Effects of Illitic Clay on the Phases, Microstructure, Physical Properties and Pyroplastic Deformation of Industrial Slag Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ceramics
2.3. Characterization and Testing
2.3.1. Sample Characterization
2.3.2. Physical Properties Testing
2.3.3. Pyroplastic Deformation Testing
3. Results and Discussion
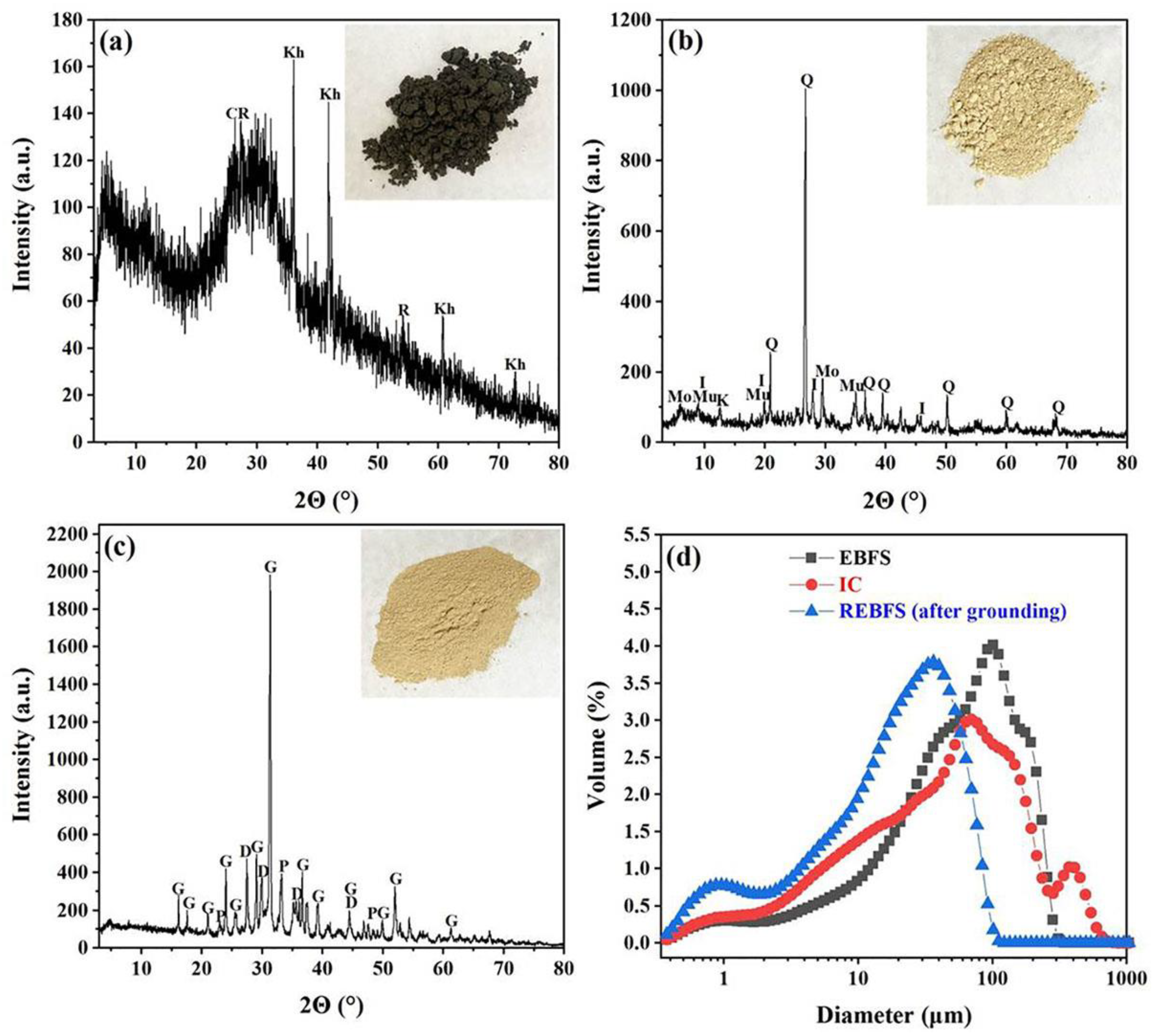
3.1. Attributes and Functions of Raw Materials
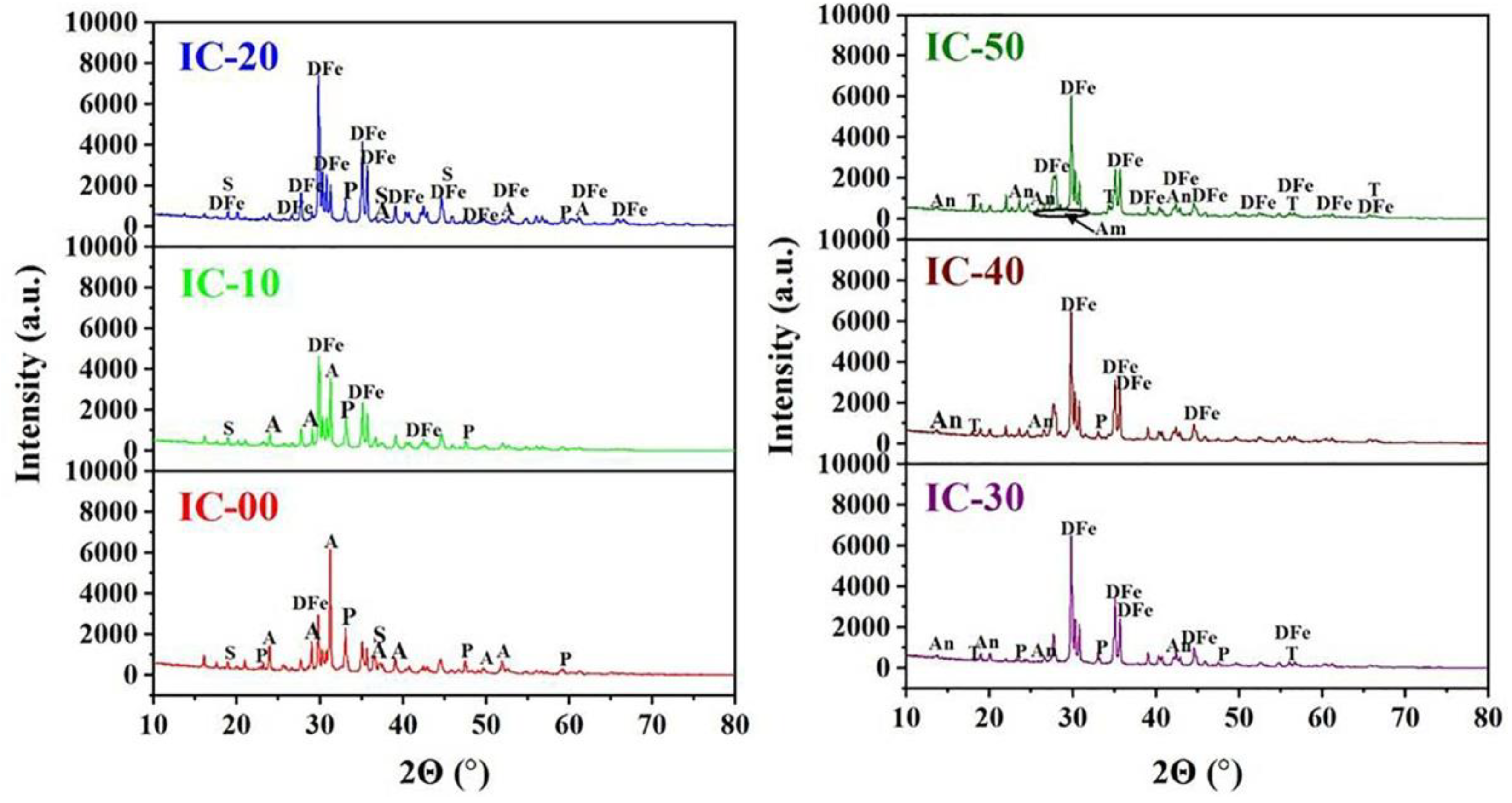
3.2. Phase Composition and Relative Contents of the Ceramic Samples
3.3. Structural Distortion of Fe-Bearing Diopside
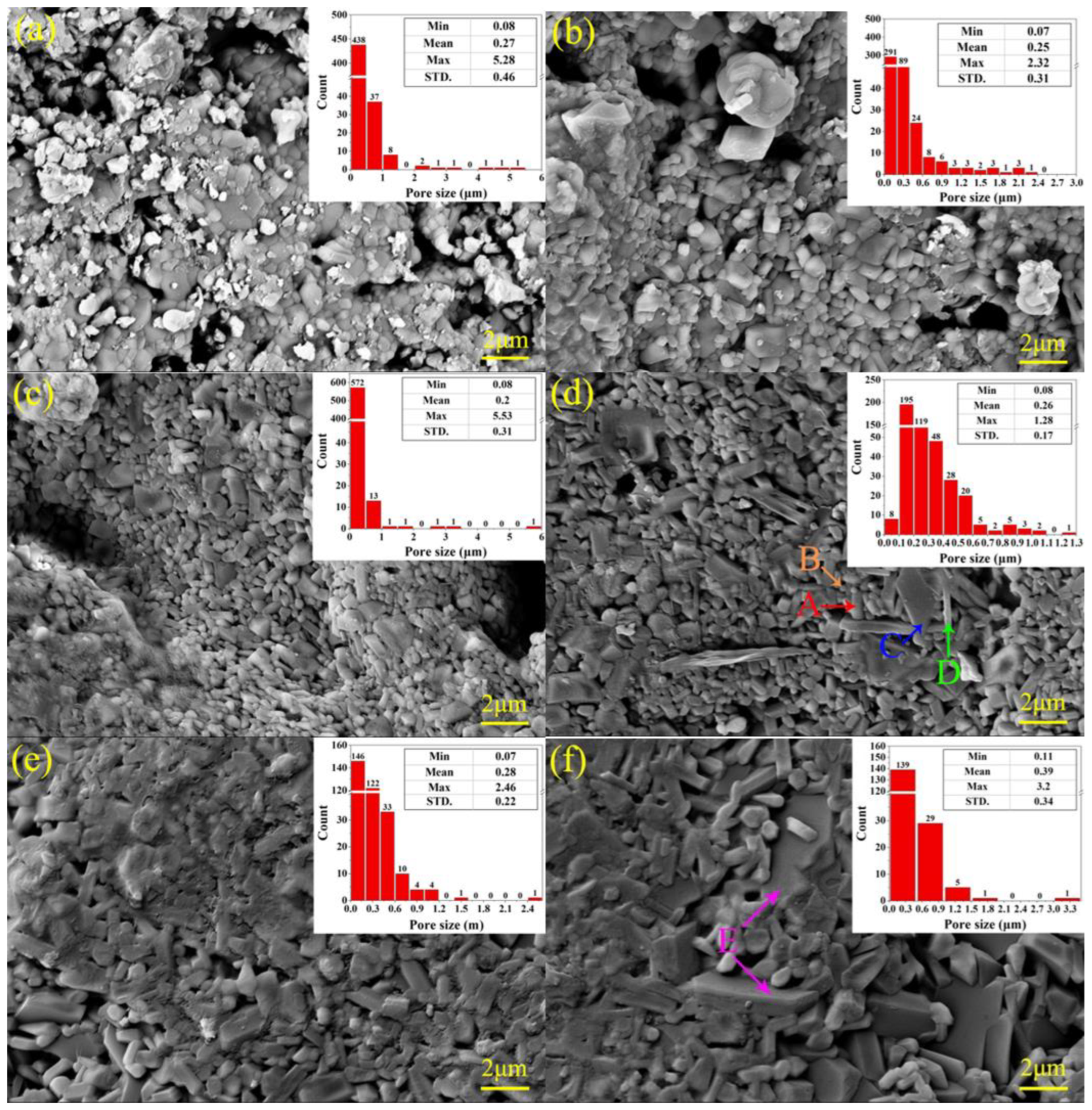
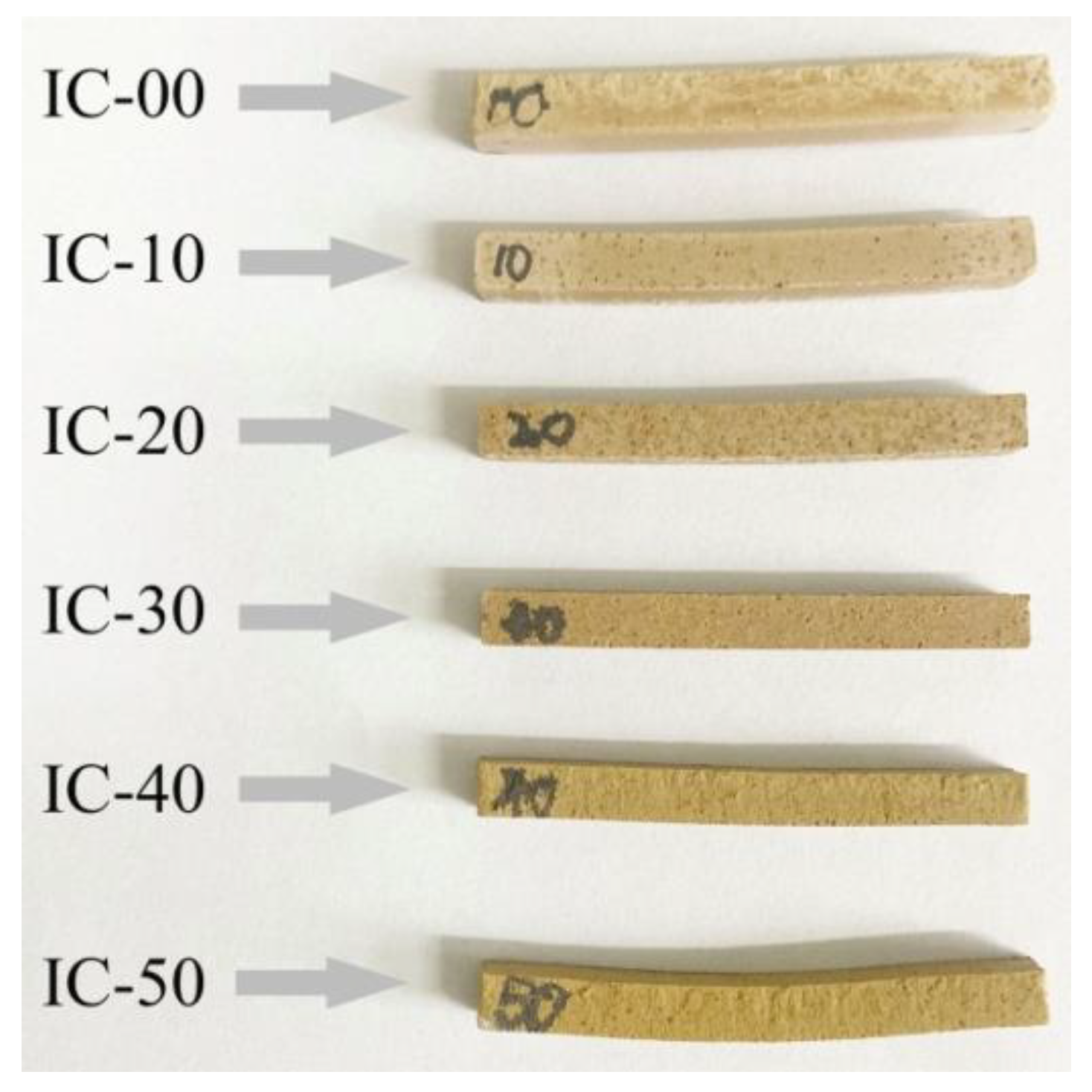
3.4. Microscopic Structure of the Ceramic Samples
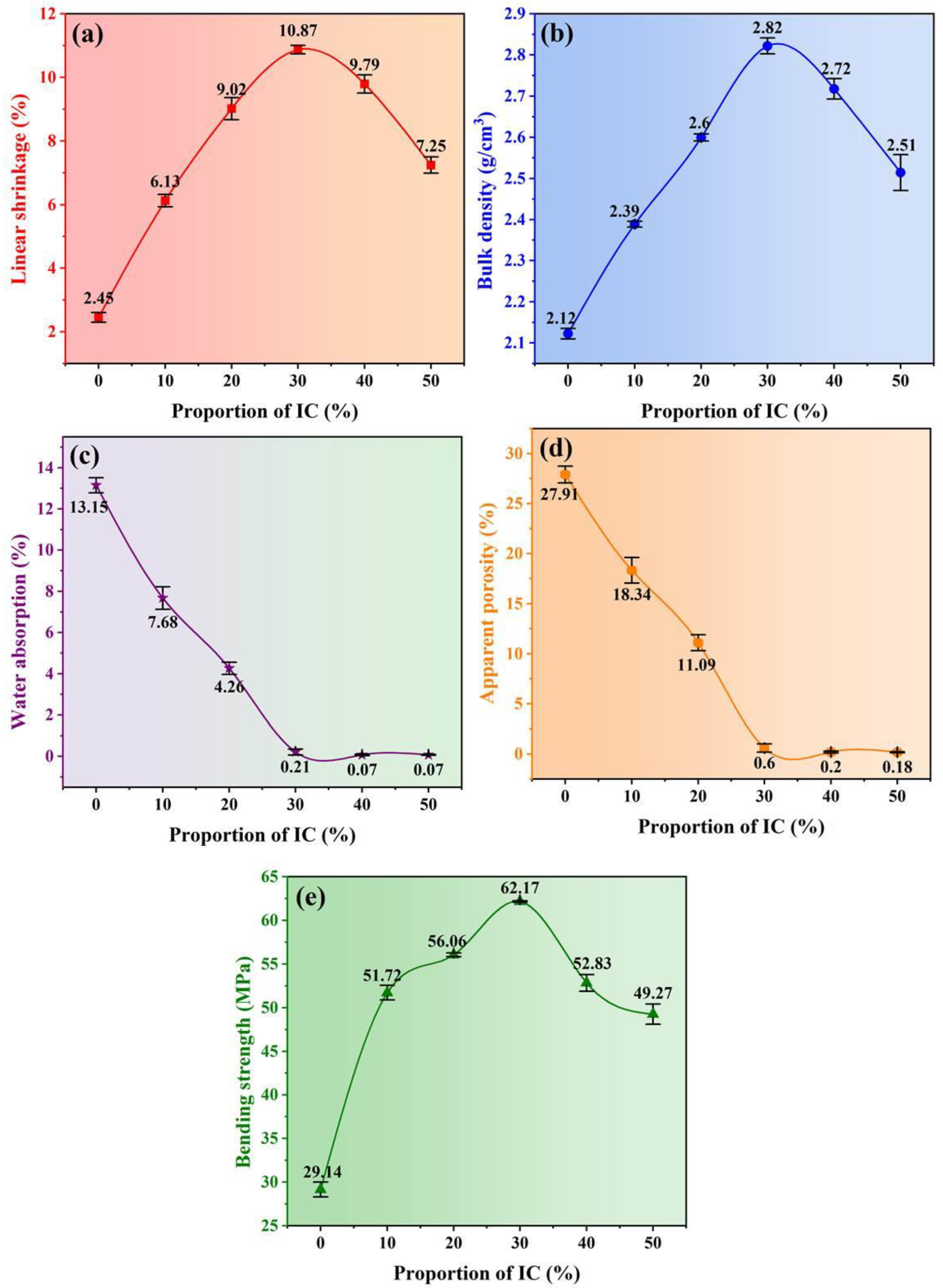
3.5. Physical Properties of the Ceramic Samples
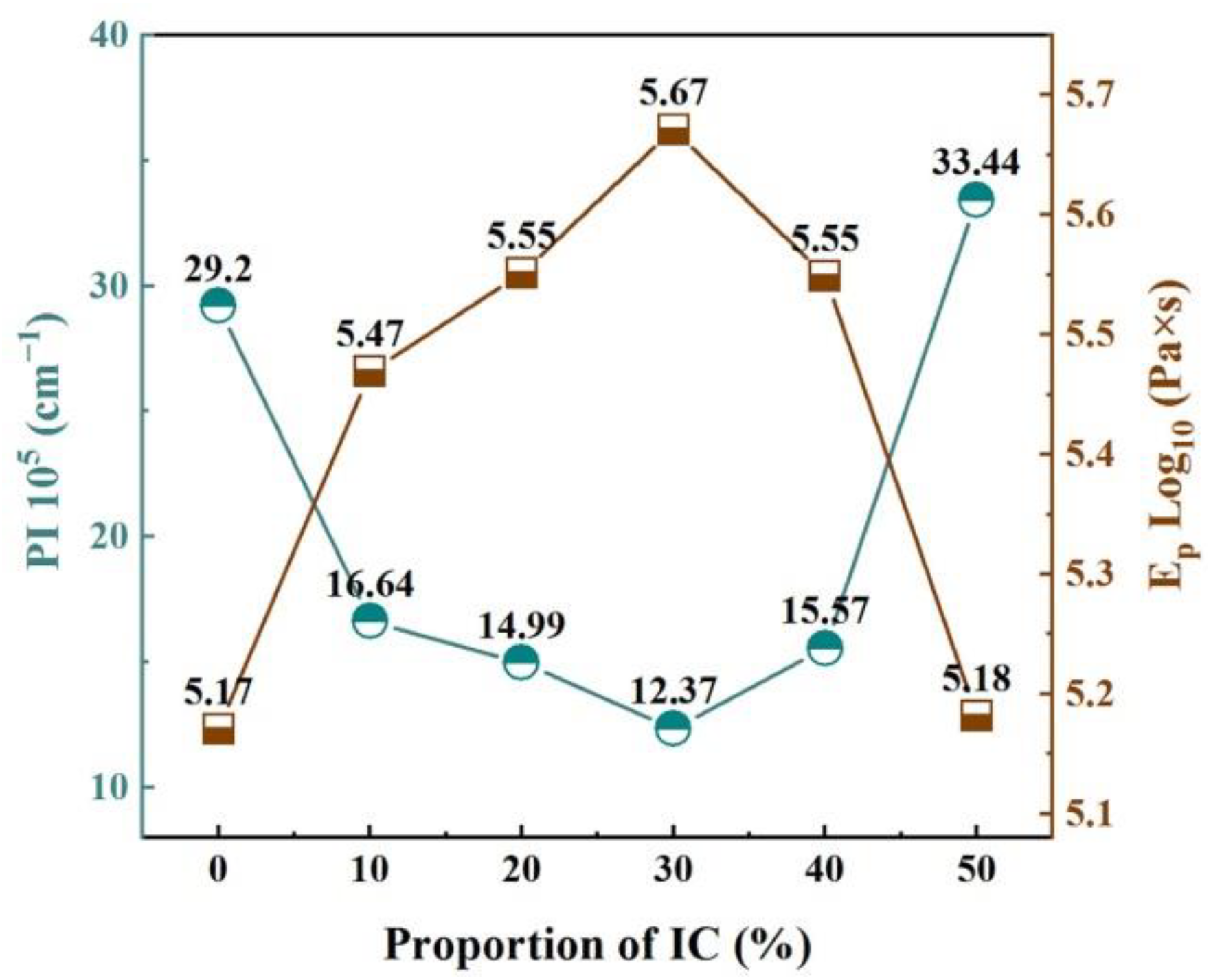
3.6. Pyroplastic Deformation of the Ceramic Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oge, M.; Ozkan, D.; Celik, M.B.; Sabri Gok, M.; Cahit Karaoglanli, A. An Overview of Utilization of Blast Furnace and Steelmaking Slag in Various Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 11, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.a.; Li, L.; Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, N.; Yu, H. A review on lead slag generation, characteristics, and utilization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Guo, Z.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.; Yang, C.; Xue, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, D. Comprehensive review on metallurgical recycling and cleaning of copper slag. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cang, D. Preparation of novel ceramics with high CaO content from steel slag. Mater. Des. 2014, 64, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.-h.; Wang, Y.-k.; Cang, D.-q. Effects of Fe2O3 on the properties of ceramics from steel slag. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2018, 25, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cang, D. Effects of CaO and Fe2O3 on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of SiO2–CaO–MgO–Fe2O3 Ceramics from Steel Slag. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Zheng, F.; Xu, J.; Yang, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J.L. Preparation of glass-ceramic foams using extracted titanium tailing and glass waste as raw materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Peng, T. Ceramics From Ti-Extraction Blast Furnace Slag and Their Crystalline Phase, Microstructure, and Photocatalytic Performance. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 652009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, F. Investigation of pyroplastic deformation of whitewares: Effect of crystal phases in the “CaO” based glassy matrix. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13360–13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, G. Pre-calcination of Asbestos Tailings and Its Recycling in Refractory Ceramics. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 79, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiee, H.; Maghsoudipour, A.; Raissi Dehkordi, B. Use of Iranian steel slag for production of ceramic floor tiles. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2008, 107, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, Z.B.; Gultekin, E.E. Preparation of ceramic wall tiling derived from blast furnace slag. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12020–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tian, K.; Wu, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X. Effect of talc on microstructure and properties of the graphite tailing stoneware tiles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 311, 125314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.; Wan, Q.; Cang, D. Preparation of anorthite-based porous ceramics using high-alumina fly ash microbeads and steel slag. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 22445–22451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Peng, T.; Sun, H.; Luo, D.; Xiao, Q.; Geng, Q. Kinetics of Iron Removal From Ti-Extraction Blast Furnace Slag by Chlorination Calcination. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, G.; Luo, D. Indirect mineral carbonation of chlorinated tailing derived from Ti-bearing blast-furnace slag coupled with simultaneous dechlorination and recovery of multiple value-added_products.pdf. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Wen, J. Overall Utilization of TiExtraction Blast Furnace Slag as a Raw Building Material_ Removal of Chlorine from Slag by Water Washing and Sintering.pdf. J. Sustain. Metall. 2021, 7, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Qin, Y.; Tang, S. Recovery of Residual Carbon from Ti-Extraction Blast Furnace Slag by Flotation with Simultaneous Dechlorination.pdf. Energies 2022, 15, 6777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xie, X.; lin, Y. Properties and hydration behavior of Ti-extracted residues-red gypsum__based cementitious materials.pdf. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z. Preparation and characterization of foamed concrete with Ti-extracted residues and red gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, C.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, F.; Gao, J.-m.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.; Zhen, Q.; Bashir, S.; Liu, J.L. Conversion of extracted titanium tailing and waste glass to value-added porous glass ceramic with improved performances. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, T.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Liu, L.; Ding, W.; Liu, B.; Wang, C. Recycling of extracted titanium slag and gold tailings for preparation of self-glazed ceramic foams. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 23415–23427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Li, Y.; Zeng, L.; Qin, Y. Effect of Sintering Time on Crystal and Structure of Chlorine-containing Low-titanium Slag Glass-ceramics.pdf. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 615, 012124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Gualtieri, A. The use of illitic clays in the production of stoneware tile ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkin, A.; Baronins, J.; Mironovs, V.; Lukac, F.; Stubna, I.; Ozolins, J. Influence of Glass Additions on Illitic Clay Ceramics. Materials 2020, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmale, G.; Randers, M.; Rundans, M.; Seglins, V. Application of differently treated illite and illite clay samples for the development of ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, A. The change of phase composition in kaolinite- and illite-rich clay-based ceramic bodies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 24, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapek, M.; Húlan, T.; Minárik, P.; Dobroň, P.; Štubňa, I.; Stráská, J.; Chmelík, F. Study of microcracking in illite-based ceramics during firing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagnin, D.; dos Santos, C.M.F.; Wanderlind, A.; Jiusti, J.; De Noni, A. Effect of kaolinite, illite and talc on the processing properties and mullite content of porcelain stoneware tiles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adcock, D.S.; Drummond, J.E.; McDowall, I.C. Pyroplastic Index and Firing Deformation of Ceramic Bodies. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1959, 42, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardin, A.M.; de Medeiros, D.S.; Riella, H.G. Pyroplasticity in porcelain tiles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvaci, E.; Tamsu, N. The role of viscosity on microstructure development and stain resistance in porcelain stoneware tiles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 3071–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.; Sanz, V.; Cañas, E.; Sales, J.; Kayacı, K.; Taşkıran, M.U.; Anıl, Ü.E.; Türk, Ş. Revisiting pyroplastic deformation. Application for porcelain stoneware tile bodies. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Fang, J.; Lan, S. The relation of pyroplastic deformation and liquid viscosity in vitreous ceramics. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 53, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Tan, W. Quantitative and structural analysis of minerals in soil clay fractions developed under different climate zones in China by XRD with Rietveld method, and its implications for pedogenesis. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sen, S.; Yu, P.; Browning, N.D.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Synthesis and spectroscopic characterization of P-doped Na4Si4. J. Solid State Chem. 2010, 183, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, K.; Wang, N.; Lu, Z.; Liang, J.; He, S. Effect of Holding Time During Sintering on Microstructure and Properties of 3D Printed Alumina Ceramics. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunçel, D.Y.; Özel, E. Evaluation of pyroplastic deformation in sanitaryware porcelain bodies. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluthe, C.; Kollenberg, W. Paper-derived stoneware ceramics: Improvement of properties by calendering and evaluation of pyroplastic deformation behaviour. Mater. Und Werkst. 2013, 44, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, M.; Eftekhari-Yekta, B.; Solati-Hashjin, M.; Marghussian, V.K. Effect of Cr2O3, Fe2O3 and TiO2 nucleants on the crystallization behaviour of SiO2–Al2O3–CaO–MgO(R2O) glass-ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, B.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Shi, Y.; McCloy, J.S. Lanthanum modification of crystalline phases and residual glass in augite glass ceramics produced with industrial solid wastes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2019, 524, 119638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastelaro, V.R.; Bayer, P.S.; Zanotto, E.D. Crystallization mechanism and kinetics of a Fe-diopside (25CaO·25MgO·50SiO2) glass–ceramic. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9313–9320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, S.; Zong, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Qin, S. Preparation of Steel Slag Ceramics with Different MgO/Al2O3 Ratios. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kang, S. Influence of Al2O3 additions on the crystallization mechanism and properties of diopside/anorthite hybrid glass-ceramics for LED packaging materials. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 326, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toya, T.; Tamura, Y.; Kameshima, Y.; Okada, K. Preparation and properties of CaO–MgO–Al2O3–SiO2 glass-ceramics from kaolin clay refining waste (Kira) and dolomite. Ceram. Int. 2004, 30, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantić, J.; Kremenović, A.; Došen, A.; Prekajski, M.; Stanković, N.; Baščarević, Z.; Matović, B. Influence of mechanical activation on sphene based ceramic material synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmale, G.; Sperberga, I.; Sedmalis, U.; Valancius, Z. Formation of high-temperature crystalline phases in ceramic from illite clay and dolomite. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, R.M.; Sadek, H.E.H.; Taha, M.A.; El-Rafei, A.M. Recycling of silica fume waste in the manufacture of β-eucryptite ceramics. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, S. Preparation and characterization of alumina/calcium-hexaluminate ceramic composites from ferrotitanium slag. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4265–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Márquez, J.; Rincón, J.M.; Romero, M. Effect of firing temperature on sintering of porcelain stoneware tiles.pdf. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 1867–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, F.; Guo, H.; Li, P.; Yan, B.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Zhu, G. Influence of low magnesia content on the CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramics: Its crystallization behaviour, microstructure and physical properties. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 20132–20139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunali, A.; Ozel, E.; Turan, S. Production and characterisation of granulated frit to achieve anorthite based glass–ceramic glaze. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.M.F.; Sánchez, R.; Monteiro, S.N. Characteristics of clays and properties of building ceramics in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maghraby, H.F.; El-Omla, M.M.; Bondioli, F.; Naga, S.M. Granite as flux in stoneware tile manufacturing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhu, M.; Li, Z. Preparation of novel ceramic tiles with high Al2O3 content derived from coal fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.T.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F.R.; de Souza, C.A.C.; de Andrade Lima, L.R.P. Structural ceramics made with clay and steel dust pollutants. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 51, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Liu, B.; Xu, X.; Wu, J. The effect of different solid phases on the pyroplastic deformation of porcelain. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 123, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwudi, B.C.; Ademusuru, P.O.; Okorie, B.A. Characterization of Sintered Ceramic Tiles Produced from Steel Slag. J. Miner. Mater. Charact. Eng. 2012, 11, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanova, E.; Avdeev, G.; Karamanov, A. Ceramics from blast furnace slag, kaolin and quartz. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 31, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvaro Guzmán, A.; Marisol Gordillo, S.; Silvio Delvasto, A.; María Francisca Quereda, V.; Enrique Sánchez, V. Optimization of the technological properties of porcelain tile bodies containing rice straw ash using the design of experiments methodology. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15383–15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
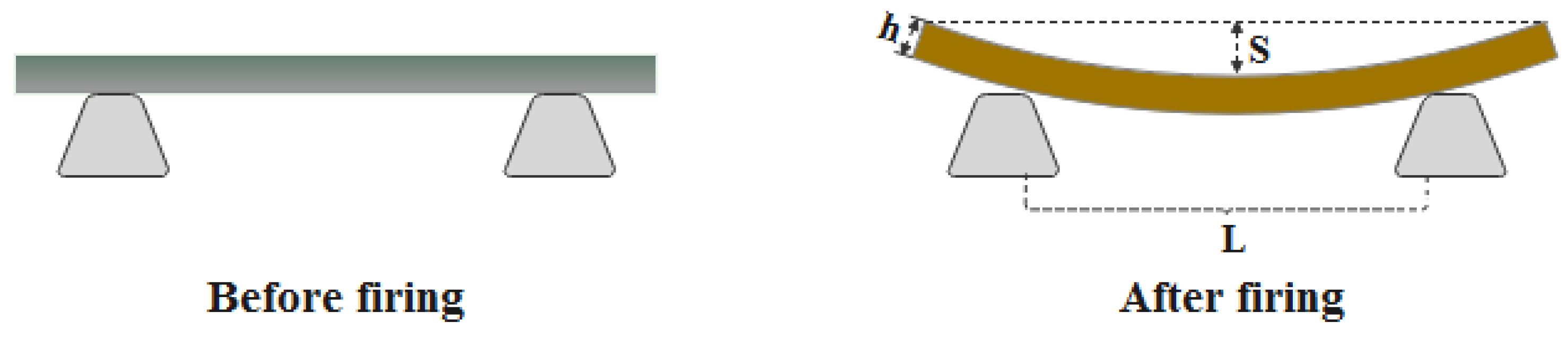


| Sample | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | Fe2O3 | Cl | R2O | Others | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBFS | 32.44 | 19.23 | 11.03 | 8.09 | 6.87 | 2.24 | 8.96 | 0.84 | 2.06 | 8.24 |
| IC | 10.52 | 48.13 | 15.84 | 0.82 | 2.18 | 7.42 | 0.03 | 3.72 | 0.54 | 10.8 |
| REBFS | 31.63 | 25.43 | 14.44 | 10.41 | 8.18 | 2.96 | 2.70 | 0.50 | 1.63 | 2.12 |
| Formula | REBFS | IC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 0 |
| 2 | 90 | 10 |
| 3 | 80 | 20 |
| 4 | 70 | 30 |
| 5 | 60 | 40 |
| 6 | 50 | 50 |
| Samples | R-Factors | E-Factors | R/E |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC-00 | 0.1302 | 0.0883 | 1.47 |
| IC-10 | 0.0982 | 0.0904 | 1.09 |
| IC-20 | 0.0889 | 0.0832 | 1.07 |
| IC-30 | 0.1080 | 0.0890 | 1.21 |
| IC-40 | 0.0834 | 0.0850 | 0.98 |
| IC-50 | 0.0746 | 0.0824 | 0.91 |
| Phases | Samples | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC-00 | IC-10 | IC-20 | IC-30 | IC-40 | IC-50 | |
| Akermanite | 43.8(3.4) | 28.4(2.7) | 12.8(1.8) | -- | -- | -- |
| Fe-bearing diopside | 31.2(2.7) | 52.3(4.0) | 73.4(5.2) | 78.3(6.1) | 65.0(5.0) | 50.5(3.9) |
| Perovskite | 14.4(1.1) | 10.5(1.1) | 6.1(0.8) | 4.4(1.1) | 1.2(0.5) | -- |
| Spinel | 5.3(1.0) | 2.7(0.8) | 1.0(0.5) | -- | -- | -- |
| Anorthite | -- | -- | -- | 9.1(1.6) | 20.5(2.4) | 35.6(3.1) |
| Titanite | -- | -- | -- | 0.5(0.4) | 4.6(1.1) | 4.7(0.9) |
| Amorphous | 5.3 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 7.7 | 8.7 | 9.2 |
| Samples | a (Å) | b (Å) | c (Å) | V (Å3) | α (°) | β (°) | γ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC-00 | 9.743 | 8.849 | 5.319 | 440.6 | 90.0 | 106.082 | 90.0 |
| IC-10 | 9.751 | 8.846 | 5.322 | 441.1 | 90.0 | 106.096 | 90.0 |
| IC-20 | 9.751 | 8.846 | 5.322 | 441.1 | 90.0 | 106.109 | 90.0 |
| IC-30 | 9.762 | 8.856 | 5.325 | 442.3 | 90.0 | 106.098 | 90.0 |
| IC-40 | 9.768 | 8.876 | 5.320 | 443.2 | 90.0 | 106.086 | 90.0 |
| IC-50 | 9.770 | 8.885 | 5.316 | 443.4 | 90.0 | 106.079 | 90.0 |
| Raw Materials | Firing Temperature (°C) | Main Phase | Water Absorption (%) | Bending Strength (MPa) | Pyroplastic Deformation Index | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel slag + Kaolinite | 1200 | Quartz + Anorthite + Wollastonite | 5.61~17.12 | 2~58 | * | [58] |
| Steel slag + Base body | 1140 | Quartz + Anorthite + Diopside | 0~15 | <117 | * | [11] |
| Blast furnace slag + Kaolin + Quartz | 1210 | Quartz + Anorthite + Pyroxene | 0~3 | 39~49 | * | [59] |
| Blast furnace slag + Clay + Kaolin + Limestone + Sand | 1136 | Quartz + Anorthite | 11.73~18.2 | * | * | [12] |
| Fly ash + Feldspar + Quartz | 1300 | Quartz + Mullite | * | * | ~17 | [60] |
| Clay + Feldspar + Quartz | * | * | 0.5~3 | >35 | * | GB/T 4100-2015 |
| Ti-extraction blast furnace slag + Illitic clay | 1170 | Fe-bearing diopside + Anorthite | 0.21 | 62.17 | 12.37 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, H.; Sun, H.; Peng, T.; Zhou, X.; Chao, L.; Wang, C. Effects of Illitic Clay on the Phases, Microstructure, Physical Properties and Pyroplastic Deformation of Industrial Slag Ceramics. Materials 2023, 16, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010233
You H, Sun H, Peng T, Zhou X, Chao L, Wang C. Effects of Illitic Clay on the Phases, Microstructure, Physical Properties and Pyroplastic Deformation of Industrial Slag Ceramics. Materials. 2023; 16(1):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010233
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Hao, Hongjuan Sun, Tongjiang Peng, Xin Zhou, Li Chao, and Can Wang. 2023. "Effects of Illitic Clay on the Phases, Microstructure, Physical Properties and Pyroplastic Deformation of Industrial Slag Ceramics" Materials 16, no. 1: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010233
APA StyleYou, H., Sun, H., Peng, T., Zhou, X., Chao, L., & Wang, C. (2023). Effects of Illitic Clay on the Phases, Microstructure, Physical Properties and Pyroplastic Deformation of Industrial Slag Ceramics. Materials, 16(1), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010233






