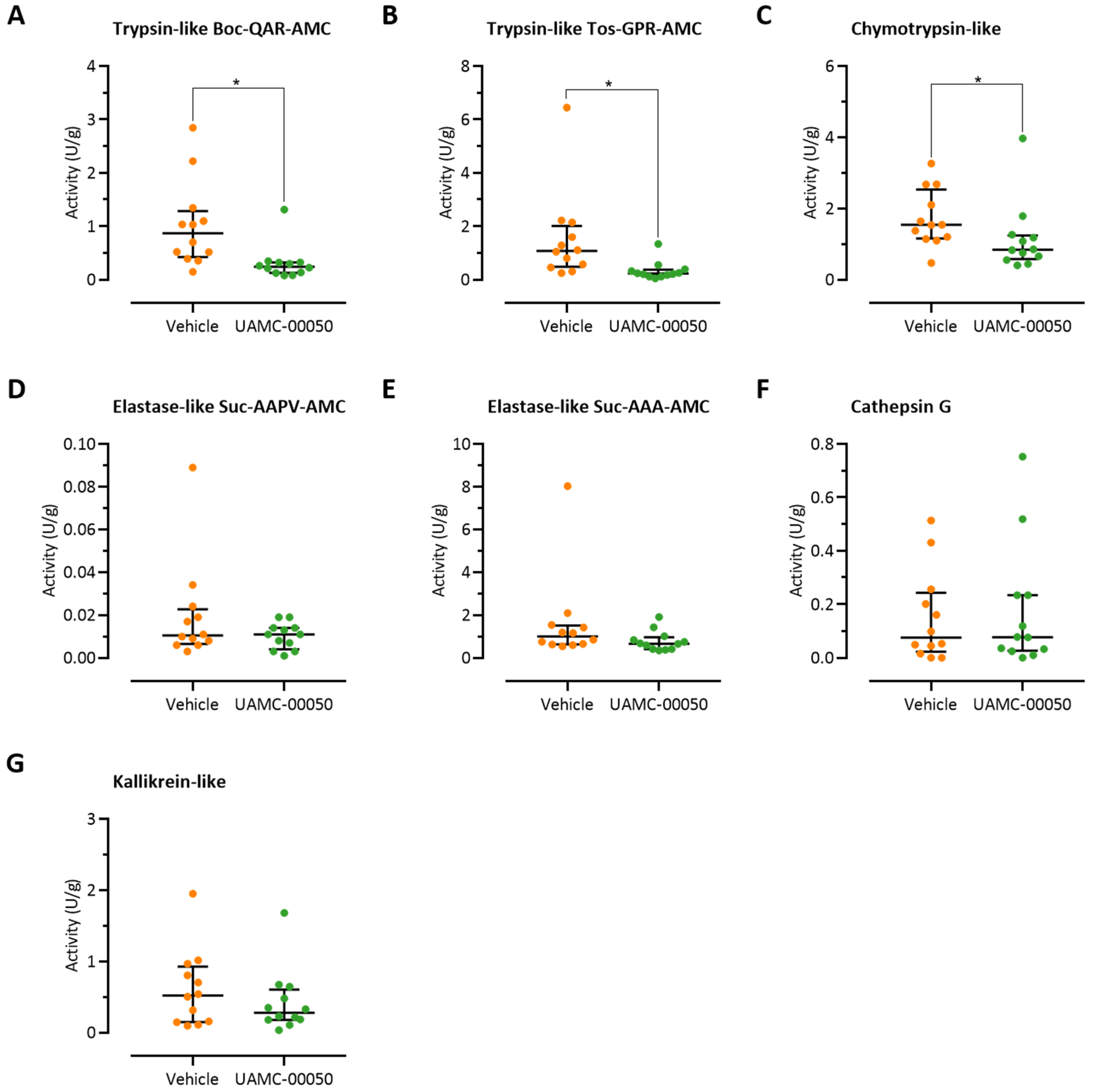
3.2. Colonic Trypsin-Like Activity Is Increased in Post-Colitis Rats
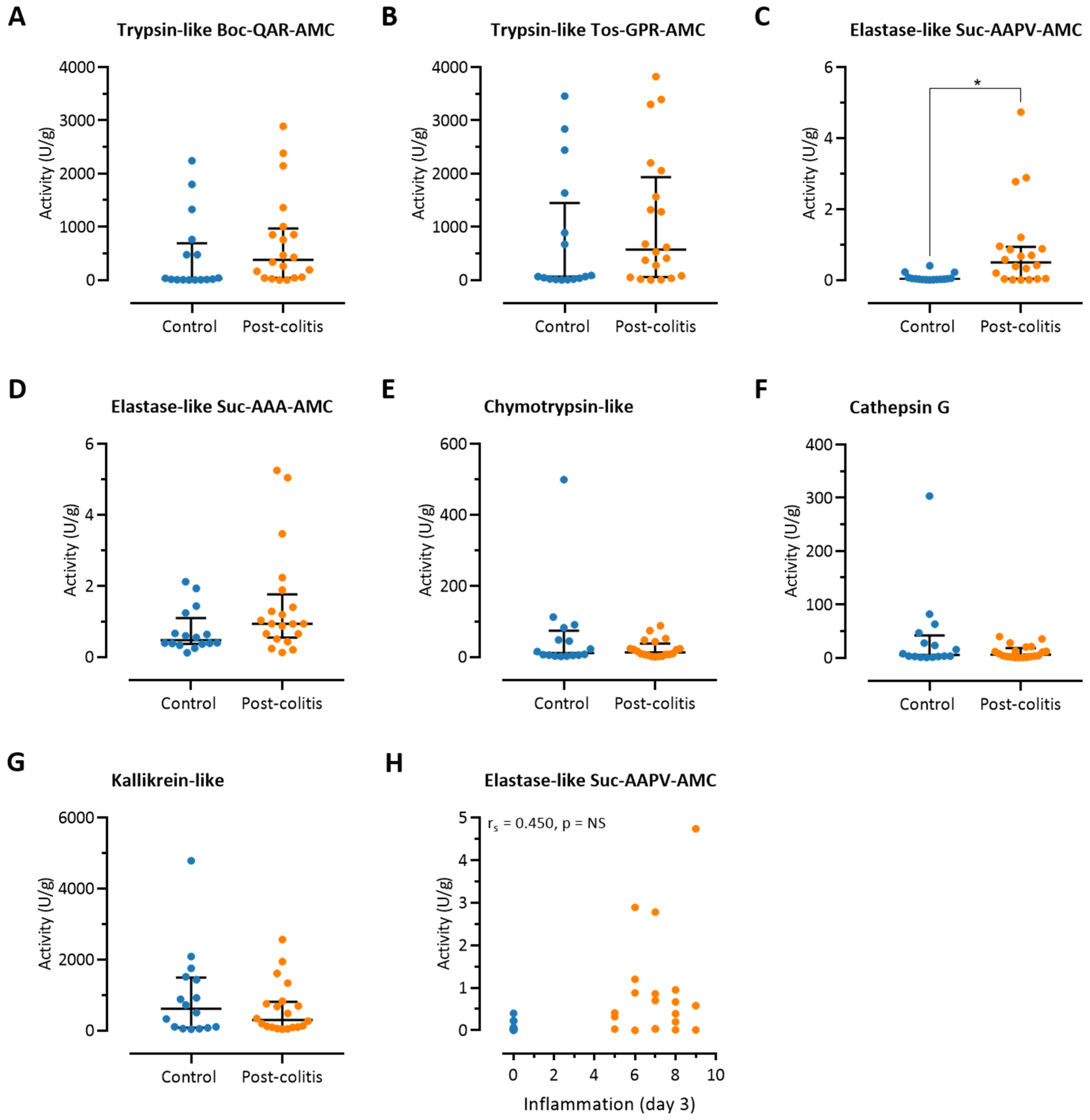
3.3. Fecal Trypsin-Like Activity Does Not Differ between Post-Colitis Rats and Controls
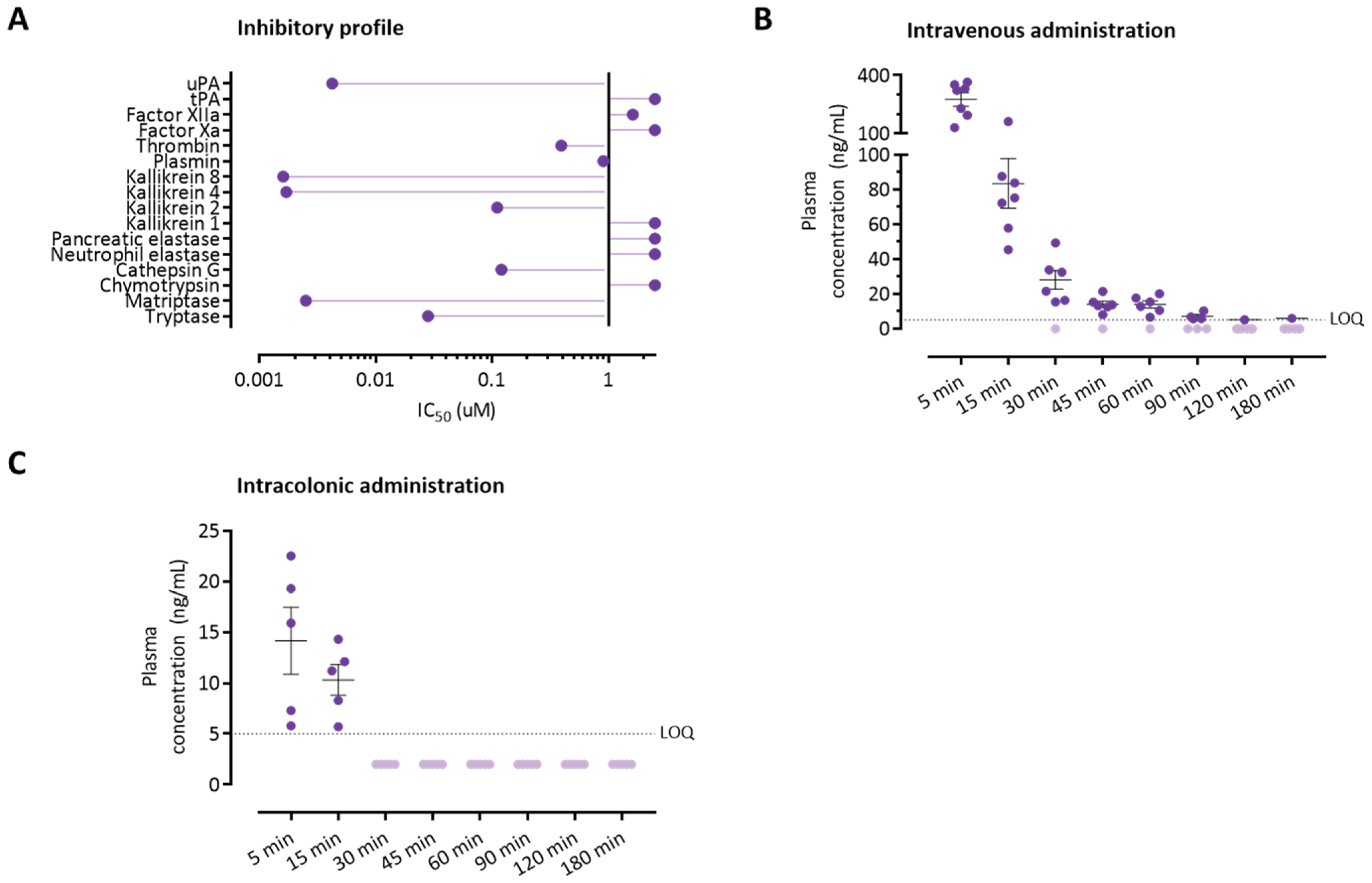
3.4. The Serine Protease Inhibitor UAMC-00050 Inhibits Trypsin-Like Enzymes In Vitro
3.5. Colonically Administered UAMC-00050 Is Not Detectable in Plasma after 30 Min
3.6. Intracolonic Administration of UAMC-00050 Alters Trypsin-Like Activity in the Colon of Post-Colitis Animals
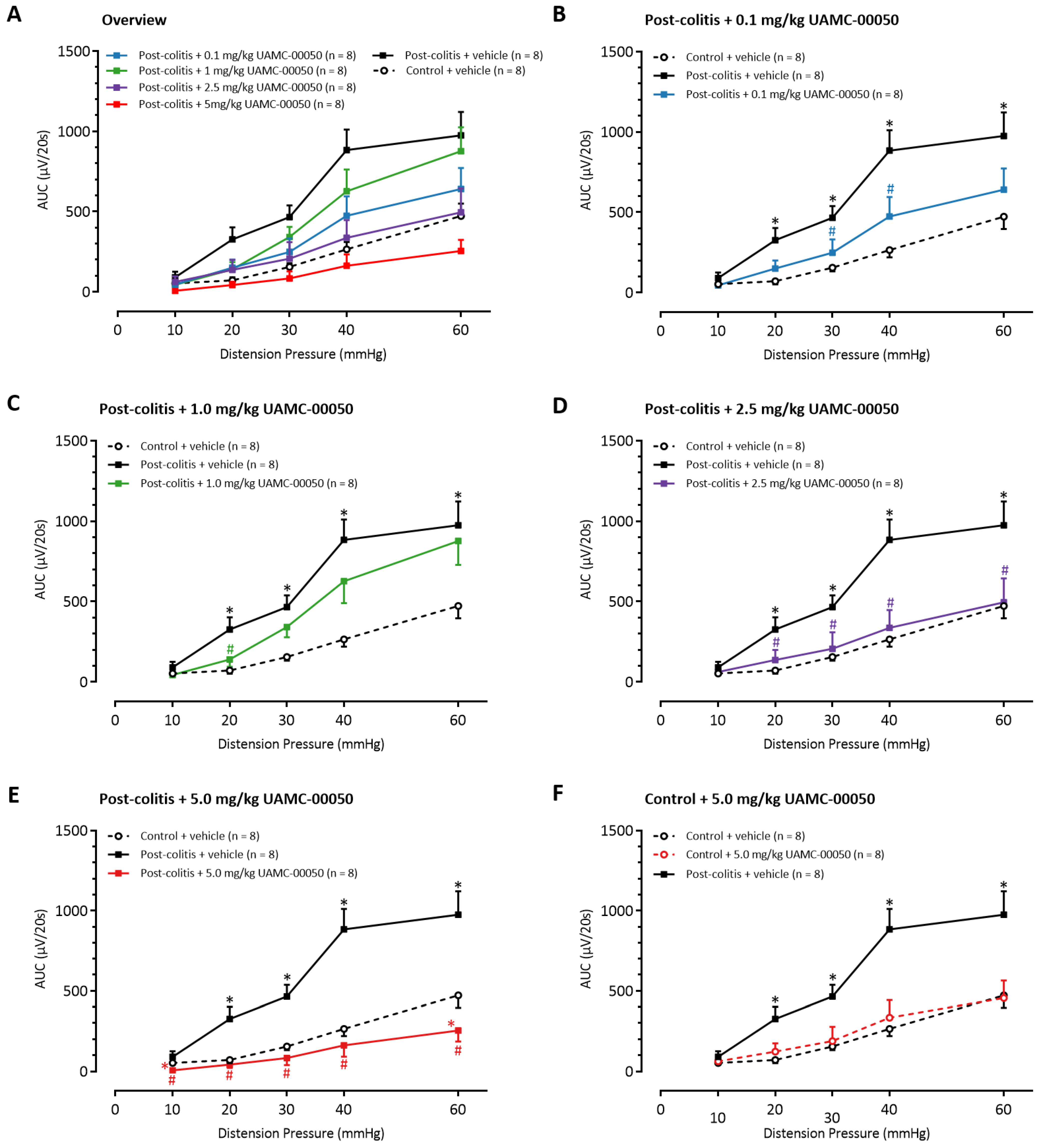
3.7. Intracolonic Administration of UAMC-00050 Decreases Visceral Hypersensitivity in Post-Colitis Rats
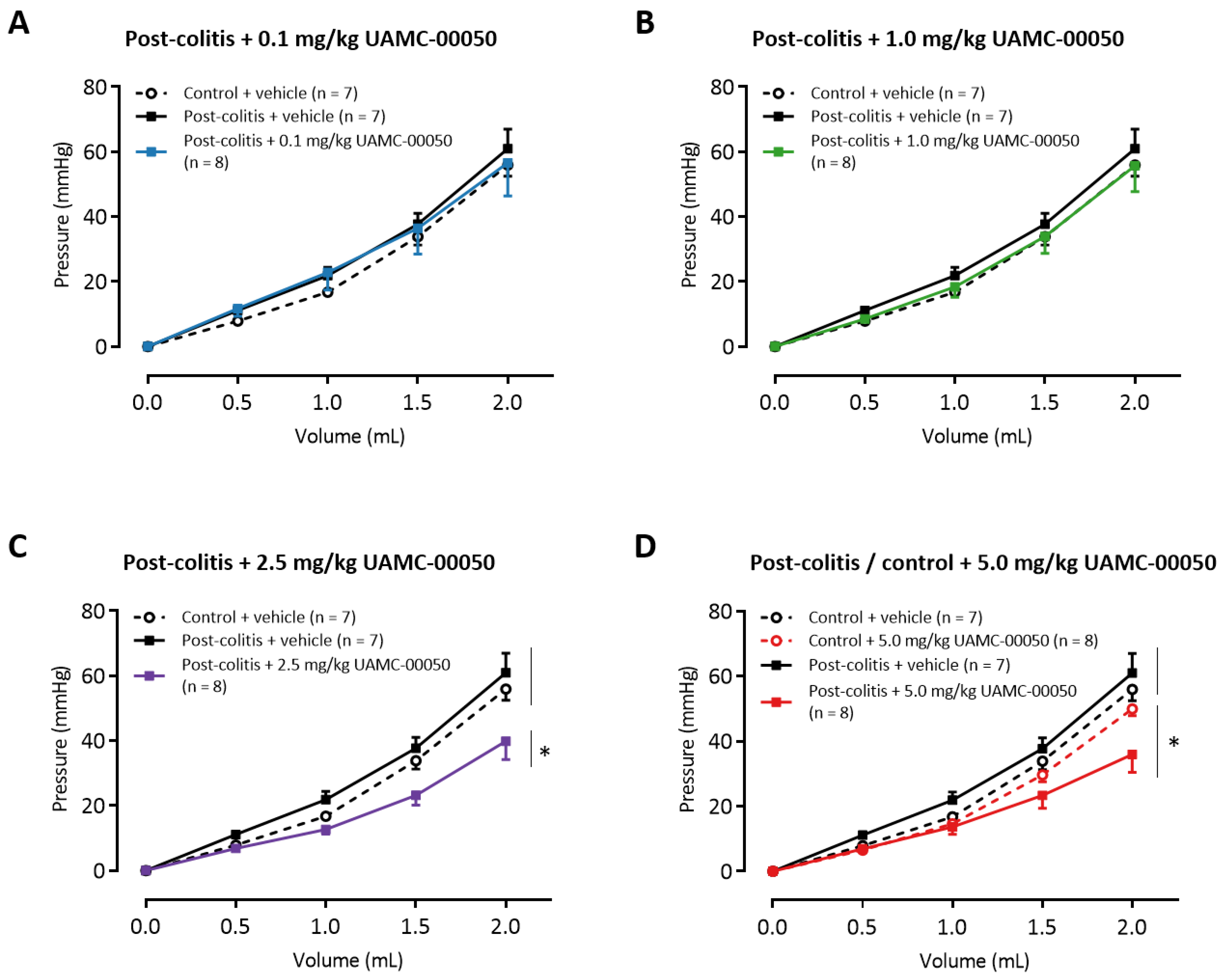
3.8. Intracolonic Administration of UAMC-00050 Increases Colonic Compliance
3.9. Intracolonic Administration of UAMC-00050 Increases MPO Activity in the Distal Colon Without Affecting Other Inflammatory Parameters
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vergnolle, N. Protease inhibition as new therapeutic strategy for GI diseases. Gut 2016, 65, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, J.P.; Palese, S.; Giorgio, C.; Chapman, K.; Denadai-Souza, A.; Rousset, P.; Sagnat, D.; Guiraud, L.; Edir, A.; Seguy, C.; et al. Increased mucosal thrombin is associated with Crohn’s disease and causes inflammatory damage through Protease-Activated Receptors activation. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2021, 15, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, J.P.; Magne, L.; Descamps, D.; Rolland, C.; Squarzoni-Dale, C.; Rousset, P.; Martin, L.; Cenac, N.; Balloy, V.; Huerre, M.; et al. Modifying the protease, antiprotease pattern by elafin overexpression protects mice from colitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, G.; Hritz, I.; Varga, M.Z.; Juhász, M.; Miheller, P.; Cierny, G.; Tulassay, Z.; Herszényi, L. The impact of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig. Dis. 2012, 30, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annaházi, A.; Gecse, K.; Dabek, M.; Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Rosztóczy, A.; Róka, R.; Molnár, T.; Theodorou, V.; Wittmann, T.; Bueno, L.; et al. Fecal proteases from diarrheic-IBS and ulcerative colitis patients exert opposite effect on visceral sensitivity in mice. Pain 2009, 144, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; De Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Cottrell, G.S.; Santini, D.; Pasquinelli, G.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Grady, E.F.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhner, S.; Li, Q.; Vignali, S.; Barbara, G.; De Giorgio, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; Zeller, F.; Langer, R.; Daniel, H.; et al. Activation of human enteric neurons by supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenac, N.; Andrews, C.N.; Holzhausen, M.; Chapman, K.; Cottrell, G.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Steinhoff, M.; Barbara, G.; Beck, P.; Bunnett, N.W.; et al. Role for protease activity in visceral pain in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gecse, K.; Róka, R.; Ferrier, L.; Leveque, M.; Eutamene, H.; Cartier, C.; Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Rosztóczy, A.; Izbéki, F.; Fioramonti, J.; et al. Increased faecal serine protease activity in diarrhoeic IBS patients: A colonic lumenal factor impairing colonic permeability and sensitivity. Gut 2008, 57, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róka, R.; Rosztóczy, A.; Leveque, M.; Izbéki, F.; Nagy, F.; Molnár, T.; Lonovics, J.; Garcia-Villar, R.; Fioramonti, J.; Wittmann, T.; et al. A pilot study of fecal serine-protease activity: A pathophysiologic factor in diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooth, D.; Garsed, K.; Singh, G.; Marciani, L.; Lam, C.; Fordham, I.; Fields, A.; Banwait, R.; Lingaya, M.; Layfield, R.; et al. Characterisation of faecal protease activity in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea: Origin and effect of gut transit. Gut 2014, 63, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland-Fourcade, C.; Denadai-Souza, A.; Cirillo, C.; Lopez, C.; Jaramillo, J.O.; Desormeaux, C.; Cenac, N.; Motta, J.P.; Larauche, M.; Taché, Y.; et al. Epithelial expression and function of trypsin-3 in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2017, 66, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edogawa, S.; Edwinson, A.L.; Peters, S.A.; Chikkamenahalli, L.L.; Sundt, W.; Graves, S.; Gurunathan, S.V.; Breen-Lyles, M.; Johnson, S.; Dyer, R.; et al. Serine proteases as luminal mediators of intestinal barrier dysfunction and symptom severity in IBS. Gut 2020, 69, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Spaendonk, H.; Ceuleers, H.; Witters, L.; Patteet, E.; Joossens, J.; Augustyns, K.; Lambeir, A.M.; De Meester, I.; De Man, J.G.; De Winter, B.Y. Regulation of intestinal permeability: The role of proteases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2106–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceuleers, H.; Van Spaendonk, H.; Hanning, N.; Heirbaut, J.; Lambeir, A.M.; Joossens, J.; Augustyns, K.; De Man, J.G.; De Meester, I.; De Winter, B.Y. Visceral hypersensitivity in inflammatory bowel diseases and irritable bowel syndrome: The role of proteases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10275–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceuleers, H.; Hanning, N.; Heirbaut, J.; Van Remoortel, S.; Joossens, J.; Van Der Veken, P.; Francque, S.M.; De Bruyn, M.; Lambeir, A.M.; De Man, J.G.; et al. Newly developed serine protease inhibitors decrease visceral hypersensitivity in a post-inflammatory rat model for irritable bowel syndrome. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3516–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, J.P.; Denadai-Souza, A.; Sagnat, D.; Guiraud, L.; Edir, A.; Bonnart, C.; Sebbag, M.; Rousset, P.; Lapeyre, A.; Seguy, C.; et al. Active thrombin produced by the intestinal epithelium controls mucosal biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, J.P.; Rolland, C.; Edir, A.; Florence, A.C.; Sagnat, D.; Bonnart, C.; Rousset, P.; Guiraud, L.; Quaranta-Nicaise, M.; Mas, E.; et al. Epithelial production of elastase is increased in inflammatory bowel disease and causes mucosal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2021, 14, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, J.P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Deraison, C.; Martin, L.; Rolland, C.; Rousset, P.; Boue, J.; Dietrich, G.; Chapman, K.; Kharrat, P.; et al. Food-grade bacteria expressing elafin protect against inflammation and restore colon homeostasis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 158ra144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, B.; Gauthier, F. Elastase-2/leukocyte elastase. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 2653–2661. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Lieu, T.; Barlow, N.; Sostegni, S.; Haerteis, S.; Korbmacher, C.; Liedtke, W.; Jimenez-Vargas, N.N.; Vanner, S.J.; Bunnett, N.W. Neutrophil Elastase Activates Protease-activated Receptor-2 (PAR2) and Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) to Cause Inflammation and Pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13875–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, M.; Tack, J. New treatments and therapeutic targets for IBS and other functional bowel disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, B. Targeting proteases: Successes, failures and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiteren, A.; De Man, J.G.; Ruyssers, N.E.; Moreels, T.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Winter, B.Y. Histamine H4 and H1 receptors contribute to postinflammatory visceral hypersensitivity. Gut 2014, 63, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiteren, A.; van der Linden, L.; de Wit, A.; Ceuleers, H.; Buckinx, R.; Timmermans, J.P.; Moreels, T.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Man, J.G.; De Winter, B.Y. P2X3 receptors mediate visceral hypersensitivity during acute chemically-induced colitis and in the post-inflammatory phase via different mechanisms of sensitization. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joossens, J.; Ali, O.M.; El-Sayed, I.; Surpateanu, G.; Van der Veken, P.; Lambeir, A.-M.; Setyono-Han, B.; Foekens, J.A.; Schneider, A.; Schmalix, W.; et al. Small, Potent, and Selective Diaryl Phosphonate Inhibitors for Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator with In Vivo Antimetastatic Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 6638–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joossen, C.; Baán, A.; Moreno-Cinos, C.; Joossens, J.; Cools, N.; Lanckacker, E.; Moons, L.; Lemmens, K.; Lambeir, A.M.; Fransen, E.; et al. A novel serine protease inhibitor as potential treatment for dry eye syndrome and ocular inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, W.; De Man, J.G.; De Schepper, H.U.; Bult, H.; Moreels, T.G.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Winter, B.Y. Role of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in visceral hypersensitivity to colorectal distension during experimental colitis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Hubmayr, R.D.; Ferber, I.J.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Viscoelastic properties of the human colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G459–G466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, W.; De Man, J.G.; Nullens, S.; Pelckmans, P.A.; De Winter, B.Y.; Moreels, T.G. The use of colonoscopy to follow the inflammatory time course of TNBS colitis in rats. Acta Gastro Enterol. Belg. 2011, 74, 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pulli, B.; Ali, M.; Forghani, R.; Schob, S.; Hsieh, K.L.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Linnoila, J.J.; Chen, J.W. Measuring myeloperoxidase activity in biological samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENZYME-3.4.21.37 Leukocyte Elastase. Available online: https://enzyme.expasy.org/EC/3.4.21.37 (accessed on 21 April 2021).
- Patel, S.K.; Dotson, J.; Allen, K.P.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Identification and molecular characterization of EatA, an autotransporter protein of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgieva, D.N.; Genov, N.; Betzel, C. Bacillus licheniformis variant DY proteinase: Specificity in relation to the geometry of the substrate recognition site. Curr. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmann, G.J.; Ford, A.C.; Talley, N.J. Pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Z.; Zeng, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Qian, L.; Wei, J.; Yang, X.; Shen, Q.; Gong, Z.; et al. The Molecular Aspect of Antitumor Effects of Protease Inhibitor Nafamostat Mesylate and Its Role in Potential Clinical Applications. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaházi, A.; Ferrier, L.; Bézirard, V.; Lévêque, M.; Eutamène, H.; Ait-Belgnaoui, A.; Coëffier, M.; Ducrotté, P.; Róka, R.; Inczefi, O.; et al. Luminal cysteine-proteases degrade colonic tight junction structure and are responsible for abdominal pain in constipation-predominant IBS. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgington-Mitchell, L.E.; Barlow, N.; Aurelio, L.; Samha, A.; Szabo, M.; Graham, B.; Bunnett, N. Fluorescent diphenylphosphonate-based probes for detection of serine protease activity during inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerckhoffs, A.P.; Ter Linde, J.J.; Akkermans, L.M.; Samsom, M. Trypsinogen IV, serotonin transporter transcript levels and serotonin content are increased in small intestine of irritable bowel syndrome patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Lizarraga, J.; Florens, M.V.; Viola, M.F.; Jain, P.; Decraecker, L.; Appeltans, I.; Cuende-Estevez, M.; Fabre, N.; Van Beek, K.; Perna, E.; et al. Local immune response to food antigens drives meal-induced abdominal pain. Nature 2021, 590, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Chapter 10.5: Many Enzymes Are Activated by Specific Proteolytic Cleavage. In Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W H Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 280–282. [Google Scholar]
- Langhorst, J.; Elsenbruch, S.; Koelzer, J.; Rueffer, A.; Michalsen, A.; Dobos, G.J. Noninvasive markers in the assessment of intestinal inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases: Performance of fecal lactoferrin, calprotectin, and PMN-elastase, CRP, and clinical indices. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, O.; Naumann, M.; Shastri, Y.; Povse, N.; Stein, J. Prospective evaluation of faecal neutrophil-derived proteins in identifying intestinal inflammation: Combination of parameters does not improve diagnostic accuracy of calprotectin. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberer, H.; Küppers, B.; Mickisch, O.; Baniewicz, W.; Drescher, M.; Traber, L.; Kempf, A.; Schmidt-Gayk, H. Fecal leukocyte proteins in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Lab. 2005, 51, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, R.; Ruano-Gallego, D.; Radhakrishnan, S.T.; Lovell, S.; Yu, L.; Kotik, O.; Glegola-Madejska, I.; Tate, E.W.; Choudhary, J.S.; Williams, H.R.T.; et al. Faecal neutrophil elastase-antiprotease balance reflects colitis severity. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Dong, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Ding, H.; Shi, H.; Lu, X. A protease inhibitor against acute stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity and paracellular permeability in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 654, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, F.X.; Du, C.; Li, C.Q.; Yu, Y.B.; Zuo, X.L.; Li, Y.Q. Increased production of BDNF in colonic epithelial cells induced by fecal supernatants from diarrheic IBS patients. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturrino, J.; Camilleri, M.; Busciglio, I.; Burton, D.; Zinsmeister, A.R. Sensations of gas and pain and their relationship with compliance during distension in human colon. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 646-e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.M.; Read, N.W.; Prior, A.; Daly, J.A.; Cheah, S.K.; Grundy, D. Sensory and motor responses to rectal distention vary according to rate and pattern of balloon inflation. Gastroenterology 1990, 99, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.M.; Frøkjaer, J.B.; Larsen, E.; Reddy, H.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Gregersen, H. Pain and mechanical properties of the rectum in patients with active ulcerative colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midenfjord, I.; Polster, A.; Sjövall, H.; Friberg, P.; Törnblom, H.; Simrén, M. Associations among neurophysiology measures in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and their relevance for IBS symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.W. Relationship of underlying abnormalities in rectal sensitivity and compliance to distension with symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion 2006, 73, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.; Arvidsson, S.; Ekman, C.; Bayati, A. A model for chronic quantitative studies of colorectal sensitivity using balloon distension in conscious mice -- effects of opioid receptor agonists. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2003, 15, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Spaendonk, H.; Nullens, S.; Ceuleers, H.; Schrijvers, D.; Francque, S.M.; De Man, J.; De Winter, B.Y. Tu1883 The Effect of a Protease Inhibitor in a Chronic Colitis Transfer Model. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, S967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Fragmentor Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAMC-00050 | 6.3 | 659.2 | 91.2 | 185 | 60 |
| 267.3 | 185 | 40 | |||
| 250.2 | 185 | 35 | |||
| Nordazepam-D5 | 7.0 | 276.0 | 140.0 | 100 | 35 |
| Group | Drug | N | Day 3 | Day of VMR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colonoscopy | Colonoscopy | Macroscopy | Microscopy | MPO Activity | |||
| Control | Vehicle | 8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| 5.0 mg/kg | 8 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.6 ± 0.2 # | |
| Post-colitis | Vehicle | 8 | 6.3 ± 0.6 * | 0.0 ± 00 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 0.3 ± 0.2 |
| 0.1 mg/kg | 8 | 7.5 ± 0.5 * | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.4 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.7 # | |
| 1.0 mg/kg | 8 | 7.4 ± 0.6 * | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 2.0 ± 0.5 # | |
| 2.5 mg/kg | 8 | 7.1 ± 0.5 * | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.5 # | |
| 5.0 mg/kg | 8 | 6.9 ± 0.5 * | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.5 # | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hanning, N.; De bruyn, M.; Ceuleers, H.; Boogaerts, T.; Berg, M.; Smet, A.; De Schepper, H.U.; Joossens, J.; van Nuijs, A.L.N.; De Man, J.G.; et al. Local Colonic Administration of a Serine Protease Inhibitor Improves Post-Inflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060811
Hanning N, De bruyn M, Ceuleers H, Boogaerts T, Berg M, Smet A, De Schepper HU, Joossens J, van Nuijs ALN, De Man JG, et al. Local Colonic Administration of a Serine Protease Inhibitor Improves Post-Inflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060811
Chicago/Turabian StyleHanning, Nikita, Michelle De bruyn, Hannah Ceuleers, Tim Boogaerts, Maya Berg, Annemieke Smet, Heiko U. De Schepper, Jurgen Joossens, Alexander L. N. van Nuijs, Joris G. De Man, and et al. 2021. "Local Colonic Administration of a Serine Protease Inhibitor Improves Post-Inflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060811
APA StyleHanning, N., De bruyn, M., Ceuleers, H., Boogaerts, T., Berg, M., Smet, A., De Schepper, H. U., Joossens, J., van Nuijs, A. L. N., De Man, J. G., Augustyns, K., De Meester, I., & De Winter, B. Y. (2021). Local Colonic Administration of a Serine Protease Inhibitor Improves Post-Inflammatory Visceral Hypersensitivity in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060811







