Abstract
Phytolith carbon sequestration has been recognized as an important mechanism for long-term carbon sequestration in forest ecosystems. Conducting relevant research in cold temperate regions that are sensitive to climate change can reveal their unique mechanisms as a stable and long-term carbon pool, fill key blind spots in global carbon cycling models, and provide necessary scientific support for developing climate-resilient ecological strategies and carbon neutrality pathways. In this study, we focused on the Larix gmelinii forest ecosystem and investigated the latitudinal spatial characteristics of soil phytolith and phytolith-occluded carbon (phytOC) in Eastern China. We analyzed the factors that influenced their accumulation and assessed their storage potential across different climatic zones. Our findings revealed an exponential increase in soil phytolith content with increasing latitude in Eastern China. Additionally, the content of soil phytoliths in tropical and subtropical forests was significantly lower than in the cold temperate forests. It was also found that soil phytOC content increased linearly with latitude and was significantly higher in cold temperate zones than in the other climatic zones. The order of soil phytOC storage was tropical (0.23 t ha−1) < middle temperate (0.24 t ha−1) < subtropical (0.27 t ha−1) < cold temperate (1.20 t ha−1). Soil phytolith and phytOC content were significantly negatively correlated with temperature and precipitation. pH, organic matter, and nutrients of soil significantly influenced the formation and accumulation of soil phytoliths. It can provide a scientific basis for the quantitative evaluation of forest soil carbon pool.
1. Introduction
Forests play a critical role in maintaining the balance of the terrestrial ecosystem by serving as a primary source and sink of atmospheric greenhouse gases. As atmospheric CO2 concentrations continue to rise due to anthropogenic activities, the ability of forests to mitigate this increase and preserve the carbon (C) balance becomes even more crucial [1,2,3,4]. The significance of forests lies in their capacity to sequester atmospheric CO2 and store it in the forest soil C pool, the largest C pool in the terrestrial ecosystem [5]. Any alteration in soil C content, no matter how small, can significantly impact atmospheric CO2 concentration, and potentially have a feedback effect on climate change [6]. Therefore, a deep understanding of the characteristics of the forest soil C pool is essential to elucidate the C cycle mechanism of the terrestrial ecosystem [7].
The storage of the soil C pool represents a significant component of the global C cycle and has important implications for climate change mitigation. Various studies have suggested that the global organic C reserves in soil range from 1.4 × 1018 g to 1.5 × 1018 g [8], emphasizing the significant role of soil in the global C storage. The main sources of forest SOC are roots and litter, which greatly impact the soil C cycle. Forest ecosystems are among the most productive natural terrestrial ecosystems that contribute significantly to the sequestration of atmospheric CO2, and therefore, the mitigation of climate change. However, differences in forest types greatly affect their C sequestration capacity, with C density being a better indicator of this capacity. Liu et al. [9] synthesized previous research, finding that the natural forest and plantation in the temperate areas had higher surface SOC than that in the subtropical and tropical areas, indicating the importance of forest types and climatic conditions in determining SOC storage. Additionally, their study showed that artificial coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forests showed significantly higher SOC storage than coniferous pure forests, emphasizing the importance of forest composition in determining C sequestration capacity.
Global warming has become an increasingly pressing concern in recent years, as Earth’s climate is significantly impacted by the rising levels of atmospheric CO2. This has led to a need for the identification of effective long-term C sequestration methods to mitigate the greenhouse effect. One promising approach is biogeochemical C sequestration, in which phytoliths or hydrated silicon minerals may be a particularly viable option [10,11]. Phytoliths are hydrated silicon minerals that can be formed through the absorption of monosilicic acid (H4SiO4) by plants, which results in the precipitation of amorphous silicon within and between cells [12]. During phytolith formation, a significant amount of organic C, roughly 0.1–6%, is often encapsulated and forms phytolith-occluded-C (phytOC), which can be stored in soils for thousands of years [13,14]. This makes phytOC a key mechanism for long-term C sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems, as it is more stable than other forms of C due to the protective effects of corrosion and oxidation-resistant phytoliths [15,16]. This form of biogeochemical C sequestration has the potential to significantly reduce atmospheric CO2 concentration and mitigate the greenhouse effect [17,18]. Given the significant potential of phytOC for long-term C sequestration, this topic has become the focus of much research over the years [10,11,14,19,20,21].
Phytolith research represents a multi-disciplinary field of investigation that encapsulates a range of scientific domains, including paleoecology, zoology, geology, pedology, agronomy, and archaeology. The study of phytoliths is integral to unraveling their biological complexities, a task compounded by the diverse range of factors that influence phytolith production, including differences in plant organs, genotypes, and ages [10]. Current research on phytoliths has primarily focused on agricultural archaeology [22,23], C isotope research [24,25], paleoclimate reconstruction [26], phytolith radioactive dating [27], and plant taxonomy [28]. Recently, there has been a growing interest in the production and accumulation of phytoliths and their potential role as C sinks in terrestrial ecosystems. Existing research has mostly focused on grasses with outstanding silicon accumulation ability, systematically elucidating the generation rules of their phytOC. Previous studies have indicated that bamboo in forest ecosystem [10,29], some herbaceous plants in grassland ecosystems [30,31], wheat in farmland ecosystems [14,32], and rice [33,34] and reed [19,20] in wetland ecosystems have significant potential as phytolith C sequestration sources, providing fresh opportunities to address global warming. However, the vegetation studied is mainly distributed in subtropical regions [35,36]. In the northern forests, which account for 30% of the global forest area, especially in the cold temperate coniferous forests dominated by Larix gmelinii, there is still a lack of quantitative research on the generation pathways, occurrence characteristics, and contribution of soil phytOC to soil carbon pools. The tannic acid rich in the litter of Larix gmelini may form a unique carbon sequestration mechanism through co-precipitation with phytoliths or by inhibiting microbial activity to prolong the retention time of phytOC. In addition, the distribution area of this tree species extensively undergoes seasonal freeze-thaw cycles, and its physical disturbance may further affect the vertical migration and stability of soil phytOC. Clarifying the above process will not only reveal the unquantified carbon sink potential of northern coniferous forests but also provide key parameters for high-dimensional ecosystem carbon balance models of global vegetation.
The latitude span of eastern China is large, including multiple climate zones such as cold temperate, middle temperate, subtropical, and tropical, forming significant temperature and precipitation gradients. This provides a natural experimental platform for studying the regulatory mechanisms of environmental factors on the formation and preservation of soil phytOC. Eastern China covers typical forest types worldwide, and different forest types correspond to differentiated plant functional traits (such as silicon absorption capacity and litter quality) and soil physicochemical properties (such as pH and clay minerals). Systematic research on phytOC dynamics in this region can comprehensively evaluate the regional carbon sink function. Therefore, this study aimed to address (1) the differences in forest soil phytOC across various latitudes in Eastern China, and (2) the impacts of climatic factors and soil chemical properties on soil phytolith and phytOC accumulations. We hypothesized that soil phytolith and phytOC would exhibit a clear zonality feature, and that any increase in temperature or precipitation would lead to a reduction in their content and storage in the soil. This research is imperative due to its potential contribution to our understanding of phytolith-based C sequestration and its subsequent impact on mitigating global warming severity. Furthermore, a deeper knowledge of the factors influencing soil phytOC variability can initiate restructuring of ecosystem management practices, improve C storage strategies, and facilitate more effective forest conservation methods.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
This study focused on four typical forest ecosystems that are regionally representative in eastern China. The research spanned across eastern China, covering an area between 19.87–50.94° N and 109.77–121.53° E, which comprises different climatic zones such as cold temperate, middle temperate, subtropical, and tropical zones. The average annual temperature ranges from −5.3 to 23.5 °C, while the average annual precipitation ranges from 369 to 1815 mm. Table 1 shows the basic geographic information of the study sites and the selected forest types.

Table 1.
Basic information of each plot.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.2.1. Soil Sampling
The forest soil data for both the cold temperate zone and the middle temperate zone were obtained through field sampling and analysis. Three sample sites were chosen based on vegetation status from each zone in the Great Khingan Mountains. Sample sites were chosen for soil profiles of 0–30 cm depth, with three soil samples collected from each site. To reduce the impact of soil heterogeneity on sampling error, three samples were combined into a mixture for analysis. After being brought to the laboratory, the soil samples were air-dried and then subjected to soil property determination and phytolith extraction, with a 2 mm sieve and a 0.15 mm sieve being used, respectively. Data for tropical and subtropical forest soils were extracted from prior research [37,38]. Four sampling sites were selected for each region based on vegetation conditions, and four surface soil samples were collected at each sampling site. The combined samples of each sampling site were analyzed to reduce the impact of soil heterogeneity on sampling errors. The local experiments and cited literature are consistent in terms of soil sample processing and phytolith extraction methods. To ensure comparability of data, soil depths of 0–30 cm were selected for both.
2.2.2. Soil Properties Determination
Soil pH was determined using a pH meter in a soil/water mass ratio of 1:5 (w/v). Soil total organic C (TOC) content was determined by the potassium dichromate oxidation spectrophotometric method (HJ 615-2011) [39], whereas rapidly-available potassium (AK) and available phosphorus (AP) were determined by the universal extract-colorimetric method (NY/T 1849-2010) [40].
2.2.3. Phytolith and PhytOC Content Extraction and Determination
Phytolith was extracted from air-dried soil (<0.15 mm) using a modified wet air oxidation method and heavy liquid flotation method [19,41,42]. The procedure involved complete removal of organic matter and separation of samples by a heavy liquid flotation and centrifugation technique, using ZnBr2 (specific gravity of 2.35) as the heavy liquid, to obtain pure phytolith samples [43]. The contents of phytOC were measured using an Element Analyzer (Thermo Fisher, FlashSmart, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Data Calculation and Statistics
The relevant indices of soil phytolith and phytOC were calculated as follows [44,45]:
Data on temperature and precipitation were collected from the ClimateAP model’s website (http://climateap.net/ (accessed on 10 March 2021)) for analysis. The data statistics were performed using SPSS 22.0 software. This study investigated the latitudinal characteristics of soil phytolith and phytOC, as well as the effects of meteorological factors and soil chemical indicators on soil phytolith and phytOC. A one-way ANOVA was employed to analyze differences in the quantitative characteristics of soil phytolith indices and soil chemical properties. The relationships between soil phytolith indices and soil chemical properties were investigated using Pearson Correlation Analysis. The results are presented in figures using Origin 2019 and Excel 2020.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties in Different Climatic Zones
Our results, as shown in Table 2, demonstrated a gradual increase in TOC content as the climatic zone shifted from south to north, with the order of cold temperate forest (94.67 g kg−1) > middle temperate forest (59.56 g kg−1) > subtropical forest (12.81 g kg−1) > tropical forest (5.54 g kg−1). The TOC contents in the tropical and subtropical forests were significantly lower than those in the temperate forests (including middle temperate and cold temperate zones). In terms of pH, the middle temperate forest exhibited the highest value (5.63), followed by the cold temperate forest (5.53), tropical forest (4.69), and subtropical forest (4.50). The values in the temperate forests were significantly higher than those in the tropical and subtropical forests, which may reflect differences in vegetation composition, soil parent material, and climate. There were significant differences among different climatic zones in the variation rule of AP content, which was consistent with the pH value. Finally, the AK content followed the order of middle temperate forest (245.85 mg kg−1), cold temperate forest (101.82 mg kg−1), subtropical forest (55.39 mg kg−1), and tropical forest (32.67 mg kg−1), and the content in the middle temperate forest being significantly higher than that in the other climatic zones. These findings suggest that climate and soil properties, such as mineralogy and texture, may influence the availability of potassium for plant growth and productivity. Overall, our results highlight the importance of considering climate and soil properties when assessing the status and sustainability of forest ecosystems.

Table 2.
Statistics of soil indexes in different climatic zones of China.
3.2. Latitudinal Zonality of Soil Phytolith and PhytOC
There was a significant exponential increase in the content of soil phytolith with increasing latitude (p < 0.01), as depicted in Figure 1a. Furthermore, we found that the order of soil phytolith content followed a geographic pattern with the cold temperate forest having the highest content (20.92 g kg−1), followed by the middle temperate forest (14.08 g kg−1), subtropical forest (9.00 g kg−1), and tropical forest having the lowest content (5.30 g kg−1). The soil phytolith contents in the tropical and subtropical forests were significantly lower than those in the cold temperate forest; however, there was no significant difference noted between adjacent climatic zones, such as tropical forest and subtropical forest, subtropical forest and middle temperate forest, and middle temperate forest and cold temperate forest. The results revealed a significant linear increasing trend (p < 0.01) in the soil phytOC content with the increase in latitude, as shown in Figure 1b, which shared the same pattern with soil phytolith content. Specifically, the soil phytOC content in the cold temperate zone was the highest (0.61 g kg−1) and significantly higher than that in other climatic zones (p < 0.05), while the tropical zone exhibited the lowest content (0.08 g kg−1). Our findings demonstrate that latitude plays an essential role in influencing the contents of soil phytolith and phytOC in different forest types. This study enhances our understanding of the biogeochemical processes of phytolith accumulation across latitudinal gradients in forest ecosystems and has important implications for global carbon cycling and the carbon sequestration potential of forest ecosystems.
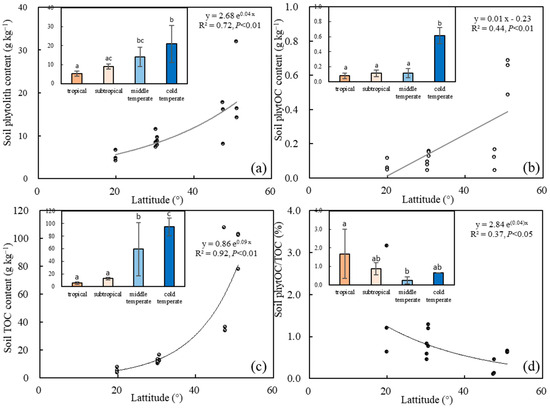
Figure 1.
Variation characteristics of soil phytolith and phytOC content with latitude. (a) Soil phytolith content with latitude; (b) Soil phytOC content with latitude; (c) Soil TOC content with latitude; (d) Soil phytOC/TOC with latitude. Lowercase letters represent statistically significant differences among different climatic zones.
The results demonstrated an evident exponential increase in TOC content with increasing latitude (p < 0.01) (Figure 1c). Our data showed that cold temperate forest had the highest TOC content (94.67 g kg−1), followed by middle temperate forest (59.56 g kg−1), subtropical forest (12.81 g kg−1), and tropical forest (5.54 g kg−1). Notably, the TOC content in the temperate forest was significantly higher than that in tropical and subtropical forests, and there was a significant difference between the cold temperate forest and the middle temperate forest. Furthermore, the proportion of soil phytOC decreased linearly with increasing latitude (p < 0.05) (Figure 1d). The order from highest to lowest proportion of soil phytOC was tropical forest (1.68%), subtropical forest (0.86%), cold temperate forest (0.65%), and middle temperate forest (0.24%). Interestingly, the proportion of soil phytOC in the middle temperate forest was significantly lower than that in the tropical forest (p < 0.05), but there was no significant difference among other climate zones (p > 0.05).
3.3. Relationship Between Soil Phytolith Factors and TOC
The correlation between the soil phytOC content, soil phytolith content, and C content occluded in phytolith was found to be significantly positive, as depicted in Figure 2 (p < 0.01). This suggests that the joint action of phytolith and C occluded in phytolith led to the increase in soil phytOC storage, with C occluded in phytolith having a greater influence. Additionally, there was a significant positive correlation between soil phytolith content, phytOC content, and TOC content (p < 0.01). An increase in TOC content would facilitate the formation and accumulation of soil phytolith and phytOC.
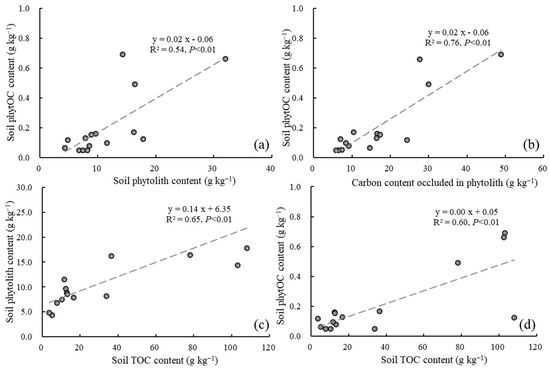
Figure 2.
Scatter plots of soil phytolith, phytOC, and TOC. (a) Scatter plot of soil phytOC content and soil phytolith content; (b) Scatter plot of soil phytOC content and carbon content occluded in phytolith; (c) Scatter plot of soil phytolith content and soil TOC content; (d) Scatter plot of soil phytOC content and soil TOC content.
3.4. Effects of Soil Chemical Properties and Climatic Factors on Soil Phytolith and PhytOC Accumulation
Temperature and precipitation played significant roles in the formation and accumulation of soil phytolith and phytOC (Figure 3). A negative correlation was observed between soil phytOC and phytolith with temperature (p < 0.01), indicating a significant increase in soil phytolith and phytOC with a decrease in temperature. Similarly, a negative correlation was observed between soil phytOC and phytolith with precipitation (p < 0.05), suggesting that a decrease in precipitation led to a significant increase in soil phytOC and phytolith. Therefore, low temperature and optimal precipitation levels are favorable for the formation and accumulation of soil phytolith and phytOC.
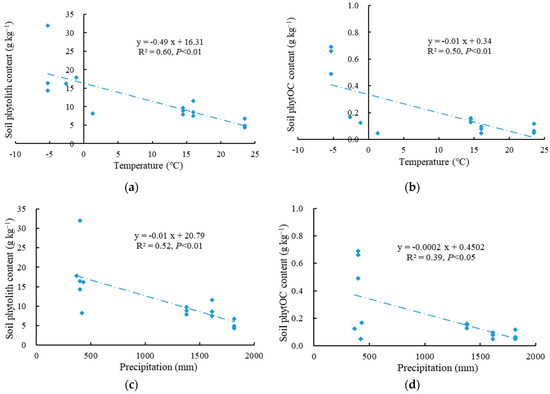
Figure 3.
Variations of soil phytolith and phytOC content with temperature and precipitation. (a) Scatter plot of soil phytolith content and temperature; (b) Scatter plot of soil phytOC content and temperature; (c) Scatter plot of soil phytolith content and precipitation; (d) Scatter plot of soil phytOC content and precipitation.
The correlation coefficients between soil phytolith indices and soil chemical properties were presented in Figure 4. The soil phytolith content showed a significant (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) positive correlation with TOC, pH, and AP, with correlation coefficients of 0.806, 0.687, and 0.521, respectively. Similarly, a positive correlation was observed between soil phytOC content and TOC content (r = 0.774, p < 0.01) and pH (r = 0.551, p < 0.01). The ratio of phytOC/TOC exhibited a negative correlation with AP (r = −0.571, p < 0.05).
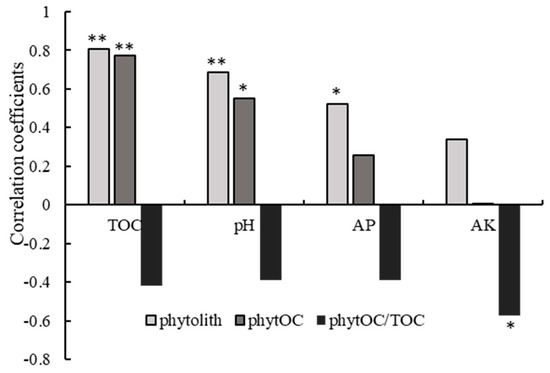
Figure 4.
Relationship between soil phytolith indexes and soil chemical properties. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
3.5. Soil Phytolith and PhytOC Storage in Different Climatic Zones
The storage of soil phytoliths among different climatic zones showed a distinct pattern from south to north, as illustrated in Figure 5. The highest phytolith storage was in the cold temperate forest, with a value of 41.01 t ha−1, followed by the middle temperate forest (29.57 t ha−1), subtropical forest (21.59 t ha−1), and tropical forest (15.88 t ha−1). The soil phytolith storage in the tropical and subtropical forests was significantly lower than that of the cold temperate zone, indicating differences in the distribution and composition of plant species among these areas. In terms of soil phytOC storage, the cold temperate forest showed the highest value of 1.20 t ha−1, followed by the subtropical forest (0.27 t ha−1), the middle temperate forest (0.24 t ha−1), and the tropical forest (0.23 t ha−1). The soil phytOC storage in the cold temperate forest was significantly higher than that in the other three climatic zones, pointing to variations in the amount and quality of organic matter and carbon fixation processes in soils across different forest types.
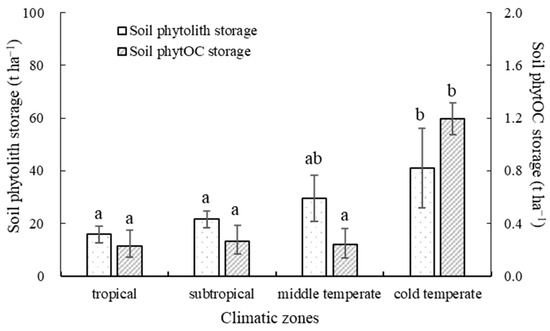
Figure 5.
Soil phytolith and phytOC storage in different climatic zones. Lowercase letters represent statistically significant differences among different climatic zones.
Overall, the study findings suggest that climatic conditions and vegetation characteristics have a significant impact on the storage and distribution of phytoliths and phytOC in soils, which in turn may influence ecosystem functions and services in different regions.
4. Discussions
4.1. Characteristics of Soil phytOC in Larix gmelinii Forests
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the study of soil phytOC content in different vegetation types and regions. Numerous studies have been conducted assessing soil phytOC content in various environments. For instance, research has shown that soil phytOC content in Moso bamboo forest is 0.195‰, compared to 0.165‰ in China fir forest [38]. Moreover, the content in paddy soil and the Loess Plateau is 0.203‰ [46] and 0.024‰ [42], respectively. Our study discovered that the mean soil phytOC content in Larix gmelinii forest is 0.588‰, which is higher than that of the other vegetation types mentioned earlier.
Several studies have highlighted the importance of organic matter encapsulation in the formation [10,14] of phytoliths during plant growth periods [19] for carbon sequestration in phytoliths. In the Larix gmelinii forest, our study observed a significant positive correlation between the soil phytOC content and soil phytolith content, as well as C content occluded in phytolith. This finding is consistent with several studies, including those by Li et al. [19,20,33], Zuo et al. [42], Guo et al. [47], and Zhao et al. [48], which suggests that the phytOC content in forest soils is jointly affected by phytolith content and C content occluded in phytolith. The C capture capacity during phytolith deposition in plants also has a significant impact on soil phytOC [10,13,14,49]. The soil phytolith content and the carbon occluded in phytolith in cold temperate forest soils are higher than those in tropical forests, resulting in a much higher phytOC content in cold temperate forest soils than in tropical forests. On one hand, coniferous tree species enhance their frost resistance and resistance to pathogens through silicification structures, resulting in higher silicon accumulation than non-grasses. On the other hand, plants in cold temperate regions have a stronger ability to capture carbon during the deposition of phytoliths, which can encapsulate more carbon; Meanwhile, the cold environment is more conducive to the stability of silicone implants.
4.2. Influencing Factors of Soil Phytolith and PhytOC
The accumulation of soil phytoliths can increase the stocks of soil phytOC, and three key factors must be taken into account: accumulation rate, dissolution, and migration of phytoliths [42]. The accumulation of phytoliths is mainly controlled by the return flux and stability of soil phytoliths in different environmental conditions. Previous studies have demonstrated that the return flux of phytoliths plays a significant role in determining the overall accumulation trend of soil phytoliths in different ecosystems [19,46,50,51]. It has been found that the release of phytoliths into the soil occurs when plants die and decay. If the input of phytoliths exceeds their decomposition and migration, phytoliths will accumulate [48].
The yield of aboveground plants is the key factor controlling phytoliths in soil. As such, the return flux of phytoliths is directly influenced by the forest types present in an ecosystem. The affected NPP is likely the most critical factor that determines soil phytOC [42]. The phytolith flux in ecological communities is also influenced by the phylogenetic level of plant species and the composition and distribution of herbs and trees in different forests [48]. Zhang et al. [50] has confirmed that there is a significant link between soil phytOC storage and the aboveground plant community. They found that higher litter recovery contributed to phytOC sequestration in forest soils. Vegetation type and growth status (i.e., age) also play a significant role in litter recovery. Yang et al. [52] found that community composition, phytolith yield for each plant, biomass ratio of aboveground herbaceous plants to tree leaves (i.e., needles), and the source of soil phytoliths could control the distribution of soil phytoliths, affecting biogenic silicon stability and geochemical cycling. Further research on these factors is vital to understand the role of phytoliths in carbon sequestration in different ecosystems fully. Furthermore, tree species also have a certain impact on the stability of phytoliths due to the differences in their chemical properties [51,53]. For instance, broad-leaved phytoliths are more unstable than coniferous phytoliths in temperate forest soils, where the biological cycle of silicon in broad-leaved leaves is faster [54]. Larix gmelinii is a dominant tree species in the cold temperate zone. As a coniferous tree species, it enhances its frost resistance and resistance to pathogens through silicification structure, and its silicon content is higher than that of non-grasses [55]. At the same time, the C/N ratio and lignin content of its leaf litter are high, and the surface is covered with a wax layer, which decomposes slowly, thereby prolonging the release time of silicon [56]. The thick layer of undecomposed litter formed by the Larix gmelinii also reduces soil disturbance and protects the lower layer of plant silicon from oxidation and water erosion. The Larix gmelinii has constructed a unique “high silicon input-slow turnover” carbon sequestration mode in cold temperate soils through the above traits. Therefore, the phytOC content in forest soils in cold temperate zones is significantly higher than that in other climatic zones.
The stability of soil phytoliths is a vital aspect that influences soil phytOC storage, and this is mainly determined by physical and chemical properties, as well as environmental conditions. Under the same environmental conditions, the stability of soil phytoliths remains constant [50]. Soil phytoliths have low water use efficiency, small surface area, and high aluminum concentration [57,58], making them less soluble in the soil compared to plants. In addition to different plant communities, soil characteristics (such as bulk density), biological disturbances (such as earthworm creep), and climatic conditions (such as precipitation and temperature) also play an important role in the distribution and migration of soil phytoliths [42,51,59,60]. Soil properties are another significant factor affecting the preservation and retention of phytoliths and phytOC in soils. Several soil characteristics, such as soil texture [61] and pH [62,63], can have significant effects. Soil factors like water and pH not only impact the accumulation of soil phytoliths [64] but also influence the assimilation of silicon by plants from the soil solution [15,52,58]. Research has demonstrated that plants growing in soils with low pH and high organic matter have the ability to absorb and accumulate greater amounts of silicon, thereby promoting the accumulation of phytoliths and enhancing carbon sequestration [11]. In our study, we discovered a significant positive correlation between soil phytolith content and TOC content (p < 0.01), demonstrating that the more litter input, the more phytolith accumulation in forest soil [50]. Furthermore, we also found a significant positive correlation between soil phytolith content and pH (p < 0.01). Generally, phytoliths tend to dissolve more easily under alkaline conditions [11]. An acidic environment with a lower pH value can reduce the nucleophilic attack of OH− on the ≡ Si-O-Si ≡ bond [65], which increases phytolith stability for a longer period, leading to increased phytOC storage [62,63,66]. However, in contrast to those findings, other studies have demonstrated a significant positive correlation between the content of available silicon in soil and soil pH [67,68], which is consistent with our results. Leaching can decrease soil phytoliths, which in turn reduces the C storage of soil phytoliths [69]. In southern China, leaching is a prominent phenomenon that is influenced by lower pH values, resulting in greater silicon leaching [67]. Zuo et al. [42] conducted a study on soil phytOC from the Loess Plateau and discovered variations in soil phytolith C density (SPCD) among different soil types having the same plant community. Therefore, the relationship between soil pH and phytoliths varies depending on soil and plant species, and a comprehensive analysis of these variables is crucial for the study of phytoliths. Additionally, there exists a significant correlation between soil phytoliths and AP (p < 0.05). As soil phytoliths remain relatively stable, soil nutrients indirectly promote their formation and accumulation of silicon by enhancing plant growth, increasing absorption of soluble silicon by plant roots, and accumulating silicon in phytoliths [48,69].
The accumulation of phytolith is influenced by several factors, including species and soil environment, such as pH, temperature, water, and nutrients. Phytoliths are also impacted by climate, human activities, and other factors, which can lead to varying levels of phytolith accumulation among different soil types and ecological settings [15,42,48,50,70]. Further analysis has shown that biogeochemical activities also affect the stability of soil phytoliths. This study indicates that temperature and precipitation play important roles in the formation and accumulation of soil phytoliths and phytOC [42]. There was a significant negative correlation between soil phytoliths and phytOC with temperature and precipitation (Figure 3), indicating that low temperature and optimal precipitation levels are conducive to the formation and accumulation of soil phytoliths and phytOC. In tropical regions, where high temperatures and humidity prevail [71], the stability of soil phytoliths is significantly reduced, limiting their accumulation in comparison to subtropical regions [72]. Therefore, phytolith storage is typically lower in tropical soils than in subtropical soils due to the weaker biogeochemical stability of soil phytoliths. The Larix gmelinii forest studies showed higher soil phytolith and phytOC contents compared to other regions. The forest is located in the cold temperate zone, where low temperature helps to preserve soil phytoliths. These results suggest that the accumulation of phytoliths is influenced by a combination of biogeochemical and environmental factors, and that cold temperate zones may provide optimal conditions for phytolith storage. We also found that the ratio of soil phytOC to TOC exhibited a latitudinal variation pattern opposite to that of soil phytolith and phytOC content. Due to the relative stability of phytOC protected by siliceous shells, this phenomenon is more influenced by soil TOC. In tropical regions, easily decomposed litter dominates, with a high proportion of activated carbon pools. Moreover, the high temperature and humidity throughout the year promote microbial activity and enzymatic reactions, leading to rapid decomposition of organic carbon (such as lignin and cellulose). Therefore, the proportion of phytOC is relatively high. As latitude increases, the low temperature season prolongs, microbial activity is limited, the overall decomposition rate of organic carbon slows down, and the accumulation increases.
The high phytOC content in cold temperate forests provides a unique “slow cycling” carbon pool for carbon neutrality goals. When afforestation or ecological restoration is considered, silicon-rich tree species (such as Picea asperata, Larix gmelinii) can be prioritized to maximize the input of plant silicon and carbon. The mixed forest configuration of high silica tree species and high productivity tree species to balance short-term and long-term carbon sequestration should be considered. Silicon fertilizer in silicon-poor areas to improve plant silicon absorption efficiency should be promoted. In forest management, the following should occur: promote low disturbance management modes, maintain understory vegetation cover, reduce soil disturbance, and extend carbon sequestration time. Phytolith carbon can be included in the “long-term soil carbon pool” of the national greenhouse gas inventory. By selecting silicon-rich tree species, managing soil silicon availability, implementing low-disturbance management, and innovating carbon accounting, a combination strategy is adopted to enhance carbon sequestration efficiency and climate resilience in cold temperate regions, providing a reference for the development of climate solutions.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study showed that there was a distinct latitudinal zonation in the content of phytolith and phytOC in Chinese forest soils. The concentration of soil phytoliths exhibits an exponential increase with higher latitudes, whereas the concentration of phytOC shows a gradual linear increase. The highest concentrations of both soil phytoliths and phytOC are observed in the cold temperate forests, whereas the tropical and subtropical forests exhibit lower concentrations. Furthermore, the storage of soil phytoliths and phytOC is significantly higher in cold temperate forests compared to their tropical and subtropical counterparts.
The increase in soil phytOC storage is primarily attributed to the occluded C in phytolith, which has a significant influence on the combined impact of phytolith and C occluded in phytolith. The formation and accumulation of soil phytolith and phytOC are influenced by temperature and precipitation, with low temperature and suitable precipitation being more conducive. Moreover, the pH, organic matter, and nutrients of soil can also play a role in the formation and accumulation of soil phytoliths.
The accumulation and stability of phytoliths in soil are impacted by various factors, including biogeochemical activities, climate, and species composition. This work highlights the role of litter recovery, phytolith content, C occluded in phytolith, and vegetation type and growth status in affecting soil phytOC content. These findings contribute to a better understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying C sequestration in phytoliths in forest soil ecosystems. Our research provides valuable insights into the patterns of soil phytolith and phytOC storage in Chinese forest soils, which can aid in enhancing our understanding of the biogeochemical cycles of C in forest ecosystems.
Of course, due to sample limitations, this study has certain spatial limits. In the future, the distribution and quantity of samples should be further expanded, and statistical methods should be used to construct a theoretical model framework to deeply explore the environmental impact mechanism of forest soil phytOC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, B.W. and Q.Z.; investigation, B.W. and N.Z.; formal analysis, B.W., N.Z. and X.Z.; manuscript writing and editing, B.W., N.Z., Q.Z. and X.Z.; funding acquisition, B.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32260389), the Key Research and Development Plan of Inner Mongolia, China (2023YFDZ0026), and the Research Team Construction Project of Forestry College, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, China.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Forest Ecosystem National Observation and Research Station of Greater Khingan Mountains in Inner Mongolia, China provided experimental platform support for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and Climate Change: Forcings, Feedbacks, and the Climate Benefits of Forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.Y.; Brown, S.; Tang, Y.H.; Nabuurs, G.J.; Wang, X.P.; Shen, H.H. Overestimated biomass carbon pools of the northern mid- and high latitude forests. Clim. Change 2006, 74, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodale, C.L.; Apps, M.J.; Birdsey, R.A.; Field, C.B.; Heath, L.S.; Houghton, R.A.; Jenkins, J.C.; Kohlmaier, G.H.; Kurz, W.; Liu, S. Forest carbon sinks in the northern hemisphere. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.D.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.Y.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Q. A reviw on soil organic carbon storage and influencing factors. Soils 2000, 32, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimann, M.; Reichstein, M. Terrestrial ecosystem carbon dynamics and climate feedbacks. Nature 2008, 451, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Schaefer, D.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Zou, X.M.; Xu, X.L.; Kuzyakov, Y. Labile carbon retention compensates for CO2 released by priming in forest soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H. Evidence from chronosequence studies for a low carbon-storage potential of soils. Nature 1990, 348, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Luan, J. A review of research progress and future prospective of forest soil carbon stock and soil carbon process in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 5437–5448. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, J.; Sullivan, L.; Chen, B.H.; Ye, G.F.; Zheng, W.P. Carbon bio-sequestration within the phytoliths of economic bamboo species. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.L.; Wang, H.L.; Strong, P.J.; Li, Z.M.; Jiang, P.K. Plant impact on the coupled terrestrial biogeochemical cycles of silicon and carbon: Implications for biogeochemical carbon sequestration. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 115, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lü, H. Research and Applications of Plant Phytoliths; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, X.X.; Lü, H.Y. Carbon sequestration within millet phytoliths from dry-farming of crops in China. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 3451–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.F.; Sullivan, L.A. Phytolith occluded carbon and silica variability in wheat cultivars. Plant Soil 2011, 342, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.F.; Sullivan, L.A. Soil carbon sequestration in phytoliths. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M. Research on Silicon Distribution and Phytolith Carbon Sequestration of Typical Artificial Forest in Temperate and Subtropical Zone of China. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A & F University, Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, C.S. Extended depth of focus image for phytolith analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 2253–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperno, D.R. Phytoliths. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments; Smol, J.P., Birks, H.J.B., Last, W.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.M.; Song, Z.L.; Li, B.L. The production and accumulation of phytolith-occluded carbon in Baiyangdian reed wetland of China. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 37, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Song, Z.L.; Li, B.L. Generation and accumulation of phytoliths on Baiyangdian reed wetland ecosystems. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2013, 53, 632–636. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Hao, Q.; Wang, H.L.; Zwieten, L.V.; Yu, C.X.; Liu, T.Z.; Yang, X.M.; Zhang, X.D.; Song, Z.L. A review of carbon isotopes of phytoliths: Implications for phytolith-occluded carbon sources. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranere, A.J.; Piperno, D.R.; Holst, I.; Dickau, R.; Iriarte, J. The cultural and chronological context of early Holocene maize and squash domestication in the Central Balsas River Valley, Mexico. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5014–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Wu, N.Q.; Liu, K.-b.; Xu, D.K.; Li, Q. Phytoliths analysis for the discrimination of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) and common millet (Panicum miliaceum). PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krull, E.S.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Graetz, D.; Grice, K.; Dunning, W.; Cook, G.; Parr, J.F. 13C-depleted charcoal from C4 grasses and the role of occluded carbon in phytoliths. Org. Geochem. 2003, 34, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Lü, H.Y.; Wang, G.A.; Yang, H.; Li, Z. C3 and C4 plants and modern soil phytolith carbon isotope analysis. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2000, 45, 978–982. [Google Scholar]
- Bremond, L.; Alexandra, A.; Wooller, M.J.; Hely, C.; Williamson, D.; Schaefer, P.A.; Majule, A.; Guiot, J. Phytolith indices as proxies of grass subfamilies on East African tropical mountains. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 61, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulholland, S.C.; Prior, C. AMS radiocarbon dating of phytoliths. MASCA Res. Pap. Sci. Archaeol. 1993, 10, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Piperno, D.R. Phytolith Analysis: An Archaeological and Geological Perspective; Harcourt Brace Jovanovich: San Diego, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 12–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.J.; Song, L.K.; Sheng, M.Y. Carbon sequestration law by phytoliths in the bamboo forests: Insights for the management of phytolith carbon sink. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 58, e03491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Si, Y.; Yin, Y. The production of phytoliths in China’s grasslands: Implications to the biogeochemical sequestration of atmospheric CO2. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Song, Z.L.; Hao, Q.; Yu, C.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Chen, C.M.; Müller, K.; Wang, H.L. Storage of soil phytoliths and phytolith-occluded carbon along a precipitation gradient in grasslands of northern China. Geoderma 2020, 364, 114200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Tan, L.; Peng, M.; Chen, H.; Tan, C.; Zhao, E.Q.; Zhang, L.; Peng, H.Y.; Liang, Y.C. The spatial distribution of phytoliths and phytolith-occluded carbon in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) ecosystem in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.M.; Song, Z.L.; Parr, J.F.; Wang, H.L. Occluded C in rice phytoliths: Implications to biogeochemical carbon sequestration. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Song, Z.L.; Guo, L.D.; Wang, J.X.; Ni, Y.L.; Li, Z.M.; Hao, Q.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.L.; Kuang, W.; et al. Specific PhytOC fractions in rice straw and consequent implications for potential of phytolith carbon sequestration in global paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Sheng, M.Y.; Wang, L.J.; He, Y.; Guo, C. Response of soil phytolith occluded organic carbon accumulation to long-term vegetation restoration in Southwest China karst. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3088–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.F.; Sheng, M.Y. Effects of Stand Age and Environmental Factors on Soil Phytolith-Occluded Organic Carbon Accumulation of Cunninghamia lanceolata Forests in Southwest Subtropics of China. Forests 2025, 16, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.Q. Variation and Stability of Phytolith-Occluded Carbon in Typical Forest-Soil Ecosystems in Tropics and Subtropics. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A & F University, Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.L. Study on Phytolith-Occluded Carbon in Soil Under Important Forest Kinds. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang A & F University, Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 615-2011; Soil-Determination of Organic Carbon-Potassium Dichromate Oxidation Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- NY/T 1849-2010; Method for Determination of Ammonium Nitrogen, Available Phosphorus and Rapidly-Available Potassium in Acid Soil Universal Extract-Colorimetric Method. Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Parr, J.F. A comparison of heavy liquid floatation and microwave digestion techniques for the extraction of fossil phytoliths from sediments. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2002, 120, 315–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.X.; Lu, H.Y.; Gu, Z.Y. Distribution of soil phytolith-occluded carbon in the Chinese Loess Plateau and its implications for silica-carbon cycles. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Meng, M.; Zhang, Q.L. Soil phytoliths in Larix gmelinii forest and their relationships with soil properties. Plant Soil 2022, 474, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.T.; Jiang, P.K.; Xiaochuan, C.S.; Yan, Z.; Ying, Y.Q. Production of carbon occluded in phytolith is season-dependent in a bamboo forest in subtropical China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Vogeler, I.; Schwendenmann, L. Conversion from tussock grassland to pine forest: Effect on soil phytoliths and phytolith-occluded carbon (PhytOC). J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.M.; Zhang, G.L. Phytoliths and its occluded organic carbon in a stagnic anthrosols chronosequence. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.S.; Song, Z.L.; Sullivan, L.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, X.D.; Li, Z.M.; Zhao, Y.Y. Enhancing phytolith carbon sequestration in rice ecosystems through basalt powder amendment. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Song, Z.L.; Xu, X.T.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, X.C.; Li, Z.M.; Guo, F.S.; Pan, W.J. Nitrogen application increases phytolith carbon sequestration in degraded grasslands of North China. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, J.; Sullivan, L.; Quirk, R. Sugarcane phytoliths: Encapsulation and sequestration of a long-lived carbon fraction. Sugar Tech 2009, 11, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Song, Z.L.; McGrouther, K.; Li, J.W.; Li, Z.M.; Ru, N.; Wang, H.L. The impact of different forest types on phytolith-occluded carbon accumulation in subtropical forest soils. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blecker, S.W.; McCulley, R.L.; Chadwick, O.A.; Kelly, E.F. Biologic cycling of silica across a grassland bioclimosequence. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2006, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Song, Z.L.; Liu, H.Y.; Zwieten, L.V.; Song, A.L.; Li, Z.M.; Hao, Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, H.L. Phytolith accumulation in broadleaf and conifer forests of northern China: Implications for phytolith carbon sequestration. Geoderma 2018, 312, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F. Crystallochemistry and surface properties of biogenic opal. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1985, 36, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F. The biogeochemical cycle of silicon in two temperate forest ecosystems. Ecol. Bull. 1983, 35, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Hodson, M.; White, P.J.; Mead, A.; Broadley, M. Phylogenetic variation in the silicon composition of plants. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 1027–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B.; McClaugherty, C. Plant Litter: Decomposition, Humus Formation, Carbon Sequestration; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, F.; Wilding, L.P. Dissolution of Biogenic Opal as a Function of its Physical and Chemical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.L.; Song, Z.L.; Wang, H.L.; Li, Z.M.; Jiang, P.K.; Zhou, G.M. Lithological control on phytolith carbon sequestration in moso bamboo forests. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J. The occurrence and significance of biogenic opal in the regolith. Earth Sci. Rev. 2003, 60, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishkis, O.; Ingwersen, J.; Streck, T. Phytolith transport in sandy sediment: Experiments and modeling. Geoderma 2009, 151, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, D.M.; Humphreys, G.S. Phytolith depth functions in surface regolith materials; Advances in Regolith. In Proceedings of the CRC LEME Regional Regolith Symposia, Adelaide, Australia, 13–14 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fraysse, F.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Schott, J.; Meunier, J.D. Surface chemistry and reactivity of plant phytoliths in aqueous solutions. Chem. Geol. 2009, 258, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraysse, F.; Pokrovsky, O.S.; Schott, J.; Meunier, J.D. Surface properties, solubility and dissolution kinetics of bamboo phytoliths. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, Z.T.; Jiang, P.K.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, J.S. Belowground phytolith-occluded carbon of monopodial bamboo in China: An overlooked carbon stock. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, P.M.; Crerar, D.A. Kinetics of quartz dissolution in electrolyte solutions using a hydrothermal mixed flow reactor. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.N.; Dultz, S.; Guggenberger, G. Effects of pretreatment and solution chemistry on solubility of rice-straw phytoliths. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Wu, J.S.; Sheng, W.X.; Jiang, P.K.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ge, J.F. Potential of phytolith-occluded organic carbon sequestration in masson pine stands at different ages in subtropical China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, W.S.; He, D.Y.; Liao, X.L. The relationship between the form of silicon in soil and soil properties in Hunan Province. Soil 1993, 25, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.T.; Li, Y.F.; Jiang, P.K.; Chang, S.X.; Song, Z.L.; Liu, J.; Zhou, G.M. Long-term intensive management increased carbon occluded in phytolith (PhytOC) in bamboo forest soils. Sci. Rep. 2015, 4, 3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Song, Z.L.; Sullivan, L.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.M.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, F.F. Topographic control on phytolith carbon sequestration in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) ecosystems. Carbon Manag. 2016, 7, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandre, A.; Meunier, J.D.; Colin, F.; Koud, J.M. Plant impact on the biogeochemical cycle of silicon and related weathering processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Song, Z.L.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zwieten, L.V.; Li, J.W.; Liu, L.N.; Xu, S.; Wang, H.L. Impact of climate and lithology on soil phytolith-occluded carbon accumulation in eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).