Abstract
The Natural Forest Protection Project (NFPP) is an ecological restoration project aimed at safeguarding natural forests, and is one of China’s six main forestry initiatives. The upper reaches of the Yangtze River represent the main distribution area of natural forests in China, and are an important area for the implementation of the NFPP. A systematic assessment of forest ecosystem changes in the upper Yangtze River region before and after implementation of the NFPP is of great scientific significance for the improvement of the project implementation effect, regional ecological protection, and further protection and restoration of natural forest resources. This study uses the NFPP area in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches as the study area; the data are primarily derived from the 1998 and 2020 forest resources category II survey data, long-term monitoring data from forest ecological stations, and public social data published by authoritative Chinese organizations. Based on the above data, we used the full index system of forest ecosystem services, continuous observation, and inventory system with the distributed measurement method to analyze the dynamic changes in forest ecosystem services in the study area in terms of three aspects: physical quality, value quality, and dominant function. The results of the study show that: (1) over the studied time scale, compared to the 1998 baseline, the physical quantities (soil erosion control, water regulation, and PM10 retention) and value of each service function of the forest ecosystem in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River project area in 2020 showed a significant increasing trend; (2) at the spatial scale, changes in forest ecosystem service functions in the upper reaches of Yangtze River under the NFPP showed significant spatial heterogeneity from 1998 to 2020; (3) in 2020, the total value of forest ecosystem services in the study area was 3,261,161,000,000 yuan/a, of which the functional value of biodiversity conservation was 1,294,426,000,000 yuan/a and the functional value of water conservation was 841,069,000,000 yuan/a, indicating that the forest ecosystem of the study area plays an important role as a “green gene pool” and “green water reservoir”; (4) the forest ecosystem service functions of the NFPP in the upper reaches of Yangtze River are intricately tied to forest resource features such as forest area, forest volume, age-group structure of arbor forest, etc., which influence the physical quantity and value of each forest ecosystem service function to varying degrees. In addition to illustrating the amazing efficiency of the natural forest preservation initiative, this study provides a scientific foundation for future natural forest resource conservation and restoration. It can serve as a reference for the project’s subsequent development as well to provide scientific foundations and guidance for the development of the natural forest protection and restoration program and to promote the protection and restoration of more natural forest resources.
1. Introduction
Forest ecosystems are important components of terrestrial ecosystems because they offer natural environmental conditions for humans and perform a range of tasks, including water retention, biodiversity protection, carbon sequestration, oxygen release, and atmospheric purification [1,2,3,4,5]. Forest ecological benefit refers to the ecological value of the forest resource itself as well as the cumulative effect of social utilization of the forest ecological function. Water conservation, soil conservation, wind and sand management, carbon sequestration, oxygen retention, atmospheric purification, noise reduction, flood and drought mitigation, wildlife protection, and increased tourism advantages are examples of these [6]. Natural forests are the main body and essence of forest resources, with the most complex structure, most stable community, largest biomass, richest biodiversity, and strongest ecological function of terrestrial ecosystems in nature [7,8,9], and play a critical role in ensuring the social stability of forest areas, ecological security of the national territory, and sustainable and stable development of the national economy [10].
Forest eco-efficiency evaluation research began in the 1950s, while economic valuation of eco-efficiency arose in the late 1980s as the economy developed [6]. Forest ecosystem assessment results assist decision-makers in improving planning measures for forest sustainability, organizing ecotourism, and making management decisions [1]. As a result, the study of forest ecological efficiency is conducted to change people’s understanding of the ecological function of forests as well as to pay attention to the ecological function of forests, and has a significant impact on the rational allocation of resources to achieve forestry compensation. As a result, it provides a scientific foundation for the long-term development of forestry [11].
The forests in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River have been severely damaged; natural forest resources have been sharply reduced, ecological functions have been degraded, soil erosion has intensified, and ecological disasters have occurred frequently, resulting in serious provincial ecological and economic consequences [9,12,13,14,15]. The Yangtze River mega-flood in 1998 produced a variety of ecological, environmental, and socio-economic issues, which explains why the state launched the effort to protect natural forest resources. The NFPP has fundamentally and effectively slowed the degradation trend of forest ecological resources in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches [12] while continuously improving the ecological environment of the Yangtze and Yellow River basins by adjusting and optimizing the economic structure of forest areas, improving forest quality, and ensuring the national economy and society’s long-term development. The study area involves Hubei, Sichuan, Chongqing, Guizhou, Yunnan, and Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), and covers the natural forest distribution area in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. The NFPP in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches is expected to significantly improve the quality and ecological functions of the forests, which play an irreplaceable role in constructing an ecological security barrier in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches, increasing forest carbon sinks, and addressing global climate change [16].
The NFPP is one of China’s important forestry ecological projects; it aims to solve the problem of resting and restoring natural forests through orderly logging restrictions, banning natural forest resources, and reducing timber production to ultimately achieve the coordinated development of resources, economy, and society in forest areas [17,18]. From the beginning of the NFPP, many scholars have carried out studies related to this project at the national [16,19], regional, and local [20,21] scales, mainly including forest resources [22], vegetation carbon stocks [23,24,25], vegetation cover [26,27,28], ecosystem services function [29,30,31], socioeconomic benefits [32,33,34], policies [35,36], and forest management [36,37,38], among others. However, previous studies have only focused on forest ecosystem service functions, forest resources, socioeconomic benefits, and studies confined to a specific region, and have not evaluated the forest ecological benefits of the entire upper Yangtze River under the NFPP from an overall perspective and over a short time span.
With the publication of the Natural Forest Protection and Restoration System Plan and the continued promotion of natural forest resource protection and restoration, as well as the ongoing promotion of the national strategy to strengthen ecological protection and ecological civilization, it has become critical to assess the ecological benefits of the study area comprehensively and clearly. As a result, in order to reveal the impact of the NFPP on forest ecosystem services in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River, in order to reveal the spatial and temporal change characteristics of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area and to combine them with the changes in forest resources to reveal the driving forces, this study refers to the “Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services” (GB/T38582-2020) [39] coupling a forest ecological linkage clearing dataset, forest resources dataset, social public dataset, and selected indicators of soil fixation, fertilizer retention, nitrogen fixation, phosphorus fixation, potassium fixation, water regulation, water purification, carbon fixation, oxygen release, anion provision, absorption of gaseous pollutants, stagnant TSP, stagnant PM2.5, stagnant PM10, etc., to assess the functions of forest ecosystems in the study area. The assessment includes a comparison between 1998 and 2020 in terms of soil conservation, nutrient retention, water conservation, carbon fixation, oxygen release, anion provision, gas absorption, stagnation TSP, stagnation PM2.5, stagnation PM10, water sources, carbon sequestration and oxygen release, purification of the atmospheric environment, and biodiversity protection, and assessed six major ecosystem service functions in terms of physical quality and value quantity [40,41,42]. Excel software 2010 was used to calculate and analyze the data.
The research objectives of this study were as follows: (a) to analyze the changes in ecosystem service functions of the NFPP in terms of both physical quantity and value quantity; (b) to demonstrate the main drivers of the changes in ecosystem service functions of the study area; and (c) to provide a theoretical foundation for scientific evaluation of ecological consequences of ecological initiatives, increased conservation of natural forest resources, and optimization of natural forest ecosystem service functions.
2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
This study intends to reflect the changes in ecological benefits of the Yangtze River’s upper reaches under the NFPP, with the time node spanning from the project’s pilot phase in 1998 to the end of the second phase in 2020. As a consequence, the study area is bounded by the Three Gorges reservoir area, which includes six provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) of Yunnan, Sichuan, Guizhou, Chongqing, Hubei, and Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) (Figure 1), and the implementation area includes 390 counties (autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the central government) and 26 state-owned Forestry Bureaux, for a total of 416 implementation units.
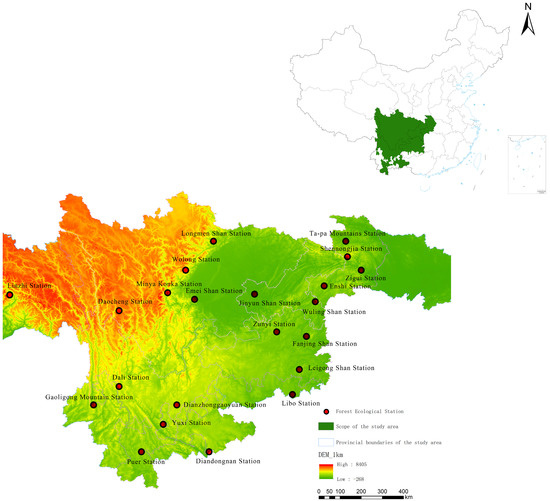
Figure 1.
The scope of the NFPP in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River.
The study area is located in the transition zone of Chinese topography, with complex and diversified landform types such as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, the Hengduan Mountains, the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, and the Sichuan Basin. The Yangtze River’s upper reaches have a diversified climate, including high mountain Highland climate, subtropical monsoon climate, subtropical humid monsoon climate, and more. The main climate threats include cold weather, flooding, and drought [43].
2.2. Research Methodology
2.2.1. Data Sources
The data sources for the changes in physical measurements of the NFPP’s ecosystem in the upper reaches of Yangtze River have three main aspects:
- (1)
- Ecological continuous clearing dataset: a continuous ecological inventory from the study area and the vicinity of the 22 forest ecology stations (Figure 1) taking long-term observation results, with data from 1998 used as background data before the NFPP began. At the same time, forest ecological continuous clearing is being carried out in the project area in accordance with the People’s Republic of China’s national standards “Methodology for field Long-Term observation of Forest Ecosystem” (GB/T 33027-2016) [44], “Indicator System for Long-Term Observation of Forest Ecosystem” (GB/T 35377-2017) [45], and “Specifications for assessment to forest ecosystem services” (GB/T 38582-2020) [39].
- (2)
- Forest resource dataset: forest resource data for 1998 and 2020 provided by the State Forestry and Grassland Administration’s Survey and Planning Design Institute.
- (3)
- Social public dataset: social public data published by authoritative institutions in China, such as the China Soil and Water Conservation Bulletin, the Water Resources Bulletin of the Yangtze River Basin and the Southwest Rivers, the China Forestry Yearbook, the Water Resources Construction Budget Quotas of the People’s Republic of China, the China Agricultural Information Network (http://www.agri.cn/) accessed on 1 January 2023, the China Statistical Yearbook National Health of the People’s Republic of China Health Commission (http://www.nhc.gov.cn/) accessed on 1 January 2023, etc.
Three types of data sources were coupled and integrated into a series of evaluation formulas. Finally, the material and value of the NFPP ecosystem services in the study area were evaluated.
2.2.2. Assessment Methods
Based on the continuous observation and inventory system of ecosystem services, coupled with the ecological linkage dataset, forest resource dataset and social public dataset, this study constructs the evaluation index system of ecosystem services for the NFPP in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River based on the national standard of the People’s Republic of China “Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services” (GB/T38582-2020) [39], and adopts the distributed measurement methodology (Figure 2) to carry out the assessment of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area.
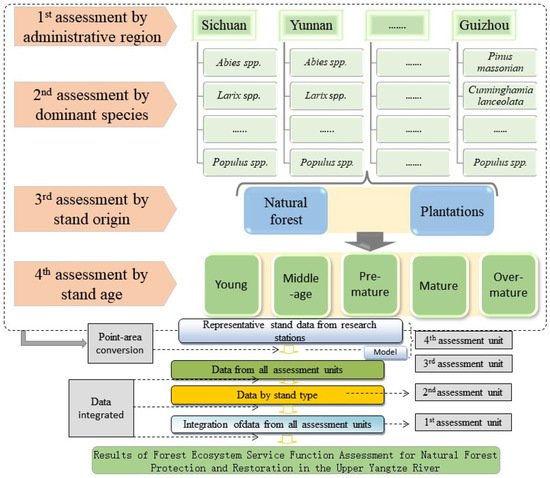
Figure 2.
Distributed measurement method of forest ecological services in the study area.
The specific steps of the distributed measurement method adopted in this report are: ① divided into six level 1 measurement units according to the provincial administrative divisions; ② each level 1 measurement unit is divided into 39 level 2 measurement units according to the dominant tree species groups; ③ each level 2 measurement unit is divided into two level 3 measurement units according to their origins; and ④ each level 3 measurement unit is divided into five level 4 measurement units according to the age groups of the forests, namely, young forest, middle-aged forest, near-mature forest, and mature forest. Each tertiary unit was divided into five tertiary units according to age groups: young forest, middle-aged forest, near-mature forest, mature forest, and over-mature forest. Finally, 2584 relatively homogenized ecological service assessment units were determined by combining comparative observations of different stand conditions. Because this report evaluates the ecological benefits before and after the implementation of Tianbao, the final number of relatively homogenized ecological service assessment units is 2584.
The index system included six ecological service functions and fifteen evaluation indices (Figure 3). The six ecological service functions were soil conservation (soil erosion control and protection of soil fertility), nutrients accumulation (nitrogen accumulation, phosphorus accumulation and potassium accumulation), water conservation (water regulation and water purification), carbon sequestration and oxygen release, purification of atmospheric environment (negative ion supply, pollutant absorption, TSP retention, PM10 retention, and PM2.5 retention), and biodiversity conservation (species conservation).
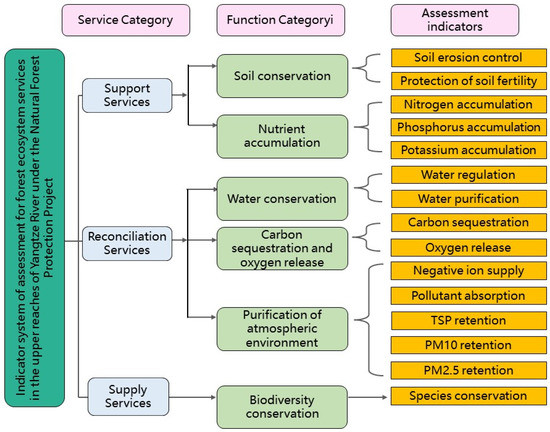
Figure 3.
Monitoring and evaluation index system of forest ecosystem service function in the study area.
2.3. Changes in Forest Resources in the Study Area
2.3.1. Characteristics of Quantitative Changes
In terms of time changes, the NFPP has achieved a “double increase” in natural forest volume and area in the research region by implementing a forest management system that focuses on the protection of forest resources, reinforced by rational exploitation. In 2020, the area and volume of natural forest protection and restoration in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River were generally on the rise, with an increase of 46,298,600 ha, or 38.31%, higher than the national level (25.71%) in the same period, and a volume increase of 1,186,000,000 m3, or 42.80%. In terms of spatial distribution (Figure 4), the NFPP areas in Hubei, Chongqing, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Guizhou Provinces all show an increasing trend of change, with the largest increase in the natural forest protection and restoration area in Sichuan Province, which increased by 3,754,300 ha, accounting for 43.74% and 39.74% of the total forest area, respectively; the forest areas of the NFPP in the TAR in both 1998 and 2020 are smaller and show a shrinking trend, from 1,227,300 ha in 1998 to 1,222,500 ha in 2020 (Table 1).
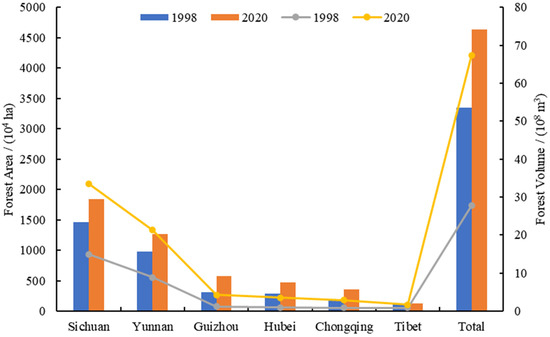
Figure 4.
Spatial and temporal changes in forest resources in the study area.

Table 1.
Changes in the area and volume of forest resources in the study area.
From Table 1, the volume of forest in the research region increased overall in 2020 compared to 1998, while the volume of forest in the NFPP in TAR fell from 87,000,000 m3 in 1998 to 84,000,000 m3 in 2020. This is due to the fact that, on the one hand, 287 forest fires occurred in TAR between 2001 and 2017, with a total affected forest area of 800 ha [46]; on the other hand, the main constituent species of forests in TAR are Abies fabri, Picea asperata, and Tsuga chinensis, with the majority of them being mature forests; and, finally, pests and viruses are wreaking the forest areas of Abies spp. in high-altitude forest areas such as Linzhi and Chamdo [47].
2.3.2. Characteristics of Structural Change
Age-Group Structure of Arbor Forest
The age classification of each dominant tree species (group) of arbor forest followed the National Standard of the People’s Republic of China “Technical Regulations for Continuous Forest Inventory” (GB/T38590-2020) [48]. Compared to 1998, the area and volume of all age groups of arbor forests in the study area had increased rapidly by 2020, with middle-aged and near-mature forests showing the most significant growth in both area and volume, with the area of medium-aged forests increasing by 2,866,600 ha and volume increasing by 386 million m3, the area of near-mature forests increasing by 2,559,100 ha, and volume increasing by 292 million m3 (Table 2).

Table 2.
Age-group structure of arbor forest in the study area.
In both 1998 and 2020, the area of arbor forest in the study area was largest in middle-aged and young forests, accounting for 63.59% and 59.52% of total area in the same period, respectively, while the proportion of near-mature, mature, and over-mature forests was smaller, indicating that the forest as a whole was in the growth and development stage and its age structure was changing. In 2020, the area of each age group increased gradually compared to 1998, with the share of near-mature forest and mature forest increasing by 4.23% and 1.07%, respectively, and the age group structure tending towards becoming rationalized.
The age group structure of forest ecosystems in each province of the study area is shown in Figure 5. The forest age structure in Sichuan and Tibet is more balanced, while the forest age structure in Yunnan, Hubei, Guizhou, and Chongqing is dominated by young forest and middle-aged forest.
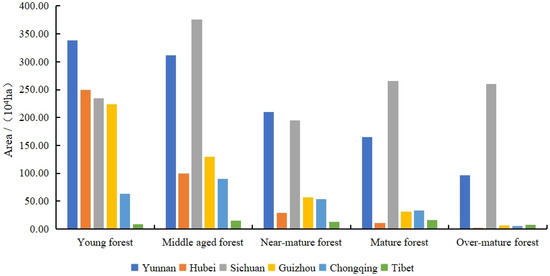
Figure 5.
Age-group structure of arbor forest in the provinces of the study area.
Dominant Tree Species (Group)
According to the dominant tree species (group), the top ten ranked forest areas were broad-leaved mixed forest, mixed conifer-broadleaf forest, mixed conifer forest, Cupressus funebris, Cunninghamia lanceolata, Abies spp., Picea asperata, Quercus spp., Pinus yunnanensis, and Pinus massoniana. Compared to 1998, the forest area of each dominant tree species (group) showed an overall increasing trend in 2020, among which the largest increases were in broadleaf tree mixed forest, conifer-broadleaf forest, and coniferous tree mixed forest, increasing by 5,457,200 ha, 1,862,400 ha, and 997,100 ha respectively (Figure 6). The area of dominant tree species (groups) in the study area, such as Pinus massoniana, Pinus yunnanensis, and Quercus spp. dropped by 512,900 ha, 420,000 ha, and 371,000 ha, respectively, compared to 1998, owing primarily to fire, pests, disease, and excessive logging [49,50,51,52].
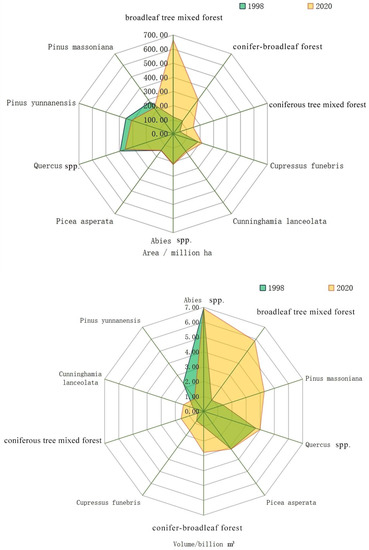
Figure 6.
Changes in area and volume dynamics of major dominant tree species (groups).
The volume of broad-leaved mixed forest, Pinus massoniana, Quercus spp., Picea asperata, mixed conifer-broadleaf forest, Cupressus funebris, mixed conifer forest, and Cunninghamia lanceolata showed an increasing trend, while Abies spp. and Pinus yunnanensis showed a decreasing trend because of their long periodicity and slow growth (Figure 6).
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Changes in the Spatial and Temporal Physical Quality of Forest Ecosystem Service Functions
The results of the evaluation of forest ecosystem service function in the study area are shown in Table 3. On the studied time scale, the forest ecosystem service function in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River under the NFPP in 2020 has improved overall compared to 1998. Soil erosion control, protection of soil fertility, nutrient accumulation, water regulation, carbon sequestration, oxygen release, negative ion supply, pollutant absorption, TSP retention, PM10 retention, and PM2.5 retention all increased significantly in the project area forest ecosystem, with increases of 41.51%, 61.94%, 53.51%, 45.81%, 70.29%, 67.64%, 56.42%, 57.17%, 53.88%, and 53.81%, respectively. This is due to the NFPP implementation in the study area between 1998 and 2020, which effectively curbed the long-term excessive consumption of forest resources, protected forest resources, and observed a good trend of recovery and growth, The forest area and volume in the study area were increased to varying degrees, the forest quality was improved, and the forest structure became more and more reasonable (Figure 4, Figure 7 and Figure 8). As a result, compared to 1998, all forest ecosystem service functions in the research region had improved significantly by 2020.

Table 3.
Results of physical quality assessment of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area.
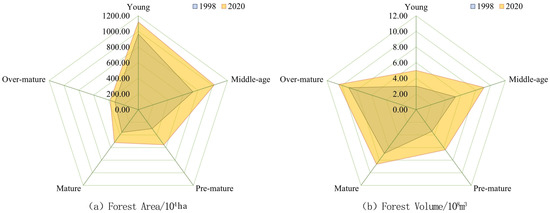
Figure 7.
Changes in the area and accumulation of age-group structure of arbor forest in the study area.
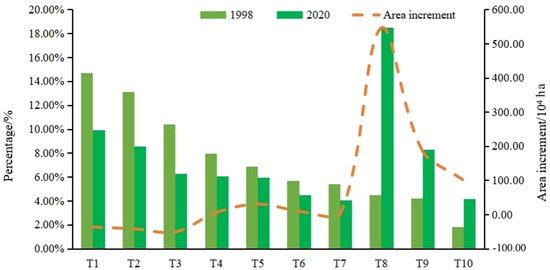
Figure 8.
Changes in tree species structure in the study area. Notes: T1: Quercus spp.; T2: Pinus yunnanensis; T3: Pinus massoniana; T4: Abies spp.; T5: Cupressus funebris; T6: Cunninghamia lanceolata; T7: Picea asperata; T8: broad-leaved mixed forest; T9: mixed conifer-broadleaf forest; T10: mixed conifer forest.
At the spatial scale, changes in the quality of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area from 1998 to 2020 show significant spatial heterogeneity (Figure 9), mainly in the following aspects.
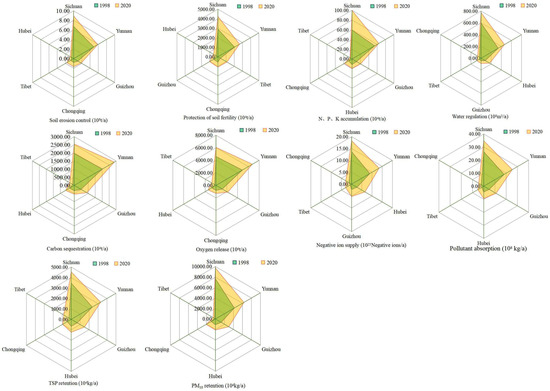
Figure 9.
Spatial pattern of physical quality of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area.
3.1.1. Soil Conservation
In terms of time, the quality of forest conservation soil functions (soil fixation and fertilizer retention) increased in all provinces of the study area from 1998 to 2020, with the largest increase in forest soil fixation (220,000,000 t/a) in the NFPP area of Sichuan Province, which is equivalent to 10.28 times the annual sand transport (21,400,000 t) at the Shigu hydrological station in 2021. The increase in fertilizer retention (13,395,700 t/a) was 6.35 times greater than the discounted quantity of agricultural fertilizer application in 2020 (2,108,200 t). In terms of spatial distribution, the forest ecosystems of the NFPP in Sichuan Province had the strongest function of soil conservation, as well as the largest amount of soil fixation and fertilizer retention.
On the one hand, natural environmental circumstances directly influence the material basis of soil consolidation capability while forming distinct hydrothermal states that influence vegetation growth and development indirectly. It has been demonstrated that regions with significant soil conservation functions in Sichuan Province are primarily concentrated in basin-peripheral mountain zones with distinctly undulating terrain [53]. This is mostly owing to Sichuan Province’s unique topography and better water and heat conditions, which support large forest ecosystems with high vegetation cover and strong soil retention capacity. On the other hand, due to the combination of tree species composition and forest age, there is some variation in their ability to repair soil and conserve fertilizer. The NFPP area in Sichuan Province has the most broadleaf tree area, accounting for 9.07% of total forest area in 2020, indicating that the forest ecosystem in the NFPP in Sichuan Province has a stronger soil conservation function.
3.1.2. Water Conservation
In terms of time, the changes in regulated water in different provinces from 1998 to 2020 are generally consistent, showing an increasing trend with the largest increase in regulated water in Sichuan Province’s forests (Figure 9); these increased by 17,777,000,000 m3/a, equivalent to 75.04% of Sichuan Province’s total water consumption in 2020 (23,690,000,000 m3). This is mostly due to the larger forest area in Sichuan Province’s NFPP area, which is 14,643,400 ha, accounting for 43.74% of the total forest area in the research region, as shown in Table 2. Second, the vegetation growth state has a stronger impact on water quantity regulation. Forests play a role in water conservation in places with high vegetation cover and good vegetation condition through canopy retention, deadfall retention, soil water storage, and surface runoff [54]. Sichuan Province’s NFPP area has high forest cover, plentiful forest resources, and a strong forest water connotation function in terms of water connotation capacity. Furthermore, the volume and water-holding capacity of apoplastic forests are important factors reflecting forest water-holding capacity [55]; studies have shown that accumulation of dead matter is significantly related to forest age and that total volume of dead matter tends to increase with the age of the same forest type under normal conditions [56]. The age-groups of arbor forest in the forest ecosystems of the NFPP in Sichuan Province are relatively well blended and are dominated by middle-aged and young-aged forests, although the proportion of near-mature, mature, and over-mature forests is higher when compared to other provinces. To summarize, the forest ecosystem in Sichuan Province’s NFPP area performs a more important role in water conservation.
3.1.3. Carbon Sequestration and Oxygen Release
Forests fix and reduce atmospheric carbon dioxide and increase atmospheric oxygen, which plays an irreplaceable role in maintaining the dynamic balance of atmospheric carbon dioxide and oxygen, thereby reducing the greenhouse effect, and providing a foundation for human survival. Therefore, with reference to the “Specifications for assessment of forest ecosystem services” (GB/T38582-2020), this study chooses two indicators, namely, carbon sequestration (vegetation carbon sequestration and soil carbon sequestration) and oxygen release, to reflect these functions of forest ecosystems. According to the photosynthesis chemical reaction formula, for every 1.00 g of dry matter gathered by forest flora, 1.63 g of carbon dioxide are produced. As a result, the two indicators of carbon sequestration (vegetation carbon sequestration and soil carbon sequestration) and oxygen release were chosen in this study to describe these functions of forest ecosystems in comparison to national norms. According to the photosynthesis chemical reaction formula, 1.63 g of carbon dioxide can be absorbed and fixed for every 1.00 g of dry matter accumulated by forest vegetation, while 1.19 g of oxygen can be released. As a result, the amount of carbon dioxide fixed and absorbed by forests producing 1 ton of dry matter per year is determined using photosynthesis and respiration equations, and the total amount of carbon dioxide fixed by forests per year is calculated using the annual net primary productivity of tree species. The formulas are:
where:
—the annual carbon sequestration of the forest stand ecosystem (t/a);
—the annual carbon sequestration of the forest stand ecosystem (t/a);
—the annual carbon sequestration of the forest stand ecosystem (t/a);
—carbon content in carbon dioxide, which is 27.27%;
—Net productivity of the measured stand [t/(ha·a)];
—sequestration of carbon in the soil of the measured forest stand per unit area [t/(ha·a)];
—the area of NFPP (ha);
—forest ecological function correction coefficients (FEFCC).
The formula calculates the potential annual carbon sequestration of the forest, from which the actual annual carbon sequestration of the forest is calculated by subtracting the amount of carbon lost due to the removal of biomass from the forest as a result of annual harvesting.
On the temporal scale, the carbon sequestration in forest ecosystems increased in all provinces of the study area, showing an increasing trend, with Yunnan and Sichuan provinces showing the most substantial increases in carbon sequestration. In terms of spatial distribution, the NFPP in Yunnan Province and Sichuan Province had the highest amounts of carbon sequestration in 2020, with carbon sequestration amounts ranging from 25,000,000.00–29,000,000 t/a, accounting for 36.73% and 32.57% of total carbon sequestration, respectively.
The spatial heterogeneity of forest ecosystem carbon sequestration and oxygen release function is mostly connected to forest area, forest age composition, forest stand type, and forest structure in the study area. First, the capacity of forest ecosystems to sequester and release carbon and oxygen is closely connected to forest area. The NFPP in Sichuan Province and Yunnan Province accounted for 39.74% and 27.41%, respectively, of the total forest area of the protected areas. Second, forests can be divided into young, middle-aged, near-mature, mature, and over-mature forests based on their ages, with middle-aged forest ecosystems having the highest carbon sequestration rate, while mature and over-mature forests have mostly balanced carbon uptake and release because their biomass has stopped growing [57]. According to Table 2, the middle-aged and young forests in the study area account for 59.52% of the study area, with the middle-aged and young forests in the NFPP in Yunnan Province and Sichuan Province being larger at 6,113,000 ha and 6,507,400 ha, respectively. Furthermore, the capacity of forest plants to sequester carbon is restricted by natural environmental variables. Precipitation can stimulate plant growth, productivity, and biomass; hence, it can aid in carbon sequestration in forest settings. Plant biomass is high in Yunnan and Sichuan provinces, where water and heat conditions are better and more conducive for plant growth and the plant carbon sequestration capability and carbon density are higher.
3.1.4. Purification of Atmospheric Environment
From a temporal perspective, changes in the quality of each indicator of the function of the forest ecosystem to purify the atmospheric environment in each province of the study area were generally consistent and showed an increasing trend, with Yunnan and Sichuan Provinces showing the greatest increases. The quality of each indicator substance of the function of forest ecosystems in purifying the atmospheric environment in the NFPP in Sichuan and Yunnan provinces was higher in 2020 in terms of spatial distribution. According to related research, air negative ions have a stronger link with wind speed, wind direction, temperature, fitness, sun radiation, air pressure, and meteorological conditions, while geographical location influences air negative ion concentration [58]. Coniferous forests contain more negative ions than broad-leaved forests owing to their needle-like leaves, which have a smaller radius of isocurvature and a “tip discharge” function that ionizes the air, increasing the level of negative ions in the air [59]. Different tree species have varied species features, such as leaf area, crown structure, leaf epidermal hairs, chemical composition, and waxy structure of the upper leaf surface, all of which are relevant to forest ecosystems’ function in purifying the atmosphere. It has been demonstrated that the structural properties of different tree species’ leaves, such as stomatal density, leaf area index, leaf surface roughness and villi, and secretion of mucilaginous oils and sap, cause them to differ greatly in their ability to retain particulate matter [60].
3.2. Variations in the Value Quality of Forest Ecosystem Service Functions
In 2020, the total value quality of forest ecosystem service function in the study area was 3,261,161,000,000 yuan/a, a net increase of 1,270,712,000,000 yuan/a compared to 1998, a 63.84% increase, with the value increase of soil conservation function, forest nutrient fixation function, water holding function, carbon sequestration and oxygen release function, air purification function, and biodiversity conservation function being the highest. Soil conservation function, nutrient sequestration function, water conservation function, carbon and oxygen sequestration function, air purification function, and biodiversity conservation function increased in value by 85.54%, 50.90%, 41.39%, 60.37%, 61.23%, and 74.67%, respectively (Table 4, Figure 10). The values of the biodiversity function and water-conserving functions increased significantly in the NFPP areas of Sichuan, Yunnan, and Guizhou Provinces from 1998 to 2020 based on the spatial distribution of the incremental value of forest ecosystem services. Sichuan and Yunnan Provinces are located in southwest China, and their unique topography, geomorphology, climate, hydrology, and soil provide suitable habitats for the survival and reproduction of many wildlife resources, thereby nurturing the region’s rich biodiversity. Guizhou Province is located at the upper Yangtze River junction, and is one of China’s richest areas of biodiversity, with a high concentration of national Class I and II key-protected wild plants.

Table 4.
The value of forest ecosystem services in the study area.
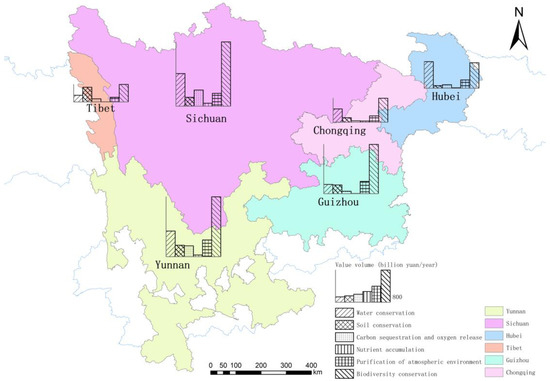
Figure 10.
Spatial pattern of incremental value quality of forest ecosystem service functions in the study area.
3.3. Changes in Dominant Functions in Space and Time
From 1998 to 2020, the following six forest ecosystem services contributed to the upper reaches of the Yangtze River Natural Forest Protection Project area: biodiversity conservation function > water conservation function > soil conservation function > purification of atmospheric environment function > carbon and oxygen sequestration function > forest nutrient sequestration function. The proportion of forest ecosystem services (Figure 11) was 35.05%, 28.00%, 15.43%, 12.69%, 7.67%, and 1.16%, respectively, in 1998, and 39.69%, 25.79%, 13.32%, and 13.16%, respectively, in 2020. It can be seen that the biodiversity conservation function and the water-support function dominate the forest ecosystem in the study area, respectively accounting for 63.05% (in 1998) and 65.48% (in 2020) of the total energy value in the same period.
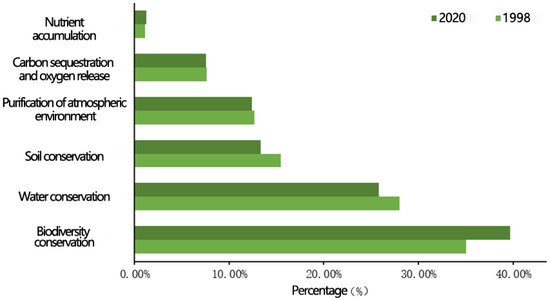
Figure 11.
Changes in the proportion of value of each service function.
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Dynamics of Ecological Benefits in the Study Area
Natural forest resources in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River have been effectively protected as a result of the NFPP [61], and in this study we discovered that the overall forest ecosystem service function in the study area showed an upward trend from 1998 to 2020, which is basically consistent with the findings of Wu et al. [16], Yang et al. [62], Guo et al. [30] and Liu et al. [63]. Chen-Yu Li [64] discovered that the forest cover and habitat quality in Sichuan Province, Yunnan Province, and Chongqing City, where the NFPP and the Yangtze River Basin Protection Forest Project were implemented, were greatly improved, which aided in soil conservation capacity.
Forest resource endowment is the most fundamental and crucial driver of the NFPP’s ecological benefits in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches. The significant construction effect of the NFPP has resulted in a significant increase in regional forest cover, forest area, and forest volume, and the quality and structure of forest resources have become more and more reasonable, resulting in more complete forest ecosystems and gradually enhanced forest ecological functions in Hubei, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, and TAR [22,35,65,66].
Aside from forest resources, the spatial and temporal dynamics of ecological benefits in the study area are influenced by natural environmental factors as well as regulatory considerations. Natural environmental factors such as slope differences [67], differences in water and heat conditions, and soil types [68] all have an impact on forest ecosystem service functions. During the NFPP’s implementation, a series of regulations and policies were introduced, including policies related to timber production reduction, resettlement of surplus personnel from enterprises, and financial reduction of local governments, and policy implementation has promoted the NFPP’s implementation and created its great effectiveness [10].
4.2. Forest Ecosystems’ Dominant Functions in the Study Area
From 1998 to 2020, the dominant functions of forest ecosystems in the study area show consistency, with all functions dominated by biodiversity conservation, water containment, and soil conservation. The study area stretches from east to west, spanning the subtropical, temperate, and highland boreal zones, with terrain ranging from the 400 m Sichuan Basin to the 4000 m Tibetan Plateau, containing complex landscape types with diverse local environmental and climatic characteristics that nurture rich and unique types of biodiversity, making it the richest region in terms of species endemism and one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots. However, the region’s biodiversity has been severely impacted by the sharp decline in natural forest resources, the decline in habitat quality, and the destruction of species habitats. Since 1998, the NFPP in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River has been launched; the establishment of forest management areas can save species diversity from extinction, and their expansion has laid an important material foundation for the improvement of forest ecosystem biodiversity functions in the NFPP area [69,70]. The NFPP eliminated the threat of large-scale commercial logging in giant panda habitat and provided long-term protection for the habitat, assisting in the conservation of species diversity, plant and animal gene-level ecosystems, and biodiversity. Through infrared cameras, the Tangjiahe Nature Reserve in Sichuan observed a significant increase in the number of both twisted-horned antelope and Sichuan golden monkeys, both protected wild animals at the national level, following the implementation of the NFPP [63].
The NFPP improves the region’s forest ecosystem’s ability to contain and conserve soil, promotes the normal circulation of water in the sky, surface water, and groundwater, holds soil through the forest’s living ground cover and apoplastic layer as well as the root system of forest trees [71], reduces the possibility of geological disasters in the region, and maintains ecological and environmental security. According to the China Statistical Yearbook (2005–2021), the number of geological disasters in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches decreased by 47.69% in 2020 compared to 2004. In Yunnan, for example, the number of geological hazards has decreased by 2681 since 2004, while in Chongqing it has decreased by 1528. Yang [72] discovered that the ecological environment in the NFPP in Shangri-La City, Yunnan Province, has significantly improved, and the function of forests to contain water resources and maintain soil and water has been enhanced, both of which contribute to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of natural disasters. Man et al. [73] found that the NFPP and the project of returning farmland to forests and grasses improved the vegetation cover of the upper reaches of the Minjiang River, which improved the ability of the forests in the region to contain water and improved the ecological security of the upper reaches of the Minjiang River.
4.3. Factors Impacting Forest Ecological Benefits in the Study Area
From the above results, it is clear that the forest ecosystem service function in the study area has been significantly enhanced, which may be related to the forest area, age structure of arbor forest, tree species composition, and natural environment.
4.3.1. Natural Environmental Factors
Great natural environmental conditions can effectively promote the growth and development of forest community vegetation, the flow of forest ecosystem capacity, and the material cycle, enhancing its ecological benefits, whereas poor natural environmental conditions can limit the growth and development of forest community vegetation or even produce negative feedback on the forest ecosystem, reducing its ecological benefits. Figure 12 depicts the interaction between the natural environment and forest vegetation, which includes terrain, climate, soil, and hydrology. Climate and hydrology are the most active and widely influenced factors in forest ecosystems, determining vegetation types, limiting forest tree growth, and influencing forest ecosystem productivity, as well as the spatial distribution of plant and animal species [74]. The function of preserved soil is mostly related to characteristics such as vegetation ground cover, vegetation type, slope, and soil type [68].
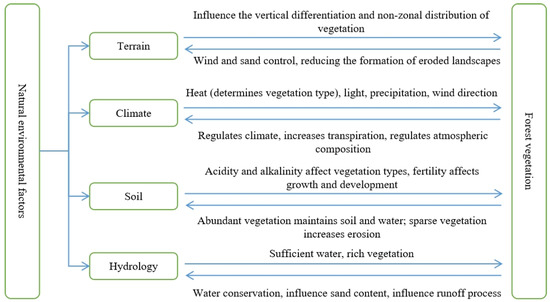
Figure 12.
Relationship between natural environmental factors and forest vegetation.
4.3.2. Forest Resource Characteristics
Forest resources are the most direct driver of the forest ecological advantages of the NFPP in the Yangtze River’s upper reaches, and favorable forest resource conditions form the foundation for creating forest ecological benefits.
First, forest acreage has the most direct influence on the strength of ecosystem services. This is supported by the present study, which found that the forest area in the study area rose by 12,823,700 ha between 1998 and 2020, an increase of up to 38.31%, and that the growth in all forest ecosystem service functions was greater than 41.51%.
Second, the forest age structure influences the ecological benefits of the woods in the study area. The age of arbor forest is positively connected with its water content benefit per unit area, and the growth rate of this benefit slows as the age of the stand increases [74]. The findings of this study indicate the existence of this phenomenon. Furthermore, the quantity of carbon absorbed by the forest is directly related to the forest’s age composition, with the rate of carbon sequestration being highest in middle-aged forest ecosystems [57].
Third, one of the main elements of ecological advantages in the study area is tree species type. Evergreen coniferous forest ecosystems have the highest total water connotation and evergreen broadleaf forests have the highest water connotation capacity [75,76]; the physical properties and nutrient status of soil in mixed woodlands have been significantly improved compared to pure woodlands, as has the water connotation capacity of forest stands [77,78,79].
5. Conclusions and Suggestion
5.1. Conclusions
Based on the People’s Republic of China’s national standard “Specification for the Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Service Functions” (GB/T38582-2020), this study employs a distributed measurement method to assess the ecosystem service functions of forest ecosystems in the study area from 1998 to 2020, such as soil conservation, nutrient sequestration, water retention, carbon sequestration and oxygen release, atmospheric pollution, and biodiversity. The NFPP’s ecological effectiveness in this area was assessed. The main findings are as follows:
- (1)
- On a temporal scale, the physical quantity and value of each service function of the forest ecosystem in the study area showed a significant increasing trend.
- (2)
- On the spatial scale, the changes in forest ecosystem service functions in the study area show significant spatial heterogeneity.
- (3)
- Forest ecosystems in the study area have the functions of biodiversity protection, water conservation, and soil conservation as their dominant functions.
- (4)
- The forest ecosystem service functions in the study area are closely related to the characteristics of forest resources (e.g., forest area, forest volume, and age structure of tree forests).
The above research findings can more clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of the study area as well as provide a scientific basis and guidance for the formulation of the Natural Forest Protection and Restoration System Plan and the promotion of further natural forest resource protection and restoration.
5.2. Suggestion
- (1)
- The NFPP has not only contributed to “double growth” in forest area and volume, it has improved forest ecosystem services and the ecological environment. As a result, it is vital to consolidate the results of the NFPP’s ecological benefits in the future process of natural forest resource protection and development.
- (2)
- The monitoring and assessment system for the ecological benefits of natural forests should be improved and the monitoring and assessment work should be strengthened.
- (3)
- In order to continue to strengthen the protection of natural forest resources, it is critical to focus on the tree species structure in terms of both increasing quantity optimizing the age group structure in order to improve the quality of natural forest resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and B.W.; methodology, Y.W.; software, Y.W.; validation, B.W., X.N. and Q.S.; formal analysis, Y.W.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, Q.S. and Y.W.; data curation, Q.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.W., B.W. and X.N.; visualization, Y.W.; supervision, X.N. and Q.S.; project administration, X.N.; funding acquisition, X.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by State Forestry and Grassland Administration Key Project: Study on hydrofunctional traits and water use efficiency of cedar seedling forests in Dagangshan Mountain, grant number CAFYBB2020ZE003; Accounting for Forest and Grassland Resources and Ecosystem Services in China, grant number 2021ZDKT003; Central-level Public Welfare Research Institutes Basic Research Business Fund Special Project: Monitoring and Evaluation of Ecological Benefits of Natural Forest Protection Project and Demonstration, grant number CAFYBB2020ZD002-2.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kitaibekova, S.; Toktassynov, Z.; Sarsekova, D.; Mohammadi Limaei, S.; Zhilkibayeva, E. Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services in Burabay National Park, Kazakhstan: A Case Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.K.; Yang, N.; Wu, F.; Ren, Y.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Bo, G.M.; Jiang, G.M.; Wang, Y.K.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Ecological benefit evaluation contents and indicator selection. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 5442–5449. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.Q.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.K.; Miao, H. Forest ecosystem services and their valuation in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2004, 19, 480–491. [Google Scholar]
- Adger, N.; Brown, K.; Cervigni, R.; Moran, D. Total economic value of forests in Mexico. Ambio 1995, 24, 286–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mäler, K.G.; Aniyar, S.; Jansson, A. Accounting for ecosystem services as a way to understand the requirements for sustainable development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9501–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F.; Li, J.Y.; Yang, J.W. Review on research of evaluation on forest ecological benefits. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2003, 25, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Song, Q.F. Dynamic change of natural forest ecological benefit in Changbai Forest Industry Group since implementation of natural forest protection project. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 15, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.X.; Zhang, D.M. Construction of Legal System for Natural Forest Protection and Restoration under the Concept of Green Development. J. Fujian Norm. Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 5, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.R.; Ma, J.M.; Miao, N. Achievements in natural forest protection, ecological restoration, and sustainable management in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 0212–0218. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.R.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, H.R.; Wang, B.; Ye, B.; Jiang, Z.P.; Xie, H.S.; Niu, X.D.; Wang, D.J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Evaluation indicator system and method designed for Natural Forest Protection Program of China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5067–5079. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.Y.; Ding, X.T.; Duan, Z.A. Advances in Forest Benefit Assessments in the Last Ten Years in China. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2009, 40, 304–308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J.; Yuan, Q.Z.; Dong, X.S.; Kou, Y.W.; Ren, P. Research Progress on Forest Ecological Resource Pattern and Change in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Heilongjiang Vocat. Inst. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.F. A Great Ecological Project: China Natural Forest Conservation Programme. World For. Res. 2001, 14, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.C.; Shao, G.F.; Zhao, G.; Le Master, D.C.; Parker, G.R.; Dunning, J.B.; Li, Q.L. China’s Forest Policy for the 21st Century. Science 2000, 288, 2135–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Shao, M.A. Soil and water loss from the Loess Plateau in China. J. Arid. Environ. 2000, 45, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cao, W.; Huang, L.; Huhe, T.L. Assessing Ecological Effects of Natural Forest Protection Project. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2023, 40, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P. Natural Forest Protection: An Overview Abroad and a Review at Home. J. Beijing For. Univ. (Soc. Sci.) 2004, 3, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.K.; Huang, X.Q.; Zhu, Z.F. A Summary of Benefit Evaluation of Natural Forest Protection Project in China. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 34, 107–111+179. [Google Scholar]
- H T.T. Study on Carbon Potential of the Natural Forest Protection Program Afforestation in China. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.X. Current situation and countermeasures on natural forest protection system in Wuding county. For. Constr. 2022, 6, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.H.; Xiao, S.S.; Zhu, B.Q. Analysis and Countermeasures of Natural Forest Protection and Restoration in Jiangxi Province. For. Investig. Des. 2023, 52, 59–63+89. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.X.; Bai, X.Y.; Bao, L.D.; Guo, Z. Analysis on Dynamic Trend of Forest Resources in Southwest China Natural Forest Protection Project Area. China For. Econ. 2019, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, M.Y.; Wu, J.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Ding, S. Analysis on the Evolution of Forest Carbon Sinks Efficiency in Natural Forest Protection Project Regions. Issues For. Econ. 2022, 42, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.F.; Liu, G.H. Carbon sequestration of China’s National Natural Forest Protection Project. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhou, W.M.; Yu, D.P.; Zhou, L.; Gu, X.P.; Wu, Z.J.; Wu, S.N.; Wang, X.Y.; Dai, L.M. Research on Forest Vegetation Carbon Storage under the National Forest Protection Project in the Upper Reaches of Yangtze River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Meng, S.L.; Shi, K.Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, X.H.; Niu, X.D.; Zhao, D.; Liu, L.Y.; Feng, M.; Qin, X.L.; et al. Forest coverage monitoring in the Natural Forest Protection Project area of China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5080–5092. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.F.; Ju, H.B. Vegetation Change Monitoring for the Natural Forest Protection Based on Spatial Analysis Techniques. For. Res. 2013, 26, 736–743. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.M.; Yang, W.N. Dynamic changes of vegetation cover in natural forest area of western Sichuan in recent 29 years based on RS. Remote Sens. Land Resour. 2018, 30, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.W.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Y.W.; Fang, X.M.; Gao, B.; Dai, L.M. Evaluation on the influence of natural forest protection program on forest ecosystem service function in Changbai mountain. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 984–992. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; She, H.; Zang, R.G. Evaluation on Comprehensive Benefit of Natural Forest Protection Project in Southwest China. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 15035–15038. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.M.; Zhou, G.H.; Hu, T.X.; Yang, W.N. Dynamic Analysis of Soil Erosion in Natural Forest Protection Project Area of Western Sichuan Province Based on RS and GIS. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 33, 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, P.X. Social Benefit Evaluation of Natural Forest Resource Protection Project in Qinghai Province. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, 141–142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.T.; Wu, S.R.; Zhang, C.; Lu, J.; Ye, B. Research on Social Benefit Evaluation of National Natural Forest Resource Protection Project. Ecol. Econ. 2023, 39, 124–128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.F.; Guan, J.; Cao, Y.K.; Song, Q.H. Study on Ecological Benefit Evaluation of Natural Forest Protection Project in Ecological Incremental Dimensions. Issues For. Econ. 2020, 40, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.H.; Xu, P.; Zhuang, J. Achievements and suggestions on construction of natural forest protection project in Tibet. For. Constr. 2019, 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.B.; Zhao, R. Research on the Finance and Taxation Policy of Protecting Natural Forest Resources. Issues For. Econ. 2020, 40, 668–672. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.G.; Zhang, Y.T.; Ning, Z. Implementation Effect of Forest Tending Subsidy Policy in Natural Forest Protection Project. Issues For. Econ. 2020, 40, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q. Problems and Countermeasures of Forest Management and Protection in Natural Forest Protection Project. China For. Econ. 2019, 2, 115–116. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 38582-2020; State Forestry Administration. Specifications fo Assessment to Forest Ecosystem Services. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Xu, T.Y.; Niu, X.; Wang, B.; Song, Q.F. Evaluation on leading functions of forest ecosystem services in Liaoning Province based onnature-based solutions. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 41, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Niu, X.; Wei, W. National forest ecosystem inventory system of China: Methodology and applications. Forests 2020, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ren, X.X.; Hu, W. Assessment of Forest Ecosystem Services Value in China. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2011, 47, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.C.; Shao, Q.Q.; Niu, L.N.; Ning, J.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Huang, H.B. Changes of ecological and the characteristics of trade-offs and synergies ofecosystem services in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1028–1039. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 33027-2016; State Forestry Administration. Methodology for Long-Term Observation of Forest Ecosystem. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016. (In Chinese)
- GB/T 35377-2017; State Forestry Administration. Indicator System for Long-Term Observation of Forest Ecosystem. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, Y.; Hu, H.Q. Characteristics of Forest Fire Data in Southwest China during 2001–2017. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2021, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.L.; Jiang, R.H. Status of forest resources in Tibet and suggestions for management measures. Tibet. Sci. Technol. 2007, 3, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 38590-2020; State Forestry Administration. Technical Regulations for Continuous Forest Inventory. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese)
- Deng, Q.X.; Huang, B.L.; Wen, Q.Z.; Hua, C.L.; Tao, J.; Zheng, J.X. Dynamic of Pinus yunnanensis Forest Resources in Yunnan. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, X.H.; Wang, D.W.; Li, G.Q. Research Advance and Prospects of Pinus yunnanensis Franch. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 13, 169–171. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Xiao, Z.L.; Chen, W.J.; Liu, F.F.; Chen, Y.P.; Jing, S.H. Analysis of spatial structure characteristics of natural secondary broad-leaved mixed forest: Taking Yuan’an county of Hubei province as an example. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2020, 40, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.R.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.X.; Huang, G.T.; Sun, L.S. Position and Function of Pinus massoniana Forest in Forest Ecological Service in Hubei Province. Hubei For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 48, 6–11+32. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, E.M.; Xiao, Y. Spatial characteristics and effects of soil conservation service in Sichuan Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8741–8749. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Li, Z.X.; Feng, Q.; Miao, C.Y.; Deng, X.H.; Di, Z.H.; Ye, A.Z.; Gong, W.; Zhang, B.J.; Gui, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of water conservation amount in the Qilian Mountains from 1980 to 2017. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2022, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, Q.L.; Dai, H.Y.; Guo, X. Surface runoff and soil erosion of different vegetations in Daqing Mountain, Inner Mongolia. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2008, 30, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Ding, G.J. Study of the litter reserves and water-holding capacity of Pinus massoniana Lamb. with different stand ages. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 51, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K.; Liu, W.W. Factors affecting carbon sequestration in forests. For. Ecol. 2021, 3, 40–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, J.E. Review on factors influencing the concentration distribution of negative air ions. Ecol. Sci. 2010, 29, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.J.; Zhang, Y. The Distribution of Air Anion Concentration above Ground at Some Scenic Sites in Guangxi. Res. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.K.; Wang, B.; Niu, X. The leaf microstructure of different trees and its impact on air particles-capturing ability. Chin. J. Ecol. 2017, 36, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Liu, X.T.; Gao, W.Q.; Li, H.K. Dynamic changes of forest vegetation carbon storage and the characteristics of carbon sink (source) in the Natural Forest Protection Project region for the past 20 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 5093–5105. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.S.; Lu, F.; Zhang, L. Comprehensive benefit assessment of natural forest protection project. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2022, 48, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Cao, M.R.; Xiong, J.W.; Nan, N.F.; Chen, Z.; Shu, Y. Impact Assessment of Natural Forest Protection Project Policies on National Nature Reserve. Cent. South For. Inventory Plan. 2016, 35, 5–9+35. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Guo, X.Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Xiao, W.F. Spatiotemporal variations of habitat quality in forestry ecological project region of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 3788–3799. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.H.; Huang, Z.L.; Ai, X.R. Service Functions of Natural Forest Ecosystem in the Three Gorges Region in Hubei Province. Hubei For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 44, 1–4+49. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.S.; Yang, P.; Zhai, H.; Wang, L.M. Study on Landscape Pattern Change of Natural Forest Resources in Sichuan Province at Recent 20 Years. Resour. Dev. Mark. 2019, 35, 1258–1261.36. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Shao, Q.Q. Water Conservation Capacity of Forest Ecosystem and Its Spatial Variation in the Upper Reaches of Wujiang River. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 987–999. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.X.; Wang, B.; Niu, X. Ecosystem services of Grain for Green Project in the provinces of the upper and middle reaches of Yangtze and Yellow River. Chin. J. Ecol. 2016, 35, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.B.; Yu, S.L.; Duan, S.Q. Management Achievement and Developing Suggestions of Xishuangbanna Reserve in Yunnan Province. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 331–334+339. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H.; Zheng, J.X.; Yu, C.Y.; Hua, C.L.; Wang, Y. Present Status and Effect Evaluation of Natural Reserve Management in Yunnan Province. For. Inventory Plan. 2018, 43, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.M.; Xie, G.D.; Zhang, C.X.; Qi, Y. Intra-annual dynamics of soil conservation value in forest ecosystem. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 3482–3490. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.-W. Analysis on the Effect and Problems of the Natural Forest Protection Project in Shangri-La City. Guizhou For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Man, Z.C.; Su, C.J.; Xu, Y. An Analysis on Water Conservation Capacity Variation of Forest in the Upper Reaches of Minjiang River. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2007, 14, 223–225+230. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Cui, X.H.; Liu, H.J.; Bai, X.L. Analysis of Regional Meteorological Factors for Dagangshan Forest Ecosystem Research Station. For. Res. 2002, 15, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.H.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Spatial patterns of ecosystem water conservation in China and its impact factors analysis. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 2455–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Chen, Z.L.; Fang, J.P. Estimation of Water Conservation in Tibet Forest Ecosystem Based on the Energy Value. J. Plateau Agric. 2018, 2, 654–659. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Liu, N.; Chen, L. Plant biodiversity of different water conservation forest models and their relationship with soil properties in northern water source area of Chongqing city, southwestern China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2009, 18, 2260–2266. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.W. Water Conservation Functions of Mixed Plantations among Pinus massoniana and Broad-leaved Trees. Prot. For. Sci. Technol. 2006, 6, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Q. The Water Holding Capacity and Soil Fertility in the Mixed Forest of Cunninghamia lanceolata and Altingia gracilides. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2002, 22, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).