Identification of Olfactory Genes in Monochamus saltuarius and Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Infestation on Their Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. RNA-Seq Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. De-Novo Sequence Assembly
2.4. Annotation
2.5. Gene Expression Quantification
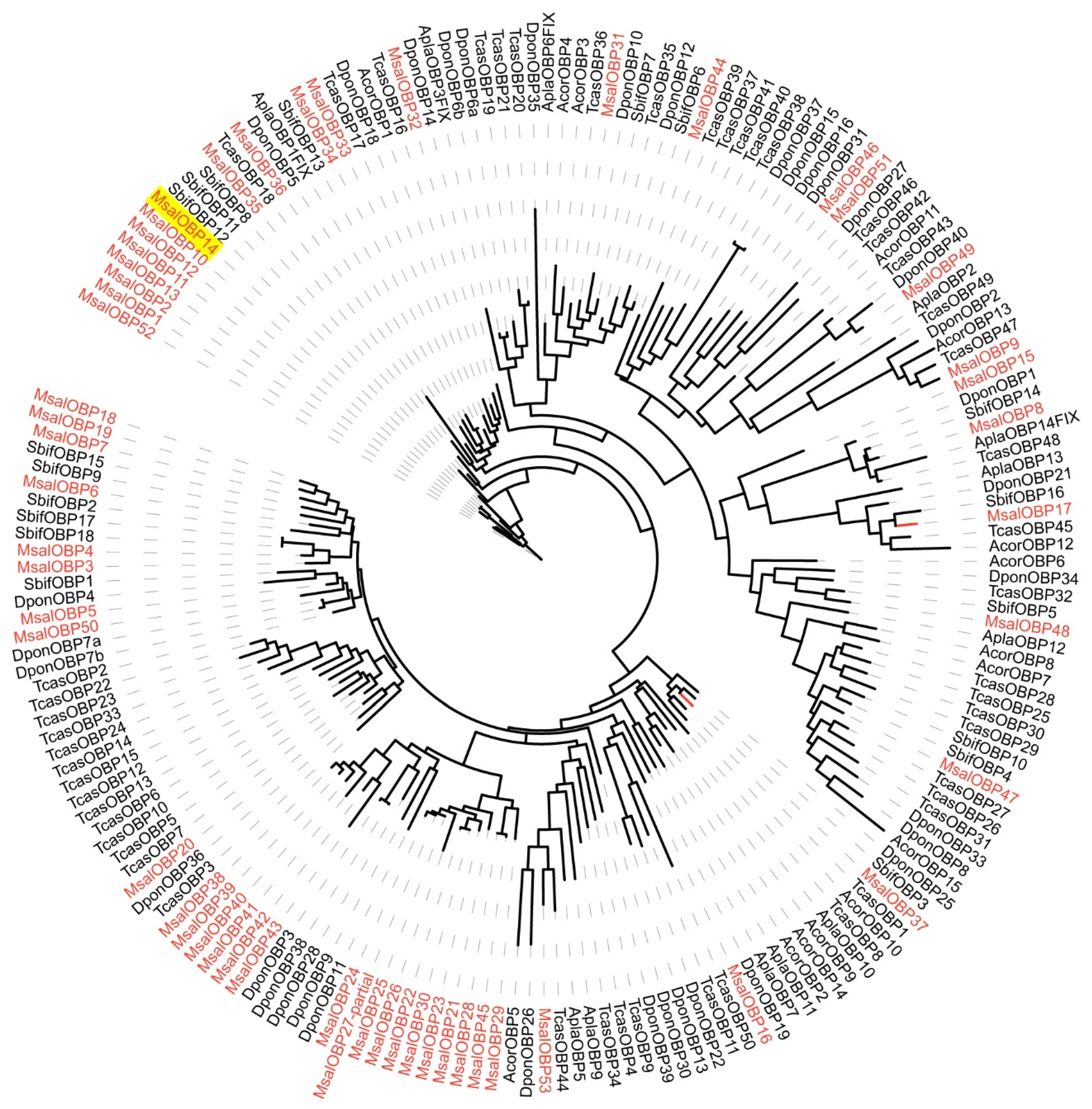
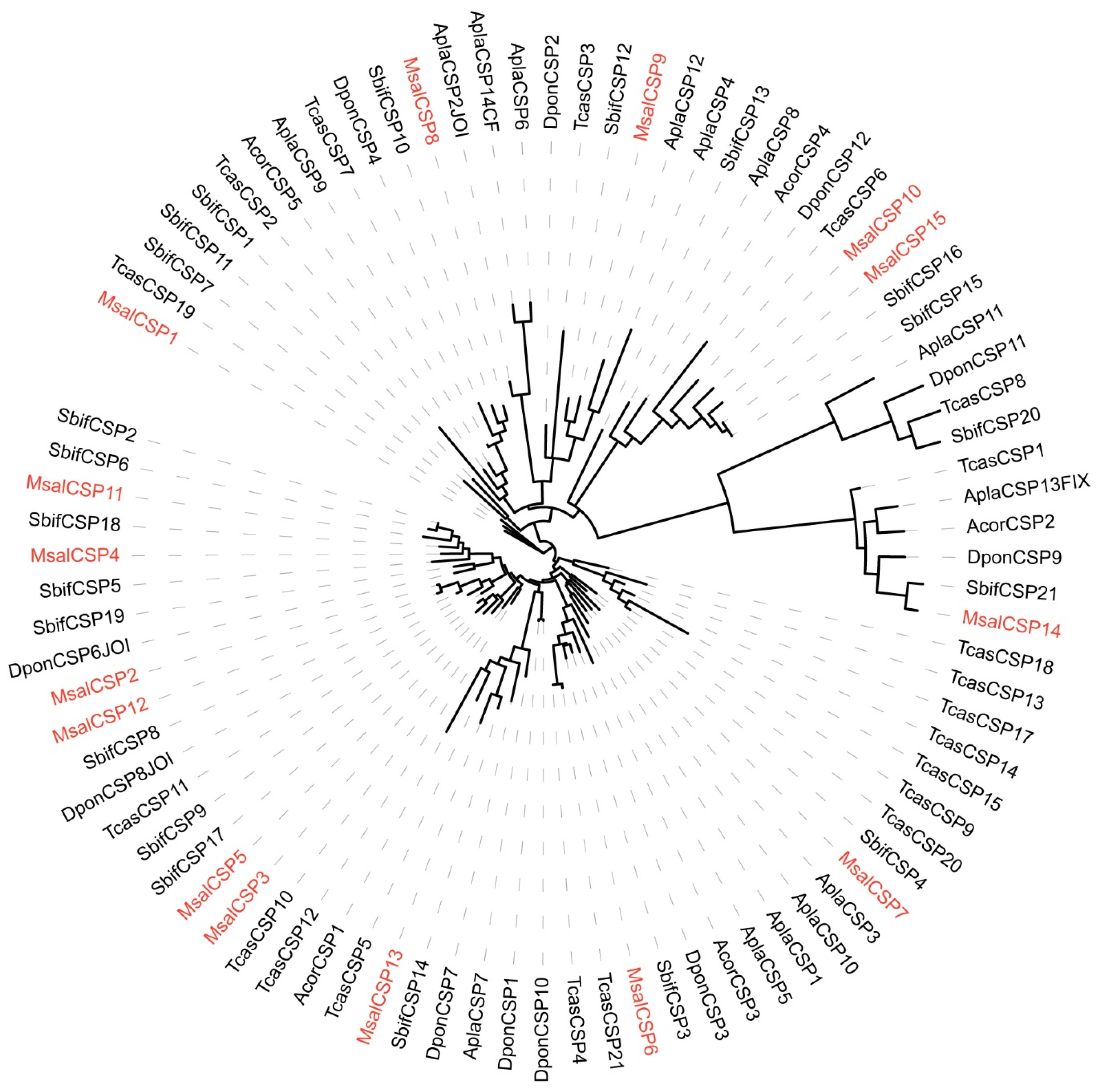
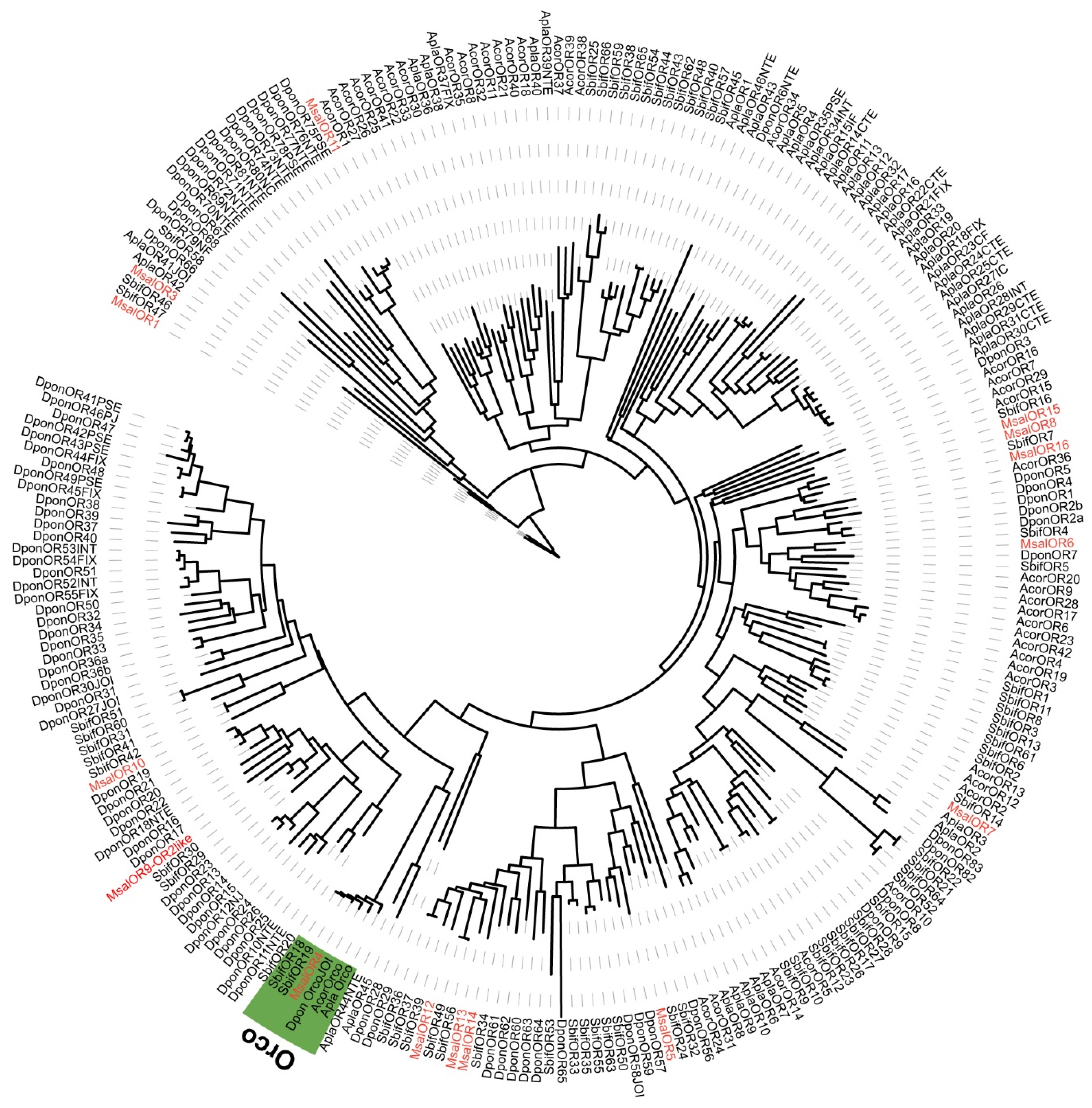
2.6. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. M. saltuarius Antennae Transcriptomes
3.2. M. saltuarius Chemosensory Genes
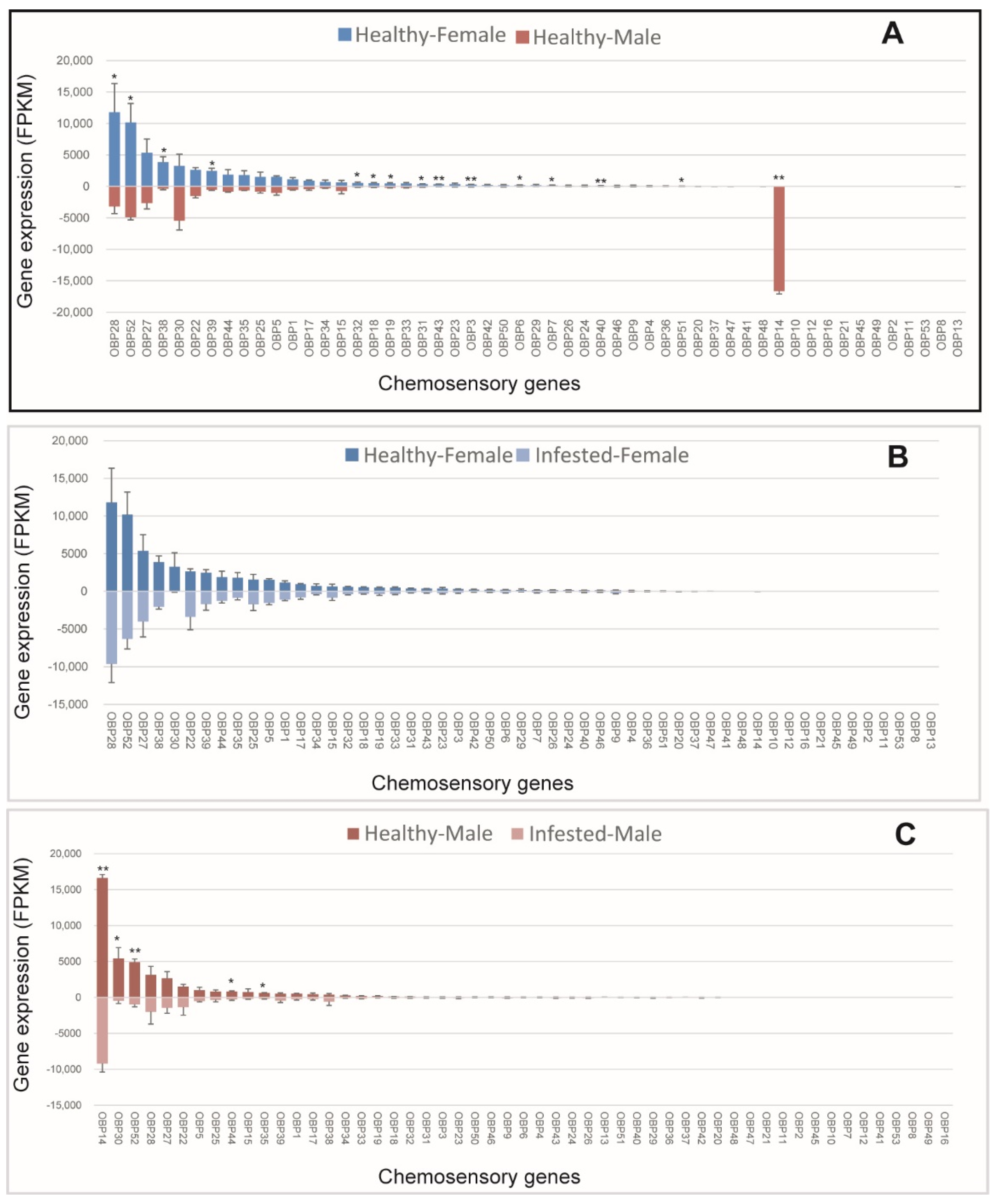
3.3. OBPs of M. saltuarius with and without B. xylophilus
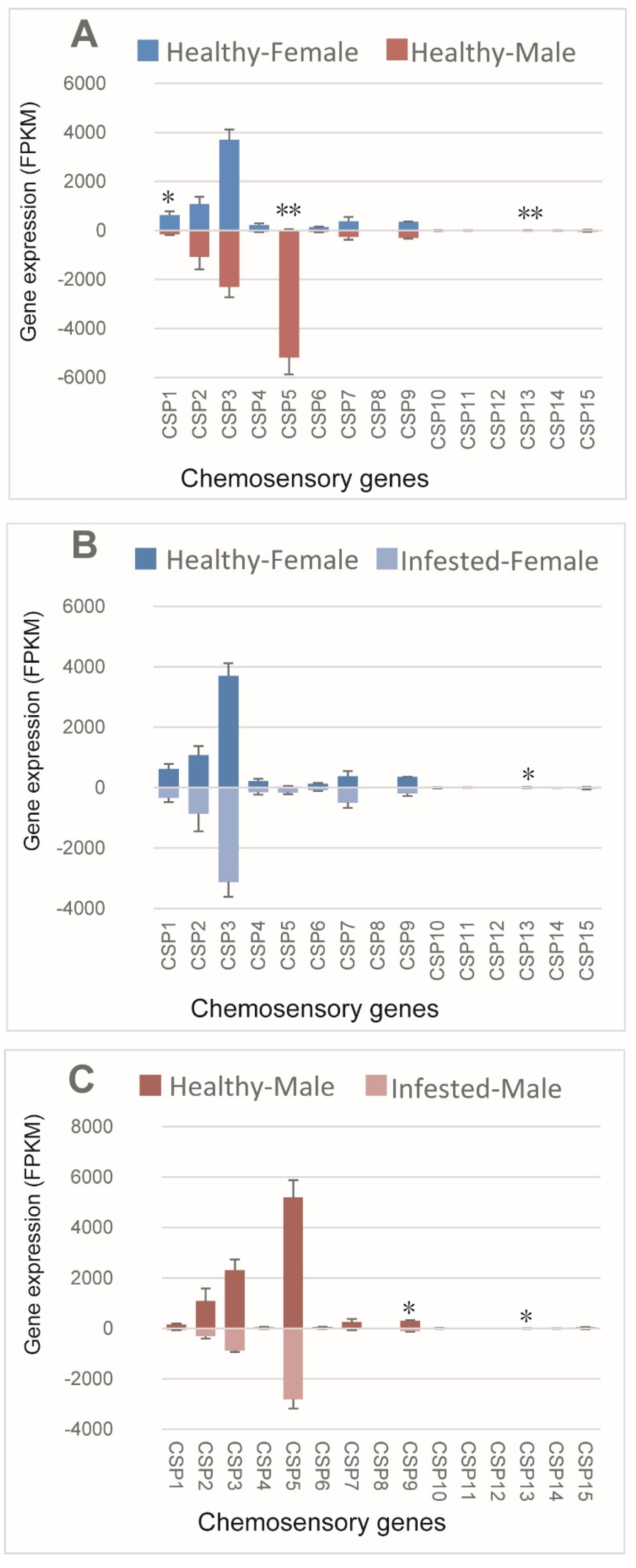
3.4. CSPs of M. saltuarius with and without B. xylophilus
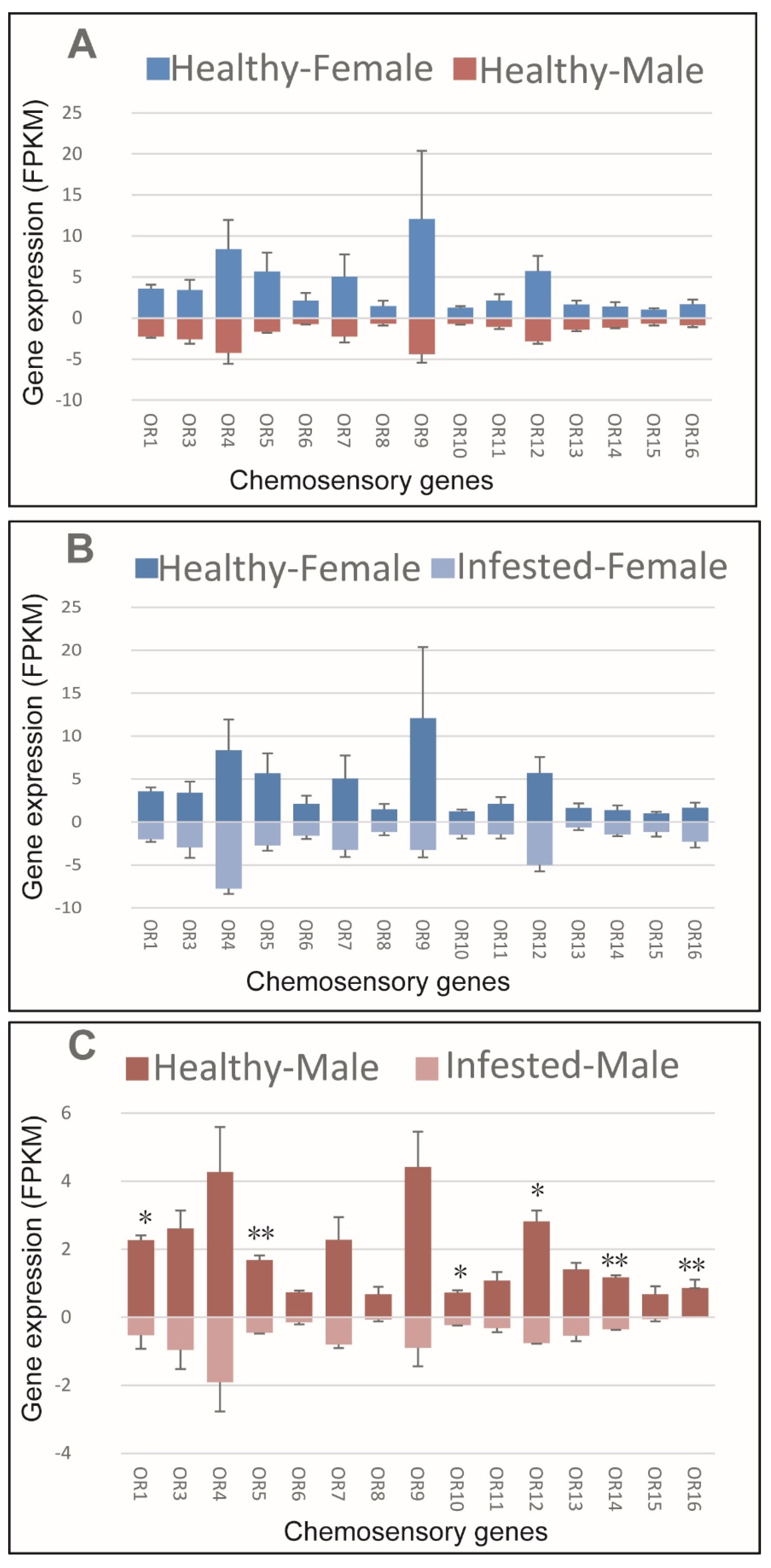
3.5. ORs of M. saltuarius with and without B. xylophilus
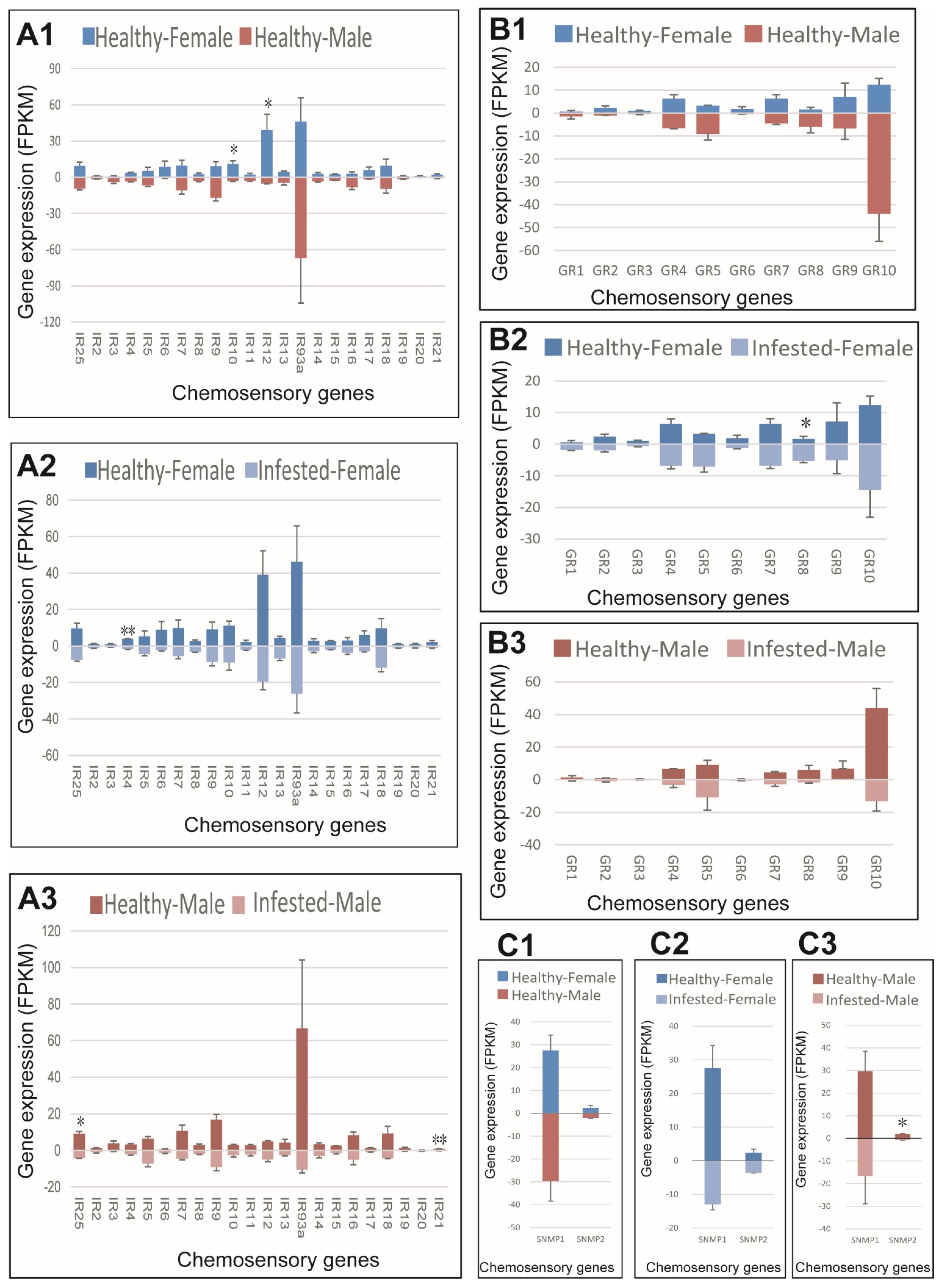
3.6. IRs, GRs, and SNMPs in Healthy and Infested M. saltuarius
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Wang, F. The most plants in Pinus. Plants 1991, 6, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Nickle, W.R. A taxonomic review of the genera of the Aphelenchoidea (Fuchs, 1937) Thorne, 1949 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). J. Nematol. 1970, 2, 375–392. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, D.Z.; Min, S.F.; Mi, F.; Zhou, S.S.; Wang, M.Q. Analysis of chemosensory gene families in the beetle Monochamus alternatus and its parasitoid Dastarcus helophoroides. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2014, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Iwasaki, A. Role of Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) as a vector of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae). Nihon Ringakkai Shi J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1972, 54, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J. Species and their dispersal ability of Monochamus as vectors to transmit Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 2007, 24, 350–356. [Google Scholar]
- Linit, M.J.; Kondo, E.; Smith, M.T. Insects associated with the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae), in missouri. Environ. Entomol. 1983, 12, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, F.; Yamane, A.; Ikeda, T. The japanese pine sawyer beetle as the vector of pine wilt disease. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1984, 29, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Qin, P.; Chinta, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; et al. Ascarosides coordinate the dispersal of a plant-parasitic nematode with the metamorphosis of its vector beetle. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enda, N.; Mamiya, Y. Transmission of Bursaphelenchus lignicolus (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) by Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Nematologica 1972, 18, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y. Monitoring, identification and control of pine wood nematode in Dandong City, Liaoning Province. Agric. Technol. 2018, 38, 62–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wickham, J.D.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J. Co2 drives the pine wood nematode off its insect vector. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R619–R620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.S.; Koo, H.N.; Yun, S.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, G.H. Electron beam-induced sterility and inhibition of ovarian development in the sakhalin pine longicorn, Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Analysis on the trend of invasion and expansion of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. For. Pest Dis. 2018, 37, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, C.S.; Koh, S.-H.; Nam, Y.; Ahn, J.J.; Lee, C.Y.; Choi, W.I. A model for predicting spring emergence of Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) from Korean white pine, pinus koraiensis. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-R.; Lee, S.-C.; Lee, D.H.; Choi, W.-S.; Jung, C.-S.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, I.-K. Identification of the aggregation-sex pheromone produced by male Monochamus saltuarius, a major insect vector of the pine wood nematode. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, H.; Sheng, R.-C.; Sun, H.; Sun, S.-H.; Chen, F.-M. The first record of Monochamus saltuarius (Coleoptera; Cerambycidae) as vector of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus and its new potential hosts in china. Insects 2020, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, J.L. The southern pine sawyer. USDA Bur. Entomol. Bull. 1909, 58, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wingfield, M.J. Transmission of pine wood nematode to cut timber and girdled trees. Plant Dis. 1983, 67, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczek, A.; Piesik, D.; Wenda-Piesik, A.; Buszewski, B.; Bocianowski, J.; Wawrzyniak, M. Volatile organic compounds released by maize following herbivory or insect extract application and communication between plants. J. Appl. Entomol. 2017, 141, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piesik, D.; Rochat, D.; Delaney, K.J.; Marion-Poll, F. Orientation of European Corn Borer first instar larvae to synthetic green leaf volatiles. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piesik, D.; Rochat, D.; van der Pers, J.; Marion-Poll, F. Pulsed odors from maize or spinach elicit orientation in European Corn Borer neonate larvae. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bruyne, M.; Baker, T.C. Odor detection in insects: Volatile codes. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshiya, I.; Nobuo, E.; Akiomi, Y.; Katsuo, O.; Takaaki, T. Attractants for the Japanese pine sawyer, Monochamus alternatus hope (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Nihon Ringakkai Shi J. Jpn. For. Soc. 1980, 15, 358–361. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, J.; Wang, Y. Feeding behavior of Monochamus alternatus and its relationship with the host volatiles. J. Zhejiang AF Univ. 2014, 31, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, D.; Fenglin, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, H. Electroantennogram and behavioral responses of Monochamus alternatus to the volatiles from pinus thunbergii with different physiological status. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 17, 1070. [Google Scholar]
- Fettköther, R.; Reddy, G.V.P.; Noldt, U.; Dettner, K. Effect of host and larval frass volatiles on behavioural response of the old house borer, Hylotrupes bajulus (L.) (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae), in a wind tunnel bioassay. Chemoecology 2000, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.W.; Wilkening, A.J.; Atkinson, T.H.; Nation, J.L.; Wilkinson, R.C.; Foltz, J.L. Synergism of turpentine and ethanol as attractants for certain pine-infesting beetles (Coleoptera). Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynand, V.D.G.V.N.; Carlson, J.R. Insects as chemosensors of humans and crops. Nature 2006, 444, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Pelosi, P.; Zhou, J.-J.; Ban, L.P.; Calvello, M. Soluble proteins in insect chemical communication. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, P.; Calvello, M.; Ban, L. Diversity of odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in insects. Chem. Senses 2005, 30, i291–i292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rützler, M.; Zwiebel, L. Molecular biology of insect olfaction:Recent progress and conceptual models. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2005, 191, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Menuz, K.; Carlson, J.R. Olfactory perception: Receptors, cells, and circuits. Cell 2009, 139, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Stocker, R.F. Molecular architecture of smell and taste in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 505–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Latief, M. A family of chemoreceptors in Tribolium castaneum (Tenebrionidae: Coleoptera). PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.N.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Keeling, C.I.; Bengtsson, J.M.; Yuen, M.M.S.; Li, M.; Hillbur, Y.; Bohlmann, J.; Hansson, B.S.; Schlyter, F. Antennal transcriptome analysis of the chemosensory gene families in the tree killing bark beetles, Ips typographus and Dendroctonus ponderosae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Li, N.; Ali, S.A.I.; Wang, M.Q. Functional characteristics of chemosensory proteins in the sawyer beetle Monochamus alternatus Hope. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2018, 109, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Wang, J.; Cui, M.; Tao, J.; Luo, Y. Antennal transcriptome analysis of the asian longhorned beetle Anoplophora glabripennis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Kong, X. Antennal transcriptome analysis and comparison of olfactory genes in two sympatric defoliators, Dendrolimus houi and Dendrolimus kikuchii (lepidoptera: Lasiocampidae). Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Liu, H.-H.; Kong, X.-B.; Wang, H.-B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Identification and expression profiling of chemosensory genes in Dendrolimus punctatus walker. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanova, E.A.; Shagin, D.A.; Lukyanov, S.A. Normalization of full-length enriched cdna. Mol. BioSystems 2008, 4, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhulidov, P.A.; Bogdanova, E.A.; Shcheglov, A.S.; Vagner, L.L.; Khaspekov, G.L.; Kozhemyako, V.B.; Matz, M.V.; Meleshkevitch, E.; Moroz, L.L.; Lukyanov, S.A.; et al. Simple cDNA normalization using Kamchatka Crab duplex-specific nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Trinity: Reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from rna-seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pertea, G.; Huang, X.; Liang, F.; Antonescu, V.; Sultana, R.; Karamycheva, S.; Lee, Y.; White, J.; Cheung, F.; Parvizi, B.; et al. TIGR gene indices clustering tools (TGICL): A software system for fast clustering of large EST datasets. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talón, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Williams, T.D.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Nueda, M.J.; Robles, M.; Talón, M.; Dopazo, J.; Conesa, A. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3420–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, J.; Grosse-Wilde, E.; Gohl, T.; Dewer, Y.M.E.; Raming, K.; Breer, H. Genes encoding candidate pheromone receptors in a moth (Heliothis virescens). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11845–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by rna-seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential Expression of RNA-Seq Data at the Gene Level—The DESeq Package; European Molecular Biology Laboratory: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. Edger: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.-T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Kong, X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Chemosensory characteristics of two semanotus bifasciatus populations. Forests 2019, 10, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, F.G.; Rozas, J. Comparative genomics of the odorant-binding and chemosensory protein gene families across the arthropoda: Origin and evolutionary history of the chemosensory system. Genome Biol. Evol. 2011, 3, 476–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Qian, J.; Jie, W.; Fei, L.; Jiang, X.; Hu, J.; Qu, M. Chemosensory gene families in adult antennae of Anomala corpulenta motschulsky (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Rutelinae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144214. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, M.N.; Keeling, C.I.; Mitchell, R.F. Genomic content of chemosensory genes correlates with host range in wood-boring beetles (Dendroctonus ponderosae, Agrilus planipennis, and Anoplophora glabripennis). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, D.D.; Scully, E.D.; Pauchet, Y.; Hoover, K.; Kirsch, R.; Geib, S.M.; Mitchell, R.F.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ahn, S.-J.; Arsala, D.; et al. Genome of the Asian longhorned beetle (Anoplophora glabripennis), a globally significant invasive species, reveals key functional and evolutionary innovations at the beetle–plant interface. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, R.F.; Hughes, D.T.; Luetje, C.W.; Millar, J.G.; Soriano-Agatón, F.; Hanks, L.M.; Robertson, H.M. Sequencing and characterizing odorant receptors of the cerambycid beetle Megacyllene caryae. Insect Biochem. Mol. 2012, 42, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; Hao, H.; Zhang, B.; Butcher, R.; Sun, J. Chemical signals synchronize the life cycles of a plant-parasitic nematode and its vector beetle. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, R. Identification of Olfactory Genes in Monochamus saltuarius and Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Infestation on Their Expression. Forests 2022, 13, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020258
Zhang S, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zheng Y, Fan Z, Zhang R. Identification of Olfactory Genes in Monochamus saltuarius and Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Infestation on Their Expression. Forests. 2022; 13(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sufang, Xizhuo Wang, Yanlong Zhang, Yanan Zheng, Zhizhi Fan, and Rong Zhang. 2022. "Identification of Olfactory Genes in Monochamus saltuarius and Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Infestation on Their Expression" Forests 13, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020258
APA StyleZhang, S., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Zheng, Y., Fan, Z., & Zhang, R. (2022). Identification of Olfactory Genes in Monochamus saltuarius and Effects of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus Infestation on Their Expression. Forests, 13(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13020258






