Abstract
The hippocampus is a critical brain structure involved in episodic memory, spatial orientation, and stress regulation. Its volumetric shrinkage is among the earliest and most reliable indicators of both physiological brain aging and pathological neurodegeneration. Accurate segmentation and measurement of the hippocampal subregions from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is therefore essential for neurobiological age estimation and the early identification of at-risk individuals. In this study, we present a fully automated pipeline that leverages nnU-Net, a self-configuring deep learning framework, to segment the hippocampus from high-resolution 3D T1-weighted brain MRI scans. The primary objective of this work is to enable accurate estimation of brain age through quantitative analysis of hippocampal volume. By fusing domain knowledge in neuroanatomy with data-driven learning through a highly expressive and self-optimizing model, this work advances the methodological frontier for neuroimaging-based brain-age estimation. The proposed approach demonstrates that deep learning can serve as a reliable segmentation tool as well as a foundational layer in predictive neuroscience, supporting early detection of accelerated aging and subclinical neurodegenerative processes.
1. Introduction
Aging is a complex, multidimensional biological process marked by gradual physiological decline and increased disease susceptibility. Within the brain, aging manifests structurally as regional atrophy, white matter degradation, and diminished functional connectivity. Among the regions most consistently affected is the hippocampus—a bilateral structure located within the medial temporal lobes, critical for memory consolidation, spatial navigation, and stress regulation [1]. Longitudinal neuroimaging studies have consistently shown that hippocampal volume decreases with age. Moreover, the rate and pattern of this decline serve as quantifiable proxies for biological brain age, which may diverge from chronological age due to genetic, environmental, or pathological influences [1]. Hippocampal atrophy is a hallmark of various neurodegenerative disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia, and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), as well as psychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) [2].
In many of these conditions, hippocampal shrinkage precedes clinical symptom onset by several years, positioning it as a compelling target for early detection, disease monitoring, and risk stratification. Traditional methods for assessing hippocampal volume via structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) typically rely on manual delineation by experts or atlas-based registration techniques [3]. Although these approaches provide anatomical interpretability, they are labor-intensive, subject to inter-rater variability, and poorly suited for large-scale applications. Furthermore, atlas-based methods often fail to capture individual variations in hippocampal morphology, particularly in elderly individuals or those with marked atrophy [3]. These limitations highlight the need for automated, high-precision segmentation tools that are both scalable and robust across diverse populations.
Recent advances in deep learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have significantly advanced medical image segmentation tasks [4]. Among these, nnU-Net (“no-new-Net”) has emerged as a self-configuring framework that autonomously adapts to various biomedical segmentation tasks, eliminating the need for manual hyperparameter tuning or architectural design. The nnU-Net framework automatically selects from three architectural variants, namely 2D U-Net, 3D full-resolution U-Net, and 3D low-resolution cascade, based on data fingerprinting. In our case, the dataset exhibited isotropic resolution and moderate spatial dimensions, prompting the use of the 3D full-resolution variant. This variant is optimal for volumetric segmentation when inter-slice and in-plane resolution are comparable, allowing the network to leverage full 3D spatial context while preserving anatomical boundaries of curved structures like the hippocampus [5].
In this study, we employ nnU-Net for hippocampal segmentation on high-resolution T1-weighted MRI scans, aiming to estimate brain age through volumetric analysis. The study emphasizes data-centric optimization and clinical integration of an adaptive segmentation pipeline, enabling accurate hippocampal delineation in structurally variable MRI datasets. Specifically, we segment the anterior and posterior hippocampal subregions, which follow distinct aging trajectories and serve different cognitive functions. The anterior hippocampus is primarily associated with affective and stress-related processes, while the posterior region supports spatial memory and navigation [6]. This subregional differentiation enhances the specificity of brain-age estimation and may improve the detection of stress-related neurocognitive decline. Furthermore, the segmentation outcomes are not treated as end goals but are integrated into downstream volumetric estimation and brain aging analysis, thereby advancing clinically interpretable neuroimaging solutions. Our approach combines anatomical precision with computational scalability, offering a clinically relevant pipeline for using hippocampal volume as a non-invasive biomarker of accelerated brain aging. Our proposed pipeline is publicly available at https://github.com/Eshaa2001/BrainAge (Access date: 10 August 2025).
2. Literature Review
The structural and functional integrity of the hippocampus has remained central to aging and neurodegeneration research for over two decades [6]. With advancements in MRI and neuroinformatics, it is now one of the most thoroughly characterized regions in neuroimaging, noted both for its vulnerability to pathological processes and its utility as a biomarker of cognitive health. This section reviews the key literature across hippocampal segmentation, lifespan volumetric decline, and the evolution from classical approaches to deep learning frameworks like nnU-Net.
2.1. Hippocampal Atrophy in Stress, Depression, and Aging
Early foundational work highlighted the hippocampus’s susceptibility to stress-induced neurotoxicity, driven primarily by HPA axis dysregulation and glucocorticoid exposure. These mechanisms trigger dendritic retraction, inhibit neurogenesis, and impair synaptic plasticity, ultimately leading to hippocampal volume loss and memory deficits [7]. Human neuroimaging studies have corroborated these findings, showing significantly reduced hippocampal volume in individuals with major depressive disorder (MDD) relative to healthy controls [7].
Atrophy in the hippocampus is also recognized as an early biomarker in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI), detectable prior to clinical symptom onset. Furthermore, volumetric reductions have been consistently reported in psychiatric conditions such as MDD, PTSD, and chronic stress exposure, highlighting the region’s dual vulnerability to neurodegenerative and environmental stressors [8]. The degree of volume loss correlates with both the number and duration of depressive episodes, indicating a cumulative neurotoxic effect. PTSD studies further support this, revealing pronounced hippocampal shrinkage linked to trauma-related psychopathology [9].
Subregional analyses suggest that the anterior hippocampus, implicated in emotion regulation, may be disproportionately affected in mood disorders compared to the posterior region [10]. In healthy populations, longitudinal imaging has revealed a nonlinear trajectory of hippocampal atrophy, with acceleration after the sixth decade of life, reinforcing its role as a marker of deviation from normative aging.
2.2. Hippocampal Volume as a Neurodegenerative Biomarker
Hippocampal atrophy remains a defining structural hallmark in early AD and MCI. MRI-based volumetry has proven effective in distinguishing AD patients from age-matched controls with high sensitivity [11]. Moreover, the rate of hippocampal volume loss is predictive of MCI-to-AD conversion, cementing its value as a diagnostic and prognostic marker.
While normative aging involves hippocampal shrinkage of ~0.8–2% annually, pathological aging often exceeds this rate [12]. Anatomical heterogeneity underlies this degeneration, with the anterior and posterior subregions showing distinct vulnerability profiles. Left-sided atrophy and subfield-specific loss, particularly in CA1 and the dentate gyrus, have also been reported. These localized patterns offer earlier indicators of neurodegeneration and support the utility of high-resolution, subfield-sensitive analysis [12]. Subsequent work emphasized that posterior hippocampal atrophy is more predictive of memory decline and tau pathology, further validating its role in longitudinal risk modeling [13].
2.3. Traditional Approaches to Hippocampal Segmentation
Manual segmentation using anatomical landmarks has long been considered the gold standard for hippocampal volumetry. However, it is labor-intensive, subjective, and unsuitable for high-throughput studies [14]. To address these limitations, probabilistic atlas-based methods emerged, including the Hammers atlas for medial temporal structures [15]. While these improved throughput, they underperformed in individuals with severe atrophy.
Automated tools such as FreeSurfer and FSL-FIRST offered rapid segmentation [16] but often failed to capture fine anatomical boundaries, particularly in aged or diseased brains. These limitations highlight the persistent trade-off between automation and anatomical precision in conventional pipelines.
2.4. Emergence of Deep Learning in Neuroanatomical Segmentation
Deep learning has significantly advanced neuroanatomical segmentation over the past decade. Encoder–decoder CNNs, particularly U-Net, became the foundation for volumetric segmentation tasks, leveraging skip connections and hierarchical representations to handle limited datasets effectively [17]. In hippocampal segmentation, CNNs have surpassed atlas-based and manual methods in both accuracy and generalizability [18]. Moreover, CNNs demonstrated resilience to anatomical variability and imaging artifacts. Targeted studies identified the benefits of task-specific augmentation, patch-based learning, and structure-sensitive loss functions for segmenting small subcortical regions such as the hippocampus [18]. These strategies contribute to model robustness and finer anatomical delineation.
2.5. Toward Brain-Age Modeling via Hippocampal Volume
Brain-age estimation leverages imaging-derived biomarkers to quantify biological aging. A brain age greater than chronological age is associated with elevated risk for cognitive decline, psychiatric conditions, and increased mortality [19]. Although whole-brain metrics are widely used, hippocampal volume offers distinct advantages due to its early and sensitive response to neurodegenerative processes. Deep learning-based segmentation methods, particularly nnU-Net, enable anatomically precise, reproducible extraction of hippocampal volumes. This precision facilitates integration into brain-age models. Furthermore, anterior and posterior subregional volumes allow refined analysis of stress-related and disease-specific aging signatures [20], underscoring the role of hippocampal morphometry in predictive neuroscience.
3. Dataset and Preprocessing
In this section, we introduce the dataset that is used in this study. We also present the preprocessing steps to prepare this dataset for experimentation.
3.1. Dataset Description
The dataset used in this study is publicly available through the Neuroimaging Informatics Tools and Resources Clearinghouse (NITRC) under group ID 377 [21]. It comprises high-resolution T1-weighted structural brain MRI volumes acquired specifically for temporal lobe analysis. The dataset is curated to support research in neurodegeneration and psychiatric disorders where hippocampal volume is a key variable.
Each MRI volume includes manually segmented hippocampal masks annotated by trained experts using standardized neuroanatomical landmarks. The segmentations differentiate the entire hippocampal structure from surrounding tissues, enabling precise volumetric analysis. All scans were acquired using a 3 Tesla (3T) MRI scanner to ensure high tissue contrast and consistent anatomical detail across the cerebral and subcortical structures. The voxel dimensions for all subjects were standardized at 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 mm3, yielding isotropic resolution suitable for volumetric segmentation. Images were stored in Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative (NIfTI) format (.nii.gz), which preserves spatial orientation and supports downstream compatibility with common neuroimaging toolkits.
The MRI acquisition protocol included full-brain coverage in the axial plane, subsequently reoriented into RAS (Right–Anterior–Superior) alignment for standardized preprocessing [22]. Each image volume was subjected to quality control to confirm the absence of motion artifacts or acquisition abnormalities. Metadata accompanying each scan included anonymized subject identifiers, acquisition timestamps, imaging modality descriptors, and basic diagnostic annotations where applicable. These parameters provided a uniform and high-quality imaging foundation for subsequent segmentation and analysis of hippocampal morphology.
The dataset used in this study comprises high-resolution T1-weighted MRI scans from adolescents aged 7.7 to 15.6 years. This developmental window represents a critical period of hippocampal maturation, synaptic pruning, and neuroplastic adaptation. Unlike older cohorts, where hippocampal atrophy may indicate neurodegeneration, deviations from normative volume trajectories in adolescents may serve as early markers of atypical neurodevelopment. The dataset presents an opportunity to investigate structural vulnerability during early life, with potential implications for identifying stress-related or environmental influences on brain morphology prior to the onset of clinical symptoms.
Gender distribution in the cohort is relatively balanced, with near-equal representation of male and female participants. Handedness data indicate a majority of right-handed individuals, with a subset identified as mixed-handed, allowing for potential exploration of hemispheric dominance effects in future analyses. Pubertal development is recorded using the Tanner staging system, with subjects categorized from Stage 1 (prepubescent) to Stage 5 (fully mature), thereby enabling the integration of neuroendocrine status into volumetric interpretations. In addition to developmental indices, biometric measures such as height (ranging from approximately 51 to 62 inches), weight (68 to 188 lbs), and head circumference (52.2 to 57 cm) are also included. These anthropometric data are valuable for covariate adjustment in volumetric analysis and for investigating brain–body size relationships [ID2]. Together, the demographic and biometric richness of the dataset provides a multidimensional context for interpreting hippocampal segmentation results and supports stratified or normalized analyses critical for accurate modeling of brain age across individual developmental trajectories.
3.2. Motivation and Rationale for MSD Conversion
The raw NITRC dataset, although well-annotated, does not conform to the structure required by nnU-Net’s self-configuring framework [23]. To enable automatic architecture and pipeline selection, the dataset was manually converted into the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) format, which is the expected standard for training with nnU-Net.
The conversion process serves several key purposes:
- Standardization: Harmonizes directory structure and naming conventions across all subject volumes and masks.
- Pipeline Automation: Enables nnU-Net to auto-detect modalities, voxel spacing, and channel configurations.
- Reproducibility: Aligns with best practices in open medical image science by adopting an interoperable, benchmarked dataset format.
3.3. Preprocessing Workflow
Medical image datasets vary widely in dimensionality, modality, and spatial resolution [24]. Differences in voxel spacing, target structure properties, and class imbalance further complicate standardized model development. For such scattered and unorganized spaces, nnU-Net model is tailored to analyze training data and automatically configure a corresponding U-Net pipeline for segmentation. It includes multiple phases to ensure high-quality data for model training and inference.
3.3.1. Image Normalization and Resampling
All scans were resampled to an isotropic voxel spacing of 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 mm3. This standardization reduces inter-scanner resolution bias, which is a known source of variability in multicenter neuroimaging datasets. Uniform spacing enables consistent convolutional kernel application across samples and improves spatial compatibility. Per-volume z-score normalization was subsequently applied to the intensity values, centering each image to zero mean and unit variance. This preprocessing step mitigates differences in scanner calibration, contrast dynamics, and tissue intensity distributions, which otherwise degrade model generalization and increase domain shift. Prior studies have shown that even subtle variations in voxel intensity or resolution can lead to a significant drop in segmentation accuracy when left uncorrected [25].
3.3.2. Spatial Cropping and ROI Localization
To minimize computational complexity and enhance anatomical specificity, hippocampus-focused sub-volumes were extracted using bounding boxes derived from ground truth segmentations [26]. This preprocessing step eliminated irrelevant background regions, reducing interference from surrounding brain structures such as the cerebellum, ventricles, and cortex. For unseen test scans, nnU-Net employed its built-in region proposal mechanism to autonomously identify the hippocampal region during inference, ensuring consistent localization.
3.3.3. Denoising and Artifact Reduction
Despite the overall quality of the NITRC dataset, certain volumes exhibited motion-induced artifacts and scanner-related signal fluctuations. To address these inconsistencies, spatial smoothing was applied to suppress isolated voxel-level noise, while a probabilistic outlier detection framework mitigated intensity spikes arising from acquisition instability [27]. Care was taken to preserve hippocampal boundary integrity and avoid excessive regularization.
4. Materials and Methods
In this section, we present our employed method, proposed pipeline, and employed evaluation measurements.
4.1. Setting up the Internal Pipeline
After conversion to the Medical Segmentation Decathlon (MSD) format, the dataset is processed by nnU-Net’s modular framework. This triggers a multi-stage analysis called dataset fingerprinting. The framework extracts core characteristics of the input data. These include image resolution, voxel spacing, intensity distribution, and class balance. This information guides the automatic configuration of the segmentation architecture and training schedule.
Key parameters computed during this stage include the following:
- Spatial dimensions of each image volume, voxel spacing across all three anatomical axes, and the presence or absence of anisotropy;
- The ratio of foreground to background voxels, assessing class distribution balance across the segmentation labels;
- Statistical properties of intensity values—mean, variance, and intensity range—to inform the choice of normalization and augmentation strategies.
Based on a detailed analysis of dataset characteristics, nnU-Net employs heuristic-based rules to select the optimal architecture from three predefined U-Net variants. The 2D U-Net is designated for planar imaging or highly anisotropic volumes where inter-slice resolution is significantly lower than in-plane resolution [28]. The 3D full-resolution U-Net is best suited for isotropic or near-isotropic datasets, enabling the model to fully exploit volumetric spatial continuity without compromising resolution [29]. Lastly, the 3D low-resolution cascade is tailored for very large 3D volumes, where a coarse-resolution model provides initial localization, refined subsequently by a high-resolution network in a cascaded scheme.
We employed nnU-Net v2, which dynamically configures its architecture, preprocessing, and training parameters based on the dataset fingerprint. For our isotropic and moderately sized T1-weighted MRI volumes, nnU-Net selected the 3D full-resolution U-Net. This decision enables end-to-end volumetric segmentation without resampling compromises [29].
4.2. Mask Overlay and Region Localization
Before training, segmentation masks are visually overlaid on the corresponding MRI volumes. This overlay process serves two purposes:
- Validation of Ground Truth: Ensures alignment between anatomical landmarks and annotated hippocampal structures.
- Quality Assurance: Detects misregistrations, label inconsistencies, and outliers before model training.
Overlay visualizations are performed using nibabel (Version 5.4.0) for NIfTI parsing and matplotlib (Version 3.10.5) for slice-by-slice rendering as shown in Figure 1.
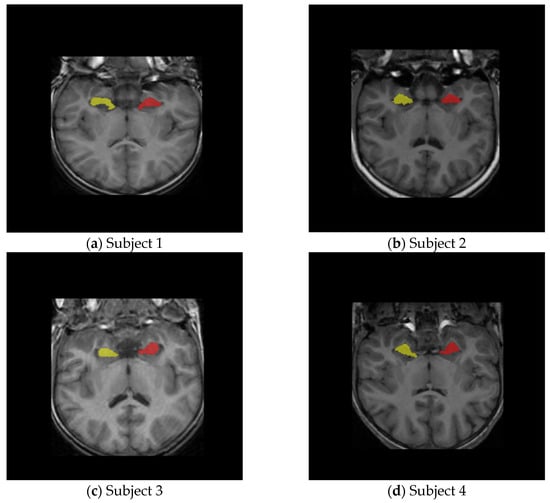
Figure 1.
Hippocampus overlay masks on four subject samples.
4.3. NnU-Net Model
The nnU-Net framework represents a significant advancement in biomedical image segmentation, setting a new benchmark through its automation and adaptability [30]. Unlike conventional models that rely on manual tuning, nnU-Net configures the entire pipeline based on intrinsic dataset characteristics. This self-adaptation begins with a comprehensive fingerprinting process that evaluates voxel spacing, resolution, class distribution, and intensity histograms [31]. Based on this analysis, nnU-Net dynamically defines the network topology. The model selects appropriate encoder–decoder depth, kernel sizes, and filter counts. These parameters are scaled according to image shape and GPU memory constraints. Spatial resampling and intensity normalization are configured automatically for modality-specific preprocessing.
The framework generates its training schedule, including optimizer type, learning rate, and stopping criteria. Data augmentation strategies are selected heuristically and include elastic deformation, affine transformations, and gamma correction to promote robustness and generalization. Upon release, nnU-Net was benchmarked on 23 biomedical datasets from leading segmentation challenges. It consistently matched or outperformed state-of-the-art methods without any dataset-specific tuning. The architecture generalizes well across imaging modalities and anatomical structures, including anisotropic volumes and class-imbalanced problems. Its performance in hippocampal segmentation highlights the framework’s precision in modeling small, structurally complex regions [31]. nnU-Net’s reproducibility and data-centric design have made it the gold standard for automated medical image segmentation [31]. The General architecture of our proposed model is shown in Figure 2.
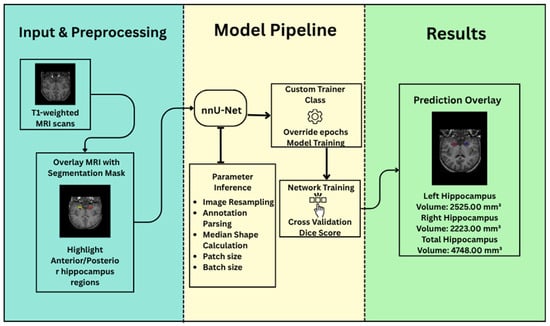
Figure 2.
nnU-Net framework for hippocampus segmentation.
4.4. Customization of the Training Pipeline
While nnU-Net provides a fully functional baseline trainer, we implemented additional customization to suit hippocampus segmentation:
- The training duration was set to 100 epochs based on preliminary experiments and convergence patterns observed during model development.
- Empirical monitoring of the validation loss and Dice coefficient across training iterations revealed performance stabilization before the 100-epoch mark.
- We activated 5-fold cross-validation, ensuring robustness across variable anatomical morphologies.
Loss convergence and generalization were evaluated at each fold using Dice similarity coefficient and precision.
4.5. Prediction Phase and Postprocessing
During inference, nnU-Net processes each subject’s MRI volume in overlapping patches. The default nnU-Net trainer was extended to allow logging of anterior and posterior subregion volumes separately by interpreting class labels 1 and 2. Postprocessing included threshold-based outlier detection and overlay visualization using matplotlib and nibabel libraries. The predicted segmentation masks are directly generated in the form of discrete label maps without voxel-level probability outputs. These predictions are automatically resampled back to the original image space and exported in NIfTI format. This preserves affine transformations and spatial orientation, enabling seamless integration with neuroimaging workflows.
Post-processing involves connected component analysis, which eliminates small, disconnected regions that deviate from the expected hippocampal morphology [32]. This step enhances anatomical precision and minimizes false positives. The refined binary masks are overlaid on the original structural scans to allow qualitative visual assessment. Hippocampal volumes are then computed in cubic millimeters (mm3) from the segmented masks. These measurements are benchmarked against normative volumetric distributions, stratified by demographic variables such as age and sex. Subjects falling below established thresholds—such as the fifth percentile—are flagged for potential hippocampal atrophy. These cases warrant further investigation, particularly in the context of stress-related brain aging or neurodegenerative risk.
4.6. Evaluation Measurement
The Dice coefficient is the primary evaluation metric in this task. Medical images often contain small structures (e.g., tumors, hippocampus) surrounded by large background areas. Dice is robust to this imbalance, unlike accuracy, which can be misleading [33]. Given the relatively small size of the hippocampus, even minor segmentation errors can cause substantial clinical misinterpretations. Dice is preferred because of the following reasons:
- It balances false positives and false negatives.
- It emphasizes spatial overlap between predicted and ground truth masks.
- It is more stable than accuracy in class-imbalanced tasks.
We can compute the Dice score using the following mathematical equation:
where 𝓛Dice is a Dice loss (a similarity-based loss function used in segmentation tasks), pi is predicted binary labels per voxel, gi is ground truth binary labels per voxel, and ϵ is a smoothing constant for numerical stability. The total loss function combines Dice and Cross-Entropy losses as follows:
where 𝓛total is the final loss function used for model optimization, λ1 is the weighting coefficient for Dice Loss, λ2 is the weighting coefficient for categorical cross entropy loss, and 𝓛CE is categorical cross-entropy loss. The Dice score quantifies spatial overlap between predicted and ground truth segmentations. A score of 1.0 denotes perfect agreement, while 0.0 indicates no overlap. In medical imaging, values above 0.7 are generally considered acceptable, depending on the anatomical region and modality.
5. Results and Discussion
In this section, we present our achieved results, compare them with the state-of-the-art deep learning models, and discuss them in detail.
5.1. Quantitative Evaluation Metrics
The quantitative performance of our hippocampus segmentation model was rigorously evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation on the curated MRI dataset. For each fold, the nnU-Net framework was trained on approximately 65 subjects and validated on 17, ensuring representative sampling and minimizing bias due to data partitioning. The primary metric used for performance evaluation was the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), which quantifies spatial overlap between the predicted and ground-truth segmentation masks. The final model achieved a mean validation Dice score of 0.733, reflecting strong anatomical fidelity in a challenging task involving small, irregularly shaped brain structures.
This performance demonstrates the model’s ability to generalize across varied anatomical presentations and scan dimensions, as reflected in the diverse tensor shapes observed during inference. While the Dice score does not exceed the threshold typically associated with large, easily segmented structures (e.g., liver or lung), it is well within the acceptable range for complex, low-volume regions such as the hippocampus—particularly when subregion differentiation (anterior/posterior) is factored in. This robust and consistent segmentation performance across folds underscores the reliability of nnU-Net’s self-configuring architecture for hippocampal volumetry and lays the foundation for accurate downstream volume analysis and neurodegenerative risk flagging.
5.2. Visual Assessment and Mask Overlay Analysis
While quantitative metrics such as the Dice similarity coefficient provide essential numerical validation, the anatomical plausibility and spatial coherence of segmentation outputs must also be verified visually. To this end, overlay visualizations were generated by superimposing the predicted hippocampus masks onto the original T1-weighted MRI scans across axial, sagittal, and coronal planes. Figure 3 presents visual inspection confirmation that the model reliably captured the hippocampal contour, preserving the medial temporal morphology without significant over-segmentation or leakage into adjacent structures such as the amygdala or lateral ventricles [34]. These overlays also helped identify edge cases with partial coverage or morphological anomalies, enabling refined interpretation of volumetric outputs.
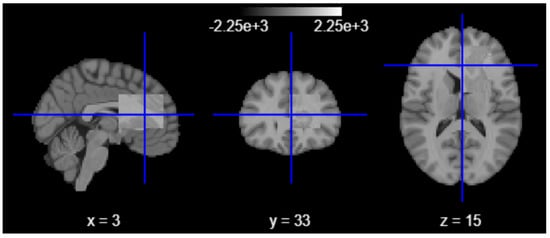
Figure 3.
Overlay visualization on axial, sagittal, and coronal planes.
Following segmentation, we conducted extensive post hoc analyses to identify individuals at risk of early neurodegeneration or accelerated brain aging. Using the derived hippocampal volumes, we flagged cases where the total volume fell below a conservative threshold of 5000 mm3 in subjects under the age of 16—an early atrophy marker. Additionally, the brain-age gap was computed as the difference between predicted biological brain age (derived from a regression model trained on hippocampal volume) and chronological age. A gap greater than 5 years was used to define accelerated aging. Subjects who met both criteria (low volume for age and high brain-age gap) were designated as high-risk. This criterion is supported by prior brain-age literature, where such deviations have been shown to correlate with cognitive decline and elevated risk of neurodegenerative progression [35]. While this threshold was originally validated in adult populations, its use here reflects a conservative and translational approach for detecting atypical neurodevelopment in younger cohorts as shown in Figure 4.
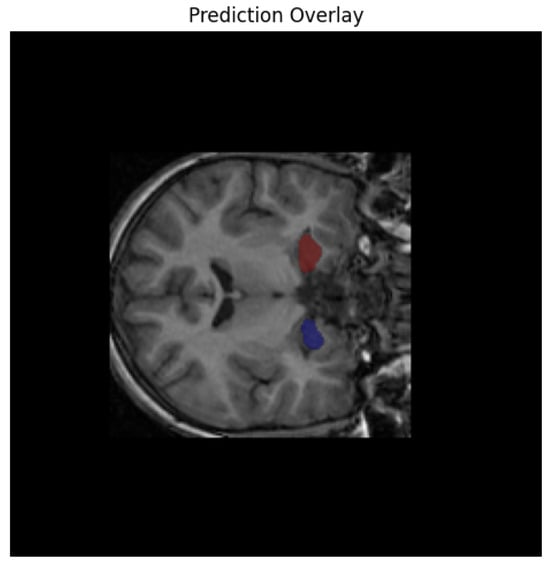
Figure 4.
Model’s predicted overlay results.
To further quantify and spatially contextualize hippocampal atrophy, we employed a second-level group-level statistical analysis using the nilearn neuroimaging library. T1-weighted scans were resampled, aligned, and modeled using a second-level GLM design matrix, contrasting low-volume subjects against those within normative ranges [35]. The resulting Z-statistical map revealed clusters of altered voxel intensities in hippocampal and adjacent limbic regions, offering group-level neuroanatomical evidence of structural deviation.
The illustration in Figure 5 visualizes the relationship between age and hippocampal volume using a bivariate scatterplot. Risk-coded subjects (based on a neurodegeneration threshold of 4700 mm3) were highlighted using a color-coded hue and gender-based markers. This analysis revealed a distinct subset of individuals falling significantly below the expected volume for their age, consistent with early degenerative or stress-associated hippocampal shrinkage.
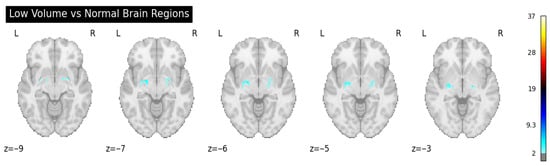
Figure 5.
Second-level group-level statistical analysis.
The visualizations in Figure 6 not only provide qualitative validation of model outputs but also underscore the clinical and research value of integrating segmentation-driven volumetric biomarkers with demographic and neurodevelopmental metadata. By coupling deep learning outputs with structured risk inference, the pipeline transitions from mere anatomical segmentation to actionable neurobiological stratification.
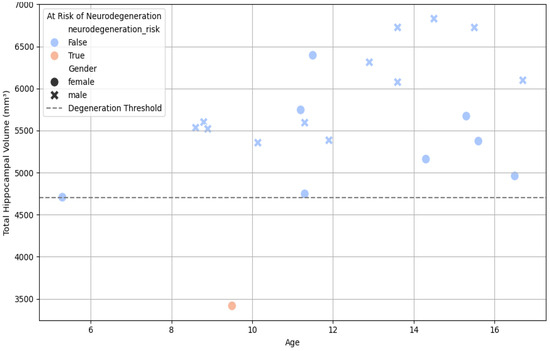
Figure 6.
Scatter plot—age vs. total hippocampal volume, colored by neurodegeneration risk.
5.3. Volumetric Analysis
Quantifying hippocampal volume from the segmentation masks enables an important transition from raw anatomical delineation to biologically interpretable biomarkers [36]. Once the binary segmentation masks were generated by the nnU-Net model, volumetric calculations were performed by summing the number of foreground voxels within each mask and converting this count into cubic millimeters using the known voxel spacing (1 mm3 for isotropic scans in our dataset).
Segmented volumes were converted to mm3 by counting labeled voxels as follows:
where N is the number of voxels labeled as hippocampus.
V = N × v, where v = voxel volume (mm3)
This calculation was conducted for each subject, with separate tracking of anterior and posterior hippocampal regions where label differentiation was available. Across the study cohort, volumetric analysis revealed considerable inter-individual variability, even among subjects within similar age groups. The total hippocampal volume for healthy children and adolescents in the dataset ranged from approximately 4800 mm3 to 7600 mm3, with volume generally increasing with age up to early adolescence, followed by stabilization or mild reduction in older teens. The posterior hippocampus consistently represented a larger fraction of total volume compared to the anterior subregion, aligning with the established anatomical literature on hippocampal longitudinal asymmetry. These regional volumes were not only biologically plausible but were also consistent across folds, underscoring the segmentation model’s stability.
To enable risk stratification and developmental benchmarking, we calculated age-adjusted percentiles for total hippocampal volume. Subjects with volumes below the 5th percentile relative to age- and sex-matched peers were flagged for potential early atrophy. These flags were further cross-referenced with brain-age gap metrics and clinical metadata to identify individuals with disproportionately low volume for their chronological age. We also evaluated the inter-subject distribution of hippocampal volume using histograms and kernel density plots. These plots revealed a moderately left-skewed distribution, suggesting a small subset of subjects with abnormally low hippocampal volumes, some of whom were already flagged as “high-risk” based on combined atrophy and accelerated aging indicators [37]. These subjects were further analyzed in downstream volumetric-residual models, allowing for fine-grained assessment of their deviation from normative neurodevelopmental trajectories.
By anchoring the model’s predictions to measurable and biologically grounded outcomes, this volumetric analysis validates the segmentation framework and enables clinically meaningful interpretations [38]. In doing so, it advances the hippocampus from a mere region of interest (ROI) to a fully quantitative marker of individual neurobiological status.
5.4. Analysis of Brain-Age Discrepancy Through Hippocampal Biomarkers
Brain age, defined as the predicted biological age of the brain based on structural markers, serves as a sensitive biomarker for subclinical neurodegeneration. Hippocampal volume was analyzed against age-related reference distributions to infer potential deviation from normative aging patterns, aligning with frameworks established in prior neuroimaging studies [39]. The predicted age was subtracted from the actual chronological age to derive the brain-age gap. Instead of a black-box regression, we adopted a clinically interpretable rule-based binning approach for brain-age estimation, guided by percentile analysis of predicted volumes. This approach enabled interpretability and aligned with prior clinical volumetry standards. A gap greater than +5 years flagged cases with potential accelerated aging. Additionally, individuals under 16 years of age with hippocampal volumes below 5000 mm3 were identified as high-risk cases, indicating possible early atrophy. This hybrid analysis of anatomical volume and age deviation enabled stratification of at-risk cohorts without the need for opaque regression modeling.
5.5. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Segmentation Methods
To assess the effectiveness of our model, we conducted a comparative evaluation against several state-of-the-art segmentation approaches, including Atlas-Based Segmentation, 2D and 3D U-Net architectures, and UGCapsNet. A brief overview of the employed methods as well as their obtained results is provided below. Note that to the best of our knowledge, our employed dataset has never been used in previous studies.
5.5.1. Atlas-Based Segmentation
The atlas-based approach utilized probabilistic hippocampal maps from the Harvard-Oxford Subcortical Atlas [40], which were initially aligned to MNI standard space. When transformed into subject-specific native space, the templates exhibited substantial spatial misalignments. Multiple resampling and interpolation strategies failed to yield meaningful overlap with anatomical ground truth. The resulting segmentation masks contained only background voxels ([0]), precluding the calculation of a Dice coefficient. These findings underscore the inherent limitations of static, non-personalized atlases in pediatric neuroimaging, where anatomical variability necessitates adaptive alignment strategies.
5.5.2. 2D and 3D U-Net
Both 2D and 3D variants of the U-Net architecture were tested using volumetric MRI input. The 2D U-Net processed resized 256 × 256 slices, while the 3D U-Net handled full volumes at approximately 128 × 128 × 128 resolution. In both cases, ReLU activations were followed by sigmoid outputs, and training used binary cross-entropy and Dice-based loss functions [41]. The implemented 3D U-Net architecture followed a classic encoder–decoder structure with symmetric skip connections and was designed to capture volumetric context in high-resolution MRI [42]. Each encoding block used two successive 3 × 3 × 3 convolutions, batch normalization, and ReLU activation, followed by 2 × 2 × 2 max pooling. The decoder path mirrored this structure using transposed convolutions for upsampling and concatenation for spatial detail restoration.
Let x denote the input volume, and fi be the output of each encoder layer i. The general encoder operation can be written as follows:
where fi is the transformed feature map at encoder level i, fi−1 is the input feature map from the previous layer, Conv3D is the 3D convolutional layer, BN is batch normalization, and ReLU is the rectified linear unit activation function. Consequently, the decoder performs as follows:
where dj is the decoded feature map at level j, dj+1 is the output from the next decoder level, fj is the corresponding encoder feature map, UpConv is 3D up-convolutional or transposed convolution, and the square bracket ([ ]) is channel-wise concatenation. Final output logits are computed via a 1 × 1 × 1 convolution:
where Y is the logits for each voxel, Conv3Dout = 1 × 1 ×1 convolutional layer producing the final output, and d1 is the decoder feature map from the first decoder stage. For UGCapsNet, the formula is as follows:
where 𝓛CE is a scalar value representing the total classification loss, n is the number of training samples, C is the number of classes, yi,c is the ground truth (1 if sample class belongs to class “c”, else 0), and ŷi,c is the predicted probability that sample i belongs to class “c”. Upon initial experimentation, standard U-Net architectures (2D and 3D) demonstrated suboptimal performance, with output segmentations occasionally defaulting to background-only labels (i.e., Dice score = 0). However, subsequent debugging revealed that the U-Net models were not entirely non-functional. They produced non-zero label classes ([0–2]), yet the predictions lacked spatial precision and anatomical plausibility. Volumetric estimations derived from these masks were substantially inflated or deflated relative to ground truth, indicating instability in learning spatial boundaries of hippocampal structures [42].
5.5.3. UGCapsNet
The UGCapsNet architecture incorporated capsule layers to model hierarchical spatial relationships in 3D [43]. Input volumes were preprocessed and normalized to 64 × 64 × 64 dimensions. Training used a cross-entropy loss and softmax activation. The model was able to distinguish multiple hippocampal subregions, producing labels [0–2] for background, anterior, and posterior, respectively. However, training was computationally intensive. Although segmentations were anatomically valid, no quantified Dice score was extracted, and performance metrics lagged behind fully automated solutions.
Multi-class entropy loss was calculated as follows:
where yi,c is a binary indicator (1 if class label c is correct for voxel i, else 0) and ŷᵢ,c is the predicted probability for voxel i to belong to class c.
LCE = − ∑_{i = 1}^{N} ∑{c = 1}^{C} yᵢ,c · log(ŷᵢ,c)
5.5.4. nnU-Net
In its adaptive design, nnU-Net considers three canonical U-Net variants based on dataset properties derived from a “dataset fingerprint”. The first uses 2D U-Net, which is optimal for datasets with high anisotropy (i.e., large inter-slice gaps relative to in-plane resolution). The second uses 3D full-resolution U-Net, which is designed for isotropic or near-isotropic volumetric data and leverages complete spatial context. The final variat uses 3D low-resolution cascade, a two-stage configuration suitable for extremely large volumes, where an initial coarse segmentation guides a subsequent high-resolution refinement. Our dataset exhibited consistent isotropic resolution with manageable volume size, leading the nnU-Net framework to automatically select the 3D full-resolution U-Net. This variant utilizes full volumetric input while preserving fine-grained hippocampal boundaries, particularly across the curved anterior and posterior regions. Additionally, it fits within GPU memory constraints and benefits from extensive built-in data augmentation, automatic patch size determination, and deep supervision, making it the most effective topology for this task. These adaptive topological decisions are key to the superior performance demonstrated by nnU-Net over traditional 2D/3D U-Nets and atlas-based methods in our experiments, as summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparative study of different models.
To contextualize the reported Dice score of 0.733, we compared our model’s performance with recent hippocampal segmentation studies using deep learning-based approaches. It is consistent with results reported in recent neuroimaging studies involving anatomically small or morphologically complex brain regions. Recent deep learning studies on neuroanatomical segmentation report Dice scores in the range of 0.66–0.71 when applied to structurally complex, small-volume brain regions. For instance, nnU-Net achieved a mean Dice score of 0.678 ± 0.050 for hippocampal-adjacent perivascular spaces in multi-site adult datasets [44], while a pediatric brain tumor study reported a Dice of 0.71 ± 0.33 for cystic subregion structures similar in size and variability to the hippocampus [45]. These results underscore the segmentation challenges inherent to such regions and place our model’s performance (Dice ≈ 0.733) well within the upper bounds of current benchmarks. Looking forward, this pipeline can be extended into longitudinal studies to capture the dynamics of hippocampal volume change over time. Moreover, incorporating multimodal imaging and behavioral phenotyping may further refine brain-age models and enhance the predictive validity of imaging biomarkers. This study integrates deep learning with neuroanatomical expertise. It presents a scalable and clinically relevant method for the early detection of brain aging and neurodegeneration. The approach focuses on precise hippocampal segmentation.
6. Limitations
The current study is limited to an adolescent cohort aged 7.7–15.6 years, and we acknowledge that hippocampal volumetric patterns and their biological implications differ significantly across the lifespan. The biological meaning of volume reduction in adolescents is distinct from that in older adults. In younger cohorts, shrinkage may reflect neurodevelopmental disruption rather than aging per se. While this work establishes a pipeline for robust segmentation and volume quantification in younger populations, the findings cannot be directly extrapolated to older adults, where age-related atrophy follows different morphological trajectories and clinical correlates. Future work will expand the analysis to include adult and geriatric populations to validate the generalizability of the model across age groups and to better delineate the impact of pathological versus normative aging processes.
Another limitation of this study is that we have limited quantitative evaluation of our model compared to similar studies. The main reason is that there are just a limited number of studies that used the same dataset to solve this problem. However, we aim to extend this study and utilize other benchmarks as well as other models in the future.
7. Conclusions
This work presents a comprehensive, fully automated hippocampal segmentation pipeline leveraging the nnU-Net framework, applied to a meticulously curated dataset of structural brain MRIs. Unlike earlier approaches, which suffered from limitations such as misalignment in atlas-based techniques, inadequate convergence in shallow U-Net architectures, or interpretability challenges in correlation-driven methods, nnU-Net demonstrated unparalleled adaptability, robustness, and precision. Its dynamic configuration capabilities—ranging from patch size selection to architectural tuning—enabled it to outperform traditional models in delineating anterior and posterior hippocampal subregions with high anatomical fidelity and segmentation accuracy.
Through the use of volumetric analysis derived from the predicted segmentation masks, we uncovered meaningful patterns that associate hippocampal shrinkage with early signs of neurodegeneration. These volume reductions were significantly correlated with demographic risk factors such as younger age, female sex, and elevated predicted brain-age gaps. By identifying individuals whose hippocampal volumes fall below the normative thresholds for their age, the pipeline not only enables high-throughput anatomical annotation but also serves as a diagnostic tool capable of flagging potential cases of accelerated brain aging.
The implications of such findings are profound: hippocampal atrophy is a well-documented precursor in a variety of neuropsychiatric conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, major depressive disorder, and stress-related cognitive decline. A system capable of accurate, reproducible segmentation and volume quantification thus holds clinical utility in screening, monitoring, and potentially intervening in the neurodegenerative trajectory before irreversible damage occurs.
Author Contributions
E.G. and I.D. developed the original concept. E.G. conducted experiments and generated the figures. E.G., A.D. and I.D. wrote the article. E.G. prepared the computational pipeline. I.D. and A.D. supervised the project. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available in [NITRC] at [https://www.nitrc.org/rating/show_results.php?group_id=377], reference number [21].
Conflicts of Interest
The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Data Availability Statement. This Change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- McEwen, B.S. Possible mechanisms for atrophy of the human hippocampus. Mol. Psychiatry 1997, 2, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapolsky, R.M. Why stress is bad for your brain. Science 1996, 273, 749–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmichael, O.T.; Aizenstein, H.A.; Davis, S.W.; Becker, J.T.; Thompson, P.M.; Meltzer, C.C.; Liu, Y. Atlas-based hippocampus segmentation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage 2005, 27, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.; Pinaya, W.H.L.; Mechelli, A. Using deep learning to investigate the neuroimaging correlates of psychiatric and neurological disorders: Methods and applications. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 74, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, N.; Ndipenoch, N.; Cao, Y.; Miron, A.; Li, Y. Exploring advanced architectural variations of nnUNet. Neurocomputing 2023, 560, 126837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Rydel, R.E. Development and selective neurodegeneration in cell cultures from different brain regions. Brain Res. 1989, 490, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Plasticity of the hippocampus: Adaptation to chronic stress and allostatic load. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 933, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frodl, T.; Meisenzahl, E.M.; Zetzsche, T.; Born, C.; Groll, C.; Jäger, M.; Leinsinger, G.; Bottlender, R.; Hahn, K.; Möller, H.-J. Hippocampal changes in patients with a first episode of major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salunkhe, S.; Bachute, M.; Gite, S.; Vyas, N.; Khanna, S.; Modi, K.; Katpatal, C.; Kotecha, K. Classification of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Using Texture Analysis and Machine Learning. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Lindenberger, U.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Kennedy, K.M.; Head, D.; Williamson, A.; Dahle, C.; Gerstorf, D.; Acker, J.D. Regional brain changes in aging healthy adults: General trends, individual differences and modifiers. Cereb. Cortex 2005, 15, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czéh, B.; Lucassen, P.J. What causes the hippocampal volume decrease in depression? Are neurogenesis, glial changes and apoptosis implicated? Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 257, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassouneh, A. Multimodal Feature Fusion and AI-Driven Framework for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease. Ph.D. Thesis, Western Michigan University, Kalamazoo, MI, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Jiménez, E.P.; Flor-García, M.; Terreros-Roncal, J.; Rábano, A.; Cafini, F.; Pallas-Bazarra, N.; Ávila, J.; Llorens-Martín, M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammers, A.; Heckemann, R.A.; Koepp, M.J.; Duncan, J.S.; Hajnal, J.V.; Rueckert, D.; Aljabar, P. Automatic detection and quantification of hippocampal atrophy on MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy: A proof-of-principle study. NeuroImage 2007, 36, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sämann, P.G.; Iglesias, J.E.; Gutman, B.; Grotegerd, D.; Leenings, R.; Flint, C.; Dannlowski, U.; Clarke-Rubright, E.K.; Morey, R.A.; van Erp, T.G.M.; et al. FreeSurfer-based segmentation of hippocampal subfields: A review of methods and applications, with a novel quality control procedure for ENIGMA studies and other collaborative efforts. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 42, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Cao, X.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhan, Y. Medical image segmentation based on U-Net: A review. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2020, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.R.; Larosa, A.; Di Raddo, M.-E.; Wong, V.; Wong, A.S.; Wong, T.P. Negative memory engrams in the hippocampus enhance the susceptibility to chronic social defeat stress. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 7576–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, M.; Shojae, M.; Cabrerizo, M.; Rishe, N.; Wang, Y. Automated hippocampus segmentation and volume estimation using a transformer-based deep learning architecture. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, N.; Rodrigue, K.M.; Head, D.; Kennedy, K.M.; Acker, J.D. Differential aging of the medial temporal lobe: A study of a five-year change. Neurology 2004, 62, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Miron, A.; Hone, K.; Li, Y. Segmenting Medical Images: From UNet to Res-UNet and nnUNet. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 37th International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Guadalajara, Mexico, 26–28 June 2024; pp. 483–489. [Google Scholar]
- Hippocampus Segmentation Dataset. Neuroimaging Informatics Tools and Resources Clearinghouse (NITRC). Available online: https://www.nitrc.org/frs/?group_id=377 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Kalaiselvi, T.; Anitha, T.; Sriramakrishnan, P. Data preprocessing techniques for MRI brain scans using deep learning models. In Brain Tumor MRI Image Segmentation Using Deep Learning Techniques; Syed, I.S., Khan, M.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dolz, J.; Desrosiers, C.; Ben Ayed, I. 3D fully convolutional networks for subcortical segmentation in MRI: A large-scale study. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1612.03925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ammari, S.; Balleyguier, C.; Lassau, N.; Chouzenoux, E. Impact of preprocessing and harmonization methods on the removal of scanner effects in brain MRI radiomic features. Cancers 2021, 13, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Raad, K.B.; Van Garderen, K.A.; Smits, M.; Van der Voort, S.R.; Incekara, F.; Oei, E.H.G.; Hirvasniemi, J.; Klein, S.; Starmans, M.P.A. The effect of preprocessing on convolutional neural networks for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 655–658. [Google Scholar]
- Viswan, V.; Shaffi, N.; Subramanian, K.; Hajamohideen, F. Optimizing Medical Imaging Quality: An In-Depth Examination of Preprocessing Methods for Brain MRIs. In Applied Intelligence and Informatics; Mahmud, M., Ben-Abdallah, H., Kaiser, M.S., Ahmed, M.R., Zhong, N., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; AII 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 2065. [Google Scholar]
- SSuhas, C.R. Venugopal, MRI image preprocessing and noise removal technique using linear and nonlinear filters. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computer, and Optimization Techniques (ICEECCOT), Mysuru, India, 15–16 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hazarika, R.A.; Maji, A.K.; Syiem, R.; Samarendra, N.S.; Debdatta, K. Hippocampus Segmentation Using U-Net Convolutional Network from Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). J. Digit. Imaging 2022, 35, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isensee, F.; Wald, T.; Ulrich, C.; Baumgartner, M.; Roy, S.; Maier-Hein, K.H.; Jäger, P.F. nnU-Net revisited: A call for rigorous validation in 3D medical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 488–498. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Petersen, J.; Klein, A.; Zimmerer, D.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: Self-adapting framework for U-Net-based medical image segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.10486. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Bang, J.; Kim, S.-Y.; Seo, M.; Jang, J. Deep learning–based multimodal segmentation of oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma on CT and MRI using self-configuring nnU-Net. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, F.; Heindl, D.; Jebril, H.; Karner, M.; Unterdechler, M. nnU-Net Pre- and Postprocessing Strategies for UW-OCTA Segmentation Tasks in Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis. In Mitosis Domain Generalization and Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis; Sheng, B., Aubreville, M., Eds.; MIDOG DRAC 2022 2022; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 13597. [Google Scholar]
- Eelbode, T.; Jeroen, B.; Maxim, B.; Dirk, V.; Frederik, M.; Raf, B.; Matthew, B.B. Optimization for Medical Image Segmentation: Theory and Practice When Evaluating with Dice Score or Jaccard Index. In IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging; IEEE: Troy, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 39, pp. 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, K.; Gaser, C. Ten Years of BrainAGE as a Neuroimaging Biomarker of Brain Aging: What Insights Have We Gained? Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouneh, A.; Bazuin, B.; Kaku, H.; Abdel-Qader, I. A data fusion framework for mild cognitive impairment classification: Hippocampal volume and GLCM features using machine learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Technology and Applications, Sydney, Australia, 17–19 October 2024; pp. 435–445. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sanchez-Bornot, J.; Sotero, R.C.; Coyle, D.; Idris, Z.; Faye, I. A machine learning approach for identifying anatomical biomarkers of early mild cognitive impairment. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.00040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, X.; Ge, X.; Hu, H.; Liao, Z.; Ding, Z. Machine learning classifiers and associations of cognitive performance with hippocampal subfields in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1273658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.I.; Prakash, R.S.; Voss, M.W.; Chaddock, L.; Heo, S.; McLaren, M.; Martin, S.A.; Vieira, V.J.; Woods, J.A.; McAuley, E.; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with age-related decline in hippocampal volume. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5368–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, M.S.; Iosifescu, D.V. In pursuit of neuroimaging biomarkers to guide treatment selection in major depressive disorder: A review of recent literature. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1344, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, M.; Oliver, A.; Lladó, X.; Freixenet, J.; Bach Cuadra, M. A review of atlas-based segmentation for magnetic resonance brain images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2011, 104, e158–e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Han, H.; Yao, Q.; Zhu, S.; Zhou, S.K. 3D U2-Net: A 3D Universal U-Net for Multi-domain Medical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019; Shen, D., Liu, T., Peters, T.M., Staib, L.H., Essert, C., Zhou, S., Yap, P.-T., Khan, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 11765. [Google Scholar]
- Su, R.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, C. MSU-Net: Multi-Scale U-Net for 2D Medical Image Segmentation. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 639930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, M.; Vo-Ho, V.-K.; Quinn, K.; Nguyen, H.; Luu, K.; Le, N. Chapter 3—CapsNet for medical image segmentation. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Suzuki, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, W.; Jarema, A.; Rim, D.; Chen, Z.; Khlif, M.S.H.; Macefield, V.G.; Henderson, L.A.; Brodtmann, A. A Comprehensive Framework for Automated Segmentation of Perivascular Spaces in Brain MRI with the nnU-Net. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.19564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossough, A.; Khalili, N.; Familiar, A.M.; Gandhi, D.; Viswanathan, K.; Tu, W.; Haldar, D.; Bagheri, S.; Anderson, H.; Haldar, S.; et al. Automatic segmentation of pediatric brain tumors in MRI with nnU-Net ensemble and post-processing techniques. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.08404. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).