Abstract
Research Highlights: Pestalotiopsis pini sp. nov. is an emerging pathogen on stone pine, Pinus pinea L., in Portugal. Background and Objectives: Stone pine is one of the most important forest tree species in Portugal and in the whole Mediterranean basin. Pestalotiopsis species are common endophytes, saprobes or pathogens in a variety of hosts and environments. The objective of the present study was to identify the Pestalotiopsis species associated with the symptomatic stone pine trees. Materials and Methods: Samples of stone pine trees showing shoot blight and stem necrosis were obtained from stone pine orchards and urban areas in Portugal, and the isolated Pestalotiopsis species were identified based on morphology and combined ITS, TEF and TUB DNA sequence data. Artificial inoculations on one-year-old stone pine seedlings were performed with the two species most frequently found in association with shoot blight disease. Results: Five Pestalotiopsis spp. were isolated. A taxonomic novelty, Pestalotiopsis pini is described, representing a new pathogen for stone pine. Conclusions: Pestalotiopsis species may represent a threat to the health of pine forests in the Mediterranean basin. Future research should be done in order to increase our knowledge about the potential impact of pestalotioid species in stone pine, in order to develop management strategies against these pathogens.
1. Introduction
Stone pine, Pinus pinea L., is one of the most important forestry species in Portugal and the Mediterranean basin. Stone pine forests play an important role in the economy of the areas where they are planted, especially due to the high value of edible pine nuts, which are the main resource of this industry [1]. Pinus pinea is broadly considered a robust species. In recent years, pine nut production has been decreasing due to several factors, including pests and diseases [1,2].
Pestalotiopsis is a widely distributed genus of appendage-bearing conidia belonging to the family Sporocadaceae [3]. Fungi within this genus are normally considered secondary pathogens that can be responsible for a variety of plant diseases, including cankers, dieback, leaf spots, needle blight, tip blight, grey blight, severe chlorosis, fruit rots and various post-harvest diseases [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. Species belonging to this genus are also commonly isolated as endophytes, and due to their ability to switch nutritional modes, many endophytic and plant pathogenic Pestalotiopsis species persist as saprobes [9,12].
Pestalotiopsis is distinguished from other pestalotioid genera in the family Sporocadaceae (Heterotruncatella, Neopestalotiopsis, Pseudopestalotiopsis and Truncatella) by the number of conidium cells and by the pigmentation of its median cells [9]. Pestalotiopsis can be easily identified based on its five-celled, fusoid conidia, with three brown concolourous median cells and hyaline end cells; Neopestalotiopsis can be distinguished from Pestalotiopsis by its five-celled, fusoid conidia, with versicolourous median cells; Pseudopestalotiopsis can be distinguished based on its five-celled, fusoid conidia, with three dark concolourous median cells; Truncatella and Heterotruncatella are easily identified based on their four-celled, fusoid conidia [3,9]. Nevertheless, identification to species level solely based on morphology is difficult, since the morphological characters used to differentiate species are limited, variable and may be influenced by different hosts and environments [10,13]. Combined phylogenetic analysis of the internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA (ITS), partial β-tubulin (TUB) and partial translation elongation factor 1-alpha (TEF) DNA sequence data is often required for accurate species identification [3,7,9,10,12].
Few studies have been conducted regarding the pathogenicity of Pestalotiopsis species on pine tree species. Nonetheless, diverse studies obtained several Pestalotiopsis species as endophytes in Pinus and other conifers [9,14,15,16,17,18]. Hu et al. [16] reported the isolation of 19 different Pestalotiopsis species as endophytes from bark and needles of Pinus armandii Franch. in China. Botella and Diez [14] reported the isolation of a Pestalotiopsis sp. from Pinus halepensis Mill. in Spain, and Maharachchikumbura et al. [9] referred to a Pestalotiopsis sp. isolated from a Pinus sp. in China. Pestalotiopsis species have also been isolated as endophytes from pine seeds of Pinus armandii in China [17] and several other pine species across Europe and North America [15].
The objective of the present study was to identify the Pestalotiopsis species associated with stone pine diseases in pine orchards and urban areas across the mainland of Portugal, based on both morphological characters and multigene DNA phylogenetic inference.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Isolation
Isolates were obtained from samples of Pinus pinea showing shoot blight, trunk necrosis, needle blight and pine cone decay. A sample of Pinus pinaster Aiton with shoot blight was also analysed. After macro- and microscopic observation of the sampled material, small pieces from the leading edge of the lesions were surface sterilized for 1 min in 1% NaClO and plated onto potato dextrose agar (PDA) amended with 0.5 mg/mL of streptomycin sulphate in order to avoid bacterial growth. Materials were incubated for seven days with a 12 h light period at 23 ± 2 °C. The hyphal tips of fungi emerging from tissue pieces were transferred to PDA, and single-spore cultures were subsequently established. Fungal isolates were deposited in the culture collection of INIAV Institute (Micoteca da Estação Agronómica Nacional (MEAN)) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Details of Pestalotiopsis isolates obtained in this study (bold) and of strains representing species of Pestalotiopsis and related genera retrieved from GenBank and used in phylogenetic analyses.
2.2. Morphology
Colony morphology was observed after 7 days of cultivation on PDA at 23 ± 2 °C at 12 h daylight. Conidiomatal development was observed on Synthetic Nutrient-poor Agar (SNA) by cultivating the isolates on autoclaved pine needles placed on the surface of SNA. Colony colour was determined on PDA using the colour charts of Rayner [19]. Conidia and conidiogenous cells were mounted in distilled water, and at least 30 measurements per structure were recorded at 400× magnification under a compound light microscope (Olympus BX51, Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) using the program Olympus DP-Soft, or under a Nikon Eclipse 80i compound microscope with differential interference contrast (DIC) illumination, equipped with a Nikon DS-Ri2 high definition colour digital camera.
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted using the “DNA, RNA and Protein Purification—NucleoSpin Plant II” (Macherey-Nagel—MN) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Fresh mycelium was disrupted by vortexing with approximately 200 μL glass beads (450–600 μm diameter) added to the extraction buffer [20].
Polymerase Chain Reactions (PCR) were performed to amplify three distinct DNA regions—the internal transcribed spacer of the ribosomal DNA (ITS), the partial translation elongation factor 1-alpha (TEF) and partial β-tubulin (TUB). The ITS, TEF and TUB genes were amplified using the primer pairs ITS5/ITS4 [21], EF1-728F/EF1-986R [22], and T1/Bt-2b [23,24].
All PCR reactions were performed in a 25 μL reaction containing DNA template (diluted 10×), 10× PCR reaction buffer, 3 mM MgCL2, 0.5 mM of each deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate, 1 U of Taq DNA Polymerase, (BioTaqTM DNA Polymerase—Bioline, London, UK) and 2 μM of each primer, for ITS and TUB amplification, or 6 μM of each primer, for TEF amplification.
PCR reactions were performed in a Biometra TGradient thermo cycler (Biometra, Göttingen, Germany) with the following thermal cycling conditions, for ITS: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles consisting of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s and extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min; for TEF: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 8 min, followed by 35 cycles consisting of denaturation at 94 °C for 15 s, annealing at 55 °C for 20 s and extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min; and for TUB: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, followed by 30 cycles consisting of denaturation at 94 °C for 1 min, annealing at 55 °C for 1 min and extension at 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min.
PCR products were sequenced in both directions at STABVida Sequencing Laboratory (Caparica, Portugal) on an ABI PRISM 3730xl DNA analyser (Applied Bio systems) using the same primers as those used for the amplification reactions. The resulting nucleotide sequences were edited using the programs FinchTV version 1.4.0 (Geospisa Inc.) and BioEdit version 7.2.6 [25], and a consensus sequence was made from the forward and reverse sequences. Sequences obtained in this study were deposited in GenBank (see Table 1).
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
A BLAST engine search was used for sequence similarity searching on GenBank (NCBI—National Centre for Biotechnology Information). Based on blast search results and the literature, additional sequences were selected from GenBank and incorporated in the analyses (Table 1). Sequence alignments of the three individual loci (ITS, TEF, TUB) were made using MAFFT v. 7 (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/index.html), and were then manually edited using BioEdit version 7.2.6. Single gene datasets were combined using SequenceMatrix [26].
Phylogenetic analyses of the combined three-locus sequence dataset comprised Maximum Likelihood (ML), Maximum Parsimony (MP) and Bayesian Inference (BI).
ML were implemented on the CIPRES Science Gateway portal (https://www.phylo.org/) [27] using RAxML-HPC2 on XSEDE v. 8.2.12 [28]. For ML analyses, a GTR+CAT substitution model with 1000 bootstrap iterations was set.
MP analysis was performed using Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (PAUP) v. 4.0b10 [29]. Gaps were treated as missing data. Trees were inferred using heuristic search with random stepwise addition and tree-bisection reconnection (TBR). Maxtrees were set to 10,000 and branches of zero length were collapsed. Bootstrap support values with 1000 replications [30] were calculated for tree branches. Tree length (TL), consistency index (CI), retention index (RI), rescaled consistency index (RC) and homoplasy index (HI) were calculated for trees generated under different optimality criteria.
BI was performed by using the Markov Chain Monte Carlo method (MCMC) with MrBayes v. 3.2.6 [31]. JModelTest2 on XSEDE [32], implemented via the CIPRES portal, was used to determine the best-fit nucleotide substitution model for each partition using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) [33]. The GTR + I + G model was selected as the most suitable for ITS and TUB data partitions, and the GTR + G model was selected for TEF data partition. Four MCMC chains were run simultaneously, starting from random trees for 1,000,000 generations. Trees were sampled every 100 generations for a total of 10,000 trees. The burn-in fraction was set to 0.25, after which posterior probabilities were determined from a majority-rule consensus tree [34].
2.5. Pathogenicity Tests
Two isolates representing the most common Pestalotiopsis species isolated from stone pine trees with shoot blight disease in this study were selected to perform the pathogenicity tests: MEAN1095—Pestalotiopsis pini sp. nov. and MEAN1096—Pestalotiopsis australis Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous.
To carry out the pathogenicity tests, 93 one-year-old stone pine seedlings were sourced from a nursery, where they were cultivated from seeds of a certified orchard. For each isolate and for the control treatment, 31 seedlings were randomly chosen and distributed along a plastic cell pack (6 × 11 plastic cells container). Each plastic cell pack with plants was randomly located in the greenhouse test area. The plants were then acclimatized during one month under greenhouse conditions, with temperatures varying from 18 to 28 °C, watered as needed (circa 2 L per plastic cell pack container, twice a week).
Spore suspensions of each isolate were prepared from cultures on PDA, grown at 25 ± 1 °C for 14 days (four plates/isolate). Sterile deionized water was added to the cultures and spores were dislodged by a sterile glass rod. The spore suspensions were resuspended in sterile deionized water and concentration adjusted to 1 × 105 conidia mL−1 with a haemocytometer.
The inoculations were performed by two combined methods. First, the stems were damaged by gently piercing them with a dissection needle that was previously dipped into the spore solution, while, in the control, the stems were pierced with a sterile needle. Five to six wounds were made per plant, approximately 3 cm apart from each other, in the upper third of the stem. Secondly, based on Talgø et al. [35], some needles were removed from plants, and the injured area subsequently brushed with the spore suspension. Sterile water was used in the control. Each container was covered with a plastic bag and maintained for one week to enhance fungal development.
The seedlings were kept in the greenhouse for four months (18 July to 17 November 2017).
At the end of the experiment, the number of affected plants was noted, and in order to attest Koch’s postulates, re-isolations of fungi were carried out from the disease margins of three symptomatic seedlings, following the methodology described in Section 2.1.
3. Results
3.1. Fungal Isolation and Identification
Among other fungi, a total of 18 pestalotiopsis-like colonies were observed. After morphological observation and ITS sequence analyses, five isolates were identified as belonging to Heterotruncatella and 13 to Pestalotiopsis. Further molecular studies were performed to identify the Pestalotiopsis species isolated.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses of Combined ITS, TEF and TUB Sequences
To determine the phylogenetic position of the Pestalotiopsis isolates, phylogenetic analyses were performed based on the combined ITS, TEF, and TUB sequence data. The combined alignment contained sequences from 104 strains (including two outgroups) with 1427 characters (including alignment gaps), divided in three partitions with 494 (ITS), 491 (TEF) and 442 (TUB) characters; 417 of these were parsimony-informative, 151 were variable and parsimony-uninformative, and 859 were constant. The combined Pestalotiopsis dataset was analysed using ML, MP and BI (Figure 1). The phylograms from the three analyses showed similar results in topology, and hence the best scoring tree resulting from ML analyses, with a final likelihood value of −10,646.254559, is shown in Figure 1. Maximum likelihood, MP bootstrap support values, and BI posterior probabilities (MLBS/MPBS/BIPP) are shown at common branches.
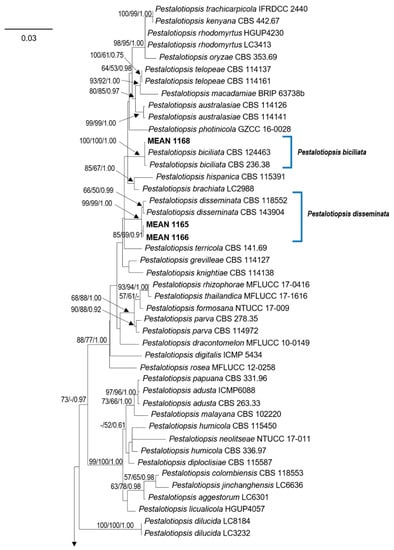
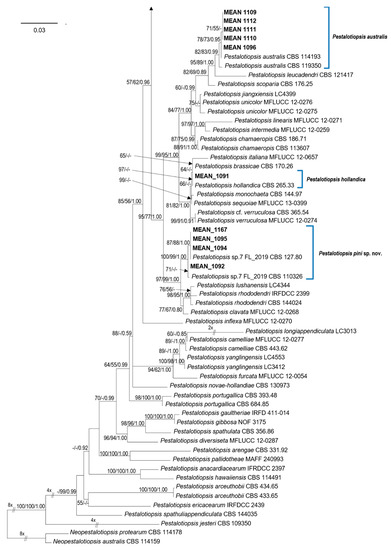
Figure 1.
Phylogram generated from maximum likelihood (ML) analysis based on combined ITS, TUB and TEF sequence alignment for species of Pestalotiopsis. The best scoring ML tree with a final likelihood value of −10,646.254559 is presented. The tree was rooted to Neopestalotiopsis australis (CBS 114159) and N. protearum (CBS 114178). Maximum likelihood and maximum parsimony bootstrap support values ≥50% and Bayesian Inference posterior probabilities ≥0.90 (MLBS/MPBS/BIPP) are given at the nodes in common branches. The isolates obtained in this study are in bold. The scale bar represents the expected number of changes per site.
Isolates MEAN 1092, MEAN 1094, MEAN 1095 and MEAN 1167 were identical in our primary observations and formed a distinct clade, separate from previously described species within the genus. These isolates are well supported by all three phylogenetic analyses, and hence they are described as a new species of Pestalotiopsis.
Phylogenetic analyses allowed to identify the remaining isolates obtained in this study as belonging to four different species of Pestalotiopsis: Pe. australis (five isolates), Pestalotiopsis disseminata (Thüm.) Steyaert (two isolates), Pestalotiopsis biciliata Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous (one isolate) and Pestalotiopsis hollandica Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous (one isolate). Isolates MEAN 1109, MEAN 1110, MEAN 1096, MEAN 1111 and MEAN 1112 formed a clade along with reference strains of Pe. australis. MEAN 1165 and MEAN 1166 clustered with strains of Pe. disseminata. Isolate MEAN 1168 grouped with Pe. biciliata, while isolate MEAN 1091 was closely related to Pe. hollandica.
3.3. Morphology and Taxonomy
Pestalotiopsis pini A.C. Silva, E. Diogo & H. Bragança, sp. nov. (Figure 2)
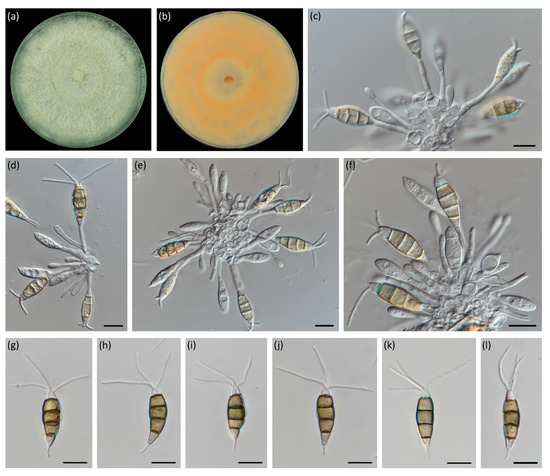
Figure 2.
Pestalotiopsis pini (MEAN 1094). (a,b) Colony on PDA after 10 days at 23 ± 2 °C—surface view and reverse, respectively. (c–f) Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and attached conidia. (g–l) Conidia. Scale bars: 10 µm.
MycoBank: MB 835952
Holotype: LISE 96316
Etymology: Named after the host genus from which it was isolated, Pinus.
Host/Distribution: On needles, shoots and trunks of Pinus pinea and on Pinus pinaster in Portugal (this study). Seen on Pinus radiata in Chile and on Pinus sp. in the USA also [3].
Description: Colonies on PDA attaining 82–85 mm diam after 7 d at 25 °C, with smooth edge, whitish to pale salmon coloured, with cottony aerial mycelium, forming abundant acervuli exuding black spore masses after two weeks. Reverse pale peach to salmon coloured. Conidiomata acervular on PDA, globose, aggregated or scattered, semi-immersed or partly erumpent, exuding black conidial masses. Conidiophores septate near base, simple or rarely branched at base, subcylindrical with a swollen base, hyaline, up to 28 μm long. Conidiogenous cells discrete, cylindrical, hyaline, smooth, 12–25 × 2–4 μm. Conidia fusoid to ellipsoid, straight to slightly curved, 4-septate, occasionally slightly constricted at septa (20.0–)23.3–24.6(–27.6) × (4.7–)7.4–7.8(–8.2) μm, av. ± S.D. = 24.0 ± 1.8 × 7.6 ± 0.6 μm; basal cell obconic, hyaline, smooth and thin-walled, 3.9–7.3 μm long; three median cells doliiform, (12.2–)14.8–15.6(–17.3) μm long, av. ± S.D. = 15.2 ± 1.3 μm, smooth and thin-walled, concolourous, but occasionally the two upper median cells are slightly darker than the lower median cell, olivaceous to brown, septa darker than the rest of the cell (second cell from the base 3.8–6.0 μm long; third cell 3.2–6.6 μm long; fourth cell 3.4–6.1 μm long); apical cell 2.4–4.8 μm long, hyaline, conical to subcylindrical, thin- and smooth-walled; with 3–4 tubular apical appendages (mostly 3), arising from the apical crest, unbranched, filiform, (9.7–)18.4–19.8(–27.8) μm long, av. ± S.D. = 19.1 ± 3.5 μm; basal appendage single, filiform, unbranched, centric, 1.4–7.6 μm long.
Material examined: PORTUGAL, Lisbon, on rotten trunk of Pinus pinea, Ana C. Silva and Helena Bragança, March 2017 (LISE 96316 holotype; ex-type culture, MEAN 1094 = CPC 36748 = CBS 146841); PORTUGAL, Santarém, on blighted shoots of Pinus pinea, Ana C. Silva and Helena Bragança, March 2016 (living culture, MEAN 1092 = CPC 36746 = CBS 146840). PORTUGAL, Santarém, on blighted shoots of Pinus pinea, Ana C. Silva and Helena Bragança, March 2017 (living culture, MEAN 1095 = CPC 36749 = CBS 146842). PORTUGAL, unknown district, on blighted shoots of Pinus pinaster, Ana C. Silva, Eugénio Diogo and Helena Bragança, November 2018 (living culture, MEAN 1167).
Notes: Pestalotiopsis pini has similar-sized conidia to Pestalotiopsis clavata Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous and Pestalotiopsis lushanensis F. Liu & L. Cai (20.0–27.6 × 4.7–8.2 µm in Pe. pini vs. 20–27 × 6.5–8 μm in Pe. clavata and 20–27 × 7.5–10 μm in Pe. lushanensis), but they are different in the number of appendages (Pe. pini has 3–4 appendages while Pe. clavata and Pe. lushanensis have 2–3 apical appendages) [12,36]. They are clearly separated in the phylogram based on combined ITS, TEF, and TUB sequence data, Pe. pini isolates formed a separate clade with strong support values on the three analyses performed (ML, MP and BI), (see Figure 1).
3.4. Pathogenicity
Two isolates, representing the most common Pestalotiopsis species isolated from pine trees with shoot blight disease in the present study, were submitted to pathogenicity tests by artificial inoculation on stone pine seedlings: MEAN1095—Pestalotiopsis pini sp. nov. and MEAN1096—Pestalotiopsis australis.
The development of disease symptoms was observed during a four-month period. Initial symptoms started after four weeks on seedlings inoculated with the Pe. pini isolate. Seedlings started to show yellowish and wilted needles in the apical third of the trunk. By the end of the experiment, symptomatic plants exhibited a dried apex in the inoculated branch/trunk (Figure 3). In total, 19.4% (6/31) of the plants inoculated with Pe. pini isolate MEAN 1095 were symptomatic. No symptoms were observed on the control treatment, nor in plants inoculated with Pe. australis isolate MEAN 1096. Pestalotiopsis pini was successfully re-isolated from the three symptomatic plants sampled, thus fulfilling Koch’s postulates and confirming its pathogenicity to stone pine.
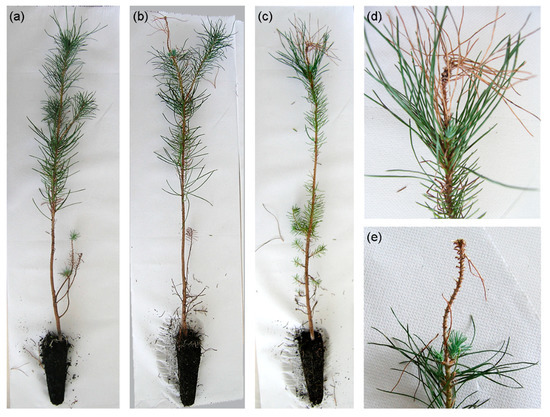

Figure 3.
Aspect of inoculated seedlings four months after the inoculations. (a) Asymptomatic plant. (b,c) Symptomatic plants inoculated with Pestalotiopsis pini sp. nov. (d,e) Detail of dead apical shoots on symptomatic plants.
4. Discussion
In the present study Pestalotiopsis pini is described as a new species causing shoot blight and stem necrosis on Pinus pinea. Based on the morphology and molecular phylogenetic analyses of combined ITS, TEF and TUB sequence data, this taxon proved distinct from other species known from pine, or from DNA sequence data. Four other species of Pestalotiopsis were identified in association with symptomatic stone pines, namely, Pe. australis, Pe. biciliata, Pe. disseminata and Pe. hollandica.
Pestalotiopsis pini isolates obtained in this study (MEAN 1095, MEAN 1092, MEAN 1094, MEAN 1167) were grouped along with two unclassified Pestalotiopsis sp. strains included in the revision of Sporocadaceae, performed by Liu et al. [3], namely CBS 110326 and CBS 127.80. In the latter study, the authors retained these two isolates as an “informal species” “Pestalotiopsis sp.7 FL-2019”, due to the lack of more isolates and limited phylogenetic support. In our phylogenetic analyses (Figure 1), these two strains were grouped with the four isolates obtained in this study, forming a separate clade with strong support values in all the phylogenetic analyses performed (MLBS = 100%, MPBS = 99%, BIPP = 1.00).
In the present study, Pe. pini was isolated from blighted shoots of P. pinea and P. pinaster trees in pine plantations, and from the necrotic wood of a decayed stone pine trunk located in Monsanto Forest Park in Lisbon. Pathogenicity tests performed confirmed that Pe. pini is pathogenic to stone pine. Furthermore, in the Monsanto Forest Park, various stone pine trees exhibited the same symptoms, and no other potential pathogens were isolated along with Pe. pini, suggesting that this could be a primary pathogen for this host. Interestingly, despite Pestalotiopsis species generally not being regarded as host-specific and normally being found on a wide range of plants and substrates [9], the two Pe. pini strains included in the study of Liu et al. [3] were also isolated in pines—Pinus sp. in the USA (CBS 110326) and Pinus radiata D. Don. in Chile (CBS 127.80)—although no information about the health of these pine trees is available.
In this study, Pestalotiopsis australis was isolated from blighted stone pine shoots in P. pinea orchards. This is the first report of Pe. australis isolated from conifers and in Europe. Under the conditions of the trials, no symptom development occurred in any of the inoculated seedlings, suggesting that Pe. australis may behave as an endophyte on stone pine. Pestalotiopsis australis has been reported from Proteaceae hosts, it was isolated from Grevillea sp. in Australia and South Africa, and from Protea neriifolia × susannae cv. ‘Pink Ice’ and dead leaves of Brabejum stellatifolium L. in South Africa [3,9].
Pestalotiopsis hollandica was isolated from the blighted shoots of stone pine trees in stone pine orchards. Pestalotiopsis hollandica was first described from Sciadopityaceae (Sciadopitys verticillata (Thunb.) Siebold & Zucc.) in the Netherlands [9] and it has already been isolated from conifers in Spain, namely from Cupressus sempervirens L. (Cupressaceae) [37]. Isolate MEAN 1091 was closely related to the reference strain of Pe. hollandica. However, Pe. hollandica was not well resolved from Pestalotiopsis brassicae Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous, Pestalotiopsis Italiana Maharachch., Camporesi & K.D. Hyde, Pestalotiopsis Monochaeta Maharachch., K.D. Hyde & Crous, Pestalotiopsis sequoiae W.J. Li, Camporesi & K.D. Hyde and Pestalotiopsis Verruculosa Maharachch. & K.D. Hyde, suggesting that these isolates may represent a single species, as suggested by Liu et al. [3]. Some of those species’ names have also been associated with conifers in the past [9,38].
Pestalotiopsis biciliata was isolated from a dry conelet (1st year) from a stone pine orchard. This species was first described by Maharachchikumbura et al. [9], isolated from dry needles of Taxus baccata L. in the Netherlands, from Paeonia sp. in Italy and from Platanus × hispanica in Slovakia. Pe. biciliata was also isolated from dry needles of Taxus baccata in the UK [3]. The fungus was referred to as the causal agent of fruit rot on withered grapes in Italy [8], and is associated with grapevine trunk diseases in France [10]. Recently Pe. biciliata was also reported as a foliar pathogen of Eucalyptus spp. [11].
Pestalotiopsis disseminata was isolated from blighted shoots of stone pine trees in a stone pine orchard. Pe. disseminata was first described from Eucalyptus botryoides Sm. in Portugal [39], and has already been isolated from a wide range of hosts and locations worldwide [3,15,18,40], including the genus Pinus [15,16,18]. It was isolated as an endophyte from Pinus armandii in China, along with 18 other pestalotioid species [16]; from Pinus parviflora Siebold & Zucc. var. pentaphylla (Mayr) in Japan [18] and from seeds of P. pinea in Turkey, Pinus elliottii Engel., Pinus patula Schltdl & Cham, P. radiata, Pinus taeda L. in the USA and P. pinaster in Portugal [15].
Isolates identified in this study were associated with symptomatic stone pine trees with shoot blight, trunk necrosis and pinecone decay in Portugal. At least one of the five identified species, Pestalotiopsis pini sp. nov., is pathogenic to stone pine. In recent years, various species of Pestalotiopsis have been described [3,4,7,9,10], with many being associated with plant diseases and shown to be pathogenic to their host under certain biotic and abiotic conditions [4,5,8,11,41,42].
The symptoms observed in stone pine orchards in Portugal, in particular shoot blight disease, might be of special concern to the forest industry, since dry shoots in the tree canopy could lead to a decrease in pinecone development and pine nut production, which is the most profitable resource of this industry [1,2].
Shoot blight disease on stone pine and other pine species is normally associated with Diplodia sapinea (Fr.) Fuckel [43,44], and has recently also been associated with Sydowia polyspora (Bref. & Tavel) E. Müller [45]. In the present study, various Pestalotiopsis species were isolated from stone pine samples with similar symptoms, moreover, Pe. pini proved to be pathogenic on stone pine, causing dry shoots on artificially inoculated seedlings, thus suggesting that Pe. pini should also have an active role in the expression of shoot blight disease on stone pine. The fact that in the pathogenicity tests, Pe. pini only caused disease symptoms in approximately 20% of the inoculated seedlings may indicate relative host resistance due to genetic differences among the seedlings. Alternatively, the development of shoot blight disease is due to more than one factor, biotic or abiotic. In fact, D. sapinea, S. polyspora and other fungi were also present in some of the sampled symptomatic material (data not shown). Diverse authors also report more than one species involved in dieback and blight diseases, including pestalotioid species and other fungi [8,45,46,47] and observed that some abiotic factors also have a major role in disease development, namely water stress and air temperature [41,42,47]. In this case, a synergic effect among Pe. pini and other pathogenic or endophytic fungi found in stone pine shoots may also trigger the development of shoot blight disease symptoms. Future research should be performed to evaluate shoot blight disease prevalence on P. pinea orchards in Portugal and other Mediterranean areas and the diverse biotic and abiotic agents that can be involved in disease development.
The present study represents a preliminary contribution of the Pestalotiopsis species diversity associated with shoot blight disease of stone pine in Portugal. Knowledge of Pestalotiopsis species associated with shoot blight and other pine diseases will provide a basis to better understand disease development and help to develop management strategies against these pathogens.
5. Conclusions
A novel fungal species, Pestalotiopsis pini was described. This study proves that Pe. pini is an emerging pathogen causing shoot blight and trunk necrosis on Pinus pinea in the Mediterranean area.
To our knowledge, this is also the first report of Pe. australis on conifers and in Europe, and of Pe. hollandica and Pe. biciliata on Pinus spp. and in Portugal. Information about Pestalotiopsis species associated with shoot blight and other diseases on pine species will help to provide a basis for a better understanding of disease development, and the development of management strategies against these pathogens.
Author Contributions
A.C.S. and H.B. designed the experiments and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; A.C.S., E.D. and H.B. performed morphologic and molecular analyses; J.H. contributed for molecular biology procedures and review of the manuscript; M.S.-D. gave support in laboratory work and review of the manuscript; A.P.R. and P.W.C. gave support during the development of the study and discussion of the manuscript. H.B. supervised the study. All authors contributed to the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária e Veterinária, I.P. and by the Portuguese program PDR2020 (Programa de Desenvolvimento Rural 2014–2020) financed by the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Development (EAFRD), under the project “Grupo Operacional + Pinhão—Gestão integrada de agentes bióticos associados à perda de produção de pinhão” (PDR2020-101-031187). Article Processing Charges were supported by Laboratório de Patologia Vegetal Veríssimo de Almeida, Instituto Superior de Agronomia.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to Engineer Rosário Amaral and Mónica Pereira from ICNF-Viveiros de Alcácer do Sal (Portugal) for the supply of the plant material included in the pathogenicity tests; to Doctor Filomena Nóbrega (INIAV, I.P.), Mieke Starink-Willemse and J.Z. Groenewald (Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute) for assistance on molecular biology procedures and phylogenetic analyses; and to Engineer Filomena Caetano (ISA, University of Lisbon, Portugal) for providing a sample. A.C.S. thanks the Westerdijk Fungal Biodiversity Institute for laboratory facilities during the Short Term Scientific Mission (STSM) grant supported by the COST Action FP1401—“A global network of nurseries as early warning system against alien tree pests (Global Warning)”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Awan, H.U.M.; Pettenella, D. Pine nuts: A review of recent sanitary conditions and market development. Forests 2017, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, S.; Calama, R.; Nasrallah Neaymeh, E.; Roques, A. Impact of the Dry Cone Syndrome on commercial kernel yield of stone pine cones. In Mediterranean Pine Nuts from Forests and Plantations; Carrasquinho, I., Correia, A.C., Mutke, S., Eds.; CIHEAM Options Méditerranéennes: Série A; Séminaires Méditerranéens: Zaragoza, Spain, 2017; Volume 122, pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Bonthond, G.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cai, L.; Crous, P.W. Sporocadaceae, a family of coelomycetous fungi with appendage-bearing conidia. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 287–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinsanmi, O.A.; Nisa, S.; Jeff-Ego, O.S.; Shivas, R.G.; Drenth, A. Dry Flower Disease of Macadamia in Australia caused by Neopestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. and Pestalotiopsis macadamiae sp. nov. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, L.; Shu, N.; Jiang, M.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Tong, H. Pestalotiopsis-like species causing gray blight disease on Camellia sinensis in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.G.; Briceño, E.X.; Keith, L.M.; Latorre, B.A. Canker and twig dieback of blueberry caused by Pestalotiopsis spp. and a Truncatella sp. In chile. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hou, L.; Raza, M.; Cai, L. Pestalotiopsis and allied genera from Camellia, with description of 11 new species from China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, M.; Zapparoli, G. Identification of Pestalotiopsis bicilita, Diplodia seriata and Diaporthe eres causing fruit rot in withered grapes in Italy. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 151, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis Revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.; Larignon, P.; Hyde, K.; Al-Sadi, A.; Liu, Z.-Y. Characterization of Neopestalotiopsis, Pestalotiopsis and Truncatella species associated with grapevine trunk diseases in France. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2017, 55, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Rodríguez, C.; Dalla Valle, M.; Aleandri, M.P.; Vannini, A. Pestalotiopsis biciliata, a new leaf pathogen of Eucalyptus spp. recorded in Italy. For. Pathol. 2019, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Cai, L.; Chukeatirote, E.; Wu, W.P.; Sun, X.; Crous, P.W.; Bhat, D.J.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Bahkali, A.H.; et al. A Multi-Locus backbone tree for Pestalotiopsis, with a polyphasic characterization of 14 new species. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 95–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Guo, L.D.; Chukeatirote, E.; Bahkali, A.H.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis-morphology, phylogeny, biochemistry and diversity. Fungal Divers. 2011, 50, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botella, L.; Javier Diez, J. Phylogenic diversity of fungal endophytes in Spanish stands of Pinus halepensis. Fungal Divers. 2011, 47, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, M.; Oskay, F.; Doğmuş, H.T.; Lehtijärvi, A.; Woodward, S.; Vettraino, A.M. Cryptic risks to forest biosecurity associated with the global movement of commercial seed. Forests 2019, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jeewon, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, T.; Hyde, K.D. Phylogenetic diversity of endophytic Pestalotiopsis species in Pinus armandii and Ribes spp.: Evidence from rDNA and β-Tubulin gene phylogenies. Fungal Divers. 2007, 24, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tibpromma, S.; Mortimer, P.E.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Zhan, F.; Xu, J.; Promputtha, I.; Yan, K. Morphology and multi-gene phylogeny reveal Pestalotiopsis pinicola sp. nov. and a new host record of Cladosporium anthropophilum from edible pine (Pinus armandii) seeds in Yunnan province, China. Pathogens 2019, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Motohashi, K.; Ono, Y. Description of Pestalotiopsis pallidotheae: A new species from Japan. Mycoscience 2010, 51, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, R.W. A Mycological Colour Chart; Commonwealth Mycological Institute: Kew, UK; British Mycological Society: Surrey, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Bragança, H.; Simões, S.; Onofre, N.; Tenreiro, R.; Rigling, D. Cryphonectria parasitica in Portugal: Diversity of vegetative compatibility types, mating types, and occurrence of hypovirulence. For. Pathol. 2007, 37, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, I.; Kohn, L.M. A method for designing primer sets for speciation studies in filamentous ascomycetes. Mycologia 1999, 91, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, N.L.; Donaldson, G.C. Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. Cladistics multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. The Cipres Science Gateway: Enabling high-impact science for phylogenetics researchers with limited resources. ACM Int. Conf. Proc. Ser. 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swofford, D.L. PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (and Other Methods), Version 4.0 Beta 10; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, ME, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the Bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: A new method of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talgø, V.; Chastagner, G.; Thomsen, I.M.; Cech, T.; Riley, K.; Lange, K.; Klemsdal, S.S.; Stensvand, A. Sydowia polyspora associated with Current Season Needle Necrosis (CSNN) on true fir (Abies spp.). Fungal Biol. 2010, 114, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Tian, Q.; Hyde, K.D. Pestalotiopsis species on ornamental plants in Yunnan province, China. Sydowia 2013, 65, 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Schumacher, R.K.; Wingfield, M.J.; Akulov, A.; Denman, S.; Roux, J.; Braun, U.; Burgess, T.I.; Carnegie, A.J.; Váczy, K.Z.; et al. New and interesting fungi. 1. Fungal Syst. Evol. 2018, 1, 169–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Bhat, D.J.; Boonmee, S.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Phookamsak, R.; Phukhamsakda, C.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 1–110: Taxonomic and phylogenetic contributions to fungal species. Fungal Divers. 2015, 72, 1–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Thümen, F. Contributiones ad Floram Mycologicam Lusitanicam. Cont. No. 9. Inst. Coimbra 1881, 28, 501–505. Available online: https://digitalis-dsp.sib.uc.pt/institutocoimbra/UCBG-A-24-37a41_v028/UCBG-A-24-37a41_v028_item1/P348.html (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Liu, A.R.; Xu, T.; Guo, L.D. Molecular and morphological description of Pestalotiopsis hainanensis sp. nov., a new endophyte from a tropical region of China. Fungal Divers. 2007, 24, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Belisário, R.; Aucique-Pérez, C.E.; Abreu, L.M.; Salcedo, S.S.; de Oliveira, W.M.; Furtado, G.Q. Infection by Neopestalotiopsis spp. occurs on unwounded Eucalyptus leaves and is favoured by long periods of leaf wetness. Plant Pathol. 2020, 69, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannath, K.; Galea, V.; Akinsanmi, O. Air Temperature an Influential Climatic Factor for Growth and Reproduction of Dry Flower Pathogens of Macadamia. Proceedings 2020, 36, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.R.; Vaillancourt, L.J.; Flowers, J.L.; Bateman, A.M. Managing Diplodia Tip Blight of Landscape Austrian Pines. J. Arboric. 2009, 35, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Luchi, N.; Oliveira Longa, C.M.; Danti, R.; Capretti, P.; Maresi, G. Diplodia sapinea: The main fungal species involved in the colonization of pine shoots in Italy. For. Pathol. 2014, 44, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Henriques, J.; Diogo, E.; Ramos, A.P.; Bragança, H. First report of Sydowia polyspora causing disease on Pinus pinea shoots. For. Pathol. 2020, 50, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvira-Recuenco, M.; Cacciola, S.O.; Sanz-Ros, A.V.; Garbelotto, M.; Aguayo, J.; Solla, A.; Mullett, M.; Drenkhan, T.; Oskay, F.; Aday Kaya, A.G.; et al. Potential interactions between invasive Fusarium circinatum and other pine pathogens in Europe. Forests 2020, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinrucken, T.V.; Raghavendra, A.K.H.; Powell, J.R.; Bissett, A.; van Klinken, R.D. Triggering dieback in an invasive plant: Endophyte diversity and pathogenicity. Australas. Plant. Pathol. 2017, 46, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).